Geometry. Class Examples (July 3) Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2014
|
|
|
- Jemimah Craig
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Geometry lass Examples (July 3) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014
2 Example 11(a): Fermat point. Given triangle, construct externally similar isosceles triangles X, Y, and Z with base angles θ. 27 Z Y θ θ (a) pplying the law of cosines to triangle X, X 2 = 2 + X 2 2 X cos X ( a ) 2 = c 2 ca + cos( + θ) 2cosθ cos θ = c 2 + a2 4cos 2 θ = c 2 + a2 4cos 2 θ X ca(cos cos θ sin sin θ) cos θ ca cos + ca sin tan θ = c 2 + a2 4cos 2 θ 1 2 (c2 + a 2 b 2 )+2Δtanθ = 1 2 (a2 + b 2 + c 2 )+ 1 4cos2 θ a 2 +2Δtanθ. 4cos 2 θ (b) This expression is symmetric in a, b, c if and only if cos θ = 1 2, i.e., θ = ±60. With θ =60,wehave X 2 = 1 2 (a2 + b 2 + c Δ). This means that if equilateral triangles X, Y, and Z are constructed externally of triangle, the segments X, Y, Z have equal lengths.
3 28 Example 11(b): The Fermat point. Given triangle, construct equilateral triangles X, Y, and Z externally on the sides. Let the circumcircle of X intersect the line X at F. Y Z F X (a) Prove that FX = XF =60. (b) Prove that, F,, Y are concyclic. Similarly,, F,, Z are also concyclic. (c) Prove that, F, Y are collinear. Similarly,, F, Z are also collinear. The point F is called the Fermat point of triangle. It is the point of concurrency of the lines X, Y, Z. It is also the common point of the circumcircles of the equilateral triangles X, Y, Z.
4 29 pollonius Theorem Theorem. Given triangle, let D be the midpoint of. The length of the median D is given by =2(D 2 + D 2 ). D Proof. pplying the law of cosines to triangles D and D, and noting that cos D = cos D,wehave 2 = D 2 + D 2 2D D cos D; 2 = D 2 + D 2 2D D cos D, 2 = D 2 + D 2 +2D D cos D. The result follows by adding the first and the third lines. If m a denotes the length of the median on the side, m 2 a = 1 4 (2b2 +2c 2 a 2 ).
5 30 Example 12. is a triangle with a =8, b =9, c =11. Two of its medians have rational lengths. What are these? 8 D 9 E F mb = 17 2 ; m c = 13 2.
6 Example 13. The lengths of the sides of a triangle are 136, 170, and 174. alculate the lengths of its medians. 31
7 ngle bisector theorem Theorem (ngle bisector theorem). The bisectors of an angle of a triangle divide its opposite side in the ratio of the remaining sides. If X and X respectively the internal and external bisectors of angle, then X : X = c : b and X : X = c : b. Z c Z b X X Proof. onstruct lines through parallel to the bisectors X and X to intersect the line at Z and Z. (1) Note that Z = X = X = Z. This means Z =. learly, X : X = : Z = : = c : b. (2) Similarly, Z =, and X : X = : Z = : = c : b.
8 2 Example D1. square is inscribed in a right triangle with sides a and b. Show that each side of the square has length l = ab a + b. a l l b
9 3 Solution to Example D1. square is inscribed in a right triangle with sides a and b. Show that each side of the square has length l = ab a + b. P a l l b Solution. P + P = = 1 2 at bt = 1 2 ab = (a + b)t = ab = t = ab a+b.
10 4 Example D2. In triangle, α = 120. X is the bisector of angle. Show that 1 t = 1 b + 1 c. c t b X
11 5 Solution to Example D2. In triangle, α = 120. X is the bisector of angle. Show that 1 t = 1 b + 1 c. c t b X
12 6 Example D3. In the diagram below, X, Y, and DZ are equilateral triangles. Suppose XY Z = 120. Show that 1 b = 1 a + 1 c. Hint: Extend ZY to intersect at T. Show that T = a. Z X Y a b c D
13 7 Solution to Example D3. In the diagram below, X, Y, and DZ are equilateral triangles. Suppose XY Z = 120. Show that 1 b = 1 a + 1 c. Z X Y a T b c D Solution. Since XY T = XT =60, the points X, Y,, T are concyclic. Therefore, XTY = XY =60 and triangle XY T is equilateral. y Ptolemy s theorem, X = T + Y, and T = T + = T + Y = X = a. Now, triangle TZ has a 120 angle at with bisector Y = b. Therefore, 1 b = 1 a + 1 c.
14 10 Theorem. (a) The lengths of the internal and external bisectors of angle are respectively t a = 2bc b + c cos α 2 and t a = 2bc b c sin α 2. c t a b t a X X Proof. Let X and X be the bisectors of angle. (1) onsider the area of triangle as the sum of those of triangles X and X. Wehave 1 2 t a(b + c)sin α 2 = 1 bc sin α. 2 From this, t a = bc b + c sin α sin α 2 = 2bc b + c cos α 2. (2) onsider the area of triangle as the difference between those of X and X. Remarks. (1) 2bc b+c is the harmonic mean of b and c. It can be constructed as follows. If the perpendicular to X at X intersects and at Y and Z, then Y = Z = 2bc b+c. c t a b Z X Y
15 12 Example D5. The lengths of the sides of a triangle are 84, 125, 169. alculate the lengths of its internal bisectors. 1 1 nswers: 975 7, ,
16 Example D6. is a right triangle in which the bisector of the right angle, and the median to the hypotenuse have lengths 24 2 and 35 respectively. alculate the sidelengths of the triangle. 13
17 14 Example D7. Find an isosceles triangle for which the bisector of a base angle is the geometric mean of the two segments it divides on the opposite side. 2 Z Y 2 nswer: (a, b, c) =(1, 1+ 2, 1+ 2).
18 15 Example D8. In, α =60, and <. The bisector of intersects at X. If X is a mean proportional between X and X, find angle. X
19 16 Solution to Example D8. In, α =60, and <. The bisector of intersects at X. If X is a mean proportional between X and X, find angle. X Solution. y the angle bisector theorem, X = ac ab b+c, X = b+c. The length of the bisector X is 2bc b+c cos 2 = 3bc b+c since =60. If X is a mean proportional of X and X, then 3b 2 c 2 (b + c) = a2 bc 2 (b + c) 2. From this, a 2 =3bc. y the law of cosines, a 2 = b 2 + c 2 bc. Therefore, b 2 + c 2 bc =3bc, b 2 + c 2 4bc =0. Solving this equation, we obtain c =(2± 3)b. Since b<c,wehavec =(2+ 3)b. tan 2 tan + 2 c b c + b = = 1 3. This means = 1 3. ut + = 120 = tan + 2 = 3. It follows that tan 2 =1, and =90. Hence, = 105 and =15.
20 Example D. Suppose is a triangle with, and let D, E, X, Y be points on the line defined as follows: D is the midpoint of, E is the foot of the perpendicular from to, X, Y bisect angle. Prove that = DE XY. 17 Y E X D
21 18 The circle of pollonius Theorem. and are two fixed points. For a given positive number k 1, 1 the locus of points P satisfying P : P = k :1is the circle with diameter XY, where X and Y are points on the line such that X : X = k :1and Y : Y= k : 1. P Y O X Proof. Since k 1, points X and Y can be found on the line satisfying the above conditions. onsider a point P not on the line with P : P = k :1. Note that PX and PY are respectively the internal and external bisectors of angle P. This means that angle XPY is a right angle, and P lies on the circle with XY as diameter. onversely, let P be a point on this circle. We show that P : P = k : 1. Let be a point on the line such that PX bisects angle P. Since P and P are perpendicular to each other, the line P is the external bisector of angle P, and Y = X = X = Y X X On the other hand, Y Y = X X = X X Y X YX. = Y X YX. omparison of the two expressions shows that coincides with, and PX is the bisector of angle P. It follows that P P = X X = k. 1 If k =1, the locus is clearly the perpendicular bisector of the segment.
22 19 Example D9. If = d, and k 1, the radius of the pollonius circle is k k 2 1 d.
23 20 Example D10. Given two disjoint circles () and (), find the locus of the point P such that the angle between the pair of tangents from P to () and that between the pair of tangents from P to () are equal. P
24 21 Steiner-Lehmus theorem Lemma. Let triangles and XY Z be equiangular. If > XY, then > XZ and > Y Z. Z Given: Equiangular triangles and XYZ with > XY. To prove: > XZ and > Y Z. onstruction: Let be a point on such that = XY. onstruct the parallel through to, intersecting the line at. Proof : must be between and, for otherwise, and are on opposite sides of, and the lines, intersect. This contradicts their parallelism. Now, triangles and XY Z are congruent. [S] Therefore, > = XZ. X Y
25 22 Theorem. triangle is isosceles if and only if it has two equal internal angle bisectors. Given: Triangle with <and bisectors E, F. To prove: E > F. onstruction: Point G on such that GF = E. Join G and let it intersect F at H. G F H E Proof : The triangles GH and GF are equiangular with G > G. Therefore, H > F. (Lemma above) Since E > H, E > F.
Chapter 3. The angle bisectors. 3.1 The angle bisector theorem
 hapter 3 The angle bisectors 3.1 The angle bisector theorem Theorem 3.1 (ngle bisector theorem). The bisectors of an angle of a triangle divide its opposite side in the ratio of the remaining sides. If
hapter 3 The angle bisectors 3.1 The angle bisector theorem Theorem 3.1 (ngle bisector theorem). The bisectors of an angle of a triangle divide its opposite side in the ratio of the remaining sides. If
Geometry. Class Examples (July 1) Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2014
 Geometry lass Examples (July 1) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 1 Example 1(a). Given a triangle, the intersection P of the perpendicular bisector of and
Geometry lass Examples (July 1) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 1 Example 1(a). Given a triangle, the intersection P of the perpendicular bisector of and
Geometry. Class Examples (July 1) Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2014
 Geometry lass Examples (July 1) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 21 Example 11: Three congruent circles in a circle. The three small circles are congruent.
Geometry lass Examples (July 1) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 21 Example 11: Three congruent circles in a circle. The three small circles are congruent.
Chapter 2. The laws of sines and cosines. 2.1 The law of sines. Theorem 2.1 (The law of sines). Let R denote the circumradius of a triangle ABC.
 hapter 2 The laws of sines and cosines 2.1 The law of sines Theorem 2.1 (The law of sines). Let R denote the circumradius of a triangle. 2R = a sin α = b sin β = c sin γ. α O O α as Since the area of a
hapter 2 The laws of sines and cosines 2.1 The law of sines Theorem 2.1 (The law of sines). Let R denote the circumradius of a triangle. 2R = a sin α = b sin β = c sin γ. α O O α as Since the area of a
Geometry. Class Examples (July 8) Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2014
 Geometry lass Examples (July 8) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 1 The incircle The internal angle bisectors of a triangle are concurrent at the incenter
Geometry lass Examples (July 8) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 1 The incircle The internal angle bisectors of a triangle are concurrent at the incenter
Geometry. Class Examples (July 10) Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2014
 Geometry lass Examples (July 10) Paul iu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 1 Menelaus theorem Theorem (Menelaus). Given a triangle with points,, on the side lines,,
Geometry lass Examples (July 10) Paul iu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c b a Summer 2014 1 Menelaus theorem Theorem (Menelaus). Given a triangle with points,, on the side lines,,
Theorem 1.2 (Converse of Pythagoras theorem). If the lengths of the sides of ABC satisfy a 2 + b 2 = c 2, then the triangle has a right angle at C.
 hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a + b = c. roof. b a a 3 b b 4 b a b 4 1 a a 3
hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a + b = c. roof. b a a 3 b b 4 b a b 4 1 a a 3
Advanced Euclidean Geometry
 dvanced Euclidean Geometry Paul iu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2016 July 11 Menelaus and eva Theorems Menelaus theorem Theorem 0.1 (Menelaus). Given a triangle with points,,
dvanced Euclidean Geometry Paul iu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2016 July 11 Menelaus and eva Theorems Menelaus theorem Theorem 0.1 (Menelaus). Given a triangle with points,,
The circumcircle and the incircle
 hapter 4 The circumcircle and the incircle 4.1 The Euler line 4.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,.
hapter 4 The circumcircle and the incircle 4.1 The Euler line 4.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,.
Geometry. Class Examples (July 29) Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Summer 2014
 Geometry lass Examples (July 29) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c a Summer 2014 1 The Pythagorean Theorem Theorem (Pythagoras). The lengths a
Geometry lass Examples (July 29) Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University c a Summer 2014 1 The Pythagorean Theorem Theorem (Pythagoras). The lengths a
Chapter 1. Some Basic Theorems. 1.1 The Pythagorean Theorem
 hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a 2 + b 2 = c 2. roof. b a a 3 2 b 2 b 4 b a b
hapter 1 Some asic Theorems 1.1 The ythagorean Theorem Theorem 1.1 (ythagoras). The lengths a b < c of the sides of a right triangle satisfy the relation a 2 + b 2 = c 2. roof. b a a 3 2 b 2 b 4 b a b
Chapter 6. Basic triangle centers. 6.1 The Euler line The centroid
 hapter 6 asic triangle centers 6.1 The Euler line 6.1.1 The centroid Let E and F be the midpoints of and respectively, and G the intersection of the medians E and F. onstruct the parallel through to E,
hapter 6 asic triangle centers 6.1 The Euler line 6.1.1 The centroid Let E and F be the midpoints of and respectively, and G the intersection of the medians E and F. onstruct the parallel through to E,
Construction of a Triangle from the Feet of Its Angle Bisectors
 onstruction of a Triangle from the Feet of Its ngle isectors Paul Yiu bstract. We study the problem of construction of a triangle from the feet of its internal angle bisectors. conic solution is possible.
onstruction of a Triangle from the Feet of Its ngle isectors Paul Yiu bstract. We study the problem of construction of a triangle from the feet of its internal angle bisectors. conic solution is possible.
Chapter 8. Feuerbach s theorem. 8.1 Distance between the circumcenter and orthocenter
 hapter 8 Feuerbach s theorem 8.1 Distance between the circumcenter and orthocenter Y F E Z H N X D Proposition 8.1. H = R 1 8 cosαcos β cosγ). Proof. n triangle H, = R, H = R cosα, and H = β γ. y the law
hapter 8 Feuerbach s theorem 8.1 Distance between the circumcenter and orthocenter Y F E Z H N X D Proposition 8.1. H = R 1 8 cosαcos β cosγ). Proof. n triangle H, = R, H = R cosα, and H = β γ. y the law
XIII GEOMETRICAL OLYMPIAD IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHARYGIN The correspondence round. Solutions
 XIII GEOMETRIL OLYMPID IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN The correspondence round. Solutions 1. (.Zaslavsky) (8) Mark on a cellular paper four nodes forming a convex quadrilateral with the sidelengths equal to
XIII GEOMETRIL OLYMPID IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN The correspondence round. Solutions 1. (.Zaslavsky) (8) Mark on a cellular paper four nodes forming a convex quadrilateral with the sidelengths equal to
Steiner s porism and Feuerbach s theorem
 hapter 10 Steiner s porism and Feuerbach s theorem 10.1 Euler s formula Lemma 10.1. f the bisector of angle intersects the circumcircle at M, then M is the center of the circle through,,, and a. M a Proof.
hapter 10 Steiner s porism and Feuerbach s theorem 10.1 Euler s formula Lemma 10.1. f the bisector of angle intersects the circumcircle at M, then M is the center of the circle through,,, and a. M a Proof.
The Menelaus and Ceva Theorems
 hapter 7 The Menelaus and eva Theorems 7.1 7.1.1 Sign convention Let and be two distinct points. point on the line is said to divide the segment in the ratio :, positive if is between and, and negative
hapter 7 The Menelaus and eva Theorems 7.1 7.1.1 Sign convention Let and be two distinct points. point on the line is said to divide the segment in the ratio :, positive if is between and, and negative
Chapter 4. The angle bisectors. 4.1 The angle bisector theorem
 hapter 4 The angle bisetors 4.1 The angle bisetor theorem Theorem 4.1 (ngle bisetor theorem). The bisetors of an angle of a triangle divide its opposite side in the ratio of the remaining sides. If and
hapter 4 The angle bisetors 4.1 The angle bisetor theorem Theorem 4.1 (ngle bisetor theorem). The bisetors of an angle of a triangle divide its opposite side in the ratio of the remaining sides. If and
= Find the value of n.
 nswers: (0- HKM Heat Events) reated by: Mr. Francis Hung Last updated: pril 0 09 099 00 - Individual 9 0 0900 - Group 0 0 9 0 0 Individual Events I How many pairs of distinct integers between and 0 inclusively
nswers: (0- HKM Heat Events) reated by: Mr. Francis Hung Last updated: pril 0 09 099 00 - Individual 9 0 0900 - Group 0 0 9 0 0 Individual Events I How many pairs of distinct integers between and 0 inclusively
(D) (A) Q.3 To which of the following circles, the line y x + 3 = 0 is normal at the point ? 2 (A) 2
 CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
Survey of Geometry. Supplementary Notes on Elementary Geometry. Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University.
 Survey of Geometry Supplementary Notes on Elementary Geometry Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2007 ontents 1 The Pythagorean theorem i 1.1 The hypotenuse of a right
Survey of Geometry Supplementary Notes on Elementary Geometry Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2007 ontents 1 The Pythagorean theorem i 1.1 The hypotenuse of a right
Definitions. (V.1). A magnitude is a part of a magnitude, the less of the greater, when it measures
 hapter 8 Euclid s Elements ooks V 8.1 V.1-3 efinitions. (V.1). magnitude is a part of a magnitude, the less of the greater, when it measures the greater. (V.2). The greater is a multiple of the less when
hapter 8 Euclid s Elements ooks V 8.1 V.1-3 efinitions. (V.1). magnitude is a part of a magnitude, the less of the greater, when it measures the greater. (V.2). The greater is a multiple of the less when
XIV GEOMETRICAL OLYMPIAD IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHARYGIN The correspondence round. Solutions
 XIV GEOMETRIL OLYMPI IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN The correspondence round. Solutions 1. (L.Shteingarts, grade 8) Three circles lie inside a square. Each of them touches externally two remaining circles. lso
XIV GEOMETRIL OLYMPI IN HONOUR OF I.F.SHRYGIN The correspondence round. Solutions 1. (L.Shteingarts, grade 8) Three circles lie inside a square. Each of them touches externally two remaining circles. lso
Conic Construction of a Triangle from the Feet of Its Angle Bisectors
 onic onstruction of a Triangle from the Feet of Its ngle isectors Paul Yiu bstract. We study an extension of the problem of construction of a triangle from the feet of its internal angle bisectors. Given
onic onstruction of a Triangle from the Feet of Its ngle isectors Paul Yiu bstract. We study an extension of the problem of construction of a triangle from the feet of its internal angle bisectors. Given
Menelaus and Ceva theorems
 hapter 3 Menelaus and eva theorems 3.1 Menelaus theorem Theorem 3.1 (Menelaus). Given a triangle with points,, on the side lines,, respectively, the points,, are collinear if and only if = 1. W Proof.
hapter 3 Menelaus and eva theorems 3.1 Menelaus theorem Theorem 3.1 (Menelaus). Given a triangle with points,, on the side lines,, respectively, the points,, are collinear if and only if = 1. W Proof.
BOARD ANSWER PAPER :OCTOBER 2014
 BRD NSWER PPER :CTBER 04 GEETRY. Solve any five sub-questions: BE i. BE ( BD) D BE 6 ( BD) 9 ΔBE (ΔBD) ----[Ratio of areas of two triangles having equal base is equal to the ratio of their corresponding
BRD NSWER PPER :CTBER 04 GEETRY. Solve any five sub-questions: BE i. BE ( BD) D BE 6 ( BD) 9 ΔBE (ΔBD) ----[Ratio of areas of two triangles having equal base is equal to the ratio of their corresponding
CIRCLES. ii) P lies in the circle S = 0 s 11 = 0
 CIRCLES 1 The set of points in a plane which are at a constant distance r ( 0) from a given point C is called a circle The fixed point C is called the centre and the constant distance r is called the radius
CIRCLES 1 The set of points in a plane which are at a constant distance r ( 0) from a given point C is called a circle The fixed point C is called the centre and the constant distance r is called the radius
Review exercise 2. 1 The equation of the line is: = 5 a The gradient of l1 is 3. y y x x. So the gradient of l2 is. The equation of line l2 is: y =
 Review exercise The equation of the line is: y y x x y y x x y 8 x+ 6 8 + y 8 x+ 6 y x x + y 0 y ( ) ( x 9) y+ ( x 9) y+ x 9 x y 0 a, b, c Using points A and B: y y x x y y x x y x 0 k 0 y x k ky k x a
Review exercise The equation of the line is: y y x x y y x x y 8 x+ 6 8 + y 8 x+ 6 y x x + y 0 y ( ) ( x 9) y+ ( x 9) y+ x 9 x y 0 a, b, c Using points A and B: y y x x y y x x y x 0 k 0 y x k ky k x a
Some Collinearities in the Heptagonal Triangle
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 16 (2016) 249 256. FRUM GEM ISSN 1534-1178 Some ollinearities in the Heptagonal Triangle bdilkadir ltintaş bstract. With the methods of barycentric coordinates, we establish
Forum Geometricorum Volume 16 (2016) 249 256. FRUM GEM ISSN 1534-1178 Some ollinearities in the Heptagonal Triangle bdilkadir ltintaş bstract. With the methods of barycentric coordinates, we establish
Inequalities for Triangles and Pointwise Characterizations
 Inequalities for Triangles and Pointwise haracterizations Theorem (The Scalene Inequality): If one side of a triangle has greater length than another side, then the angle opposite the longer side has the
Inequalities for Triangles and Pointwise haracterizations Theorem (The Scalene Inequality): If one side of a triangle has greater length than another side, then the angle opposite the longer side has the
Examples: Identify three pairs of parallel segments in the diagram. 1. AB 2. BC 3. AC. Write an equation to model this theorem based on the figure.
 5.1: Midsegments of Triangles NOTE: Midsegments are also to the third side in the triangle. Example: Identify the 3 midsegments in the diagram. Examples: Identify three pairs of parallel segments in the
5.1: Midsegments of Triangles NOTE: Midsegments are also to the third side in the triangle. Example: Identify the 3 midsegments in the diagram. Examples: Identify three pairs of parallel segments in the
Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad Training Problems
 Singapore International athematical Olympiad Training Problems 18 January 2003 1 Let be a point on the segment Squares D and EF are erected on the same side of with F lying on The circumcircles of D and
Singapore International athematical Olympiad Training Problems 18 January 2003 1 Let be a point on the segment Squares D and EF are erected on the same side of with F lying on The circumcircles of D and
Plane geometry Circles: Problems with some Solutions
 The University of Western ustralia SHL F MTHMTIS & STTISTIS UW MY FR YUNG MTHMTIINS Plane geometry ircles: Problems with some Solutions 1. Prove that for any triangle, the perpendicular bisectors of the
The University of Western ustralia SHL F MTHMTIS & STTISTIS UW MY FR YUNG MTHMTIINS Plane geometry ircles: Problems with some Solutions 1. Prove that for any triangle, the perpendicular bisectors of the
MT - GEOMETRY - SEMI PRELIM - II : PAPER - 4
 017 1100 MT.1. ttempt NY FIVE of the following : (i) In STR, line l side TR S SQ T = RQ x 4.5 = 1.3 3.9 x = MT - GEOMETRY - SEMI RELIM - II : ER - 4 Time : Hours Model nswer aper Max. Marks : 40 4.5 1.3
017 1100 MT.1. ttempt NY FIVE of the following : (i) In STR, line l side TR S SQ T = RQ x 4.5 = 1.3 3.9 x = MT - GEOMETRY - SEMI RELIM - II : ER - 4 Time : Hours Model nswer aper Max. Marks : 40 4.5 1.3
22 SAMPLE PROBLEMS WITH SOLUTIONS FROM 555 GEOMETRY PROBLEMS
 22 SPL PROLS WITH SOLUTIOS FRO 555 GOTRY PROLS SOLUTIOS S O GOTRY I FIGURS Y. V. KOPY Stanislav hobanov Stanislav imitrov Lyuben Lichev 1 Problem 3.9. Let be a quadrilateral. Let J and I be the midpoints
22 SPL PROLS WITH SOLUTIOS FRO 555 GOTRY PROLS SOLUTIOS S O GOTRY I FIGURS Y. V. KOPY Stanislav hobanov Stanislav imitrov Lyuben Lichev 1 Problem 3.9. Let be a quadrilateral. Let J and I be the midpoints
MAHESH TUTORIALS. Time : 1 hr. 15 min. Q.1. Solve the following : 3
 S.S.. MHESH TUTRILS Test - II atch : S Marks : 30 Date : GEMETRY hapter : 1,, 3 Time : 1 hr. 15 min..1. Solve the following : 3 The areas of two similar triangles are 18 cm and 3 cm respectively. What
S.S.. MHESH TUTRILS Test - II atch : S Marks : 30 Date : GEMETRY hapter : 1,, 3 Time : 1 hr. 15 min..1. Solve the following : 3 The areas of two similar triangles are 18 cm and 3 cm respectively. What
Heptagonal Triangles and Their Companions
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 9 (009) 15 148. FRUM GEM ISSN 1534-1178 Heptagonal Triangles and Their ompanions Paul Yiu bstract. heptagonal triangle is a non-isosceles triangle formed by three vertices of
Forum Geometricorum Volume 9 (009) 15 148. FRUM GEM ISSN 1534-1178 Heptagonal Triangles and Their ompanions Paul Yiu bstract. heptagonal triangle is a non-isosceles triangle formed by three vertices of
Problem Solving and Recreational Mathematics
 Problem Solving and Recreational Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2012 Chapters 16 33 July 20 Monday 6/25 7/2 7/9 7/16 7/23 7/30 Wednesday 6/27 *** 7/11
Problem Solving and Recreational Mathematics Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Summer 2012 Chapters 16 33 July 20 Monday 6/25 7/2 7/9 7/16 7/23 7/30 Wednesday 6/27 *** 7/11
Integrated Math II. IM2.1.2 Interpret given situations as functions in graphs, formulas, and words.
 Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday October Problem Set 3
 The CETRE for EDUCTI in MTHEMTICS and CMPUTIG Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday ctober 24 2012 Problem Set 3.. Unless otherwise stated, any point labelled is assumed to represent the centre of the circle.
The CETRE for EDUCTI in MTHEMTICS and CMPUTIG Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday ctober 24 2012 Problem Set 3.. Unless otherwise stated, any point labelled is assumed to represent the centre of the circle.
GEOMETRY. Similar Triangles
 GOMTRY Similar Triangles SIMILR TRINGLS N THIR PROPRTIS efinition Two triangles are said to be similar if: (i) Their corresponding angles are equal, and (ii) Their corresponding sides are proportional.
GOMTRY Similar Triangles SIMILR TRINGLS N THIR PROPRTIS efinition Two triangles are said to be similar if: (i) Their corresponding angles are equal, and (ii) Their corresponding sides are proportional.
2. (i) Find the equation of the circle which passes through ( 7, 1) and has centre ( 4, 3).
 Circle 1. (i) Find the equation of the circle with centre ( 7, 3) and of radius 10. (ii) Find the centre of the circle 2x 2 + 2y 2 + 6x + 8y 1 = 0 (iii) What is the radius of the circle 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 5x
Circle 1. (i) Find the equation of the circle with centre ( 7, 3) and of radius 10. (ii) Find the centre of the circle 2x 2 + 2y 2 + 6x + 8y 1 = 0 (iii) What is the radius of the circle 3x 2 + 3y 2 + 5x
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE
 QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
XI Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. Grade 8. First day. Solutions Ratmino, 2015, July 30.
 XI Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. Grade 8. First day. Solutions Ratmino, 2015, July 30. 1. (V. Yasinsky) In trapezoid D angles and are right, = D, D = + D, < D. Prove that
XI Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. Grade 8. First day. Solutions Ratmino, 2015, July 30. 1. (V. Yasinsky) In trapezoid D angles and are right, = D, D = + D, < D. Prove that
Chapter 19 Exercise 19.1
 hapter 9 xercise 9... (i) n axiom is a statement that is accepted but cannot be proven, e.g. x + 0 = x. (ii) statement that can be proven logically: for example, ythagoras Theorem. (iii) The logical steps
hapter 9 xercise 9... (i) n axiom is a statement that is accepted but cannot be proven, e.g. x + 0 = x. (ii) statement that can be proven logically: for example, ythagoras Theorem. (iii) The logical steps
Trigonometric Fundamentals
 1 Trigonometric Fundamentals efinitions of Trigonometric Functions in Terms of Right Triangles Let S and T be two sets. function (or mapping or map) f from S to T (written as f : S T ) assigns to each
1 Trigonometric Fundamentals efinitions of Trigonometric Functions in Terms of Right Triangles Let S and T be two sets. function (or mapping or map) f from S to T (written as f : S T ) assigns to each
IX Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. Ratmino, 2013, August 1 = 90 ECD = 90 DBC = ABF,
 IX Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. Ratmino, 013, ugust 1 Solutions First day. 8 grade 8.1. (N. Moskvitin) Let E be a pentagon with right angles at vertices and E and such that
IX Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. Ratmino, 013, ugust 1 Solutions First day. 8 grade 8.1. (N. Moskvitin) Let E be a pentagon with right angles at vertices and E and such that
Circles in Neutral Geometry
 Everything we do in this set of notes is Neutral. Definitions: 10.1 - Circles in Neutral Geometry circle is the set of points in a plane which lie at a positive, fixed distance r from some fixed point.
Everything we do in this set of notes is Neutral. Definitions: 10.1 - Circles in Neutral Geometry circle is the set of points in a plane which lie at a positive, fixed distance r from some fixed point.
Harmonic Division and its Applications
 Harmonic ivision and its pplications osmin Pohoata Let d be a line and,,, and four points which lie in this order on it. he four-point () is called a harmonic division, or simply harmonic, if =. If is
Harmonic ivision and its pplications osmin Pohoata Let d be a line and,,, and four points which lie in this order on it. he four-point () is called a harmonic division, or simply harmonic, if =. If is
The Apollonian Circles and Isodynamic Points
 The pollonian ircles and Isodynamic Points Tarik dnan oon bstract This paper is on the pollonian circles and isodynamic points of a triangle. Here we discuss some of the most intriguing properties of pollonian
The pollonian ircles and Isodynamic Points Tarik dnan oon bstract This paper is on the pollonian circles and isodynamic points of a triangle. Here we discuss some of the most intriguing properties of pollonian
11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers, and Hints
 view.php3 (JPEG Image, 840x888 pixels) - Scaled (71%) https://mail.ateneo.net/horde/imp/view.php3?mailbox=inbox&inde... 1 of 1 11/5/2008 5:02 PM 11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers,
view.php3 (JPEG Image, 840x888 pixels) - Scaled (71%) https://mail.ateneo.net/horde/imp/view.php3?mailbox=inbox&inde... 1 of 1 11/5/2008 5:02 PM 11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers,
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch
 Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. in the parallelogram, each two opposite
Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. in the parallelogram, each two opposite
XII Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. Solutions. First day. 8 grade
 XII Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. Solutions. First day. 8 grade Ratmino, 2016, July 31 1. (Yu.linkov) n altitude H of triangle bisects a median M. Prove that the medians of
XII Geometrical Olympiad in honour of I.F.Sharygin Final round. Solutions. First day. 8 grade Ratmino, 2016, July 31 1. (Yu.linkov) n altitude H of triangle bisects a median M. Prove that the medians of
= 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ]
![= 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ] = 0 1 (3 4 ) 1 (4 4) + 1 (4 3) = = + 1 = 0 = 1 = ± 1 ]](/thumbs/74/71228184.jpg) STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; x + y + = 0 and x + y + = 0, where + =, are concurrent then (A) =, = (B) =, = ± (C) =, = ± (D*) = ±, = [Sol. Lines are x + y + = 0
STRAIGHT LINE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; x + y + = 0 and x + y + = 0, where + =, are concurrent then (A) =, = (B) =, = ± (C) =, = ± (D*) = ±, = [Sol. Lines are x + y + = 0
Survey of Geometry. Paul Yiu. Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University. Spring 2007
 Survey of Geometry Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Spring 2007 ontents 1 The circumcircle and the incircle 1 1.1 The law of cosines and its applications.............. 1 1.2
Survey of Geometry Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida tlantic University Spring 2007 ontents 1 The circumcircle and the incircle 1 1.1 The law of cosines and its applications.............. 1 1.2
Affine Transformations
 Solutions to hapter Problems 435 Then, using α + β + γ = 360, we obtain: ( ) x a = (/2) bc sin α a + ac sin β b + ab sin γ c a ( ) = (/2) bc sin α a 2 + (ac sin β)(ab cos γ ) + (ab sin γ )(ac cos β) =
Solutions to hapter Problems 435 Then, using α + β + γ = 360, we obtain: ( ) x a = (/2) bc sin α a + ac sin β b + ab sin γ c a ( ) = (/2) bc sin α a 2 + (ac sin β)(ab cos γ ) + (ab sin γ )(ac cos β) =
Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths
![Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths](/thumbs/86/93150791.jpg) Topic 2 [312 marks] 1 The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths [12 marks] 3 cm and (\9\) cm respectively E is a point on side [AB] such that AE is 3 cm Side [DE] is
Topic 2 [312 marks] 1 The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths [12 marks] 3 cm and (\9\) cm respectively E is a point on side [AB] such that AE is 3 cm Side [DE] is
GEOMETRY OF KIEPERT AND GRINBERG MYAKISHEV HYPERBOLAS
 GEOMETRY OF KIEPERT ND GRINERG MYKISHEV HYPEROLS LEXEY. ZSLVSKY bstract. new synthetic proof of the following fact is given: if three points,, are the apices of isosceles directly-similar triangles,, erected
GEOMETRY OF KIEPERT ND GRINERG MYKISHEV HYPEROLS LEXEY. ZSLVSKY bstract. new synthetic proof of the following fact is given: if three points,, are the apices of isosceles directly-similar triangles,, erected
INVERSION IN THE PLANE BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE
 INVERSION IN THE PLANE BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE ZVEZDELINA STANKOVA MILLS COLLEGE/UC BERKELEY SEPTEMBER 26TH 2004 Contents 1. Definition of Inversion in the Plane 1 Properties of Inversion 2 Problems 2 2.
INVERSION IN THE PLANE BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE ZVEZDELINA STANKOVA MILLS COLLEGE/UC BERKELEY SEPTEMBER 26TH 2004 Contents 1. Definition of Inversion in the Plane 1 Properties of Inversion 2 Problems 2 2.
Triangles III. Stewart s Theorem (1746) Stewart s Theorem (1746) 9/26/2011. Stewart s Theorem, Orthocenter, Euler Line
 Triangles III Stewart s Theorem, Orthocenter, uler Line 23-Sept-2011 M 341 001 1 Stewart s Theorem (1746) With the measurements given in the triangle below, the following relationship holds: a 2 n + b
Triangles III Stewart s Theorem, Orthocenter, uler Line 23-Sept-2011 M 341 001 1 Stewart s Theorem (1746) With the measurements given in the triangle below, the following relationship holds: a 2 n + b
6.2: Isosceles Triangles
 6.2: Isosceles Triangles Dec 5 4:34 PM 1 Define an Isosceles Triangle. A triangle that has (at least) two sides of equal length. Dec 5 4:34 PM 2 Draw an Isosceles Triangle. Label all parts and mark the
6.2: Isosceles Triangles Dec 5 4:34 PM 1 Define an Isosceles Triangle. A triangle that has (at least) two sides of equal length. Dec 5 4:34 PM 2 Draw an Isosceles Triangle. Label all parts and mark the
MT - MATHEMATICS (71) GEOMETRY - PRELIM II - PAPER - 1 (E)
 04 00 eat No. MT - MTHEMTI (7) GEOMETY - PELIM II - PPE - (E) Time : Hours (Pages 3) Max. Marks : 40 Note : (i) ll questions are compulsory. Use of calculator is not allowed. Q.. olve NY FIVE of the following
04 00 eat No. MT - MTHEMTI (7) GEOMETY - PELIM II - PPE - (E) Time : Hours (Pages 3) Max. Marks : 40 Note : (i) ll questions are compulsory. Use of calculator is not allowed. Q.. olve NY FIVE of the following
Hagge circles revisited
 agge circles revisited Nguyen Van Linh 24/12/2011 bstract In 1907, Karl agge wrote an article on the construction of circles that always pass through the orthocenter of a given triangle. The purpose of
agge circles revisited Nguyen Van Linh 24/12/2011 bstract In 1907, Karl agge wrote an article on the construction of circles that always pass through the orthocenter of a given triangle. The purpose of
Introduction Circle Some terms related with a circle
 141 ircle Introduction In our day-to-day life, we come across many objects which are round in shape, such as dials of many clocks, wheels of a vehicle, bangles, key rings, coins of denomination ` 1, `
141 ircle Introduction In our day-to-day life, we come across many objects which are round in shape, such as dials of many clocks, wheels of a vehicle, bangles, key rings, coins of denomination ` 1, `
Time : 2 Hours (Pages 3) Max. Marks : 40. Q.1. Solve the following : (Any 5) 5 In PQR, m Q = 90º, m P = 30º, m R = 60º. If PR = 8 cm, find QR.
 Q.P. SET CODE Q.1. Solve the following : (ny 5) 5 (i) (ii) In PQR, m Q 90º, m P 0º, m R 60º. If PR 8 cm, find QR. O is the centre of the circle. If m C 80º, the find m (arc C) and m (arc C). Seat No. 01
Q.P. SET CODE Q.1. Solve the following : (ny 5) 5 (i) (ii) In PQR, m Q 90º, m P 0º, m R 60º. If PR 8 cm, find QR. O is the centre of the circle. If m C 80º, the find m (arc C) and m (arc C). Seat No. 01
On the Circumcenters of Cevasix Configurations
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 3 (2003) 57 63. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On the ircumcenters of evasix onfigurations lexei Myakishev and Peter Y. Woo bstract. We strengthen Floor van Lamoen s theorem that
Forum Geometricorum Volume 3 (2003) 57 63. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On the ircumcenters of evasix onfigurations lexei Myakishev and Peter Y. Woo bstract. We strengthen Floor van Lamoen s theorem that
chapter 1 vector geometry solutions V Consider the parallelogram shown alongside. Which of the following statements are true?
 chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
Objective Mathematics
 . In BC, if angles, B, C are in geometric seq- uence with common ratio, then is : b c a (a) (c) 0 (d) 6. If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 4 : :, then the ratio of the longest side to the perimeter
. In BC, if angles, B, C are in geometric seq- uence with common ratio, then is : b c a (a) (c) 0 (d) 6. If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 4 : :, then the ratio of the longest side to the perimeter
MATH 243 Winter 2008 Geometry II: Transformation Geometry Solutions to Problem Set 1 Completion Date: Monday January 21, 2008
 MTH 4 Winter 008 Geometry II: Transformation Geometry Solutions to Problem Set 1 ompletion Date: Monday January 1, 008 Department of Mathematical Statistical Sciences University of lberta Question 1. Let
MTH 4 Winter 008 Geometry II: Transformation Geometry Solutions to Problem Set 1 ompletion Date: Monday January 1, 008 Department of Mathematical Statistical Sciences University of lberta Question 1. Let
Properties of Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
 Properties of Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles In an isosceles triangle, the sides and the angles of the triangle are classified by their position in relation to the triangle s congruent sides. Leg
Properties of Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles In an isosceles triangle, the sides and the angles of the triangle are classified by their position in relation to the triangle s congruent sides. Leg
Menelaus and Ceva theorems
 hapter 21 Menelaus and eva theorems 21.1 Menelaus theorem Theorem 21.1 (Menelaus). Given a triangle with points,, on the side lines,, respectively, the points,, are collinear if and only if = 1. W Proof.
hapter 21 Menelaus and eva theorems 21.1 Menelaus theorem Theorem 21.1 (Menelaus). Given a triangle with points,, on the side lines,, respectively, the points,, are collinear if and only if = 1. W Proof.
Q1. If (1, 2) lies on the circle. x 2 + y 2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0. which is concentric with the circle x 2 + y 2 +4x + 2y 5 = 0 then c =
 Q1. If (1, 2) lies on the circle x 2 + y 2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentric with the circle x 2 + y 2 +4x + 2y 5 = 0 then c = a) 11 b) -13 c) 24 d) 100 Solution: Any circle concentric with x 2 +
Q1. If (1, 2) lies on the circle x 2 + y 2 + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0 which is concentric with the circle x 2 + y 2 +4x + 2y 5 = 0 then c = a) 11 b) -13 c) 24 d) 100 Solution: Any circle concentric with x 2 +
Homework Assignments Math /02 Fall 2017
 Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2017 Assignment 1 Due date : Wednesday, August 30 Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14, 16, 17, 18, 20, 22,
Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2017 Assignment 1 Due date : Wednesday, August 30 Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14, 16, 17, 18, 20, 22,
Chapter 1. Theorems of Ceva and Menelaus
 hapter 1 Theorems of eva and Menelaus We start these lectures by proving some of the most basic theorems in the geometry of a planar triangle. Let,, be the vertices of the triangle and,, be any points
hapter 1 Theorems of eva and Menelaus We start these lectures by proving some of the most basic theorems in the geometry of a planar triangle. Let,, be the vertices of the triangle and,, be any points
1. Matrices and Determinants
 Important Questions 1. Matrices and Determinants Ex.1.1 (2) x 3x y Find the values of x, y, z if 2x + z 3y w = 0 7 3 2a Ex 1.1 (3) 2x 3x y If 2x + z 3y w = 3 2 find x, y, z, w 4 7 Ex 1.1 (13) 3 7 3 2 Find
Important Questions 1. Matrices and Determinants Ex.1.1 (2) x 3x y Find the values of x, y, z if 2x + z 3y w = 0 7 3 2a Ex 1.1 (3) 2x 3x y If 2x + z 3y w = 3 2 find x, y, z, w 4 7 Ex 1.1 (13) 3 7 3 2 Find
1 k. cos tan? Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. 1. A sequence is defined by the recurrence relation u 2u 1, u 3.
 Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
Higher Maths Non Calculator Practice Practice Paper A. A sequence is defined b the recurrence relation u u, u. n n What is the value of u?. The line with equation k 9 is parallel to the line with gradient
NEW YORK CITY INTERSCHOLASTIC MATHEMATICS LEAGUE Senior A Division CONTEST NUMBER 1
 Senior A Division CONTEST NUMBER 1 PART I FALL 2011 CONTEST 1 TIME: 10 MINUTES F11A1 Larry selects a 13-digit number while David selects a 10-digit number. Let be the number of digits in the product of
Senior A Division CONTEST NUMBER 1 PART I FALL 2011 CONTEST 1 TIME: 10 MINUTES F11A1 Larry selects a 13-digit number while David selects a 10-digit number. Let be the number of digits in the product of
History of Mathematics Workbook
 History of Mathematics Workbook Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Last Update: April 7, 2014 Student: Spring 2014 Problem A1. Given a square ABCD, equilateral triangles ABX
History of Mathematics Workbook Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Last Update: April 7, 2014 Student: Spring 2014 Problem A1. Given a square ABCD, equilateral triangles ABX
10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152]
![10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152] 10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152]](/thumbs/94/121826807.jpg) foot of the altitude of ABM from M and let A M 1 B. Prove that then MA > MB if and only if M 1 A > M 1 B. 8. If M is the midpoint of BC then AM is called a median of ABC. Consider ABC such that AB < AC.
foot of the altitude of ABM from M and let A M 1 B. Prove that then MA > MB if and only if M 1 A > M 1 B. 8. If M is the midpoint of BC then AM is called a median of ABC. Consider ABC such that AB < AC.
In this article we examine a famous and important result in
 How to Prove It In this episode of How To Prove It, we prove a striking theorem first discovered by Ptolemy. We then discuss some nice applications of the theorem. lassroom In this article we examine a
How to Prove It In this episode of How To Prove It, we prove a striking theorem first discovered by Ptolemy. We then discuss some nice applications of the theorem. lassroom In this article we examine a
Another Variation on the Steiner-Lehmus Theme
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 8 (2008) 131 140. FORUM GOM ISSN 1534-1178 Another Variation on the Steiner-Lehmus Theme Sadi Abu-Saymeh, Mowaffaq Hajja, and Hassan Ali ShahAli Abstract. Let the internal angle
Forum Geometricorum Volume 8 (2008) 131 140. FORUM GOM ISSN 1534-1178 Another Variation on the Steiner-Lehmus Theme Sadi Abu-Saymeh, Mowaffaq Hajja, and Hassan Ali ShahAli Abstract. Let the internal angle
Arkansas Council of Teachers of Mathematics 2012 State Competition Geometry Exam. B. 28 (5x-41) 3 m (2x+25)
 rkansas ouncil of Teachers of Mathematics 2012 State ompetition Geometry Exam For questions 1 through 25, mark your answer choice on the answer sheet provided. (Figures may not be drawn to scale.) fter
rkansas ouncil of Teachers of Mathematics 2012 State ompetition Geometry Exam For questions 1 through 25, mark your answer choice on the answer sheet provided. (Figures may not be drawn to scale.) fter
Homework Assignments Math /02 Fall 2014
 Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2014 Assignment 1 Due date : Friday, September 5 6th Edition Problem Set Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14,
Homework Assignments Math 119-01/02 Fall 2014 Assignment 1 Due date : Friday, September 5 6th Edition Problem Set Section 6.1, Page 178: #1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6. Section 6.2, Page 185: #1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10-14,
( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear.
 Problems 01 - POINT Page 1 ( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear. ( ) Prove that the two lines joining the mid-points of the pairs of opposite sides and the line
Problems 01 - POINT Page 1 ( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear. ( ) Prove that the two lines joining the mid-points of the pairs of opposite sides and the line
MT - w A.P. SET CODE MT - w - MATHEMATICS (71) GEOMETRY- SET - A (E) Time : 2 Hours Preliminary Model Answer Paper Max.
 .P. SET CODE.. Solve NY FIVE of the following : (i) ( BE) ( BD) ( BE) ( BD) BE D 6 9 MT - w 07 00 - MT - w - MTHEMTICS (7) GEOMETRY- (E) Time : Hours Preliminary Model nswer Paper Max. Marks : 40 [Triangles
.P. SET CODE.. Solve NY FIVE of the following : (i) ( BE) ( BD) ( BE) ( BD) BE D 6 9 MT - w 07 00 - MT - w - MTHEMTICS (7) GEOMETRY- (E) Time : Hours Preliminary Model nswer Paper Max. Marks : 40 [Triangles
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example altitude of a triangle. centroid of a triangle. circumcenter of a triangle. circumscribed circle
 CHAPTER Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying eample. Term Page Definition Clarifying
CHAPTER Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying eample. Term Page Definition Clarifying
Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad 2008 Senior Team Training. Take Home Test Solutions. 15x 2 7y 2 = 9 y 2 0 (mod 3) x 0 (mod 3).
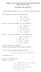 Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad 2008 Senior Team Training Take Home Test Solutions. Show that the equation 5x 2 7y 2 = 9 has no solution in integers. If the equation has a solution in integer,
Singapore International Mathematical Olympiad 2008 Senior Team Training Take Home Test Solutions. Show that the equation 5x 2 7y 2 = 9 has no solution in integers. If the equation has a solution in integer,
OLYMON. Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Issue 5:10.
 OLYMON Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Issue 5:10 November, 2004 Please send your solutions to Prof. Edward J. Barbeau Department
OLYMON Produced by the Canadian Mathematical Society and the Department of Mathematics of the University of Toronto. Issue 5:10 November, 2004 Please send your solutions to Prof. Edward J. Barbeau Department
Problems First day. 8 grade. Problems First day. 8 grade
 First day. 8 grade 8.1. Let ABCD be a cyclic quadrilateral with AB = = BC and AD = CD. ApointM lies on the minor arc CD of its circumcircle. The lines BM and CD meet at point P, thelinesam and BD meet
First day. 8 grade 8.1. Let ABCD be a cyclic quadrilateral with AB = = BC and AD = CD. ApointM lies on the minor arc CD of its circumcircle. The lines BM and CD meet at point P, thelinesam and BD meet
UNIT 1: SIMILARITY, CONGRUENCE, AND PROOFS. 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1).
 1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1). The dilation is Which statement is true? A. B. C. D. AB B' C' A' B' BC AB BC A' B' B' C' AB BC A' B' D'
1) Figure A'B'C'D'F' is a dilation of figure ABCDF by a scale factor of 1. 2 centered at ( 4, 1). The dilation is Which statement is true? A. B. C. D. AB B' C' A' B' BC AB BC A' B' B' C' AB BC A' B' D'
Three Natural Homoteties of The Nine-Point Circle
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) 209 218. FRUM GEM ISS 1534-1178 Three atural omoteties of The ine-point ircle Mehmet Efe kengin, Zeyd Yusuf Köroğlu, and Yiğit Yargiç bstract. Given a triangle with
Forum Geometricorum Volume 13 (2013) 209 218. FRUM GEM ISS 1534-1178 Three atural omoteties of The ine-point ircle Mehmet Efe kengin, Zeyd Yusuf Köroğlu, and Yiğit Yargiç bstract. Given a triangle with
Higher Geometry Problems
 Higher Geometry Problems (1) Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
Higher Geometry Problems (1) Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
Chapter 6 Summary 6.1. Using the Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) Congruence Theorem. Example
 Chapter Summary Key Terms corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent (CPCTC) (.2) vertex angle of an isosceles triangle (.3) inverse (.4) contrapositive (.4) direct proof (.4) indirect proof
Chapter Summary Key Terms corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent (CPCTC) (.2) vertex angle of an isosceles triangle (.3) inverse (.4) contrapositive (.4) direct proof (.4) indirect proof
RMT 2014 Geometry Test Solutions February 15, 2014
 RMT 014 Geometry Test Solutions February 15, 014 1. The coordinates of three vertices of a parallelogram are A(1, 1), B(, 4), and C( 5, 1). Compute the area of the parallelogram. Answer: 18 Solution: Note
RMT 014 Geometry Test Solutions February 15, 014 1. The coordinates of three vertices of a parallelogram are A(1, 1), B(, 4), and C( 5, 1). Compute the area of the parallelogram. Answer: 18 Solution: Note
 Solved Paper SSC Maharashtra Exam March 207 Class - X Geometry Time : 2 Hours Max. Marks : 40 Note : (i) Solve all questions. Draw diagrams wherever necessary. (ii) Use of calculator is not allowed. (iii)
Solved Paper SSC Maharashtra Exam March 207 Class - X Geometry Time : 2 Hours Max. Marks : 40 Note : (i) Solve all questions. Draw diagrams wherever necessary. (ii) Use of calculator is not allowed. (iii)
(c) log 1 4 (d) log 3 3. Use logarithm properties for expanding to rewrite the expression in
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment for 2017-2018 School Year Mrs. Brennan In order to be prepared for next year and be ready to move on to new work, you must have skills required to do these problems with
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment for 2017-2018 School Year Mrs. Brennan In order to be prepared for next year and be ready to move on to new work, you must have skills required to do these problems with
Generalized Archimedean Arbelos Twins
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 4 (204) 409 48 FORUM GEOM ISSN 534-78 Generalized rchimedean rbelos Twins Nikolaos Dergiades bstract We generalize the well known rchimedean arbelos twins by extending the notion
Forum Geometricorum Volume 4 (204) 409 48 FORUM GEOM ISSN 534-78 Generalized rchimedean rbelos Twins Nikolaos Dergiades bstract We generalize the well known rchimedean arbelos twins by extending the notion
2002 Solutions Euclid Contest(Grade 12)
 Canadian Mathematics Competition n activity of The Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 00 Solutions Euclid Contest(Grade ) for The CENTRE for EDUCTION
Canadian Mathematics Competition n activity of The Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 00 Solutions Euclid Contest(Grade ) for The CENTRE for EDUCTION
Name: GEOMETRY: EXAM (A) A B C D E F G H D E. 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane?
 GMTRY: XM () Name: 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane? ) none ) one ) two ) three 2. How many edges does a heagonal prism have? ) 6 ) 12 ) 18 ) 2. Name the intersection of planes Q and
GMTRY: XM () Name: 1. How many non collinear points determine a plane? ) none ) one ) two ) three 2. How many edges does a heagonal prism have? ) 6 ) 12 ) 18 ) 2. Name the intersection of planes Q and
The Kiepert Pencil of Kiepert Hyperbolas
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 1 (2001) 125 132. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 The Kiepert Pencil of Kiepert Hyperbolas Floor van Lamoen and Paul Yiu bstract. We study Kiepert triangles K(φ) and their iterations
Forum Geometricorum Volume 1 (2001) 125 132. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 The Kiepert Pencil of Kiepert Hyperbolas Floor van Lamoen and Paul Yiu bstract. We study Kiepert triangles K(φ) and their iterations
