PARAMETRIC STUDY ON MOMENT REDISTRIBUTION IN CONTINUOUS RC BEAMS USING DUCTILITY DEMAND AND DUCTILITY CAPACITY CONCEPT *
|
|
|
- Angelina Summers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Tranacion B, Engineering, Vol. 31, No. B, Prined in The Ilamic Reublic of Iran, 7 Shiraz Univeri PARAMETRIC STUDY ON MOMENT REDISTRIBUTION IN CONTINUOUS RC BEAMS USING DUCTILITY DEMAND AND DUCTILITY CAPACITY CONCEPT * D. MOSTOFINEJAD ** AND F. FARAHBOD De. of Civil Engineering, Ifahan Univeri of Technolog, Ifahan, , I. R. of Iran dmoofi@cc.iu.ac.ir Abrac Exerimenal udie how ha an indeerminae rucure or a coninuou concree beam doe no fail when criical ecion reach heir ulimae rengh. Therefore, if a rucure ha adequae ducili, re and momen rediribuion will ake lace in he flexural member b develoing laic hinge a criical ecion. Thi caue he oher oin of beam o achieve heir ulimae rengh and caaciie. Beide, momen rediribuion allow deigner o adju he bending momen diagram comued b elaic anali. The uual reul i a reducion in he value of negaive momen a he uor face a well a an increae in he value of oiive momen along he an. In he curren inveigaion, a arameric ud on momen rediribuion in coninuou RC beam wih equal an under uniform loading wa erformed. Fir, he governing equaion for he allowable ercen of momen rediribuion wa exraced uing ducili demand and ducili caaci conce. The effec of differen arameer uch a he concree comreive rengh, he amoun and he rengh of reinforcing eel, he magniude of elaic momen a he uor and he raio of he lengh o he effecive deh of he coninuou beam on momen rediribuion were hen inveigaed. Furhermore, he allowable momen rediribuion were calculaed according o he regulaion of differen code in each cae. The reul howed ha, wherea he ermiible momen rediribuion in coninuou reinforced concree beam baed on he relevan rule in he curren code i no in a afe margin in ome cae, i i raher conervaive in mo cae. Keword Momen rediribuion, reinforced concree, ducili demand, ducili caaci 1. INTRODUCTION Elaic anali of coninuou reinforced concree beam i no able o demonrae a realiic behavior of he rucure a ulimae load. According o he code, coninuou member mu be deigned o rei more han one configuraion of live load. An elaic anali i erformed for each loading arrangemen and an enveloe momen value i obained for he deign of each ecion. Therefore, for an loading aern, cerain ecion in a given an will reach he ulimae momen, while he full caaci in he oher ecion i no uilized. Exerimenal e have hown ha a rucure can carr ome addiional load in exce o i elaic caaci if he ecion ha reach heir momen caaciie coninue o roae a laic hinge and rediribue he momen o oher ecion unil a collae mechanim form. Such addiional load caaci rovide he oibili of momen rediribuion in concree rucure [1]. Momen rediribuion ermi deigner o ue he bending momen diagram comued b elaic anali and modif i o accoun for laic behavior. Uuall hi rediribuion i carried ou b decreaing he negaive momen a he fir laic hinge region, wih correonding change in he oiive momen required b he equilibrium. The change in momen ma be uch a o reduce boh he Received b he edior Aril 16, 6; final revied form December 16, 6. Correonding auhor
2 46 D. Moofinejad / F. Farahbod maximum oiive and negaive momen in he final enveloe diagram. Accordingl, momen rediribuion ma avoid reinforcemen congeion in he negaive momen region wihou an increae in he reinforcemen of he oiive momen region. The rimar exerimen regarding he momen rediribuion in coninuou reinforced concree beam were erformed b Maock in 199, and Cohn in 1964 [, 3]. Their work indicaed ha he rediribuion of he deign bending momen u o ercen doe no ignificanl change he curvaure and he crack widh in a coninuou RC beam deigned b he elaic heor. In 1993 Scholz inveigaed and verified he influence of he varing beam lenderne and iffne on he momen rediribuion in coninuou RC beam uing he ducili conce. He comared hi rooed mehod wih he allowable momen rediribuion given in he Canadian code, and concluded ha hi mehod redic more realiic reul for momen rediribuion comared o he reul of he Canadian code (CAN3-A3.3) [4]. In Lin and Chien udied he effec of longiudinal and ranvere reinforcemen on he ducili and momen rediribuion of 6 coninuou RC beam. The concluded ha he ranvere reinforcemen confine he concree and increae he ducili and momen rediribuion in he coninuou flexural member []. The aim of he curren ud i o deermine he allowable momen rediribuion uing ducili demand and ducili caaci conce. Furhermore, he influence of differen variable on he allowable momen rediribuion are inveigaed and dicued. The reul of hi ud how ha he allowable value exraced from he ducili-baed relaionhi are le han hoe ermied b code in ome cae.. RESEARCH SCOPE The curren andard in he world ae he ermiible momen rediribuion in variou form. Some of he code, i.e. CAN-A3., AS 36, BS 81 and CEB-FIP, define he allowable momen rediribuion direcl on he bai of he raio of he deh of he neural axi, c, o he effecive deh of beam, d [6-9]. ACI have limied he ercenage of he momen rediribuion o he maximum value of { 1 ( ρ ρ ) ρb }%, where ρ, ρ and ρb are he raio of he enile reinforcemen, ρ = A bd he raio of he comreive reinforcemen, ρ = A bd, and he reinforcemen raio correonding o he balance condiion, reecivel; while he rediribuion i limied o he condiion ha ρ or ρ ρ are no greaer han.ρb []. However he ACI 318- define he allowable momen rediribuion in erm of ne enile rain in exreme enile eel, ε, and exree i a ε ercen. According o hi code, he momen rediribuion i ermied if he criical ecion have adequae ducili; i.e. ε i equal or greaer han.7 a he ecion under conideraion [11]. Uing equilibrium equaion in a beam ecion, he ermiible momen rediribuion in an code could be exreed a a funcion of c / d. Such relaionhi are hown in Fig. 1 for ix differen code. I could be oberved from hi figure ha ACI 318 and CAN-A3. have limied he maximum rediribuion o he value of %, while he oher 4 code have limied he rediribuion of he momen o he maximum value of 3%. On he oher hand, he raio of c / d could be eail exreed a a funcion of he ne enile rain in he exreme enile reinforcemen, ε, uing he comaibili equaion in he rain diagram of a beam ecion. Such relaionhi are hown in Fig. for he relevan exreion in he aforemenioned 6 code. I could be een from hi figure ha ACI 318 and CAN-A3. have conidered a more conervaive afe margin for momen rediribuion comared o he oher 4 code. Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B Ocober 7
3 Parameric ud on momen rediribuion in 461 Momen rediribuion % 3 ACI [1 1] ACI [1 ] CAN-A3. [6] BS 811 [8] CEB-FIP [9] AS 36 [7] c / d Fig. 1. Permiible momen rediribuion veru he raio of c/d baed on differen code 3 Percen Change in Momen 3 ACI 318- [11] ACI [] CAN-A3. [6] BS 811 [8] CEB-FIP [9] AS 36 [7] Ne Tenile Srain Fig.. Permiible momen rediribuion veru he ne enile rain baed on differen code In he curren reearch, i i inended o ud he influence of differen arameer on momen rediribuion, i.e. he effec of he comreive rengh of concree, ield rengh of eel, he amoun of enile and comreive eel, he magniude of he elaic momen of he uor and he raio of he an o he effecive deh of he beam. To do o, he governing equaion of he allowable momen rediribuion in coninuou RC beam i obained wih regard o he minimum roaional caaci and he required ducili in he laic hinge region. Aferward, he effec of he aforemenioned arameer on he amoun of momen rediribuion are inveigaed and he reul are comared wih he limiaion of he momen rediribuion rovided b ACI 318- and he relevan requiremen in ome oher code. 3. CONVENTIONAL MOMENT REDISTRIBUTION Figure 3 illurae an inernal an of a coninuou reinforced concree beam wih lengh L, ubjeced o uniforml diribued load W. The maximum momen a he uor and he mid-an of he beam obained from he elaic anali for a aricular loading configuraion are M e, and M e, reecivel. A hown in Fig. 3 hee value will be reecivel changed o M u and M u afer comleion of rediribuion. The ercenage of momen rediribuion in he negaive momen region, R, i defined a follow: R = M M / M (1) ( e u ) e From Eq. (1), M u can be exreed in erm of he ercenage of momen rediribuion, R, and he elaic momen a he uor, M ; e M u = M ( 1 R ) () e Ocober 7 Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B
4 46 D. Moofinejad / F. Farahbod Plaic Hinge W Plaic Hinge EI L θ L P φu z φ Fig. 3. Elaic and inelaic momen 4. DUCTILITY DEMAND Aume ha he coninuou beam in Fig. 4 ha a conan iffne EI, and rimaril he laic hinge ake lace a he uor; alo aume an elao-laic bilinear momen-curvaure for he beam. Therefore, he demand value of laic hinge roaion uing he momen area mehod a hown in Fig. can be exreed b; d L WL θ = = ( θ θ ) M u EI (3) 1 where E i he modulu of elaici, I i he momen of ineria of he beam, and θ P and θ P are illuraed in Fig.. W Mu Me M ' e M ' u z L Fig. 4. Plaic hinge roaion and curvaure Mu W θ d Mu W = + θ 'P Mu θ '' Mu WL /8EI L L/ Mu /EI L L/ Fig.. Demand roaion uing momen area mehod The relaionhi beween he available laic hinge roaion and he curvaure of a criical ecion i given b [1]; a θ = ( φ φ ) L (4) where φ u i he curvaure a ulimae, φ i he curvaure a ield, and LP i he effecive lengh of he laic hinge (Fig. 4). Beide, baed on he bi-linear momen-curvaure diagram for he beam ecion, i i oible o exre he ecion curvaure a ield a; Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B Ocober 7 u
5 Parameric ud on momen rediribuion in 463 φ = M u EI () To have ufficien ducili for he occurrence of full momen rediribuion in a coninuou beam, θ mu be equal or greaer hanθ d. To mee hi requiremen and ubiuing he EI value from Eq. () ino Eq. (3), i can be aed; L WL φ ( φ u φ ) L φ (6) 1M u a Subiuing φ u L WL 1+ 1 φ L 1M u M u from Eq. () ino Eq. (7) will reul in: where φ φ i he ducili demand curvaure. u φ u L ( WL 1) 1+ 1 φ L M e(1 R ) (7) (8). DUCTILITY CAPACITY The curvaure of a beam ecion a i ulimae behavior wih reec o he rain diagram a failure i; φ = c (9) u ε cu wih ε. 3 a he ulimae rain of concree. The curvaure a ield i obained a; cu ( f E ) [ d( 1 k) ] φ = () where f and E are ield re and modulu of elaici of eel, reecivel; d i effecive deh. The value of k, he raio of he deh of he neural axi o an effecive deh of a beam ecion a he verge of he ield of reinforcemen could be obained a follow [1]: d 1 k = [( ρ + ρ ) n + ( ρ + ρ ) n ( ) n d ] ρ + ρ (11) wih n = E Ec and d equal o he diance from comreion eel o he exreme comreion fiber. Dividing Eq. (9) b Eq. (), he ducili caaci index will be calculaed a follow: The relaionhi beween indicaed a; φu ε cu (1 k) η φ = = (1) φ ( f E )( c d) c d and ε uing comaibili equaion of rain, a hown in Fig. 6, can be c d = ε ( ε + ε cu ) (13) where d i he diance from he exreme comreion fiber o he exreme enion eel. Furhermore, he raio of c d could be obained a follow: c d = d d)[ ε ( ε + ε )] (14) cu ( cu cu Subiuing he value of c d in Eq. (1), he raio of φ u φ will be found o be a follow: φu ( ε + ε cu )(1 k) η φ = = () φ ( d d)( f E ) Ocober 7 Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B
6 464 D. Moofinejad / F. Farahbod Fig. 6. Sre and rain diribuion of beam ecion a ulimae 6. ALLOWABLE MOMENT REDISTRIBUTION Sufficien roaional caaci and adequae ducili for momen rediribuion of flexural member will be rovided, if ducili caaci would be a lea equal o ducili demand. Equaing he righ ide of inequali (8) and Eq. (), he allowable momen rediribuion R i exraced a: R = 1 L M e L WL 1 ( ε + ε cu )(1 k) ( d )( ) d f E The variaion in he allowable momen rediribuion veru he ne enile rain in exreme enile eel of he beam ecion i hown in Fig. 7. For a coninuou beam wih equal an, L L P = 38, f = 4 MPa, ε cu =. 3, d = d and he elaic momen of uor M e = WL 1. Figure 7 illurae adequae agreemen beween he momen rediribuion curve obained from Eq. (16) and reference [13]. I could be een from hi figure ha he ACI 318- code rovide an adequae margin of momen rediribuion, while he oher andard reen exceive and higher value of rediribuion; for examle AS 36 and CEB-FIP how high value of momen rediribuion for ε =.1. and ε =.., reecivel. Noe ha Eq. (16) could alo be direcl ued for momen rediribuion in coninuou reinforced concree beam rovided for he conrol of erviceabili requiremen. (16) Percen Change in Momen ACI 318- [1 1] ACI [1 ] CAN-A3. [6] CEB-FIP [9] AS 36 [7] Eq. 1 6 & L/L=38 Reference [1 3] Ne Tenile Srain Fig. 7. Variaion of ermiible momen rediribuion veru ne enile rain in exreme enile eel baed on differen code 7. EFFECT OF L d RATIO ON MOMENT REDISTRIBUTION A indicaed in Eq. (16), he ermiible momen rediribuion i relaed o L L. To inveigae he effec of he raio of he beam an o he effecive deh of he beam, L d, on he amoun of he momen rediribuion in a coninuou beam, he lengh of he laic hinge, L, mu be quanified. Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B Ocober 7
7 Parameric ud on momen rediribuion in 46 a) The laic hinge lengh Variou exreion have been rooed for deermining he equivalen lengh of he laic hinge; ome of hem are ummarized a follow [1]: Baker, 1964: 1 4 L P = k k ( z d d [mm] (17) 1 3 ) where k 1 i aken equal o.7 for mild eel, k 3 i aken equal o.6 when f = 3. MPa, and.9 when fc = 11.7 MPa; d i he effecive deh of he beam; and z i he diance of criical ecion from he oin of inflecion in he bending momen diagram. Sawer, 1964 L P =.7z +. d [mm] (18) Maock, 1967 L =.z +. d [mm] (19) Paula and Priele, 199 [14]: f i he ield rengh of eel and where Leman e al, 1998 []: P L =.8z +. f d. 44 f d [mm] () b d b i he diameer of longiudinal eel. L =.α z + 1.α ( f 4 f ) d [mm] (1) u u c b b M u M α = () M where f u i he ulimae rengh of eel, f c i he comreive rengh of concree, a he fir ield of enile eel and M u i he ulimae momen of beam ecion. Panagioako and Fardi, 1 [16]: P b c M i he momen L =.1z f d [mm] (3) I could be een ha he lengh of he laic hinge in Eq. (17) o (19) i defined in erm of z and effecive beam deh, d ; while L in Eq. () o (3) i comried of he effec of he arameer z and he anchorage li of longiudinal reinforcing bar. b) The relaionhi beween L d and L L To deermine relaion beween L d and L L, i i required o fir calculae z. For racical cae, in a coninuou beam wih equal an under uniform loading, z varie from.l o.l for M u = WL 16 o M u = WL 1, reecivel. Beide, he ACI 318- code limi he raio of lengh o he effecive deh of he coninuou beam, L d, o he maximum value of 1 for deflecion. Since h varie from 1.1d o 1.d in convenional beam; herefore, L d will be limied o he maximum value of. Hence, for calculaing L baed on Eq. (17), ubiuing k1 =. 7 and auming z =. L and an average value of. 7 for k 3, he laic hinge lengh, L, will be equal o L P = (.)(.L) d (4) 3/ 4 L L P =.8483( L d) (Baker equaion) () Ocober 7 Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B
8 466 D. Moofinejad / F. Farahbod Furhermore, auming z =. L in Eq. (18) and (19), L L will be a follow for Sawer and Maock exreion, reecivel; L L P = 1 (. +. d L) (6) L L P = 1 (. +. d L) (7) Similar equaion could be obained for L L, wih he aumion of z =. L ; for inance uing Eq. (18), L L will equal o; L L P = 1 (.1 +.d L) (Sawer equaion) (8) The amoun of L L have been calculaed and reened in Table 1 for L d =, and, according o Baker, Sawer, and Maock equaion and for z =. L and.l. Furhermore, auming L = 8 mm, d b = mm and f = 4 MPa, he raio of L L ha been reened in hi able, baed on Eq. () and (3). A hown in Table 1, exce for Sawer equaion ha indicae higher value for L L, he oher redicion of L L are cloe ogeher. Table 1. Raio of L L for differen value of z z L/d L/L Eq. () L/L Eq. (6) L/L Eq. (7) L/L Eq. () L/L Eq. (3).L.L Figure 8 illurae he variaion of he ermiible momen rediribuion in erm of ε, baed on Eq. (16), auming f = 4 MPa and M e = WL 1, for z =. L and for differen value of L d. To draw Fig. 8, Eq. (6), which i baed on Sawer equaion, wa ued for he relaionhi of L L and L d. A hown in Fig. 8, he ermiible momen rediribuion decreae when he raio of L d increae. Furhermore, i could be oberved in hi figure ha CAN-A3. and AS 36 code iml exceive rediribuion for ε <. and ε =.1., reecivel. Percen Change in Momen 3 3 Eq. (6), L/d= & L/L=4 Eq. (6), L/d= & L/L=36 Eq. (6), L/d= & L/L=3 Eq. (8), L/d= & L/L=47 ACI 318- [11] CAN-A3. [6] AS 36 [7] Ne Tenile Sre Fig. 8. Allowable momen rediribuion for differen raio of L/d The variaion of ermiible momen rediribuion for z =. L, L d = and L L = 47, ha been alo indicaed in Fig. 8. I could be een from hi figure ha for high level of L L, e.g. Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B Ocober 7
9 Parameric ud on momen rediribuion in 467 L L = 47, ACI 318- rovide a afe margin for momen rediribuion, while oher code like CAN-A3. and AS 36 give higher amoun of rediribuion in he ame condiion. 8. EFFECT OF CONCRETE COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH To evaluae he effec of he comreive rengh of concree on momen rediribuion in coninuou beam, i i required o deermine he relaion of ε and f c. A hown in Fig. 9, auming ρ = and uing he rain comaibili rincial, Eq. (14) can be rewrien a below: c d = d d)[ ε ( ε + ε )] = ( ρ f ) (.8 f β ) (9) ( cu cu c 1 ε + ε ) ( d d) = (.8β f ε ) ( ρ f ) (3) ( cu 1 c cu Subiuing Eq. (3) ino Eq. (16) and auming ε cu =.3 and momen rediribuion i obained in erm of f c ; MPa E =, he ermiible R = 1 M e L L ( WL 1) β 1 fc (1 k) ρ( f ) (31) Figure 9 how he ermiible momen rediribuion in erm of ε for variou amoun of f c, auming f = 4 MPa, L L = 38 and M e = WL 1. I could be een from Fig. 9 ha higher value of f c rovide higher amoun for oible momen rediribuion. Such a reul i alicable for concree rengh which coml wih he code aumion on comreion re block arameer. Furhermore, Fig. 9 how ha for low value of concree comreive rengh, i.e. f c = 17 MPa, ACI 318- overeimae he ermiible momen rediribuion; alo he oher curren code like CAN- A3.., AS 36 and CEB-FIP, allow for higher amoun of momen rediribuion, comared o he quaniie aken from heoreical anali. Percen Change in Momen 3 3 f ' c=3 & f=4 MPa f ' c= & f=4 MPa f ' c= & f=4 MPa f ' c=1 7 & f=4 MPa ACI [11] CAN-A3. [6] AS 36 [7] CEB-FIP [9] Ne Tenile Srain Fig. 9. Permiible momen rediribuion veru ne enile rain of eel for variou concree comreive rengh 9. EFFECT OF YIELD STRENGTH OF STEEL The ield rengh of eel i couned a an influenial arameer on momen rediribuion in RC coninuou beam. Auming M e = WL 1 and L d =, he ermiible momen rediribuion in erm of rain ε, for f = 4 and MPa i indicaed in Fig.. I could be een from Fig. ha a Ocober 7 Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B
10 468 D. Moofinejad / F. Farahbod long a he ield rengh of reinforcing eel i no greaer han ha of convenional eel, i.e. f 4 MPa, he ACI 318- code ermi for momen rediribuion in a afe margin, while he oher andard, i.e. CAN-A3. and AS 36 allow for higher amoun of rediribuion. However, for higher value of f, all code ma overeimae he amoun of ermiible momen rediribuion, eeciall when he beam i deigned in uch a wa ha i enile reinforcemen i no much enioned. Percen ercen Change Change in in Momen Momen f=4 M Pa & L/d= f= M Pa & L/d= 3 f= M Pa & L/d= 3 ACI 318- CAN-A3. [6] AS 36 [7] Ne Tenile Sre Fig.. Permiible momen rediribuion for differen value of ield rengh of reinforcing eel. EFFECT OF THE AMOUNT OF REINFORCING STEEL The amoun of enile and comreive reinforcing eel in a coninuou beam alo affec on he oible momen rediribuion. For an under-reinforced concree ecion which i hown in Fig. 6, uing equilibrium and comaibili equaion and olving he reuling equaion wih reec o he neural axi deh, c, he following equaion could be obained; c = ( ρf.3ρ de ) + ( ρf.3ρ E ) fc β1(.3ρ Ed / d ) d 1.7β f 1 c (3) where ρ and ρ are he enile and comreive reinforcemen raio, reecivel; and d and d are reecivel he diance of enile and comreive eel from he exreme comreion fiber in concree. fc 6 Subiuing c from Eq. (3) ino Eq. (14) and uing he balanced eel raio a ρ b =.8β1, f 6 + f he following equaion i exraced; ε + ε d d cu = ρb ( f + 6)( f 6) ( ρf.3ρ E ) + ( ρf.3ρ E ) f β (.3ρ E d d ) Equaion (33) accomanied b Eq. (16) can be ued o how he effec of he amoun of eel reinforcemen on he oible ercenage of momen rediribuion. Uing hee equaion and auming f = 4 MPa, L L = 38 and M e = WL 1, he ermiible momen rediribuion in erm of ρ ρ b i calculaed and illuraed in Fig. 11 for differen raio of comreive and enile eel. Figure 11 how ha increae in he raio of enile reinforcemen o he balanced reinforcemen, ρ ρ b, decreae he allowable momen rediribuion. Furhermore, increaing he amoun of comreive reinforcemen, ρ, increae he amoun of he momen rediribuion. I could be oberved from he figure ha ACI 318-, deie he oher code, rovide acceable amoun of momen rediribuion for differen combinaion of ρ ρ and ρ ρ. Neverhele, he rocedure of b c 1 (33) Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B Ocober 7
11 Parameric ud on momen rediribuion in 469 ACI 318- lead o ver conervaive value of momen rediribuion for low raio of raio of ρ ρ. Percen Change in Momen 3 ρ ' / ρ = 3 ρ ' / ρ =. ρ ' / ρ =. ρ ' / ρ =.7 ρ ' / ρ = 1. ACI 318- [11] CAN-A3. [6] AS 36 [7] Tenion Seel Raio ( ρ ρ b ) Fig. 11. Permiible momen rediribuion veru he enile eel raio, for differen value of comreive eel 11. EFFECT OF THE ELASTIC MOMENT OF SUPPORT ρ ρb and high To inveigae he effec of he amoun of elaic momen of uor on he momen rediribuion baed on Eq. (16), he variaion of he ermiible momen rediribuion in erm of ε for L L = 38, M e = WL 11 and M e = WL 1 i hown in Fig. 1. Noe ha in convenional coninuou beam, he negaive elaic momen a he face of inernal uor normall varie wihin WL 11 and WL 1. I could be een from Fig. 1 ha if he elaic momen in he uor region of a reinforced concree beam increae, he ermiible momen rediribuion in he beam would alo increae. Figure 1 how ha for a aricular ne enile rain of ε =., he ercenage of rediribuion in momen are 8% and 34% for elaic momen of he uor equal o WL 1 and WL 11, reecivel. However mo code including ACI 318- and CAN-3. limi he maximum ermiible momen rediribuion o %, robabl o reven he evere roagaion of he crack under erviceabili condiion. Neverhele, ome oher code including AS 36, BS 81 and CEB-FIP allow for rediribuion of he momen u o 3% [7-9]. 3 Percen change in momen 3 Eq. (16) & M e=wl /1 Eq. (16) & M e=wl /11 ACI 318- CAN-A3. [6] AS 36 [7] BS 81 [8] CEB-FIP [9] Ne enile rain Fig. 1. Permiible momen rediribuion for differen value of uor elaic momen 1. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In he curren ud, uing ducili demand and ducili caaci conce, he effec of differen arameer on he momen rediribuion of reinforced concree coninuou beam wih equal an, under uniform loading were inveigaed. Providing minimum roaional caaci in he laic hinge region of he beam, he coniuive equaion of ermiible momen rediribuion in erm of ne enile rain, ε, a well a in erm of raio of enile and comreive reinforcemen wa obained. The variaion of Ocober 7 Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B
12 47 D. Moofinejad / F. Farahbod ercen change in momen rediribuion wih regard o ome arameer were drawn and comared wih he roviion of ome curren andard including ACI 318-, CAN-A3., AS 36, BS 81 and CEB-FIP code in ome cae. The reul of hi ud wihin he aumion which were made in he anali are ummarized a follow: 1. Increaing he ne enile rain in exreme enile eel increae he ermiible momen rediribuion value.. Increaing he raio L d and L L, and uilizing he convenional equaion for he eimaion of he laic hinge lengh, decreae he ermiible momen rediribuion. 3. The ermiible momen rediribuion i decreaed b decreaing he concree comreive rengh; alo, i i decreaed b he increae of ield rengh of enile reinforcemen. Furhermore, increae in enile reinforcemen raio, decreae he value of ermiible momen rediribuion. 4. Comreive eel advanageoul affec on momen rediribuion enhancemen. The higher raio of comreive o enile reinforcemen in he beam ecion augmen he oible momen rediribuion.. The ermiible momen rediribuion would enhance b increae in he elaic momen of uor. 6. Alhough he ACI 318- code exhibi a afe margin for ermiible momen rediribuion in mo cae: he code roviion lead o higher amoun of momen rediribuion in ome cae; for inance, in coninuou beam wih high raio of L d and eel ield rengh, or in beam wih low comreive rengh of concree. Furhermore, oher curren code, i.e. Canadian, Auralian and Euroean andard rovide exceive value of momen rediribuion for he cae whenε <., ε >. 1 and. < ε <., reecivel. 7. Proviion of he curren code including ACI 318-, CAN-A3. and AS 36 lead o ver conervaive value for momen rediribuion in ome cae, i.e. in coninuou reinforced concree beam wih enile and comreive reinforcemen wih he raio of ρ ρ >.. 8. Comared o he roviion of he code, higher value of momen rediribuion could be obained for coninuou reinforced concree beam wih high value of ε a ulimae; however, i ma no be adviable o uilize hee value due o evere crack roagaion a he erviceabili age. REFERENCES 1. Noe on ACI 318-, (). Building code requiremen for rucural concree wih deign alicaion. PCA, USA.. Maock, A. H. (199) Rediribuion of deign bending momen in reinforced concree coninuou beam, Proceeding, Iniuion of Civil Engineer (London), Vol. 13, Cohn, M. Z. (1964). Roaional comaibili in he limi deign of reinforced concree coninuou beam. Proceeding, Inernaional Smoium on he Flexural Mechanic of Reinforced Concree, ASCE-ACI, Miami, Scholz, H. (1993). Conribuion o rediribuion of momen in coninuou reinforced concree beam, ACI Sruc. J., Vol. 9, No.,. -.. Lin, Chien-Hung, & Chien, Yu-Min. (). Effec of ecion ducili on momen rediribuion of coninuou concree beam, Journal of Chinee Iniue of Engineer, Tranacion of he Chinee Iniue of Engineer, Vol. 3, No., CAN-A3.. (1994). Code for he deign of concree rucure for building, Canadian Sandard Aociaion. Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B Ocober 7
13 Parameric ud on momen rediribuion in AS 36, (1994). Auralian concree rucure andard. Sandard Auralia, Sdne, Auralia. 8. BS 81, (199) Srucural Ue of Concree-ar 1, Briih Sandard Iniuion. 9. CEB-FIP, (199). Inernaional em of unified andard code of racice for rucure. Model Code for Concree Srucure, Euroe.. ACI , (1999). Building code requiremen for rucural concree (ACI ) and commenar-aci 318 RM-99. ACI, Farmingon Hill, MI, USA. 11. ACI 318-, (). Building code requiremen for rucural concree (ACI 318-) and commenar-aci 318 R-. ACI, Farmingon Hill, MI, USA. 1. Park, R. & Paula, T. (197). Reinforced concree rucure. John Wile & Son. 13. Ma, R. F. (199). Unified deign roviion for reinforced and rereed concree flexural and comreion member. ACI Sruc. J., Vol. 89, No., Paula, T. & Priele, M. J. N. (199). Seimic deign of reinforced concree and maonar building. John Wile & Son, New York.. Leman, D. E., Calderone, A. J. & Moehle, J. P. (1998). Behavior and deign of lender column ubjeced o laeral loading. 6h US Naional Conference on Earhquake Engineering, EERI, Seale, Wahingon, Ma Panagioako, T. & Fardi, M. N. (1). Deformaion of RC member a eilding and uimae. ACI Sruc. J., Vol. 98, No., Ocober 7 Iranian Journal of Science & Technolog, Volume 31, Number B
Buckling of a structure means failure due to excessive displacements (loss of structural stiffness), and/or
 Buckling Buckling of a rucure mean failure due o exceive diplacemen (lo of rucural iffne), and/or lo of abiliy of an equilibrium configuraion of he rucure The rule of humb i ha buckling i conidered a mode
Buckling Buckling of a rucure mean failure due o exceive diplacemen (lo of rucural iffne), and/or lo of abiliy of an equilibrium configuraion of he rucure The rule of humb i ha buckling i conidered a mode
Lecture 5 Buckling Buckling of a structure means failure due to excessive displacements (loss of structural stiffness), and/or
 AOE 204 Inroducion o Aeropace Engineering Lecure 5 Buckling Buckling of a rucure mean failure due o exceive diplacemen (lo of rucural iffne), and/or lo of abiliy of an equilibrium configuraion of he rucure
AOE 204 Inroducion o Aeropace Engineering Lecure 5 Buckling Buckling of a rucure mean failure due o exceive diplacemen (lo of rucural iffne), and/or lo of abiliy of an equilibrium configuraion of he rucure
( ) - maximum permissible bending. IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 01, 2016 ISSN (online):
 IJSRD - Inernaional Journal for Scienific Reearch & Developmen Vol. 4, Iue 01, 016 ISSN (online): 31-0613 Dr.N.Arunachalam 1 P.Prakah K.Jayakarhik 3 M.Narmadha 4 1 Profeor & Dean,3 PG Scholar 4 Aociae
IJSRD - Inernaional Journal for Scienific Reearch & Developmen Vol. 4, Iue 01, 016 ISSN (online): 31-0613 Dr.N.Arunachalam 1 P.Prakah K.Jayakarhik 3 M.Narmadha 4 1 Profeor & Dean,3 PG Scholar 4 Aociae
AN ANALYTICAL METHOD OF SOLUTION FOR SYSTEMS OF BOOLEAN EQUATIONS
 CHAPTER 5 AN ANALYTICAL METHOD OF SOLUTION FOR SYSTEMS OF BOOLEAN EQUATIONS 51 APPLICATIONS OF DE MORGAN S LAWS A we have een in Secion 44 of Chaer 4, any Boolean Equaion of ye (1), (2) or (3) could be
CHAPTER 5 AN ANALYTICAL METHOD OF SOLUTION FOR SYSTEMS OF BOOLEAN EQUATIONS 51 APPLICATIONS OF DE MORGAN S LAWS A we have een in Secion 44 of Chaer 4, any Boolean Equaion of ye (1), (2) or (3) could be
u(t) Figure 1. Open loop control system
 Open loop conrol v cloed loop feedbac conrol The nex wo figure preen he rucure of open loop and feedbac conrol yem Figure how an open loop conrol yem whoe funcion i o caue he oupu y o follow he reference
Open loop conrol v cloed loop feedbac conrol The nex wo figure preen he rucure of open loop and feedbac conrol yem Figure how an open loop conrol yem whoe funcion i o caue he oupu y o follow he reference
Control Systems. Lecture 9 Frequency Response. Frequency Response
 Conrol Syem Lecure 9 Frequency eone Frequency eone We now know how o analyze and deign yem via -domain mehod which yield dynamical informaion The reone are decribed by he exonenial mode The mode are deermined
Conrol Syem Lecure 9 Frequency eone Frequency eone We now know how o analyze and deign yem via -domain mehod which yield dynamical informaion The reone are decribed by he exonenial mode The mode are deermined
5.2 GRAPHICAL VELOCITY ANALYSIS Polygon Method
 ME 352 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS 52 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS olygon Mehod Velociy analyi form he hear of kinemaic and dynamic of mechanical yem Velociy analyi i uually performed following a poiion analyi; ie,
ME 352 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS 52 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS olygon Mehod Velociy analyi form he hear of kinemaic and dynamic of mechanical yem Velociy analyi i uually performed following a poiion analyi; ie,
13.1 Accelerating Objects
 13.1 Acceleraing Objec A you learned in Chaper 12, when you are ravelling a a conan peed in a raigh line, you have uniform moion. However, mo objec do no ravel a conan peed in a raigh line o hey do no
13.1 Acceleraing Objec A you learned in Chaper 12, when you are ravelling a a conan peed in a raigh line, you have uniform moion. However, mo objec do no ravel a conan peed in a raigh line o hey do no
Combined Bending with Induced or Applied Torsion of FRP I-Section Beams
 Combined Bending wih Induced or Applied Torsion of FRP I-Secion Beams MOJTABA B. SIRJANI School of Science and Technology Norfolk Sae Universiy Norfolk, Virginia 34504 USA sirjani@nsu.edu STEA B. BONDI
Combined Bending wih Induced or Applied Torsion of FRP I-Secion Beams MOJTABA B. SIRJANI School of Science and Technology Norfolk Sae Universiy Norfolk, Virginia 34504 USA sirjani@nsu.edu STEA B. BONDI
CHAPTER 7: SECOND-ORDER CIRCUITS
 EEE5: CI RCUI T THEORY CHAPTER 7: SECOND-ORDER CIRCUITS 7. Inroducion Thi chaper conider circui wih wo orage elemen. Known a econd-order circui becaue heir repone are decribed by differenial equaion ha
EEE5: CI RCUI T THEORY CHAPTER 7: SECOND-ORDER CIRCUITS 7. Inroducion Thi chaper conider circui wih wo orage elemen. Known a econd-order circui becaue heir repone are decribed by differenial equaion ha
Chapter 7: Inverse-Response Systems
 Chaper 7: Invere-Repone Syem Normal Syem Invere-Repone Syem Baic Sar ou in he wrong direcion End up in he original eady-ae gain value Two or more yem wih differen magniude and cale in parallel Main yem
Chaper 7: Invere-Repone Syem Normal Syem Invere-Repone Syem Baic Sar ou in he wrong direcion End up in he original eady-ae gain value Two or more yem wih differen magniude and cale in parallel Main yem
An Improved Anti-windup Control Using a PI Controller
 05 Third nernaional Conference on Arificial nelligence, Modelling and Simulaion An mroved Ani-windu Conrol Uing a P Conroller Kyohei Saai Graduae School of Science and Technology Meiji univeriy Kanagawa,
05 Third nernaional Conference on Arificial nelligence, Modelling and Simulaion An mroved Ani-windu Conrol Uing a P Conroller Kyohei Saai Graduae School of Science and Technology Meiji univeriy Kanagawa,
TP B.2 Rolling resistance, spin resistance, and "ball turn"
 echnical proof TP B. olling reiance, pin reiance, and "ball urn" upporing: The Illuraed Principle of Pool and Billiard hp://billiard.coloae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore, PhD, PE ("Dr. Dae") echnical proof originally
echnical proof TP B. olling reiance, pin reiance, and "ball urn" upporing: The Illuraed Principle of Pool and Billiard hp://billiard.coloae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore, PhD, PE ("Dr. Dae") echnical proof originally
20. Applications of the Genetic-Drift Model
 0. Applicaions of he Geneic-Drif Model 1) Deermining he probabiliy of forming any paricular combinaion of genoypes in he nex generaion: Example: If he parenal allele frequencies are p 0 = 0.35 and q 0
0. Applicaions of he Geneic-Drif Model 1) Deermining he probabiliy of forming any paricular combinaion of genoypes in he nex generaion: Example: If he parenal allele frequencies are p 0 = 0.35 and q 0
At the end of this lesson, the students should be able to understand
 Insrucional Objecives A he end of his lesson, he sudens should be able o undersand Sress concenraion and he facors responsible. Deerminaion of sress concenraion facor; experimenal and heoreical mehods.
Insrucional Objecives A he end of his lesson, he sudens should be able o undersand Sress concenraion and he facors responsible. Deerminaion of sress concenraion facor; experimenal and heoreical mehods.
ANALYSIS OF SOME SAFETY ASSESSMENT STANDARD ON GROUNDING SYSTEMS
 ANAYSIS OF SOME SAFETY ASSESSMENT STANDARD ON GROUNDING SYSTEMS Shang iqun, Zhang Yan, Cheng Gang School of Elecrical and Conrol Engineering, Xi an Univeriy of Science & Technology, 710054, Xi an, China,
ANAYSIS OF SOME SAFETY ASSESSMENT STANDARD ON GROUNDING SYSTEMS Shang iqun, Zhang Yan, Cheng Gang School of Elecrical and Conrol Engineering, Xi an Univeriy of Science & Technology, 710054, Xi an, China,
Made by AAT Date June Checked by JEK Date June Revised by JBL/MEB Date April 2006
 Job No. RSU658 See 1 of 7 Rev B Kemiinie, oo P.O.Box 185, FN VTT, Finland Teleone: + 58 9 561 Fax: + 58 9 56 7 Job Tile Subjec Clien Sainle Seel Valoriaion Projec Deign xamle Deign of a wo-an raezoidal
Job No. RSU658 See 1 of 7 Rev B Kemiinie, oo P.O.Box 185, FN VTT, Finland Teleone: + 58 9 561 Fax: + 58 9 56 7 Job Tile Subjec Clien Sainle Seel Valoriaion Projec Deign xamle Deign of a wo-an raezoidal
Analysis of Boundedness for Unknown Functions by a Delay Integral Inequality on Time Scales
 Inernaional Conference on Image, Viion and Comuing (ICIVC ) IPCSIT vol. 5 () () IACSIT Pre, Singaore DOI:.7763/IPCSIT..V5.45 Anali of Boundedne for Unknown Funcion b a Dela Inegral Ineuali on Time Scale
Inernaional Conference on Image, Viion and Comuing (ICIVC ) IPCSIT vol. 5 () () IACSIT Pre, Singaore DOI:.7763/IPCSIT..V5.45 Anali of Boundedne for Unknown Funcion b a Dela Inegral Ineuali on Time Scale
A Dynamic Model of Economic Fluctuations
 CHAPTER 15 A Dynamic Model of Economic Flucuaions Modified for ECON 2204 by Bob Murphy 2016 Worh Publishers, all righs reserved IN THIS CHAPTER, OU WILL LEARN: how o incorporae dynamics ino he AD-AS model
CHAPTER 15 A Dynamic Model of Economic Flucuaions Modified for ECON 2204 by Bob Murphy 2016 Worh Publishers, all righs reserved IN THIS CHAPTER, OU WILL LEARN: how o incorporae dynamics ino he AD-AS model
Physics 240: Worksheet 16 Name
 Phyic 4: Workhee 16 Nae Non-unifor circular oion Each of hee proble involve non-unifor circular oion wih a conan α. (1) Obain each of he equaion of oion for non-unifor circular oion under a conan acceleraion,
Phyic 4: Workhee 16 Nae Non-unifor circular oion Each of hee proble involve non-unifor circular oion wih a conan α. (1) Obain each of he equaion of oion for non-unifor circular oion under a conan acceleraion,
Macroeconomics 1. Ali Shourideh. Final Exam
 4780 - Macroeconomic 1 Ali Shourideh Final Exam Problem 1. A Model of On-he-Job Search Conider he following verion of he McCall earch model ha allow for on-he-job-earch. In paricular, uppoe ha ime i coninuou
4780 - Macroeconomic 1 Ali Shourideh Final Exam Problem 1. A Model of On-he-Job Search Conider he following verion of he McCall earch model ha allow for on-he-job-earch. In paricular, uppoe ha ime i coninuou
Discussion Session 2 Constant Acceleration/Relative Motion Week 03
 PHYS 100 Dicuion Seion Conan Acceleraion/Relaive Moion Week 03 The Plan Today you will work wih your group explore he idea of reference frame (i.e. relaive moion) and moion wih conan acceleraion. You ll
PHYS 100 Dicuion Seion Conan Acceleraion/Relaive Moion Week 03 The Plan Today you will work wih your group explore he idea of reference frame (i.e. relaive moion) and moion wih conan acceleraion. You ll
Chapter 3 (Lectures 12, 13 and 14) Longitudinal stick free static stability and control
 Fligh dynamics II Sabiliy and conrol haper 3 (Lecures 1, 13 and 14) Longiudinal sick free saic sabiliy and conrol Keywords : inge momen and is variaion wih ail angle, elevaor deflecion and ab deflecion
Fligh dynamics II Sabiliy and conrol haper 3 (Lecures 1, 13 and 14) Longiudinal sick free saic sabiliy and conrol Keywords : inge momen and is variaion wih ail angle, elevaor deflecion and ab deflecion
Introduction to Congestion Games
 Algorihmic Game Theory, Summer 2017 Inroducion o Congeion Game Lecure 1 (5 page) Inrucor: Thoma Keelheim In hi lecure, we ge o know congeion game, which will be our running example for many concep in game
Algorihmic Game Theory, Summer 2017 Inroducion o Congeion Game Lecure 1 (5 page) Inrucor: Thoma Keelheim In hi lecure, we ge o know congeion game, which will be our running example for many concep in game
IB Physics Kinematics Worksheet
 IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
A STUDY ON COMPLICATED ROLL MOTION OF A SHIP EQUIPPED WITH AN ANTI-ROLLING TANK
 607 A STUDY ON COMPLICATED ROLL MOTION OF A SHIP EQUIPPED WITH AN ANTI-ROLLING TANK Harukuni Taguchi, Hirohi Sawada and Kauji Tanizawa Naional Mariime Reearch Iniue (JAPAN) Abrac Nonlinear roll moion of
607 A STUDY ON COMPLICATED ROLL MOTION OF A SHIP EQUIPPED WITH AN ANTI-ROLLING TANK Harukuni Taguchi, Hirohi Sawada and Kauji Tanizawa Naional Mariime Reearch Iniue (JAPAN) Abrac Nonlinear roll moion of
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 31 Signal & Syem Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #27 C-T Syem: Laplace Tranform Power Tool for yem analyi Reading Aignmen: Secion 6.1 6.3 of Kamen and Heck 1/18 Coure Flow Diagram The arrow here how concepual
EECE 31 Signal & Syem Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #27 C-T Syem: Laplace Tranform Power Tool for yem analyi Reading Aignmen: Secion 6.1 6.3 of Kamen and Heck 1/18 Coure Flow Diagram The arrow here how concepual
6.8 Laplace Transform: General Formulas
 48 HAP. 6 Laplace Tranform 6.8 Laplace Tranform: General Formula Formula Name, ommen Sec. F() l{ f ()} e f () d f () l {F()} Definiion of Tranform Invere Tranform 6. l{af () bg()} al{f ()} bl{g()} Lineariy
48 HAP. 6 Laplace Tranform 6.8 Laplace Tranform: General Formula Formula Name, ommen Sec. F() l{ f ()} e f () d f () l {F()} Definiion of Tranform Invere Tranform 6. l{af () bg()} al{f ()} bl{g()} Lineariy
To become more mathematically correct, Circuit equations are Algebraic Differential equations. from KVL, KCL from the constitutive relationship
 Laplace Tranform (Lin & DeCarlo: Ch 3) ENSC30 Elecric Circui II The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranformaion. I ranform: f ( ) F( ) ime variable complex variable From Euler > Lagrange > Laplace. Hence,
Laplace Tranform (Lin & DeCarlo: Ch 3) ENSC30 Elecric Circui II The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranformaion. I ranform: f ( ) F( ) ime variable complex variable From Euler > Lagrange > Laplace. Hence,
2. VECTORS. R Vectors are denoted by bold-face characters such as R, V, etc. The magnitude of a vector, such as R, is denoted as R, R, V
 ME 352 VETS 2. VETS Vecor algebra form he mahemaical foundaion for kinemaic and dnamic. Geomer of moion i a he hear of boh he kinemaic and dnamic of mechanical em. Vecor anali i he imehonored ool for decribing
ME 352 VETS 2. VETS Vecor algebra form he mahemaical foundaion for kinemaic and dnamic. Geomer of moion i a he hear of boh he kinemaic and dnamic of mechanical em. Vecor anali i he imehonored ool for decribing
Influence of High Axial Tension on the Shear Strength of non-shear RC Beams
 Influence of High Axial Tension on he Shear Srengh of non-shear RC Beams Henrik B. JOERGENSEN PhD candidae Univ. of Souhern Denmark hebj@ii.sdu.dk Joergen MAAGAARD Associae Professor Univ. of Souhern Denmark
Influence of High Axial Tension on he Shear Srengh of non-shear RC Beams Henrik B. JOERGENSEN PhD candidae Univ. of Souhern Denmark hebj@ii.sdu.dk Joergen MAAGAARD Associae Professor Univ. of Souhern Denmark
Single Phase Line Frequency Uncontrolled Rectifiers
 Single Phae Line Frequency Unconrolle Recifier Kevin Gaughan 24-Nov-03 Single Phae Unconrolle Recifier 1 Topic Baic operaion an Waveform (nucive Loa) Power Facor Calculaion Supply curren Harmonic an Th
Single Phae Line Frequency Unconrolle Recifier Kevin Gaughan 24-Nov-03 Single Phae Unconrolle Recifier 1 Topic Baic operaion an Waveform (nucive Loa) Power Facor Calculaion Supply curren Harmonic an Th
Sterilization D Values
 Seriliaion D Values Seriliaion by seam consis of he simple observaion ha baceria die over ime during exposure o hea. They do no all live for a finie period of hea exposure and hen suddenly die a once,
Seriliaion D Values Seriliaion by seam consis of he simple observaion ha baceria die over ime during exposure o hea. They do no all live for a finie period of hea exposure and hen suddenly die a once,
ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS IN FIRE
 ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS IN FIRE Dr Zhaohui Huang Universiy of Sheffield 6 May 2005 1 VULCAN layered slab elemens: connecion o beam elemens Plae Elemen Slab nodes y x Reference Plane h
ANALYSIS OF REINFORCED CONCRETE BUILDINGS IN FIRE Dr Zhaohui Huang Universiy of Sheffield 6 May 2005 1 VULCAN layered slab elemens: connecion o beam elemens Plae Elemen Slab nodes y x Reference Plane h
A novel semi-active TMD with folding variable stiffness spring
 A novel emi-acive wih folding variable iffne pring The MIT Faculy ha made hi aricle openly available. Pleae hare how hi acce benefi you. Your ory maer. Ciaion Rafieipour, M. H., A. K. Ghorbani-Tanha, M.
A novel emi-acive wih folding variable iffne pring The MIT Faculy ha made hi aricle openly available. Pleae hare how hi acce benefi you. Your ory maer. Ciaion Rafieipour, M. H., A. K. Ghorbani-Tanha, M.
Curling Stress Equation for Transverse Joint Edge of a Concrete Pavement Slab Based on Finite-Element Method Analysis
 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 155 35 Curling Sress Equaion for Transverse Join Edge of a Concree Pavemen Slab Based on Finie-Elemen Mehod Analysis TATSUO NISHIZAWA, TADASHI FUKUDA, SABURO MATSUNO, AND
TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 155 35 Curling Sress Equaion for Transverse Join Edge of a Concree Pavemen Slab Based on Finie-Elemen Mehod Analysis TATSUO NISHIZAWA, TADASHI FUKUDA, SABURO MATSUNO, AND
Randomized Perfect Bipartite Matching
 Inenive Algorihm Lecure 24 Randomized Perfec Biparie Maching Lecurer: Daniel A. Spielman April 9, 208 24. Inroducion We explain a randomized algorihm by Ahih Goel, Michael Kapralov and Sanjeev Khanna for
Inenive Algorihm Lecure 24 Randomized Perfec Biparie Maching Lecurer: Daniel A. Spielman April 9, 208 24. Inroducion We explain a randomized algorihm by Ahih Goel, Michael Kapralov and Sanjeev Khanna for
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Poisson s Ratio
 Poisson s Raio For a slender bar subjeced o axial loading: ε x x y 0 The elongaion in he x-direcion i is accompanied by a conracion in he oher direcions. Assuming ha he maerial is isoropic (no direcional
Poisson s Raio For a slender bar subjeced o axial loading: ε x x y 0 The elongaion in he x-direcion i is accompanied by a conracion in he oher direcions. Assuming ha he maerial is isoropic (no direcional
Network Flow. Data Structures and Algorithms Andrei Bulatov
 Nework Flow Daa Srucure and Algorihm Andrei Bulao Algorihm Nework Flow 24-2 Flow Nework Think of a graph a yem of pipe We ue hi yem o pump waer from he ource o ink Eery pipe/edge ha limied capaciy Flow
Nework Flow Daa Srucure and Algorihm Andrei Bulao Algorihm Nework Flow 24-2 Flow Nework Think of a graph a yem of pipe We ue hi yem o pump waer from he ource o ink Eery pipe/edge ha limied capaciy Flow
NECESSARY AND SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR LATENT SEPARABILITY
 NECESSARY AND SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR LATENT SEPARABILITY Ian Crawford THE INSTITUTE FOR FISCAL STUDIES DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS, UCL cemmap working paper CWP02/04 Neceary and Sufficien Condiion for Laen
NECESSARY AND SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR LATENT SEPARABILITY Ian Crawford THE INSTITUTE FOR FISCAL STUDIES DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS, UCL cemmap working paper CWP02/04 Neceary and Sufficien Condiion for Laen
v A Since the axial rigidity k ij is defined by P/v A, we obtain Pa 3
 The The rd rd Inernaional Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES 14 Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech Augus Republic, 1 Sepember 1-, 14 In-plane and Ou-of-plane Deflecion of J-shaped
The The rd rd Inernaional Conference on on Design Engineering and Science, ICDES 14 Pilsen, Czech Pilsen, Republic, Czech Augus Republic, 1 Sepember 1-, 14 In-plane and Ou-of-plane Deflecion of J-shaped
Final Spring 2007
 .615 Final Spring 7 Overview The purpose of he final exam is o calculae he MHD β limi in a high-bea oroidal okamak agains he dangerous n = 1 exernal ballooning-kink mode. Effecively, his corresponds o
.615 Final Spring 7 Overview The purpose of he final exam is o calculae he MHD β limi in a high-bea oroidal okamak agains he dangerous n = 1 exernal ballooning-kink mode. Effecively, his corresponds o
Stat13 Homework 7. Suggested Solutions
 Sa3 Homework 7 hp://www.a.ucla.edu/~dinov/coure_uden.hml Suggeed Soluion Queion 7.50 Le denoe infeced and denoe noninfeced. H 0 : Malaria doe no affec red cell coun (µ µ ) H A : Malaria reduce red cell
Sa3 Homework 7 hp://www.a.ucla.edu/~dinov/coure_uden.hml Suggeed Soluion Queion 7.50 Le denoe infeced and denoe noninfeced. H 0 : Malaria doe no affec red cell coun (µ µ ) H A : Malaria reduce red cell
Rocket Theories Continued
 38 Rocke Theories ---------------------- Coninued and Nozzle heory fundamenals Various Liquid Proellans and heir yical Characerisics Pro Ox/F Thrus I s P c C F V * raio Vac SL Vac SL Vac (kn) (kn) s s
38 Rocke Theories ---------------------- Coninued and Nozzle heory fundamenals Various Liquid Proellans and heir yical Characerisics Pro Ox/F Thrus I s P c C F V * raio Vac SL Vac SL Vac (kn) (kn) s s
V L. DT s D T s t. Figure 1: Buck-boost converter: inductor current i(t) in the continuous conduction mode.
 ECE 445 Analysis and Design of Power Elecronic Circuis Problem Se 7 Soluions Problem PS7.1 Erickson, Problem 5.1 Soluion (a) Firs, recall he operaion of he buck-boos converer in he coninuous conducion
ECE 445 Analysis and Design of Power Elecronic Circuis Problem Se 7 Soluions Problem PS7.1 Erickson, Problem 5.1 Soluion (a) Firs, recall he operaion of he buck-boos converer in he coninuous conducion
An Improved Suggestion in Stratified Random Sampling Using Two Auxiliary Variables
 Raje ing Dearmen of Maemaic, RM Univeriy Deli CR, onea- 309, India acin Malik Dearmen of aiic, Banara Hindu Univeriy aranai-005, India Florenin marandace Dearmen of Maemaic, Univeriy of ew Mexico Gallu,
Raje ing Dearmen of Maemaic, RM Univeriy Deli CR, onea- 309, India acin Malik Dearmen of aiic, Banara Hindu Univeriy aranai-005, India Florenin marandace Dearmen of Maemaic, Univeriy of ew Mexico Gallu,
Algorithmic Discrete Mathematics 6. Exercise Sheet
 Algorihmic Dicree Mahemaic. Exercie Shee Deparmen of Mahemaic SS 0 PD Dr. Ulf Lorenz 7. and 8. Juni 0 Dipl.-Mah. David Meffer Verion of June, 0 Groupwork Exercie G (Heap-Sor) Ue Heap-Sor wih a min-heap
Algorihmic Dicree Mahemaic. Exercie Shee Deparmen of Mahemaic SS 0 PD Dr. Ulf Lorenz 7. and 8. Juni 0 Dipl.-Mah. David Meffer Verion of June, 0 Groupwork Exercie G (Heap-Sor) Ue Heap-Sor wih a min-heap
Module 2: Analysis of Stress
 Module/Leon Module : Anali of Sre.. INTRODUCTION A bod under he acion of eernal force, undergoe diorion and he effec due o hi em of force i ranmied hroughou he bod developing inernal force in i. To eamine
Module/Leon Module : Anali of Sre.. INTRODUCTION A bod under he acion of eernal force, undergoe diorion and he effec due o hi em of force i ranmied hroughou he bod developing inernal force in i. To eamine
- The whole joint distribution is independent of the date at which it is measured and depends only on the lag.
 Saionary Processes Sricly saionary - The whole join disribuion is indeenden of he dae a which i is measured and deends only on he lag. - E y ) is a finie consan. ( - V y ) is a finie consan. ( ( y, y s
Saionary Processes Sricly saionary - The whole join disribuion is indeenden of he dae a which i is measured and deends only on he lag. - E y ) is a finie consan. ( - V y ) is a finie consan. ( ( y, y s
The Contradiction within Equations of Motion with Constant Acceleration
 The Conradicion wihin Equaions of Moion wih Consan Acceleraion Louai Hassan Elzein Basheir (Daed: July 7, 0 This paper is prepared o demonsrae he violaion of rules of mahemaics in he algebraic derivaion
The Conradicion wihin Equaions of Moion wih Consan Acceleraion Louai Hassan Elzein Basheir (Daed: July 7, 0 This paper is prepared o demonsrae he violaion of rules of mahemaics in he algebraic derivaion
Analysis of Members with Axial Loads and Moments. (Length effects Disregarded, Short Column )
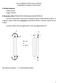 Analyi o emer wih Axial Loa an omen (Lengh ee Diregare, Shor Column ) A. Reaing Aignmen Chaper 9 o ex Chaper 10 o ACI B. reenaion o he INTERACTION DIAGRA or FAILURE ENVELO We have een ha a given eion an
Analyi o emer wih Axial Loa an omen (Lengh ee Diregare, Shor Column ) A. Reaing Aignmen Chaper 9 o ex Chaper 10 o ACI B. reenaion o he INTERACTION DIAGRA or FAILURE ENVELO We have een ha a given eion an
Program: RFEM 5, RSTAB 8, RF-DYNAM Pro, DYNAM Pro. Category: Isotropic Linear Elasticity, Dynamics, Member
 Verificaion Example Program: RFEM 5, RSTAB 8, RF-DYNAM Pro, DYNAM Pro Caegory: Isoropic Linear Elasiciy, Dynamics, Member Verificaion Example: 0104 Canilever Beam wih Periodic Exciaion 0104 Canilever Beam
Verificaion Example Program: RFEM 5, RSTAB 8, RF-DYNAM Pro, DYNAM Pro Caegory: Isoropic Linear Elasiciy, Dynamics, Member Verificaion Example: 0104 Canilever Beam wih Periodic Exciaion 0104 Canilever Beam
1 Motivation and Basic Definitions
 CSCE : Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Noe on Max Flow Fall 20 (Baed on he preenaion in Chaper 26 of Inroducion o Algorihm, 3rd Ed. by Cormen, Leieron, Rive and Sein.) Moivaion and Baic Definiion Conider
CSCE : Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Noe on Max Flow Fall 20 (Baed on he preenaion in Chaper 26 of Inroducion o Algorihm, 3rd Ed. by Cormen, Leieron, Rive and Sein.) Moivaion and Baic Definiion Conider
1 exp( c) 1 ( )
 Maerial Model LS-DYNA Theory Manual For exponenial relaionhip: 0 ε 0 cε h( ε) exp ε > 0 c 0 exp( c) Lmax ε Lmax ε > 0 c 0 where Lmax SSM ; and c CER. Sre of Damping Elemen i: σ D ε ε (9.56.5) 3 max Toal
Maerial Model LS-DYNA Theory Manual For exponenial relaionhip: 0 ε 0 cε h( ε) exp ε > 0 c 0 exp( c) Lmax ε Lmax ε > 0 c 0 where Lmax SSM ; and c CER. Sre of Damping Elemen i: σ D ε ε (9.56.5) 3 max Toal
1.054/1.541 Mechanics and Design of Concrete Structures (3-0-9) Outline 10 Torsion, Shear, and Flexure
 .54/.54 Mehani and Deign of Conree Srre Spring 4 Prof. Oral Bkozrk Maahe Inie of ehnolog Oline.54/.54 Mehani and Deign of Conree Srre (3--9) Oline orion, Shear, and Flere orion o Sre diribion on a ro eion
.54/.54 Mehani and Deign of Conree Srre Spring 4 Prof. Oral Bkozrk Maahe Inie of ehnolog Oline.54/.54 Mehani and Deign of Conree Srre (3--9) Oline orion, Shear, and Flere orion o Sre diribion on a ro eion
Graphs III - Network Flow
 Graph III - Nework Flow Flow nework eup graph G=(V,E) edge capaciy w(u,v) 0 - if edge doe no exi, hen w(u,v)=0 pecial verice: ource verex ; ink verex - no edge ino and no edge ou of Aume every verex v
Graph III - Nework Flow Flow nework eup graph G=(V,E) edge capaciy w(u,v) 0 - if edge doe no exi, hen w(u,v)=0 pecial verice: ource verex ; ink verex - no edge ino and no edge ou of Aume every verex v
6.302 Feedback Systems Recitation : Phase-locked Loops Prof. Joel L. Dawson
 6.32 Feedback Syem Phae-locked loop are a foundaional building block for analog circui deign, paricularly for communicaion circui. They provide a good example yem for hi cla becaue hey are an excellen
6.32 Feedback Syem Phae-locked loop are a foundaional building block for analog circui deign, paricularly for communicaion circui. They provide a good example yem for hi cla becaue hey are an excellen
Module 2 F c i k c s la l w a s o s f dif di fusi s o i n
 Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
A study on the influence of design parameters on the power output characteristic of piezoelectric vibration energy harvester
 A udy on he influence of deign arameer on he ower ouu characeriic of iezoelecric vibraion energy harveer N. Aboulfooh, J. Twiefel Iniue of Dynamic and Vibraion eearch Leibniz Univeriä Hannover Aelr. 67
A udy on he influence of deign arameer on he ower ouu characeriic of iezoelecric vibraion energy harveer N. Aboulfooh, J. Twiefel Iniue of Dynamic and Vibraion eearch Leibniz Univeriä Hannover Aelr. 67
, the. L and the L. x x. max. i n. It is easy to show that these two norms satisfy the following relation: x x n x = (17.3) max
 ecure 8 7. Sabiliy Analyi For an n dimenional vecor R n, he and he vecor norm are defined a: = T = i n i (7.) I i eay o how ha hee wo norm aify he following relaion: n (7.) If a vecor i ime-dependen, hen
ecure 8 7. Sabiliy Analyi For an n dimenional vecor R n, he and he vecor norm are defined a: = T = i n i (7.) I i eay o how ha hee wo norm aify he following relaion: n (7.) If a vecor i ime-dependen, hen
G. =, etc.
 Maerial Models υ υ3 0 0 0 υ υ 3 0 0 0 υ3 υ3 0 0 0 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 3 l (9..4) he subscris denoe he maerial axes, i.e., υ = υ and = (9..5) i j xi xj ii xi Since l is symmeric υ υ =, ec.
Maerial Models υ υ3 0 0 0 υ υ 3 0 0 0 υ3 υ3 0 0 0 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 3 l (9..4) he subscris denoe he maerial axes, i.e., υ = υ and = (9..5) i j xi xj ii xi Since l is symmeric υ υ =, ec.
Algorithms and Data Structures 2011/12 Week 9 Solutions (Tues 15th - Fri 18th Nov)
 Algorihm and Daa Srucure 2011/ Week Soluion (Tue 15h - Fri 18h No) 1. Queion: e are gien 11/16 / 15/20 8/13 0/ 1/ / 11/1 / / To queion: (a) Find a pair of ube X, Y V uch ha f(x, Y) = f(v X, Y). (b) Find
Algorihm and Daa Srucure 2011/ Week Soluion (Tue 15h - Fri 18h No) 1. Queion: e are gien 11/16 / 15/20 8/13 0/ 1/ / 11/1 / / To queion: (a) Find a pair of ube X, Y V uch ha f(x, Y) = f(v X, Y). (b) Find
Life Cycle Cost Calculation for Investment Decision in Manufacturing
 Life Cycle Co Calculaion for Invemen Deciion in Manufacuring L. Molinari Toai Iniue of Indurial Technology and Auomaion Naional Reearch Council ITIA-CNR Milano Ialy Abrac The growing global comeiion i
Life Cycle Co Calculaion for Invemen Deciion in Manufacuring L. Molinari Toai Iniue of Indurial Technology and Auomaion Naional Reearch Council ITIA-CNR Milano Ialy Abrac The growing global comeiion i
Navneet Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (2013); Term Project AML310; Indian Institute of Technology Delhi
 Creep in Viscoelasic Subsances Numerical mehods o calculae he coefficiens of he Prony equaion using creep es daa and Herediary Inegrals Mehod Navnee Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (23); Term Projec
Creep in Viscoelasic Subsances Numerical mehods o calculae he coefficiens of he Prony equaion using creep es daa and Herediary Inegrals Mehod Navnee Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (23); Term Projec
Shear Strength of Reinforced Concrete Columns Strengthened with Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic Sheet
 Shear Srengh of Reinforced Concree Columns Srenghened wih Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plasic Shee Lieping Ye 1 Qingrui Yue 2 Deparmen of Civil Engineering Naional Engineering Technical Tsinghua Universiy Technique
Shear Srengh of Reinforced Concree Columns Srenghened wih Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plasic Shee Lieping Ye 1 Qingrui Yue 2 Deparmen of Civil Engineering Naional Engineering Technical Tsinghua Universiy Technique
Laplace Transform. Inverse Laplace Transform. e st f(t)dt. (2)
 Laplace Tranform Maoud Malek The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranform named in honor of mahemaician and aronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace, who ued he ranform in hi work on probabiliy heory. I i a powerful
Laplace Tranform Maoud Malek The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranform named in honor of mahemaician and aronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace, who ued he ranform in hi work on probabiliy heory. I i a powerful
Today: Max Flow Proofs
 Today: Max Flow Proof COSC 58, Algorihm March 4, 04 Many of hee lide are adaped from everal online ource Reading Aignmen Today cla: Chaper 6 Reading aignmen for nex cla: Chaper 7 (Amorized analyi) In-Cla
Today: Max Flow Proof COSC 58, Algorihm March 4, 04 Many of hee lide are adaped from everal online ource Reading Aignmen Today cla: Chaper 6 Reading aignmen for nex cla: Chaper 7 (Amorized analyi) In-Cla
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
Chickens vs. Eggs: Replicating Thurman and Fisher (1988) by Arianto A. Patunru Department of Economics, University of Indonesia 2004
 Chicens vs. Eggs: Relicaing Thurman and Fisher (988) by Ariano A. Paunru Dearmen of Economics, Universiy of Indonesia 2004. Inroducion This exercise lays ou he rocedure for esing Granger Causaliy as discussed
Chicens vs. Eggs: Relicaing Thurman and Fisher (988) by Ariano A. Paunru Dearmen of Economics, Universiy of Indonesia 2004. Inroducion This exercise lays ou he rocedure for esing Granger Causaliy as discussed
4.1.1 Mindlin plates: Bending theory and variational formulation
 Chaper 4 soropic fla shell elemens n his chaper, fia shell elemens are formulaed hrough he assembly of membrane and plae elemens. The exac soluion of a shell approximaed by fia faces compared o he exac
Chaper 4 soropic fla shell elemens n his chaper, fia shell elemens are formulaed hrough he assembly of membrane and plae elemens. The exac soluion of a shell approximaed by fia faces compared o he exac
Angular Motion, Speed and Velocity
 Add Imporan Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy Page: 163 Noe/Cue Here Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy NGSS Sandard: N/A MA Curriculum Framework (006): 1.1, 1. AP Phyic 1 Learning Objecive: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3
Add Imporan Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy Page: 163 Noe/Cue Here Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy NGSS Sandard: N/A MA Curriculum Framework (006): 1.1, 1. AP Phyic 1 Learning Objecive: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3
Flow-Induced Vibration Analysis of Supported Pipes with a Crack
 Flow-Induced Vibraion Analsis of Suppored Pipes wih a Crack Jin-Huk Lee, Samer Masoud Al-Said Deparmen of Mechanical Engineering American Universi of Sharjah, UAE Ouline Inroducion and Moivaion Aeroacousicall
Flow-Induced Vibraion Analsis of Suppored Pipes wih a Crack Jin-Huk Lee, Samer Masoud Al-Said Deparmen of Mechanical Engineering American Universi of Sharjah, UAE Ouline Inroducion and Moivaion Aeroacousicall
Stability in Distribution for Backward Uncertain Differential Equation
 Sabiliy in Diribuion for Backward Uncerain Differenial Equaion Yuhong Sheng 1, Dan A. Ralecu 2 1. College of Mahemaical and Syem Science, Xinjiang Univeriy, Urumqi 8346, China heng-yh12@mail.inghua.edu.cn
Sabiliy in Diribuion for Backward Uncerain Differenial Equaion Yuhong Sheng 1, Dan A. Ralecu 2 1. College of Mahemaical and Syem Science, Xinjiang Univeriy, Urumqi 8346, China heng-yh12@mail.inghua.edu.cn
EE202 Circuit Theory II
 EE202 Circui Theory II 2017-2018, Spring Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN I. Inroducion & eview of Fir Order Circui (Chaper 7 of Nilon - 3 Hr. Inroducion, C and L Circui, Naural and Sep epone of Serie and Parallel L/C
EE202 Circui Theory II 2017-2018, Spring Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN I. Inroducion & eview of Fir Order Circui (Chaper 7 of Nilon - 3 Hr. Inroducion, C and L Circui, Naural and Sep epone of Serie and Parallel L/C
Non-uniform circular motion *
 OpenSax-CNX module: m14020 1 Non-uniform circular moion * Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by OpenSax-CNX and licensed under he Creaive Commons Aribuion License 2.0 Wha do we mean by non-uniform
OpenSax-CNX module: m14020 1 Non-uniform circular moion * Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by OpenSax-CNX and licensed under he Creaive Commons Aribuion License 2.0 Wha do we mean by non-uniform
BOX-JENKINS MODEL NOTATION. The Box-Jenkins ARMA(p,q) model is denoted by the equation. pwhile the moving average (MA) part of the model is θ1at
 BOX-JENKINS MODEL NOAION he Box-Jenkins ARMA(,q) model is denoed b he equaion + + L+ + a θ a L θ a 0 q q. () he auoregressive (AR) ar of he model is + L+ while he moving average (MA) ar of he model is
BOX-JENKINS MODEL NOAION he Box-Jenkins ARMA(,q) model is denoed b he equaion + + L+ + a θ a L θ a 0 q q. () he auoregressive (AR) ar of he model is + L+ while he moving average (MA) ar of he model is
Section 4.4 Logarithmic Properties
 Secion. Logarihmic Properies 5 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Secion. Logarihmic Properies 5 Secion. Logarihmic Properies In he previous secion, we derived wo imporan properies of arihms, which allowed us o solve some asic eponenial and arihmic equaions. Properies
Explaining Total Factor Productivity. Ulrich Kohli University of Geneva December 2015
 Explaining Toal Facor Produciviy Ulrich Kohli Universiy of Geneva December 2015 Needed: A Theory of Toal Facor Produciviy Edward C. Presco (1998) 2 1. Inroducion Toal Facor Produciviy (TFP) has become
Explaining Toal Facor Produciviy Ulrich Kohli Universiy of Geneva December 2015 Needed: A Theory of Toal Facor Produciviy Edward C. Presco (1998) 2 1. Inroducion Toal Facor Produciviy (TFP) has become
On Measuring Pro-Poor Growth. 1. On Various Ways of Measuring Pro-Poor Growth: A Short Review of the Literature
 On Measuring Pro-Poor Growh 1. On Various Ways of Measuring Pro-Poor Growh: A Shor eview of he Lieraure During he pas en years or so here have been various suggesions concerning he way one should check
On Measuring Pro-Poor Growh 1. On Various Ways of Measuring Pro-Poor Growh: A Shor eview of he Lieraure During he pas en years or so here have been various suggesions concerning he way one should check
S. S. Patil, S.B.Javheri, C.G.Konapure. Main structure
 ISSN: 77-3754 ISO 900:008 Ceriied Inernaional Journal o Engineering and Innovaive Technology (IJEIT) Volume, Iue 6, June0 Eecivene o Muliple Tuned Ma Damper S. S. Pail, S.B.Javheri, C.G.Konapure Abrac
ISSN: 77-3754 ISO 900:008 Ceriied Inernaional Journal o Engineering and Innovaive Technology (IJEIT) Volume, Iue 6, June0 Eecivene o Muliple Tuned Ma Damper S. S. Pail, S.B.Javheri, C.G.Konapure Abrac
Performance Comparison of LCMV-based Space-time 2D Array and Ambiguity Problem
 Inernaional journal of cience Commerce and umaniie Volume No 2 No 3 April 204 Performance Comparion of LCMV-baed pace-ime 2D Arra and Ambigui Problem 2 o uan Chang and Jin hinghia Deparmen of Communicaion
Inernaional journal of cience Commerce and umaniie Volume No 2 No 3 April 204 Performance Comparion of LCMV-baed pace-ime 2D Arra and Ambigui Problem 2 o uan Chang and Jin hinghia Deparmen of Communicaion
Interaction Diagram - Tied Reinforced Concrete Column (Using CSA A )
 Interaction Diagram - Tied Reinforced Concrete Column (Uing CSA A23.3-14) Interaction Diagram - Tied Reinforced Concrete Column Develop an interaction diagram for the quare tied concrete column hown in
Interaction Diagram - Tied Reinforced Concrete Column (Uing CSA A23.3-14) Interaction Diagram - Tied Reinforced Concrete Column Develop an interaction diagram for the quare tied concrete column hown in
A Risk-Averse Insider and Asset Pricing in Continuous Time
 Managemen Science and Financial Engineering Vol 9, No, May 3, pp-6 ISSN 87-43 EISSN 87-36 hp://dxdoiorg/7737/msfe39 3 KORMS A Rik-Avere Inider and Ae Pricing in oninuou Time Byung Hwa Lim Graduae School
Managemen Science and Financial Engineering Vol 9, No, May 3, pp-6 ISSN 87-43 EISSN 87-36 hp://dxdoiorg/7737/msfe39 3 KORMS A Rik-Avere Inider and Ae Pricing in oninuou Time Byung Hwa Lim Graduae School
Stability of an ideal (flat) plate. = k. critical stresses σ* (or N*) take the. Thereof infinitely many solutions: Critical stresses are given as:
 . Buckling of plaes Linear and nonlinear heor of uckling, uckling under direc sresses (class secions), uckling under shear, local loading and Eurocode approach. Saili of an ideal (fla) plae various loading
. Buckling of plaes Linear and nonlinear heor of uckling, uckling under direc sresses (class secions), uckling under shear, local loading and Eurocode approach. Saili of an ideal (fla) plae various loading
Reminder: Flow Networks
 0/0/204 Ma/CS 6a Cla 4: Variou (Flow) Execie Reminder: Flow Nework A flow nework i a digraph G = V, E, ogeher wih a ource verex V, a ink verex V, and a capaciy funcion c: E N. Capaciy Source 7 a b c d
0/0/204 Ma/CS 6a Cla 4: Variou (Flow) Execie Reminder: Flow Nework A flow nework i a digraph G = V, E, ogeher wih a ource verex V, a ink verex V, and a capaciy funcion c: E N. Capaciy Source 7 a b c d
Comparing Means: t-tests for One Sample & Two Related Samples
 Comparing Means: -Tess for One Sample & Two Relaed Samples Using he z-tes: Assumpions -Tess for One Sample & Two Relaed Samples The z-es (of a sample mean agains a populaion mean) is based on he assumpion
Comparing Means: -Tess for One Sample & Two Relaed Samples Using he z-tes: Assumpions -Tess for One Sample & Two Relaed Samples The z-es (of a sample mean agains a populaion mean) is based on he assumpion
TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION OF COMPLIANT MECHANISM DESIGN WITH STA- TIONARY FLUID-STRUCTURE INTERACTION
 Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceeding May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.roceeding.blucher.com.br/eveno/10wccm TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION OF COMPLIANT MECHANISM DESIGN WITH STA- TIONARY FLUID-STRUCTURE INTERACTION
Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceeding May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.roceeding.blucher.com.br/eveno/10wccm TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION OF COMPLIANT MECHANISM DESIGN WITH STA- TIONARY FLUID-STRUCTURE INTERACTION
Linear Algebra Primer
 Linear Algebra rimer And a video dicuion of linear algebra from EE263 i here (lecure 3 and 4): hp://ee.anford.edu/coure/ee263 lide from Sanford CS3 Ouline Vecor and marice Baic Mari Operaion Deerminan,
Linear Algebra rimer And a video dicuion of linear algebra from EE263 i here (lecure 3 and 4): hp://ee.anford.edu/coure/ee263 lide from Sanford CS3 Ouline Vecor and marice Baic Mari Operaion Deerminan,
V AK (t) I T (t) I TRM. V AK( full area) (t) t t 1 Axial turn-on. Switching losses for Phase Control and Bi- Directionally Controlled Thyristors
 Applicaion Noe Swiching losses for Phase Conrol and Bi- Direcionally Conrolled Thyrisors V AK () I T () Causing W on I TRM V AK( full area) () 1 Axial urn-on Plasma spread 2 Swiching losses for Phase Conrol
Applicaion Noe Swiching losses for Phase Conrol and Bi- Direcionally Conrolled Thyrisors V AK () I T () Causing W on I TRM V AK( full area) () 1 Axial urn-on Plasma spread 2 Swiching losses for Phase Conrol
Recursive Construction of Optimal Smoothing Spline Surfaces with Constraints
 Prerin of he 1h IFAC World Congre Milano Ialy) Augu - Seember, 11 Recurive Conrucion of Oimal Smoohing Sline Surface wih Conrain Hiroyuki Fujioka Hiroyuki Kano Dearmen of Syem Managemen, Fukuoka Iniue
Prerin of he 1h IFAC World Congre Milano Ialy) Augu - Seember, 11 Recurive Conrucion of Oimal Smoohing Sline Surface wih Conrain Hiroyuki Fujioka Hiroyuki Kano Dearmen of Syem Managemen, Fukuoka Iniue
STATIC BEHAVIOR OF AXIALLY COMPRESSED CIRCULAR CONCRETE FILLED CFRP-STEEL TUBULAR (C-CF-CFRP-ST) COLUMNS WITH MODERATE SLENDERNESS RATIO
 Advanced Seel Conrucion Vol. 12, No. 3, pp. 263-295 (216) 263 STATIC BEHAVIOR OF AXIALLY COMPRESSED CIRCULAR CONCRETE FILLED CFRP-STEEL TUBULAR (C-CF-CFRP-ST) COLUMNS WITH MODERATE SLENDERNESS RATIO Q.L.
Advanced Seel Conrucion Vol. 12, No. 3, pp. 263-295 (216) 263 STATIC BEHAVIOR OF AXIALLY COMPRESSED CIRCULAR CONCRETE FILLED CFRP-STEEL TUBULAR (C-CF-CFRP-ST) COLUMNS WITH MODERATE SLENDERNESS RATIO Q.L.
* l/d > 5 and H/D = 1 Mass term of Morison dominates
 1 3.6 LOADS Source and conequence of non-lineariie Sinuoidal wave and ylinder rucure: η =H/ in z λ H d x * l/d > 5 and H/D = 1 Ma erm of Morion dominae * linear wave eory: D fz;x= =.5 π c m D H/ gk co
1 3.6 LOADS Source and conequence of non-lineariie Sinuoidal wave and ylinder rucure: η =H/ in z λ H d x * l/d > 5 and H/D = 1 Ma erm of Morion dominae * linear wave eory: D fz;x= =.5 π c m D H/ gk co
Problem Set If all directed edges in a network have distinct capacities, then there is a unique maximum flow.
 CSE 202: Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Winer 2013 Problem Se 3 Inrucor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Due on: Tue. Feb 26, 2013 Inrucion For your proof, you may ue any lower bound, algorihm or daa rucure from he ex
CSE 202: Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Winer 2013 Problem Se 3 Inrucor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Due on: Tue. Feb 26, 2013 Inrucion For your proof, you may ue any lower bound, algorihm or daa rucure from he ex
Cumulative Damage Evaluation based on Energy Balance Equation
 Cumulaive Damage Evaluaion based on Energy Balance Equaion K. Minagawa Saiama Insiue of Technology, Saiama S. Fujia Tokyo Denki Universiy, Tokyo! SUMMARY: This paper describes an evaluaion mehod for cumulaive
Cumulaive Damage Evaluaion based on Energy Balance Equaion K. Minagawa Saiama Insiue of Technology, Saiama S. Fujia Tokyo Denki Universiy, Tokyo! SUMMARY: This paper describes an evaluaion mehod for cumulaive
LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION
 CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
Electrical and current self-induction
 Elecrical and curren self-inducion F. F. Mende hp://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.hml mende_fedor@mail.ru Absrac The aricle considers he self-inducance of reacive elemens. Elecrical self-inducion To he laws of
Elecrical and curren self-inducion F. F. Mende hp://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.hml mende_fedor@mail.ru Absrac The aricle considers he self-inducance of reacive elemens. Elecrical self-inducion To he laws of
A Theoretical Analysis on Dynamic Marginal Cost Pricing. Masao Kuwahara Institute of Industrial Science, University of Tokyo.
 A Theoreical Analyi on Dynamic Marginal Co Pricing Maao Kuahara Iniue of Indurial Science, Univeriy of Tokyo Abrac Thi udy exend he aic marginal co analyi o he dynamic one o ha he dynamic boleneck phenomena
A Theoreical Analyi on Dynamic Marginal Co Pricing Maao Kuahara Iniue of Indurial Science, Univeriy of Tokyo Abrac Thi udy exend he aic marginal co analyi o he dynamic one o ha he dynamic boleneck phenomena
NEUTRON DIFFUSION THEORY
 NEUTRON DIFFUSION THEORY M. Ragheb 4//7. INTRODUCTION The diffuion heory model of neuron ranpor play a crucial role in reacor heory ince i i imple enough o allow cienific inigh, and i i ufficienly realiic
NEUTRON DIFFUSION THEORY M. Ragheb 4//7. INTRODUCTION The diffuion heory model of neuron ranpor play a crucial role in reacor heory ince i i imple enough o allow cienific inigh, and i i ufficienly realiic
Lecture 4 Kinetics of a particle Part 3: Impulse and Momentum
 MEE Engineering Mechanics II Lecure 4 Lecure 4 Kineics of a paricle Par 3: Impulse and Momenum Linear impulse and momenum Saring from he equaion of moion for a paricle of mass m which is subjeced o an
MEE Engineering Mechanics II Lecure 4 Lecure 4 Kineics of a paricle Par 3: Impulse and Momenum Linear impulse and momenum Saring from he equaion of moion for a paricle of mass m which is subjeced o an
3.1.3 INTRODUCTION TO DYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION: DISCRETE TIME PROBLEMS. A. The Hamiltonian and First-Order Conditions in a Finite Time Horizon
 3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
