Nicholas J. Giordano. Chapter 13 Sound
|
|
|
- Gillian Powers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nicholas J. Giordano Chapter 13 Sound
2 Sound Sounds waves are an important example of wave motion Sound is central to hearing, speech, music and many other daily activities Characteristics of sound waves that will be considered include How they are generated How they propagate How they are detected by the ear Introduction
3 Sound In Air Sound waves can travel through gases, liquids, and solids Gas molecules are in constant random motion A typical air molecule at room temperature has a speed of 500 m/s Call this the background velocity, The direction is different for every molecule Section 13.1
4 Sound in Air, 2 The loudspeaker generates a sound wave in the air When the speaker is off, the density of the air molecules is the same throughout the tube Section 13.1
5 Sound in Air, 3 When the loudspeaker is on, its diaphragm moves back and forth As it moves, it collides with air molecules It gives the air molecules a small extra velocity, At some times, this velocity is directed toward the right and at other times toward the left Section 13.1
6 Sound in Air, 4 This extra velocity is the velocity of the molecule, not the velocity of the wave Since the extra velocity is parallel to the direction of motion, this is a longitudinal wave Since the displacement alternates between +x and x, the density of molecules is increased in some regions and decreased in others Oscillations in air density cause oscillations in the air pressure Sound can also be viewed as a pressure wave Section 13.1
7 Sound as a Pressure Wave The regions of high density and high pressure are called regions of condensation The regions of low density and low pressure are called regions of rarefaction Section 13.1
8 Speed of Sound Adjacent regions of high pressure are separated by a distance equal to the wavelength Adjacent regions of low pressure are also separated by the wavelength The speed of the sound wave is given by v sound = ƒ λ It is very important to distinguish between the velocity of the wave and the velocity of the particles within the medium They are not the same Section 13.1
9 Sound Waves in Other Media Sound traveling through liquids or solids is similar to air The sound wave causes a displacement of the molecules in the solid or liquid parallel to the propagation direction So sound is a longitudinal wave in solids and liquids as well as in gas There can be no transverse waves in a gas or liquid There can be transverse waves in a solid Section 13.1
10 Speed of Sound The speed of sound depends on the medium the wave is traveling through See table 13.1 In general, the speed of sound is fastest in solids and slowest in gases In general, the speed of sound can be expressed as Section 13.1
11 Speed of Sound, cont. A stiffer material generates a larger restoring force Hooke s Law This leads to larger particle accelerations This also leads to a larger speed of sound Solids are stiffer than liquids, and liquids are stiffer than gases This explains the pattern of speeds The density factor indicates the less dense the material, the higher the speed A smaller mass has a greater acceleration for any given force and so the speed of the wave will be higher Section 13.1
12 Speed of Sound Equations The speed of sound in a solid is The speed of sound in a fluid is The speed of sound in a gas depends on its temperature and pressure For air near room temperature and pressure, v sound = (T 20 ) m/s T is in Celsius Section 13.1
13 Speed and Frequency of Sound The general relationship for a wave, v = ƒ λ, holds The speed of the sound wave is a function of the medium and is independent of the frequency and amplitude The frequency and amplitude depend on how the wave is generated Frequency range of normal human hearing is 20 Hz to 20 khz Sound waves below 20 Hz are called infrasonic Sound waves above 20 khz are called ultrasonic Section 13.1
14 Musical Tones A sound wave described by a single frequency is called a pure tone Most sounds are combinations of many pure tones Many sounds are a combination of frequencies that are harmonically related A harmonic sequence is related to the fundamental frequency by ƒ n = n ƒ 1 One way to characterize a combination tone is by a property called pitch Generally, the pitch of a pure tone is its frequency With more complex sounds, the pitch is associated with the fundamental frequency Section 13.1
15 Hearing When a sound wave reaches your ear, the pressure on the outside of your eardrum is the atmospheric pressure plus the oscillating sound pressure On the inside of your eardrum, the pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressure Generally, your eardrum is insensitive to atmospheric pressure, but detects the sound pressure Section 13.2
16 Intensity and Amplitude The intensity of the sound wave equals the power carried by the wave per unit area of wave front The intensity of a wave is proportional to the amplitude of the pressure oscillation In many cases, sound waves propagate as spherical waves Therefore, Section 13.2
17 Decibels The sensitivity of the ear depends on the frequency of the sound In the most favorable frequency range, the ear can detect intensities as small as about W/m 2 A more convenient unit, the decibel (db), is often used to look at sound intensity The sound intensity level, β, is measured in decibels Section 13.2
18 Sound Intensity Level To find the sound intensity level, I o = 1.00 x W/m 2 If I = I o, then β = 0 db This does not mean there is no sound It does mean that the sound is at the same intensity as the lower limit of human hearing For every factor of 10 increase in intensity, the intensity level increases by10 db The intensity levels of some common sounds are listed in table 13.2 Section 13.2
19 Intensity Level of Some Sounds Section 13.2
20 Human Perception of Sound The lowest line plots the intensity of the minimum detectable sound as a function of the frequency Doubling the perceived loudness corresponds to moving from one contour line to the next The highest contour curve has a loudness at which the ear is damaged Occurs at β 120 db The loudness contours depend on frequency Section 13.2
21 Ear as a Pressure Detector Intensity is proportional to the square of the pressure amplitude There is a relationship between the threshold intensity for human hearing I o and the smallest pressure oscillation that can be detected by the ear A sound intensity of I o = 1.00 x W/m 2 corresponds to a pressure amplitude of p o = 2 x 10-5 Pa This is about 2 x times smaller than atmospheric pressure Section 13.2
22 Standing Sound Waves Closed Pipe Assume a sound wave traveling back and forth in a pipe closed at both ends The velocity and displacement will be zero at the ends of the pipe Nodes occur where there is zero displacement Antinodes are the largest displacements The pressure forms pressure antinodes at the ends of the tube Section 13.3
23 Closed Pipe Harmonics Some other possible standing waves for displacement and pressure are shown The frequencies of the standing waves are ƒ 1 is the fundamental frequency n is the harmonic number Section 13.3
24 Standing Waves Pipe Open at One End At the closed end, there will be a displacement node and a pressure antinode At the open end, there will be a pressure node and a displacement antinode Section 13.3
25 Pipe Closed at One End Harmonics Some other possible standing waves for displacement and pressure are shown The frequencies of the standing waves are ƒ 1 is the fundamental frequency and n is the harmonic number These harmonics are different than those in a pipe closed at both ends Section 13.3
26 Standing Wave Summary The closed end of a pipe is a pressure antinode for the standing wave The open end of a pipe is a pressure node for the standing wave A pressure node is always a displacement antinode, and a pressure antinode is always a displacement node These three points will allow you to predict the allowed frequencies of standing sound waves in pipes Section 13.3
27 Harmonics Summary The patterns of standing wave frequencies are shown The frequencies depend on whether the ends of the pipe are opened or closed Section 13.3
28 Real Musical Tones Pipes are the basis for many musical instruments The standing wave in the instrument is a combination of standing waves with different frequencies These combination tones are often said to have a property called timbre Also called tone color The timbre depends on the mix of frequencies The timbre is different for different instruments and how the instrument is played Section 13.3
29 Beat Frequency When two tones are played together, the superposition principle indicates the sound pressures will add The amplitude of this combination pressure wave oscillates These amplitude oscillations are called beats The frequency of the oscillations is the beat frequency, ƒ beat ƒ beat = ƒ 1 ƒ 2 Beats can be used to tune musical instruments Section 13.4
30 Reflection A sound wave with a plane front reflects from a flat surface The reflection is mirrorlike The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection Mirror-like reflection will occur as long as the size of the reflecting surface is large compared to the wavelength of the sound Section 13.5
31 Scattering When an incoming plane wave strikes a small object, it does not undergo mirror-like reflection At least some sound is scattered in all directions This process is called scattering
32 Doppler Effect The phenomenon of the frequency heard by an observer being different that the frequency emitted by the source is called the Doppler Effect Named for Christian Doppler, who discovered it Object moving toward the observer The distance between wave crests decreases The frequency measured by the observer is higher Object moving away from the observer The distance between wave crests increases The frequency measured by the observer is lower Section 13.6
33 Doppler Effect Diagrams Section 13.6
34 Doppler Effect Equations For a source moving toward an observer: For a source moving away from an observer: The difference between the frequency heard by the observer and the source frequency is called the Doppler Shift Section 13.6
35 Doppler Effect General The observer could also be moving and thus produce a Doppler shift The + or signs are chosen depending on whether the source and observer are moving toward or away from each other Frequency is increased when moving toward each other Frequency is decreased when moving away from each other Section 13.6
36 Doppler Effect Example: Speed Gun A speed gun uses the Doppler effect with reflected electro-magnetic waves to measure the speed of a moving object As the initial waves hit the object, it acts like a moving observer For the scattered rays, the object acts like a moving source The speed gun uses the Doppler-shifted frequency to deduce the speed of the object Section 13.6
37 Doppler Effect Example: Bats Bats employ an approach similar to the speed gun Bats generate pulses of ultrasonic waves These waves are reflected and the bat uses the reflected sound to judge its environment Section 13.6
38 Shock Waves The speed of the wave s source can be greater than the speed of the wave When the source moves at or faster than the speed of the wave, the pressure in front of the object piles up along a conic envelope As many different sound waves arrive at a point on the envelope, they produce a very loud sound intensity and form a shock wave Section 13.6
39 Acoustic Thermometry Acoustic thermometry has been developed to study global warming It uses the temperature dependence of the speed of sound to measure changes in the temperature of the oceans The wave can travel long distances and by determining the travel time, its speed can be found Current precision for the time is about 20 ms From the speed, the temperature of the water can be determined Section 13.7
40 Ultrasound Images Ultrasonic imaging uses sound waves to obtain images inside a material The most familiar use is to produce views inside the human body The depth of objects inside the body is determined by the time it takes the reflected ray to return to the detector Some medical ultrasounds also use the Doppler effect Section 13.6
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220. Final Exam. Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total)
 Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
Lecture 14 1/38 Phys 220 Final Exam Wednesday, August 6 th 10:30 am 12:30 pm Phys 114 20 multiple choice problems (15 points each 300 total) 75% will be from Chapters 10-16 25% from Chapters 1-9 Students
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 21. Textbook Sections Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 21 Sound Textbook Sections 13.1 13.7 Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Overview Last Lecture Interference and Diffraction Constructive, destructive Diffraction: bending of
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 21 Sound Textbook Sections 13.1 13.7 Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Overview Last Lecture Interference and Diffraction Constructive, destructive Diffraction: bending of
Producing a Sound Wave. Chapter 14. Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a Sound Wave. Using a Tuning Fork, cont.
 Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Producing a Sound Wave Chapter 14 Sound Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave Using a Tuning Fork to Produce a
Sound Waves. Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects.
 Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
Sound Waves Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium Sound waves are produced from vibrating objects Introduction Sound Waves: Molecular View When sound travels through a medium, there
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration and waves Hooke s law Potential energy
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES
 Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND WAVES - Periodic motion any type of motion that repeats itself in a regular cycle. Ex: a pendulum swinging, a mass bobbing up and down on a spring.
General Physics (PHY 2130)
 General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
General Physics (PHY 2130) Lecture XII Sound sound waves Doppler effect Standing waves Light Reflection and refraction http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2130/ Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Vibration
Wave Motions and Sound
 EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
EA Notes (Scen 101), Tillery Chapter 5 Wave Motions and Sound Introduction Microscopic molecular vibrations determine temperature (last Chapt.). Macroscopic vibrations of objects set up what we call Sound
CLASS 2 CLASS 2. Section 13.5
 CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
CLASS 2 CLASS 2 Section 13.5 Simple Pendulum The simple pendulum is another example of a system that exhibits simple harmonic motion The force is the component of the weight tangent to the path of motion
Chapters 11 and 12. Sound and Standing Waves
 Chapters 11 and 12 Sound and Standing Waves The Nature of Sound Waves LONGITUDINAL SOUND WAVES Speaker making sound waves in a tube The Nature of Sound Waves The distance between adjacent condensations
Chapters 11 and 12 Sound and Standing Waves The Nature of Sound Waves LONGITUDINAL SOUND WAVES Speaker making sound waves in a tube The Nature of Sound Waves The distance between adjacent condensations
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves
 Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Chapter 20: Mechanical Waves Section 20.1: Observations: Pulses and Wave Motion Oscillation Plus Propagation Oscillation (or vibration): Periodic motion (back-and-forth, upand-down) The motion repeats
Page # Physics 103: Lecture 26 Sound. Lecture 26, Preflight 2. Lecture 26, Preflight 1. Producing a Sound Wave. Sound from a Tuning Fork
 Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
Physics 103: Lecture 6 Sound Producing a Sound Wave Sound waves are longitudinal waves traveling through a medium A tuning fork can be used as an example of producing a sound wave A tuning fork will produce
SoundWaves. Lecture (2) Special topics Dr.khitam Y, Elwasife
 SoundWaves Lecture (2) Special topics Dr.khitam Y, Elwasife VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt 2 Mode Shapes and Boundary Conditions, VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI
SoundWaves Lecture (2) Special topics Dr.khitam Y, Elwasife VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt 2 Mode Shapes and Boundary Conditions, VGTU EF ESK stanislovas.staras@el.vgtu.lt ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI
Work. Work and Energy Examples. Energy. To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or:
 Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Work To move an object we must do work Work is calculated as the force applied to the object through a distance or: W F( d) Work has the units Newton meters (N m) or Joules 1 Joule = 1 N m Energy Work
Chapter 2 SOUND WAVES
 Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
Chapter SOUND WAVES Introduction: A sound wave (or pressure or compression wave) results when a surface (layer of molecules) moves back and forth in a medium producing a sequence of compressions C and
42 TRAVELING WAVES (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G)
 42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
42 TRAVELING WAVES 1. Wave progagation Source Disturbance Medium (D) Speed (E) Traveling waves (F) Mechanical waves (G) Electromagnetic waves (D) (E) (F) (G) 2. Transverse Waves have the classic sinusoidal
Physics Mechanics. Lecture 34 Waves and sound II
 1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 34 Waves and sound II 2 Sound Waves Sound waves are pressure waves in solids, liquids, and gases. They are longitudinal in liquids and gases, and may have transverse components
1 Physics 170 - Mechanics Lecture 34 Waves and sound II 2 Sound Waves Sound waves are pressure waves in solids, liquids, and gases. They are longitudinal in liquids and gases, and may have transverse components
PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section VIII
 PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section VIII Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and
PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section VIII Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser East Tennessee State University Edition 4.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use of the instructor and
What does the speed of a wave depend on?
 Today s experiment Goal answer the question What does the speed of a wave depend on? Materials: Wave on a String PHeT Simulation (link in schedule) and Wave Machine Write a CER in pairs. Think about the
Today s experiment Goal answer the question What does the speed of a wave depend on? Materials: Wave on a String PHeT Simulation (link in schedule) and Wave Machine Write a CER in pairs. Think about the
Chap 12. Sound. Speed of sound is different in different material. Depends on the elasticity and density of the medium. T v sound = v string =
 Chap 12. Sound Sec. 12.1 - Characteristics of Sound Sound is produced due to source(vibrating object and travels in a medium (londitudinal sound waves and can be heard by a ear (vibrations. Sound waves
Chap 12. Sound Sec. 12.1 - Characteristics of Sound Sound is produced due to source(vibrating object and travels in a medium (londitudinal sound waves and can be heard by a ear (vibrations. Sound waves
Physics 11. Unit 7 (Part 2) The Physics of Sound
 Physics 11 Unit 7 (Part 2) The Physics of Sound 1. Sound waves As introduced in the previous section, sound is one of the many types of waves we encounter in our daily lives. It possesses the properties
Physics 11 Unit 7 (Part 2) The Physics of Sound 1. Sound waves As introduced in the previous section, sound is one of the many types of waves we encounter in our daily lives. It possesses the properties
Sound Waves SOUND VIBRATIONS THAT TRAVEL THROUGH THE AIR OR OTHER MEDIA WHEN THESE VIBRATIONS REACH THE AIR NEAR YOUR EARS YOU HEAR THE SOUND.
 SOUND WAVES Objectives: 1. WHAT IS SOUND? 2. HOW DO SOUND WAVES TRAVEL? 3. HOW DO PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A MEDIUM AFFECT THE SPEED OF SOUND WAVES? 4. WHAT PROPERTIES OF WAVES AFFECT WHAT WE HEAR? 5. WHAT
SOUND WAVES Objectives: 1. WHAT IS SOUND? 2. HOW DO SOUND WAVES TRAVEL? 3. HOW DO PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF A MEDIUM AFFECT THE SPEED OF SOUND WAVES? 4. WHAT PROPERTIES OF WAVES AFFECT WHAT WE HEAR? 5. WHAT
Vågrörelselära och optik
 Vågrörelselära och optik Kapitel 16 - Ljud 1 Vågrörelselära och optik Kurslitteratur: University Physics by Young & Friedman Harmonisk oscillator: Kapitel 14.1 14.4 Mekaniska vågor: Kapitel 15.1 15.8 Ljud
Vågrörelselära och optik Kapitel 16 - Ljud 1 Vågrörelselära och optik Kurslitteratur: University Physics by Young & Friedman Harmonisk oscillator: Kapitel 14.1 14.4 Mekaniska vågor: Kapitel 15.1 15.8 Ljud
Chapter 16. Waves and Sound
 Chapter 16 Waes and Sound 16.1 The Nature of Waes 1. A wae is a traeling disturbance. 2. A wae carries energy from place to place. 16.1 The Nature of Waes Transerse Wae 16.1 The Nature of Waes Longitudinal
Chapter 16 Waes and Sound 16.1 The Nature of Waes 1. A wae is a traeling disturbance. 2. A wae carries energy from place to place. 16.1 The Nature of Waes Transerse Wae 16.1 The Nature of Waes Longitudinal
due to striking, rubbing, Any vibration of matter spinning, plucking, etc. Find frequency first, then calculate period.
 Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
Equilibrium Position Disturbance Period (T in sec) # sec T = # cycles Frequency (f in Hz) f = # cycles # sec Amplitude (A in cm, m or degrees [θ]) Other Harmonic Motion Basics Basic Definitions Pendulums
Lecture 18. Waves and Sound
 Lecture 18 Waves and Sound Today s Topics: Nature o Waves Periodic Waves Wave Speed The Nature o Sound Speed o Sound Sound ntensity The Doppler Eect Disturbance Wave Motion DEMO: Rope A wave is a traveling
Lecture 18 Waves and Sound Today s Topics: Nature o Waves Periodic Waves Wave Speed The Nature o Sound Speed o Sound Sound ntensity The Doppler Eect Disturbance Wave Motion DEMO: Rope A wave is a traveling
PHYSICS. Chapter 16 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT Pearson Education, Inc.
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 16 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 16 Traveling Waves IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn the basic properties
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
 WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
WAVES SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibration about an equilibrium position in which a restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium TYPES OF SHM THE PENDULUM
Exam 3 Review. Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations A stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations.
 Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Exam 3 Review Chapter 10: Elasticity and Oscillations stress will deform a body and that body can be set into periodic oscillations. Elastic Deformations of Solids Elastic objects return to their original
Physics 140. Sound. Chapter 12
 Physics 140 Sound Chapter 12 Sound waves Sound is composed of longitudinal pressure waves. wave propagabon Compression Compression Compression è when parbcles come together RarefacBon RarefacBon RarefacBon
Physics 140 Sound Chapter 12 Sound waves Sound is composed of longitudinal pressure waves. wave propagabon Compression Compression Compression è when parbcles come together RarefacBon RarefacBon RarefacBon
Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2)
 Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things:
Exam tomorrow on Chapter 15, 16, and 17 (Oscilla;ons and Waves 1 &2) What to study: Quiz 6 Homework problems for Chapters 15 & 16 Material indicated in the following review slides Other Specific things:
Mathematical Models of Fluids
 SOUND WAVES Mathematical Models of Fluids Fluids molecules roam and collide no springs Collisions cause pressure in fluid (Units: Pascal Pa = N/m 2 ) 2 mathematical models for fluid motion: 1) Bulk properties
SOUND WAVES Mathematical Models of Fluids Fluids molecules roam and collide no springs Collisions cause pressure in fluid (Units: Pascal Pa = N/m 2 ) 2 mathematical models for fluid motion: 1) Bulk properties
Saint Lucie County Science Scope and Sequence
 Course: Physics 1 Course Code: 2003380 SEMESTER 2 QUARTER 3 UNIT 7 TOPIC of STUDY: Thermal Energy STANDARDS: 8:Matter, 10: Energy, 12: Motion KEY LEARNING: ~Mathematically relate heat, phase change, energy,
Course: Physics 1 Course Code: 2003380 SEMESTER 2 QUARTER 3 UNIT 7 TOPIC of STUDY: Thermal Energy STANDARDS: 8:Matter, 10: Energy, 12: Motion KEY LEARNING: ~Mathematically relate heat, phase change, energy,
Wave Motion and Sound
 Wave Motion and Sound 1. A back and forth motion that repeats itself is a a. Spring b. Vibration c. Wave d. Pulse 2. The number of vibrations that occur in 1 second is called a. A Period b. Frequency c.
Wave Motion and Sound 1. A back and forth motion that repeats itself is a a. Spring b. Vibration c. Wave d. Pulse 2. The number of vibrations that occur in 1 second is called a. A Period b. Frequency c.
Origin of Sound. Those vibrations compress and decompress the air (or other medium) around the vibrating object
 Sound Each celestial body, in fact each and every atom, produces a particular sound on account of its movement, its rhythm or vibration. All these sounds and vibrations form a universal harmony in which
Sound Each celestial body, in fact each and every atom, produces a particular sound on account of its movement, its rhythm or vibration. All these sounds and vibrations form a universal harmony in which
Schedule for the remainder of class
 Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
Schedule for the remainder of class 04/25 (today): Regular class - Sound and the Doppler Effect 04/27: Cover any remaining new material, then Problem Solving/Review (ALL chapters) 04/29: Problem Solving/Review
16 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES
 Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
Chapter 6 SUPERPOSITION & STANDING WAVES 6. Superposition of waves Principle of superposition: When two or more waves overlap, the resultant wave is the algebraic sum of the individual waves. Illustration:
3/9/2011. Outline Chapter 7 Waves Water Waves Water Waves. Water waves are really circular. They are an example of Mechanical waves.
 Outline Chapter 7 Waves 7-1. Water Waves 7-2. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves 7-3. Describing Waves 7-4. Standing Waves 7-5. Sound 7-6. Doppler Effect 7-7. Musical Sounds 7-8. Electromagnetic Waves 7-9.
Outline Chapter 7 Waves 7-1. Water Waves 7-2. Transverse and Longitudinal Waves 7-3. Describing Waves 7-4. Standing Waves 7-5. Sound 7-6. Doppler Effect 7-7. Musical Sounds 7-8. Electromagnetic Waves 7-9.
Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string)
 1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
1 Part 5: Waves 5.1: Harmonic Waves Wave a disturbance in a medium that propagates Transverse wave - the disturbance is perpendicular to the propagation direction (e.g., wave on a string) Longitudinal
Sound. Speed of Sound
 Sound TUNING FORK CREATING SOUND WAVES GUITAR STRING CREATING SOUND WAVES Speed of Sound Sound travels at a speed that depends on the medium through which it propagates. The speed of sound depends: - directly
Sound TUNING FORK CREATING SOUND WAVES GUITAR STRING CREATING SOUND WAVES Speed of Sound Sound travels at a speed that depends on the medium through which it propagates. The speed of sound depends: - directly
Superposition and Standing Waves
 Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
Physics 1051 Lecture 9 Superposition and Standing Waves Lecture 09 - Contents 14.5 Standing Waves in Air Columns 14.6 Beats: Interference in Time 14.7 Non-sinusoidal Waves Trivia Questions 1 How many wavelengths
17 SOUND. Introduction. Chapter Outline
 Chapter 17 Sound 867 17 SOUND Figure 17.1 Hearing is an important human sense that can detect frequencies of sound, ranging between 20 Hz and 20 khz. However, other species have very different ranges of
Chapter 17 Sound 867 17 SOUND Figure 17.1 Hearing is an important human sense that can detect frequencies of sound, ranging between 20 Hz and 20 khz. However, other species have very different ranges of
Chapter 6. Wave Motion. Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
 Chapter 6 Waves We know that when matter is disturbed, energy emanates from the disturbance. This propagation of energy from the disturbance is know as a wave. We call this transfer of energy wave motion.
Chapter 6 Waves We know that when matter is disturbed, energy emanates from the disturbance. This propagation of energy from the disturbance is know as a wave. We call this transfer of energy wave motion.
Class Average = 71. Counts Scores
 30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
30 Class Average = 71 25 20 Counts 15 10 5 0 0 20 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Scores Chapter 12 Mechanical Waves and Sound To describe mechanical waves. To study superposition, standing waves, and interference.
Thermodynamics continued
 Chapter 15 Thermodynamics continued 15 Work The area under a pressure-volume graph is the work for any kind of process. B Pressure A W AB W AB is positive here volume increases Volume Clicker Question
Chapter 15 Thermodynamics continued 15 Work The area under a pressure-volume graph is the work for any kind of process. B Pressure A W AB W AB is positive here volume increases Volume Clicker Question
Homework Book. Wave Properties. Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2. Name: Homeroom: Physics Class:
 Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Homework Book Wave Properties Huijia Physics Homework Book 1 Semester 2 Name: Homeroom: Physics Class: Week 1 Reflection, Refraction, wave equations 1. If the wavelength of an incident wave is 1.5cm and
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section
 Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 3: 30 Sep. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Sound Sound = longitudinal wave in a medium. The medium can be anything:
Fall 2004 Physics 3 Tu-Th Section Claudio Campagnari Lecture 3: 30 Sep. 2004 Web page: http://hep.ucsb.edu/people/claudio/ph3-04/ 1 Sound Sound = longitudinal wave in a medium. The medium can be anything:
Final Exam Notes 8am WednesdayDecember 16, 2015 Physics 1320 Music & Physics Prof. Tunks & Olness
 Final Exam Notes 8am WednesdayDecember 16, 2015 Physics 1320 Music & Physics Prof. Tunks & Olness 1)This contains review material for the Final exam. It consists of review sheets for exams 1 and 2, as
Final Exam Notes 8am WednesdayDecember 16, 2015 Physics 1320 Music & Physics Prof. Tunks & Olness 1)This contains review material for the Final exam. It consists of review sheets for exams 1 and 2, as
1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear?
 1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear? The vibrating object produces a series of compressions and rarefactions, one after the other in the medium. These pulses
1. How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear? The vibrating object produces a series of compressions and rarefactions, one after the other in the medium. These pulses
KEY TERMS. compression rarefaction pitch Doppler effect KEY TERMS. intensity decibel resonance KEY TERMS
 CHAPTER 12 SECTION 1 Sound Waves Summary The frequency of a sound wave determines its pitch. The speed of sound depends on the medium. The relative motion between the source of waves and an observer creates
CHAPTER 12 SECTION 1 Sound Waves Summary The frequency of a sound wave determines its pitch. The speed of sound depends on the medium. The relative motion between the source of waves and an observer creates
Marketed and Distributed By FaaDoOEngineers.com
 WAVES GUPTA CLASSES For any help contact: 995368795, 968789880 Nishant Gupta, D-, Prashant vihar, Rohini, Delhi-85 Waves Wave motion A wave motion is a kind of disturbance which is transferred from one
WAVES GUPTA CLASSES For any help contact: 995368795, 968789880 Nishant Gupta, D-, Prashant vihar, Rohini, Delhi-85 Waves Wave motion A wave motion is a kind of disturbance which is transferred from one
Waves Encountering Barriers
 Waves Encountering Barriers Reflection and Refraction: When a wave is incident on a boundary that separates two regions of different wave speed, part of the wave is reflected and part is transmitted. Figure
Waves Encountering Barriers Reflection and Refraction: When a wave is incident on a boundary that separates two regions of different wave speed, part of the wave is reflected and part is transmitted. Figure
Homework #4 Reminder Due Wed. 10/6
 Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Due Wed. 10/6 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating
Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Due Wed. 10/6 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating
1. a) A flag waving in the breeze flaps once each s. What is the period and frequency of the flapping flag?
 PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
PHYSICS 20N UNIT 4 REVIEW NAME: Be sure to show explicit formulas and substitutions for all calculational questions, where appropriate. Round final answers correctly; give correct units. Be sure to show
Oscillations and Waves
 Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
Oscillations and Waves Periodic Motion Simple Harmonic Motion Connections between Uniform Circular Motion and Simple Harmonic Motion The Period of a Mass on a Spring Energy Conservation in Oscillatory
General Physics I. Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves. Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 )
 General Physics I Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Motivation When analyzing a linear medium that is, one in which the restoring force
General Physics I Lecture 14: Sinusoidal Waves Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Motivation When analyzing a linear medium that is, one in which the restoring force
Longitudinal Waves. Reading: Chapter 17, Sections 17-7 to Sources of Musical Sound. Pipe. Closed end: node Open end: antinode
 Longitudinal Waes Reading: Chapter 7, Sections 7-7 to 7-0 Sources o Musical Sound Pipe Closed end: node Open end: antinode Standing wae pattern: Fundamental or irst harmonic: nodes at the ends, antinode
Longitudinal Waes Reading: Chapter 7, Sections 7-7 to 7-0 Sources o Musical Sound Pipe Closed end: node Open end: antinode Standing wae pattern: Fundamental or irst harmonic: nodes at the ends, antinode
Chapter 8: Wave Motion. Homework #4 Reminder. But what moves? Wave properties. Waves can reflect. Waves can pass through each other
 Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating disturbance
Homework #4 Reminder Chap. 6 Concept: 36 Problems 14, 18 Chap. 8 Concept: 8, 12, 30, 34 Problems 2, 10 Chapter 8: Wave Motion A wave is a sort of motion But unlike motion of particles A propagating disturbance
TYPES OF WAVES. 4. Waves and Sound 1
 TYPES OF WAVES Consider a set of playground swings attached by a rope from seat to seat If you sit in the first swing and begin oscillating, this disturbs the equilibrium The connecting ropes cause the
TYPES OF WAVES Consider a set of playground swings attached by a rope from seat to seat If you sit in the first swing and begin oscillating, this disturbs the equilibrium The connecting ropes cause the
Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations
 Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Oscillation the vibration of an object. Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter
 Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Oscillation the vibration of an object Wave a transfer of energy without a transfer of matter Equilibrium Position position of object at rest (mean position) Displacement (x) distance in a particular direction
Physics 11 Chapters 15: Traveling Waves and Sound and 16: Superposition and Standing Waves
 Physics 11 Chapters 15: Traeling Waes and Sound and 16: Superposition and Standing Waes We are what we beliee we are. Benjamin Cardozo We would accomplish many more things if we did not think of them as
Physics 11 Chapters 15: Traeling Waes and Sound and 16: Superposition and Standing Waes We are what we beliee we are. Benjamin Cardozo We would accomplish many more things if we did not think of them as
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves
 Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Chapter 11 Vibrations and Waves 11-1 Simple Harmonic Motion If an object vibrates or oscillates back and forth over the same path, each cycle taking the same amount of time, the motion is called periodic.
Physics 25 Section 2 Exam #1 February 1, 2012 Dr. Alward
 1.The tension in a taut rope is increased by a factor of 9, and the mass per length is reduced to one-fourth of its former value.. How does the speed of wave pulses on the rope change, if at all? A) The
1.The tension in a taut rope is increased by a factor of 9, and the mass per length is reduced to one-fourth of its former value.. How does the speed of wave pulses on the rope change, if at all? A) The
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
3 THE P HYSICS PHYSICS OF SOUND
 Chapter 3 THE PHYSICS OF SOUND Contents What is sound? What is sound wave?» Wave motion» Source & Medium How do we analyze sound?» Classifications» Fourier Analysis How do we measure sound?» Amplitude,
Chapter 3 THE PHYSICS OF SOUND Contents What is sound? What is sound wave?» Wave motion» Source & Medium How do we analyze sound?» Classifications» Fourier Analysis How do we measure sound?» Amplitude,
Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound
 EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Standing Waves Fixed Endpoints Fundamental n=1 (2 nodes) l n = 2L/n f n = n v / (2L)
EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Standing Waves Fixed Endpoints Fundamental n=1 (2 nodes) l n = 2L/n f n = n v / (2L)
Lectures Chapter 16 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition)
 PH 201-4A spring 2007 Waves and Sound Lectures 26-27 Chapter 16 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 Waves A wave is a vibrational, trembling motion in an elastic, deformable body. The wave is initiated
PH 201-4A spring 2007 Waves and Sound Lectures 26-27 Chapter 16 (Cutnell & Johnson, Physics 7 th edition) 1 Waves A wave is a vibrational, trembling motion in an elastic, deformable body. The wave is initiated
Physics Worksheet Sound and Light Section: Name:
 Do Now: What is common between sound and light? What are the differences between sound and light? Sound Waves 1. Define Sound Waves from three different perspectives 6. Speed of sound =. Formula: v =.
Do Now: What is common between sound and light? What are the differences between sound and light? Sound Waves 1. Define Sound Waves from three different perspectives 6. Speed of sound =. Formula: v =.
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 24 Chapter 11: Waves 11.8 Reflection and Refraction 11.10 Standing Waves Chapter 12: Sound 12.1 Sound Waves 12.4 Standing Sound Waves Lecture 24 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 ILQ
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984
 Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Oscillations - AP Physics B 1984 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1 2 (B) (C) 1 1 2 (D) 2 (E) 2 A block oscillates
Introduction to Acoustics. Phil Joseph
 Introduction to Acoustics Phil Joseph INTRODUCTION TO ACOUSTICS Sound and Noise Sound waves Frequency, wavelength and wavespeed Point sources Sound power and intensity Wave reflection Standing waves Measures
Introduction to Acoustics Phil Joseph INTRODUCTION TO ACOUSTICS Sound and Noise Sound waves Frequency, wavelength and wavespeed Point sources Sound power and intensity Wave reflection Standing waves Measures
Serway_ISM_V1 1 Chapter 14
 Serway_ISM_V1 1 Chapter 14 14 Sound ANSWERS TO MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. All sound waves travel at the same speed in air of a given temperature. Thus,, giving and the correct choice is (b). 2. The Celsius
Serway_ISM_V1 1 Chapter 14 14 Sound ANSWERS TO MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. All sound waves travel at the same speed in air of a given temperature. Thus,, giving and the correct choice is (b). 2. The Celsius
Standing waves. The interference of two sinusoidal waves of the same frequency and amplitude, travel in opposite direction, produce a standing wave.
 Standing waves The interference of two sinusoidal waves of the same frequency and amplitude, travel in opposite direction, produce a standing wave. y 1 (x, t) = y m sin(kx ωt), y 2 (x, t) = y m sin(kx
Standing waves The interference of two sinusoidal waves of the same frequency and amplitude, travel in opposite direction, produce a standing wave. y 1 (x, t) = y m sin(kx ωt), y 2 (x, t) = y m sin(kx
Physics 231 Lecture 25
 Physics 231 Lecture 25 Spherical waves P Main points of today s I = lecture: 2 4πr Wave Dopper speed shift for a string v + v o ƒ' = ƒ F v = v vs µ Interference of sound waves L Here F is the string tension
Physics 231 Lecture 25 Spherical waves P Main points of today s I = lecture: 2 4πr Wave Dopper speed shift for a string v + v o ƒ' = ƒ F v = v vs µ Interference of sound waves L Here F is the string tension
Physics 202 Homework 7
 Physics 202 Homework 7 May 15, 2013 1. On a cello, the string with the largest linear density (0.0156 kg/m) is the C 171 newtons string. This string produces a fundamental frequency of 65.4 Hz and has
Physics 202 Homework 7 May 15, 2013 1. On a cello, the string with the largest linear density (0.0156 kg/m) is the C 171 newtons string. This string produces a fundamental frequency of 65.4 Hz and has
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
 CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
CHAPTER 11 VIBRATIONS AND WAVES http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/waves/u10l1a.html UNITS Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator The Period and Sinusoidal Nature of SHM The
Quiz on Chapters 13-15
 Quiz on Chapters 13-15 Final Exam, Thursday May 3, 8:00 10:00PM ANH 1281 (Anthony Hall). Seat assignments TBD RCPD students: Thursday May 3, 5:00 9:00PM, BPS 3239. Email will be sent. Alternate Final Exam,
Quiz on Chapters 13-15 Final Exam, Thursday May 3, 8:00 10:00PM ANH 1281 (Anthony Hall). Seat assignments TBD RCPD students: Thursday May 3, 5:00 9:00PM, BPS 3239. Email will be sent. Alternate Final Exam,
Lecture 17. Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves.
 Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
Lecture 17 Mechanical waves. Transverse waves. Sound waves. Standing Waves. What is a wave? A wave is a traveling disturbance that transports energy but not matter. Examples: Sound waves (air moves back
INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPT. OF PHYSICS P105, Basic Physics of Sound, Spring 2010
 Name: Joe E. Physics ID#: 999 999 999 INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPT. OF PHYSICS P105, Basic Physics of Sound, Spring 2010 Midterm Exam #1 Thursday, 11 Feb. 2010, 7:30 9:30 p.m. Closed book. You are allowed
Name: Joe E. Physics ID#: 999 999 999 INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPT. OF PHYSICS P105, Basic Physics of Sound, Spring 2010 Midterm Exam #1 Thursday, 11 Feb. 2010, 7:30 9:30 p.m. Closed book. You are allowed
Lecture 18. Sound Waves: Intensity, Interference, Beats and Doppler Effect.
 Lecture 18 Sound Waes: Intensity, Interference, Beats and Doppler Effect. Speed of sound Speed of soun in air, depends on temperature: = (331 + 0.60 T ) m/s where T in C Sound intensity leel β = 10log
Lecture 18 Sound Waes: Intensity, Interference, Beats and Doppler Effect. Speed of sound Speed of soun in air, depends on temperature: = (331 + 0.60 T ) m/s where T in C Sound intensity leel β = 10log
Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids
 Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids To round out our discussion of interference and waves, we should talk about beats. When you combine two waves (sound is a good example), if the frequencies
Lecture 23 Sound Beats Sound Solids and Fluids To round out our discussion of interference and waves, we should talk about beats. When you combine two waves (sound is a good example), if the frequencies
Sound Waves. Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium
 Chapter 16 Sound Waves Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium An example of a compressional wave Waves can spread out in all directions Their speed depends on its medium
Chapter 16 Sound Waves Sound waves are caused by vibrations and carry energy through a medium An example of a compressional wave Waves can spread out in all directions Their speed depends on its medium
Chapter 17: Waves II. Sound waves are one example of Longitudinal Waves. Sound waves are pressure waves: Oscillations in air pressure and air density
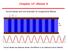 Sound waves are one example of Longitudinal Waves Sound waves are pressure waves: Oscillations in air pressure and air density Before we can understand pressure waves in detail, we need to understand what
Sound waves are one example of Longitudinal Waves Sound waves are pressure waves: Oscillations in air pressure and air density Before we can understand pressure waves in detail, we need to understand what
1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place.
 v = fλ 1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place. Transverse Wave Longitudinal Wave How is a guitar made to create different notes/pitches/frequencies? A wave s
v = fλ 1. A wave is a traveling disturbance. 2. A wave carries energy from place to place. Transverse Wave Longitudinal Wave How is a guitar made to create different notes/pitches/frequencies? A wave s
Phys101 Lectures 28, 29. Wave Motion
 Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Phys101 Lectures 8, 9 Wave Motion Key points: Types of Waves: Transverse and Longitudinal Mathematical Representation of a Traveling Wave The Principle of Superposition Standing Waves; Resonance Ref: 11-7,8,9,10,11,16,1,13,16.
Chapter 16 Sound and Hearing by C.-R. Hu
 1. What is sound? Chapter 16 Sound and Hearing by C.-R. Hu Sound is a longitudinal wave carried by a gas liquid or solid. When a sound wave passes through a point in space the molecule at that point will
1. What is sound? Chapter 16 Sound and Hearing by C.-R. Hu Sound is a longitudinal wave carried by a gas liquid or solid. When a sound wave passes through a point in space the molecule at that point will
Lecture 5 Notes: 07 / 05. Energy and intensity of sound waves
 Lecture 5 Notes: 07 / 05 Energy and intensity of sound waves Sound waves carry energy, just like waves on a string do. This energy comes in several types: potential energy due to the compression of the
Lecture 5 Notes: 07 / 05 Energy and intensity of sound waves Sound waves carry energy, just like waves on a string do. This energy comes in several types: potential energy due to the compression of the
Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound
 EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Speed of Sound Recall for pulse on string: v = sqrt(t / m) For fluids: v = sqrt(b/r)
EXAM III Physics 101: Lecture 22 Sound Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 12 Physics 101: Lecture 22, Pg 1 Speed of Sound Recall for pulse on string: v = sqrt(t / m) For fluids: v = sqrt(b/r)
Lecture Sound Waves EM Waves. Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org. The Doppler Effect 11/11/2014
 Lecture 1102 Sound Waves EM Waves Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org The Doppler Effect The Doppler effect (or Doppler shift) is the change in frequency (or wavelength) of a wave for an observer moving
Lecture 1102 Sound Waves EM Waves Physics Help Q&A: tutor.leiacademy.org The Doppler Effect The Doppler effect (or Doppler shift) is the change in frequency (or wavelength) of a wave for an observer moving
Physics 111. Lecture 31 (Walker: ) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Standing Waves Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature
 Physics 111 Lecture 31 (Walker: 14.7-8) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same
Physics 111 Lecture 31 (Walker: 14.7-8) Wave Superposition Wave Interference Physics of Musical Instruments Temperature Superposition and Interference Waves of small amplitude traveling through the same
Physics General Physics. Lecture 25 Waves. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 25 Waves Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 Final Exam 2 3 Mechanical Waves Waves and wave fronts: 4 Wave Motion 5 Two Kinds of Waves 6 Reflection of Waves When
2016 AP Physics Unit 6 Oscillations and Waves.notebook December 09, 2016
 AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
AP Physics Unit Six Oscillations and Waves 1 2 A. Dynamics of SHM 1. Force a. since the block is accelerating, there must be a force acting on it b. Hooke's Law F = kx F = force k = spring constant x =
to calculate gravitational force. d - Know how changes in mass or distance affect the gravitational force between two objects.
 PHYSICS 2 ND SEMESTER REVIEW Semester Test Notes: - You may use a 5 x 8 index card (NO LARGER) with equations, diagrams, and notes. - Your index card will be turned in with your test. - Most constants
PHYSICS 2 ND SEMESTER REVIEW Semester Test Notes: - You may use a 5 x 8 index card (NO LARGER) with equations, diagrams, and notes. - Your index card will be turned in with your test. - Most constants
WAVES( SUB) 2. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity and inertia
 WAES( SUB). What is meant by a wave? Ans: The disturbance set up in a medium is known as a wave. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity
WAES( SUB). What is meant by a wave? Ans: The disturbance set up in a medium is known as a wave. What is the property of the medium that is essential for the propagation of mechanical wave? Ans: Elasticity
Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties
 Lesson35.notebook May 27, 2013 Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties Today's goal: I can explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves and their properties. Waves are a disturbances
Lesson35.notebook May 27, 2013 Unit 4 Waves and Sound Waves and Their Properties Today's goal: I can explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves and their properties. Waves are a disturbances
chapter 17 Sound Intensity of sound (Section 17.2) 1. Number of speakers 2. Point source
 chapter 17 Sound Intensity of sound (Section 17.2) 1. Number of speakers 2. Point source Standing waves (Section 17.3) 3. Standing waves in air columns Doppler effect (Section 17.4) 4. Doppler shift I
chapter 17 Sound Intensity of sound (Section 17.2) 1. Number of speakers 2. Point source Standing waves (Section 17.3) 3. Standing waves in air columns Doppler effect (Section 17.4) 4. Doppler shift I
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
SOUND. Representative Sample Physics: Sound. 1. Periodic Motion of Particles PLANCESS CONCEPTS
 Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
Representative Sample Physics: Sound SOUND 1. Periodic Motion of Particles Before we move on to study the nature and transmission of sound, we need to understand the different types of vibratory or oscillatory
1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is:
 1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is: 2) The bob of simple Pendulum is a spherical hallow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near
1) The K.E and P.E of a particle executing SHM with amplitude A will be equal to when its displacement is: 2) The bob of simple Pendulum is a spherical hallow ball filled with water. A plugged hole near
