a) The minimum work with which this process could be accomplished b) The entropy generated during the process
|
|
|
- Gerard Rodgers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
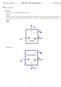
1 ENSC 46 Tutorial, Week#6 Exergy: Control Mass Analysis An insulated piston-cylinder device contains L of saturated liquid water at a pressure of 50 kpa which is constant throughout the process. An electric resistance heater inside the cylinder is turned on, and electrical work is done on the water in the amount of 00 kj. Assuming the surroundings to be at 5C and 00 kpa, determine: a) The minimum work with which this process could be accomplished b) The entropy generated during the process Step : Draw a diagram to represent the system (show control mass of interest) The control mass boundary encloses the water in the cylinder Surroundings T 0 =5 C P =00 kpa 0 State Intermediate State W Q=0 b State Surroundings T 0 =5 C P =00 kpa 0 Sat. Liquid H O P =50 kpa V =L W e = 00 kj H 0 P =50 kpa Step : Write out what is required to solve for Find: a) The minimum work with which this process could be accomplished b) The entropy generated during the process Step 3: Property table Property State T[K] P[kPa] h[kj/kg] s[kj/kg*k] v[m 3 /kg] V[m 3 ] (sat liq) Step 4: Assumptions Assumptions: ) Insulated piston-cylinder (Q=0) ) KE, PE 0 3) Compression/expansion processes are in quasi-equilibrium Step 5: Solve Part a) The solution for part a) involves finding the MINIMUM work with which this process could be accomplished. As stated in Cengel and Boles (Ch7), Reversible Work, W rev, is defined as the minimum work that needs to be supplied as a system undergoes a process between the specified initial and final states. Therefore, the minimum work with which this process M. Bahrami ENSC 46 (S ) Tutorial 6
2 can be accomplished is equal to the reversible work. Before the reversible work can be determined, the properties of the H O at the initial and final states must be determined. We can determine the properties at state using the information given in the problem (saturated liquid H O at P = 50 kpa) with Table A-5. From Table A-5 s = s f@50kpa =.4336 [kj/kg*k] v = v f@50kpa = [m 3 /kg] h = h f@50kpa = 467.[kJ/kg] From the specific volume at state, v, and the volume of state, V, we can determine the mass of H O in the cylinder. m V v m kg 3 m. kg H O 9 The properties at state must now be determined (the pressure at state (50 kpa) is known because this is a constant pressure process). An energy balance on the system can be written to link state to state, as shown in Eq. E W W (Eq) e b E Using the assumption KE, PE 0, and noting that W b = P(V -V ), Eq can be re-expressed as Eq. Eq can be rearranged to Eq3. U U We P( V ) (Eq) V U PV U PV We (Eq3) Recognizing that U+PV = H, and that H = m H0 h, Eq3 can be rewritten as Eq4. m H O h h W (Eq4) e Isolating h in Eq4, and substituting in the values for W e, m H0, and h, h can be determined. M. Bahrami ENSC 46 (S ) Tutorial 6
3 h kj kj kj 467. kg kg kg We 00 h 65 mh O.9 Using h = 65 kj/kg and P = 50kPa with Table A-5, we find that state is within the vapor dome, in between the saturated liquid and vapor states on the 50 kpa isobar line. The properties at state can determine by first finding the quality, and then using this to interpolate in Table A-5. x h h g h f h f s = s f@50kpa + xs fg@50kpa = (5.7897) = 4.44 [kj/kg*k] v = v f@50kpa + x(v g@50kpa -v f@50kpa) = (.58) = [m 3 /kg] As mentioned previously, the minimum work that needs to be provided to accomplish this process represents the reversible work input, which can be computed from the difference in the system exergy at state and state, as expressed in Eq5. W rev (Eq5) The system of exergy at states and can be determined from the expressions in Eq6 and Eq7 respectively. ( V0 U U ) T ( S S ) P ( V ) (Eq6) ( V0 U U ) T ( S S ) P ( V ) (Eq7) Substituting Eq6 and Eq7 into Eq5, an expression for the reversible work can be obtained as shown in Eq8. Wmin Wrev ( U U) T0 ( S S) P0 ( V V ) (Eq8) Note how the dead state properties U 0, S 0, and V 0 cancel each other out in Eq8. Substituting the previously obtained expression for internal energy represented in Eq into Eq8 and bringing the m HO outside the bracket to convert the properties to specific properties, Eq8 can be written as Eq9. W rev P P v v W m T ( s ) (Eq9) e H O 0 0 s M. Bahrami ENSC 46 (S ) Tutorial 6 3
4 Substituting the known property values into Eq9, we can calculate the minimum work input. kj kj Wmin 00[ kj ].9[ kg] (50 00)( ) (98)( ) kg kg = kj Answer a) Part b) The exergy can be calculated from the expression shown in Eq0. T0S gen (Eq0) To find the entropy generated during the process we can perform an entropy balance on the system as shown in Eq. S in S S S (Eq) out gen system For a closed system, entropy can only be carried across the system boundary by heat transfer. Since the system is insulated, S in = 0 and S out = 0. The change in the system entropy is the difference in entropy between state and state i.e. S system = m HO (s -s ). Using this information with Eq, the (Irreversibility) can be determined from Eq. T m ( s ) (Eq) 0 H O s Substituting in the know values into Eq, the (Irreversibility) can be calculated. kj T0 S gen T0mH O ( s s) (98[ K])(.9[ kg])( ) kg K = 70. kj Answer b) Step 6: Concluding Statement and Remarks The minimum work with which this process could be accomplished is 440.6kJ. The amount of exergy during the actual process is 70. kj. One may question why an input of 00kJ is required in the actual process if the process requires a minimum of 440.6kJ to accomplish it with 70.kJ of exergy in the actual process (which sums to 4.8 kj). In the actual process we still have an excess amount of work out of the system above that which is required to expand M. Bahrami ENSC 46 (S ) Tutorial 6 4
5 against the surroundings pressure. This excess work can be expressed as (P-P 0 )m HO (v -v ), which is equal to 57.kJ. Summing these three components together accounts for the 00kJ input. Minimum Work Input = kj + Exergy Destroyed = 70. kj + Excess Work Output = 57. kj = Actual Work Input = 00 kj M. Bahrami ENSC 46 (S ) Tutorial 6 5
III. Evaluating Properties. III. Evaluating Properties
 F. Property Tables 1. What s in the tables and why specific volumes, v (m /kg) (as v, v i, v f, v g ) pressure, P (kpa) temperature, T (C) internal energy, u (kj/kg) (as u, u i, u f, u g, u ig, u fg )
F. Property Tables 1. What s in the tables and why specific volumes, v (m /kg) (as v, v i, v f, v g ) pressure, P (kpa) temperature, T (C) internal energy, u (kj/kg) (as u, u i, u f, u g, u ig, u fg )
Exergy and the Dead State
 EXERGY The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that
EXERGY The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA
 Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
PROBLEM 6.3. Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property. In each case, locate the state on sketches of the T-v and T-s diagrams.
 PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
PROBLEM 63 Using the appropriate table, determine the indicated property In each case, locate the state on sketches of the -v and -s diagrams (a) water at p = 040 bar, h = 147714 kj/kg K Find s, in kj/kg
First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 utorial # First Law of hermodynamics: Closed Systems Problem -7 A 0.-m tank contains oxygen initially at 00kPa and 7 C. A paddle wheel within the tank is rotated until the pressure inside rise to 50kPa.
utorial # First Law of hermodynamics: Closed Systems Problem -7 A 0.-m tank contains oxygen initially at 00kPa and 7 C. A paddle wheel within the tank is rotated until the pressure inside rise to 50kPa.
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
ME Thermodynamics I = = = 98.3% 1
 HW-08 (25 points) i) : a) 1 Since ν f < ν < ν g we conclude the state is a Saturated Liquid-Vapor Mixture (SLVM) 1, from the saturation tables we obtain p 3.6154 bar. 1 Calculating the quality, x: x ν
HW-08 (25 points) i) : a) 1 Since ν f < ν < ν g we conclude the state is a Saturated Liquid-Vapor Mixture (SLVM) 1, from the saturation tables we obtain p 3.6154 bar. 1 Calculating the quality, x: x ν
ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number:
 ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION June 19, 2015 2:30 pm - 4:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted
ECE309 THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER MIDTERM EXAMINATION June 19, 2015 2:30 pm - 4:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Permitted
Find: a) Mass of the air, in kg, b) final temperature of the air, in K, and c) amount of entropy produced, in kj/k.
 PROBLEM 6.25 Three m 3 of air in a rigid, insulated container fitted with a paddle wheel is initially at 295 K, 200 kpa. The air receives 1546 kj of work from the paddle wheel. Assuming the ideal gas model,
PROBLEM 6.25 Three m 3 of air in a rigid, insulated container fitted with a paddle wheel is initially at 295 K, 200 kpa. The air receives 1546 kj of work from the paddle wheel. Assuming the ideal gas model,
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
 First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
KNOWN: Data are provided for a closed system undergoing a process involving work, heat transfer, change in elevation, and change in velocity.
 Problem 44 A closed system of mass of 10 kg undergoes a process during which there is energy transfer by work from the system of 0147 kj per kg, an elevation decrease of 50 m, and an increase in velocity
Problem 44 A closed system of mass of 10 kg undergoes a process during which there is energy transfer by work from the system of 0147 kj per kg, an elevation decrease of 50 m, and an increase in velocity
MAE 110A. Homework 3: Solutions 10/20/2017
 MAE 110A Homework 3: Solutions 10/20/2017 3.10: For H 2O, determine the specified property at the indicated state. Locate the state on a sketch of the T-v diagram. Given a) T 140 C, v 0.5 m 3 kg b) p 30MPa,
MAE 110A Homework 3: Solutions 10/20/2017 3.10: For H 2O, determine the specified property at the indicated state. Locate the state on a sketch of the T-v diagram. Given a) T 140 C, v 0.5 m 3 kg b) p 30MPa,
Appendix F. Steam Tables
 Appendix F Steam Tables F.1 INTERPOLATION When a value is required from a table at conditions which lie between listed values, interpolation is necessary. If M, the quantity sought, is a function of a
Appendix F Steam Tables F.1 INTERPOLATION When a value is required from a table at conditions which lie between listed values, interpolation is necessary. If M, the quantity sought, is a function of a
Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams
 Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams In this chapter we consider the property values and relationships of a pure substance (such as water) which can exist in three phases - solid,
Pure Substances Phase Change, Property Tables and Diagrams In this chapter we consider the property values and relationships of a pure substance (such as water) which can exist in three phases - solid,
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
CHAPTER 8 ENTROPY. Blank
 CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
Dr Ali Jawarneh. Hashemite University
 Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Examine the moving boundary work or P d work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors.
Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Examine the moving boundary work or P d work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors.
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Content. Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas.
 Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 20 June 2005
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 20 June 2005 Midterm Examination R. Culham & M. Bahrami This is a 90 minute, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 20 June 2005 Midterm Examination R. Culham & M. Bahrami This is a 90 minute, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib
ME 200 Final Exam December 14, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
TDEC202 - Energy II (Recitation #3)
 TDEC202 - Energy II (Recitation #3) Summer Term, 2007 M. Carchidi Solution to Problem 3-029 We are given that the substance is R-134a and metric units so that Tables A-11, A-12 and A-13 in Appendix 1 will
TDEC202 - Energy II (Recitation #3) Summer Term, 2007 M. Carchidi Solution to Problem 3-029 We are given that the substance is R-134a and metric units so that Tables A-11, A-12 and A-13 in Appendix 1 will
ME 300 Thermodynamics II Exam 1 September 27, :00 p.m. 9:00 p.m.
 ME 00 Thermodynamics II Exam 1 September 7, 01 8:00 p.m. 9:00 p.m. Name: Solution Section (Circle One): Sojka Naik 11:0 a.m. 1:0 p.m. Instructions: This is a closed book/notes exam. You may use a calculator.
ME 00 Thermodynamics II Exam 1 September 7, 01 8:00 p.m. 9:00 p.m. Name: Solution Section (Circle One): Sojka Naik 11:0 a.m. 1:0 p.m. Instructions: This is a closed book/notes exam. You may use a calculator.
0.5 kpa (1000 Pa/kPa) *A. A = 70*9.81 N/500 N/m 2 = 1.37 m 2
 AREN 2110 Spring 2010 Homework #2: Due Friday, Jan 29, 6 PM Solutions 1. Consider a 70-kg woman who has a total footprint area of 400 cm2. She wishes to walk on the snow, but the snow cannot withstand
AREN 2110 Spring 2010 Homework #2: Due Friday, Jan 29, 6 PM Solutions 1. Consider a 70-kg woman who has a total footprint area of 400 cm2. She wishes to walk on the snow, but the snow cannot withstand
ME Thermodynamics I
 HW-22 (25 points) Given: 1 A gas power cycle with initial properties as listed on the EFD. The compressor pressure ratio is 25:1 Find: 1 Sketch all the processes on a p-h diagram and calculate the enthalpy,
HW-22 (25 points) Given: 1 A gas power cycle with initial properties as listed on the EFD. The compressor pressure ratio is 25:1 Find: 1 Sketch all the processes on a p-h diagram and calculate the enthalpy,
EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES. By Ertanto Vetra
 EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines - TV, PV, PT, PVT Diagram - Property Tables - Introduction to Enthalpy - Reference State & Reference Values - Ideal Gas Equation
EVALUATING PROPERTIES FOR A PURE SUBSTANCES 1 By Ertanto Vetra Outlines - TV, PV, PT, PVT Diagram - Property Tables - Introduction to Enthalpy - Reference State & Reference Values - Ideal Gas Equation
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Today lecture. 1. Entropy change in an isolated system 2. Exergy
 Today lecture 1. Entropy change in an isolated system. Exergy - What is exergy? - Reversible Work & Irreversibility - Second-Law Efficiency - Exergy change of a system For a fixed mass For a flow stream
Today lecture 1. Entropy change in an isolated system. Exergy - What is exergy? - Reversible Work & Irreversibility - Second-Law Efficiency - Exergy change of a system For a fixed mass For a flow stream
Chapter 6. Using Entropy
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
(SP 1) DLLL. Given: In a closed rigid tank,
 (SP 1) Given: In a closed rigid tank, State 1: m 1,ice = 1, m 1,g = 0.05 P1= 0.0381 kpa, T1= -30 o C State 2: the liquid vapor equilibrium line, either saturated liquid or saturated vapor Find: (a) The
(SP 1) Given: In a closed rigid tank, State 1: m 1,ice = 1, m 1,g = 0.05 P1= 0.0381 kpa, T1= -30 o C State 2: the liquid vapor equilibrium line, either saturated liquid or saturated vapor Find: (a) The
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
ME 354 Tutorial, Week#5 Refrigeration Cycle A large refrigeration plant is to be maintained at -15 o C, and it requires refrigeration at a rate of
 ME 54 Tutorial, Week#5 Refrigeration Cyle A large eration plant is to be maintained at -5 o C, and it requires eration at a rate of 00 kw. The ondenser of the plant is to be ooled by liquid water, whih
ME 54 Tutorial, Week#5 Refrigeration Cyle A large eration plant is to be maintained at -5 o C, and it requires eration at a rate of 00 kw. The ondenser of the plant is to be ooled by liquid water, whih
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 Spring 01 ME 01 Thermodynamics Property Evaluation Practice Problems II Solutions 1. Air at 100 K and 1 MPa goes to MPa isenthapically. Determine the entropy change. Substance Type: Ideal Gas (air) Process:
Spring 01 ME 01 Thermodynamics Property Evaluation Practice Problems II Solutions 1. Air at 100 K and 1 MPa goes to MPa isenthapically. Determine the entropy change. Substance Type: Ideal Gas (air) Process:
Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 Fall 204 ME 20 Thermodynamics Homework #8 Solutions. A rigid wall, insulated container is divided into two regions by a removable wall. One region contains 0. lb m of CO at 00 F, while the other region
Fall 204 ME 20 Thermodynamics Homework #8 Solutions. A rigid wall, insulated container is divided into two regions by a removable wall. One region contains 0. lb m of CO at 00 F, while the other region
AC : ON THE WORK BY ELECTRICITY IN THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS
 AC 2011-2088: ON THE WORK BY ELECTRICITY IN THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS Hyun W. Kim, Youngstown State University Hyun W. Kim, Ph.D., P.E. Hyun W. Kim is a professor of mechanical engineering
AC 2011-2088: ON THE WORK BY ELECTRICITY IN THE FIRST AND SECOND LAWS OF THERMODYNAMICS Hyun W. Kim, Youngstown State University Hyun W. Kim, Ph.D., P.E. Hyun W. Kim is a professor of mechanical engineering
In the next lecture...
 16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
EXAM # 1 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 8:30 am 11:30 am 2:30 pm Prof. Memon Prof. Naik Prof. Lucht INSTRUCTIONS
 Last Name First Name CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 8: am : am : pm Prof. Memon Prof. Naik Prof. Lucht EXAM # INSTRUCTIONS. This is a closed book examination. An equation sheet and all needed property tables
Last Name First Name CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 8: am : am : pm Prof. Memon Prof. Naik Prof. Lucht EXAM # INSTRUCTIONS. This is a closed book examination. An equation sheet and all needed property tables
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
To receive full credit all work must be clearly provided. Please use units in all answers.
 Exam is Open Textbook, Open Class Notes, Computers can be used (Computer limited to class notes, lectures, homework, book material, calculator, conversion utilities, etc. No searching for similar problems
Exam is Open Textbook, Open Class Notes, Computers can be used (Computer limited to class notes, lectures, homework, book material, calculator, conversion utilities, etc. No searching for similar problems
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008
 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Objectives Introduce the concept of a pure substance. Discuss
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Objectives Introduce the concept of a pure substance. Discuss
SCHOOL OF COMPUTING, ENGINEERING AND MATHEMATICS SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATIONS 2014/2015 ME258. Thermodynamics
 s SCHOOL OF COMPUING, ENGINEERING AND MAHEMAICS SEMESER EXAMINAIONS 04/05 ME58 hermodynamics ime allowed: WO hours Answer: Any FOUR Questions Items permitted: Any approved calculator Items supplied: Steam
s SCHOOL OF COMPUING, ENGINEERING AND MAHEMAICS SEMESER EXAMINAIONS 04/05 ME58 hermodynamics ime allowed: WO hours Answer: Any FOUR Questions Items permitted: Any approved calculator Items supplied: Steam
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 12 June 2006
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 1 June 006 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a hour, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib sheet (one side
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 1 June 006 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a hour, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib sheet (one side
Chapter 4. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
 Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
Name: I have observed the honor code and have neither given nor received aid on this exam.
 ME 235 FINAL EXAM, ecember 16, 2011 K. Kurabayashi and. Siegel, ME ept. Exam Rules: Open Book and one page of notes allowed. There are 4 problems. Solve each problem on a separate page. Name: I have observed
ME 235 FINAL EXAM, ecember 16, 2011 K. Kurabayashi and. Siegel, ME ept. Exam Rules: Open Book and one page of notes allowed. There are 4 problems. Solve each problem on a separate page. Name: I have observed
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances
 Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances Mohsin Mohd Sies Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Properties of Pure Substances (Motivation) To quantify the changes
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances Mohsin Mohd Sies Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Properties of Pure Substances (Motivation) To quantify the changes
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 10 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Outline. Example. Solution. Property evaluation examples Specific heat Internal energy, enthalpy, and specific heats of solids and liquids Examples
 Outline Property ealuation examples Specific heat Internal energy, enthalpy, and specific heats of solids and liquids s A piston-cylinder deice initially contains 0.5m of saturated water apor at 00kPa.
Outline Property ealuation examples Specific heat Internal energy, enthalpy, and specific heats of solids and liquids s A piston-cylinder deice initially contains 0.5m of saturated water apor at 00kPa.
Physics 111. Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, Latent Heats
 Physics 111 Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, 2009 Lecture 39 1/26 Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called
Physics 111 Lecture 39 (Walker: 17.6, 18.2) Latent Heat Internal Energy First Law of Thermodynamics May 8, 2009 Lecture 39 1/26 Latent Heats The heat required to convert from one phase to another is called
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
Using the Entropy Rate Balance to Determine the Heat Transfer and Work in an Internally Reversible, Polytropic, Steady State Flow Process
 Undergraduate Journal of Mathematical Modeling: One + Two Volume 8 08 Spring 08 Issue Article Using the Entropy Rate Balance to Determine the Heat Transfer and Work in an Internally Reversible, Polytropic,
Undergraduate Journal of Mathematical Modeling: One + Two Volume 8 08 Spring 08 Issue Article Using the Entropy Rate Balance to Determine the Heat Transfer and Work in an Internally Reversible, Polytropic,
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
MAE 110A. Homework 6: Solutions 11/9/2017
 MAE 110A Hoework 6: Solutions 11/9/2017 H6.1: Two kg of H2O contained in a piston-cylinder assebly, initially at 1.0 bar and 140 C undergoes an internally ersible, isotheral copression to 25 bar. Given
MAE 110A Hoework 6: Solutions 11/9/2017 H6.1: Two kg of H2O contained in a piston-cylinder assebly, initially at 1.0 bar and 140 C undergoes an internally ersible, isotheral copression to 25 bar. Given
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON. University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS. For The Following Qualifications:-
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Thermodynamic Systems
 Thermodynamic Systems For purposes of analysis we consider two types of Thermodynamic Systems: Closed System - usually referred to as a System or a Control Mass. This type of system is separated from its
Thermodynamic Systems For purposes of analysis we consider two types of Thermodynamic Systems: Closed System - usually referred to as a System or a Control Mass. This type of system is separated from its
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
CHAPTER. The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 CHAPTER 3 The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems Closed system Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two forms: Heat and work FIGURE 3-1 Specifying the directions of heat and work.
CHAPTER 3 The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems Closed system Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two forms: Heat and work FIGURE 3-1 Specifying the directions of heat and work.
GAS. Outline. Experiments. Device for in-class thought experiments to prove 1 st law. First law of thermodynamics Closed systems (no mass flow)
 Outline First law of thermodynamics Closed systems (no mass flow) Device for in-class thought experiments to prove 1 st law Rubber stops GAS Features: Quasi-equlibrium expansion/compression Constant volume
Outline First law of thermodynamics Closed systems (no mass flow) Device for in-class thought experiments to prove 1 st law Rubber stops GAS Features: Quasi-equlibrium expansion/compression Constant volume
The First Law of Thermodynamics. By: Yidnekachew Messele
 The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
ME 354 Tutorial, Week#13 Reacting Mixtures
 ME 354 Tutorial, Week#13 Reacting Mixtures Question 1: Determine the mole fractions of the products of combustion when octane, C 8 H 18, is burned with 200% theoretical air. Also, determine the air-fuel
ME 354 Tutorial, Week#13 Reacting Mixtures Question 1: Determine the mole fractions of the products of combustion when octane, C 8 H 18, is burned with 200% theoretical air. Also, determine the air-fuel
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 ME 0 Thermodynamics Solutions First Law Practice Problems. Consider a balloon that has been blown up inside a building and has been allowed to come to equilibrium with the inside temperature of 5 C and
ME 0 Thermodynamics Solutions First Law Practice Problems. Consider a balloon that has been blown up inside a building and has been allowed to come to equilibrium with the inside temperature of 5 C and
Availability and Irreversibility
 Availability and Irreversibility 1.0 Overview A critical application of thermodynamics is finding the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from a given energy resource. This calculation forms the
Availability and Irreversibility 1.0 Overview A critical application of thermodynamics is finding the maximum amount of work that can be extracted from a given energy resource. This calculation forms the
Department: Machines and equipments. Stage: First Stage Title: Thermodynamic week: 19
 Department: Machines and equipments Stage: First Stage Title: Thermodynamic week: 19 Entropy, changes on closed systems and temperature entropy plane Entropy is an extensive property of a system and sometimes
Department: Machines and equipments Stage: First Stage Title: Thermodynamic week: 19 Entropy, changes on closed systems and temperature entropy plane Entropy is an extensive property of a system and sometimes
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Entropy ME 203 (2017) 2 / 27 T037
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 8 ME 0 Thermodynamics Practice Problems or Property Evaluation For each process described below provide the temperature, pressure, and speciic volume at each state and the change in enthalpy, internal
8 ME 0 Thermodynamics Practice Problems or Property Evaluation For each process described below provide the temperature, pressure, and speciic volume at each state and the change in enthalpy, internal
ME Thermodynamics I
 HW-03 (25 points) i) Given: for writing Given, Find, Basic equations Rigid tank containing nitrogen gas in two sections initially separated by a membrane. Find: Initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas
HW-03 (25 points) i) Given: for writing Given, Find, Basic equations Rigid tank containing nitrogen gas in two sections initially separated by a membrane. Find: Initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Engineering Thermodynamics
 David Ng Summer 2017 Contents 1 July 5, 2017 3 1.1 Thermodynamics................................ 3 2 July 7, 2017 3 2.1 Properties.................................... 3 3 July 10, 2017 4 3.1 Systems.....................................
David Ng Summer 2017 Contents 1 July 5, 2017 3 1.1 Thermodynamics................................ 3 2 July 7, 2017 3 2.1 Properties.................................... 3 3 July 10, 2017 4 3.1 Systems.....................................
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems. GENESYS Laboratory
 Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 13 June 2007
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
Last Name: First Name: Purdue ID: Please write your name in BLOCK letters. Otherwise Gradescope may not recognize your name.
 Solution Key Last Name: First Name: Purdue ID: Please write your name in BLOCK letters. Otherwise Gradescope may not recognize your name. CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: MWF 10:30 am MWF 3:30 pm TR 8:30 am
Solution Key Last Name: First Name: Purdue ID: Please write your name in BLOCK letters. Otherwise Gradescope may not recognize your name. CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: MWF 10:30 am MWF 3:30 pm TR 8:30 am
20 m neon m propane. g 20. Problems with solutions:
 Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
374 Exergy Analysis. sys (u u 0 ) + P 0 (v v 0 ) T 0 (s s 0 ) where. e sys = u + ν 2 /2 + gz.
 374 Exergy Analysis The value of the exergy of the system depends only on its initial and final state, which is set by the conditions of the environment The term T 0 P S is always positive, and it does
374 Exergy Analysis The value of the exergy of the system depends only on its initial and final state, which is set by the conditions of the environment The term T 0 P S is always positive, and it does
Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles
 Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Oeriew... 4.0 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics... 4.1 Temperature
Introduction to Thermodynamic Cycles Part 1 1 st Law of Thermodynamics and Gas Power Cycles by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Oeriew... 4.0 Basic Concepts of Thermodynamics... 4.1 Temperature
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
EXAM # 1 ME 300 SP2017
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 8:3 am :3 am 3:3 pm Prof. Lucht Prof. Chen Prof. Goldenstein EXAM # ME 3 SP7 INSTRUCTIONS. Please place all your electronics, including but not limited to cell phones, computers,
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: 8:3 am :3 am 3:3 pm Prof. Lucht Prof. Chen Prof. Goldenstein EXAM # ME 3 SP7 INSTRUCTIONS. Please place all your electronics, including but not limited to cell phones, computers,
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 6. Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6.1 Introduction
 Engineering hermodynamics AAi Chapter 6 Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6. Introduction he second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of
Engineering hermodynamics AAi Chapter 6 Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6. Introduction he second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of
ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 4 ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 4 ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1
 Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Chapter 8. The increased awareness that the world s energy EXERGY: A MEASURE OF WORK POTENTIAL. Objectives
 Chapter 8 EXERGY: A MEASURE OF WORK POTENTIAL The increased awareness that the world s energy resources are limited has caused many countries to reexamine their energy policies and take drastic measures
Chapter 8 EXERGY: A MEASURE OF WORK POTENTIAL The increased awareness that the world s energy resources are limited has caused many countries to reexamine their energy policies and take drastic measures
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Thermodynamic Processes & Efficiency ME 6101 (2017) 2 / 25 T145 = Q + W cv + i h 2 = h (V2 1 V 2 2)
 Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002
 16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
Fuel, Air, and Combustion Thermodynamics
 Chapter 3 Fuel, Air, and Combustion Thermodynamics 3.1) What is the molecular weight, enthalpy (kj/kg), and entropy (kj/kg K) of a gas mixture at P = 1000 kpa and T = 500 K, if the mixture contains the
Chapter 3 Fuel, Air, and Combustion Thermodynamics 3.1) What is the molecular weight, enthalpy (kj/kg), and entropy (kj/kg K) of a gas mixture at P = 1000 kpa and T = 500 K, if the mixture contains the
MAE 320 THERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM - Practice. Name: You are allowed three sheets of notes.
 50 MAE 320 THERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM - Practice Name: You are allowed three sheets of notes. 1. Fill in the blanks for each of the two (Carnot) cycles below. (a) 5 a) Heat engine or Heat pump/refrigerator
50 MAE 320 THERODYNAMICS FINAL EXAM - Practice Name: You are allowed three sheets of notes. 1. Fill in the blanks for each of the two (Carnot) cycles below. (a) 5 a) Heat engine or Heat pump/refrigerator
Chapter 4 ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 4 ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 4 ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMS Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Chapter 7. Dr Ali Jawarneh. Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University
 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
Energy: The ability to cause changes. thermodynamics stems from therme (heat) and dynamis (power).
 Energy: The ability to cause changes. thermodynamics stems from therme (heat) and dynamis (power). Thermodynamics: The science of energy. Conservation of energy principle: During an interaction, energy
Energy: The ability to cause changes. thermodynamics stems from therme (heat) and dynamis (power). Thermodynamics: The science of energy. Conservation of energy principle: During an interaction, energy
The first law of thermodynamics continued
 Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
