R a. R b. Figure 4B.1
|
|
|
- Julianna Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4B.1 Lecture 4B Manetc Crcuts The anetc crcut. Manetc and eectrc equvaent crcuts. DC exctaton. AC exctaton. Characterstcs. Deternn F ven φ. Deternn φ ven F (oad ne). Equvaent crcut of a peranent anet. The Manetc Crcut N turns csa A φ v suppy R a R R b ar ap Fure 4B.1 Consder a torod wth a core of ferroanetc atera. A sa ap s ade n the core. We know fro prevous anayss and by deonstraton, that the anetc fed nsde a torod s fary unfor. No anetc fed es outsde the torod. For ths case, the fux path s defned aost exacty. The ferroanetc atera can be consdered a ood "conductor" of fux, just ke a eta wre s a ood conductor of chare. The surroundn ar, because of ts ow pereabty, acts ke an nsuator to the fux, just ke ordnary nsuaton around a eta wre. Snce the fux path s we defned, and snce the anetc fed s assued to be unfor, Apère's Law w reduce to a spe suaton. The anetc fed n a thn torod s unfor An anaoy between anetc and eectrc crcuts
2 4B.2 Inore frnn of the fux n sa ar aps If the ar ap s sa, there w not be uch frnn of the anetc fed, and the cross secton of the ar that the fux passes throuh w be approxatey equa to the core cross secton. Let the cross sectona area of the torod's core be A. The ean enth of the core w be defned as the crcuference of a crce wth a radus the averae of the nner and outer rad of the core: R 2 2 a + R R π b 2 π (4B.1) Apère's Law around the anetc crcut ves: Apère s Law for a thn torod H d Hd N H U N (4B.2) The ntera can be spfed to a suaton, snce the fed H s n the sae drecton as the path. Ths s a drect resut of havn a ferroanetc atera to drect the fux throuh a we defned path. In a cases we w et the subscrpt ean ron (or any ferroanetc atera) and subscrpt ean ap (n ar). Apère's Law wrtten expcty then ves: turns nto a spe suaton N H + H B B + µ µ φ + µ A µ A φ (4B.3) that s anaoous to KVL n eectrc crcuts Ths ooks ke the anetc anao of KVL, taken around a crcut consstn of a DC source and two resstors. We w therefore expot ths anaoy and deveop the concept of reuctance and f.
3 4B.3 Defne reuctance as: R (4B.4) µ A Reuctance defned and anetootve force (f) as: F N (4B.5) Manetootve force (f) defned then Apère's Law ves: F ( R + R ) Rφ φ (4B.6) Apère s Law ooks ke a anetc Oh s Law for ths spe case Ths s anaoous to Oh's aw. It shoud be ephassed that ths s ony true where µ s a constant. That s, t ony appes when the atera s near or assued to be near over a partcuar reon. The nductance of the toroda co s ven by the defnton of nductance: L λ Nφ H N 2 N φ Rφ N R 2 (4B.7) The nductance of a torod usn physca characterstcs Eectroechanca devces have one anetc crcut and at east one eectrc crcut. The anetc atera serves as a coupn devce for power. Such devces ncude the transforer, enerator, otor and eter. Because anetc crcuts contann ferroanetc ateras are nonnear, the reatonshp where µ s a constant. F Rφ s not vad, snce ths was derved for the case Apère's Law, on the other hand, s aways vad, and the concept of anetc potenta w be used where µ s nonnear.
4 4B.4 Gauss Law s the anetc anao of KCL The anetc anao to KVL s Apère's Law. What s the anetc anao to KCL? In spe systes where the fux path s known, the fux entern a pont ust aso eave t. The anao to KCL for anetc crcuts s therefore Gauss' Law. The two aws we w use for anetc crcuts are: Apère s Law and Gauss Law are spe suatons for anetc crcuts F U, φ, around a oop at a node (4B.8a) (4B.8b) Manetc and Eectrc Equvaent Crcuts A eectroanetc systes shoud be reduced to spe anetc and eectrc equvaent crcuts To forase our probe sovn capabtes, we w convert every concevabe eectroanetc devce nto an equvaent anetc crcut and an equvaent eectrc crcut. We can anayse such crcuts usn technques wth whch we are faar. The anetc crcut for the toroda co s: R F φ U U R Fure 4B.2 There are varous ways to anayse the crcut, dependn on whether we know the current or fux, but a ethods nvove Apère's Law around the oop: F U H + U + H (4B.9)
5 4B.5 The eectrc crcut for the toroda co s: R v e L Fure 4B.3 KVL around the oop ves: v R+ e (4B.1) It s noray a dffcut crcut to anayse because of the nonnear nductance (whch ust be taken fro a λ - characterstc). The votae source apped to the co s sad to excte the co, and s known as votae exctaton. Two speca cases of exctaton are of partcuar nterest and practca snfcance DC exctaton and AC exctaton. DC Exctaton DC exctaton refers to the case where a source s apped to the co whch s constant wth respect to te. DC exctaton defned For DC exctaton, n the steady-state, the eectrc crcut s easy to anayse. Faraday s Law for the nductor s: ( L) d d e λ dt dt d L dt (4B.11) where L ay be nonnear. Intay, the crcut w undero a perod of transent behavour, where the current w bud up and raduay convere to a steady-state vaue. The crcut w be n the steady-state when there s no
6 4B.6 ore chane n the current,.e. d dt. Then Faraday s Law ves the votae across the nductor as vots (reardess of whether the nductance s near or not). KVL around the equvaent crcut then ves: V RI (4B.12) where we use a capta etter for I to ndcate a constant, or DC, current. Therefore, there s a drect reatonshp, n the for of Oh s Law, between the apped votae and the resutant steady-state current,.e. the votae source sets the current, so we need to ook up the resutant fux on the nductor s λ ~ characterstc. Ths fux s obvousy constant wth respect to te, snce the current s constant wth respect to te. AC Exctaton AC exctaton defned AC exctaton anaysed wthout consdern the effect of the resstance AC exctaton refers to the case where a source s apped to the co whch s contnuousy chann wth respect to te n ost cases the exctaton s snusoda. For AC exctaton, we spfy the anayss by assun the resstance s nebe. KVL then ves: ( t) v V ˆ cos ω e dλ dt (4B.13) and: t λ edτ Vˆ cos t Vˆ ω ( ωτ ) dτ sn( ωτ ) (4B.14) Therefore, there s a drect reatonshp between the apped votae and the resutant snusoda fux,.e. the votae source sets the fux, so we need to ook up the resutant current on the nductor s λ ~ characterstc. Even thouh the
7 4B.7 fux s snusoda, the resutn current s not snusoda, due to the hysteress characterstc of the ferroanetc atera used to ake the nductor. However, the current s perodc, and t does possess haf-wave syetry. Characterstcs The B-H characterstc can be converted to a φ -U characterstc for a ven atera: φ BA U H (4B.15) For ths partcuar case, there s ony one path that the fux takes, so the fux s the sae throuh each atera (ron and ar). We shoud, for a ven fux, be abe to ook up on each atera's characterstc how uch U there s because of ths fux. The tota U for the anetc crcut for a ven fux s just the addton of the two Us. For each vaue of fux, we can draw the correspondn tota vaue of U. The resut s a coposte characterstc. It s usefu f there s ore than one ferroanetc atera n the crcut. A B-H characterstc can be rescaed to ve a φ -U characterstc How a coposte B-H characterstc takes nto account the propertes of a the ateras n a anetc crcut Fux (Wb) Coposte Characterstc Manetc Potenta (A) Iron Gap Coposte Fure 4B.4
8 4B.8 Deternn F ven φ If we are ven the fux, then the potentas can be obtaned fro a φ -U characterstc. If ven φ, then ook up U Iron Characterstc Fux (Wb) Manetc Potenta (A) Fure 4B.5 For ar aps, we don't need a characterstc, snce t s near. We use: For ar aps, the characterstc s a straht ne, so use the equaton U R φ µ A φ (4B.16) Apère's Law s apped, and we et: F U + U N (4B.17) Gven F, the choce of N and s dctated by other consderatons The nuber of turns and current can be chosen to sut the physca condtons, e.. sa wre (ow current ratn) wth ots of turns or are wre (hh current ratn) wth a few turns.
9 4B.9 Deternn φ ven F (Load Lne) An teratve procedure ay be carred out n ths case. A better way s to use a concept caed the oad ne. (A ap s sad to oad a anetc crcut, snce t Gven φ, the oad ne deternes F has a hh U). Ths concept s used n raphca anayss of nonnear systes. The oad ne, ben near, ust be derved fro a near part of the syste. In a anetc crcut, the ar ap has a near reatonshp between φ and U. Usn Apère's Law, we et: F U 1 φ R + U U ( U F ) + R φ (4B.18) The oad ne equaton for a anetc crcut wth one ap Ths s the equaton of the oad ne. The unknown quanttes are φ and U. Ths equaton ust be satsfed at a tes (Apère's Law s aways obeyed). There are two unknowns and one equaton. How do we sove t? We need another equaton. The other equaton that ust be obeyed at a tes s one whch s ven n the for of a raph the atera s characterstc. It s nonnear.
10 4B.1 The oad ne and the ferroanetc atera s characterstc are both satsfed at the pont of ntersecton To sove the syste of two equatons n two unknowns, we pot the oad ne on the characterstc. Both raphs are satsfed at the pont of ntersecton. We can read off the fux and potenta. Fux (Wb) Iron B -H Characterstc souton oad ne Manetc Potenta (A) Fure 4B.6 If the atera s specfed n ters of a B-H characterstc, then the equaton of the ne becoes: F B H + µ B µ H F (4B.19)
11 4B.11 Equvaent Crcut of a Peranent Manet PM soft ron ar ap Fure 4B.7 In ths case, we know the f t s zero snce there s no apped current. The ethod of fndn the fux n a anetc crcut contann a peranent anet (PM) therefore foows the sae procedure as above. We nore the soft ron A peranent anet (PM) produces fux wthout f (t has nfnte pereabty copared to the ar ap): U + U U + R φ 1 φ R U (4B.2) Apère s Law (oad ne equaton) for a PM To sove for the fux, we need the PM's characterstc. We can see that for a postve fux, the anet exhbts a neatve potenta. Ths akes sense because we have aways assued that the anetc potenta s a drop. A neatve drop s equvaent to a rse a PM s a source of potenta and therefore fux. The oad ne ntersects the B-H hysteress oop (not the nora For a PM, ony one part of the hysteress oop s vad anetzaton characterstc) to ve the operatn pont (or quescent pont, or Q-pont for short).
12 4B.12 φ oad ne Q P φ Q reco pereabty ne -F U Q U anet characterstc Fure 4B.8 The operatn pont of a PM oves aon the reco ne for chanes n oad A PM exhbts hysteress, so when the ap s repaced wth a soft ron keeper, the characterstc s not traced back. The operatn pont oves aon another ne caed the reco pereabty ne (PQ n Fure 4B.8) to P. Subsequent openn and cosn of the ap w cause the operatn pont to ove aon PQ. A ood peranent anet w operate aon PQ aost contnuousy. If the operatn pont aways es between P and Q, then we can use the equaton for ths straht ne n the anayss. Ths s aso equvaent to oden the PM wth near eeents. A near ode of a PM hysteress oop φ sope 1 R Q P - F U Fure 4B.9
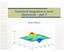
13 4B.13 The PM near ode s therefore: R φ φ A near crcut ode of a PM F U or φ R U Fure 4B.1 The near crcut ode for the PM s ony vad for oad nes that cross the reco ne between P and Q.
14 4B.14 Exape Deterne F ven φ Consder the foown eectroanetc syste: 5 Ia a 4 b c Ic Nc Na 2 1 Fure 4B.11 Gven: The core s anated sheet stee wth a stackn factor.9. φ a 18. Wb, φ b 8. Wb, φ c 1 Wb. I a s n the drecton shown.
15 4B.15 Sheet Stee B -H Characterstc 1.2 Manetc Fux Densty B, T Manetc Fed Intensty H, A/ Fure 4B.12 Draw the anetc equvaent crcut. Show the drectons of φ a, φ b and φ c. Deterne the antude of I a and the antude and drecton of I c.
16 4B.16 Souton: The anetc equvaent crcut s: R a R c F a φ a R b φ b φ c F c Fure 4B.13 As the cross sectona area s unfor, branches a and c are taken rht up to the dde of the centre b. Therefore: a 36., b 1. and.36. c Fro the B-H characterstc, snce B φ A and φ s ven, we just ook up: H a 2 A -1, H b 5 A -1 and H c 75 A -1. Appyn Apère s Law around the eft hand sde (LHS) oop ves: F a U a + Ub H aa + Hbb A Appyn Apère s Law around the rht hand sde (RHS) oop ves: F c Uc Ub A Therefore: I F N.385 A and I F N.22 A ( ). a a a c c c
17 4B.17 Exape Peranent Manet Operatn Pont Consder the foown peranent anet (PM) arraneent: PM soft ron ar ap or soft ron keeper Fure 4B.14 The PM has the foown B-H characterstc: PMs operate wth a neatve H Peranent Manet B -H Characterstc Manetc Fux Densty B, T Q ar ap ne reco ne Manetc Fed Intensty H, ka/ Fure 4B.15
18 4B.18 a) Reove keeper. Deterne ap fux densty B. b) Insert keeper. Deterne resdua fux densty. Inore eakae and frnn fux. Assue µ reco 2µ and µ soft ron. anet, soft ron, ap. Souton: a) As there s no externay apped current, Apère s Law ves: (snce µ ) U + U + U Therefore: U R φ or U The ar ap ne for a PM φ 1 R U (4B.21).e. the equaton of a straht ne (the ar ap ne or oad ne). If the B-H characterstc of the PM s re-scaed to ve a φ -U characterstc, the oad ne (sope 1 R ) ntersects t at the operatn pont Q. Otherwse, as φ BA and U H: rewrtten n a for sutabe for pottn on a B-H characterstc B µ A A H (4B.22) Fro the densons ven (and µ 4π 1 B 7 H -1 ) we et 72π 1 7 H. Therefore, at H A -1, B T. We draw the oad ne throuh ths pont and the orn. At the operatn pont Q, B 112. T. Therefore B A A B 2 B T.
19 4B.19 b) When the keeper s renserted: We draw a ne fro the Q-pont, wth sope 2µ to the B axs. The ntersecton ves the resdua fux densty B. or: The chane n anetc fed ntensty s δh The fux densty chane s δ B 2µ δh 13. T. Therefore resdua B T. Exape Peranent Manet Mnu Voue Consder the PM and characterstc of the prevous exape. The fux n the PM s: B A B A and the potenta across the PM s: H H The voue of the PM can therefore be expressed as: V A A H B HB (4B.23) The voue of a PM can be nsed by carefu choce of the Q-pont whch s a nu f H B s a axu.
20 4B.2 If we pot B- HB for the anet we et: 1.6 Peranent Manet B -H, B -BH Characterstc Manetc Fux Densty B, T Q 1.2 ar ap ne H (eft), ka/ and -HB (rht), kat/ HB ax Fure 4B.16 Fure 4B.16 shows how the pot s constructed fro the PMs B-H characterstc. The pot shows that f we choose a PM wth nu voue (sa cost PMs are expensve) then we shoud choose an operatn pont ven by Q. The prevous exape was therefore a ood desn.
21 4B.21 Suary We defne the reuctance of a anetc atera as: R. µ A Wed defne the anetootve force (f) of a co as: F N. For unfor anetc feds and near anetc atera, Apère's Law s the anetc anao of Oh s Law: F Rφ. The nductance of a toroda co s ven by: 2 N L. R Apère's Law and Gauss Law are the anetc anaos of Krchhoff s Votae Law and Krchhoff s Current Law, respectvey: U F and φ. We can convert every eectroanetc devce nto an equvaent anetc crcut and an equvaent eectrc crcut. For ferroanetc ateras, we use the nonnear B-H characterstc anayse the anetc crcut. A oad ne represents a near reatonshp between crcut quanttes and s usuay raphed on a crcut eeent s characterstc to deterne the operatn pont, or Q-pont. A peranent anet exhbts an nterna neatve anetc potenta and can be used to create fux n a anetc crcut wthout the need for an externa f. The operatn pont of a anetc crcut that uses a peranent anet can be optsed to nse the voue of peranent anetc atera. References Ponus, Martn A.: Apped Eectroanetcs, McGraw H Koakusha, Ltd., Snapore, 1978.
22 4B.22 Probes 1. Consder the foown anetc structure: The nora anetsaton characterstc of the core atera s, H ( A 1 ) ( ) B T Deterne the fux densty n the centre b and the necessary f for a wndn on the centre b: (a) (b) For a fux densty of 1.2 T n each ar ap, For a fux densty of 1.2 T n one ar ap when the other s cosed wth a anetc atera of the sae pereabty as the core atera.
23 4B Consder the anetc structure of Q1. The centre b has a wndn of 5 turns, carryn 1 A. Draw the equvaent anetc crcut and deterne the tota reuctance of the crcut and the fux densty n the RHS ar ap for: (a) (b) Both ar aps open, LHS ar ap cosed. Assue a constant pereabty µ H -1.
24 4B Consder the anetc core and anetzaton characterstc shown. a b c I turns 2 I 2 2 turns The core has a unfor cross sectona area (csa) A , a 88. and b 16.. Co 1 has I 1 5. A (DC). c (a) Deterne the antude and drecton of I 2 needed to ve φ b. (b) Deveop expressons for L 21 and L 12, and cacuate ther vaue for the currents and fuxes deterned n (a).
25 4B Refer to the exape Peranent Manet Operatn Pont. The ar ap fux was assued to be confned wthn the ar ap. Consder now the eakae fux between the upper and ower horzonta sectons of the soft anetc atera, and assue that the eakae fux densty s unfor. (a) (b) Deterne the fux densty n the PM when the keeper s reoved. Copare the ar ap fux densty wth that cacuated n the exape. The eakae fux ay be reduced by pacn the PM coser to the ar ap. Sketch an proved arraneent of the syste.
26 4B The PM asseby shown s to be used as a door hoder (keeper attached to the door, reander attached to the frae). 2 PM 2 soft ron 2 x 5 soft ron keeper 1 2 deased B-H ch H(A ) B (T).4.15 Assue that for soft ron µ. (a) (b) Derve a nearsed anetc equvaent crcut (neect eakae and frnn), and deterne the axu ar ap enth x ax for whch t s vad. The near ode used n (a) assues that the anet w be deanetsed when x > x ax. Show that the eakae reuctance between the upper and ower soft ron peces s ow enouh to prevent deanetsaton fro occurrn.
IX Mechanics of Rigid Bodies: Planar Motion
 X Mechancs of Rd Bodes: Panar Moton Center of Mass of a Rd Bod Rotaton of a Rd Bod About a Fed As Moent of nerta Penduu, A Genera heore Concernn Anuar Moentu puse and Coson nvovn Rd Bodes. Rd bod: dea
X Mechancs of Rd Bodes: Panar Moton Center of Mass of a Rd Bod Rotaton of a Rd Bod About a Fed As Moent of nerta Penduu, A Genera heore Concernn Anuar Moentu puse and Coson nvovn Rd Bodes. Rd bod: dea
Class: Life-Science Subject: Physics
 Class: Lfe-Scence Subject: Physcs Frst year (6 pts): Graphc desgn of an energy exchange A partcle (B) of ass =g oves on an nclned plane of an nclned angle α = 3 relatve to the horzontal. We want to study
Class: Lfe-Scence Subject: Physcs Frst year (6 pts): Graphc desgn of an energy exchange A partcle (B) of ass =g oves on an nclned plane of an nclned angle α = 3 relatve to the horzontal. We want to study
Einstein Summation Convention
 Ensten Suaton Conventon Ths s a ethod to wrte equaton nvovng severa suatons n a uncuttered for Exape:. δ where δ or 0 Suaton runs over to snce we are denson No ndces appear ore than two tes n the equaton
Ensten Suaton Conventon Ths s a ethod to wrte equaton nvovng severa suatons n a uncuttered for Exape:. δ where δ or 0 Suaton runs over to snce we are denson No ndces appear ore than two tes n the equaton
Boundary Value Problems. Lecture Objectives. Ch. 27
 Boundar Vaue Probes Ch. 7 Lecture Obectves o understand the dfference between an nta vaue and boundar vaue ODE o be abe to understand when and how to app the shootng ethod and FD ethod. o understand what
Boundar Vaue Probes Ch. 7 Lecture Obectves o understand the dfference between an nta vaue and boundar vaue ODE o be abe to understand when and how to app the shootng ethod and FD ethod. o understand what
Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Steady-State Power Calculations
 Chapter 0 Snusodal Steady-State Power Calculatons n Chapter 9, we calculated the steady state oltages and currents n electrc crcuts dren by snusodal sources. We used phasor ethod to fnd the steady state
Chapter 0 Snusodal Steady-State Power Calculatons n Chapter 9, we calculated the steady state oltages and currents n electrc crcuts dren by snusodal sources. We used phasor ethod to fnd the steady state
Revision: December 13, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 .9.1: AC power analyss Reson: Deceber 13, 010 15 E Man Sute D Pullan, WA 99163 (509 334 6306 Voce and Fax Oerew n chapter.9.0, we ntroduced soe basc quanttes relate to delery of power usng snusodal sgnals.
.9.1: AC power analyss Reson: Deceber 13, 010 15 E Man Sute D Pullan, WA 99163 (509 334 6306 Voce and Fax Oerew n chapter.9.0, we ntroduced soe basc quanttes relate to delery of power usng snusodal sgnals.
LECTURE 21 Mohr s Method for Calculation of General Displacements. 1 The Reciprocal Theorem
 V. DEMENKO MECHANICS OF MATERIALS 05 LECTURE Mohr s Method for Cacuaton of Genera Dspacements The Recproca Theorem The recproca theorem s one of the genera theorems of strength of materas. It foows drect
V. DEMENKO MECHANICS OF MATERIALS 05 LECTURE Mohr s Method for Cacuaton of Genera Dspacements The Recproca Theorem The recproca theorem s one of the genera theorems of strength of materas. It foows drect
k p theory for bulk semiconductors
 p theory for bu seconductors The attce perodc ndependent partce wave equaton s gven by p + V r + V p + δ H rψ ( r ) = εψ ( r ) (A) 4c In Eq. (A) V ( r ) s the effectve attce perodc potenta caused by the
p theory for bu seconductors The attce perodc ndependent partce wave equaton s gven by p + V r + V p + δ H rψ ( r ) = εψ ( r ) (A) 4c In Eq. (A) V ( r ) s the effectve attce perodc potenta caused by the
Research on Complex Networks Control Based on Fuzzy Integral Sliding Theory
 Advanced Scence and Technoogy Letters Vo.83 (ISA 205), pp.60-65 http://dx.do.org/0.4257/ast.205.83.2 Research on Compex etworks Contro Based on Fuzzy Integra Sdng Theory Dongsheng Yang, Bngqng L, 2, He
Advanced Scence and Technoogy Letters Vo.83 (ISA 205), pp.60-65 http://dx.do.org/0.4257/ast.205.83.2 Research on Compex etworks Contro Based on Fuzzy Integra Sdng Theory Dongsheng Yang, Bngqng L, 2, He
Chapter 6. Rotations and Tensors
 Vector Spaces n Physcs 8/6/5 Chapter 6. Rotatons and ensors here s a speca knd of near transformaton whch s used to transforms coordnates from one set of axes to another set of axes (wth the same orgn).
Vector Spaces n Physcs 8/6/5 Chapter 6. Rotatons and ensors here s a speca knd of near transformaton whch s used to transforms coordnates from one set of axes to another set of axes (wth the same orgn).
where v means the change in velocity, and t is the
 1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 4 MECHANICS (3) Ths lecture covers the eneral case of moton wth constant acceleraton and free fall (whch s one of the more mportant examples of moton wth constant acceleraton) n a more
1 PHYS:100 LECTURE 4 MECHANICS (3) Ths lecture covers the eneral case of moton wth constant acceleraton and free fall (whch s one of the more mportant examples of moton wth constant acceleraton) n a more
Negative Birefraction of Acoustic Waves in a Sonic Crystal
 Negatve Brefracton of Acoustc Waves n a Sonc Crysta Mng-Hu Lu 1, Chao Zhang 1, Lang Feng 1, * Jun Zhao 1, Yan-Feng Chen 1, Y-We Mao 2, Jan Z 3, Yong-Yuan Zhu 1, Sh-Nng Zhu 1 and Na-Ben Mng 1 1 Natona Laboratory
Negatve Brefracton of Acoustc Waves n a Sonc Crysta Mng-Hu Lu 1, Chao Zhang 1, Lang Feng 1, * Jun Zhao 1, Yan-Feng Chen 1, Y-We Mao 2, Jan Z 3, Yong-Yuan Zhu 1, Sh-Nng Zhu 1 and Na-Ben Mng 1 1 Natona Laboratory
EXAMPLES of THEORETICAL PROBLEMS in the COURSE MMV031 HEAT TRANSFER, version 2017
 EXAMPLES of THEORETICAL PROBLEMS n the COURSE MMV03 HEAT TRANSFER, verson 207 a) What s eant by sotropc ateral? b) What s eant by hoogeneous ateral? 2 Defne the theral dffusvty and gve the unts for the
EXAMPLES of THEORETICAL PROBLEMS n the COURSE MMV03 HEAT TRANSFER, verson 207 a) What s eant by sotropc ateral? b) What s eant by hoogeneous ateral? 2 Defne the theral dffusvty and gve the unts for the
Applied Mathematics Letters
 Appled Matheatcs Letters 2 (2) 46 5 Contents lsts avalable at ScenceDrect Appled Matheatcs Letters journal hoepage: wwwelseverco/locate/al Calculaton of coeffcents of a cardnal B-splne Gradr V Mlovanovć
Appled Matheatcs Letters 2 (2) 46 5 Contents lsts avalable at ScenceDrect Appled Matheatcs Letters journal hoepage: wwwelseverco/locate/al Calculaton of coeffcents of a cardnal B-splne Gradr V Mlovanovć
Scattering by a perfectly conducting infinite cylinder
 Scatterng by a perfectly conductng nfnte cylnder Reeber that ths s the full soluton everywhere. We are actually nterested n the scatterng n the far feld lt. We agan use the asyptotc relatonshp exp exp
Scatterng by a perfectly conductng nfnte cylnder Reeber that ths s the full soluton everywhere. We are actually nterested n the scatterng n the far feld lt. We agan use the asyptotc relatonshp exp exp
Physics 4B. Question and 3 tie (clockwise), then 2 and 5 tie (zero), then 4 and 6 tie (counterclockwise) B i. ( T / s) = 1.74 V.
 Physcs 4 Solutons to Chapter 3 HW Chapter 3: Questons:, 4, 1 Problems:, 15, 19, 7, 33, 41, 45, 54, 65 Queston 3-1 and 3 te (clockwse), then and 5 te (zero), then 4 and 6 te (counterclockwse) Queston 3-4
Physcs 4 Solutons to Chapter 3 HW Chapter 3: Questons:, 4, 1 Problems:, 15, 19, 7, 33, 41, 45, 54, 65 Queston 3-1 and 3 te (clockwse), then and 5 te (zero), then 4 and 6 te (counterclockwse) Queston 3-4
Physics 114 Exam 3 Spring Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam 3 Sprng 015 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem 4. Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse
Physcs 114 Exam 3 Sprng 015 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem 4. Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse
On the number of regions in an m-dimensional space cut by n hyperplanes
 6 On the nuber of regons n an -densonal space cut by n hyperplanes Chungwu Ho and Seth Zeran Abstract In ths note we provde a unfor approach for the nuber of bounded regons cut by n hyperplanes n general
6 On the nuber of regons n an -densonal space cut by n hyperplanes Chungwu Ho and Seth Zeran Abstract In ths note we provde a unfor approach for the nuber of bounded regons cut by n hyperplanes n general
Elastic Collisions. Definition: two point masses on which no external forces act collide without losing any energy.
 Elastc Collsons Defnton: to pont asses on hch no external forces act collde thout losng any energy v Prerequstes: θ θ collsons n one denson conservaton of oentu and energy occurs frequently n everyday
Elastc Collsons Defnton: to pont asses on hch no external forces act collde thout losng any energy v Prerequstes: θ θ collsons n one denson conservaton of oentu and energy occurs frequently n everyday
PHYS 1443 Section 002 Lecture #20
 PHYS 1443 Secton 002 Lecture #20 Dr. Jae Condtons for Equlbru & Mechancal Equlbru How to Solve Equlbru Probles? A ew Exaples of Mechancal Equlbru Elastc Propertes of Solds Densty and Specfc Gravty lud
PHYS 1443 Secton 002 Lecture #20 Dr. Jae Condtons for Equlbru & Mechancal Equlbru How to Solve Equlbru Probles? A ew Exaples of Mechancal Equlbru Elastc Propertes of Solds Densty and Specfc Gravty lud
ECE 2C, notes set 7: Basic Transistor Circuits; High-Frequency Response
 class notes, M. odwell, copyrhted 013 EE, notes set 7: Basc Transstor rcuts; Hh-Frequency esponse Mark odwell Unversty of alforna, Santa Barbara rodwell@ece.ucsb.edu 805-893-344, 805-893-36 fax oals class
class notes, M. odwell, copyrhted 013 EE, notes set 7: Basc Transstor rcuts; Hh-Frequency esponse Mark odwell Unversty of alforna, Santa Barbara rodwell@ece.ucsb.edu 805-893-344, 805-893-36 fax oals class
4 Time varying electromagnetic field
 ectrodynamcs and Optcs GFIT5 4 Tme varyng eectromagnetc fed 4.1 ectromagnetc Inducton 4.1.1 Inducton due to moton of conductor onsder the Faraday s experment. The fgure shows a co of wre connected to a
ectrodynamcs and Optcs GFIT5 4 Tme varyng eectromagnetc fed 4.1 ectromagnetc Inducton 4.1.1 Inducton due to moton of conductor onsder the Faraday s experment. The fgure shows a co of wre connected to a
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 28: INDUCTION AND INDUCTANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
Designing Information Devices and Systems II Spring 2018 J. Roychowdhury and M. Maharbiz Discussion 3A
 EECS 16B Desgnng Informaton Devces and Systems II Sprng 018 J. Roychowdhury and M. Maharbz Dscusson 3A 1 Phasors We consder snusodal voltages and currents of a specfc form: where, Voltage vt) = V 0 cosωt
EECS 16B Desgnng Informaton Devces and Systems II Sprng 018 J. Roychowdhury and M. Maharbz Dscusson 3A 1 Phasors We consder snusodal voltages and currents of a specfc form: where, Voltage vt) = V 0 cosωt
INDUCTANCE. RC Cicuits vs LR Circuits
 INDUTANE R cuts vs LR rcuts R rcut hargng (battery s connected): (1/ )q + (R)dq/ dt LR rcut = (R) + (L)d/ dt q = e -t/ R ) = / R(1 - e -(R/ L)t ) q ncreases from 0 to = dq/ dt decreases from / R to 0 Dschargng
INDUTANE R cuts vs LR rcuts R rcut hargng (battery s connected): (1/ )q + (R)dq/ dt LR rcut = (R) + (L)d/ dt q = e -t/ R ) = / R(1 - e -(R/ L)t ) q ncreases from 0 to = dq/ dt decreases from / R to 0 Dschargng
Sections begin this week. Cancelled Sections: Th Labs begin this week. Attend your only second lab slot this week.
 Announcements Sectons begn ths week Cancelled Sectons: Th 122. Labs begn ths week. Attend your only second lab slot ths week. Cancelled labs: ThF 25. Please check your Lab secton. Homework #1 onlne Due
Announcements Sectons begn ths week Cancelled Sectons: Th 122. Labs begn ths week. Attend your only second lab slot ths week. Cancelled labs: ThF 25. Please check your Lab secton. Homework #1 onlne Due
Chapter 32 Inductance
 Chapter 3 nductance 3. Sef-nduction and nductance Sef-nductance Φ BA na --> Φ The unit of the inductance is henry (H). Wb T H A A When the current in the circuit is changing, the agnetic fux is aso changing.
Chapter 3 nductance 3. Sef-nduction and nductance Sef-nductance Φ BA na --> Φ The unit of the inductance is henry (H). Wb T H A A When the current in the circuit is changing, the agnetic fux is aso changing.
Remark: Positive work is done on an object when the point of application of the force moves in the direction of the force.
 Unt 5 Work and Energy 5. Work and knetc energy 5. Work - energy theore 5.3 Potenta energy 5.4 Tota energy 5.5 Energy dagra o a ass-sprng syste 5.6 A genera study o the potenta energy curve 5. Work and
Unt 5 Work and Energy 5. Work and knetc energy 5. Work - energy theore 5.3 Potenta energy 5.4 Tota energy 5.5 Energy dagra o a ass-sprng syste 5.6 A genera study o the potenta energy curve 5. Work and
Fermi-Dirac statistics
 UCC/Physcs/MK/EM/October 8, 205 Fer-Drac statstcs Fer-Drac dstrbuton Matter partcles that are eleentary ostly have a type of angular oentu called spn. hese partcles are known to have a agnetc oent whch
UCC/Physcs/MK/EM/October 8, 205 Fer-Drac statstcs Fer-Drac dstrbuton Matter partcles that are eleentary ostly have a type of angular oentu called spn. hese partcles are known to have a agnetc oent whch
1 Definition of Rademacher Complexity
 COS 511: Theoretcal Machne Learnng Lecturer: Rob Schapre Lecture #9 Scrbe: Josh Chen March 5, 2013 We ve spent the past few classes provng bounds on the generalzaton error of PAClearnng algorths for the
COS 511: Theoretcal Machne Learnng Lecturer: Rob Schapre Lecture #9 Scrbe: Josh Chen March 5, 2013 We ve spent the past few classes provng bounds on the generalzaton error of PAClearnng algorths for the
Inner Product. Euclidean Space. Orthonormal Basis. Orthogonal
 Inner Product Defnton 1 () A Eucldean space s a fnte-dmensonal vector space over the reals R, wth an nner product,. Defnton 2 (Inner Product) An nner product, on a real vector space X s a symmetrc, blnear,
Inner Product Defnton 1 () A Eucldean space s a fnte-dmensonal vector space over the reals R, wth an nner product,. Defnton 2 (Inner Product) An nner product, on a real vector space X s a symmetrc, blnear,
Physics 4B. A positive value is obtained, so the current is counterclockwise around the circuit.
 Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
[WAVES] 1. Waves and wave forces. Definition of waves
![[WAVES] 1. Waves and wave forces. Definition of waves [WAVES] 1. Waves and wave forces. Definition of waves](/thumbs/94/120548750.jpg) 1. Waves and forces Defnton of s In the smuatons on ong-crested s are consdered. The drecton of these s (μ) s defned as sketched beow n the goba co-ordnate sstem: North West East South The eevaton can
1. Waves and forces Defnton of s In the smuatons on ong-crested s are consdered. The drecton of these s (μ) s defned as sketched beow n the goba co-ordnate sstem: North West East South The eevaton can
Our focus will be on linear systems. A system is linear if it obeys the principle of superposition and homogenity, i.e.
 SSTEM MODELLIN In order to solve a control syste proble, the descrptons of the syste and ts coponents ust be put nto a for sutable for analyss and evaluaton. The followng ethods can be used to odel physcal
SSTEM MODELLIN In order to solve a control syste proble, the descrptons of the syste and ts coponents ust be put nto a for sutable for analyss and evaluaton. The followng ethods can be used to odel physcal
Quantum Runge-Lenz Vector and the Hydrogen Atom, the hidden SO(4) symmetry
 Quantum Runge-Lenz ector and the Hydrogen Atom, the hdden SO(4) symmetry Pasca Szrftgser and Edgardo S. Cheb-Terrab () Laboratore PhLAM, UMR CNRS 85, Unversté Le, F-59655, France () Mapesoft Let's consder
Quantum Runge-Lenz ector and the Hydrogen Atom, the hdden SO(4) symmetry Pasca Szrftgser and Edgardo S. Cheb-Terrab () Laboratore PhLAM, UMR CNRS 85, Unversté Le, F-59655, France () Mapesoft Let's consder
Physics 114 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Solutions. Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
PHYSICS - CLUTCH 1E CH 28: INDUCTION AND INDUCTANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
PHY2049 Exam 2 solutions Fall 2016 Solution:
 PHY2049 Exam 2 solutons Fall 2016 General strategy: Fnd two resstors, one par at a tme, that are connected ether n SERIES or n PARALLEL; replace these two resstors wth one of an equvalent resstance. Now
PHY2049 Exam 2 solutons Fall 2016 General strategy: Fnd two resstors, one par at a tme, that are connected ether n SERIES or n PARALLEL; replace these two resstors wth one of an equvalent resstance. Now
Chapter 6: Dynamic Simulation Environment
 Chapter 6: Dnac Suaton Envronent Prevous neatc and dnac anass has deonstrated the snguart-free worspace and the hgh force-bearng characterstcs of the Wrst. Ths chapter copetes the dnac ode of the Carpa
Chapter 6: Dnac Suaton Envronent Prevous neatc and dnac anass has deonstrated the snguart-free worspace and the hgh force-bearng characterstcs of the Wrst. Ths chapter copetes the dnac ode of the Carpa
ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis
 ECE 00 Crcut Analyss Lesson 3 Chapter : AC Power Analyss (nstant & Ae Power; Max Ae Power Transfer; Effecte or RMS alue, Power Factor, Coplex Power, Power Trangle, Power Factor Correcton Danel M. Ltynsk,
ECE 00 Crcut Analyss Lesson 3 Chapter : AC Power Analyss (nstant & Ae Power; Max Ae Power Transfer; Effecte or RMS alue, Power Factor, Coplex Power, Power Trangle, Power Factor Correcton Danel M. Ltynsk,
Advanced Circuits Topics - Part 1 by Dr. Colton (Fall 2017)
 Advanced rcuts Topcs - Part by Dr. olton (Fall 07) Part : Some thngs you should already know from Physcs 0 and 45 These are all thngs that you should have learned n Physcs 0 and/or 45. Ths secton s organzed
Advanced rcuts Topcs - Part by Dr. olton (Fall 07) Part : Some thngs you should already know from Physcs 0 and 45 These are all thngs that you should have learned n Physcs 0 and/or 45. Ths secton s organzed
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis
 ECE 00 Crcut Analyss Lesson 3 Chapter : AC Power Analyss (nstant & Ae Power; Max Ae Power Transfer; Effecte or RMS alue, Power Factor, Coplex Power, Power Trangle, Power Factor Correcton Danel M. Ltynsk,
ECE 00 Crcut Analyss Lesson 3 Chapter : AC Power Analyss (nstant & Ae Power; Max Ae Power Transfer; Effecte or RMS alue, Power Factor, Coplex Power, Power Trangle, Power Factor Correcton Danel M. Ltynsk,
G : Statistical Mechanics
 G25.2651: Statstca Mechancs Notes for Lecture 11 I. PRINCIPLES OF QUANTUM STATISTICAL MECHANICS The probem of quantum statstca mechancs s the quantum mechanca treatment of an N-partce system. Suppose the
G25.2651: Statstca Mechancs Notes for Lecture 11 I. PRINCIPLES OF QUANTUM STATISTICAL MECHANICS The probem of quantum statstca mechancs s the quantum mechanca treatment of an N-partce system. Suppose the
Local operations on labelled dot patterns
 Pattern Reconton Letters 9 (1989) 225 232 May 1989 North-Holland Local operatons on labelled dot patterns Azrel RSENFEL and Jean-Mchel JLN Coputer Vson Laboratory, Center J~r Autoaton Research, Unversty
Pattern Reconton Letters 9 (1989) 225 232 May 1989 North-Holland Local operatons on labelled dot patterns Azrel RSENFEL and Jean-Mchel JLN Coputer Vson Laboratory, Center J~r Autoaton Research, Unversty
Flux-Uncertainty from Aperture Photometry. F. Masci, version 1.0, 10/14/2008
 Flux-Uncertanty from Aperture Photometry F. Masc, verson 1.0, 10/14/008 1. Summary We derve a eneral formula for the nose varance n the flux of a source estmated from aperture photometry. The 1-σ uncertanty
Flux-Uncertanty from Aperture Photometry F. Masc, verson 1.0, 10/14/008 1. Summary We derve a eneral formula for the nose varance n the flux of a source estmated from aperture photometry. The 1-σ uncertanty
Week 9: Multivibrators, MOSFET Amplifiers
 ELE 2110A Electronc Crcuts Week 9: Multbrators, MOSFET Aplfers Lecture 09-1 Multbrators Topcs to coer Snle-stae MOSFET aplfers Coon-source aplfer Coon-dran aplfer Coon-ate aplfer eadn Assnent: Chap 14.1-14.5
ELE 2110A Electronc Crcuts Week 9: Multbrators, MOSFET Aplfers Lecture 09-1 Multbrators Topcs to coer Snle-stae MOSFET aplfers Coon-source aplfer Coon-dran aplfer Coon-ate aplfer eadn Assnent: Chap 14.1-14.5
Page 1. SPH4U: Lecture 7. New Topic: Friction. Today s Agenda. Surface Friction... Surface Friction...
 SPH4U: Lecture 7 Today s Agenda rcton What s t? Systeatc catagores of forces How do we characterze t? Model of frcton Statc & Knetc frcton (knetc = dynac n soe languages) Soe probles nvolvng frcton ew
SPH4U: Lecture 7 Today s Agenda rcton What s t? Systeatc catagores of forces How do we characterze t? Model of frcton Statc & Knetc frcton (knetc = dynac n soe languages) Soe probles nvolvng frcton ew
CHAPTER 10 ROTATIONAL MOTION
 CHAPTER 0 ROTATONAL MOTON 0. ANGULAR VELOCTY Consder argd body rotates about a fxed axs through pont O n x-y plane as shown. Any partcle at pont P n ths rgd body rotates n a crcle of radus r about O. The
CHAPTER 0 ROTATONAL MOTON 0. ANGULAR VELOCTY Consder argd body rotates about a fxed axs through pont O n x-y plane as shown. Any partcle at pont P n ths rgd body rotates n a crcle of radus r about O. The
1.3 Hence, calculate a formula for the force required to break the bond (i.e. the maximum value of F)
 EN40: Dynacs and Vbratons Hoework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Moentu Due Frday March 6 th School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The Rydberg potental s a sple odel of atoc nteractons. It specfes the potental
EN40: Dynacs and Vbratons Hoework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Moentu Due Frday March 6 th School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The Rydberg potental s a sple odel of atoc nteractons. It specfes the potental
Chapter 10 ACSS Power
 Objectives: Power concepts: instantaneous power, average power, reactive power, coplex power, power factor Relationships aong power concepts the power triangle Balancing power in AC circuits Condition
Objectives: Power concepts: instantaneous power, average power, reactive power, coplex power, power factor Relationships aong power concepts the power triangle Balancing power in AC circuits Condition
corresponding to those of Heegaard diagrams by the band moves
 Agebra transformatons of the fundamenta groups correspondng to those of Heegaard dagrams by the band moves By Shun HORIGUCHI Abstract. Ths paper gves the basc resut of [1](1997),.e., a hande sdng and a
Agebra transformatons of the fundamenta groups correspondng to those of Heegaard dagrams by the band moves By Shun HORIGUCHI Abstract. Ths paper gves the basc resut of [1](1997),.e., a hande sdng and a
A finite difference method for heat equation in the unbounded domain
 Internatona Conerence on Advanced ectronc Scence and Technoogy (AST 6) A nte derence method or heat equaton n the unbounded doman a Quan Zheng and Xn Zhao Coege o Scence North Chna nversty o Technoogy
Internatona Conerence on Advanced ectronc Scence and Technoogy (AST 6) A nte derence method or heat equaton n the unbounded doman a Quan Zheng and Xn Zhao Coege o Scence North Chna nversty o Technoogy
Physics 1202: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda
 Physcs 122: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems start ths Thursday Team 1: Hend Ouda, Mke Glnsk, Stephane Auger Team 2: Analese Bruder, Krsten Dean, Alson Smth Offce hours: Monday 2:3-3:3
Physcs 122: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems start ths Thursday Team 1: Hend Ouda, Mke Glnsk, Stephane Auger Team 2: Analese Bruder, Krsten Dean, Alson Smth Offce hours: Monday 2:3-3:3
Lesson 4: Relative motion, Forces, Newton s laws (sections )
 Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons 3.6-4.4) We start wth a projectle problem. A olf ball s ht from the round at 35 m/s at an anle of 55º. The round s leel.. How lon s the ball n the
Lesson 4: Relate moton, Forces, Newton s laws (sectons 3.6-4.4) We start wth a projectle problem. A olf ball s ht from the round at 35 m/s at an anle of 55º. The round s leel.. How lon s the ball n the
Least Squares Fitting of Data
 Least Squares Fttng of Data Davd Eberly Geoetrc Tools, LLC http://www.geoetrctools.co/ Copyrght c 1998-2014. All Rghts Reserved. Created: July 15, 1999 Last Modfed: February 9, 2008 Contents 1 Lnear Fttng
Least Squares Fttng of Data Davd Eberly Geoetrc Tools, LLC http://www.geoetrctools.co/ Copyrght c 1998-2014. All Rghts Reserved. Created: July 15, 1999 Last Modfed: February 9, 2008 Contents 1 Lnear Fttng
total If no external forces act, the total linear momentum of the system is conserved. This occurs in collisions and explosions.
 Lesson 0: Collsons, Rotatonal netc Energy, Torque, Center o Graty (Sectons 7.8 Last te we used ewton s second law to deelop the pulse-oentu theore. In words, the theore states that the change n lnear oentu
Lesson 0: Collsons, Rotatonal netc Energy, Torque, Center o Graty (Sectons 7.8 Last te we used ewton s second law to deelop the pulse-oentu theore. In words, the theore states that the change n lnear oentu
MARKOV CHAIN AND HIDDEN MARKOV MODEL
 MARKOV CHAIN AND HIDDEN MARKOV MODEL JIAN ZHANG JIANZHAN@STAT.PURDUE.EDU Markov chan and hdden Markov mode are probaby the smpest modes whch can be used to mode sequenta data,.e. data sampes whch are not
MARKOV CHAIN AND HIDDEN MARKOV MODEL JIAN ZHANG JIANZHAN@STAT.PURDUE.EDU Markov chan and hdden Markov mode are probaby the smpest modes whch can be used to mode sequenta data,.e. data sampes whch are not
Solutions for Homework #9
 Solutons for Hoewor #9 PROBEM. (P. 3 on page 379 n the note) Consder a sprng ounted rgd bar of total ass and length, to whch an addtonal ass s luped at the rghtost end. he syste has no dapng. Fnd the natural
Solutons for Hoewor #9 PROBEM. (P. 3 on page 379 n the note) Consder a sprng ounted rgd bar of total ass and length, to whch an addtonal ass s luped at the rghtost end. he syste has no dapng. Fnd the natural
Note 2. Ling fong Li. 1 Klein Gordon Equation Probablity interpretation Solutions to Klein-Gordon Equation... 2
 Note 2 Lng fong L Contents Ken Gordon Equaton. Probabty nterpretaton......................................2 Soutons to Ken-Gordon Equaton............................... 2 2 Drac Equaton 3 2. Probabty nterpretaton.....................................
Note 2 Lng fong L Contents Ken Gordon Equaton. Probabty nterpretaton......................................2 Soutons to Ken-Gordon Equaton............................... 2 2 Drac Equaton 3 2. Probabty nterpretaton.....................................
CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS
 CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS We defne a conductor as a materal n whch charges are free to move over macroscopc dstances.e., they can leave ther nucle and move around the materal. An nsulator s anythng else.
CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS We defne a conductor as a materal n whch charges are free to move over macroscopc dstances.e., they can leave ther nucle and move around the materal. An nsulator s anythng else.
Special Relativity and Riemannian Geometry. Department of Mathematical Sciences
 Tutoral Letter 06//018 Specal Relatvty and Reannan Geoetry APM3713 Seester Departent of Matheatcal Scences IMPORTANT INFORMATION: Ths tutoral letter contans the solutons to Assgnent 06. BAR CODE Learn
Tutoral Letter 06//018 Specal Relatvty and Reannan Geoetry APM3713 Seester Departent of Matheatcal Scences IMPORTANT INFORMATION: Ths tutoral letter contans the solutons to Assgnent 06. BAR CODE Learn
Drift Design Method for High-rise Buildings using Dynamic Resizing Algorithm
 ctbuh.org/papers Tte: Authors: Subject: Keywords: Drft Desgn Method for Hgh-rse Budngs usng Dynac Reszng Agorth Hyo Seon Park, Ph.D Canddate, Yonse Unversty Seo J Hyun, Assocate Professor, Yonse Unversty
ctbuh.org/papers Tte: Authors: Subject: Keywords: Drft Desgn Method for Hgh-rse Budngs usng Dynac Reszng Agorth Hyo Seon Park, Ph.D Canddate, Yonse Unversty Seo J Hyun, Assocate Professor, Yonse Unversty
RELUCTANCE The resistance of a material to the flow of charge (current) is determined for electric circuits by the equation
 INTRODUCTION Magnetism pays an integra part in amost every eectrica device used today in industry, research, or the home. Generators, motors, transformers, circuit breakers, teevisions, computers, tape
INTRODUCTION Magnetism pays an integra part in amost every eectrica device used today in industry, research, or the home. Generators, motors, transformers, circuit breakers, teevisions, computers, tape
Phase Diagrams. Chapter 8. Conditions for the Coexistence of Multiple Phases. d S dt V
 hase Diaras Chapter 8 hase - a for of atter that is unifor with respect to cheica coposition and the physica state of areation (soid, iquid, or aseous phases) icroscopicay and acroscopicay. Conditions
hase Diaras Chapter 8 hase - a for of atter that is unifor with respect to cheica coposition and the physica state of areation (soid, iquid, or aseous phases) icroscopicay and acroscopicay. Conditions
Xiangwen Li. March 8th and March 13th, 2001
 CS49I Approxaton Algorths The Vertex-Cover Proble Lecture Notes Xangwen L March 8th and March 3th, 00 Absolute Approxaton Gven an optzaton proble P, an algorth A s an approxaton algorth for P f, for an
CS49I Approxaton Algorths The Vertex-Cover Proble Lecture Notes Xangwen L March 8th and March 3th, 00 Absolute Approxaton Gven an optzaton proble P, an algorth A s an approxaton algorth for P f, for an
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Winter 16 Midterm, February 5
 Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Wnter 16 Mdterm, February 5 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Wnter 16 Mdterm, February 5 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Least Squares Fitting of Data
 Least Squares Fttng of Data Davd Eberly Geoetrc Tools, LLC http://www.geoetrctools.co/ Copyrght c 1998-2015. All Rghts Reserved. Created: July 15, 1999 Last Modfed: January 5, 2015 Contents 1 Lnear Fttng
Least Squares Fttng of Data Davd Eberly Geoetrc Tools, LLC http://www.geoetrctools.co/ Copyrght c 1998-2015. All Rghts Reserved. Created: July 15, 1999 Last Modfed: January 5, 2015 Contents 1 Lnear Fttng
APPENDIX A Some Linear Algebra
 APPENDIX A Some Lnear Algebra The collecton of m, n matrces A.1 Matrces a 1,1,..., a 1,n A = a m,1,..., a m,n wth real elements a,j s denoted by R m,n. If n = 1 then A s called a column vector. Smlarly,
APPENDIX A Some Lnear Algebra The collecton of m, n matrces A.1 Matrces a 1,1,..., a 1,n A = a m,1,..., a m,n wth real elements a,j s denoted by R m,n. If n = 1 then A s called a column vector. Smlarly,
Computer-Aided Circuit Simulation and Verification. CSE245 Fall 2004 Professor:Chung-Kuan Cheng
 Computer-Aded Crcut Smulaton and Verfcaton CSE245 Fall 24 Professor:Chung-Kuan Cheng Admnstraton Lectures: 5:pm ~ 6:2pm TTH HSS 252 Offce Hours: 4:pm ~ 4:45pm TTH APM 4256 Textbook Electronc Crcut and
Computer-Aded Crcut Smulaton and Verfcaton CSE245 Fall 24 Professor:Chung-Kuan Cheng Admnstraton Lectures: 5:pm ~ 6:2pm TTH HSS 252 Offce Hours: 4:pm ~ 4:45pm TTH APM 4256 Textbook Electronc Crcut and
Electrical Circuits 2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER
 CHAPTE Electrcal Crcuts. INTODUCTION In ths chapter, we brefly revew the three types of basc passve electrcal elements: resstor, nductor and capactor. esstance Elements: Ohm s Law: The voltage drop across
CHAPTE Electrcal Crcuts. INTODUCTION In ths chapter, we brefly revew the three types of basc passve electrcal elements: resstor, nductor and capactor. esstance Elements: Ohm s Law: The voltage drop across
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Orbital Angular Momentum
 Obta Anua Moentu In cassca echancs consevaton o anua oentu s soetes teated b an eectve epusve potenta Soon we w sove the 3D Sch. Eqn. The R equaton w have an anua oentu te whch ases o the Theta equaton
Obta Anua Moentu In cassca echancs consevaton o anua oentu s soetes teated b an eectve epusve potenta Soon we w sove the 3D Sch. Eqn. The R equaton w have an anua oentu te whch ases o the Theta equaton
COXREG. Estimation (1)
 COXREG Cox (972) frst suggested the modes n whch factors reated to fetme have a mutpcatve effect on the hazard functon. These modes are caed proportona hazards (PH) modes. Under the proportona hazards
COXREG Cox (972) frst suggested the modes n whch factors reated to fetme have a mutpcatve effect on the hazard functon. These modes are caed proportona hazards (PH) modes. Under the proportona hazards
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Fall 13 Midterm, October 31
 Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Fall 13 Mdterm, October 31 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Instructons ME140 - Lnear Crcuts - Fall 13 Mdterm, October 31 () Ths exam s open book. You may use whatever wrtten materals you choose, ncludng your class notes and textbook. You may use a hand calculator
Numerical integration in more dimensions part 2. Remo Minero
 Numerca ntegraton n more dmensons part Remo Mnero Outne The roe of a mappng functon n mutdmensona ntegraton Gauss approach n more dmensons and quadrature rues Crtca anass of acceptabt of a gven quadrature
Numerca ntegraton n more dmensons part Remo Mnero Outne The roe of a mappng functon n mutdmensona ntegraton Gauss approach n more dmensons and quadrature rues Crtca anass of acceptabt of a gven quadrature
System in Weibull Distribution
 Internatonal Matheatcal Foru 4 9 no. 9 94-95 Relablty Equvalence Factors of a Seres-Parallel Syste n Webull Dstrbuton M. A. El-Dacese Matheatcs Departent Faculty of Scence Tanta Unversty Tanta Egypt eldacese@yahoo.co
Internatonal Matheatcal Foru 4 9 no. 9 94-95 Relablty Equvalence Factors of a Seres-Parallel Syste n Webull Dstrbuton M. A. El-Dacese Matheatcs Departent Faculty of Scence Tanta Unversty Tanta Egypt eldacese@yahoo.co
ES 330 Electronics II Homework 04 (Fall 2017 Due Wednesday, September 27, 2017)
 Pae1 Nae Solutons ES 330 Electroncs II Hoework 04 (Fall 2017 Due Wednesday, Septeer 27, 2017) Prole 1 onsder the FET aplfer of F. 7.10 for the case of t =0.4, kn = 5 A/ 2, GS =0.6, DD = 1.8 and RD = 10
Pae1 Nae Solutons ES 330 Electroncs II Hoework 04 (Fall 2017 Due Wednesday, Septeer 27, 2017) Prole 1 onsder the FET aplfer of F. 7.10 for the case of t =0.4, kn = 5 A/ 2, GS =0.6, DD = 1.8 and RD = 10
MATH 5630: Discrete Time-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March 1, 2018
 MATH 5630: Dscrete Tme-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March, 08 Newton s Law of Coolng Consder the coolng of a well strred coffee so that the temperature does not depend on space Newton s law of collng
MATH 5630: Dscrete Tme-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March, 08 Newton s Law of Coolng Consder the coolng of a well strred coffee so that the temperature does not depend on space Newton s law of collng
ON AUTOMATIC CONTINUITY OF DERIVATIONS FOR BANACH ALGEBRAS WITH INVOLUTION
 European Journa of Mathematcs and Computer Scence Vo. No. 1, 2017 ON AUTOMATC CONTNUTY OF DERVATONS FOR BANACH ALGEBRAS WTH NVOLUTON Mohamed BELAM & Youssef T DL MATC Laboratory Hassan Unversty MORO CCO
European Journa of Mathematcs and Computer Scence Vo. No. 1, 2017 ON AUTOMATC CONTNUTY OF DERVATONS FOR BANACH ALGEBRAS WTH NVOLUTON Mohamed BELAM & Youssef T DL MATC Laboratory Hassan Unversty MORO CCO
Quantum Particle Motion in Physical Space
 Adv. Studes Theor. Phys., Vol. 8, 014, no. 1, 7-34 HIKARI Ltd, www.-hkar.co http://dx.do.org/10.1988/astp.014.311136 Quantu Partcle Moton n Physcal Space A. Yu. Saarn Dept. of Physcs, Saara State Techncal
Adv. Studes Theor. Phys., Vol. 8, 014, no. 1, 7-34 HIKARI Ltd, www.-hkar.co http://dx.do.org/10.1988/astp.014.311136 Quantu Partcle Moton n Physcal Space A. Yu. Saarn Dept. of Physcs, Saara State Techncal
Chapter 6 Electrical Systems and Electromechanical Systems
 ME 43 Systems Dynamcs & Control Chapter 6: Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems Chapter 6 Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems 6. INTODUCTION A. Bazoune The majorty of engneerng systems
ME 43 Systems Dynamcs & Control Chapter 6: Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems Chapter 6 Electrcal Systems and Electromechancal Systems 6. INTODUCTION A. Bazoune The majorty of engneerng systems
Coupling Element and Coupled circuits. Coupled inductor Ideal transformer Controlled sources
 Couplng Element and Coupled crcuts Coupled nductor Ideal transformer Controlled sources Couplng Element and Coupled crcuts Coupled elements hae more that one branch and branch oltages or branch currents
Couplng Element and Coupled crcuts Coupled nductor Ideal transformer Controlled sources Couplng Element and Coupled crcuts Coupled elements hae more that one branch and branch oltages or branch currents
D hh ν. Four-body charm semileptonic decay. Jim Wiss University of Illinois
 Four-body charm semeptonc decay Jm Wss Unversty of Inos D hh ν 1 1. ector domnance. Expected decay ntensty 3. SU(3) apped to D s φν 4. Anaytc forms for form factors 5. Non-parametrc form factors 6. Future
Four-body charm semeptonc decay Jm Wss Unversty of Inos D hh ν 1 1. ector domnance. Expected decay ntensty 3. SU(3) apped to D s φν 4. Anaytc forms for form factors 5. Non-parametrc form factors 6. Future
Glued-in rod connections in bending: experiment and stochastic finite-element modelling
 ued-n rod connectons n bendng: experent and stochastc fnte-eeent odeng J. BAROTH, L. BODÉ, Ph. BRESSOLETTE, E. FOURNELY, P. RACHER Cv Engneerng Laboratory, C/U/S/T/ - Base Pasca Unversty, Ceront-Ferrand
ued-n rod connectons n bendng: experent and stochastc fnte-eeent odeng J. BAROTH, L. BODÉ, Ph. BRESSOLETTE, E. FOURNELY, P. RACHER Cv Engneerng Laboratory, C/U/S/T/ - Base Pasca Unversty, Ceront-Ferrand
Formulation of Circuit Equations
 ECE 570 Sesson 2 IC 752E Computer Aded Engneerng for Integrated Crcuts Formulaton of Crcut Equatons Bascs of crcut modelng 1. Notaton 2. Crcut elements 3. Krchoff laws 4. ableau formulaton 5. Modfed nodal
ECE 570 Sesson 2 IC 752E Computer Aded Engneerng for Integrated Crcuts Formulaton of Crcut Equatons Bascs of crcut modelng 1. Notaton 2. Crcut elements 3. Krchoff laws 4. ableau formulaton 5. Modfed nodal
Excess Error, Approximation Error, and Estimation Error
 E0 370 Statstcal Learnng Theory Lecture 10 Sep 15, 011 Excess Error, Approxaton Error, and Estaton Error Lecturer: Shvan Agarwal Scrbe: Shvan Agarwal 1 Introducton So far, we have consdered the fnte saple
E0 370 Statstcal Learnng Theory Lecture 10 Sep 15, 011 Excess Error, Approxaton Error, and Estaton Error Lecturer: Shvan Agarwal Scrbe: Shvan Agarwal 1 Introducton So far, we have consdered the fnte saple
ADIABATIC CAPILLARY TUBE FLOW IN A TRANSCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE HEAT PUMP
 ADIABATIC CAPILLARY TUBE FLOW IN A TRANSCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE HEAT PUMP Neeraj Arawa, Souvk Bhattacharyya Department of Mechanca Enneern Indan Insttute of Technooy Kharapur, Inda 730 ABSTRACT An adabatc
ADIABATIC CAPILLARY TUBE FLOW IN A TRANSCRITICAL CARBON DIOXIDE HEAT PUMP Neeraj Arawa, Souvk Bhattacharyya Department of Mechanca Enneern Indan Insttute of Technooy Kharapur, Inda 730 ABSTRACT An adabatc
Solutions to Practice Problems
 Phys A Solutons to Practce Probles hapter Inucton an Maxwell s uatons (a) At t s, the ef has a agntue of t ag t Wb s t Wb s Wb s t Wb s V t 5 (a) Table - gves the resstvty of copper Thus, L A 8 9 5 (b)
Phys A Solutons to Practce Probles hapter Inucton an Maxwell s uatons (a) At t s, the ef has a agntue of t ag t Wb s t Wb s Wb s t Wb s V t 5 (a) Table - gves the resstvty of copper Thus, L A 8 9 5 (b)
Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 121 Lecture 10 - Sources of Magnetic Fields (Currents) Y&F Chapter 28, Sec. 1-7
 Electrcty and Magnetsm - Physcs 11 Lecture 10 - Sources of Magnetc Felds (Currents) Y&F Chapter 8, Sec. 1-7 Magnetc felds are due to currents The Bot-Savart Law Calculatng feld at the centers of current
Electrcty and Magnetsm - Physcs 11 Lecture 10 - Sources of Magnetc Felds (Currents) Y&F Chapter 8, Sec. 1-7 Magnetc felds are due to currents The Bot-Savart Law Calculatng feld at the centers of current
Module 1 : The equation of continuity. Lecture 1: Equation of Continuity
 1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
ˆ (0.10 m) E ( N m /C ) 36 ˆj ( j C m)
 7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
Electrical Circuits II (ECE233b)
 Electrcal Crcuts (ECE33b SteadyState Power Analyss Anests Dounas The Unersty of Western Ontaro Faculty of Engneerng Scence SteadyState Power Analyss (t AC crcut: The steady state oltage and current can
Electrcal Crcuts (ECE33b SteadyState Power Analyss Anests Dounas The Unersty of Western Ontaro Faculty of Engneerng Scence SteadyState Power Analyss (t AC crcut: The steady state oltage and current can
Final Exam Solutions, 1998
 58.439 Fnal Exa Solutons, 1998 roble 1 art a: Equlbru eans that the therodynac potental of a consttuent s the sae everywhere n a syste. An exaple s the Nernst potental. If the potental across a ebrane
58.439 Fnal Exa Solutons, 1998 roble 1 art a: Equlbru eans that the therodynac potental of a consttuent s the sae everywhere n a syste. An exaple s the Nernst potental. If the potental across a ebrane
Computational and Statistical Learning theory Assignment 4
 Coputatonal and Statstcal Learnng theory Assgnent 4 Due: March 2nd Eal solutons to : karthk at ttc dot edu Notatons/Defntons Recall the defnton of saple based Radeacher coplexty : [ ] R S F) := E ɛ {±}
Coputatonal and Statstcal Learnng theory Assgnent 4 Due: March 2nd Eal solutons to : karthk at ttc dot edu Notatons/Defntons Recall the defnton of saple based Radeacher coplexty : [ ] R S F) := E ɛ {±}
On Pfaff s solution of the Pfaff problem
 Zur Pfaff scen Lösung des Pfaff scen Probles Mat. Ann. 7 (880) 53-530. On Pfaff s soluton of te Pfaff proble By A. MAYER n Lepzg Translated by D. H. Delpenc Te way tat Pfaff adopted for te ntegraton of
Zur Pfaff scen Lösung des Pfaff scen Probles Mat. Ann. 7 (880) 53-530. On Pfaff s soluton of te Pfaff proble By A. MAYER n Lepzg Translated by D. H. Delpenc Te way tat Pfaff adopted for te ntegraton of
we have E Y x t ( ( xl)) 1 ( xl), e a in I( Λ ) are as follows:
 APPENDICES Aendx : the roof of Equaton (6 For j m n we have Smary from Equaton ( note that j '( ( ( j E Y x t ( ( x ( x a V ( ( x a ( ( x ( x b V ( ( x b V x e d ( abx ( ( x e a a bx ( x xe b a bx By usng
APPENDICES Aendx : the roof of Equaton (6 For j m n we have Smary from Equaton ( note that j '( ( ( j E Y x t ( ( x ( x a V ( ( x a ( ( x ( x b V ( ( x b V x e d ( abx ( ( x e a a bx ( x xe b a bx By usng
,..., k N. , k 2. ,..., k i. The derivative with respect to temperature T is calculated by using the chain rule: & ( (5) dj j dt = "J j. k i.
 Suppleentary Materal Dervaton of Eq. 1a. Assue j s a functon of the rate constants for the N coponent reactons: j j (k 1,,..., k,..., k N ( The dervatve wth respect to teperature T s calculated by usng
Suppleentary Materal Dervaton of Eq. 1a. Assue j s a functon of the rate constants for the N coponent reactons: j j (k 1,,..., k,..., k N ( The dervatve wth respect to teperature T s calculated by usng
Norms, Condition Numbers, Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
 Norms, Condton Numbers, Egenvalues and Egenvectors 1 Norms A norm s a measure of the sze of a matrx or a vector For vectors the common norms are: N a 2 = ( x 2 1/2 the Eucldean Norm (1a b 1 = =1 N x (1b
Norms, Condton Numbers, Egenvalues and Egenvectors 1 Norms A norm s a measure of the sze of a matrx or a vector For vectors the common norms are: N a 2 = ( x 2 1/2 the Eucldean Norm (1a b 1 = =1 N x (1b
Dirac cones induced by accidental degeneracy in photonic crystals and zero-refractive-index materials
 UPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI:.38/NMAT33 Drac cones nduced by accdental deeneracy n photonc crystals and zero-refractve-ndex aterals Xueqn Huan #, Yun La #, Zh Hon Han #, Huhuo Zhen, C. T. Chan * Departent
UPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI:.38/NMAT33 Drac cones nduced by accdental deeneracy n photonc crystals and zero-refractve-ndex aterals Xueqn Huan #, Yun La #, Zh Hon Han #, Huhuo Zhen, C. T. Chan * Departent
