Tilted Transverse Isotropy
|
|
|
- Lynn Jefferson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NAFA-GAZ listopa ROK LXVII Anej Kostecki Institute of Oil an Gas, Kakow ilte ansvese Isotop Intouction In seismic pospecting, the tansvese isotop (I) moel, i.e. a moel of thinl statifie (laminate) meium, is the most common one. he moel has been popose b Postma [], an assumes that bounaies sepaating isotopic laes ae paallel planes. In the case when the ais of smmet is vetical, the moel is efee to as the vetical tansvese isotop (VI) moel, while if the ais of smmet an the vetical ais fom an angle θ, this is a monoclinal meium escibe b the tilte tansvese isotop (I) moel. his is a vesatile moel of anisotop, which can be use to obtain fomulas escibing moels with hoiontal aes of smmet, i.e. hoiontal tansvese isotop (HI) moels as well as compose moels [7]. ntil now, stuies of the mathematical esciption of the I meium [, ] ealt with one of two possible cases of monoclinal meia (fo eve vaiant). his aticle pesents esciptions of both cases fo eve vaiant of the moel. Basic elationships Knowlege of tansvese isotop paametes is ve useful fo analsis of othe tpes of anisotop. Geneall in the case of anisotopic meia escibe b the moels of tansvese isotop, elasticit matices, which pesent the components of the elasticit tenso, epen on the spatial oientation of I moels. Figue pesents a ight-hane cooinate sstem,, an a cooinate sstem of,, associate with ipping paallel stata which coespon with the I meium. he spatial aangement of the meium in elation to the cooinate sstem,, is efine b an angle θ between planes an, i.e. its inclination. he elation between the stess an stain tensos in the,, cooinate sstem ae the same as in the VI meium. In oe to etemine the pinciples of wave popagation in the,, cooinate sstem, otation of the,, sstem to the,, sstem shoul be one using the mati of cosines of angles between these two sstems (angles ae measue in the clockwise iection). he geometical situation pesente in Figue is escibe b the following mati of iection cosines: Fig.. Dawing of monoclinal stata ipping at an angle θ (between the - an -aes) of tansvesel isotopic meium 3 3 cos, cos, cos cos ' ' o, ' cos9 cos, cos, cos, cos cos ' ' ' cos o, ' cos7, ', ' cos sin sin () 769
2 NAFA-GAZ B using Bon s law [, 3, ], we can eive the geneal elationship between the mati D of elastic mouli, ecoe in the,, sstem, an the mati of known tenso elements in the,, sstem, whee the plane foms an angle θ with the plane: whee the R mati is as follows: D = R R () R (3) while the mati R is the tanspose of the mati R. B using equation (), we obtain Bon s mati R (+) (otation aoun the -ais, inclination oiente towas the positive -ais): R cos sin sin cos sin cos sin cos cos sin sin sin cos sin cos () while the mati escibing the elationship between stess an stain in the I/VI meium is as follows: (5) hus, b using fomulas () an (5), we obtain fom elationship () the elasticit mati D (+) ( inicates otation aoun the -ais, while (+) inicates the inclination of the plane). D (6) he elements of the mati D (+) ae: ` cos cos sin sin sin cos sin 77 n /
3 atkuł sin cos sin cos sin cos sin sin cos sin cos sin cos cos sin cos sin sin cos sin cos cos sin cos 6 sin cos sin cos cos sin sin sin sin cos cos (7) Let us now consie the same vesion of the I moel, i.e. otation aoun the -ais, but in a situation whee the plane is ipping towas the negative -ais (Figue ). In such a case, the mati of iection cosines is epesse as: 3 3 cos sin sin cos (8) while Bon s mati is epesse as: R cos sin sin cos sin cos sin cos cos sin sin sin cos sin cos (9) Fig.. Geometical epesentation of coincience of the - an -aes. he -ais is incline towas the stata inclination i.e. negative -ais. Aows inicate the clockwise iection of measuing angles B using matices (5) an (9), the elasticit mati D (-) is obtaine an it epesents a monoclinal meium incline towas the negative -ais: D () n / 77
4 NAFA-GAZ whee elements ae efine b equations (7). A compaison of matices D (+) an D (-) shows that the matices iffe onl b signs fo elements 5, 5, 35, 6 an fo the smmetical elements. Let us now consie the secon vesion of the I meium which is a esult of otating the isotop plane aoun the -ais. We will analse the case whee the lamination plane of the meium is oiente towas the positive -ais an foms an angle θ with the ecoing suface (Figue 3). Fig. 3. Ovelap of the - an -aes. he -ais is oiente towas the positive -ais an in the same iection as the inclination of the stata In such a situation, the mati of iection cosines is: cos sin sin cos () while the elasticit mati D (+) calculate in a simila wa as in the pevious cases is: D () whee the elements of the mati ae: ` sin cos cos sin sin 3 3 sin cos cos sin sin cos sin cos sin cos sin sin cos cos sin cos sin sin cos cos 65 cos sin cos cos sin sin cos sin sin sin cos cos sin cos sin cos sin () 77 n /
5 atkuł Let us consie anothe case of otating the isotop plane aoun the -ais whee the ipping -ais is oiente towas the negative -ais (Figue ). Fig.. he geomet of the,, an,, cooinate sstems. he -ais is oiente towas the stata inclination, i.e. the negative -ais In such a case the mati of iection cosines is: cos sin sin cos () Fom elationships () an (3), the elasticit mati D (-) is obtaine: D (5) whee elements of the mati ae epesse b equations (). A compaison of matices () an (5) shows that iffeent esults ae obtaine epening on the oientation of the incline plane also in this vesion of a monoclinal meium. he elasticit matices D an D, compose of elements which ae tenso components D ijkl (using the shotene Voigt notation), ae veifie hee both in tems of using the cooinate sstem,, oiente in an iection in elation to the cooinate sstem,, an in tems of the metho of calculating the tenso D ijkl. he veification can be one using elationship [6]: D ijkl = ii jj kk ll i j k l (6) It gives the same esults (7) an () fo the elements of mati D in both cases of the monoclinal meium, i.e. the two-imensional wavefiel ecoe up-ip an ecoe own-ip, as well as in the case when acquisition is caie out along the etent of the stuctue fo both tpes of ipping stata. B using the basic elationship between the tenso of stess ij an the tenso of stain E ik (Hooke s law) the following mati is obtaine: 3 E E E E,, E, D E,,,, (7) n / 773
6 NAFA-GAZ he elationships between the components of the elasticit tenso an the eivatives of paticle movement in the meium, an ae escibe in the two-imensional case, i.e. the eivatives of the wavefiel in elation to the -ais ae equal to eo. Stating with the law of motion (ignoing etenal foces) fo each component, the following equations ae obtaine:,,,,3 3.3,3 ρ t ρ t ρ t 3 (8) whee ρ is ensit of stata an t is time. Analsing the case of the I stata, whee the smmet ais is locate on the plane, i.e. fo mati D (+, -), in both cases we get the following wave equations: 5, 5,, 53, ρ (9) t,, 6, ρ () t,, () t 5, 35,,,, 35, In fomulas (9-), the sign (+) efes to acquisition along the -ais moving in the positive iection of the ais, i.e. own-ip (Figue ), while the sign ( ) efes to the up-ip iection. he above elationships inicate that the coss-line isplacement is neithe inclue in fomula (9) no in fomula (). he shea wave SH is escibe sepaatel b equation (). In the case of low angles of inclination (θ ), we can assume that the elements of the elasticit mati 5 = 5, 53 = 35, 6 an thus the influence of the ip iections of the isotop plane on the wave equation can be ignoe. Fom fomulas (9-) with θ = o, the following wave equations fo the VI moel with a vetical ais of smmet ae obtaine:,,, () t,, (3) t () t,,, while the following ae obtaine fo the HI moel with the smmet ais oiente paallel to the -ais when the angle of inclination is θ = 9 o :,,, (5) t,, (6) t 77 n /
7 atkuł (7) t,,, Let us now consie the secon case of the I moel, whee the ecoing is caie out in the stike iection of the statifie meium, i.e. the smmet ais is paallel to the -ais. In that case, the following is obtaine fom equations (), (5) an (8):,,,, 56, (8) t, 65, 65, 3, (9) t,,, 56, 3, (3) t Fomulas (8-3) impl that the iection of the isotop plane incline at an angle θ has a iect influence on the chaacte of the wave equation. his influence isappeas when the angle θ is elativel low, while in the eteme case, when the angle is θ = o, the epecte wavefiel equations fo the VI moel, i.e. equations (-), ae obtaine. It is eas to notice that in the case of the wavefiel ecoe along the etent of the stuctue (the -ais) thee is no sepaation of the longituinal an shea SH waves which eist both in equations (8) an (3) espite the assumption of vanishing eivatives of movement i, =. In the case of vetical isotop plane (o factues, iscontinuities) with the angle of θ = 9 o, fom (8-3) we obtain equations escibing the wavefiel in the HI meium, i.e. with a hoiontal ais of smmet pepenicula to the ecoing iection along the -ais:,,, () t,, (3) t,,, () t he above equations inicate that the elationship fo the shea SH wave is the sepaate fomula (3), while thee is no component in equations () an (). he above motion equations fo each tpe of the anisotopic meia fom a basis fo calculations of ispesive equations. hese ae necessa fo analsis of the popagation of all tpes of waves in the wavenumbe-fequenc omain. When equations (9) an () ae use togethe with the Fouie tansfom ( k, t ω), an elements 5, 53, 6 ae ignoe ue to the low angle of inclination, the following mati equation is epesse: k k k k k k k k (3) whee k an k ae the hoiontal an vetical wavenumbes, an ω is the angle fequenc. When we assume that the velocit of the shea SV wave is eo fo low angles θ, i.e. similal as fo the VI meium [, 5], an we assume that: cos cos cos (35) n / 775
8 NAFA-GAZ the ispesive equation fo the vetical wavenumbe k I in the I-tpe anisotopic meium is obtaine: k I S p S p qi k cos (36) S p I k whee: q S I I p q VI VI V pp cos cos (37) while V pp is the velocit of longituinal wave in the vetical iection, i.e. V pp = V p^ cosθ, whee V p^ is the longituinal wave velocit in the iection pepenicula to the statification in the I meium, while q VI = + ε, η VI = (ε δ) ae homsen s paametes [] fo the hoiontall statifie meium (VI) with the vetical ais of smmet. In a simila wa, ispesive equations can be obtaine fo othe oientations of the I stata. Such equations ae essential fo solving ual-omain migation algoithms pefome in the fequenc-space an fequenc-wavenumbe omains [7, 8, ]. he aticle was sent to the Eitoial Section on Accepte fo pinting on Liteatue [] Alkhalifah.: Acoustic appoimation fo pocessing in tansvesel isotopic, inhomogeneous meia. Geophsics, 63, 63-6, 998. [] Aul B.: Acoustic fiel an waves in soli. Kiege Publishing ompan, vol., 99. [3] Bansal R., Sen M.: Finite iffeence moelling of S-wave splitting in anisotopic meia. Geophsical Pospecting, 56, 93-, 8. [] Danek., Leśniak A., Pięta A.: Numeical moeling of seismic wave popagation in selecte anisotopic meia. Stuia, Ropaw, Monogafie n 6, Insttut Gospoaki Suowcami Minealnmi i Enegią, PAN,. [5] Han Q., Wu R.: A one wa ual omain popagato fo scala qp waves in VI meia. Geophsics, vol. 7, D9 D7, 5. [6] Helbig K.: Founations of anisotop fo eploation seismics. Seismic eploation, vol., Pegamon, 99. [7] Kostecki A.: Algoithm of migation MG(F-K) in othohombic meium. Nafta-Ga n, 5-5,. [8] Kostecki A.: Algotm migacji MG(F-K) la aniotopowego ośoka tpu HI (Hoiontal ansvese Isotop). Nafta-Ga n, 8-8,. Reviewe: Anna Półchłopek [9] Kostecki A.: Algotm głębokościowej migacji w aniotopowm ośoku VI. Nafta-Ga n, -7, 7. [] Kostecki A.: he algoithm of migation MG(F-K) in monoclinal anisotopic meium (moel I). Nafta-Ga n,. [] Postma G.: Wave popagation in statifie meium. Geophsics, vol., 78-86, 9. [] homsen L.: Weak elastic anisotop. Geophsics, vol. 5, 95-9, 986. [] Zhu I., Doman I.: wo-imensional thee component wave popagation in a tansvesel isotopic meium, with abita oientation finite element moeling. Geophsics, 65, no. 3, 93-9,. Anej Kostecki Pofesso of geophsics. he main subject of inteest electomagnetic an seismic wave popagation, epouction of eep geological stuctues b means of seismic migation, the analsis of migation velocities, seismic anisotop. he autho of publications. 776 n /
Much that has already been said about changes of variable relates to transformations between different coordinate systems.
 MULTIPLE INTEGRLS I P Calculus Cooinate Sstems Much that has alea been sai about changes of vaiable elates to tansfomations between iffeent cooinate sstems. The main cooinate sstems use in the solution
MULTIPLE INTEGRLS I P Calculus Cooinate Sstems Much that has alea been sai about changes of vaiable elates to tansfomations between iffeent cooinate sstems. The main cooinate sstems use in the solution
That is, the acceleration of the electron is larger than the acceleration of the proton by the same factor the electron is lighter than the proton.
 PHYS 55 Pactice Test Solutions Fall 8 Q: [] poton an an electon attact each othe electicall so, when elease fom est, the will acceleate towa each othe Which paticle will have a lage acceleation? (Neglect
PHYS 55 Pactice Test Solutions Fall 8 Q: [] poton an an electon attact each othe electicall so, when elease fom est, the will acceleate towa each othe Which paticle will have a lage acceleation? (Neglect
PH126 Exam I Solutions
 PH6 Exam I Solutions q Q Q q. Fou positively chage boies, two with chage Q an two with chage q, ae connecte by fou unstetchable stings of equal length. In the absence of extenal foces they assume the equilibium
PH6 Exam I Solutions q Q Q q. Fou positively chage boies, two with chage Q an two with chage q, ae connecte by fou unstetchable stings of equal length. In the absence of extenal foces they assume the equilibium
Physics Courseware Physics II Electric Field and Force
 Physics Cousewae Physics II lectic iel an oce Coulomb s law, whee k Nm /C test Definition of electic fiel. This is a vecto. test Q lectic fiel fo a point chage. This is a vecto. Poblem.- chage of µc is
Physics Cousewae Physics II lectic iel an oce Coulomb s law, whee k Nm /C test Definition of electic fiel. This is a vecto. test Q lectic fiel fo a point chage. This is a vecto. Poblem.- chage of µc is
Chapter 28: Magnetic Field and Magnetic Force. Chapter 28: Magnetic Field and Magnetic Force. Chapter 28: Magnetic fields. Chapter 28: Magnetic fields
 Chapte 8: Magnetic fiels Histoically, people iscoe a stone (e 3 O 4 ) that attact pieces of ion these stone was calle magnets. two ba magnets can attact o epel epening on thei oientation this is ue to
Chapte 8: Magnetic fiels Histoically, people iscoe a stone (e 3 O 4 ) that attact pieces of ion these stone was calle magnets. two ba magnets can attact o epel epening on thei oientation this is ue to
7.2.1 Basic relations for Torsion of Circular Members
 Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
Section 7. 7. osion In this section, the geomety to be consideed is that of a long slende cicula ba and the load is one which twists the ba. Such poblems ae impotant in the analysis of twisting components,
15. SIMPLE MHD EQUILIBRIA
 15. SIMPLE MHD EQUILIBRIA In this Section we will examine some simple examples of MHD equilibium configuations. These will all be in cylinical geomety. They fom the basis fo moe the complicate equilibium
15. SIMPLE MHD EQUILIBRIA In this Section we will examine some simple examples of MHD equilibium configuations. These will all be in cylinical geomety. They fom the basis fo moe the complicate equilibium
Jerk and Hyperjerk in a Rotating Frame of Reference
 Jek an Hypejek in a Rotating Fame of Refeence Amelia Caolina Spaavigna Depatment of Applie Science an Technology, Politecnico i Toino, Italy. Abstact: Jek is the eivative of acceleation with espect to
Jek an Hypejek in a Rotating Fame of Refeence Amelia Caolina Spaavigna Depatment of Applie Science an Technology, Politecnico i Toino, Italy. Abstact: Jek is the eivative of acceleation with espect to
Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5
 Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5 Apil 7, 015 1 Commuting opeatos - an example Remine: You saw in class that Â, ˆB ae commuting opeatos iff they have a complete set of commuting obsevables. In aition you
Quantum Mechanics I - Session 5 Apil 7, 015 1 Commuting opeatos - an example Remine: You saw in class that Â, ˆB ae commuting opeatos iff they have a complete set of commuting obsevables. In aition you
ME 210 Applied Mathematics for Mechanical Engineers
 Tangent and Ac Length of a Cuve The tangent to a cuve C at a point A on it is defined as the limiting position of the staight line L though A and B, as B appoaches A along the cuve as illustated in the
Tangent and Ac Length of a Cuve The tangent to a cuve C at a point A on it is defined as the limiting position of the staight line L though A and B, as B appoaches A along the cuve as illustated in the
General Relativity Homework 5
 Geneal Relativity Homewok 5. In the pesence of a cosmological constant, Einstein s Equation is (a) Calculate the gavitational potential point souce with = M 3 (). R µ Rg µ + g µ =GT µ. in the Newtonian
Geneal Relativity Homewok 5. In the pesence of a cosmological constant, Einstein s Equation is (a) Calculate the gavitational potential point souce with = M 3 (). R µ Rg µ + g µ =GT µ. in the Newtonian
That is, the acceleration of the electron is larger than the acceleration of the proton by the same factor the electron is lighter than the proton.
 PHY 8 Test Pactice Solutions Sping Q: [] A poton an an electon attact each othe electically so, when elease fom est, they will acceleate towa each othe. Which paticle will have a lage acceleation? (Neglect
PHY 8 Test Pactice Solutions Sping Q: [] A poton an an electon attact each othe electically so, when elease fom est, they will acceleate towa each othe. Which paticle will have a lage acceleation? (Neglect
( )( )( ) ( ) + ( ) ( ) ( )
 3.7. Moel: The magnetic fiel is that of a moving chage paticle. Please efe to Figue Ex3.7. Solve: Using the iot-savat law, 7 19 7 ( ) + ( ) qvsinθ 1 T m/a 1.6 1 C. 1 m/s sin135 1. 1 m 1. 1 m 15 = = = 1.13
3.7. Moel: The magnetic fiel is that of a moving chage paticle. Please efe to Figue Ex3.7. Solve: Using the iot-savat law, 7 19 7 ( ) + ( ) qvsinθ 1 T m/a 1.6 1 C. 1 m/s sin135 1. 1 m 1. 1 m 15 = = = 1.13
Static equilibrium requires a balance of forces and a balance of moments.
 Static Equilibium Static equilibium equies a balance of foces and a balance of moments. ΣF 0 ΣF 0 ΣF 0 ΣM 0 ΣM 0 ΣM 0 Eample 1: painte stands on a ladde that leans against the wall of a house at an angle
Static Equilibium Static equilibium equies a balance of foces and a balance of moments. ΣF 0 ΣF 0 ΣF 0 ΣM 0 ΣM 0 ΣM 0 Eample 1: painte stands on a ladde that leans against the wall of a house at an angle
Article : 8 Article : 8 Stress Field. and. Singularity Problem
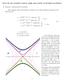
 Aticle : 8 Aticle : 8 Stess Field and Singulaity Poblem (fatigue cack gowth) Repeated load cycles cack development Time (cycles) Cack length 3 Weakening due to gowing cacks Cack length stess concentation
Aticle : 8 Aticle : 8 Stess Field and Singulaity Poblem (fatigue cack gowth) Repeated load cycles cack development Time (cycles) Cack length 3 Weakening due to gowing cacks Cack length stess concentation
b) The array factor of a N-element uniform array can be written
 to Eam in Antenna Theo Time: 18 Mach 010, at 8.00 13.00. Location: Polacksbacken, Skivsal You ma bing: Laboato epots, pocket calculato, English ictiona, Råe- Westegen: Beta, Noling-Östeman: Phsics Hanbook,
to Eam in Antenna Theo Time: 18 Mach 010, at 8.00 13.00. Location: Polacksbacken, Skivsal You ma bing: Laboato epots, pocket calculato, English ictiona, Råe- Westegen: Beta, Noling-Östeman: Phsics Hanbook,
A Crash Course in (2 2) Matrices
 A Cash Couse in ( ) Matices Seveal weeks woth of matix algeba in an hou (Relax, we will only stuy the simplest case, that of matices) Review topics: What is a matix (pl matices)? A matix is a ectangula
A Cash Couse in ( ) Matices Seveal weeks woth of matix algeba in an hou (Relax, we will only stuy the simplest case, that of matices) Review topics: What is a matix (pl matices)? A matix is a ectangula
Electric Potential and Gauss s Law, Configuration Energy Challenge Problem Solutions
 Poblem 1: Electic Potential an Gauss s Law, Configuation Enegy Challenge Poblem Solutions Consie a vey long o, aius an chage to a unifom linea chage ensity λ a) Calculate the electic fiel eveywhee outsie
Poblem 1: Electic Potential an Gauss s Law, Configuation Enegy Challenge Poblem Solutions Consie a vey long o, aius an chage to a unifom linea chage ensity λ a) Calculate the electic fiel eveywhee outsie
2 Governing Equations
 2 Govening Equations This chapte develops the govening equations of motion fo a homogeneous isotopic elastic solid, using the linea thee-dimensional theoy of elasticity in cylindical coodinates. At fist,
2 Govening Equations This chapte develops the govening equations of motion fo a homogeneous isotopic elastic solid, using the linea thee-dimensional theoy of elasticity in cylindical coodinates. At fist,
Section 5: Magnetostatics
 ection 5: Magnetostatics In electostatics, electic fiels constant in time ae pouce by stationay chages. In magnetostatics magnetic fiels constant in time ae pouces by steay cuents. Electic cuents The electic
ection 5: Magnetostatics In electostatics, electic fiels constant in time ae pouce by stationay chages. In magnetostatics magnetic fiels constant in time ae pouces by steay cuents. Electic cuents The electic
Outline. Classes of polarizing devices Polarization states. Eigen-polarization of crystals. Momentum matching at boundaries Polarization calculations
 Cstal optics lectue C 566 Adv. Optics Lab Outline Classes of polaizing devices Polaization states igen-polaization of cstals Momentum matching at boundaies Polaization calculations Muelle matices Jones
Cstal optics lectue C 566 Adv. Optics Lab Outline Classes of polaizing devices Polaization states igen-polaization of cstals Momentum matching at boundaies Polaization calculations Muelle matices Jones
4. Compare the electric force holding the electron in orbit ( r = 0.53
 Electostatics WS Electic Foce an Fiel. Calculate the magnitue of the foce between two 3.60-µ C point chages 9.3 cm apat.. How many electons make up a chage of 30.0 µ C? 3. Two chage ust paticles exet a
Electostatics WS Electic Foce an Fiel. Calculate the magnitue of the foce between two 3.60-µ C point chages 9.3 cm apat.. How many electons make up a chage of 30.0 µ C? 3. Two chage ust paticles exet a
MATHEMATICAL TOOLS. Contents. Theory Exercise Exercise Advance Level Problems Answer Key
 MATHEMATICAL TOOLS Contents Topic Page No. Theoy - 6 Eecise - 7 - Eecise - - 7 Avance Level Poblems 8 - Answe Key - 9 Syllabus Diffeentiation, Integation & Vecto Name : Contact No. ARRIDE LEARNING ONLINE
MATHEMATICAL TOOLS Contents Topic Page No. Theoy - 6 Eecise - 7 - Eecise - - 7 Avance Level Poblems 8 - Answe Key - 9 Syllabus Diffeentiation, Integation & Vecto Name : Contact No. ARRIDE LEARNING ONLINE
of Technology: MIT OpenCourseWare). (accessed MM DD, YYYY). License: Creative Commons Attribution- Noncommercial-Share Alike.
 MIT OpenCouseWae http://ocw.mit.eu 6.013/ESD.013J Electomagnetics an Applications, Fall 005 Please use the following citation fomat: Makus Zahn, Eich Ippen, an Davi Staelin, 6.013/ESD.013J Electomagnetics
MIT OpenCouseWae http://ocw.mit.eu 6.013/ESD.013J Electomagnetics an Applications, Fall 005 Please use the following citation fomat: Makus Zahn, Eich Ippen, an Davi Staelin, 6.013/ESD.013J Electomagnetics
Notes for the standard central, single mass metric in Kruskal coordinates
 Notes fo the stana cental, single mass metic in Kuskal cooinates I. Relation to Schwazschil cooinates One oiginally elates the Kuskal cooinates to the Schwazschil cooinates in the following way: u = /2m
Notes fo the stana cental, single mass metic in Kuskal cooinates I. Relation to Schwazschil cooinates One oiginally elates the Kuskal cooinates to the Schwazschil cooinates in the following way: u = /2m
A Lattice Energy Calculation for LiH
 A Lattice Enegy Calculation fo LiH Fank Riou Lithium hyie is a white cystalline soli with the face-centee cubic cystal stuctue (see lattice shown below). The moel fo LiH(s) popose in this stuy constists
A Lattice Enegy Calculation fo LiH Fank Riou Lithium hyie is a white cystalline soli with the face-centee cubic cystal stuctue (see lattice shown below). The moel fo LiH(s) popose in this stuy constists
Stability of a Discrete-Time Predator-Prey System with Allee Effect
 Nonlinea Analsis an Diffeential Equations, Vol. 4, 6, no. 5, 5-33 HIKARI Lt, www.m-hikai.com http://.oi.og/.988/nae.6.633 Stabilit of a Discete-Time Peato-Pe Sstem with Allee Effect Ming Zhao an Yunfei
Nonlinea Analsis an Diffeential Equations, Vol. 4, 6, no. 5, 5-33 HIKARI Lt, www.m-hikai.com http://.oi.og/.988/nae.6.633 Stabilit of a Discete-Time Peato-Pe Sstem with Allee Effect Ming Zhao an Yunfei
Rigid Body Dynamics 2. CSE169: Computer Animation Instructor: Steve Rotenberg UCSD, Winter 2018
 Rigid Body Dynamics 2 CSE169: Compute Animation nstucto: Steve Rotenbeg UCSD, Winte 2018 Coss Poduct & Hat Opeato Deivative of a Rotating Vecto Let s say that vecto is otating aound the oigin, maintaining
Rigid Body Dynamics 2 CSE169: Compute Animation nstucto: Steve Rotenbeg UCSD, Winte 2018 Coss Poduct & Hat Opeato Deivative of a Rotating Vecto Let s say that vecto is otating aound the oigin, maintaining
CHAPTER 2 DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE. 2.1 Derivation of Machine Equations
 1 CHAPTER DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE 1 Deivation of Machine Equations A moel of a phase PM machine is shown in Figue 1 Both the abc an the q axes ae shown
1 CHAPTER DERIVATION OF STATE EQUATIONS AND PARAMETER DETERMINATION OF AN IPM MACHINE 1 Deivation of Machine Equations A moel of a phase PM machine is shown in Figue 1 Both the abc an the q axes ae shown
As is natural, our Aerospace Structures will be described in a Euclidean three-dimensional space R 3.
 Appendix A Vecto Algeba As is natual, ou Aeospace Stuctues will be descibed in a Euclidean thee-dimensional space R 3. A.1 Vectos A vecto is used to epesent quantities that have both magnitude and diection.
Appendix A Vecto Algeba As is natual, ou Aeospace Stuctues will be descibed in a Euclidean thee-dimensional space R 3. A.1 Vectos A vecto is used to epesent quantities that have both magnitude and diection.
Supplementary Information for On characterizing protein spatial clusters with correlation approaches
 Supplementay Infomation fo On chaacteizing potein spatial clustes with coelation appoaches A. Shivananan, J. Unnikishnan, A. Raenovic Supplementay Notes Contents Deivation of expessions fo p = a t................................
Supplementay Infomation fo On chaacteizing potein spatial clustes with coelation appoaches A. Shivananan, J. Unnikishnan, A. Raenovic Supplementay Notes Contents Deivation of expessions fo p = a t................................
This lecture. Transformations in 2D. Where are we at? Why do we need transformations?
 Thi lectue Tanfomation in 2D Thoma Sheme Richa (Hao) Zhang Geomet baic Affine pace an affine tanfomation Ue of homogeneou cooinate Concatenation of tanfomation Intouction to Compute Gaphic CMT 36 Lectue
Thi lectue Tanfomation in 2D Thoma Sheme Richa (Hao) Zhang Geomet baic Affine pace an affine tanfomation Ue of homogeneou cooinate Concatenation of tanfomation Intouction to Compute Gaphic CMT 36 Lectue
Acoustic Impedances of Audiometric Earphones Coupled to Different Loads
 Acoustic Impeances of Auiometic Eaphones Couple to Diffeent Loas Dejan Ćiić, Dote Hammeshøi Depatment of Acoustics, Aalbog Univesity, DK-9 Aalbog, Feeik Bajes Vej 7B 5, Denmak, {c, h}@acoustics.aau.k The
Acoustic Impeances of Auiometic Eaphones Couple to Diffeent Loas Dejan Ćiić, Dote Hammeshøi Depatment of Acoustics, Aalbog Univesity, DK-9 Aalbog, Feeik Bajes Vej 7B 5, Denmak, {c, h}@acoustics.aau.k The
INVESTIGATION OF A FREE JET
 M. MEASUREMENT GUIDELINE DEPARTMENT OF FLUID DYNAMICS M INVESTIGATION OF A FREE JET. Aim of the measuement A fee jet efes to a flow which is enteing a stationa fiel though an oifice. The olume flow ate
M. MEASUREMENT GUIDELINE DEPARTMENT OF FLUID DYNAMICS M INVESTIGATION OF A FREE JET. Aim of the measuement A fee jet efes to a flow which is enteing a stationa fiel though an oifice. The olume flow ate
Stress, Cauchy s equation and the Navier-Stokes equations
 Chapte 3 Stess, Cauchy s equation and the Navie-Stokes equations 3. The concept of taction/stess Conside the volume of fluid shown in the left half of Fig. 3.. The volume of fluid is subjected to distibuted
Chapte 3 Stess, Cauchy s equation and the Navie-Stokes equations 3. The concept of taction/stess Conside the volume of fluid shown in the left half of Fig. 3.. The volume of fluid is subjected to distibuted
A THEORETICAL ANALYSIS OF THE ELECTROSTATIC FILTERS
 PUBLISHING HOUS PROCDINGS OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY, Seies A, OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY Volume 5, Numbe /4, pp.- A THORTICAL ANALYSIS OF TH LCTROSTATIC FILTRS Gleb DRAGAN* Romanian Acaem Calea Victoiei 5, 7 Bucaest,
PUBLISHING HOUS PROCDINGS OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY, Seies A, OF TH ROMANIAN ACADMY Volume 5, Numbe /4, pp.- A THORTICAL ANALYSIS OF TH LCTROSTATIC FILTRS Gleb DRAGAN* Romanian Acaem Calea Victoiei 5, 7 Bucaest,
SPH4UI 28/02/2011. Total energy = K + U is constant! Electric Potential Mr. Burns. GMm
 8//11 Electicity has Enegy SPH4I Electic Potential M. Buns To sepaate negative an positive chages fom each othe, wok must be one against the foce of attaction. Theefoe sepeate chages ae in a higheenegy
8//11 Electicity has Enegy SPH4I Electic Potential M. Buns To sepaate negative an positive chages fom each othe, wok must be one against the foce of attaction. Theefoe sepeate chages ae in a higheenegy
TRANSILVANIA UNIVERSITY OF BRASOV MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FACULTY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ONLY FOR STUDENTS
 TNSILVNI UNIVSITY OF BSOV CHNICL NGINING FCULTY DPTNT OF CHNICL NGINING Couse 9 Cuved as 9.. Intoduction The eams with plane o spatial cuved longitudinal axes ae called cuved as. Thee ae consideed two
TNSILVNI UNIVSITY OF BSOV CHNICL NGINING FCULTY DPTNT OF CHNICL NGINING Couse 9 Cuved as 9.. Intoduction The eams with plane o spatial cuved longitudinal axes ae called cuved as. Thee ae consideed two
Solutions to Problems : Chapter 19 Problems appeared on the end of chapter 19 of the Textbook
 Solutions to Poblems Chapte 9 Poblems appeae on the en of chapte 9 of the Textbook 8. Pictue the Poblem Two point chages exet an electostatic foce on each othe. Stategy Solve Coulomb s law (equation 9-5)
Solutions to Poblems Chapte 9 Poblems appeae on the en of chapte 9 of the Textbook 8. Pictue the Poblem Two point chages exet an electostatic foce on each othe. Stategy Solve Coulomb s law (equation 9-5)
MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewart, Sections 12.2, 12.3) INTRO: In MATH 1114 vectors were written either as rows (a1, a2,..., an) or as columns a 1 a. ...
 MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewat, Sections 2.2, 2.3) INTRO: In MATH 4 vectos wee witten eithe as ows (a, a2,..., an) o as columns a a 2... a n and the set of all such vectos of fixed length n was called the vecto
MODULE 5a and 5b (Stewat, Sections 2.2, 2.3) INTRO: In MATH 4 vectos wee witten eithe as ows (a, a2,..., an) o as columns a a 2... a n and the set of all such vectos of fixed length n was called the vecto
Integral Control via Bias Estimation
 1 Integal Contol via Bias stimation Consie the sstem ẋ = A + B +, R n, R p, R m = C +, R q whee is an nknown constant vecto. It is possible to view as a step istbance: (t) = 0 1(t). (If in fact (t) vaies
1 Integal Contol via Bias stimation Consie the sstem ẋ = A + B +, R n, R p, R m = C +, R q whee is an nknown constant vecto. It is possible to view as a step istbance: (t) = 0 1(t). (If in fact (t) vaies
EE 5337 Computational Electromagnetics
 Instucto D. Ramond Rumpf (95) 747 6958 cumpf@utep.edu EE 5337 Computational Electomagnetics Lectue # WEM Etas Lectue These notes ma contain copighted mateial obtained unde fai use ules. Distibution of
Instucto D. Ramond Rumpf (95) 747 6958 cumpf@utep.edu EE 5337 Computational Electomagnetics Lectue # WEM Etas Lectue These notes ma contain copighted mateial obtained unde fai use ules. Distibution of
Formulation of Rigorous Coupled Wave Analysis
 1/8/18 Instucto D. Ramon Rumpf (915) 747 6958 cumpf@utep.eu EE 5337 Computational Electomagnetics Lectue #1 Fomulation of Rigoous Couple Wave Analsis Lectue 1 These notes ma contain copighte mateial obtaine
1/8/18 Instucto D. Ramon Rumpf (915) 747 6958 cumpf@utep.eu EE 5337 Computational Electomagnetics Lectue #1 Fomulation of Rigoous Couple Wave Analsis Lectue 1 These notes ma contain copighte mateial obtaine
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Sensos an ctuatos Intouction to sensos Sane Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Depatment of Electical Engineeing Electonic Systems PITIE SENSORS (hapte 3., 7., 9.,.6, 3., 3.) 3 Senso classification type / quantity
Sensos an ctuatos Intouction to sensos Sane Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Depatment of Electical Engineeing Electonic Systems PITIE SENSORS (hapte 3., 7., 9.,.6, 3., 3.) 3 Senso classification type / quantity
Example
 Chapte.4 iffusion with Chemical eaction Example.4- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ fluiize coal eacto opeates at 45 K an atm. The pocess will be limite by
Chapte.4 iffusion with Chemical eaction Example.4- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ fluiize coal eacto opeates at 45 K an atm. The pocess will be limite by
Simulation of a 2-link Brachiating Robot with Open-Loop Controllers
 Simulation of a -link Bachiating Robot with Open-oop Contolles David Uffod Nothwesten Univesit June 009 . Poject Oveview The goal of this poject was to wite a complete simulation of a -link swinging obot
Simulation of a -link Bachiating Robot with Open-oop Contolles David Uffod Nothwesten Univesit June 009 . Poject Oveview The goal of this poject was to wite a complete simulation of a -link swinging obot
GLE 594: An introduction to applied geophysics
 GLE 594: An intoduction to applied geophsics Electical Resistivit Methods Fall 4 Theo and Measuements Reading: Toda: -3 Net Lectue: 3-5 Two Cuent Electodes: Souce and Sink Wh un an electode to infinit
GLE 594: An intoduction to applied geophsics Electical Resistivit Methods Fall 4 Theo and Measuements Reading: Toda: -3 Net Lectue: 3-5 Two Cuent Electodes: Souce and Sink Wh un an electode to infinit
SEE LAST PAGE FOR SOME POTENTIALLY USEFUL FORMULAE AND CONSTANTS
 Cicle instucto: Moow o Yethiaj Name: MEMORIL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLND DEPRTMENT OF PHYSICS ND PHYSICL OCENOGRPHY Final Eam Phsics 5 Winte 3:-5: pil, INSTRUCTIONS:. Do all SIX (6) questions in section
Cicle instucto: Moow o Yethiaj Name: MEMORIL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLND DEPRTMENT OF PHYSICS ND PHYSICL OCENOGRPHY Final Eam Phsics 5 Winte 3:-5: pil, INSTRUCTIONS:. Do all SIX (6) questions in section
Equilibria of a cylindrical plasma
 // Miscellaneous Execises Cylinical equilibia Equilibia of a cylinical plasma Consie a infinitely long cyline of plasma with a stong axial magnetic fiel (a geat fusion evice) Plasma pessue will cause the
// Miscellaneous Execises Cylinical equilibia Equilibia of a cylinical plasma Consie a infinitely long cyline of plasma with a stong axial magnetic fiel (a geat fusion evice) Plasma pessue will cause the
Conjugate Gradient (CG) Method
 Optimization II Conugate Gaient CG Metho Anothe metho oes not equie explicit secon eivatives, an oes not even stoe appoximation to Hessian matix CG geneates sequence of conugate seach iections, implicitly
Optimization II Conugate Gaient CG Metho Anothe metho oes not equie explicit secon eivatives, an oes not even stoe appoximation to Hessian matix CG geneates sequence of conugate seach iections, implicitly
Equations to Calculate Characteristic Frequencies of Multiple Chamber Aligned in Parallel Cavity Resonator (MCAP-CR)
 MCAPE Equations to Calculate Chaacteistic Fequencies of Multiple Chabe Aligne in Paallel Cavity Resonato (MCAP-CR) Shigeu Suzui Mach, (Revise in ovebe, ). Peface It is necessay to solve the equations of
MCAPE Equations to Calculate Chaacteistic Fequencies of Multiple Chabe Aligne in Paallel Cavity Resonato (MCAP-CR) Shigeu Suzui Mach, (Revise in ovebe, ). Peface It is necessay to solve the equations of
Homework Set 3 Physics 319 Classical Mechanics
 Homewok Set 3 Phsics 319 lassical Mechanics Poblem 5.13 a) To fin the equilibium position (whee thee is no foce) set the eivative of the potential to zeo U 1 R U0 R U 0 at R R b) If R is much smalle than
Homewok Set 3 Phsics 319 lassical Mechanics Poblem 5.13 a) To fin the equilibium position (whee thee is no foce) set the eivative of the potential to zeo U 1 R U0 R U 0 at R R b) If R is much smalle than
Conservation of Linear Momentum using RTT
 07/03/2017 Lectue 21 Consevation of Linea Momentum using RTT Befoe mi-semeste exam, we have seen the 1. Deivation of Reynols Tanspot Theoem (RTT), 2. Application of RTT in the Consevation of Mass pinciple
07/03/2017 Lectue 21 Consevation of Linea Momentum using RTT Befoe mi-semeste exam, we have seen the 1. Deivation of Reynols Tanspot Theoem (RTT), 2. Application of RTT in the Consevation of Mass pinciple
N igerian Journal of M athematics and Applications V olume 24, (2015),
 N igeian Jounal of M athematics an Applications V olume 24, 205), 228 236 c N ig. J. M ath. Appl. http : //www.kwsman.com Flow of an Incompessible MHD Thi Gae Flui Though a Cylinical Pipe with Isothemal
N igeian Jounal of M athematics an Applications V olume 24, 205), 228 236 c N ig. J. M ath. Appl. http : //www.kwsman.com Flow of an Incompessible MHD Thi Gae Flui Though a Cylinical Pipe with Isothemal
Review: Electrostatics and Magnetostatics
 Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
Review: Electostatics and Magnetostatics In the static egime, electomagnetic quantities do not vay as a function of time. We have two main cases: ELECTROSTATICS The electic chages do not change postion
J. N. R E DDY ENERGY PRINCIPLES AND VARIATIONAL METHODS APPLIED MECHANICS
 J. N. E DDY ENEGY PINCIPLES AND VAIATIONAL METHODS IN APPLIED MECHANICS T H I D E DI T IO N JN eddy - 1 MEEN 618: ENEGY AND VAIATIONAL METHODS A EVIEW OF VECTOS AND TENSOS ead: Chapte 2 CONTENTS Physical
J. N. E DDY ENEGY PINCIPLES AND VAIATIONAL METHODS IN APPLIED MECHANICS T H I D E DI T IO N JN eddy - 1 MEEN 618: ENEGY AND VAIATIONAL METHODS A EVIEW OF VECTOS AND TENSOS ead: Chapte 2 CONTENTS Physical
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 303: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves. Fall 2007
 School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
School of Electical and Compute Engineeing, Conell Univesity ECE 303: Electomagnetic Fields and Waves Fall 007 Homewok 8 Due on Oct. 19, 007 by 5:00 PM Reading Assignments: i) Review the lectue notes.
Physics 207 Lecture 5. Lecture 5
 Lectue 5 Goals: Addess sstems with multiple acceleations in 2- dimensions (including linea, pojectile and cicula motion) Discen diffeent efeence fames and undestand how the elate to paticle motion in stationa
Lectue 5 Goals: Addess sstems with multiple acceleations in 2- dimensions (including linea, pojectile and cicula motion) Discen diffeent efeence fames and undestand how the elate to paticle motion in stationa
Physics 122, Fall December 2012
 Physics 1, Fall 01 6 Decembe 01 Toay in Physics 1: Examples in eview By class vote: Poblem -40: offcente chage cylines Poblem 8-39: B along axis of spinning, chage isk Poblem 30-74: selfinuctance of a
Physics 1, Fall 01 6 Decembe 01 Toay in Physics 1: Examples in eview By class vote: Poblem -40: offcente chage cylines Poblem 8-39: B along axis of spinning, chage isk Poblem 30-74: selfinuctance of a
, the tangent line is an approximation of the curve (and easier to deal with than the curve).
 114 Tangent Planes and Linea Appoimations Back in-dimensions, what was the equation of the tangent line of f ( ) at point (, ) f ( )? (, ) ( )( ) = f Linea Appoimation (Tangent Line Appoimation) of f at
114 Tangent Planes and Linea Appoimations Back in-dimensions, what was the equation of the tangent line of f ( ) at point (, ) f ( )? (, ) ( )( ) = f Linea Appoimation (Tangent Line Appoimation) of f at
2. Plane Elasticity Problems
 S0 Solid Mechanics Fall 009. Plane lasticity Poblems Main Refeence: Theoy of lasticity by S.P. Timoshenko and J.N. Goodie McGaw-Hill New Yok. Chaptes 3..1 The plane-stess poblem A thin sheet of an isotopic
S0 Solid Mechanics Fall 009. Plane lasticity Poblems Main Refeence: Theoy of lasticity by S.P. Timoshenko and J.N. Goodie McGaw-Hill New Yok. Chaptes 3..1 The plane-stess poblem A thin sheet of an isotopic
The geometric construction of Ewald sphere and Bragg condition:
 The geometic constuction of Ewald sphee and Bagg condition: The constuction of Ewald sphee must be done such that the Bagg condition is satisfied. This can be done as follows: i) Daw a wave vecto k in
The geometic constuction of Ewald sphee and Bagg condition: The constuction of Ewald sphee must be done such that the Bagg condition is satisfied. This can be done as follows: i) Daw a wave vecto k in
On the Stoney Formula for a Thin Film/Substrate System With Nonuniform Substrate Thickness
 X. Feng Y. Huang Depatment of Mechanical an Inustial Engineeing, Univesity of Illinois, Ubana, IL 61801 A. J. osakis Gauate Aeonautical Laboatoy, Califonia Institute of Technology, Pasaena, CA 9115 On
X. Feng Y. Huang Depatment of Mechanical an Inustial Engineeing, Univesity of Illinois, Ubana, IL 61801 A. J. osakis Gauate Aeonautical Laboatoy, Califonia Institute of Technology, Pasaena, CA 9115 On
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS - THE JACOBIAN DETERMINANT
 COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS - THE JACOBIAN DETERMINANT Link to: phsicspages home page. To leave a comment o epot an eo, please use the auilia blog. Refeence: d Inveno, Ra, Intoducing Einstein s Relativit
COORDINATE TRANSFORMATIONS - THE JACOBIAN DETERMINANT Link to: phsicspages home page. To leave a comment o epot an eo, please use the auilia blog. Refeence: d Inveno, Ra, Intoducing Einstein s Relativit
RADIATION OF ANTENNA ARRAYS WITH GENERALLY ORIENTED DIPOLES
 Jounal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 53, NO. 7-8, 22, 22 27 RADIATION OF ANTENNA ARRAYS WITH GENERALLY ORIENTED DIOLES Štefan Beník ete Hajach The aim of this aticle is to show the possibilities of shaping
Jounal of ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 53, NO. 7-8, 22, 22 27 RADIATION OF ANTENNA ARRAYS WITH GENERALLY ORIENTED DIOLES Štefan Beník ete Hajach The aim of this aticle is to show the possibilities of shaping
Moment. F r F r d. Magnitude of moment depends on magnitude of F and the length d
 Moment Tanslation Tanslation + Rotation This otation tenency is known as moment M of foce (toque) xis of otation may be any line which neithe intesects no paallel to the line of action of foce Magnitue
Moment Tanslation Tanslation + Rotation This otation tenency is known as moment M of foce (toque) xis of otation may be any line which neithe intesects no paallel to the line of action of foce Magnitue
Exact Solution for Electro- Thermo- Mechanical Behavior of Composite Cylinder Reinforced by BNNTs under Non- Axisymmetric Thermo- Mechanical Loads
 mikabi Univesity of Technology (Tehan Polytechnic) Vol, No, Sping 3, pp - mikabi Intenational Jounal of Science & Reseach (Moeling, Ientification, Simulation & Contol) (IJ - MISC) Exact Solution fo Electo-
mikabi Univesity of Technology (Tehan Polytechnic) Vol, No, Sping 3, pp - mikabi Intenational Jounal of Science & Reseach (Moeling, Ientification, Simulation & Contol) (IJ - MISC) Exact Solution fo Electo-
Fluid flow in curved geometries: Mathematical Modeling and Applications
 Fluid flow in cuved geometies: Mathematical Modeling and Applications D. Muhammad Sajid Theoetical Plasma Physics Division PINSTECH, P.O. Niloe, PAEC, Islamabad Mach 01-06, 010 Islamabad, Paistan Pesentation
Fluid flow in cuved geometies: Mathematical Modeling and Applications D. Muhammad Sajid Theoetical Plasma Physics Division PINSTECH, P.O. Niloe, PAEC, Islamabad Mach 01-06, 010 Islamabad, Paistan Pesentation
Transfer Matrix Method
 9/6/17 Instucto D. Ramond Rumpf (915) 747 6958 cumpf@utep.edu 5337 Computational lectomagnetics Lectue #4 Tansfe Mati Method Lectue 4These notes ma contain copighted mateial obtained unde fai use ules.
9/6/17 Instucto D. Ramond Rumpf (915) 747 6958 cumpf@utep.edu 5337 Computational lectomagnetics Lectue #4 Tansfe Mati Method Lectue 4These notes ma contain copighted mateial obtained unde fai use ules.
GRAVITATION. Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., New Delhi -18 PG 1
 Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa Plaza, Vikas Pui Extn., New Delhi -8 Ph. : 96905, 857, E-mail einsteinclasses00@gmail.com, PG GRAVITATION Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa Plaza, Vikas Pui Extn., New Delhi -8 Ph. : 96905, 857, E-mail einsteinclasses00@gmail.com, PG GRAVITATION Einstein Classes, Unit No. 0, 0, Vahman Ring Roa
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS 140AU0402 UNIT 3: BEAMS - LOADS AND STRESSES
 STRENGTH OF MATERALS 140AU040 UNT 3: BEAMS - LOADS AND STRESSES Tpes of beams: Suppots and Loads Shea foce and Bending Moment in beams Cantileve, Simpl suppoted and Ovehanging beams Stesses in beams Theo
STRENGTH OF MATERALS 140AU040 UNT 3: BEAMS - LOADS AND STRESSES Tpes of beams: Suppots and Loads Shea foce and Bending Moment in beams Cantileve, Simpl suppoted and Ovehanging beams Stesses in beams Theo
Hidden Two-Step Phase Transition and Competing
 Suppoting Infomation fo Hien Two-Step Phase Tansition an Competing Reaction Pathways in LiFePO 4 Yukinoi Koyama, Takeshi Uyama, Yuki Oikasa, Takahio Naka, Hieyuki Komatsu, Keiji Shimoa, Hauno Muayama,
Suppoting Infomation fo Hien Two-Step Phase Tansition an Competing Reaction Pathways in LiFePO 4 Yukinoi Koyama, Takeshi Uyama, Yuki Oikasa, Takahio Naka, Hieyuki Komatsu, Keiji Shimoa, Hauno Muayama,
This full text version, available on TeesRep, is the post-print (final version prior to publication) of:
 This full text vesion, available on TeesRep, is the post-pint (final vesion pio to publication) of: Zhang, J., Coultha, J., Cheng, R. an Amstong Bian, (003) 'Theoetical an expeimental stuies of the spatial
This full text vesion, available on TeesRep, is the post-pint (final vesion pio to publication) of: Zhang, J., Coultha, J., Cheng, R. an Amstong Bian, (003) 'Theoetical an expeimental stuies of the spatial
Introduction to Vectors and Frames
 Intoduction to Vectos and Fames CIS - 600.445 Russell Taylo Saah Gaham Infomation Flow Diagam Model the Patient Plan the Pocedue Eecute the Plan Real Wold Coodinate Fame Tansfomation F = [ R, p] 0 F y
Intoduction to Vectos and Fames CIS - 600.445 Russell Taylo Saah Gaham Infomation Flow Diagam Model the Patient Plan the Pocedue Eecute the Plan Real Wold Coodinate Fame Tansfomation F = [ R, p] 0 F y
1.6. Trigonometric Functions. 48 Chapter 1: Preliminaries. Radian Measure
 48 Chapte : Peliminaies.6 Tigonometic Functions Cicle B' B θ C A Unit of cicle adius FIGURE.63 The adian measue of angle ACB is the length u of ac AB on the unit cicle centeed at C. The value of u can
48 Chapte : Peliminaies.6 Tigonometic Functions Cicle B' B θ C A Unit of cicle adius FIGURE.63 The adian measue of angle ACB is the length u of ac AB on the unit cicle centeed at C. The value of u can
BENDING OF BEAM. Compressed layer. Elongated. layer. Un-strained. layer. NA= Neutral Axis. Compression. Unchanged. Elongation. Two Dimensional View
 BNDING OF BA Compessed laye N Compession longation Un-stained laye Unchanged longated laye NA Neutal Axis Two Dimensional View A When a beam is loaded unde pue moment, it can be shown that the beam will
BNDING OF BA Compessed laye N Compession longation Un-stained laye Unchanged longated laye NA Neutal Axis Two Dimensional View A When a beam is loaded unde pue moment, it can be shown that the beam will
transformation Earth V-curve (meridian) λ Conical projection. u,v curves on the datum surface projected as U,V curves on the projection surface
 . CONICAL PROJECTIONS In elementay texts on map pojections, the pojection sufaces ae often descibed as developable sufaces, such as the cylinde (cylindical pojections) and the cone (conical pojections),
. CONICAL PROJECTIONS In elementay texts on map pojections, the pojection sufaces ae often descibed as developable sufaces, such as the cylinde (cylindical pojections) and the cone (conical pojections),
THE NAVIER-STOKES EQUATION: The Queen of Fluid Dynamics. A proof simple, but complete.
 THE NAIER-TOKE EQUATION: The Queen of Fluid Dnamics. A poof simple, but complete. Leonado Rubino leonubino@ahoo.it eptembe 010 Rev. 00 Fo www.via.og Abstact: in this pape ou will find a simple demonstation
THE NAIER-TOKE EQUATION: The Queen of Fluid Dnamics. A poof simple, but complete. Leonado Rubino leonubino@ahoo.it eptembe 010 Rev. 00 Fo www.via.og Abstact: in this pape ou will find a simple demonstation
11) A thin, uniform rod of mass M is supported by two vertical strings, as shown below.
 Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
Fall 2007 Qualifie Pat II 12 minute questions 11) A thin, unifom od of mass M is suppoted by two vetical stings, as shown below. Find the tension in the emaining sting immediately afte one of the stings
16.1 Permanent magnets
 Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
Unit 16 Magnetism 161 Pemanent magnets 16 The magnetic foce on moving chage 163 The motion of chaged paticles in a magnetic field 164 The magnetic foce exeted on a cuent-caying wie 165 Cuent loops and
Supporting Information Wedge Dyakonov Waves and Dyakonov Plasmons in Topological Insulator Bi 2 Se 3 Probed by Electron Beams
 Suppoting Infomation Wedge Dyakonov Waves and Dyakonov Plasmons in Topological Insulato Bi 2 Se 3 Pobed by Electon Beams Nahid Talebi, Cigdem Osoy-Keskinboa, Hadj M. Benia, Klaus Ken, Chistoph T. Koch,
Suppoting Infomation Wedge Dyakonov Waves and Dyakonov Plasmons in Topological Insulato Bi 2 Se 3 Pobed by Electon Beams Nahid Talebi, Cigdem Osoy-Keskinboa, Hadj M. Benia, Klaus Ken, Chistoph T. Koch,
MAE 210B. Homework Solution #6 Winter Quarter, U 2 =r U=r 2 << 1; ) r << U : (1) The boundary conditions written in polar coordinates,
 MAE B Homewok Solution #6 Winte Quate, 7 Poblem a Expecting a elocity change of oe oe a aial istance, the conition necessay fo the ow to be ominate by iscous foces oe inetial foces is O( y ) O( ) = =
MAE B Homewok Solution #6 Winte Quate, 7 Poblem a Expecting a elocity change of oe oe a aial istance, the conition necessay fo the ow to be ominate by iscous foces oe inetial foces is O( y ) O( ) = =
CS-184: Computer Graphics. Today. Lecture #5: 3D Transformations and Rotations. 05-3DTransformations.key - September 21, 2016
 1 CS-184: Compute Gaphics Lectue #5: D Tansfomations and Rotations Pof. James O Bien Univesity of Califonia, Bekeley V016-S-05-1.0 Today Tansfomations in D Rotations Matices Eule angles Eponential maps
1 CS-184: Compute Gaphics Lectue #5: D Tansfomations and Rotations Pof. James O Bien Univesity of Califonia, Bekeley V016-S-05-1.0 Today Tansfomations in D Rotations Matices Eule angles Eponential maps
On the integration of the equations of hydrodynamics
 Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Uebe die Integation de hydodynamischen Gleichungen J f eine u angew Math 56 (859) -0 On the integation of the equations of hydodynamics (By A Clebsch at Calsuhe) Tanslated by D H Delphenich In a pevious
Falls in the realm of a body force. Newton s law of gravitation is:
 GRAVITATION Falls in the ealm of a body foce. Newton s law of avitation is: F GMm = Applies to '' masses M, (between thei centes) and m. is =. diectional distance between the two masses Let ˆ, thus F =
GRAVITATION Falls in the ealm of a body foce. Newton s law of avitation is: F GMm = Applies to '' masses M, (between thei centes) and m. is =. diectional distance between the two masses Let ˆ, thus F =
THE HERMITE POLYNOMIAL & QUANTIZATION OF THE HARMONIC OSCILLATOR
 THE HERMITE POLYNOMIAL & QUANTIZATION OF THE HARMONIC OSCILLATOR TIMOTHY JONES Abstact. The hamonic oscillato possesses a singula place in quantum mechanics. It is use in a wie vaiety of moels. Hee we
THE HERMITE POLYNOMIAL & QUANTIZATION OF THE HARMONIC OSCILLATOR TIMOTHY JONES Abstact. The hamonic oscillato possesses a singula place in quantum mechanics. It is use in a wie vaiety of moels. Hee we
Magnetic nanoparticle traveling in external magnetic field
 Magnetic nanopaticle taveling in etenal magnetic field N. A. Usov and B. Ya. Liubimov Institute of Teestial Magnetism, Ionosphee and Radio Wave Popagation, Russian Academ of Sciences, (IZMIRAN), 49, Toits,
Magnetic nanopaticle taveling in etenal magnetic field N. A. Usov and B. Ya. Liubimov Institute of Teestial Magnetism, Ionosphee and Radio Wave Popagation, Russian Academ of Sciences, (IZMIRAN), 49, Toits,
1) Consider an object of a parabolic shape with rotational symmetry z
 Umeå Univesitet, Fysik 1 Vitaly Bychkov Pov i teknisk fysik, Fluid Mechanics (Stömningsläa), 01-06-01, kl 9.00-15.00 jälpmedel: Students may use any book including the tetbook Lectues on Fluid Dynamics.
Umeå Univesitet, Fysik 1 Vitaly Bychkov Pov i teknisk fysik, Fluid Mechanics (Stömningsläa), 01-06-01, kl 9.00-15.00 jälpmedel: Students may use any book including the tetbook Lectues on Fluid Dynamics.
Physics 2020, Spring 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8. Lab 5. Magnetism
 Physics 2020, Sping 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8 Lab 5. Magnetism PART I: INTRODUCTION TO MAGNETS This week we will begin wok with magnets and the foces that they poduce. By now you ae an expet on setting up
Physics 2020, Sping 2005 Lab 5 page 1 of 8 Lab 5. Magnetism PART I: INTRODUCTION TO MAGNETS This week we will begin wok with magnets and the foces that they poduce. By now you ae an expet on setting up
radians). Figure 2.1 Figure 2.2 (a) quadrant I angle (b) quadrant II angle is in standard position Terminal side Terminal side Terminal side
 . TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS OF GENERAL ANGLES In ode to etend the definitions of the si tigonometic functions to geneal angles, we shall make use of the following ideas: In a Catesian coodinate sstem, an
. TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS OF GENERAL ANGLES In ode to etend the definitions of the si tigonometic functions to geneal angles, we shall make use of the following ideas: In a Catesian coodinate sstem, an
Transformations in Homogeneous Coordinates
 Tansfomations in Homogeneous Coodinates (Com S 4/ Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Aug 4 Complete Section Homogeneous Tansfomations A pojective tansfomation of the pojective plane is a mapping L : P P defined as u a
Tansfomations in Homogeneous Coodinates (Com S 4/ Notes) Yan-Bin Jia Aug 4 Complete Section Homogeneous Tansfomations A pojective tansfomation of the pojective plane is a mapping L : P P defined as u a
P-2: The screw eye is subjected to two forces, ԦF 1 and ԦF 2. Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant force.
 P-1: ԦA=Ԧi +Ԧj -5k and B =Ԧi - 7Ԧj -6k. Detemine;?????? - A B B A A B B A B A B A 7 P-: The scew ee is subjected to two foces, Ԧ 1 and Ԧ. Detemine the magnitude and diection of the esultant foce. P-: The
P-1: ԦA=Ԧi +Ԧj -5k and B =Ԧi - 7Ԧj -6k. Detemine;?????? - A B B A A B B A B A B A 7 P-: The scew ee is subjected to two foces, Ԧ 1 and Ԧ. Detemine the magnitude and diection of the esultant foce. P-: The
3.6 Applied Optimization
 .6 Applied Optimization Section.6 Notes Page In this section we will be looking at wod poblems whee it asks us to maimize o minimize something. Fo all the poblems in this section you will be taking the
.6 Applied Optimization Section.6 Notes Page In this section we will be looking at wod poblems whee it asks us to maimize o minimize something. Fo all the poblems in this section you will be taking the
So, if we are finding the amount of work done over a non-conservative vector field F r, we do that long ur r b ur =
 3.4 Geen s Theoem Geoge Geen: self-taught English scientist, 793-84 So, if we ae finding the amount of wok done ove a non-consevative vecto field F, we do that long u b u 3. method Wok = F d F( () t )
3.4 Geen s Theoem Geoge Geen: self-taught English scientist, 793-84 So, if we ae finding the amount of wok done ove a non-consevative vecto field F, we do that long u b u 3. method Wok = F d F( () t )
Geometry of the homogeneous and isotropic spaces
 Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
Geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces H. Sonoda Septembe 2000; last evised Octobe 2009 Abstact We summaize the aspects of the geomety of the homogeneous and isotopic spaces which ae most elevant
= ρ. Since this equation is applied to an arbitrary point in space, we can use it to determine the charge density once we know the field.
 Gauss s Law In diffeentia fom D = ρ. ince this equation is appied to an abita point in space, we can use it to detemine the chage densit once we know the fied. (We can use this equation to ve fo the fied
Gauss s Law In diffeentia fom D = ρ. ince this equation is appied to an abita point in space, we can use it to detemine the chage densit once we know the fied. (We can use this equation to ve fo the fied
A Contribution to the Voltage Stability Studies within Power Systems: Some Aspects Related to the Load Representation
 Poceeings of the Wol Congess on Engineeing 27 Vol I WCE 27, Jul 2-4, 27, Lonon, U.K. A Contibution to the Voltage Stabilit Stuies within Powe Sstems: Some Aspects Relate to the Loa Repesentation José Gealo
Poceeings of the Wol Congess on Engineeing 27 Vol I WCE 27, Jul 2-4, 27, Lonon, U.K. A Contibution to the Voltage Stabilit Stuies within Powe Sstems: Some Aspects Relate to the Loa Repesentation José Gealo
General Solution of EM Wave Propagation in Anisotropic Media
 Jounal of the Koean Physical Society, Vol. 57, No. 1, July 2010, pp. 55 60 Geneal Solution of EM Wave Popagation in Anisotopic Media Jinyoung Lee Electical and Electonic Engineeing Depatment, Koea Advanced
Jounal of the Koean Physical Society, Vol. 57, No. 1, July 2010, pp. 55 60 Geneal Solution of EM Wave Popagation in Anisotopic Media Jinyoung Lee Electical and Electonic Engineeing Depatment, Koea Advanced
2.3. SLIDING MODE BASED OUTER CONTROL LOOP FOR INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVES WITH FORCED DYNAMICS
 2.3. SLIDING MODE BASED OUTER CONTROL LOOP FOR INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVES WITH FORCED DYNAMICS Abstact: Though the loa toque estimation, the basic FDC base IM ive contol system pesente in the last two sections
2.3. SLIDING MODE BASED OUTER CONTROL LOOP FOR INDUCTION MOTOR DRIVES WITH FORCED DYNAMICS Abstact: Though the loa toque estimation, the basic FDC base IM ive contol system pesente in the last two sections
A method for solving dynamic problems for cylindrical domains
 Tansactions of NAS of Azebaijan, Issue Mechanics, 35 (7), 68-75 (016). Seies of Physical-Technical and Mathematical Sciences. A method fo solving dynamic poblems fo cylindical domains N.B. Rassoulova G.R.
Tansactions of NAS of Azebaijan, Issue Mechanics, 35 (7), 68-75 (016). Seies of Physical-Technical and Mathematical Sciences. A method fo solving dynamic poblems fo cylindical domains N.B. Rassoulova G.R.
