Reasoning and programming. Lecture 5: Invariants and Logic. Boolean expressions. Reasoning. Examples
|
|
|
- Daniela Townsend
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chir of Softwre Engineering Resoning nd progrmming Einführung in die Progrmmierung Introduction to Progrmming Prof. Dr. Bertrnd Meyer Octoer 2006 Ferury 2007 Lecture 5: Invrints nd Logic Logic is the sis of Mthemtics: proofs re only vlid if they follow the rules of logic. Softwre development: Conditions in contrcts: x must not e zero, so tht we cn clculte x+ 7 x. Conditions in progrm ctions: If i is positive, then execute this instruction. (to e introduced in lter lecture) Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 4 Boolen expressions A condition is expressed s oolen expression. It consists of oolen vriles (identifiers denoting oolen vlues) oolen opertors (not, or, nd, =, implies) nd represents possile oolen vlues (truth vlues, either or ). 2 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 5 Resoning Exmples Progrmming is resoning. Logic is the science of resoning. We use logic in our every dys life: Socrtes is humn. All humns re mortl. Therefore Socrtes must e mortl. Exmples of oolen expressions (with rin_tody nd cuckoo_sng_lst_night s oolen vriles): rin_tody ( oolen vrile is oolen expression) not rin_tody (not cuckoo_sng_lst_night) implies rin_tody (Prentheses group su-expressions.) Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 3 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 6 1
2 Negtion (not) Complex expressions not For ny oolen expression e nd ny vlues of vriles: Exctly one of e nd not e hs vlue. Exctly one of e nd not e hs vlue. One of e nd not e hs vlue. (Principle of the Excluded Middle.) Not oth of e nd not e hve vlue. (Principle of Non-Contrdiction.) Build more complex oolen expressions y using the oolen opertors. Exmple: nd ( nd (not c)) Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 7 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 10 Disjunction (or) Truth ssignment nd truth tle or Truth ssignment for set of vriles: prticulr choice of vlues ( or ), for every vrile. or opertor is non-exclusive. or opertor is commuttive. Disjunction principle: An or disjunction hs vlue except if oth opernds hve vlue. A truth ssignment stisfies n expression if the vlue for the expression is. A truth tle for n expression with n vriles hs n+1 columns 2 n rows Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 8 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 11 Conjunction (nd) Comined truth tle for sic opertors nd not or nd nd opertor is commuttive. Dulity of nd nd or: properties of either opertor yield properties of other (negting + swpping nd ) Conjunction principle: An nd conjunction hs vlue except if oth opernds hve vlue. Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 9 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 12 2
3 Tutologies De Morgn s lws Tutology: oolen expression tht hs vlue for every possile truth ssignment. Exmples: or (not ) not ( nd (not )) ( nd ) or ((not ) or (not )) De Morgn s Lws: Tutologies (not ( or )) = ((not ) nd (not )) (not ( nd )) = ((not ) or (not )) More tutologies: ( nd ( or c)) = (( nd ) or ( nd c)) ( or ( nd c)) = (( or ) nd ( or c)) Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 13 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 16 Contrdictions Contrdiction: oolen expression tht hs vlue for every possile truth ssignment. Exmples: nd (not ) Stisfile: for t lest one truth ssignment the expression yields. Any tutology is stisfile. No contrdiction is stisfile. Binding Order of inding (strting with tightest inding): not, nd, or, implies (to e introduced), =. nd nd or re ssocitive: nd ( nd c) = ( nd ) nd c or ( or c) = ( or ) or c Style rules: When writing oolen expression, drop the prentheses: Around the expressions of ech side of = if whole expression is n equivlence. Around successive elementry terms if they re seprted y the sme ssocitive opertors. Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 14 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 17 Equivlence (=) = = opertor is commuttive ( = hs sme vlue s = ). = opertor is reflexive ( = is tutology for ny ). Sustitution: For ny expressions u, v nd e, if u = v is tutology nd e is the expression otined from e y replcing every occurrence of u y v, then e = e is tutology. Impliction (implies) implies implies, for ny nd, is the vlue of (not ) or In implies : is ntecedent, consequent Impliction principle: An impliction hs vlue except if its ntecedent hs vlue nd its consequent hs vlue In prticulr, lwys if ntecedent is Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 15 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 18 3
4 Impliction in ordinry lnguge implies in ordinry lnguge often mens custion, s in if then Reversing implictions (2) Correct: implies = (not ) implies (not ) If the wether stys like this, skiing will e gret this week-end. If you put this stuff in your hnd luggge, they won t let you through. Exmple: All the people who live ner the lke re rich. She is not rich, so she cn t e living in Küsncht live_ner_lke implies rich = (not rich) implies (not live_ner_lke ) Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 19 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 22 Misunderstnding implictions Impliction Whenever is, implies is, regrdless of : If tody is Wednesdy, 2+2=5. If 2+2=5, tody is Wednesdy. Both of the ove implictions re. Cses in which is tell us nothing out the truth of the consequent. Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 20 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 23 Reversing implictions (1) It is not generlly true tht implies = (not ) implies (not ) Exmple (wrong!): All the people in Zurich who live ner the lke re rich. I do not live ner the lke, so I m not rich. live_ner_lke implies rich [1] Semistrict oolen opertors (1) Exmple oolen-vlued expression (x is n integer): x +7 x >1 for x <= -7 Undefined for x = 0 (not live_ner_lke ) implies (not rich ) [2] Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 21 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 24 4
5 Semistrict oolen opertors (2) Ordinry vs. non-strict oolen opertors BUT: Division y zero: x must not e 0. (x /= 0) nd ( x +7 > 0 ) x Use Ordinry oolen opertors (nd nd or) if you cn gurntee tht oth opernds re defined. nd then, if condition only mkes sense when nother is true. or else, if condition only mkes sense when nother is flse. Exmple: If you re not single, then your spouse must sign the contrct. is_single or else spouse_must_sign Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 25 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 28 Semistrict oolen opertors (3) Non-strict impliction BUT: nd is commuttive (progrm would crsh). We need non-commuttive version of nd (nd or): Non-strict oolen opertors. Exmple: If you re not single, then your spouse must sign the contrct. (not is_single) implies spouse_must_sign Definition of implies: in our cse, lwys non-strict! implies = (not ) or else Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 26 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 29 Non-strict opertors (nd then, or else) Eiffel keywords nd mthemticl symols nd then : hs sme vlue s nd if nd re defined, nd hs whenever hs vlue. or else : hs sme vlue s or if nd re defined, nd hs whenever hs vlue. (x /= 0) nd then ( x +7 ) x >0 Non-strict opertors llow us to define n order of expression evlution (left to right). Importnt for progrmming when undefined ojects my cuse progrm crshes. Eiffel keyword not or nd = implies Common mthemticl symol ~ or Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 27 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 30 5
6 Propositionl nd predicte clculus Existentilly quntified expression Propositionl clculus: property p holds for single oject Predicte clculus: property p holds for severl ojects Boolen expression: s : SOME_SET s.some_property if nd only if t lest one memer of SOME_SET stisfies property some_property Proving : Find one element of SOME_SET tht stisfies the property : Prove tht no element of SOME_SET stisfies the property (test ll elements) Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 31 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 34 Generlizing or Universlly quntified expression G : group of ojects, p : property or: Does t lest one of the ojects in G stisfy p? Is t lest one sttion of Line 8 n exchnge? Sttion_Blrd.is_exchnge or Sttion_Lourmel.is_exchnge or Sttion_Boucicut.is_exchnge or (ll sttions of Line 8) Existentil quntifier: exists, or s : Sttions_8 s.is_exchnge There exists n s in Sttions_8 such tht s.is_exchnge is true Boolen expression: s: SOME_SET s.some_property if nd only if every memer of SOME_SET stisfies property some_property wht out empty sets? not ( s: SOME_SET not s.some_property) Proving : Prove tht every element of SOME_SET stisfies the property (test ll elements) : Find one element of SOME_SET tht does not stisfies the property Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 32 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 35 Generlizing nd Dulity nd: Does every oject in G stisfy p? Are ll sttions of Trm 8 exchnges? Sttion_Blrd.is_exchnge nd Sttion_Lourmel.is_exchnge nd Sttion_Boucicut.is_exchnge nd (ll sttions of Line 8) Generliztion of DeMorgn s lws: not ( s : SOME_SET P ) = s : SOME_SET not P not ( s : SOME_SET P ) = s : SOME_SET not P Universl quntifier: for_ll, or s: Sttions_8 s.is_exchnge For ll s in Sttions8 s.is_exchnge is true Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 33 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 36 6
7 Empty sets s : SOME_SET some_property with SOME_SET empty lwys s : SOME_SET some_property with SOME_SET empty lwys Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 37 Key concepts Logic s tool for resoning Boolen opertors: truth tles Properties of oolen opertors: don t use truth tles! Predicte clculus: to tlk out logicl properties of sets Non-strict oolen opertors Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 38 End of lecture 5 Intro. to Progrmming, lecture 1: Overview 39 7
Boolean algebra.
 http://en.wikipedi.org/wiki/elementry_boolen_lger Boolen lger www.tudorgir.com Computer science is not out computers, it is out computtion nd informtion. computtion informtion computer informtion Turing
http://en.wikipedi.org/wiki/elementry_boolen_lger Boolen lger www.tudorgir.com Computer science is not out computers, it is out computtion nd informtion. computtion informtion computer informtion Turing
Boolean Algebra. Boolean Algebra
 Boolen Alger Boolen Alger A Boolen lger is set B of vlues together with: - two inry opertions, commonly denoted y + nd, - unry opertion, usully denoted y ˉ or ~ or, - two elements usully clled zero nd
Boolen Alger Boolen Alger A Boolen lger is set B of vlues together with: - two inry opertions, commonly denoted y + nd, - unry opertion, usully denoted y ˉ or ~ or, - two elements usully clled zero nd
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models
 CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 2 1. Prove ((( p q) q) p) is tutology () (3pts) y truth tle. p q p q
CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 2 1. Prove ((( p q) q) p) is tutology () (3pts) y truth tle. p q p q
KNOWLEDGE-BASED AGENTS INFERENCE
 AGENTS THAT REASON LOGICALLY KNOWLEDGE-BASED AGENTS Two components: knowledge bse, nd n inference engine. Declrtive pproch to building n gent. We tell it wht it needs to know, nd It cn sk itself wht to
AGENTS THAT REASON LOGICALLY KNOWLEDGE-BASED AGENTS Two components: knowledge bse, nd n inference engine. Declrtive pproch to building n gent. We tell it wht it needs to know, nd It cn sk itself wht to
Lecture 2 : Propositions DRAFT
 CS/Mth 240: Introduction to Discrete Mthemtics 1/20/2010 Lecture 2 : Propositions Instructor: Dieter vn Melkeeek Scrie: Dlior Zelený DRAFT Lst time we nlyzed vrious mze solving lgorithms in order to illustrte
CS/Mth 240: Introduction to Discrete Mthemtics 1/20/2010 Lecture 2 : Propositions Instructor: Dieter vn Melkeeek Scrie: Dlior Zelený DRAFT Lst time we nlyzed vrious mze solving lgorithms in order to illustrte
Parse trees, ambiguity, and Chomsky normal form
 Prse trees, miguity, nd Chomsky norml form In this lecture we will discuss few importnt notions connected with contextfree grmmrs, including prse trees, miguity, nd specil form for context-free grmmrs
Prse trees, miguity, nd Chomsky norml form In this lecture we will discuss few importnt notions connected with contextfree grmmrs, including prse trees, miguity, nd specil form for context-free grmmrs
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models Dana Richards, George Mason University, Spring 2016 Quiz Solutions
 CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 9 1. (4pts) ((p q) (q r)) (p r), prove tutology using truth tles. p
CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Spring 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Ferury 9 1. (4pts) ((p q) (q r)) (p r), prove tutology using truth tles. p
Fachgebiet Rechnersysteme1. 1. Boolean Algebra. 1. Boolean Algebra. Verification Technology. Content. 1.1 Boolean algebra basics (recap)
 . Boolen Alger Fchgeiet Rechnersysteme. Boolen Alger Veriiction Technology Content. Boolen lger sics (recp).2 Resoning out Boolen expressions . Boolen Alger 2 The prolem o logic veriiction: Show tht two
. Boolen Alger Fchgeiet Rechnersysteme. Boolen Alger Veriiction Technology Content. Boolen lger sics (recp).2 Resoning out Boolen expressions . Boolen Alger 2 The prolem o logic veriiction: Show tht two
CS12N: The Coming Revolution in Computer Architecture Laboratory 2 Preparation
 CS2N: The Coming Revolution in Computer Architecture Lortory 2 Preprtion Ojectives:. Understnd the principle of sttic CMOS gte circuits 2. Build simple logic gtes from MOS trnsistors 3. Evlute these gtes
CS2N: The Coming Revolution in Computer Architecture Lortory 2 Preprtion Ojectives:. Understnd the principle of sttic CMOS gte circuits 2. Build simple logic gtes from MOS trnsistors 3. Evlute these gtes
Boolean Algebra. Boolean Algebras
 Boolen Algebr Boolen Algebrs A Boolen lgebr is set B of vlues together with: - two binry opertions, commonly denoted by + nd, - unry opertion, usully denoted by or ~ or, - two elements usully clled zero
Boolen Algebr Boolen Algebrs A Boolen lgebr is set B of vlues together with: - two binry opertions, commonly denoted by + nd, - unry opertion, usully denoted by or ~ or, - two elements usully clled zero
Lecture 3: Equivalence Relations
 Mthcmp Crsh Course Instructor: Pdric Brtlett Lecture 3: Equivlence Reltions Week 1 Mthcmp 2014 In our lst three tlks of this clss, we shift the focus of our tlks from proof techniques to proof concepts
Mthcmp Crsh Course Instructor: Pdric Brtlett Lecture 3: Equivlence Reltions Week 1 Mthcmp 2014 In our lst three tlks of this clss, we shift the focus of our tlks from proof techniques to proof concepts
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models
 CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, section 003, George Mson University, Fll 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 7 1. Prove (p q) (p q), () (5pts) using truth tles. p q
CS 330 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, section 003, George Mson University, Fll 2017 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 7 1. Prove (p q) (p q), () (5pts) using truth tles. p q
INF1383 -Bancos de Dados
 3//0 INF383 -ncos de Ddos Prof. Sérgio Lifschitz DI PUC-Rio Eng. Computção, Sistems de Informção e Ciênci d Computção LGER RELCIONL lguns slides sedos ou modificdos dos originis em Elmsri nd Nvthe, Fundmentls
3//0 INF383 -ncos de Ddos Prof. Sérgio Lifschitz DI PUC-Rio Eng. Computção, Sistems de Informção e Ciênci d Computção LGER RELCIONL lguns slides sedos ou modificdos dos originis em Elmsri nd Nvthe, Fundmentls
Revision Sheet. (a) Give a regular expression for each of the following languages:
 Theoreticl Computer Science (Bridging Course) Dr. G. D. Tipldi F. Bonirdi Winter Semester 2014/2015 Revision Sheet University of Freiurg Deprtment of Computer Science Question 1 (Finite Automt, 8 + 6 points)
Theoreticl Computer Science (Bridging Course) Dr. G. D. Tipldi F. Bonirdi Winter Semester 2014/2015 Revision Sheet University of Freiurg Deprtment of Computer Science Question 1 (Finite Automt, 8 + 6 points)
Homework 3 Solutions
 CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 3 Solutions 1. Give NFAs with the specified numer of sttes recognizing ech of the following lnguges. In ll cses, the lphet is Σ = {,1}.
BİL 354 Veritabanı Sistemleri. Relational Algebra (İlişkisel Cebir)
 BİL 354 Veritnı Sistemleri Reltionl lger (İlişkisel Ceir) Reltionl Queries Query lnguges: llow mnipultion nd retrievl of dt from dtse. Reltionl model supports simple, powerful QLs: Strong forml foundtion
BİL 354 Veritnı Sistemleri Reltionl lger (İlişkisel Ceir) Reltionl Queries Query lnguges: llow mnipultion nd retrievl of dt from dtse. Reltionl model supports simple, powerful QLs: Strong forml foundtion
Improper Integrals. The First Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, as we ve discussed in class, goes as follows:
 Improper Integrls The First Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus, s we ve discussed in clss, goes s follows: If f is continuous on the intervl [, ] nd F is function for which F t = ft, then ftdt = F F. An integrl
Improper Integrls The First Fundmentl Theorem of Clculus, s we ve discussed in clss, goes s follows: If f is continuous on the intervl [, ] nd F is function for which F t = ft, then ftdt = F F. An integrl
Convert the NFA into DFA
 Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
Convert the NF into F For ech NF we cn find F ccepting the sme lnguge. The numer of sttes of the F could e exponentil in the numer of sttes of the NF, ut in prctice this worst cse occurs rrely. lgorithm:
CS 330 Formal Methods and Models
 CS 0 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Fll 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 8 1. Prove q (q p) p q p () (4pts) with truth tle. p q p q p (q p) p q
CS 0 Forml Methods nd Models Dn Richrds, George Mson University, Fll 2016 Quiz Solutions Quiz 1, Propositionl Logic Dte: Septemer 8 1. Prove q (q p) p q p () (4pts) with truth tle. p q p q p (q p) p q
Things to Memorize: A Partial List. January 27, 2017
 Things to Memorize: A Prtil List Jnury 27, 2017 Chpter 2 Vectors - Bsic Fcts A vector hs mgnitude (lso clled size/length/norm) nd direction. It does not hve fixed position, so the sme vector cn e moved
Things to Memorize: A Prtil List Jnury 27, 2017 Chpter 2 Vectors - Bsic Fcts A vector hs mgnitude (lso clled size/length/norm) nd direction. It does not hve fixed position, so the sme vector cn e moved
Fast Boolean Algebra
 Fst Boolen Alger ELEC 267 notes with the overurden removed A fst wy to lern enough to get the prel done honorly Printed; 3//5 Slide Modified; Jnury 3, 25 John Knight Digitl Circuits p. Fst Boolen Alger
Fst Boolen Alger ELEC 267 notes with the overurden removed A fst wy to lern enough to get the prel done honorly Printed; 3//5 Slide Modified; Jnury 3, 25 John Knight Digitl Circuits p. Fst Boolen Alger
Bases for Vector Spaces
 Bses for Vector Spces 2-26-25 A set is independent if, roughly speking, there is no redundncy in the set: You cn t uild ny vector in the set s liner comintion of the others A set spns if you cn uild everything
Bses for Vector Spces 2-26-25 A set is independent if, roughly speking, there is no redundncy in the set: You cn t uild ny vector in the set s liner comintion of the others A set spns if you cn uild everything
Handout: Natural deduction for first order logic
 MATH 457 Introduction to Mthemticl Logic Spring 2016 Dr Json Rute Hndout: Nturl deduction for first order logic We will extend our nturl deduction rules for sententil logic to first order logic These notes
MATH 457 Introduction to Mthemticl Logic Spring 2016 Dr Json Rute Hndout: Nturl deduction for first order logic We will extend our nturl deduction rules for sententil logic to first order logic These notes
Complexity in Modal Team Logic
 ThI Theoretische Informtik Complexity in Modl Tem Logic Julin-Steffen Müller Theoretische Informtik 18. Jnur 2012 Theorietg 2012 Theoretische Informtik Inhlt 1 Preliminries 2 Closure properties 3 Model
ThI Theoretische Informtik Complexity in Modl Tem Logic Julin-Steffen Müller Theoretische Informtik 18. Jnur 2012 Theorietg 2012 Theoretische Informtik Inhlt 1 Preliminries 2 Closure properties 3 Model
Learning Goals. Relational Query Languages. Formal Relational Query Languages. Formal Query Languages: Relational Algebra and Relational Calculus
 Forml Query Lnguges: Reltionl Alger nd Reltionl Clculus Chpter 4 Lerning Gols Given dtse ( set of tles ) you will e le to express dtse query in Reltionl Alger (RA), involving the sic opertors (selection,
Forml Query Lnguges: Reltionl Alger nd Reltionl Clculus Chpter 4 Lerning Gols Given dtse ( set of tles ) you will e le to express dtse query in Reltionl Alger (RA), involving the sic opertors (selection,
Linear Inequalities. Work Sheet 1
 Work Sheet 1 Liner Inequlities Rent--Hep, cr rentl compny,chrges $ 15 per week plus $ 0.0 per mile to rent one of their crs. Suppose you re limited y how much money you cn spend for the week : You cn spend
Work Sheet 1 Liner Inequlities Rent--Hep, cr rentl compny,chrges $ 15 per week plus $ 0.0 per mile to rent one of their crs. Suppose you re limited y how much money you cn spend for the week : You cn spend
Combinational Logic. Precedence. Quick Quiz 25/9/12. Schematics à Boolean Expression. 3 Representations of Logic Functions. Dr. Hayden So.
 5/9/ Comintionl Logic ENGG05 st Semester, 0 Dr. Hyden So Representtions of Logic Functions Recll tht ny complex logic function cn e expressed in wys: Truth Tle, Boolen Expression, Schemtics Only Truth
5/9/ Comintionl Logic ENGG05 st Semester, 0 Dr. Hyden So Representtions of Logic Functions Recll tht ny complex logic function cn e expressed in wys: Truth Tle, Boolen Expression, Schemtics Only Truth
p-adic Egyptian Fractions
 p-adic Egyptin Frctions Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Trditionl Egyptin Frctions nd Greedy Algorithm 2 3 Set-up 3 4 p-greedy Algorithm 5 5 p-egyptin Trditionl 10 6 Conclusion 1 Introduction An Egyptin frction
p-adic Egyptin Frctions Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Trditionl Egyptin Frctions nd Greedy Algorithm 2 3 Set-up 3 4 p-greedy Algorithm 5 5 p-egyptin Trditionl 10 6 Conclusion 1 Introduction An Egyptin frction
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, November 14, 2018 Finite Automata II. Nickolas Rollick a b b. a b 4
 Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
Intermedite Mth Circles Wednesdy, Novemer 14, 2018 Finite Automt II Nickols Rollick nrollick@uwterloo.c Regulr Lnguges Lst time, we were introduced to the ide of DFA (deterministic finite utomton), one
CS103B Handout 18 Winter 2007 February 28, 2007 Finite Automata
 CS103B ndout 18 Winter 2007 Ferury 28, 2007 Finite Automt Initil text y Mggie Johnson. Introduction Severl childrens gmes fit the following description: Pieces re set up on plying ord; dice re thrown or
CS103B ndout 18 Winter 2007 Ferury 28, 2007 Finite Automt Initil text y Mggie Johnson. Introduction Severl childrens gmes fit the following description: Pieces re set up on plying ord; dice re thrown or
The University of Nottingham SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE A LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER LANGUAGES AND COMPUTATION ANSWERS
 The University of Nottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER 2016 2017 LNGUGES ND COMPUTTION NSWERS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my complete the front cover of their nswer ook
The University of Nottinghm SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE LEVEL 2 MODULE, SPRING SEMESTER 2016 2017 LNGUGES ND COMPUTTION NSWERS Time llowed TWO hours Cndidtes my complete the front cover of their nswer ook
Overview of Today s Lecture:
 CPS 4 Computer Orgniztion nd Progrmming Lecture : Boolen Alger & gtes. Roert Wgner CPS4 BA. RW Fll 2 Overview of Tody s Lecture: Truth tles, Boolen functions, Gtes nd Circuits Krnugh mps for simplifying
CPS 4 Computer Orgniztion nd Progrmming Lecture : Boolen Alger & gtes. Roert Wgner CPS4 BA. RW Fll 2 Overview of Tody s Lecture: Truth tles, Boolen functions, Gtes nd Circuits Krnugh mps for simplifying
Coalgebra, Lecture 15: Equations for Deterministic Automata
 Colger, Lecture 15: Equtions for Deterministic Automt Julin Slmnc (nd Jurrin Rot) Decemer 19, 2016 In this lecture, we will study the concept of equtions for deterministic utomt. The notes re self contined
Colger, Lecture 15: Equtions for Deterministic Automt Julin Slmnc (nd Jurrin Rot) Decemer 19, 2016 In this lecture, we will study the concept of equtions for deterministic utomt. The notes re self contined
Lecture Solution of a System of Linear Equation
 ChE Lecture Notes, Dept. of Chemicl Engineering, Univ. of TN, Knoville - D. Keffer, 5/9/98 (updted /) Lecture 8- - Solution of System of Liner Eqution 8. Why is it importnt to e le to solve system of liner
ChE Lecture Notes, Dept. of Chemicl Engineering, Univ. of TN, Knoville - D. Keffer, 5/9/98 (updted /) Lecture 8- - Solution of System of Liner Eqution 8. Why is it importnt to e le to solve system of liner
1B40 Practical Skills
 B40 Prcticl Skills Comining uncertinties from severl quntities error propgtion We usully encounter situtions where the result of n experiment is given in terms of two (or more) quntities. We then need
B40 Prcticl Skills Comining uncertinties from severl quntities error propgtion We usully encounter situtions where the result of n experiment is given in terms of two (or more) quntities. We then need
The Evaluation Theorem
 These notes closely follow the presenttion of the mteril given in Jmes Stewrt s textook Clculus, Concepts nd Contexts (2nd edition) These notes re intended primrily for in-clss presenttion nd should not
These notes closely follow the presenttion of the mteril given in Jmes Stewrt s textook Clculus, Concepts nd Contexts (2nd edition) These notes re intended primrily for in-clss presenttion nd should not
The Regulated and Riemann Integrals
 Chpter 1 The Regulted nd Riemnn Integrls 1.1 Introduction We will consider severl different pproches to defining the definite integrl f(x) dx of function f(x). These definitions will ll ssign the sme vlue
Chpter 1 The Regulted nd Riemnn Integrls 1.1 Introduction We will consider severl different pproches to defining the definite integrl f(x) dx of function f(x). These definitions will ll ssign the sme vlue
IST 4 Information and Logic
 IST 4 Informtion nd Logic T = tody x= hw#x out x= hw#x due mon tue wed thr fri 31 M1 1 7 oh M1 14 oh 1 oh 2M2 21 oh oh 2 oh Mx= MQx out Mx= MQx due 28 oh M2 oh oh = office hours 5 3 12 oh 3 T 4 oh oh 19
IST 4 Informtion nd Logic T = tody x= hw#x out x= hw#x due mon tue wed thr fri 31 M1 1 7 oh M1 14 oh 1 oh 2M2 21 oh oh 2 oh Mx= MQx out Mx= MQx due 28 oh M2 oh oh = office hours 5 3 12 oh 3 T 4 oh oh 19
Introduction to Electrical & Electronic Engineering ENGG1203
 Introduction to Electricl & Electronic Engineering ENGG23 2 nd Semester, 27-8 Dr. Hden Kwok-H So Deprtment of Electricl nd Electronic Engineering Astrction DIGITAL LOGIC 2 Digitl Astrction n Astrct ll
Introduction to Electricl & Electronic Engineering ENGG23 2 nd Semester, 27-8 Dr. Hden Kwok-H So Deprtment of Electricl nd Electronic Engineering Astrction DIGITAL LOGIC 2 Digitl Astrction n Astrct ll
Elements of Computing Systems, Nisan & Schocken, MIT Press. Boolean Logic
 Elements of Computing Systems, Nisn & Schocken, MIT Press www.idc.c.il/tecs Usge nd Copyright Notice: Boolen Logic Copyright 2005 Nom Nisn nd Shimon Schocken This presenttion contins lecture mterils tht
Elements of Computing Systems, Nisn & Schocken, MIT Press www.idc.c.il/tecs Usge nd Copyright Notice: Boolen Logic Copyright 2005 Nom Nisn nd Shimon Schocken This presenttion contins lecture mterils tht
Let's start with an example:
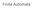 Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
Finite Automt Let's strt with n exmple: Here you see leled circles tht re sttes, nd leled rrows tht re trnsitions. One of the sttes is mrked "strt". One of the sttes hs doule circle; this is terminl stte
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter Final Exam (solutions) SOLUTIONS
 CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
CS 310 (sec 20) - Winter 2003 - Finl Exm (solutions) SOLUTIONS 1. (Logic) Use truth tles to prove the following logicl equivlences: () p q (p p) (q q) () p q (p q) (p q) () p q p q p p q q (q q) (p p)
Lecture 1. Functional series. Pointwise and uniform convergence.
 1 Introduction. Lecture 1. Functionl series. Pointwise nd uniform convergence. In this course we study mongst other things Fourier series. The Fourier series for periodic function f(x) with period 2π is
1 Introduction. Lecture 1. Functionl series. Pointwise nd uniform convergence. In this course we study mongst other things Fourier series. The Fourier series for periodic function f(x) with period 2π is
Software Engineering using Formal Methods
 Softwre Engineering using Forml Methods Propositionl nd (Liner) Temporl Logic Wolfgng Ahrendt 13th Septemer 2016 SEFM: Liner Temporl Logic /GU 160913 1 / 60 Recpitultion: FormlistionFormlistion: Syntx,
Softwre Engineering using Forml Methods Propositionl nd (Liner) Temporl Logic Wolfgng Ahrendt 13th Septemer 2016 SEFM: Liner Temporl Logic /GU 160913 1 / 60 Recpitultion: FormlistionFormlistion: Syntx,
Quadratic Forms. Quadratic Forms
 Qudrtic Forms Recll the Simon & Blume excerpt from n erlier lecture which sid tht the min tsk of clculus is to pproximte nonliner functions with liner functions. It s ctully more ccurte to sy tht we pproximte
Qudrtic Forms Recll the Simon & Blume excerpt from n erlier lecture which sid tht the min tsk of clculus is to pproximte nonliner functions with liner functions. It s ctully more ccurte to sy tht we pproximte
Symbolic enumeration methods for unlabelled structures
 Go & Šjn, Comintoril Enumertion Notes 4 Symolic enumertion methods for unlelled structures Definition A comintoril clss is finite or denumerle set on which size function is defined, stisfying the following
Go & Šjn, Comintoril Enumertion Notes 4 Symolic enumertion methods for unlelled structures Definition A comintoril clss is finite or denumerle set on which size function is defined, stisfying the following
Review of Gaussian Quadrature method
 Review of Gussin Qudrture method Nsser M. Asi Spring 006 compiled on Sundy Decemer 1, 017 t 09:1 PM 1 The prolem To find numericl vlue for the integrl of rel vlued function of rel vrile over specific rnge
Review of Gussin Qudrture method Nsser M. Asi Spring 006 compiled on Sundy Decemer 1, 017 t 09:1 PM 1 The prolem To find numericl vlue for the integrl of rel vlued function of rel vrile over specific rnge
CHAPTER 1 PROGRAM OF MATRICES
 CHPTER PROGRM OF MTRICES -- INTRODUCTION definition of engineering is the science y which the properties of mtter nd sources of energy in nture re mde useful to mn. Thus n engineer will hve to study the
CHPTER PROGRM OF MTRICES -- INTRODUCTION definition of engineering is the science y which the properties of mtter nd sources of energy in nture re mde useful to mn. Thus n engineer will hve to study the
Nondeterminism and Nodeterministic Automata
 Nondeterminism nd Nodeterministic Automt 61 Nondeterminism nd Nondeterministic Automt The computtionl mchine models tht we lerned in the clss re deterministic in the sense tht the next move is uniquely
Nondeterminism nd Nodeterministic Automt 61 Nondeterminism nd Nondeterministic Automt The computtionl mchine models tht we lerned in the clss re deterministic in the sense tht the next move is uniquely
DATABASE DESIGN I - 1DL300
 DATABASE DESIGN I - DL300 Fll 00 An introductory course on dtse systems http://www.it.uu.se/edu/course/homepge/dstekn/ht0/ Mnivskn Sesn Uppsl Dtse Lortory Deprtment of Informtion Technology, Uppsl University,
DATABASE DESIGN I - DL300 Fll 00 An introductory course on dtse systems http://www.it.uu.se/edu/course/homepge/dstekn/ht0/ Mnivskn Sesn Uppsl Dtse Lortory Deprtment of Informtion Technology, Uppsl University,
How do we solve these things, especially when they get complicated? How do we know when a system has a solution, and when is it unique?
 XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk out solving systems of liner equtions. These re prolems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6= x + x 7=
XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk out solving systems of liner equtions. These re prolems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6= x + x 7=
Lecture 9: LTL and Büchi Automata
 Lecture 9: LTL nd Büchi Automt 1 LTL Property Ptterns Quite often the requirements of system follow some simple ptterns. Sometimes we wnt to specify tht property should only hold in certin context, clled
Lecture 9: LTL nd Büchi Automt 1 LTL Property Ptterns Quite often the requirements of system follow some simple ptterns. Sometimes we wnt to specify tht property should only hold in certin context, clled
MATH 573 FINAL EXAM. May 30, 2007
 MATH 573 FINAL EXAM My 30, 007 NAME: Solutions 1. This exm is due Wednesdy, June 6 efore the 1:30 pm. After 1:30 pm I will NOT ccept the exm.. This exm hs 1 pges including this cover. There re 10 prolems.
MATH 573 FINAL EXAM My 30, 007 NAME: Solutions 1. This exm is due Wednesdy, June 6 efore the 1:30 pm. After 1:30 pm I will NOT ccept the exm.. This exm hs 1 pges including this cover. There re 10 prolems.
IST 4 Information and Logic
 IST 4 Informtion nd Logic T = tody x= hw#x out x= hw#x due mon tue wed thr 28 M1 oh 1 4 oh M1 11 oh oh 1 2 M2 18 oh oh 2 fri oh oh = office hours oh 25 oh M2 2 3 oh midterms oh Mx= MQx out 9 oh 3 T 4 oh
IST 4 Informtion nd Logic T = tody x= hw#x out x= hw#x due mon tue wed thr 28 M1 oh 1 4 oh M1 11 oh oh 1 2 M2 18 oh oh 2 fri oh oh = office hours oh 25 oh M2 2 3 oh midterms oh Mx= MQx out 9 oh 3 T 4 oh
1 Probability Density Functions
 Lis Yn CS 9 Continuous Distributions Lecture Notes #9 July 6, 28 Bsed on chpter by Chris Piech So fr, ll rndom vribles we hve seen hve been discrete. In ll the cses we hve seen in CS 9, this ment tht our
Lis Yn CS 9 Continuous Distributions Lecture Notes #9 July 6, 28 Bsed on chpter by Chris Piech So fr, ll rndom vribles we hve seen hve been discrete. In ll the cses we hve seen in CS 9, this ment tht our
CS 267: Automated Verification. Lecture 8: Automata Theoretic Model Checking. Instructor: Tevfik Bultan
 CS 267: Automted Verifiction Lecture 8: Automt Theoretic Model Checking Instructor: Tevfik Bultn LTL Properties Büchi utomt [Vrdi nd Wolper LICS 86] Büchi utomt: Finite stte utomt tht ccept infinite strings
CS 267: Automted Verifiction Lecture 8: Automt Theoretic Model Checking Instructor: Tevfik Bultn LTL Properties Büchi utomt [Vrdi nd Wolper LICS 86] Büchi utomt: Finite stte utomt tht ccept infinite strings
Lecture 08: Feb. 08, 2019
 4CS4-6:Theory of Computtion(Closure on Reg. Lngs., regex to NDFA, DFA to regex) Prof. K.R. Chowdhry Lecture 08: Fe. 08, 2019 : Professor of CS Disclimer: These notes hve not een sujected to the usul scrutiny
4CS4-6:Theory of Computtion(Closure on Reg. Lngs., regex to NDFA, DFA to regex) Prof. K.R. Chowdhry Lecture 08: Fe. 08, 2019 : Professor of CS Disclimer: These notes hve not een sujected to the usul scrutiny
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 20: Complexity V (Polynomial-Time Reducibility)
 CS5371 Theory of Computtion Lecture 20: Complexity V (Polynomil-Time Reducibility) Objectives Polynomil Time Reducibility Prove Cook-Levin Theorem Polynomil Time Reducibility Previously, we lernt tht if
CS5371 Theory of Computtion Lecture 20: Complexity V (Polynomil-Time Reducibility) Objectives Polynomil Time Reducibility Prove Cook-Levin Theorem Polynomil Time Reducibility Previously, we lernt tht if
4.1. Probability Density Functions
 STT 1 4.1-4. 4.1. Proility Density Functions Ojectives. Continuous rndom vrile - vers - discrete rndom vrile. Proility density function. Uniform distriution nd its properties. Expected vlue nd vrince of
STT 1 4.1-4. 4.1. Proility Density Functions Ojectives. Continuous rndom vrile - vers - discrete rndom vrile. Proility density function. Uniform distriution nd its properties. Expected vlue nd vrince of
Grammar. Languages. Content 5/10/16. Automata and Languages. Regular Languages. Regular Languages
 5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
5//6 Grmmr Automt nd Lnguges Regulr Grmmr Context-free Grmmr Context-sensitive Grmmr Prof. Mohmed Hmd Softwre Engineering L. The University of Aizu Jpn Regulr Lnguges Context Free Lnguges Context Sensitive
Assignment 1 Automata, Languages, and Computability. 1 Finite State Automata and Regular Languages
 Deprtment of Computer Science, Austrlin Ntionl University COMP2600 Forml Methods for Softwre Engineering Semester 2, 206 Assignment Automt, Lnguges, nd Computility Smple Solutions Finite Stte Automt nd
Deprtment of Computer Science, Austrlin Ntionl University COMP2600 Forml Methods for Softwre Engineering Semester 2, 206 Assignment Automt, Lnguges, nd Computility Smple Solutions Finite Stte Automt nd
Chapter 2 Finite Automata
 Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Chpter 2 Finite Automt 28 2.1 Introduction Finite utomt: first model of the notion of effective procedure. (They lso hve mny other pplictions). The concept of finite utomton cn e derived y exmining wht
Some Theory of Computation Exercises Week 1
 Some Theory of Computtion Exercises Week 1 Section 1 Deterministic Finite Automt Question 1.3 d d d d u q 1 q 2 q 3 q 4 q 5 d u u u u Question 1.4 Prt c - {w w hs even s nd one or two s} First we sk whether
Some Theory of Computtion Exercises Week 1 Section 1 Deterministic Finite Automt Question 1.3 d d d d u q 1 q 2 q 3 q 4 q 5 d u u u u Question 1.4 Prt c - {w w hs even s nd one or two s} First we sk whether
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computation. Lecture #31: What DFA s Can and Can t Do David Mix Barrington 9 April 2014
 CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
CMPSCI 250: Introduction to Computtion Lecture #31: Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Dvid Mix Brrington 9 April 2014 Wht DFA s Cn nd Cn t Do Deterministic Finite Automt Forml Definition of DFA s Exmples of DFA
Minimal DFA. minimal DFA for L starting from any other
 Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Miniml DFA Among the mny DFAs ccepting the sme regulr lnguge L, there is exctly one (up to renming of sttes) which hs the smllest possile numer of sttes. Moreover, it is possile to otin tht miniml DFA
Math 4310 Solutions to homework 1 Due 9/1/16
 Mth 4310 Solutions to homework 1 Due 9/1/16 1. Use the Eucliden lgorithm to find the following gretest common divisors. () gcd(252, 180) = 36 (b) gcd(513, 187) = 1 (c) gcd(7684, 4148) = 68 252 = 180 1
Mth 4310 Solutions to homework 1 Due 9/1/16 1. Use the Eucliden lgorithm to find the following gretest common divisors. () gcd(252, 180) = 36 (b) gcd(513, 187) = 1 (c) gcd(7684, 4148) = 68 252 = 180 1
CM10196 Topic 4: Functions and Relations
 CM096 Topic 4: Functions nd Reltions Guy McCusker W. Functions nd reltions Perhps the most widely used notion in ll of mthemtics is tht of function. Informlly, function is n opertion which tkes n input
CM096 Topic 4: Functions nd Reltions Guy McCusker W. Functions nd reltions Perhps the most widely used notion in ll of mthemtics is tht of function. Informlly, function is n opertion which tkes n input
308K. 1 Section 3.2. Zelaya Eufemia. 1. Example 1: Multiplication of Matrices: X Y Z R S R S X Y Z. By associativity we have to choices:
 8K Zely Eufemi Section 2 Exmple : Multipliction of Mtrices: X Y Z T c e d f 2 R S X Y Z 2 c e d f 2 R S 2 By ssocitivity we hve to choices: OR: X Y Z R S cr ds er fs X cy ez X dy fz 2 R S 2 Suggestion
8K Zely Eufemi Section 2 Exmple : Multipliction of Mtrices: X Y Z T c e d f 2 R S X Y Z 2 c e d f 2 R S 2 By ssocitivity we hve to choices: OR: X Y Z R S cr ds er fs X cy ez X dy fz 2 R S 2 Suggestion
RELATIONAL MODEL.
 RELATIONAL MODEL Structure of Reltionl Dtbses Reltionl Algebr Tuple Reltionl Clculus Domin Reltionl Clculus Extended Reltionl-Algebr- Opertions Modifiction of the Dtbse Views EXAMPLE OF A RELATION BASIC
RELATIONAL MODEL Structure of Reltionl Dtbses Reltionl Algebr Tuple Reltionl Clculus Domin Reltionl Clculus Extended Reltionl-Algebr- Opertions Modifiction of the Dtbse Views EXAMPLE OF A RELATION BASIC
CS 301. Lecture 04 Regular Expressions. Stephen Checkoway. January 29, 2018
 CS 301 Lecture 04 Regulr Expressions Stephen Checkowy Jnury 29, 2018 1 / 35 Review from lst time NFA N = (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where δ Q Σ P (Q) mps stte nd n lphet symol (or ) to set of sttes We run n NFA
CS 301 Lecture 04 Regulr Expressions Stephen Checkowy Jnury 29, 2018 1 / 35 Review from lst time NFA N = (Q, Σ, δ, q 0, F ) where δ Q Σ P (Q) mps stte nd n lphet symol (or ) to set of sttes We run n NFA
ɛ-closure, Kleene s Theorem,
 DEGefW5wiGH2XgYMEzUKjEmtCDUsRQ4d 1 A nice pper relevnt to this course is titled The Glory of the Pst 2 NICTA Resercher, Adjunct t the Austrlin Ntionl University nd Griffith University ɛ-closure, Kleene
DEGefW5wiGH2XgYMEzUKjEmtCDUsRQ4d 1 A nice pper relevnt to this course is titled The Glory of the Pst 2 NICTA Resercher, Adjunct t the Austrlin Ntionl University nd Griffith University ɛ-closure, Kleene
The area under the graph of f and above the x-axis between a and b is denoted by. f(x) dx. π O
 1 Section 5. The Definite Integrl Suppose tht function f is continuous nd positive over n intervl [, ]. y = f(x) x The re under the grph of f nd ove the x-xis etween nd is denoted y f(x) dx nd clled the
1 Section 5. The Definite Integrl Suppose tht function f is continuous nd positive over n intervl [, ]. y = f(x) x The re under the grph of f nd ove the x-xis etween nd is denoted y f(x) dx nd clled the
378 Relations Solutions for Chapter 16. Section 16.1 Exercises. 3. Let A = {0,1,2,3,4,5}. Write out the relation R that expresses on A.
 378 Reltions 16.7 Solutions for Chpter 16 Section 16.1 Exercises 1. Let A = {0,1,2,3,4,5}. Write out the reltion R tht expresses > on A. Then illustrte it with digrm. 2 1 R = { (5,4),(5,3),(5,2),(5,1),(5,0),(4,3),(4,2),(4,1),
378 Reltions 16.7 Solutions for Chpter 16 Section 16.1 Exercises 1. Let A = {0,1,2,3,4,5}. Write out the reltion R tht expresses > on A. Then illustrte it with digrm. 2 1 R = { (5,4),(5,3),(5,2),(5,1),(5,0),(4,3),(4,2),(4,1),
Homework 4. 0 ε 0. (00) ε 0 ε 0 (00) (11) CS 341: Foundations of Computer Science II Prof. Marvin Nakayama
 CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 4 1. UsetheproceduredescriedinLemm1.55toconverttheregulrexpression(((00) (11)) 01) into n NFA. Answer: 0 0 1 1 00 0 0 11 1 1 01 0 1 (00)
CS 341: Foundtions of Computer Science II Prof. Mrvin Nkym Homework 4 1. UsetheproceduredescriedinLemm1.55toconverttheregulrexpression(((00) (11)) 01) into n NFA. Answer: 0 0 1 1 00 0 0 11 1 1 01 0 1 (00)
Kleene s Theorem. Kleene s Theorem. Kleene s Theorem. Kleene s Theorem. Kleene s Theorem. Kleene s Theorem 2/16/15
 Models of Comput:on Lecture #8 Chpter 7 con:nued Any lnguge tht e defined y regulr expression, finite utomton, or trnsi:on grph cn e defined y ll three methods We prove this y showing tht ny lnguge defined
Models of Comput:on Lecture #8 Chpter 7 con:nued Any lnguge tht e defined y regulr expression, finite utomton, or trnsi:on grph cn e defined y ll three methods We prove this y showing tht ny lnguge defined
Closure Properties of Regular Languages
 Closure Properties of Regulr Lnguges Regulr lnguges re closed under mny set opertions. Let L 1 nd L 2 e regulr lnguges. (1) L 1 L 2 (the union) is regulr. (2) L 1 L 2 (the conctention) is regulr. (3) L
Closure Properties of Regulr Lnguges Regulr lnguges re closed under mny set opertions. Let L 1 nd L 2 e regulr lnguges. (1) L 1 L 2 (the union) is regulr. (2) L 1 L 2 (the conctention) is regulr. (3) L
Dually quasi-de Morgan Stone semi-heyting algebras II. Regularity
 Volume 2, Number, July 204, 65-82 ISSN Print: 2345-5853 Online: 2345-586 Dully qusi-de Morgn Stone semi-heyting lgebrs II. Regulrity Hnmntgoud P. Snkppnvr Abstrct. This pper is the second of two prt series.
Volume 2, Number, July 204, 65-82 ISSN Print: 2345-5853 Online: 2345-586 Dully qusi-de Morgn Stone semi-heyting lgebrs II. Regulrity Hnmntgoud P. Snkppnvr Abstrct. This pper is the second of two prt series.
Genetic Programming. Outline. Evolutionary Strategies. Evolutionary strategies Genetic programming Summary
 Outline Genetic Progrmming Evolutionry strtegies Genetic progrmming Summry Bsed on the mteril provided y Professor Michel Negnevitsky Evolutionry Strtegies An pproch simulting nturl evolution ws proposed
Outline Genetic Progrmming Evolutionry strtegies Genetic progrmming Summry Bsed on the mteril provided y Professor Michel Negnevitsky Evolutionry Strtegies An pproch simulting nturl evolution ws proposed
I1 = I2 I1 = I2 + I3 I1 + I2 = I3 + I4 I 3
 2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
2 The Prllel Circuit Electric Circuits: Figure 2- elow show ttery nd multiple resistors rrnged in prllel. Ech resistor receives portion of the current from the ttery sed on its resistnce. The split is
Definite Integrals. The area under a curve can be approximated by adding up the areas of rectangles = 1 1 +
 Definite Integrls --5 The re under curve cn e pproximted y dding up the res of rectngles. Exmple. Approximte the re under y = from x = to x = using equl suintervls nd + x evluting the function t the left-hnd
Definite Integrls --5 The re under curve cn e pproximted y dding up the res of rectngles. Exmple. Approximte the re under y = from x = to x = using equl suintervls nd + x evluting the function t the left-hnd
Complexity of intuitionistic logic. Martin Mundhenk
 Complexity of intuitionistic logic Mrtin Mundhenk 2 The formul evlution problem k the model checking problem Given: formul α for the logic L nd model M ccording to the semntics of L Decide: does M stisfy
Complexity of intuitionistic logic Mrtin Mundhenk 2 The formul evlution problem k the model checking problem Given: formul α for the logic L nd model M ccording to the semntics of L Decide: does M stisfy
5. (±±) Λ = fw j w is string of even lengthg [ 00 = f11,00g 7. (11 [ 00)± Λ = fw j w egins with either 11 or 00g 8. (0 [ ffl)1 Λ = 01 Λ [ 1 Λ 9.
 Regulr Expressions, Pumping Lemm, Right Liner Grmmrs Ling 106 Mrch 25, 2002 1 Regulr Expressions A regulr expression descries or genertes lnguge: it is kind of shorthnd for listing the memers of lnguge.
Regulr Expressions, Pumping Lemm, Right Liner Grmmrs Ling 106 Mrch 25, 2002 1 Regulr Expressions A regulr expression descries or genertes lnguge: it is kind of shorthnd for listing the memers of lnguge.
Worked out examples Finite Automata
 Worked out exmples Finite Automt Exmple Design Finite Stte Automton which reds inry string nd ccepts only those tht end with. Since we re in the topic of Non Deterministic Finite Automt (NFA), we will
Worked out exmples Finite Automt Exmple Design Finite Stte Automton which reds inry string nd ccepts only those tht end with. Since we re in the topic of Non Deterministic Finite Automt (NFA), we will
Lecture 3. In this lecture, we will discuss algorithms for solving systems of linear equations.
 Lecture 3 3 Solving liner equtions In this lecture we will discuss lgorithms for solving systems of liner equtions Multiplictive identity Let us restrict ourselves to considering squre mtrices since one
Lecture 3 3 Solving liner equtions In this lecture we will discuss lgorithms for solving systems of liner equtions Multiplictive identity Let us restrict ourselves to considering squre mtrices since one
Rudimentary Matrix Algebra
 Rudimentry Mtrix Alger Mrk Sullivn Decemer 4, 217 i Contents 1 Preliminries 1 1.1 Why does this document exist?.................... 1 1.2 Why does nyone cre out mtrices?................ 1 1.3 Wht is mtrix?...........................
Rudimentry Mtrix Alger Mrk Sullivn Decemer 4, 217 i Contents 1 Preliminries 1 1.1 Why does this document exist?.................... 1 1.2 Why does nyone cre out mtrices?................ 1 1.3 Wht is mtrix?...........................
set is not closed under matrix [ multiplication, ] and does not form a group.
![set is not closed under matrix [ multiplication, ] and does not form a group. set is not closed under matrix [ multiplication, ] and does not form a group.](/thumbs/78/78412113.jpg) Prolem 2.3: Which of the following collections of 2 2 mtrices with rel entries form groups under [ mtrix ] multipliction? i) Those of the form for which c d 2 Answer: The set of such mtrices is not closed
Prolem 2.3: Which of the following collections of 2 2 mtrices with rel entries form groups under [ mtrix ] multipliction? i) Those of the form for which c d 2 Answer: The set of such mtrices is not closed
Chapter 3 MATRIX. In this chapter: 3.1 MATRIX NOTATION AND TERMINOLOGY
 Chpter 3 MTRIX In this chpter: Definition nd terms Specil Mtrices Mtrix Opertion: Trnspose, Equlity, Sum, Difference, Sclr Multipliction, Mtrix Multipliction, Determinnt, Inverse ppliction of Mtrix in
Chpter 3 MTRIX In this chpter: Definition nd terms Specil Mtrices Mtrix Opertion: Trnspose, Equlity, Sum, Difference, Sclr Multipliction, Mtrix Multipliction, Determinnt, Inverse ppliction of Mtrix in
Lecture 2e Orthogonal Complement (pages )
 Lecture 2e Orthogonl Complement (pges -) We hve now seen tht n orthonorml sis is nice wy to descrie suspce, ut knowing tht we wnt n orthonorml sis doesn t mke one fll into our lp. In theory, the process
Lecture 2e Orthogonl Complement (pges -) We hve now seen tht n orthonorml sis is nice wy to descrie suspce, ut knowing tht we wnt n orthonorml sis doesn t mke one fll into our lp. In theory, the process
STRUCTURE OF CONCURRENCY Ryszard Janicki. Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, ON, L8S 4K1 Canada
 STRUCTURE OF CONCURRENCY Ryszrd Jnicki Deprtment of Computing nd Softwre McMster University Hmilton, ON, L8S 4K1 Cnd jnicki@mcmster.c 1 Introduction Wht is concurrency? How it cn e modelled? Wht re the
STRUCTURE OF CONCURRENCY Ryszrd Jnicki Deprtment of Computing nd Softwre McMster University Hmilton, ON, L8S 4K1 Cnd jnicki@mcmster.c 1 Introduction Wht is concurrency? How it cn e modelled? Wht re the
AUTOMATED REASONING. Agostino Dovier. Udine, November Università di Udine CLPLAB
 AUTOMATED REASONING Agostino Dovier Università di Udine CLPLAB Udine, Novemer 2017 AGOSTINO DOVIER (CLPLAB) AUTOMATED REASONING UDINE, NOVEMBER 2017 1 / 15 Semntics of Logic Progrms AGOSTINO DOVIER (CLPLAB)
AUTOMATED REASONING Agostino Dovier Università di Udine CLPLAB Udine, Novemer 2017 AGOSTINO DOVIER (CLPLAB) AUTOMATED REASONING UDINE, NOVEMBER 2017 1 / 15 Semntics of Logic Progrms AGOSTINO DOVIER (CLPLAB)
Mathematics Number: Logarithms
 plce of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Deprtment of Curriculum nd Pedgogy Mthemtics Numer: Logrithms Science nd Mthemtics Eduction Reserch Group Supported y UBC Teching nd Lerning Enhncement
plce of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Deprtment of Curriculum nd Pedgogy Mthemtics Numer: Logrithms Science nd Mthemtics Eduction Reserch Group Supported y UBC Teching nd Lerning Enhncement
Polynomials and Division Theory
 Higher Checklist (Unit ) Higher Checklist (Unit ) Polynomils nd Division Theory Skill Achieved? Know tht polynomil (expression) is of the form: n x + n x n + n x n + + n x + x + 0 where the i R re the
Higher Checklist (Unit ) Higher Checklist (Unit ) Polynomils nd Division Theory Skill Achieved? Know tht polynomil (expression) is of the form: n x + n x n + n x n + + n x + x + 0 where the i R re the
INTRODUCTION TO LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ME Applied Mthemtics for Mechnicl Engineers INTRODUCTION TO INEAR AGEBRA Mtrices nd Vectors Prof. Dr. Bülent E. Pltin Spring Sections & / ME Applied Mthemtics for Mechnicl Engineers INTRODUCTION TO INEAR
ME Applied Mthemtics for Mechnicl Engineers INTRODUCTION TO INEAR AGEBRA Mtrices nd Vectors Prof. Dr. Bülent E. Pltin Spring Sections & / ME Applied Mthemtics for Mechnicl Engineers INTRODUCTION TO INEAR
Name Ima Sample ASU ID
 Nme Im Smple ASU ID 2468024680 CSE 355 Test 1, Fll 2016 30 Septemer 2016, 8:35-9:25.m., LSA 191 Regrding of Midterms If you elieve tht your grde hs not een dded up correctly, return the entire pper to
Nme Im Smple ASU ID 2468024680 CSE 355 Test 1, Fll 2016 30 Septemer 2016, 8:35-9:25.m., LSA 191 Regrding of Midterms If you elieve tht your grde hs not een dded up correctly, return the entire pper to
W. We shall do so one by one, starting with I 1, and we shall do it greedily, trying
 Vitli covers 1 Definition. A Vitli cover of set E R is set V of closed intervls with positive length so tht, for every δ > 0 nd every x E, there is some I V with λ(i ) < δ nd x I. 2 Lemm (Vitli covering)
Vitli covers 1 Definition. A Vitli cover of set E R is set V of closed intervls with positive length so tht, for every δ > 0 nd every x E, there is some I V with λ(i ) < δ nd x I. 2 Lemm (Vitli covering)
Propositional models. Historical models of computation. Application: binary addition. Boolean functions. Implementation using switches.
 Propositionl models Historil models of omputtion Steven Lindell Hverford College USA 1/22/2010 ISLA 2010 1 Strt with fixed numer of oolen vriles lled the voulry: e.g.,,. Eh oolen vrile represents proposition,
Propositionl models Historil models of omputtion Steven Lindell Hverford College USA 1/22/2010 ISLA 2010 1 Strt with fixed numer of oolen vriles lled the voulry: e.g.,,. Eh oolen vrile represents proposition,
Chapter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automata. Formal Language, chapter 5, slide 1
 Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Chpter Five: Nondeterministic Finite Automt Forml Lnguge, chpter 5, slide 1 1 A DFA hs exctly one trnsition from every stte on every symol in the lphet. By relxing this requirement we get relted ut more
Chapter 1: Boolean Logic
 Elements of Computing Systems, Nisn & Schocken, MIT Press, 2005 www.idc.c.il/tecs Chpter 1: Boolen Logic Usge nd Copyright Notice: Copyright 2005 Nom Nisn nd Shimon Schocken This presenttion contins lecture
Elements of Computing Systems, Nisn & Schocken, MIT Press, 2005 www.idc.c.il/tecs Chpter 1: Boolen Logic Usge nd Copyright Notice: Copyright 2005 Nom Nisn nd Shimon Schocken This presenttion contins lecture
The Bernoulli Numbers John C. Baez, December 23, x k. x e x 1 = n 0. B k n = n 2 (n + 1) 2
 The Bernoulli Numbers John C. Bez, December 23, 2003 The numbers re defined by the eqution e 1 n 0 k. They re clled the Bernoulli numbers becuse they were first studied by Johnn Fulhber in book published
The Bernoulli Numbers John C. Bez, December 23, 2003 The numbers re defined by the eqution e 1 n 0 k. They re clled the Bernoulli numbers becuse they were first studied by Johnn Fulhber in book published
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON INTRODUCTION TO ANALYSIS. Brooklyn College of the City University of New York. April 2002 Last Revised: January 2013
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON INTRODUCTION TO ANALYSIS Attil Máté Brooklyn College of the City University of New York April 2002 Lst Revised: Jnury 2013 c 2002, 2013 by Attil Máté Typeset by AMS-TEX ii Tble of
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES ON INTRODUCTION TO ANALYSIS Attil Máté Brooklyn College of the City University of New York April 2002 Lst Revised: Jnury 2013 c 2002, 2013 by Attil Máté Typeset by AMS-TEX ii Tble of
