Solutions to Practice Problems
|
|
|
- Maria Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phys A Solutons to Practce Probles hapter Inucton an Maxwell s uatons (a) At t s, the ef has a agntue of t ag t Wb s t Wb s Wb s t Wb s V t 5 (a) Table - gves the resstvty of copper Thus, L A (b) The current nuce n the loop has a agntue of t t ag r, where r s the raus of the loop Therefore, to prouce a current of A reures that the fel change at a rate of t A r 5 4T s The prary fference between ths an the stuaton escrbe n Touchstone xaple - s n the uantty A The area through whch there s agnetc flux s not the area of the short col, n ths case, but s the area of the soleno (snce there s no fel outse an eal soleno) 4 So n ths case, A 8 The agntue of the nuce ef s ag N N na t t 4 4 T A 8 5A 5 s V Fro Oh's law, the nuce current has a agntue of
2 V 5 A 9 Snce a suare's area s relate to the length of ts ses by Thus, Faraay's law gves the agntue of the ef as A, we have A t t ag A 4T 5 /s 9 V t t t (a) In the regon of the saller loop the agnetc fel prouce by the larger loop ay be taken to be unfor an eual to ts value at the center of the saller loop, on the axs Fro -9 for the fel ue to a agnetc pole on the pole axs, x Gven the approxaton that ths fel s approxately constant over the loop area, the agnetc flux through the sall loop s (b) The ef s gven by Faraay s law: ag A r x r r r v t t x x t x ag x 4 4 (c) The flux through the saller loop s prouce by a agnetc fel that ponts up through the loop As the saller loop oves upwar, the flux through t ecreases, an the nuce current wll flow n a recton such that the resultng agnetc fel woul oppose that ecrease So the current wll flow n the sae sense as t oes n the larger loop, proucng a fel that ponts upwar all the angle between the agnetc fel vector an the loop's area vector Snce the col s rotate at a freuency f, the angle ft, where we've chosen ra at the te t s The ef nuce n the col has an apltue of ag N NA cos ft fna sn ft t t Snce the area of the rectangular col s value of ths ef s A 5 5, the axu
3 fna rev s 5 T 5 55 V ax 9 (a) The agnetc flux through the loop (ro rals en strp) s ncreasng because the area s ncreasng Faraay's law gves the agntue of the nuce ef as t ag A t Lv 5 T 5 55 s 48 V (b) y Oh s law, the nuce current s 48 V 8 A y Lenz s law, the current s clockwse n Fg -4 (c) Mechancal energy s transfore to theral energy at a rate of P A 8 9 W (a) The agnetc flux through the loop (ro rals en strp) s ncreasng because the area s ncreasng Faraay's law gves the agntue of the nuce ef as t ag A t Lv T 5 s V (b) y Oh s law, the nuce current s V 4 5 A y Lenz s law, the current s clockwse n Fg -4 (c) Mechancal energy s transfore to theral energy at a rate of P 5A 4 9 W () The agnetc fel apples a force to the current n the ro The force s recte rghtwar an has agntue F L (5 A)( )( T) 8 N To keep the ro ovng at constant velocty, an external agent ust apply a leftwar force of that sae agntue (e) The power exerte by the external agent s P Fv 8 N 5 s 9W, whch s the sae as our result fro part (c)
4 hapter Magnetc Fels ue to currents Usng the result of proble an -, we wsh to show that a a, or, 4 where a s the length of a se of the suare an s the raus of the crcle oth wres have the sae length L, so a L 4 an L Therefore, what we wsh to show s that L L 8 or, whch s true, snce 8 5 Let the x axs pont to the rght an the y axs pont up on the page The wre on the top wll prouce a agnetc fel wth a postve y-coponent an a postve x-coponent The wre on the botto wll prouce a agnetc fel wth a postve y-coponent an a negatve x- coponent Snce the wres carry the sae current an are eustant fro the pont P, the x- coponents of the fels a to zero Wth as the angle between x axs an the lne between P an one of the wres, the y-coponents a to gve the agntue of the fel: cos 4 T A 4 A 4 5 T 4 (a) If the currents are parallel, the two fels are n opposte rectons n the regon between the wres Snce the currents are the sae, the total fel s zero along the lne that runs halfway between the wres There s no possble current for whch the fel oes not vansh (b) If the currents are antparallel, the fels are n the sae recton n the regon between the wres The total fel at the pont (a stance r 4 fro each wre) has agntue so the reure current s, r r r 4 T 4 T A A 5 Usng the rght-han rule, we see that the current carre by wre ust be out of the page The fel ue to wre s r where 5 A an r 5 c The fel ue to wre
5 s r, where r 5 c The agntues of the fels ust be eual f they are to cancel at pont P Ths reures r r 5 c 5A 4A 5 c The agnetc fel prouce by the current n the long straght wre exerts a force on each of the four segents of the rectangle The segent on the rght se of the rectangle experences a force to the rght, whle the segent on the left se of the rectangle experences an eual force to the left These forces su to zero The top an botto of the rectangle experence fferent agntues of force because they are at fferent stances fro the straght wre The net force has a agntue of F net L L b a a b a a b 4 T A A A 8 9 N, an F net ponts towar the wre (a) Two of the currents are out of the page an one s nto the page, so the net current enclose by the path s A, out of the page Snce the path s traverse n the clockwse sense, a current nto the page s postve an a current out of the page s negatve, as ncate by the rght-han rule assocate wth Apere s law Thus, s enc 4 T A A 5 T (b) The net current enclose by the path s zero (two currents are out of the page an two are nto the page), so s enc 4 It s clear that the unknown current ust be recte nto the page n orer that ther fels be antparallel at P The value of the current s set by the reureent that the two fels have eual agntues Wth c, A, an the unknown current, that eans A 4 The agnetc fel nse a soleno has a agntue gven by N n, where N =, 5, an = A Ths yels = T
6 45 Snce the toro has a suare cross-secton, there are unue nner an outer ra We use - to evaluate the fel (a) The nner raus s r = 5 c, so the fel there s N 5 4 T /A 8A 5 4 T r 5 (b) The outer raus s r = c The fel there s N 5 4 T /A 8 A 4 r 4 T 5 (a) The agnetc fel at the center of a col of raus has a agntue of N Therefore, the rato s b b a a a b 4 (b) The pole oent of a col of raus has a agntue of N, so the rato of the agnetc pole oents s b a b a hapter 9 Magnetc Fels (a) The spee of the alpha partcle s foun fro 9-: v er 9 T 45 4 u kg u s (b) The pero s T e 4 u kg u 9 T 9 s (c) The knetc energy of the alpha partcle s
7 4 u kg u s 5 9 K v J ev 4 ev () The reure acceleratng potental s V K e 4 5eV e 4V 5 The partcles wll travel n crcular paths wth a spee obtane fro 9- as v r The knetc energy of each partcle s K r v In orer for the other partcles to crculate n the sae path as the proton, (a) K alpha proton alpha Kproton 4 proton alpha MeV MeV; (b) K euteron proton euteron Kproton proton euteron MeV 5 MeV (a) After acceleratng through the potental fference V, the partcles have a velocty gven by v K V The agnetc fel reure to cause the partcles to ove n the state path s foun fro 9- as V 9 5 kg V v r r T (b) Let N be the nuber of ons that are separate by the achne per unt te The current s = N an the ass that s separate per unt te s M = N, where s the ass of a sngle on M has the value M kg s 8 8 kg s Snce N = M/ we have
8 M kg s 9 5 kg A (c) ach on eposts energy V n the cup, so the energy eposte n te t s gven by N V t V t For t = h, g 5 kg 98 s NL 5T 45A If the two forces are to a to a zero net force, then v The electrc fel between the two plates has a agntue of V, where s the plate separaton The velocty can be foun fro the knetc energy K kev The reure agnetc fel has a agntue of V v K e V 9 kg ev 9 J ev 4 T The agnetc force on the wre ust be upwar an have a agntue eual to the gravtatonal force g on the wre Applyng the rght-han rule reveals that the current ust be fro left to rght n the fgure Snce the fel an the current are perpencular to each other the agntue of the agnetc force s gven by F ag L, where L s the length of the wre Thus, L g g L kg 98 s 44T 4 A 45 (a) The agntue of the agnetc pole oent s gven by N A, where N s the nuber of turns, s the current n each turn, an A s the area of a loop In ths case the loops are crcular, so A = r, where r s the raus of the col Thus N r A 9 A (b) The axu torue occurs when the pole oent s perpencular to the fel (or the plane of the loop s parallel to the fel) It s gven by A 5 T 85 N hapter 8
9 apactors an are n parallel, so ther euvalent capactance s 5?F That parallel cobnaton s n seres wth The euvalent capactance of the set of three capactors s 5 F 4 F F (a) The potental fference across s V = V Thus, the charge on capactor s V F V (b) Let = F We frst conser the three-capactor cobnaton consstng of an ts two closest neghbors, each of capactance The euvalent capactance of ths cobnaton s tro 5 5 F Ths tro s n seres wth the capactor on the lower rght; that set of four capactors has an euvalent capactance of e tro F The charge on ths euvalent capactor s e V F V Ths s also eual to the aount of charge on our upper tro of capactors Therefore, the potental fference across that cobnaton s V tro tro 4 V 5 F Snce ths potental fference s ve eually between an the one connecte n seres wth t, the voltage fference across s V V tro V Thus V F V 8 (a) Frst, the euvalent capactance of the two 4 F capactors connecte n seres s a 4 F F Ths cobnaton s then connecte n parallel wth two other F capactors (one on each se), resultng n an euvalent capactance of b a F F F Ths cobnaton s n seres wth another cobnaton (the two F capactors n parallel, wth an euvalent capactance of F F ) Thus, the euvalent capactance of the whole crcut s e b F F (b) Let V = V be the potental fference supple by the battery Then e V F V
10 (c) The upper set of four capactors has an effectve capactance of b F The lower par of capactors has an effectve capactance of F Snce these two cobnatons are n seres wth each other, they have the sae charge Snce they also have the sae capactance, the potental fference across each ust be the sae an ust be eual to half the potental fference of the battery Hence, V V Snce the lower cobnaton s a par of capactors n parallel, ths s also the potental across capactor : V V The charge on the plates of capactor s V F V () Fro the arguent presente n (c), the potental fference across s gven by V V onseuently, the charge carre by s b V V F V (e) Snce ths voltage fference V b s ve eually between an the other 4 F capactor connecte n seres wth t, the voltage fference across s gven by V V 5 V b Thus, V 4 F 5 V The euvalent capactance of parallel capactors, each wth a capactance of 5 F, s e 5 F F The total energy store n the capactor bank s e F 5,V 5 J U V Thus, the cost s 5 J kw h J kw h 4 5 The capactance wth the electrc n place s gven by ar The energy store s gven by U V V, so ar ar U (4 J) V (4 F)(5 V) 4 Accorng to Table 8-, you shoul use Pyrex t 4 (a) We use e an solve for t: t ln, where = s the capactve te constant Thus, when the capactor has lost / of ts orgnal charge, t ln ln 4 (b) When / of the orgnal charge has been lost,
11 t ln ln 5 The te t takes for the voltage fference across the capactor to reach V L s gven by e t, where s the ef of the battery We solve for : VL t ln V L 5 s 5 F ln 95 V 95 V V 5 where we use t = 5 s so that ths event woul occur twce per secon 5 The potental fference across the capactor vares as a functon of te t as V V t e, where V 5 V s the ntal potental fference across the capactor The resstance s relate to the te to scharge to V 8 s by t ln V V The nu scharge te s gven as s, so the nu value the resstance shoul take s s n 48 F ln 8 5 The axu scharge te s gven as s, so the axu value the resstor shoul take s n s F ln k
University of Bahrain College of Science Dept. of Physics PHYCS 102 FINAL EXAM
 Unversty o Bahran College o Scence Dept. o Physcs PHYCS 10 FINAL XAM Date: 15/1/001 Tme:Two Hours Name:-------------------------------------------------ID#---------------------- Secton:----------------
Unversty o Bahran College o Scence Dept. o Physcs PHYCS 10 FINAL XAM Date: 15/1/001 Tme:Two Hours Name:-------------------------------------------------ID#---------------------- Secton:----------------
Physics 4B. Question and 3 tie (clockwise), then 2 and 5 tie (zero), then 4 and 6 tie (counterclockwise) B i. ( T / s) = 1.74 V.
 Physcs 4 Solutons to Chapter 3 HW Chapter 3: Questons:, 4, 1 Problems:, 15, 19, 7, 33, 41, 45, 54, 65 Queston 3-1 and 3 te (clockwse), then and 5 te (zero), then 4 and 6 te (counterclockwse) Queston 3-4
Physcs 4 Solutons to Chapter 3 HW Chapter 3: Questons:, 4, 1 Problems:, 15, 19, 7, 33, 41, 45, 54, 65 Queston 3-1 and 3 te (clockwse), then and 5 te (zero), then 4 and 6 te (counterclockwse) Queston 3-4
Physics 114 Exam 3 Spring Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam 3 Sprng 015 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem 4. Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse
Physcs 114 Exam 3 Sprng 015 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem 4. Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse
Physics 4B. A positive value is obtained, so the current is counterclockwise around the circuit.
 Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
Physcs 4B Solutons to Chapter 7 HW Chapter 7: Questons:, 8, 0 Problems:,,, 45, 48,,, 7, 9 Queston 7- (a) no (b) yes (c) all te Queston 7-8 0 μc Queston 7-0, c;, a;, d; 4, b Problem 7- (a) Let be the current
PHY2049 Exam 2 solutions Fall 2016 Solution:
 PHY2049 Exam 2 solutons Fall 2016 General strategy: Fnd two resstors, one par at a tme, that are connected ether n SERIES or n PARALLEL; replace these two resstors wth one of an equvalent resstance. Now
PHY2049 Exam 2 solutons Fall 2016 General strategy: Fnd two resstors, one par at a tme, that are connected ether n SERIES or n PARALLEL; replace these two resstors wth one of an equvalent resstance. Now
PHYS 1101 Practice problem set 12, Chapter 32: 21, 22, 24, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 12, 32, 38, 44, 49, 76
 PHYS 1101 Practce problem set 1, Chapter 3: 1,, 4, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 1, 3, 38, 44, 49, 76 3.1. Vsualze: Please reer to Fgure Ex3.1. Solve: Because B s n the same drecton as the ntegraton path s
PHYS 1101 Practce problem set 1, Chapter 3: 1,, 4, 57, 61, 83 Chapter 33: 7, 1, 3, 38, 44, 49, 76 3.1. Vsualze: Please reer to Fgure Ex3.1. Solve: Because B s n the same drecton as the ntegraton path s
Physics 3A: Linear Momentum. Physics 3A: Linear Momentum. Physics 3A: Linear Momentum. Physics 3A: Linear Momentum
 Recall that there was ore to oton than just spee A ore coplete escrpton of oton s the concept of lnear oentu: p v (8.) Beng a prouct of a scalar () an a vector (v), oentu s a vector: p v p y v y p z v
Recall that there was ore to oton than just spee A ore coplete escrpton of oton s the concept of lnear oentu: p v (8.) Beng a prouct of a scalar () an a vector (v), oentu s a vector: p v p y v y p z v
Class: Life-Science Subject: Physics
 Class: Lfe-Scence Subject: Physcs Frst year (6 pts): Graphc desgn of an energy exchange A partcle (B) of ass =g oves on an nclned plane of an nclned angle α = 3 relatve to the horzontal. We want to study
Class: Lfe-Scence Subject: Physcs Frst year (6 pts): Graphc desgn of an energy exchange A partcle (B) of ass =g oves on an nclned plane of an nclned angle α = 3 relatve to the horzontal. We want to study
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 28: INDUCTION AND INDUCTANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
Physics 114 Exam 2 Spring Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam Sprng 013 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red wth the amount beng
Physcs 114 Exam Sprng 013 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red wth the amount beng
A capacitor is simply two pieces of metal near each other, separated by an insulator or air. A capacitor is used to store charge and energy.
 -1 apactors A capactor s smply two peces of metal near each other, separate by an nsulator or ar. A capactor s use to store charge an energy. A parallel-plate capactor conssts of two parallel plates separate
-1 apactors A capactor s smply two peces of metal near each other, separate by an nsulator or ar. A capactor s use to store charge an energy. A parallel-plate capactor conssts of two parallel plates separate
PHYSICS - CLUTCH 1E CH 28: INDUCTION AND INDUCTANCE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION A col of wre wth a VOLTAGE across each end wll have a current n t - Wre doesn t HAVE to have voltage source, voltage can be INDUCED V Common ways
1.3 Hence, calculate a formula for the force required to break the bond (i.e. the maximum value of F)
 EN40: Dynacs and Vbratons Hoework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Moentu Due Frday March 6 th School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The Rydberg potental s a sple odel of atoc nteractons. It specfes the potental
EN40: Dynacs and Vbratons Hoework 4: Work, Energy and Lnear Moentu Due Frday March 6 th School of Engneerng Brown Unversty 1. The Rydberg potental s a sple odel of atoc nteractons. It specfes the potental
Chapter 7: Conservation of Energy
 Lecture 7: Conservaton o nergy Chapter 7: Conservaton o nergy Introucton I the quantty o a subject oes not change wth tme, t means that the quantty s conserve. The quantty o that subject remans constant
Lecture 7: Conservaton o nergy Chapter 7: Conservaton o nergy Introucton I the quantty o a subject oes not change wth tme, t means that the quantty s conserve. The quantty o that subject remans constant
Lecture #4 Capacitors and Inductors Energy Stored in C and L Equivalent Circuits Thevenin Norton
 EES ntro. electroncs for S Sprng 003 Lecture : 0/03/03 A.R. Neureuther Verson Date 0/0/03 EES ntroducton to Electroncs for omputer Scence Andrew R. Neureuther Lecture # apactors and nductors Energy Stored
EES ntro. electroncs for S Sprng 003 Lecture : 0/03/03 A.R. Neureuther Verson Date 0/0/03 EES ntroducton to Electroncs for omputer Scence Andrew R. Neureuther Lecture # apactors and nductors Energy Stored
CHAPTER 10 ROTATIONAL MOTION
 CHAPTER 0 ROTATONAL MOTON 0. ANGULAR VELOCTY Consder argd body rotates about a fxed axs through pont O n x-y plane as shown. Any partcle at pont P n ths rgd body rotates n a crcle of radus r about O. The
CHAPTER 0 ROTATONAL MOTON 0. ANGULAR VELOCTY Consder argd body rotates about a fxed axs through pont O n x-y plane as shown. Any partcle at pont P n ths rgd body rotates n a crcle of radus r about O. The
Physics 114 Exam 2 Fall 2014 Solutions. Name:
 Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
Physcs 114 Exam Fall 014 Name: For gradng purposes (do not wrte here): Queston 1. 1... 3. 3. Problem Answer each of the followng questons. Ponts for each queston are ndcated n red. Unless otherwse ndcated,
Field and Wave Electromagnetic. Chapter.4
 Fel an Wave Electromagnetc Chapter.4 Soluton of electrostatc Problems Posson s s an Laplace s Equatons D = ρ E = E = V D = ε E : Two funamental equatons for electrostatc problem Where, V s scalar electrc
Fel an Wave Electromagnetc Chapter.4 Soluton of electrostatc Problems Posson s s an Laplace s Equatons D = ρ E = E = V D = ε E : Two funamental equatons for electrostatc problem Where, V s scalar electrc
Chapter 10 Sinusoidal Steady-State Power Calculations
 Chapter 0 Snusodal Steady-State Power Calculatons n Chapter 9, we calculated the steady state oltages and currents n electrc crcuts dren by snusodal sources. We used phasor ethod to fnd the steady state
Chapter 0 Snusodal Steady-State Power Calculatons n Chapter 9, we calculated the steady state oltages and currents n electrc crcuts dren by snusodal sources. We used phasor ethod to fnd the steady state
WYSE Academic Challenge 2004 State Finals Physics Solution Set
 WYSE Acaemc Challenge 00 State nals Physcs Soluton Set. Answer: c. Ths s the enton o the quantty acceleraton.. Answer: b. Pressure s orce per area. J/m N m/m N/m, unts o orce per area.. Answer: e. Aerage
WYSE Acaemc Challenge 00 State nals Physcs Soluton Set. Answer: c. Ths s the enton o the quantty acceleraton.. Answer: b. Pressure s orce per area. J/m N m/m N/m, unts o orce per area.. Answer: e. Aerage
Phys 331: Ch 7,.2 Unconstrained Lagrange s Equations 1
 Phys 33: Ch 7 Unconstrane agrange s Equatons Fr0/9 Mon / We /3 hurs /4 7-3 agrange s wth Constrane 74-5 Proof an Eaples 76-8 Generalze Varables & Classcal Haltonan (ecoen 79 f you ve ha Phys 33) HW7 ast
Phys 33: Ch 7 Unconstrane agrange s Equatons Fr0/9 Mon / We /3 hurs /4 7-3 agrange s wth Constrane 74-5 Proof an Eaples 76-8 Generalze Varables & Classcal Haltonan (ecoen 79 f you ve ha Phys 33) HW7 ast
Elastic Collisions. Definition: two point masses on which no external forces act collide without losing any energy.
 Elastc Collsons Defnton: to pont asses on hch no external forces act collde thout losng any energy v Prerequstes: θ θ collsons n one denson conservaton of oentu and energy occurs frequently n everyday
Elastc Collsons Defnton: to pont asses on hch no external forces act collde thout losng any energy v Prerequstes: θ θ collsons n one denson conservaton of oentu and energy occurs frequently n everyday
Physics 2102 Spring 2007 Lecture 10 Current and Resistance
 esstance Is Futle! Physcs 0 Sprng 007 Jonathan Dowlng Physcs 0 Sprng 007 Lecture 0 Current and esstance Georg Smon Ohm (789-854) What are we gong to learn? A road map lectrc charge lectrc force on other
esstance Is Futle! Physcs 0 Sprng 007 Jonathan Dowlng Physcs 0 Sprng 007 Lecture 0 Current and esstance Georg Smon Ohm (789-854) What are we gong to learn? A road map lectrc charge lectrc force on other
Linear Momentum. Center of Mass.
 Lecture 16 Chapter 9 Physcs I 11.06.2013 Lnear oentu. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.ul.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.ul.edu/danylov2013/physcs1fall.htl
Lecture 16 Chapter 9 Physcs I 11.06.2013 Lnear oentu. Center of ass. Course webste: http://faculty.ul.edu/ndry_danylov/teachng/physcsi Lecture Capture: http://echo360.ul.edu/danylov2013/physcs1fall.htl
Revision: December 13, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 .9.1: AC power analyss Reson: Deceber 13, 010 15 E Man Sute D Pullan, WA 99163 (509 334 6306 Voce and Fax Oerew n chapter.9.0, we ntroduced soe basc quanttes relate to delery of power usng snusodal sgnals.
.9.1: AC power analyss Reson: Deceber 13, 010 15 E Man Sute D Pullan, WA 99163 (509 334 6306 Voce and Fax Oerew n chapter.9.0, we ntroduced soe basc quanttes relate to delery of power usng snusodal sgnals.
Review & Summary. Questions
 QUESTIONS 87 Reew & Summar Magnetc Fel A magnetc fel s efne n terms of the force F : actng on a test partcle wth charge q mong through the fel wth eloct : The SI unt for : : : F : q : :. s the tesla (T):
QUESTIONS 87 Reew & Summar Magnetc Fel A magnetc fel s efne n terms of the force F : actng on a test partcle wth charge q mong through the fel wth eloct : The SI unt for : : : F : q : :. s the tesla (T):
Physics 1202: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda
 Physcs 122: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems start ths Thursday Team 1: Hend Ouda, Mke Glnsk, Stephane Auger Team 2: Analese Bruder, Krsten Dean, Alson Smth Offce hours: Monday 2:3-3:3
Physcs 122: Lecture 11 Today s Agenda Announcements: Team problems start ths Thursday Team 1: Hend Ouda, Mke Glnsk, Stephane Auger Team 2: Analese Bruder, Krsten Dean, Alson Smth Offce hours: Monday 2:3-3:3
EMF induced in a coil by moving a bar magnet. Induced EMF: Faraday s Law. Induction and Oscillations. Electromagnetic Induction.
 Inducton and Oscllatons Ch. 3: Faraday s Law Ch. 3: AC Crcuts Induced EMF: Faraday s Law Tme-dependent B creates nduced E In partcular: A changng magnetc flux creates an emf n a crcut: Ammeter or voltmeter.
Inducton and Oscllatons Ch. 3: Faraday s Law Ch. 3: AC Crcuts Induced EMF: Faraday s Law Tme-dependent B creates nduced E In partcular: A changng magnetc flux creates an emf n a crcut: Ammeter or voltmeter.
ˆ (0.10 m) E ( N m /C ) 36 ˆj ( j C m)
 7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
7.. = = 3 = 4 = 5. The electrc feld s constant everywhere between the plates. Ths s ndcated by the electrc feld vectors, whch are all the same length and n the same drecton. 7.5. Model: The dstances to
DC Circuits. Crossing the emf in this direction +ΔV
 DC Crcuts Delverng a steady flow of electrc charge to a crcut requres an emf devce such as a battery, solar cell or electrc generator for example. mf stands for electromotve force, but an emf devce transforms
DC Crcuts Delverng a steady flow of electrc charge to a crcut requres an emf devce such as a battery, solar cell or electrc generator for example. mf stands for electromotve force, but an emf devce transforms
total If no external forces act, the total linear momentum of the system is conserved. This occurs in collisions and explosions.
 Lesson 0: Collsons, Rotatonal netc Energy, Torque, Center o Graty (Sectons 7.8 Last te we used ewton s second law to deelop the pulse-oentu theore. In words, the theore states that the change n lnear oentu
Lesson 0: Collsons, Rotatonal netc Energy, Torque, Center o Graty (Sectons 7.8 Last te we used ewton s second law to deelop the pulse-oentu theore. In words, the theore states that the change n lnear oentu
Chaper 2: Stress in beams
 Chaper : Stress n eams FLEURE Beams suject to enng wll fle COPRESSON TENSON On the lower surface the eam s stretche lengthwse. Ths sujects t to tensle stress. N.A. N.A. s the neutral as On the upper surface
Chaper : Stress n eams FLEURE Beams suject to enng wll fle COPRESSON TENSON On the lower surface the eam s stretche lengthwse. Ths sujects t to tensle stress. N.A. N.A. s the neutral as On the upper surface
JEE ADVANCE : 2015 P1 PHASE TEST 4 ( )
 I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y IN D IA JEE ADVANCE : 5 P PHASE TEST (.8.7) ANSWER KEY PHYSICS CHEMISTRY MATHEMATICS Q.No. Answer Key Q.No. Answer Key Q.No. Answer Key. () () (). () () (). (9) () (). () ()
I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y IN D IA JEE ADVANCE : 5 P PHASE TEST (.8.7) ANSWER KEY PHYSICS CHEMISTRY MATHEMATICS Q.No. Answer Key Q.No. Answer Key Q.No. Answer Key. () () (). () () (). (9) () (). () ()
Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 11
 Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
Physcs 111: Mechancs Lecture 11 Bn Chen NJIT Physcs Department Textbook Chapter 10: Dynamcs of Rotatonal Moton q 10.1 Torque q 10. Torque and Angular Acceleraton for a Rgd Body q 10.3 Rgd-Body Rotaton
PHYS 1443 Section 002 Lecture #20
 PHYS 1443 Secton 002 Lecture #20 Dr. Jae Condtons for Equlbru & Mechancal Equlbru How to Solve Equlbru Probles? A ew Exaples of Mechancal Equlbru Elastc Propertes of Solds Densty and Specfc Gravty lud
PHYS 1443 Secton 002 Lecture #20 Dr. Jae Condtons for Equlbru & Mechancal Equlbru How to Solve Equlbru Probles? A ew Exaples of Mechancal Equlbru Elastc Propertes of Solds Densty and Specfc Gravty lud
Electrical Circuits 2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER
 CHAPTE Electrcal Crcuts. INTODUCTION In ths chapter, we brefly revew the three types of basc passve electrcal elements: resstor, nductor and capactor. esstance Elements: Ohm s Law: The voltage drop across
CHAPTE Electrcal Crcuts. INTODUCTION In ths chapter, we brefly revew the three types of basc passve electrcal elements: resstor, nductor and capactor. esstance Elements: Ohm s Law: The voltage drop across
Page 1. SPH4U: Lecture 7. New Topic: Friction. Today s Agenda. Surface Friction... Surface Friction...
 SPH4U: Lecture 7 Today s Agenda rcton What s t? Systeatc catagores of forces How do we characterze t? Model of frcton Statc & Knetc frcton (knetc = dynac n soe languages) Soe probles nvolvng frcton ew
SPH4U: Lecture 7 Today s Agenda rcton What s t? Systeatc catagores of forces How do we characterze t? Model of frcton Statc & Knetc frcton (knetc = dynac n soe languages) Soe probles nvolvng frcton ew
Fermi-Dirac statistics
 UCC/Physcs/MK/EM/October 8, 205 Fer-Drac statstcs Fer-Drac dstrbuton Matter partcles that are eleentary ostly have a type of angular oentu called spn. hese partcles are known to have a agnetc oent whch
UCC/Physcs/MK/EM/October 8, 205 Fer-Drac statstcs Fer-Drac dstrbuton Matter partcles that are eleentary ostly have a type of angular oentu called spn. hese partcles are known to have a agnetc oent whch
Electricity and Magnetism Review Faraday s Law
 Electrcty and Magnetsm Revew Faraday s Law Lana Sherdan De Anza College Dec 3, 2015 Overvew Faraday s law Lenz s law magnetc feld from a movng charge Gauss s law Remnder: (30.18) Magnetc Flux feld S that
Electrcty and Magnetsm Revew Faraday s Law Lana Sherdan De Anza College Dec 3, 2015 Overvew Faraday s law Lenz s law magnetc feld from a movng charge Gauss s law Remnder: (30.18) Magnetc Flux feld S that
= 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W]
![= 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W] = 1.23 m/s 2 [W] Required: t. Solution:!t = = 17 m/s [W]! m/s [W] (two extra digits carried) = 2.1 m/s [W]](/thumbs/78/76802454.jpg) Secton 1.3: Acceleraton Tutoral 1 Practce, page 24 1. Gven: 0 m/s; 15.0 m/s [S]; t 12.5 s Requred: Analyss: a av v t v f v t a v av f v t 15.0 m/s [S] 0 m/s 12.5 s 15.0 m/s [S] 12.5 s 1.20 m/s 2 [S] Statement:
Secton 1.3: Acceleraton Tutoral 1 Practce, page 24 1. Gven: 0 m/s; 15.0 m/s [S]; t 12.5 s Requred: Analyss: a av v t v f v t a v av f v t 15.0 m/s [S] 0 m/s 12.5 s 15.0 m/s [S] 12.5 s 1.20 m/s 2 [S] Statement:
Scattering by a perfectly conducting infinite cylinder
 Scatterng by a perfectly conductng nfnte cylnder Reeber that ths s the full soluton everywhere. We are actually nterested n the scatterng n the far feld lt. We agan use the asyptotc relatonshp exp exp
Scatterng by a perfectly conductng nfnte cylnder Reeber that ths s the full soluton everywhere. We are actually nterested n the scatterng n the far feld lt. We agan use the asyptotc relatonshp exp exp
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
 Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Complex Numbers, Signals, and Circuits
 Complex Numbers, Sgnals, and Crcuts 3 August, 009 Complex Numbers: a Revew Suppose we have a complex number z = x jy. To convert to polar form, we need to know the magntude of z and the phase of z. z =
Complex Numbers, Sgnals, and Crcuts 3 August, 009 Complex Numbers: a Revew Suppose we have a complex number z = x jy. To convert to polar form, we need to know the magntude of z and the phase of z. z =
Linearity. If kx is applied to the element, the output must be ky. kx ky. 2. additivity property. x 1 y 1, x 2 y 2
 Lnearty An element s sad to be lnear f t satsfes homogenety (scalng) property and addte (superposton) property. 1. homogenety property Let x be the nput and y be the output of an element. x y If kx s appled
Lnearty An element s sad to be lnear f t satsfes homogenety (scalng) property and addte (superposton) property. 1. homogenety property Let x be the nput and y be the output of an element. x y If kx s appled
High-Contrast Gratings based Spoof Surface Plasmons
 Suppleentary Inforaton Hgh-Contrast Gratngs base Spoof Surface Plasons Zhuo L 123*+ Langlang Lu 1+ ngzheng Xu 1 Pngpng Nng 1 Chen Chen 1 Ja Xu 1 Xnle Chen 1 Changqng Gu 1 & Quan Qng 3 1 Key Laboratory
Suppleentary Inforaton Hgh-Contrast Gratngs base Spoof Surface Plasons Zhuo L 123*+ Langlang Lu 1+ ngzheng Xu 1 Pngpng Nng 1 Chen Chen 1 Ja Xu 1 Xnle Chen 1 Changqng Gu 1 & Quan Qng 3 1 Key Laboratory
ENGI9496 Lecture Notes Multiport Models in Mechanics
 ENGI9496 Moellng an Smulaton of Dynamc Systems Mechancs an Mechansms ENGI9496 Lecture Notes Multport Moels n Mechancs (New text Secton 4..3; Secton 9.1 generalzes to 3D moton) Defntons Generalze coornates
ENGI9496 Moellng an Smulaton of Dynamc Systems Mechancs an Mechansms ENGI9496 Lecture Notes Multport Moels n Mechancs (New text Secton 4..3; Secton 9.1 generalzes to 3D moton) Defntons Generalze coornates
Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 121 Lecture 10 - Sources of Magnetic Fields (Currents) Y&F Chapter 28, Sec. 1-7
 Electrcty and Magnetsm - Physcs 11 Lecture 10 - Sources of Magnetc Felds (Currents) Y&F Chapter 8, Sec. 1-7 Magnetc felds are due to currents The Bot-Savart Law Calculatng feld at the centers of current
Electrcty and Magnetsm - Physcs 11 Lecture 10 - Sources of Magnetc Felds (Currents) Y&F Chapter 8, Sec. 1-7 Magnetc felds are due to currents The Bot-Savart Law Calculatng feld at the centers of current
CHAPTER 8 Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 CHAPTER 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton o Energy One orm o energy can be converted nto another orm o energy. Conservatve and non-conservatve orces Physcs 1 Knetc energy: Potental energy: Energy assocated
CHAPTER 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton o Energy One orm o energy can be converted nto another orm o energy. Conservatve and non-conservatve orces Physcs 1 Knetc energy: Potental energy: Energy assocated
Advanced Circuits Topics - Part 1 by Dr. Colton (Fall 2017)
 Advanced rcuts Topcs - Part by Dr. olton (Fall 07) Part : Some thngs you should already know from Physcs 0 and 45 These are all thngs that you should have learned n Physcs 0 and/or 45. Ths secton s organzed
Advanced rcuts Topcs - Part by Dr. olton (Fall 07) Part : Some thngs you should already know from Physcs 0 and 45 These are all thngs that you should have learned n Physcs 0 and/or 45. Ths secton s organzed
PHYS 1443 Section 004 Lecture #12 Thursday, Oct. 2, 2014
 PHYS 1443 Secton 004 Lecture #1 Thursday, Oct., 014 Work-Knetc Energy Theorem Work under rcton Potental Energy and the Conservatve Force Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Conservaton o
PHYS 1443 Secton 004 Lecture #1 Thursday, Oct., 014 Work-Knetc Energy Theorem Work under rcton Potental Energy and the Conservatve Force Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Conservaton o
K = 100 J. [kg (m/s) ] K = mv = (0.15)(36.5) !!! Lethal energies. m [kg ] J s (Joule) Kinetic Energy (energy of motion) E or KE.
![K = 100 J. [kg (m/s) ] K = mv = (0.15)(36.5) !!! Lethal energies. m [kg ] J s (Joule) Kinetic Energy (energy of motion) E or KE. K = 100 J. [kg (m/s) ] K = mv = (0.15)(36.5) !!! Lethal energies. m [kg ] J s (Joule) Kinetic Energy (energy of motion) E or KE.](/thumbs/80/81648220.jpg) Knetc Energy (energy of moton) E or KE K = m v = m(v + v y + v z ) eample baseball m=0.5 kg ptche at v = 69 mph = 36.5 m/s K = mv = (0.5)(36.5) [kg (m/s) ] Unts m [kg ] J s (Joule) v = 69 mph K = 00 J
Knetc Energy (energy of moton) E or KE K = m v = m(v + v y + v z ) eample baseball m=0.5 kg ptche at v = 69 mph = 36.5 m/s K = mv = (0.5)(36.5) [kg (m/s) ] Unts m [kg ] J s (Joule) v = 69 mph K = 00 J
Electricity and Magnetism Gauss s Law
 Electrcty and Magnetsm Gauss s Law Ampère s Law Lana Sherdan De Anza College Mar 1, 2018 Last tme magnetc feld of a movng charge magnetc feld of a current the Bot-Savart law magnetc feld around a straght
Electrcty and Magnetsm Gauss s Law Ampère s Law Lana Sherdan De Anza College Mar 1, 2018 Last tme magnetc feld of a movng charge magnetc feld of a current the Bot-Savart law magnetc feld around a straght
Physics 181. Particle Systems
 Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
Physcs 181 Partcle Systems Overvew In these notes we dscuss the varables approprate to the descrpton of systems of partcles, ther defntons, ther relatons, and ther conservatons laws. We consder a system
Work is the change in energy of a system (neglecting heat transfer). To examine what could
 Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
Work Work s the change n energy o a system (neglectng heat transer). To eamne what could cause work, let s look at the dmensons o energy: L ML E M L F L so T T dmensonally energy s equal to a orce tmes
( ) = : a torque vector composed of shoulder torque and elbow torque, corresponding to
 Supplementary Materal for Hwan EJ, Donchn O, Smth MA, Shamehr R (3 A Gan-Fel Encon of Lmb Poston an Velocty n the Internal Moel of Arm Dynamcs. PLOS Boloy, :9-. Learnn of ynamcs usn bass elements he nternal
Supplementary Materal for Hwan EJ, Donchn O, Smth MA, Shamehr R (3 A Gan-Fel Encon of Lmb Poston an Velocty n the Internal Moel of Arm Dynamcs. PLOS Boloy, :9-. Learnn of ynamcs usn bass elements he nternal
Selected Student Solutions for Chapter 2
 /3/003 Assessment Prolems Selected Student Solutons for Chapter. Frst note that we know the current through all elements n the crcut except the 6 kw resstor (the current n the three elements to the left
/3/003 Assessment Prolems Selected Student Solutons for Chapter. Frst note that we know the current through all elements n the crcut except the 6 kw resstor (the current n the three elements to the left
XII.3 The EM (Expectation-Maximization) Algorithm
 XII.3 The EM (Expectaton-Maxzaton) Algorth Toshnor Munaata 3/7/06 The EM algorth s a technque to deal wth varous types of ncoplete data or hdden varables. It can be appled to a wde range of learnng probles
XII.3 The EM (Expectaton-Maxzaton) Algorth Toshnor Munaata 3/7/06 The EM algorth s a technque to deal wth varous types of ncoplete data or hdden varables. It can be appled to a wde range of learnng probles
kq r 2 2kQ 2kQ (A) (B) (C) (D)
 PHYS 1202W MULTIPL CHOIC QUSTIONS QUIZ #1 Answer the followng multple choce questons on the bubble sheet. Choose the best answer, 5 pts each. MC1 An uncharged metal sphere wll (A) be repelled by a charged
PHYS 1202W MULTIPL CHOIC QUSTIONS QUIZ #1 Answer the followng multple choce questons on the bubble sheet. Choose the best answer, 5 pts each. MC1 An uncharged metal sphere wll (A) be repelled by a charged
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Electric Potential Energy & Potential. Electric Potential Energy. Potential Energy. Potential Energy. Example: Charge launcher
 Electrc & Electrc Gravtatonal Increases as you move farther from Earth mgh Sprng Increases as you ncrease sprng extenson/comp resson Δ Increases or decreases as you move farther from the charge U ncreases
Electrc & Electrc Gravtatonal Increases as you move farther from Earth mgh Sprng Increases as you ncrease sprng extenson/comp resson Δ Increases or decreases as you move farther from the charge U ncreases
Chapter 8. Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy
 Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Chapter 8 Potental Energy and Conservaton of Energy In ths chapter we wll ntroduce the followng concepts: Potental Energy Conservatve and non-conservatve forces Mechancal Energy Conservaton of Mechancal
Study Guide For Exam Two
 Study Gude For Exam Two Physcs 2210 Albretsen Updated: 08/02/2018 All Other Prevous Study Gudes Modules 01-06 Module 07 Work Work done by a constant force F over a dstance s : Work done by varyng force
Study Gude For Exam Two Physcs 2210 Albretsen Updated: 08/02/2018 All Other Prevous Study Gudes Modules 01-06 Module 07 Work Work done by a constant force F over a dstance s : Work done by varyng force
Chapter 2: Electric Energy and Capacitance
 Chapter : Electrc Energy and Capactance Potental One goal of physcs s to dentfy basc forces n our world, such as the electrc force as studed n the prevous lectures. Expermentally, we dscovered that the
Chapter : Electrc Energy and Capactance Potental One goal of physcs s to dentfy basc forces n our world, such as the electrc force as studed n the prevous lectures. Expermentally, we dscovered that the
What is LP? LP is an optimization technique that allocates limited resources among competing activities in the best possible manner.
 (C) 998 Gerald B Sheblé, all rghts reserved Lnear Prograng Introducton Contents I. What s LP? II. LP Theor III. The Splex Method IV. Refneents to the Splex Method What s LP? LP s an optzaton technque that
(C) 998 Gerald B Sheblé, all rghts reserved Lnear Prograng Introducton Contents I. What s LP? II. LP Theor III. The Splex Method IV. Refneents to the Splex Method What s LP? LP s an optzaton technque that
How does the momentum before an elastic and an inelastic collision compare to the momentum after the collision?
 Experent 9 Conseraton o Lnear Moentu - Collsons In ths experent you wll be ntroduced to the denton o lnear oentu. You wll learn the derence between an elastc and an nelastc collson. You wll explore how
Experent 9 Conseraton o Lnear Moentu - Collsons In ths experent you wll be ntroduced to the denton o lnear oentu. You wll learn the derence between an elastc and an nelastc collson. You wll explore how
Yukawa Potential and the Propagator Term
 PHY304 Partcle Physcs 4 Dr C N Booth Yukawa Potental an the Propagator Term Conser the electrostatc potental about a charge pont partcle Ths s gven by φ = 0, e whch has the soluton φ = Ths escrbes the
PHY304 Partcle Physcs 4 Dr C N Booth Yukawa Potental an the Propagator Term Conser the electrostatc potental about a charge pont partcle Ths s gven by φ = 0, e whch has the soluton φ = Ths escrbes the
Sections begin this week. Cancelled Sections: Th Labs begin this week. Attend your only second lab slot this week.
 Announcements Sectons begn ths week Cancelled Sectons: Th 122. Labs begn ths week. Attend your only second lab slot ths week. Cancelled labs: ThF 25. Please check your Lab secton. Homework #1 onlne Due
Announcements Sectons begn ths week Cancelled Sectons: Th 122. Labs begn ths week. Attend your only second lab slot ths week. Cancelled labs: ThF 25. Please check your Lab secton. Homework #1 onlne Due
Physics Electricity and Magnetism Lecture 12 - Inductance, RL Circuits. Y&F Chapter 30, Sect 1-4
 Physcs - lectrcty and Magnetsm ecture - Inductance, Crcuts Y&F Chapter 30, Sect - 4 Inductors and Inductance Self-Inductance Crcuts Current Growth Crcuts Current Decay nergy Stored n a Magnetc Feld nergy
Physcs - lectrcty and Magnetsm ecture - Inductance, Crcuts Y&F Chapter 30, Sect - 4 Inductors and Inductance Self-Inductance Crcuts Current Growth Crcuts Current Decay nergy Stored n a Magnetc Feld nergy
On the number of regions in an m-dimensional space cut by n hyperplanes
 6 On the nuber of regons n an -densonal space cut by n hyperplanes Chungwu Ho and Seth Zeran Abstract In ths note we provde a unfor approach for the nuber of bounded regons cut by n hyperplanes n general
6 On the nuber of regons n an -densonal space cut by n hyperplanes Chungwu Ho and Seth Zeran Abstract In ths note we provde a unfor approach for the nuber of bounded regons cut by n hyperplanes n general
Vote today! Physics 122, Fall November (c) University of Rochester 1. Today in Physics 122: applications of induction
 Phscs 1, Fall 01 6 Noember 01 Toda n Phscs 1: applcatons of nducton Generators, motors and back EMF Transformers Edd currents Vote toda! Hdropower generators on the Nagara Rer below the Falls. The ste
Phscs 1, Fall 01 6 Noember 01 Toda n Phscs 1: applcatons of nducton Generators, motors and back EMF Transformers Edd currents Vote toda! Hdropower generators on the Nagara Rer below the Falls. The ste
Gravitational Acceleration: A case of constant acceleration (approx. 2 hr.) (6/7/11)
 Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Gravtatonal Acceleraton: A case of constant acceleraton (approx. hr.) (6/7/11) Introducton The gravtatonal force s one of the fundamental forces of nature. Under the nfluence of ths force all objects havng
Physics 2A Chapter 3 HW Solutions
 Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
Phscs A Chapter 3 HW Solutons Chapter 3 Conceptual Queston: 4, 6, 8, Problems: 5,, 8, 7, 3, 44, 46, 69, 70, 73 Q3.4. Reason: (a) C = A+ B onl A and B are n the same drecton. Sze does not matter. (b) C
2. High dimensional data
 /8/00. Hgh mensons. Hgh mensonal ata Conser representng a ocument by a vector each component of whch correspons to the number of occurrences of a partcular wor n the ocument. The Englsh language has on
/8/00. Hgh mensons. Hgh mensonal ata Conser representng a ocument by a vector each component of whch correspons to the number of occurrences of a partcular wor n the ocument. The Englsh language has on
Physics 123. Exam #1. October 11, 2006
 hyscs Exa # October, 006 roble /0 roble /0 roble /0 roble 4 /0 roble 5 /0 roble 6 /0 roble 7 /0 roble 8 /0 roble 9 /0 roble 0 /0 Total /00 Free-Response robles: lease show all work n order to receve partal
hyscs Exa # October, 006 roble /0 roble /0 roble /0 roble 4 /0 roble 5 /0 roble 6 /0 roble 7 /0 roble 8 /0 roble 9 /0 roble 0 /0 Total /00 Free-Response robles: lease show all work n order to receve partal
Math1110 (Spring 2009) Prelim 3 - Solutions
 Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Dr. Fritz Wilhelm, Physics 230 E:\Excel files\230 lecture\ch26 capacitance.docx 1 of 13 Last saved: 12/27/2008; 8:40 PM. Homework: See website.
 Dr. Frtz Wlhelm, Physcs 3 E:\Excel fles\3 lecture\ch6 capactance.docx of 3 Last saved: /7/8; 8:4 PM Homework: See webste. Table of ontents: h.6. Defnton of apactance, 6. alculatng apactance, 6.a Parallel
Dr. Frtz Wlhelm, Physcs 3 E:\Excel fles\3 lecture\ch6 capactance.docx of 3 Last saved: /7/8; 8:4 PM Homework: See webste. Table of ontents: h.6. Defnton of apactance, 6. alculatng apactance, 6.a Parallel
Physics 231. Topic 8: Rotational Motion. Alex Brown October MSU Physics 231 Fall
 Physcs 231 Topc 8: Rotatonal Moton Alex Brown October 21-26 2015 MSU Physcs 231 Fall 2015 1 MSU Physcs 231 Fall 2015 2 MSU Physcs 231 Fall 2015 3 Key Concepts: Rotatonal Moton Rotatonal Kneatcs Equatons
Physcs 231 Topc 8: Rotatonal Moton Alex Brown October 21-26 2015 MSU Physcs 231 Fall 2015 1 MSU Physcs 231 Fall 2015 2 MSU Physcs 231 Fall 2015 3 Key Concepts: Rotatonal Moton Rotatonal Kneatcs Equatons
Lecture 14: More MOS Circuits and the Differential Amplifier
 Lecture 4: More MOS rcuts an the Dfferental Aplfer Gu-Yeon We Dson of nneern an Apple Scences Harar Unersty uyeon@eecs.harar.eu We Oerew Rean S&S: hapter 5.0, 6.~, 6.6 ackroun Han seen soe of the basc
Lecture 4: More MOS rcuts an the Dfferental Aplfer Gu-Yeon We Dson of nneern an Apple Scences Harar Unersty uyeon@eecs.harar.eu We Oerew Rean S&S: hapter 5.0, 6.~, 6.6 ackroun Han seen soe of the basc
,..., k N. , k 2. ,..., k i. The derivative with respect to temperature T is calculated by using the chain rule: & ( (5) dj j dt = "J j. k i.
 Suppleentary Materal Dervaton of Eq. 1a. Assue j s a functon of the rate constants for the N coponent reactons: j j (k 1,,..., k,..., k N ( The dervatve wth respect to teperature T s calculated by usng
Suppleentary Materal Dervaton of Eq. 1a. Assue j s a functon of the rate constants for the N coponent reactons: j j (k 1,,..., k,..., k N ( The dervatve wth respect to teperature T s calculated by usng
Mechanics Physics 151
 Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecture 3 Contnuous Systems an Fels (Chapter 3) Where Are We Now? We ve fnshe all the essentals Fnal wll cover Lectures through Last two lectures: Classcal Fel Theory Start wth wave equatons
Mechancs Physcs 5 Lecture 3 Contnuous Systems an Fels (Chapter 3) Where Are We Now? We ve fnshe all the essentals Fnal wll cover Lectures through Last two lectures: Classcal Fel Theory Start wth wave equatons
High-Order Hamilton s Principle and the Hamilton s Principle of High-Order Lagrangian Function
 Commun. Theor. Phys. Bejng, Chna 49 008 pp. 97 30 c Chnese Physcal Socety Vol. 49, No., February 15, 008 Hgh-Orer Hamlton s Prncple an the Hamlton s Prncple of Hgh-Orer Lagrangan Functon ZHAO Hong-Xa an
Commun. Theor. Phys. Bejng, Chna 49 008 pp. 97 30 c Chnese Physcal Socety Vol. 49, No., February 15, 008 Hgh-Orer Hamlton s Prncple an the Hamlton s Prncple of Hgh-Orer Lagrangan Functon ZHAO Hong-Xa an
Chapter 07: Kinetic Energy and Work
 Chapter 07: Knetc Energy and Work Conservaton o Energy s one o Nature s undamental laws that s not volated. Energy can take on derent orms n a gven system. Ths chapter we wll dscuss work and knetc energy.
Chapter 07: Knetc Energy and Work Conservaton o Energy s one o Nature s undamental laws that s not volated. Energy can take on derent orms n a gven system. Ths chapter we wll dscuss work and knetc energy.
First Law: A body at rest remains at rest, a body in motion continues to move at constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.
 Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Secton 1. Dynamcs (Newton s Laws of Moton) Two approaches: 1) Gven all the forces actng on a body, predct the subsequent (changes n) moton. 2) Gven the (changes n) moton of a body, nfer what forces act
Solutions for Homework #9
 Solutons for Hoewor #9 PROBEM. (P. 3 on page 379 n the note) Consder a sprng ounted rgd bar of total ass and length, to whch an addtonal ass s luped at the rghtost end. he syste has no dapng. Fnd the natural
Solutons for Hoewor #9 PROBEM. (P. 3 on page 379 n the note) Consder a sprng ounted rgd bar of total ass and length, to whch an addtonal ass s luped at the rghtost end. he syste has no dapng. Fnd the natural
Part C Dynamics and Statics of Rigid Body. Chapter 5 Rotation of a Rigid Body About a Fixed Axis
 Part C Dynamcs and Statcs of Rgd Body Chapter 5 Rotaton of a Rgd Body About a Fxed Axs 5.. Rotatonal Varables 5.. Rotaton wth Constant Angular Acceleraton 5.3. Knetc Energy of Rotaton, Rotatonal Inerta
Part C Dynamcs and Statcs of Rgd Body Chapter 5 Rotaton of a Rgd Body About a Fxed Axs 5.. Rotatonal Varables 5.. Rotaton wth Constant Angular Acceleraton 5.3. Knetc Energy of Rotaton, Rotatonal Inerta
Chapter 8. Linear Momentum, Impulse, and Collisions
 Chapte 8 Lnea oentu, Ipulse, and Collsons 8. Lnea oentu and Ipulse The lnea oentu p of a patcle of ass ovng wth velocty v s defned as: p " v ote that p s a vecto that ponts n the sae decton as the velocty
Chapte 8 Lnea oentu, Ipulse, and Collsons 8. Lnea oentu and Ipulse The lnea oentu p of a patcle of ass ovng wth velocty v s defned as: p " v ote that p s a vecto that ponts n the sae decton as the velocty
System in Weibull Distribution
 Internatonal Matheatcal Foru 4 9 no. 9 94-95 Relablty Equvalence Factors of a Seres-Parallel Syste n Webull Dstrbuton M. A. El-Dacese Matheatcs Departent Faculty of Scence Tanta Unversty Tanta Egypt eldacese@yahoo.co
Internatonal Matheatcal Foru 4 9 no. 9 94-95 Relablty Equvalence Factors of a Seres-Parallel Syste n Webull Dstrbuton M. A. El-Dacese Matheatcs Departent Faculty of Scence Tanta Unversty Tanta Egypt eldacese@yahoo.co
PHYS 1441 Section 002 Lecture #15
 PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
PHYS 1441 Secton 00 Lecture #15 Monday, March 18, 013 Work wth rcton Potental Energy Gravtatonal Potental Energy Elastc Potental Energy Mechancal Energy Conservaton Announcements Mdterm comprehensve exam
CHAPTER 13. Exercises. E13.1 The emitter current is given by the Shockley equation:
 HPT 3 xercses 3. The emtter current s gen by the Shockley equaton: S exp VT For operaton wth, we hae exp >> S >>, and we can wrte VT S exp VT Solng for, we hae 3. 0 6ln 78.4 mv 0 0.784 5 4.86 V VT ln 4
HPT 3 xercses 3. The emtter current s gen by the Shockley equaton: S exp VT For operaton wth, we hae exp >> S >>, and we can wrte VT S exp VT Solng for, we hae 3. 0 6ln 78.4 mv 0 0.784 5 4.86 V VT ln 4
Chapter 3 and Chapter 4
 Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 Chapter 3 Energy 3. Introducton:Work Work W s energy transerred to or rom an object by means o a orce actng on the object. Energy transerred to the object s postve work, and energy
Chapter 3 and Chapter 4 Chapter 3 Energy 3. Introducton:Work Work W s energy transerred to or rom an object by means o a orce actng on the object. Energy transerred to the object s postve work, and energy
Spring 2002 Lecture #13
 44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
44-50 Sprng 00 ecture # Dr. Jaehoon Yu. Rotatonal Energy. Computaton of oments of nerta. Parallel-as Theorem 4. Torque & Angular Acceleraton 5. Work, Power, & Energy of Rotatonal otons Remember the md-term
Spring Force and Power
 Lecture 13 Chapter 9 Sprng Force and Power Yeah, energy s better than orces. What s net? Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn how to solve problems
Lecture 13 Chapter 9 Sprng Force and Power Yeah, energy s better than orces. What s net? Course webste: http://aculty.uml.edu/andry_danylov/teachng/physcsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you wll learn how to solve problems
AN ANALYSIS OF A FRACTAL KINETICS CURVE OF SAVAGEAU
 AN ANALYI OF A FRACTAL KINETIC CURE OF AAGEAU by John Maloney and Jack Hedel Departent of Matheatcs Unversty of Nebraska at Oaha Oaha, Nebraska 688 Eal addresses: aloney@unoaha.edu, jhedel@unoaha.edu Runnng
AN ANALYI OF A FRACTAL KINETIC CURE OF AAGEAU by John Maloney and Jack Hedel Departent of Matheatcs Unversty of Nebraska at Oaha Oaha, Nebraska 688 Eal addresses: aloney@unoaha.edu, jhedel@unoaha.edu Runnng
Section 8.1 Exercises
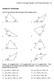 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES. PHYS 2211, Exam 2 Section 1 Version 1 October 18, 2013 Total Weight: 100 points
 TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS, Exam Secton Verson October 8, 03 Total Weght: 00 ponts. Check your examnaton or completeness pror to startng. There are a total o nne
TIME OF COMPLETION NAME SOLUTION DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS, Exam Secton Verson October 8, 03 Total Weght: 00 ponts. Check your examnaton or completeness pror to startng. There are a total o nne
SCALARS AND VECTORS All physical quantities in engineering mechanics are measured using either scalars or vectors.
 SCALARS AND ECTORS All phscal uanttes n engneerng mechancs are measured usng ether scalars or vectors. Scalar. A scalar s an postve or negatve phscal uantt that can be completel specfed b ts magntude.
SCALARS AND ECTORS All phscal uanttes n engneerng mechancs are measured usng ether scalars or vectors. Scalar. A scalar s an postve or negatve phscal uantt that can be completel specfed b ts magntude.
Chapter Newton s Method
 Chapter 9. Newton s Method After readng ths chapter, you should be able to:. Understand how Newton s method s dfferent from the Golden Secton Search method. Understand how Newton s method works 3. Solve
Chapter 9. Newton s Method After readng ths chapter, you should be able to:. Understand how Newton s method s dfferent from the Golden Secton Search method. Understand how Newton s method works 3. Solve
Analytical classical dynamics
 Analytcal classcal ynamcs by Youun Hu Insttute of plasma physcs, Chnese Acaemy of Scences Emal: yhu@pp.cas.cn Abstract These notes were ntally wrtten when I rea tzpatrck s book[] an were later revse to
Analytcal classcal ynamcs by Youun Hu Insttute of plasma physcs, Chnese Acaemy of Scences Emal: yhu@pp.cas.cn Abstract These notes were ntally wrtten when I rea tzpatrck s book[] an were later revse to
E40M Device Models, Resistors, Voltage and Current Sources, Diodes, Solar Cells. M. Horowitz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1
 E40M Devce Models, Resstors, Voltage and Current Sources, Dodes, Solar Cells M. Horowtz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1 Understandng the Solar Charger Lab Project #1 We need to understand how: 1. Current, voltage
E40M Devce Models, Resstors, Voltage and Current Sources, Dodes, Solar Cells M. Horowtz, J. Plummer, R. Howe 1 Understandng the Solar Charger Lab Project #1 We need to understand how: 1. Current, voltage
Lecture 09 Systems of Particles and Conservation of Linear Momentum
 Lecture 09 Systes o Partcles and Conseraton o Lnear oentu 9. Lnear oentu and Its Conseraton 9. Isolated Syste lnear oentu: P F dp dt d( dt d dt a solated syste F ext 0 dp dp F, F dt dt dp dp d F F 0, 0
Lecture 09 Systes o Partcles and Conseraton o Lnear oentu 9. Lnear oentu and Its Conseraton 9. Isolated Syste lnear oentu: P F dp dt d( dt d dt a solated syste F ext 0 dp dp F, F dt dt dp dp d F F 0, 0
