Physics 101: Lecture 27 Thermodynamics
|
|
|
- Pierce Hill
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Final hysics 101: Lecture 27 Thermodynamics Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter Check your grades in grade book!! hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 1
2 0 N=81 Mean=76.5 Number of students Scaled Score hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 2
3 First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Conservation The change in internal energy of a system ( U) is equal to the heat flow into the system (Q) plus the work done on the system (W) U = Q + W Increase in internal energy of system Heat flow into system Work done on system hysics 101: Lecture 27, g
4 Work Done on a System ACT M M The work done on the gas as it contracts is A) ositive B) Zero C) Negative W = work done ON system=- (work done BY system) = - W = -p : true for constant ressure W < 0 if > 0 negative work required to expand system W > 0 if < 0 positive work required to contract system W = 0 if = 0 no work needed to keep system at const hysics 101: Lecture 27, g
5 Thermodynamic Systems and - Diagrams ideal gas law: = nrt for n fixed, and determine state of system T = /nr U = (/2)nRT = (/2) for monatomic gas Examples (ACT): which point has highest T?» B which point has lowest U?» C to change the system from C to B, energy must be added to system A B 1 C hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 5
6 First Law of Thermodynamics Isobaric Example 2 moles of monatomic ideal gas is taken from state 1 to state 2 at constant pressure p=1000 a, where 1 =2m and 2 =m. Find T 1, T 2, U, W, Q. (R=8.1 J/k mole) 1. 1 = nrt 1 T 1 = 1 /nr = 120K = nrt 2 T 2 = 2 /nr = 180K. U = (/2) nr T = 1500 J U = (/2) p = 1500 J (has to be the same). W = -p = J 5. Q = U - W = = 2500 J hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 6
7 First Law of Thermodynamics Isochoric Example 2 moles of monatomic ideal gas is taken from state 1 to state 2 at constant volume =2m, where T 1 =120K and T 2 =180K. Find Q. 1. Q = U - W U = (/2) nr T = 1500 J. W = - = 0 J. Q = U - W = = 1500 J requires less heat to raise T at const. volume than at const. pressure hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 7
8 Homework roblem: Thermo I W tot =?? W = - (<0) W = - = 0 W tot < 0 > 0 = 0 W = - (>0) W = - = 0 < 0 = 0 hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 8
9 ACTs Shown in the picture below are the pressure versus volume graphs for two thermal processes, in each case moving a system from state A to state B along the straight line shown. In which case is the work done on the system the biggest? (atm) (atm) A. Case 1 B. Case 2 B A C. Same correct 2 A Case 1 2 Case 2 B 9 (m ) 9 (m ) Net Work = area under - curve Area the same in both cases! hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 9
10 ACT 2 Shown in the picture below are the pressure versus volume graphs for two thermal processes, in each case moving a system from state A to state B along the straight line shown. In which case is the change in internal energy of the system the biggest? (atm) (atm) A. Case 1 correct B. Case 2 B A C. Same A 2 Case 1 2 Case 2 B 9 (m ) 9 (m ) U = /2 (p f f p i i ) Case 1: U = /2(x9-2x)=5 atm-m Case 2: U = /2(2x9-x)= 9 atm-m hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 10
11 ACT Shown in the picture below are the pressure versus volume graphs for two thermal processes, in each case moving a system from state A to state B along the straight line shown. In which case is the heat added to the system the biggest? A. Case 1 B. Case 2 correct (atm) (atm) C. Same B A 2 A Case 1 2 Case 2 B Q = U - W 9 (m ) 9 (m ) W is same for both U is larger for Case 1 Therefore, Q is larger for Case 1 hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 11
12 First Law Questions Q = U - W Work done on system Heat flow into system Some questions: Increase in internal energy of system Which part of cycle has largest change in internal energy, U? 2 (since U = /2 p) Which part of cycle involves the least work W? 1 (since W = -p ) What is change in internal energy for full cycle? U = 0 for closed cycle (since both p & are back where they started) What is net heat into system for full cycle (positive or negative)? U = 0 Q = -W = area of triangle (>0) 1 hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 12
13 Special Cases Constant ressure (isobaric) W = - (<0) Constant olume W = - = 0 > 0 Constant Temp U = 0 = 0 hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 1
14 reflights 1-1 Consider a hypothetical device that takes 1000 J of heat from a hot reservoir at 00K, ejects 200 J of heat to a cold reservoir at 100K, and produces 800 J of work. Does this device violate the first law of thermodynamics? 1. Yes the change in U=Q+W 2. No correct -W (800) = Q hot (1000) - Q cold (200) Efficiency = -W/Q hot = 800/1000 = 80% 26% 7% 80% efficient 20% efficient 25% efficient 12% 21% 68% 0% 20% 0% 60% 80% 0% 20% 0% 60% 80% hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 1
15 Summary: 1st Law of Thermodynamics: Energy Conservation Q = U - W Work done on system Heat flow into system Increase in internal energy of system point on p- plot completely specifies state of system (p = nrt) work done is area under curve U depends only on T (U = nrt/2 = p/2) for a complete cycle U=0 Q=-W hysics 101: Lecture 27, g 15
PHYS 1101 Practice problem set 6, Chapter 19: 7, 12, 19, 30, 37, 44, 53, 61, 69
 PYS 0 Practice problem set 6, hapter 9: 7,, 9, 0, 7, 44,, 6, 69 9.7. Solve: (a) he heat extracted from the cold reservoir is calculated as follows: (b) he heat exhausted to the hot reservoir is K 4.0 00
PYS 0 Practice problem set 6, hapter 9: 7,, 9, 0, 7, 44,, 6, 69 9.7. Solve: (a) he heat extracted from the cold reservoir is calculated as follows: (b) he heat exhausted to the hot reservoir is K 4.0 00
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II
 Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! (send me your net ID if
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! (send me your net ID if
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II
 Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! Physics 101: Lecture 28,
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! Physics 101: Lecture 28,
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II
 Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! Physics 101: Lecture 28,
Physics 101: Lecture 28 Thermodynamics II Final Today s lecture will cover Textbook Chapter 15.6-15.9 Check Final Exam Room Assignment! Bring ID! Be sure to check your gradebook! Physics 101: Lecture 28,
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Physics 202 Homework 5
 Physics 202 Homework 5 Apr 29, 2013 1. A nuclear-fueled electric power plant utilizes a so-called boiling water reac- 5.8 C tor. In this type of reactor, nuclear energy causes water under pressure to boil
Physics 202 Homework 5 Apr 29, 2013 1. A nuclear-fueled electric power plant utilizes a so-called boiling water reac- 5.8 C tor. In this type of reactor, nuclear energy causes water under pressure to boil
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester
 Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, Physics 121. April 24, Course Information
 Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
Physics 121, April 24. Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics. Physics 121. April 24, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: Heat First law of thermodynamics Second law of thermodynamics
The laws of Thermodynamics. Work in thermodynamic processes
 The laws of Thermodynamics ork in thermodynamic processes The work done on a gas in a cylinder is directly proportional to the force and the displacement. = F y = PA y It can be also expressed in terms
The laws of Thermodynamics ork in thermodynamic processes The work done on a gas in a cylinder is directly proportional to the force and the displacement. = F y = PA y It can be also expressed in terms
Quiz C&J page 365 (top), Check Your Understanding #12: Consider an ob. A) a,b,c,d B) b,c,a,d C) a,c,b,d D) c,b,d,a E) b,a,c,d
 Quiz on Chapter 12 Quiz 10 1. C&J page 365 (top), Check Your Understanding #12: Consider an ob A) a,b,c,d B) b,c,a,d C) a,c,b,d D) c,b,d,a E) b,a,c,d Quiz 10 1. C&J page 365 (top), Check Your Understanding
Quiz on Chapter 12 Quiz 10 1. C&J page 365 (top), Check Your Understanding #12: Consider an ob A) a,b,c,d B) b,c,a,d C) a,c,b,d D) c,b,d,a E) b,a,c,d Quiz 10 1. C&J page 365 (top), Check Your Understanding
PHYsics 1150 Homework, Chapter 14, Thermodynamics Ch 14: 1, 17, 26, 27, 37, 44, 46, 52, 58
 PHYsics 1150 Homework, Chapter 14, Thermodynamics Ch 14: 1, 17, 6, 7, 37, 44, 46, 5, 58 14.1 An ideal gas is sealed in a rigid container at 5 C and. What will its temperature be when the pressure is incresed
PHYsics 1150 Homework, Chapter 14, Thermodynamics Ch 14: 1, 17, 6, 7, 37, 44, 46, 5, 58 14.1 An ideal gas is sealed in a rigid container at 5 C and. What will its temperature be when the pressure is incresed
Physics 150. Thermodynamics. Chapter 15
 Physics 150 Thermodynamics Chapter 15 The First Law of Thermodynamics Let s consider an ideal gas confined in a chamber with a moveable piston If we press the piston è the gas in the chamber compresses
Physics 150 Thermodynamics Chapter 15 The First Law of Thermodynamics Let s consider an ideal gas confined in a chamber with a moveable piston If we press the piston è the gas in the chamber compresses
S = = = nrln = 10.0 mol ln = 35.9
 hy 212: General hysics II 1 hapter 20 orksheet (2 nd Law of hermodynamics & eat Engines) Entropy: 1. A sample of 10.0 moles of a monatomic ideal gas, held at constant temperature (1000), is expanded from
hy 212: General hysics II 1 hapter 20 orksheet (2 nd Law of hermodynamics & eat Engines) Entropy: 1. A sample of 10.0 moles of a monatomic ideal gas, held at constant temperature (1000), is expanded from
Irreversible Processes
 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Phase Changes and Latent Heat
 Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Lecture 5. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 5 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Ch. 19 First Law of Thermodynamics In a thermodynamic process, changes occur in the state of the system. Careful of signs! Q is positive when heat flows into a system. W is
Lecture 5 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Ch. 19 First Law of Thermodynamics In a thermodynamic process, changes occur in the state of the system. Careful of signs! Q is positive when heat flows into a system. W is
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
Physics 111. Thursday, Dec. 9, 3-5pm and 7-9pm. Announcements. Thursday, December 9, 2004
 ics day, ember 9, 2004 Ch 18: diagrams isobaric process isochoric process isothermal process adiabatic process 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Class Reviews/Evaluations For the rest of the semester day,. 9,
ics day, ember 9, 2004 Ch 18: diagrams isobaric process isochoric process isothermal process adiabatic process 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Class Reviews/Evaluations For the rest of the semester day,. 9,
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an extension of the principle of conservation of energy. It includes the transfer of both mechanical and thermal energy. First
Chapter 19 The First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is an extension of the principle of conservation of energy. It includes the transfer of both mechanical and thermal energy. First
Worksheet for Exploration 21.1: Engine Efficiency W Q H U
 Worksheet for Exploration 21.1: Engine Efficiency In this animation, N = nr (i.e., k B = 1). This, then, gives the ideal gas law as PV = NT. Assume an ideal monatomic gas. The efficiency of an engine is
Worksheet for Exploration 21.1: Engine Efficiency In this animation, N = nr (i.e., k B = 1). This, then, gives the ideal gas law as PV = NT. Assume an ideal monatomic gas. The efficiency of an engine is
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws
 Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Survey of Thermodynamic Processes and First and Second Laws Please select only one of the five choices, (a)-(e) for each of the 33 questions. All temperatures T are absolute temperatures. All experiments
Physics 231. Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics. Alex Brown Dec MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
Physics 231 Topic 14: Laws of Thermodynamics Alex Brown Dec 7-11 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 8 th 10 pm correction for 3 rd exam 9 th 10 pm attitude survey (1% for participation) 10 th 10 pm concept
The first law of thermodynamics continued
 Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Irreversible Processes
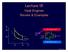 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Irreversible Processes Entropy-increasing
Lecture 13. Heat Engines. Thermodynamic processes and entropy Thermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat
 Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Handout 12: Thermodynamics. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
 1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
1 Handout 12: Thermodynamics Zeroth law of thermodynamics When two objects with different temperature are brought into contact, heat flows from the hotter body to a cooler one Heat flows until the temperatures
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 22. Textbook Sections Lecture 22 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 22 Temperature and Ideal Gas Textbook Sections 14.1 14.3 Lecture 22 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Overview Last Lecture Speed of sound v = sqrt(b/ρ) Intensity level β = (10 db) log
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 22 Temperature and Ideal Gas Textbook Sections 14.1 14.3 Lecture 22 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Overview Last Lecture Speed of sound v = sqrt(b/ρ) Intensity level β = (10 db) log
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers!
 AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
AP PHYSICS 2 WHS-CH-15 Thermodynamics Show all your work, equations used, and box in your answers! Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832) Sadi Carnot was a French military engineer and physicist, often
Lecture 13 Heat Engines
 Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Lecture 3 Heat Engines hermodynamic rocesses and entroy hermodynamic cycles Extracting work from heat - How do we define engine efficiency? - Carnot cycle: the best ossible efficiency Reading for this
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics When we previously studied the first law of thermodynamics, we observed how conservation of energy provided us with a relationship between U, Q, and W, namely
Chapter 20 The Second Law of Thermodynamics When we previously studied the first law of thermodynamics, we observed how conservation of energy provided us with a relationship between U, Q, and W, namely
Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics To examine the directions of thermodynamic processes. To study heat engines. To understand internal combustion engines and refrigerators. To learn and apply
Chapter 16 The Second Law of Thermodynamics To examine the directions of thermodynamic processes. To study heat engines. To understand internal combustion engines and refrigerators. To learn and apply
ΔU = Q W. Tue Dec 1. Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM WALTER 145. Thermodynamics 1st Law. 2 nd Law. Heat Engines and Refrigerators
 Tue Dec 1 Thermodynamics 1st Law ΔU = Q W 2 nd Law SYS Heat Engines and Refrigerators Isobaric: W = PΔV Isochoric: W = 0 Isothermal: ΔU = 0 Adiabatic: Q = 0 Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM
Tue Dec 1 Thermodynamics 1st Law ΔU = Q W 2 nd Law SYS Heat Engines and Refrigerators Isobaric: W = PΔV Isochoric: W = 0 Isothermal: ΔU = 0 Adiabatic: Q = 0 Assign 13/14 Friday Final: Fri Dec 11 2:30PM
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
What is thermodynamics? and what can it do for us?
 What is thermodynamics? and what can it do for us? The overall goal of thermodynamics is to describe what happens to a system (anything of interest) when we change the variables that characterized the
What is thermodynamics? and what can it do for us? The overall goal of thermodynamics is to describe what happens to a system (anything of interest) when we change the variables that characterized the
Chapter 19. Heat Engines
 Chapter 19 Heat Engines Thermo Processes Eint = Q+ W Adiabatic No heat exchanged Q = 0 and E int = W Isobaric Constant pressure W = P (V f V i ) and E int = Q + W Isochoric Constant Volume W = 0 and E
Chapter 19 Heat Engines Thermo Processes Eint = Q+ W Adiabatic No heat exchanged Q = 0 and E int = W Isobaric Constant pressure W = P (V f V i ) and E int = Q + W Isochoric Constant Volume W = 0 and E
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS. Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5
 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Professor Benjamin G. Levine CEM 182H Lecture 5 Chemical Equilibrium N 2 + 3 H 2 2 NH 3 Chemical reactions go in both directions Systems started from any initial state
Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas (2)
 1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
1. This question is about thermodynamic processes. (a) Distinguish between an isothermal process and an adiabatic process as applied to an ideal gas.......... An ideal gas is held in a container by a moveable
Moving Observer and Source. Demo 4C - 02 Doppler. Molecular Picture of Gas PHYSICS 220. Lecture 22. Combine: f o = f s (1-v o /v) / (1-v s /v)
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 22 Temperature and Ideal Gas Moving Observer and Source Combine: f o = f s (1-v o /v) / (1-v s /v) A: You are driving along the highway at 65 mph, and behind you a police car, also
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 22 Temperature and Ideal Gas Moving Observer and Source Combine: f o = f s (1-v o /v) / (1-v s /v) A: You are driving along the highway at 65 mph, and behind you a police car, also
Chemistry 163B Winter 2013 notes for lecture 4
 Chemistry 163B Lecture 4 Winter 013 Challenged enmanship Notes 1 st Law recapitulation U internal energy du = dq + dw + dn sys sys sys sys sys surr du du energy conserved (n=number of moles; dn=0 for closed
Chemistry 163B Lecture 4 Winter 013 Challenged enmanship Notes 1 st Law recapitulation U internal energy du = dq + dw + dn sys sys sys sys sys surr du du energy conserved (n=number of moles; dn=0 for closed
Efficiency of the Carnot Cycle at Maximum Power Output. Introduction. Module 3, Lesson 2
 Module 3, Lesson 2 Efficiency of the Carnot Cycle at Maximum Power Output Objective: Be the end of this lesson you will be able to identify and describe some of the basic thermodynamic processes. To facilitate
Module 3, Lesson 2 Efficiency of the Carnot Cycle at Maximum Power Output Objective: Be the end of this lesson you will be able to identify and describe some of the basic thermodynamic processes. To facilitate
Heat and Thermodynamics. February. 2, Solution of Recitation 2. Consider the first case when air is allowed to expand isothermally.
 Heat and Thermodynamics. February., 0 Solution of Recitation Answer : We have given that, Initial volume of air = = 0.4 m 3 Initial pressure of air = P = 04 kpa = 04 0 3 Pa Final pressure of air = P =
Heat and Thermodynamics. February., 0 Solution of Recitation Answer : We have given that, Initial volume of air = = 0.4 m 3 Initial pressure of air = P = 04 kpa = 04 0 3 Pa Final pressure of air = P =
Physics 121, April 29, The Second Law of Thermodynamics.
 Physics 121, April 29, 2008. The Second Law of Thermodynamics. http://www.horizons.uc.edu/masterjuly1998/oncampus.htm Physics 121. April 29, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: The Second
Physics 121, April 29, 2008. The Second Law of Thermodynamics. http://www.horizons.uc.edu/masterjuly1998/oncampus.htm Physics 121. April 29, 2008. Course Information Topics to be discussed today: The Second
Physics Fall Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids. Lecture 32: Heat and Work II. Slide 32-1
 Physics 1501 Fall 2008 Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids Lecture 32: Heat and Work II Slide 32-1 Recap: the first law of thermodynamics Two ways to raise temperature: Thermally: flow of heat Energy
Physics 1501 Fall 2008 Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids Lecture 32: Heat and Work II Slide 32-1 Recap: the first law of thermodynamics Two ways to raise temperature: Thermally: flow of heat Energy
The First Law of Thermodynamics. Lecture 5
 The First Law of Thermodynamics Lecture 5 First Law of Thermodynamics Overlooks the fine microscopic details (which in many cases are irrelevant). Describes the conversion of one form of energy (heat)
The First Law of Thermodynamics Lecture 5 First Law of Thermodynamics Overlooks the fine microscopic details (which in many cases are irrelevant). Describes the conversion of one form of energy (heat)
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CH. 19 PRACTICE Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When a fixed amount of ideal gas goes through an isobaric expansion, A) its
CH. 19 PRACTICE Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) When a fixed amount of ideal gas goes through an isobaric expansion, A) its
CH 15. Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics
 CH 15 Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics Branch of Physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing
CH 15 Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamics THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics Branch of Physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey. Central Heating Objectives: After finishing
AP PHYSICS B 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP PHYSICS B 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 3 10 points total Distribution of points (a) i. 2 points For correctly ranking all 4 labeled points 1 A 2 B 4 C 3 D Note: one point is earned for a ranking
AP PHYSICS B 2014 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 3 10 points total Distribution of points (a) i. 2 points For correctly ranking all 4 labeled points 1 A 2 B 4 C 3 D Note: one point is earned for a ranking
Results of. Midterm 1. Points < Grade C D,F C B points.
 esults of Midterm 0 0 0 0 40 50 60 70 80 90 points Grade C D,F oints A 80-95 + 70-79 55-69 C + 45-54 0-44
esults of Midterm 0 0 0 0 40 50 60 70 80 90 points Grade C D,F oints A 80-95 + 70-79 55-69 C + 45-54 0-44
Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases Unit Concepts: A) A bit more about temperature B) Ideal Gas Law C) Molar specific heats D) Using them all Unit 05 Kinetic Theory, Slide 1 Temperature and Velocity Recall:
Unit 05 Kinetic Theory of Gases Unit Concepts: A) A bit more about temperature B) Ideal Gas Law C) Molar specific heats D) Using them all Unit 05 Kinetic Theory, Slide 1 Temperature and Velocity Recall:
Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter
 Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter To understand the mole and Avogadro's number. To understand equations of state. To study the kinetic theory of ideal gas. To understand heat capacity. To learn and
Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter To understand the mole and Avogadro's number. To understand equations of state. To study the kinetic theory of ideal gas. To understand heat capacity. To learn and
11/15/2017. F GonP. F PonG THERMAL ENERGY OF IDEAL GAS HIGH PRESSURE GAS IN A CYLINDER REMEMBER HIGH PRESSURE GAS IN A CYLINDER
 UNIT Thermodynamics: Laws of thermodynamics, ideal gases, and kinetic theory A HYSICS THERMAL ENERGY OF IDEAL GAS IDEAL GAS ASSUMTION Ideal gas particles do not interact at a distance; thus the system
UNIT Thermodynamics: Laws of thermodynamics, ideal gases, and kinetic theory A HYSICS THERMAL ENERGY OF IDEAL GAS IDEAL GAS ASSUMTION Ideal gas particles do not interact at a distance; thus the system
T s change via collisions at boundary (not mechanical interaction)
 Lecture 14 Interaction of 2 systems at different temperatures Irreversible processes: 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 19: Heat Engines and Refrigerators Thermal interactions T s change via collisions
Lecture 14 Interaction of 2 systems at different temperatures Irreversible processes: 2nd Law of Thermodynamics Chapter 19: Heat Engines and Refrigerators Thermal interactions T s change via collisions
Chemistry 163B Winter Lectures 2-3. Heat and Work
 Chemistry 163B Winter 2014 Lectures 2-3 Heat and Work Chemistry 163B reserve books 2014 (S&E Library) handout #7 heat capacity (E&R section 2.5) -d q C heat capacity 1 J K dt the amount of heat requires
Chemistry 163B Winter 2014 Lectures 2-3 Heat and Work Chemistry 163B reserve books 2014 (S&E Library) handout #7 heat capacity (E&R section 2.5) -d q C heat capacity 1 J K dt the amount of heat requires
Reading Assignment #13 :Ch.23: (23-3,5,6,7,8), Ch24: (24-1,2,4,5,6) )] = 450J. ) ( 3x10 5 Pa) ( 1x10 3 m 3
![Reading Assignment #13 :Ch.23: (23-3,5,6,7,8), Ch24: (24-1,2,4,5,6) )] = 450J. ) ( 3x10 5 Pa) ( 1x10 3 m 3 Reading Assignment #13 :Ch.23: (23-3,5,6,7,8), Ch24: (24-1,2,4,5,6) )] = 450J. ) ( 3x10 5 Pa) ( 1x10 3 m 3](/thumbs/75/71840722.jpg) Ph70A Spring 004 Prof. Pui Lam SOLUTION Reading Assignment #3 :h.3: (3-3,5,6,7,8), h4: (4-,,4,5,6) Homework #3: First Law and Second of Thermodynamics Due: Monday 5/3/004.. A monatomic ideal gas is allowed
Ph70A Spring 004 Prof. Pui Lam SOLUTION Reading Assignment #3 :h.3: (3-3,5,6,7,8), h4: (4-,,4,5,6) Homework #3: First Law and Second of Thermodynamics Due: Monday 5/3/004.. A monatomic ideal gas is allowed
6) BTW: Your TA has Exam3. It should have been returned to you on Nov 16 (Mon) at Recitation if you
 Chap. 15: pv = nrt Mole and Avogadro s number. Equations of state. Kinetic theory of an ideal gas. Heat capacities. First Law of Thermodynamics. Thermodynamic processes. Properties of an ideal gas. 1 3
Chap. 15: pv = nrt Mole and Avogadro s number. Equations of state. Kinetic theory of an ideal gas. Heat capacities. First Law of Thermodynamics. Thermodynamic processes. Properties of an ideal gas. 1 3
People s Physics book 3e
 The Big Ideas Heat is a form of energy transfer. It can change the kinetic energy of a substance. For example, the average molecular kinetic energy of gas molecules is related to temperature. A heat engine
The Big Ideas Heat is a form of energy transfer. It can change the kinetic energy of a substance. For example, the average molecular kinetic energy of gas molecules is related to temperature. A heat engine
1985B4. A kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100
 1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
1985B4. A 0.020-kilogram sample of a material is initially a solid at a temperature of 20 C. Heat is added to the sample at a constant rate of 100 joules per second until the temperature increases to 60
Review of classical thermodynamics
 Review of classical thermodynamics Fundamental Laws, Properties and Processes (2) Entropy and the Second Law Concepts of equilibrium Reversible and irreversible processes he direction of spontaneous change
Review of classical thermodynamics Fundamental Laws, Properties and Processes (2) Entropy and the Second Law Concepts of equilibrium Reversible and irreversible processes he direction of spontaneous change
, is placed in thermal contact with object B, with mass m, specific heat c B. and initially at temperature T B
 4C_PLC http://www.cabrillo.edu/~jmccullough/physics4c/files/4c_plc/4c_plc.htm Page 1 of 8 /6/201 1. The heat capacity at constant volume and the heat capacity at constant pressure have different values
4C_PLC http://www.cabrillo.edu/~jmccullough/physics4c/files/4c_plc/4c_plc.htm Page 1 of 8 /6/201 1. The heat capacity at constant volume and the heat capacity at constant pressure have different values
Theory (NOTE: This theory is the same that we covered before in Experiment 11on the Ideal Gas model)
 Experiment 12 CHARLES LAW Objectives 1. To set up a model of thermal machine, 2. To put to work the model to verify Charles law, 3. To describe and explain Charles law Theory (NOTE: This theory is the
Experiment 12 CHARLES LAW Objectives 1. To set up a model of thermal machine, 2. To put to work the model to verify Charles law, 3. To describe and explain Charles law Theory (NOTE: This theory is the
PHYSICS 214A Midterm Exam February 10, 2009
 Clearly Print LAS NAME: FIRS NAME: SIGNAURE: I.D. # PHYSICS 2A Midterm Exam February 0, 2009. Do not open the exam until instructed to do so. 2. Write your answers in the spaces provided for each part
Clearly Print LAS NAME: FIRS NAME: SIGNAURE: I.D. # PHYSICS 2A Midterm Exam February 0, 2009. Do not open the exam until instructed to do so. 2. Write your answers in the spaces provided for each part
 第 1 頁, 共 6 頁 Chap20 1. Test Bank, Question 5 Which of the following is NOT a state variable? Work Internal energy Entropy Temperature Pressure 2. Test Bank, Question 18 Let denote the change in entropy
第 1 頁, 共 6 頁 Chap20 1. Test Bank, Question 5 Which of the following is NOT a state variable? Work Internal energy Entropy Temperature Pressure 2. Test Bank, Question 18 Let denote the change in entropy
The need for something else: Entropy
 Lecture 27 Goals: Ch. 18 ualitatively understand 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics Ch. 19 Understand the relationship between work and heat in a cycling process Follow the physics of basic heat engines and refrigerators.
Lecture 27 Goals: Ch. 18 ualitatively understand 2 nd Law of Thermodynamics Ch. 19 Understand the relationship between work and heat in a cycling process Follow the physics of basic heat engines and refrigerators.
Thermodynamics. AP Physics B
 Thermodynamics AP Physics B Important Distinctions Thermodynamics study of processes in which energy is transferred as heat and work. There is a difference between heat and work: Heat is energy transferred
Thermodynamics AP Physics B Important Distinctions Thermodynamics study of processes in which energy is transferred as heat and work. There is a difference between heat and work: Heat is energy transferred
Chapter 14. The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number The atomic number of an element is the # of protons in its nucleus. Isotopes of an element have different
Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number The atomic number of an element is the # of protons in its nucleus. Isotopes of an element have different
The First Law of Thermodynamics and Some Simple Processes
 OpenStax-CNX module: m42233 1 The First Law of Thermodynamics and Some Simple Processes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m42233 1 The First Law of Thermodynamics and Some Simple Processes OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Processes (isobaric, isochoric, isothermal, adiabatic) Reversible and Irreversible Processes Heat Engines Refrigerators and Heat Pumps The Carnot
The First Law of Thermodynamics and Some Simple Processes
 The First Law of Thermodynamics and Some Simple Processes Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Beginning with the Industrial Revolution, humans have harnessed power through the use of the first law of thermodynamics,
The First Law of Thermodynamics and Some Simple Processes Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Beginning with the Industrial Revolution, humans have harnessed power through the use of the first law of thermodynamics,
Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.)
 Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.) Heat and temperature Gases & Kinetic theory http://candidchatter.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/hell.jpg Specific Heat Specific Heat: heat capacity per unit
Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.) Heat and temperature Gases & Kinetic theory http://candidchatter.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/hell.jpg Specific Heat Specific Heat: heat capacity per unit
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Phys102 Term: 103 First Major- July 16, 2011
 Q1. A stretched string has a length of.00 m and a mass of 3.40 g. A transverse sinusoidal wave is travelling on this string, and is given by y (x, t) = 0.030 sin (0.75 x 16 t), where x and y are in meters,
Q1. A stretched string has a length of.00 m and a mass of 3.40 g. A transverse sinusoidal wave is travelling on this string, and is given by y (x, t) = 0.030 sin (0.75 x 16 t), where x and y are in meters,
UNIVESITY OF SWAZILAND FACl.JLTY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
 UNIVESITY OF SWAZILAND FACl.LTY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Main Examination 2016/2017. COURSE NAME: Thermodynamics/Thermofluids COURSE CODE: PHY242/EEE202 TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours ANSWER
UNIVESITY OF SWAZILAND FACl.LTY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Main Examination 2016/2017. COURSE NAME: Thermodynamics/Thermofluids COURSE CODE: PHY242/EEE202 TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours ANSWER
HEAT, WORK, AND THE FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
 HET, ORK, ND THE FIRST L OF THERMODYNMIS 8 EXERISES Section 8. The First Law of Thermodynamics 5. INTERPRET e identify the system as the water in the insulated container. The roblem involves calculating
HET, ORK, ND THE FIRST L OF THERMODYNMIS 8 EXERISES Section 8. The First Law of Thermodynamics 5. INTERPRET e identify the system as the water in the insulated container. The roblem involves calculating
Chapter 17. Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics Topics: Chapter Goal: Conservation of Energy Work in Ideal-Gas Processes
 Chapter 17. Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics This false-color thermal image (an infrared photo) shows where heat energy is escaping from a house. In this chapter we investigate the connection
Chapter 17. Work, Heat, and the First Law of Thermodynamics This false-color thermal image (an infrared photo) shows where heat energy is escaping from a house. In this chapter we investigate the connection
Physics 1301, Exam 4 Review
 c V Andersen, 2006 1 Physics 1301, Exam 4 Review The following is a list of things you should definitely know for the exam, however, the list is not exhaustive. You are responsible for all the material
c V Andersen, 2006 1 Physics 1301, Exam 4 Review The following is a list of things you should definitely know for the exam, however, the list is not exhaustive. You are responsible for all the material
Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
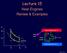 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
CHAPTER - 12 THERMODYNAMICS
 CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
CHAPER - HERMODYNAMICS ONE MARK QUESIONS. What is hermodynamics?. Mention the Macroscopic variables to specify the thermodynamics. 3. How does thermodynamics differ from Mechanics? 4. What is thermodynamic
Classical Physics I. PHY131 Lecture 36 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Lecture 36 1
 Classical Physics I PHY131 Lecture 36 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Lecture 36 1 Recap: (Ir)reversible( Processes Reversible processes are processes that occur under quasi-equilibrium conditions:
Classical Physics I PHY131 Lecture 36 Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics Lecture 36 1 Recap: (Ir)reversible( Processes Reversible processes are processes that occur under quasi-equilibrium conditions:
Understanding KMT using Gas Properties and States of Matter
 Understanding KMT using Gas Properties and States of Matter Learning Goals: Students will be able to describe matter in terms of particle motion. The description should include Diagrams to support the
Understanding KMT using Gas Properties and States of Matter Learning Goals: Students will be able to describe matter in terms of particle motion. The description should include Diagrams to support the
Ch. 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Ch. 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases In this chapter we consider the physics of gases. If the atoms or molecules that make up a gas collide with the walls of their container, they exert a pressure p on
Ch. 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases In this chapter we consider the physics of gases. If the atoms or molecules that make up a gas collide with the walls of their container, they exert a pressure p on
δq T = nr ln(v B/V A )
 hysical Chemistry 007 Homework assignment, solutions roblem 1: An ideal gas undergoes the following reversible, cyclic rocess It first exands isothermally from state A to state B It is then comressed adiabatically
hysical Chemistry 007 Homework assignment, solutions roblem 1: An ideal gas undergoes the following reversible, cyclic rocess It first exands isothermally from state A to state B It is then comressed adiabatically
Thermodynamics: More Entropy
 Thermodynamics: More Entropy From Warmup Yay for only having to read one section! I thought the entropy statement of the second law made a lot more sense than the other two. Just probability. I haven't
Thermodynamics: More Entropy From Warmup Yay for only having to read one section! I thought the entropy statement of the second law made a lot more sense than the other two. Just probability. I haven't
THE ZEROTH AND FISRT LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS. Saeda Al-Mhyawi secend Tearm 1435H
 H ZROH AND FISR LAW OF HRMODYNAMIS Saeda Al-Mhyawi secend earm 435H HAR II H ZROH AND FISR LAW OF HRMODYNAMIS Lecture () Outline Introduction he Zeroth Law of hermodynamics he First Law of hermodynamics
H ZROH AND FISR LAW OF HRMODYNAMIS Saeda Al-Mhyawi secend earm 435H HAR II H ZROH AND FISR LAW OF HRMODYNAMIS Lecture () Outline Introduction he Zeroth Law of hermodynamics he First Law of hermodynamics
Chemistry 163B. Lecture 5 Winter Challenged Penmanship. Notes
 Chemistry 163B Lecture 5 Winter 2014 Challenged enmanship Notes 1 total differential (math handout #4; E&R ch. 3) infinitesimal change in value of state function (well behaved function) total change in
Chemistry 163B Lecture 5 Winter 2014 Challenged enmanship Notes 1 total differential (math handout #4; E&R ch. 3) infinitesimal change in value of state function (well behaved function) total change in
Heat What is heat? Work = 2. PdV 1
 eat What is heat? eat (Q) is the flow or transfer of energy from one system to another Often referred to as heat flow or heat transfer Requires that one system must be at a higher temperature than the
eat What is heat? eat (Q) is the flow or transfer of energy from one system to another Often referred to as heat flow or heat transfer Requires that one system must be at a higher temperature than the
Kinetic Theory continued
 Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Announcements 13 Nov 2014
 Announcements 13 Nov 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 3 starts on Tues Nov 25 a. Covers Ch 9-12, HW 18-24 b. Late fee on Wed after Thanksgiving, 3 pm c. Closes on Thursday after Thanksgiving, 3 pm d. Jerika review
Announcements 13 Nov 2014 1. Prayer 2. Exam 3 starts on Tues Nov 25 a. Covers Ch 9-12, HW 18-24 b. Late fee on Wed after Thanksgiving, 3 pm c. Closes on Thursday after Thanksgiving, 3 pm d. Jerika review
Student Review Packet Answer Key
 Student Review acket Answer Key. Convert the following temperatures as indicated. a 0 o C to K 73 K e atm to ka 0.3 ka (s.f. = 00 b -0 o C to K 63 K f 0.878 atm to ka 88.9 ka c 45 o C to K 38 K g 3. atm
Student Review acket Answer Key. Convert the following temperatures as indicated. a 0 o C to K 73 K e atm to ka 0.3 ka (s.f. = 00 b -0 o C to K 63 K f 0.878 atm to ka 88.9 ka c 45 o C to K 38 K g 3. atm
Physics 2 week 7. Chapter 3 The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 Physics week 7 Chapter 3 The Kinetic Theory of Gases 3.1. Ideal Gases 3.1.1. Experimental Laws and the Equation of State 3.1.. Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3.. Mean Free Path 3.3. The Boltzmann Distribution
Physics week 7 Chapter 3 The Kinetic Theory of Gases 3.1. Ideal Gases 3.1.1. Experimental Laws and the Equation of State 3.1.. Molecular Model of an Ideal Gas 3.. Mean Free Path 3.3. The Boltzmann Distribution
12 The Laws of Thermodynamics
 June 14, 1998 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics Using Thermal Energy to do Work Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to use thermal energy in a practical way. The first law of thermodynamics
June 14, 1998 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics Using Thermal Energy to do Work Understanding the laws of thermodynamics allows us to use thermal energy in a practical way. The first law of thermodynamics
Kinetic Theory continued
 Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory continued 12.4 Kinetic Theory of Gases The particles are in constant, random motion, colliding with each other and with the walls of the container. Each collision changes the
Chapter 12. The Laws of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Chapter 12 The Laws of Thermodynamics First Law of Thermodynamics The First Law of Thermodynamics tells us that the internal energy of a system can be increased by Adding energy to the system Doing work
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines
 Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third
Temperature Thermal Expansion Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory Heat Heat Transfer Phase Changes Specific Heat Calorimetry Heat Engines Zeroeth Law Two systems individually in thermal equilibrium with a third
What is Physical Chemistry?
 Chemistry 313 Dr. Caleb Arrington 10:30 am - 11:20 am M,W,&F Lab: Wednesday 2:00-5:00 Office RMSC 306-A What do we do the first day of every class? syllabus What is Physical Chemistry? Mathematically redictive
Chemistry 313 Dr. Caleb Arrington 10:30 am - 11:20 am M,W,&F Lab: Wednesday 2:00-5:00 Office RMSC 306-A What do we do the first day of every class? syllabus What is Physical Chemistry? Mathematically redictive
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
NY Times 11/25/03 Physics L 22 Frank Sciulli slide 1
 NY Times /5/03 slide Thermodynamics and Gases Last Time specific heats phase transitions Heat and Work st law of thermodynamics heat transfer conduction convection radiation Today Kinetic Theory of Gases
NY Times /5/03 slide Thermodynamics and Gases Last Time specific heats phase transitions Heat and Work st law of thermodynamics heat transfer conduction convection radiation Today Kinetic Theory of Gases
Chemistry 163B Winter 2013 Clausius Inequality and ΔS ideal gas
 Chemistry 163B q rev, Clausius Inequality and calculating ΔS for ideal gas,, changes (HW#5) Challenged enmanship Notes 1 statements of the Second Law of hermodynamics 1. Macroscopic properties of an isolated
Chemistry 163B q rev, Clausius Inequality and calculating ΔS for ideal gas,, changes (HW#5) Challenged enmanship Notes 1 statements of the Second Law of hermodynamics 1. Macroscopic properties of an isolated
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 452/456 Summer Quarter 2011
 Homework Assignment #: Due at 500 pm Wednesday July 6. University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 45/456 Summer Quarter 0 ) he respiratory system uses oxygen to degrade glucose to carbon
Homework Assignment #: Due at 500 pm Wednesday July 6. University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 45/456 Summer Quarter 0 ) he respiratory system uses oxygen to degrade glucose to carbon
Thermodynamics of an Ideal Gas
 Thermodynamics of an Ideal Gas A State Function Does not depend on how the system arrived at its present state; only on the characteristics of the present state. Volume, Pressure, Temperature, ΔE, ΔH State
Thermodynamics of an Ideal Gas A State Function Does not depend on how the system arrived at its present state; only on the characteristics of the present state. Volume, Pressure, Temperature, ΔE, ΔH State
