THE EFFFCT OF TORSIONAL OSCILLATIONS ON EARTHQUAKE STRESSES
|
|
|
- Mervin Roberts
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
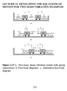
1 Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. Vol. 48, pp July 1958 THE EFFFCT OF TORSIONAL OSCILLATIONS ON EARTHQUAKE STRESSES By GEORGE W. HOUSNER and HANNU OUTINEN ABSTRACT A comparison is made between the maximum stresses induced by earthquake-excited vibrations of an unsymmetrical structure and those induced in a symmetrical structure. These stresses are compared with the commonly used equivalent static method of analysis, and it is shown that the static method underestimates significantly the magnitude of the maximum stresses. Although the maximum stresses are quite sensitive to changes in the relative rigidity of the walls, an energy analysis of the vibration problem shows that the relative rigidities are not crucially important in determining the ultimate strength of the building. DURING an earthquake, buildings that are not symmetrical in mass and stiffness will undergo torsional oscillations in addition to the normal horizontally directed oscillations. The nonsymmetrical features will affect the induced stresses, and it is customary to compute the resulting stresses by means of a static analysis. For example, in the case of a one-story building a certain equivalent static force is assumed to act through the center of mass of the structure, and the forces in the resisting members are computed on the basis of an elastic analysis. For more complicated structures it can become very difficult to conceive of a static method of analysis, and even for a simple structure the accuracy of the static method has not been investigated. The present paper reports the results of an investigation of the accuracy of the static method. The results obtained by this method are compared with the results of a dynamic analysis. The investigation was concerned only with rectangular, onestory buildings. Similar studies should be made of multistory buildings. Dynamic analysis of the structure.--the building has plan dimensions as indicated in figure la. The roof of the building is assumed to be a rigid slab and the walls to be linearly elastic with spring constants ks, k2, k3. The center of mass of the structure is assumed to coincide with the geometric center of the building. The equivalent vibration problem is then as shown in figure lb, where four springs restrain a block having mass m and moment of inertia I about the mass center. Under the action of ground acceleration?) the block's center of mass will be excited into horizontal oscillations, and the block will also execute torsional oscillations about the center of mass. These motions can be described by the horizontal displacements y, and y2 as shown in figure lb. The forces in the springs (or walls) will be given byc~y~ and k~y~ so that yl and y~ are the displacements relative to the ground. The differential equations describing the motion are + I yl+ 4 ~ ~)2+ ] 1 + ~a 2 ]~3 yl- ~a ~ ]~3 y~ -- 2 ~) (1) (a i ~]~+ + ~ ij~ - ~a ~k~yl k2 + ~a 2ks y~ = 2 y (2) Manuscript received for publication January 29, 1958.
2 - $1-222 BULLETIN OF THE SEIS]V[OLOGICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA The roots of the frequency equations are where 2 ci + k2 pl, 2-2o~m [(1 + ~ + 8) ± I( ~)2 + 4.(1 - R)2}~] O - I ma 2 k~b 2 (3) R - 2kl kl -~ k2 k 3 kz C,m. The displacements are given by a l * k3 a Fig. la. yl - 2aliA1 2a12 A $2 = CIS1 ~- DIS2 (4) P~ P: y~ = -2a21A1 - S1 pl 2a22A2 $2 = C2S1 "1- D2S2 p2 (5) where ax~ = ~ + ~?(1 -.) nl all -~- a21 (1 + o~)(all + a2~) aa12a21 a22 = 2R +3-2 X2(1 +a) A2 a12 -[- a22 (1 -F a)(a12 ~- a2~) aa12a2e (_ m ~ ~i = pl \kl k2 S1,2 ~ fo t?) sin pl, ~ (t -- r)dz X2 = P2 l+k
3 EFFECT OF TORSIONAL OSCILLATIONS ON EARTI-IQUAKE STRESSES 223 The forces in the walls are given by F1 = klyl Fs = k2ys Analysis of strong earthquake records shows that the maximum value attained by the integral S during the ground motion may be considered, for practical purposes, to be constant over a range of periods from approximately 0.3 second to 2.5 seconds. I Therefore, in this range $1 (max) -- $2 (max) -- S. The highest stresses will be produced when the maximum values of 81 and $2 occur at the same time with additive signs. There is always a possibility that this Yz -gb: k3 1 Yl 0 c.rn. K31 "kz kl l Fig. lb. condition will occur, although usually the two maxima will not concur exactly. Studies have shown that assuming the maximum values of $1 and S= to occur at the same time will usually result in an overestimation of the order of 5 to 10 per cent. It is here assumed that the maximum values of & and $2 are additive, and hence the maximum displacements are given by Y1 = (C~ + D1)S Ys = (Cs + D~)S (6) The maximum forces corresponding to yl and ys will be compared with the maximum forces that would be obtained if the building were symmetrical with kl' = ks' and kl' q- k2' = kl --k ks, that is, the total stiffness kl q- k2 is divided equally between the two walls while everything else remains unchanged. In the symmetrical case the maximum forces are 1 D. E. Hudson, Response Spectrum Techniques in Engineering Seismology, Proceedings of the World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, June, 1956; Earthquake Engineering Research Institute, San Francisco.
4 224 BULLETIN OF THE SEISMOLOGICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA 10 0 o o Stiffness Ratio R Fig. 2. P1 ratio of maximum force in flexible wall of unsymmetrical structure to maximum force in wall of symmetrical structure. and the ratio of maximum forces are pl _ Fl _ 2R [~ 4- ~] (7) r~ rat~a1 ~] P2 - F--~- 2(2-R) L X~ + (8) If the same comparison is made for the customary static method of analysis the ratios are P~ = R 1-2(2-R+~R) P~ = 2 - P18 (10)
5 Z.O EFFECT OF TORSIONAL OSCILLATIONS ON EARTHQUAKE STRESSES \ P2 1.2! I'00 O.Z Stiffness Ratio R Fig. 3. P, ratio of maximum force in stiff wall of unsymmetrical structure to maximum force in wall of symmetrical structure. Numerical results.--to exhibit the results, calculations have been made for some typical structures. In order to associate the parameters with physical dimensions the buildings may be thought of as having rigidities that are proportional to the lengths of the walls. In this case the structures are as follows: Structure 1. ba = 14;a = 0.3;9 = 0.5;0 < R < 1 Structure 2. ba = 12;a = 0.42; ;0 < R < 1 Structure3. ba = 1;a = 0.66;9 = 1.6;0 < R < 1 Structure4. ba = 2;a = 1.66;9 = 2.3;0 < R < 1 Structure 1 is a long, narrow building with one of the short walls more flexible than the other. At the other extreme structure 4 has one of the long walls more flexible than the other. The results of the calculations are plotted in figures 2 and 3. The parameter R represents the unbalance in rigidities; if R = 1 the two walls have the same rigidity and the structure is symmetrical; if R = 0 one of the walls has 0 rigidity.
6 226 BULLETIN O] ~ THE SEISMOLOGICAL SOCIETY OF AMERICA It will be noted that the static analysis gives an almost linear variation with R and that the force in the flexible wall goes from one-half the lateral load to zero as R goes from 1 to 0. The force in the rigid wall goes from one-half the lateral load to 100 per cent of the lateral load as R goes from 1 to 0. The dynamic analysis shows the force in the flexible wall to be larger than that given by the static analysis, and the force in the stiff wall to be less than in the static case. In particular, when R = 0 the force in the stiff wall is appreciably less. This result could have been foretold, for when R = 0 the structure has only three walls and it behaves like a horizontal pendulum and the torsional oscillations are severe whereas the lateral oscillations are only moderate. Hence, the usual concept of equivalent static lateral load is not applicable. Figures 2 and 3 show that the greater the eccentricity between the center of mass and the center of rigidity the greater is the deviation between the dynamic and the static analysis. For eccentricities giving R = 0.6 the flexible wall has a maximum force approximately 50 per cent larger than computed by tbe static method and the stiff wall has a maximum force approximately 80 per cent as large as computed by the static method. These differences are due to the torsional oscillations of the structure whose effect is not included in the static analysis. The foregoing analysis was for a one-story structure, but it can be concluded that unsymmetrical multistory structures will behave similarly and that the flexible walls will sustain larger forces than a static analysis would indicate. Energy considerations.--the foregoing remarks are pertinent to the stresses developed during an earthquake, but it is not always feasible to design a structure so that the maximum stresses do not exceed the normally allowable working stresses for the material. In such a ease some of the vibrational energy may be absorbed by cracking, stressing beyond the yield point, etc., while still maintaining an adequate factor of safety against serious damage. The elastic stresses are then not reliable indicators of the ultimate strength of the structure, but rather it is the energyabsorbing capacity of the structure that determines the ultimate strength. In this regard it is possible to draw some general conclusions about the vibrational energy of structures during earthquakes. Consider a structure having normal modes of vibration. For convenience, only undamped structures will be considered, though the same results are obtained if the structure has linear damping. Only horizontal planar vibrations will be considered, but it will be seen that the same results hold for more complex structures that vibrate with three-dimensional motion. The displacement and velocity of such a multi-degree-of-freedom structure during free vibrations that are excited by a unit impulse are described by equations having the forms Y = ~-]BnC~sinp~t n pn = ~_,B~ ncosp~t n (11) B~ - f (k~dp f dp
7 EFFECT OF TORSIONAL OSCILLATIONS ON EARTHQUAKE STRESSES 227 where dp is an element of mass and the integrals are taken over the mass of the structure, and ~ is the normal mode shape and is a function of the space cosrdinares. Let each element of mass dp be acted upon by a horizontal force equal to (-~dp). The resulting motion will then be the same as if the base of the structure were shaken with horizontal acceleration 9. The displacement generated at time t is y = ~n Bn dp,~ p~ t 9 sin p~(t -- r)dr ~ B~ ~nn{ sin pnt t?) cos p~ rdr -- cos p~t t?) sin p, rd TI The kinetic energy in the structure at time t is (12) T = f (13) - 21 ~ B ~ 4~ dp cos p~t ~ cos p~ rdr + sin p~t ~ sin p~ rd Using D'Alambert's principle, the potential energy at time t is V = -f ½y(~z _ ij)dp ~ B~ q~ dp sin p,,t cos pn rdr -- cos p~t ij sin p~ rd~ 2 i, sin p~t ~ cos p~ rdr - cos p~t ~ sin p~ rdr (14) The total energy in the structure at time t is 1 )2} = Z O,od sinp~ rdr -4- ~ cos p~ rdr (15) As shown in figure 4, the expression within the brackets in equation (15) is just the envelope of the integral, S, appearing in equation (12). Hence for practical purposes the maximum value of S may be equated to the square root of the maximum value of the expression in brackets. Letting Sn represent this maximum value, the maximum energy attained by the structure may be written If the value of Sn is independent Of the period of vibration ($1 = $2 = S~ = S) the energy is 1 S~ Be I- n
8 228 BULLETIN O~ TI=IE SEISMOLOGICAL SOCIETY OF A:MEI?4CA As may be seen from the equations of free vibration the coefficient B. is determined so that Y = 1 at t = 0 and hence n 1 and from the orthogonality relations f \\ \ \ tz sin pt dt) z +(~ cos pt dr) z) \ k cos ~t dt l Fig. 4. where M is the total mass of the structure. The maximum energy attained by the structure is thus E = 1~ MS2 The maximum energy thus depends only on the mass and on S and is independent of how the mass is distributed and how the stiffness is distributed. The value of S computed from strong ground motion is not itself a constant, but varies a bit. However, for a number of earthquakes the average value of S may be taken to have a constant value for periods from approximately 0.3 seeond to 2.5+ seconds. It can thus be said that if the modes of a structure are in this period range the expected value of the maximum energy will be independent of the distribution of mass and stiffness. The foregoing value of E = 1~MS2 represents the maximum energy attained by the undamped, elastic, structure. In an actual strueture this energy will be partly stored as potential and kinetic energy and partly dissipated by the damping. If the
9 EFFECT OF TORSIONAL OSCILLATIONS ON EARTHQUAKE STRESSES 229 amount of energy involved is sufficiently large the stresses will go beyond the yield point, or cracks may form with consequent energy loss. In the case of torsional oscillations of an unsymmetrical building it can thus be concluded that the asymmetry does not appreciably affect the total energy received by the building, but only affects the magnitude of the maximum stress. However, if the flexible wall were designed to be relatively too weak it would be the first to be overstressed and it would absorb the excess energy and the damage would tend to be concentrated there. SUMMARY Summary.--It has been shown that an unsymmetrical building undergoing torsional accelerations can be expected to sustain stresses in the more flexible wall that are higher than those predicted by the customary static method of analysis. If the objective of the design is to keep the maximum stress within the usual allowable limits, a correction should be made to the results given by the usual static method of analysis. On the other hand, if the objective of the design is to provide a certain ultimate strength, the relative rigidity of the wall is not so important a factor as is the ability of the wall to absorb energy. DIVISION OF ENGINEERING, CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY~ PASADENA, CALIFORNIA.
Introduction to Mechanical Vibration
 2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
2103433 Introduction to Mechanical Vibration Nopdanai Ajavakom (NAV) 1 Course Topics Introduction to Vibration What is vibration? Basic concepts of vibration Modeling Linearization Single-Degree-of-Freedom
Structural Dynamics Lecture 7. Outline of Lecture 7. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) System Reduction. Vibration due to Movable Supports.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) System Reduction. Truncated Modal Expansion with Quasi-Static Correction. Guyan Reduction. Vibration due to Movable Supports. Earthquake Excitations.
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) System Reduction. Truncated Modal Expansion with Quasi-Static Correction. Guyan Reduction. Vibration due to Movable Supports. Earthquake Excitations.
Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian
 Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: Mode-Superposition Method Mode-Superposition Method:
Structural Dynamics Lecture Eleven: Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: (Chapter 11) By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Dynamic Response of MDOF Systems: Mode-Superposition Method Mode-Superposition Method:
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration
 Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration Module 15 Lecture 38 Vibration of Rigid Bodies Part-1 Today,
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration Module 15 Lecture 38 Vibration of Rigid Bodies Part-1 Today,
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Introduction to structural dynamics
 Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
Introduction to structural dynamics p n m n u n p n-1 p 3... m n-1 m 3... u n-1 u 3 k 1 c 1 u 1 u 2 k 2 m p 1 1 c 2 m2 p 2 k n c n m n u n p n m 2 p 2 u 2 m 1 p 1 u 1 Static vs dynamic analysis Static
EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION
 1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
1 EQUIVALENT SINGLE-DEGREE-OF-FREEDOM SYSTEM AND FREE VIBRATION The course on Mechanical Vibration is an important part of the Mechanical Engineering undergraduate curriculum. It is necessary for the development
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in
 Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Codal Provisions IS 1893 (Part 1) 2002
 Abstract Codal Provisions IS 1893 (Part 1) 00 Paresh V. Patel Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Nirma Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad 38481 In this article codal provisions of IS 1893
Abstract Codal Provisions IS 1893 (Part 1) 00 Paresh V. Patel Assistant Professor, Civil Engineering Department, Nirma Institute of Technology, Ahmedabad 38481 In this article codal provisions of IS 1893
Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody
 Lecture 27. THE COMPOUND PENDULUM Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody diagram The term compound is used to distinguish the present
Lecture 27. THE COMPOUND PENDULUM Figure 5.16 Compound pendulum: (a) At rest in equilibrium, (b) General position with coordinate θ, Freebody diagram The term compound is used to distinguish the present
COLUMN INTERACTION EFFECT ON PUSH OVER 3D ANALYSIS OF IRREGULAR STRUCTURES
 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, Paper No. 6 COLUMN INTERACTION EFFECT ON PUSH OVER D ANALYSIS OF IRREGULAR STRUCTURES Jaime DE-LA-COLINA, MariCarmen HERNANDEZ
th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August -6, Paper No. 6 COLUMN INTERACTION EFFECT ON PUSH OVER D ANALYSIS OF IRREGULAR STRUCTURES Jaime DE-LA-COLINA, MariCarmen HERNANDEZ
Preliminary Examination in Dynamics
 Fall Semester 2017 Problem 1 The simple structure shown below weighs 1,000 kips and has a period of 1.25 sec. It has no viscous damping. It is subjected to the impulsive load shown in the figure. If the
Fall Semester 2017 Problem 1 The simple structure shown below weighs 1,000 kips and has a period of 1.25 sec. It has no viscous damping. It is subjected to the impulsive load shown in the figure. If the
Preliminary Examination - Dynamics
 Name: University of California, Berkeley Fall Semester, 2018 Problem 1 (30% weight) Preliminary Examination - Dynamics An undamped SDOF system with mass m and stiffness k is initially at rest and is then
Name: University of California, Berkeley Fall Semester, 2018 Problem 1 (30% weight) Preliminary Examination - Dynamics An undamped SDOF system with mass m and stiffness k is initially at rest and is then
RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOR ACCELERATION DEMAND
 RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOR ACCELERATION DEMAND Shahram Taghavi 1 and Eduardo Miranda 2 1 Senior catastrophe risk modeler, Risk Management Solutions, CA, USA 2 Associate Professor,
RESPONSE SPECTRUM METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF PEAK FLOOR ACCELERATION DEMAND Shahram Taghavi 1 and Eduardo Miranda 2 1 Senior catastrophe risk modeler, Risk Management Solutions, CA, USA 2 Associate Professor,
If the number of unknown reaction components are equal to the number of equations, the structure is known as statically determinate.
 1 of 6 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY AND ANALYSIS OF ETRUCTURAS II 9.1 reactions in supports and joints of a two-dimensional structure and statically indeterminate reactions: Statically indeterminate structures
1 of 6 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY AND ANALYSIS OF ETRUCTURAS II 9.1 reactions in supports and joints of a two-dimensional structure and statically indeterminate reactions: Statically indeterminate structures
 University of California at Berkeley Structural Engineering Mechanics & Materials Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Spring 2012 Student name : Doctoral Preliminary Examination in Dynamics
University of California at Berkeley Structural Engineering Mechanics & Materials Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Spring 2012 Student name : Doctoral Preliminary Examination in Dynamics
Design of Earthquake-Resistant Structures
 NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS LABORATORY OF EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING Design of Earthquake-Resistant Structures Basic principles Ioannis N. Psycharis Basic considerations Design earthquake: small
NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS LABORATORY OF EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING Design of Earthquake-Resistant Structures Basic principles Ioannis N. Psycharis Basic considerations Design earthquake: small
THE EFFECTS OF EARTHQUAKES ON BUILDINGS WITH A FLEXIBLE FIRST STORY 1
 EFFECTS OF EARTHQUAKES ON A FLEXIBLE FIRST STORY 167 THE EFFECTS OF EARTHQUAKES ON BUILDINGS WITH A FLEXIBLE FIRST STORY 1 BY R. R. MARTEL 2 The title of this paper is a misnomer, purposely selected to
EFFECTS OF EARTHQUAKES ON A FLEXIBLE FIRST STORY 167 THE EFFECTS OF EARTHQUAKES ON BUILDINGS WITH A FLEXIBLE FIRST STORY 1 BY R. R. MARTEL 2 The title of this paper is a misnomer, purposely selected to
Review of Strain Energy Methods and Introduction to Stiffness Matrix Methods of Structural Analysis
 uke University epartment of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE 42L. Matrix Structural Analysis Henri P. Gavin Fall, 22 Review of Strain Energy Methods and Introduction to Stiffness Matrix Methods
uke University epartment of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE 42L. Matrix Structural Analysis Henri P. Gavin Fall, 22 Review of Strain Energy Methods and Introduction to Stiffness Matrix Methods
EVALUATING DYNAMIC STRESSES OF A PIPELINE
 EVALUATING DYNAMIC STRESSES OF A PIPELINE by K.T. TRUONG Member ASME Mechanical & Piping Division THE ULTRAGEN GROUP LTD 2255 Rue De La Province Longueuil (Quebec) J4G 1G3 This document is provided to
EVALUATING DYNAMIC STRESSES OF A PIPELINE by K.T. TRUONG Member ASME Mechanical & Piping Division THE ULTRAGEN GROUP LTD 2255 Rue De La Province Longueuil (Quebec) J4G 1G3 This document is provided to
A METHOD OF LOAD INCREMENTS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF SECOND-ORDER LIMIT LOAD AND COLLAPSE SAFETY OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAMED STRUCTURES
 A METHOD OF LOAD INCREMENTS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF SECOND-ORDER LIMIT LOAD AND COLLAPSE SAFETY OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAMED STRUCTURES Konuralp Girgin (Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Science and Technology,
A METHOD OF LOAD INCREMENTS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF SECOND-ORDER LIMIT LOAD AND COLLAPSE SAFETY OF REINFORCED CONCRETE FRAMED STRUCTURES Konuralp Girgin (Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Science and Technology,
ANALYSIS OF HIGHRISE BUILDING STRUCTURE WITH SETBACK SUBJECT TO EARTHQUAKE GROUND MOTIONS
 ANALYSIS OF HIGHRISE BUILDING SRUCURE WIH SEBACK SUBJEC O EARHQUAKE GROUND MOIONS 157 Xiaojun ZHANG 1 And John L MEEK SUMMARY he earthquake response behaviour of unframed highrise buildings with setbacks
ANALYSIS OF HIGHRISE BUILDING SRUCURE WIH SEBACK SUBJEC O EARHQUAKE GROUND MOIONS 157 Xiaojun ZHANG 1 And John L MEEK SUMMARY he earthquake response behaviour of unframed highrise buildings with setbacks
International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational and Applied Sciences (IJETCAS)
 International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
International Association of Scientific Innovation and Research (IASIR) (An Association Unifying the Sciences, Engineering, and Applied Research) International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Computational
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
 Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 2 Simpul Rotors Lecture - 2 Jeffcott Rotor Model In the
Theory and Practice of Rotor Dynamics Prof. Dr. Rajiv Tiwari Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Module - 2 Simpul Rotors Lecture - 2 Jeffcott Rotor Model In the
T1 T e c h n i c a l S e c t i o n
 1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
1.5 Principles of Noise Reduction A good vibration isolation system is reducing vibration transmission through structures and thus, radiation of these vibration into air, thereby reducing noise. There
Dynamic Loads CE 543. Examples. Harmonic Loads
 CE 543 Structural Dynamics Introduction Dynamic Loads Dynamic loads are time-varying loads. (But time-varying loads may not require dynamic analysis.) Dynamics loads can be grouped in one of the following
CE 543 Structural Dynamics Introduction Dynamic Loads Dynamic loads are time-varying loads. (But time-varying loads may not require dynamic analysis.) Dynamics loads can be grouped in one of the following
A Modified Response Spectrum Analysis Procedure (MRSA) to Determine the Nonlinear Seismic Demands of Tall Buildings
 Fawad A. Najam Pennung Warnitchai Asian Institute of Technology (AIT), Thailand Email: fawad.ahmed.najam@ait.ac.th A Modified Response Spectrum Analysis Procedure (MRSA) to Determine the Nonlinear Seismic
Fawad A. Najam Pennung Warnitchai Asian Institute of Technology (AIT), Thailand Email: fawad.ahmed.najam@ait.ac.th A Modified Response Spectrum Analysis Procedure (MRSA) to Determine the Nonlinear Seismic
Advanced Vibrations. Elements of Analytical Dynamics. By: H. Ahmadian Lecture One
 Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
Advanced Vibrations Lecture One Elements of Analytical Dynamics By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir Elements of Analytical Dynamics Newton's laws were formulated for a single particle Can be extended to
Support Idealizations
 IVL 3121 nalysis of Statically Determinant Structures 1/12 nalysis of Statically Determinate Structures nalysis of Statically Determinate Structures The most common type of structure an engineer will analyze
IVL 3121 nalysis of Statically Determinant Structures 1/12 nalysis of Statically Determinate Structures nalysis of Statically Determinate Structures The most common type of structure an engineer will analyze
STRONG -MOTION EARTHQUAKE
 53 STRONG -MOTION EARTHQUAKE RECORDS P. W. Taylor* SYNOPSIS: This article reviews, at an elementary level, the ways in which information from strong-motion earthquake records may be presented. The various
53 STRONG -MOTION EARTHQUAKE RECORDS P. W. Taylor* SYNOPSIS: This article reviews, at an elementary level, the ways in which information from strong-motion earthquake records may be presented. The various
Combined Effect of Soil Structure Interaction and Infill Wall Stiffness on Building_- A Review
 Combined Effect of Soil Structure Interaction and Infill Wall Stiffness on Building_- A Review Prof. Wakchaure M. R a* a Dean & Asso. Professor, Dept.of Civil Engineering, Amrutvahini College of Engineering,
Combined Effect of Soil Structure Interaction and Infill Wall Stiffness on Building_- A Review Prof. Wakchaure M. R a* a Dean & Asso. Professor, Dept.of Civil Engineering, Amrutvahini College of Engineering,
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV
 VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
VIBRATION ANALYSIS OF E-GLASS FIBRE RESIN MONO LEAF SPRING USED IN LMV Mohansing R. Pardeshi 1, Dr. (Prof.) P. K. Sharma 2, Prof. Amit Singh 1 M.tech Research Scholar, 2 Guide & Head, 3 Co-guide & Assistant
PARAMETERS CHARACTERIZING THE SEISMIC DEMAND FOR EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE SCENARIO EVALUATION
 PARAMETERS CHARACTERIZING THE SEISMIC DEMAND FOR EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE SCENARIO EVALUATION Response spectra SDF SYSTEMS The ground acceleration can be registered using accelerographs: A SDF system is subjected
PARAMETERS CHARACTERIZING THE SEISMIC DEMAND FOR EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE SCENARIO EVALUATION Response spectra SDF SYSTEMS The ground acceleration can be registered using accelerographs: A SDF system is subjected
Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum
 STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum Overview of Structural Dynamics Structure Members, joints, strength, stiffness, ductility Structure
STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS Dr.Vinod Hosur, Professor, Civil Engg.Dept., Gogte Institute of Technology, Belgaum Overview of Structural Dynamics Structure Members, joints, strength, stiffness, ductility Structure
Application of pseudo-symmetric technique in dynamic analysis of concrete gravity dams
 Application of pseudo-symmetric technique in dynamic analysis of concrete gravity dams V. Lotfi Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Amirkabir University, Iran Abstract A new approach is
Application of pseudo-symmetric technique in dynamic analysis of concrete gravity dams V. Lotfi Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Amirkabir University, Iran Abstract A new approach is
Theory of structure I 2006/2013. Chapter one DETERMINACY & INDETERMINACY OF STRUCTURES
 Chapter one DETERMINACY & INDETERMINACY OF STRUCTURES Introduction A structure refers to a system of connected parts used to support a load. Important examples related to civil engineering include buildings,
Chapter one DETERMINACY & INDETERMINACY OF STRUCTURES Introduction A structure refers to a system of connected parts used to support a load. Important examples related to civil engineering include buildings,
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Application of Capacity Spectrum Method to timber houses considering shear deformation of horizontal frames
 Application of Capacity Spectrum Method to timber houses considering shear deformation of horizontal frames Kawai, N. 1 ABSTRACT Relating to the revision of Building Standard Law of Japan, the application
Application of Capacity Spectrum Method to timber houses considering shear deformation of horizontal frames Kawai, N. 1 ABSTRACT Relating to the revision of Building Standard Law of Japan, the application
Dynamics of structures
 Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 1 Lecture - 10 Methods of Writing Equation of Motion (Refer
Dynamics of Ocean Structures Prof. Dr. Srinivasan Chandrasekaran Department of Ocean Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module - 1 Lecture - 10 Methods of Writing Equation of Motion (Refer
CE 6701 Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering Dr. P. Venkateswara Rao
 CE 6701 Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering Dr. P. Venkateswara Rao Associate Professor Dept. of Civil Engineering SVCE, Sriperumbudur Difference between static loading and dynamic loading Degree
CE 6701 Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering Dr. P. Venkateswara Rao Associate Professor Dept. of Civil Engineering SVCE, Sriperumbudur Difference between static loading and dynamic loading Degree
Dynamic Analysis and Modeling of Wood-framed Shear Walls
 Dynamic Analysis and Modeling of Wood-framed Shear Walls Yasumura, M. 1 ABSTRACT Dynamic performance of wood-framed shear walls was analyzed by means of the non-linear earthquake response analysis and
Dynamic Analysis and Modeling of Wood-framed Shear Walls Yasumura, M. 1 ABSTRACT Dynamic performance of wood-framed shear walls was analyzed by means of the non-linear earthquake response analysis and
Dynamics of Structures
 Dynamics of Structures Elements of structural dynamics Roberto Tomasi 11.05.2017 Roberto Tomasi Dynamics of Structures 11.05.2017 1 / 22 Overview 1 SDOF system SDOF system Equation of motion Response spectrum
Dynamics of Structures Elements of structural dynamics Roberto Tomasi 11.05.2017 Roberto Tomasi Dynamics of Structures 11.05.2017 1 / 22 Overview 1 SDOF system SDOF system Equation of motion Response spectrum
TORSIONAL IRREGULARITY IN MULTI-STORY STRUCTURES
 TORSIONAL IRREGULARITY IN MULTI-STORY STRUCTURES Günay Özmen Konuralp Girgin Yavuz Durgun ABSTRACT In contemporary earthquake-regulations, effects of torsional irregularity are represented by augmenting
TORSIONAL IRREGULARITY IN MULTI-STORY STRUCTURES Günay Özmen Konuralp Girgin Yavuz Durgun ABSTRACT In contemporary earthquake-regulations, effects of torsional irregularity are represented by augmenting
C. points X and Y only. D. points O, X and Y only. (Total 1 mark)
 Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
Grade 11 Physics -- Homework 16 -- Answers on a separate sheet of paper, please 1. A cart, connected to two identical springs, is oscillating with simple harmonic motion between two points X and Y that
ΙApostolos Konstantinidis Diaphragmatic behaviour. Volume B
 Volume B 3.1.4 Diaphragmatic behaviour In general, when there is eccentric loading at a floor, e.g. imposed by the horizontal seismic action, the in-plane rigidity of the slab forces all the in-plane points
Volume B 3.1.4 Diaphragmatic behaviour In general, when there is eccentric loading at a floor, e.g. imposed by the horizontal seismic action, the in-plane rigidity of the slab forces all the in-plane points
NONLINEAR SEISMIC SOIL-STRUCTURE (SSI) ANALYSIS USING AN EFFICIENT COMPLEX FREQUENCY APPROACH
 NONLINEAR SEISMIC SOIL-STRUCTURE (SSI) ANALYSIS USING AN EFFICIENT COMPLEX FREQUENCY APPROACH Dan M. GHIOCEL 1 ABSTRACT The paper introduces a novel approach for modeling nonlinear hysteretic behavior
NONLINEAR SEISMIC SOIL-STRUCTURE (SSI) ANALYSIS USING AN EFFICIENT COMPLEX FREQUENCY APPROACH Dan M. GHIOCEL 1 ABSTRACT The paper introduces a novel approach for modeling nonlinear hysteretic behavior
Table of Contents. Preface... 13
 Table of Contents Preface... 13 Chapter 1. Vibrations of Continuous Elastic Solid Media... 17 1.1. Objective of the chapter... 17 1.2. Equations of motion and boundary conditions of continuous media...
Table of Contents Preface... 13 Chapter 1. Vibrations of Continuous Elastic Solid Media... 17 1.1. Objective of the chapter... 17 1.2. Equations of motion and boundary conditions of continuous media...
WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery
 WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2011 Mechanical Vibrations, Singiresu S. Rao, 2010 Mechanical Vibrations: Theory and
WEEKS 8-9 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J.Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2011 Mechanical Vibrations, Singiresu S. Rao, 2010 Mechanical Vibrations: Theory and
Collapse modes of structures under strong motions of earthquake
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 45, N. 6, December 2002 Collapse modes of structures under strong motions of earthquake Hiroshi Akiyama Real Estate Science, School of Science and Technology, Nihon University,
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 45, N. 6, December 2002 Collapse modes of structures under strong motions of earthquake Hiroshi Akiyama Real Estate Science, School of Science and Technology, Nihon University,
Some Aspects of Structural Dynamics
 Appendix B Some Aspects of Structural Dynamics This Appendix deals with some aspects of the dynamic behavior of SDOF and MDOF. It starts with the formulation of the equation of motion of SDOF systems.
Appendix B Some Aspects of Structural Dynamics This Appendix deals with some aspects of the dynamic behavior of SDOF and MDOF. It starts with the formulation of the equation of motion of SDOF systems.
Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A, ONE QUESTION FROM SECTION B and ONE QUESTION FROM SECTION C Linear graph paper will be provided.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2015-2016 ENERGY ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES ENG-5001Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A, ONE QUESTION FROM
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2015-2016 ENERGY ENGINEERING PRINCIPLES ENG-5001Y Time allowed: 3 Hours Attempt ALL QUESTIONS IN SECTION A, ONE QUESTION FROM
UNIT- I Thin plate theory, Structural Instability:
 UNIT- I Thin plate theory, Structural Instability: Analysis of thin rectangular plates subject to bending, twisting, distributed transverse load, combined bending and in-plane loading Thin plates having
UNIT- I Thin plate theory, Structural Instability: Analysis of thin rectangular plates subject to bending, twisting, distributed transverse load, combined bending and in-plane loading Thin plates having
Chapter 14 Oscillations. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
Chapter 14 Oscillations Oscillations of a Spring Simple Harmonic Motion Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator Simple Harmonic Motion Related to Uniform Circular Motion The Simple Pendulum The Physical
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping
 A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
A Guide to linear dynamic analysis with Damping This guide starts from the applications of linear dynamic response and its role in FEA simulation. Fundamental concepts and principles will be introduced
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS ABSTRACT : P Mata1, AH Barbat1, S Oller1, R Boroschek2 1 Technical University of Catalonia, Civil Engineering
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS ABSTRACT : P Mata1, AH Barbat1, S Oller1, R Boroschek2 1 Technical University of Catalonia, Civil Engineering
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Department of Architecture & Civil Engineering ( ) 2 2a. L = 65 2 ρπa4 L. + asinα = 3aθ 2. ( ) = a 1 cos( θ ρπa4 L.
 MODE ANSWER age: 1 QUESTION Mass of tube = ρπ 3a ( ) ( a) Moment of inertia of tube = ρπ 3 Mass of bar = ρπa Moment of inertia of bar = = 5ρπa ( 3a) 4 a ( ) 4 ρπ ( a )4 = 1 3 ρπa4 Horizontal displacement
MODE ANSWER age: 1 QUESTION Mass of tube = ρπ 3a ( ) ( a) Moment of inertia of tube = ρπ 3 Mass of bar = ρπa Moment of inertia of bar = = 5ρπa ( 3a) 4 a ( ) 4 ρπ ( a )4 = 1 3 ρπa4 Horizontal displacement
Seismic Analysis of Structures Prof. T.K. Datta Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Seismic Analysis of Structures Prof. T.K. Datta Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 20 Response Spectrum Method of Analysis In the last few lecture, we discussed
Seismic Analysis of Structures Prof. T.K. Datta Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 20 Response Spectrum Method of Analysis In the last few lecture, we discussed
Frequency-dependent Strong Motion Duration Using Total Threshold Intervals of Velocity Response Envelope
 Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 015, Sydney, Australia Frequency-dependent Strong Motion Duration Using Total
Proceedings of the Tenth Pacific Conference on Earthquake Engineering Building an Earthquake-Resilient Pacific 6-8 November 015, Sydney, Australia Frequency-dependent Strong Motion Duration Using Total
Introduction to Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering
 Module 1 Introduction to Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in URL:
Module 1 Introduction to Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Dr. Deepankar Choudhury Professor Department of Civil Engineering IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai 400 076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in URL:
Structural Dynamics. Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma).
 Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Structural Dynamics Lecture 2. Outline of Lecture 2. Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.)
 Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
Outline of Single-Degree-of-Freedom Systems (cont.) Linear Viscous Damped Eigenvibrations. Logarithmic decrement. Response to Harmonic and Periodic Loads. 1 Single-Degreee-of-Freedom Systems (cont.). Linear
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2)
 PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2) We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. As discussed in Chapter 16, when
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2) We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. As discussed in Chapter 16, when
Structural Dynamics A Graduate Course in Aerospace Engineering
 Structural Dynamics A Graduate Course in Aerospace Engineering By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir The Science and Art of Structural Dynamics What do all the followings have in common? > A sport-utility
Structural Dynamics A Graduate Course in Aerospace Engineering By: H. Ahmadian ahmadian@iust.ac.ir The Science and Art of Structural Dynamics What do all the followings have in common? > A sport-utility
AA 242B / ME 242B: Mechanical Vibrations (Spring 2016)
 AA 242B / ME 242B: Mechanical Vibrations (Spring 206) Solution of Homework #3 Control Tab Figure : Schematic for the control tab. Inadequacy of a static-test A static-test for measuring θ would ideally
AA 242B / ME 242B: Mechanical Vibrations (Spring 206) Solution of Homework #3 Control Tab Figure : Schematic for the control tab. Inadequacy of a static-test A static-test for measuring θ would ideally
Final Exam December 11, 2017
 Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are NOT allowed to use a calculator with communication capabilities during the exam. Usage
Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete this exam. This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are NOT allowed to use a calculator with communication capabilities during the exam. Usage
This Technical Note describes how the program checks column capacity or designs reinforced concrete columns when the ACI code is selected.
 COMPUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., BERKELEY, CALIFORNIA DECEMBER 2001 CONCRETE FRAME DESIGN ACI-318-99 Technical Note This Technical Note describes how the program checks column capacity or designs reinforced
COMPUTERS AND STRUCTURES, INC., BERKELEY, CALIFORNIA DECEMBER 2001 CONCRETE FRAME DESIGN ACI-318-99 Technical Note This Technical Note describes how the program checks column capacity or designs reinforced
on the figure. Someone has suggested that, in terms of the degrees of freedom x1 and M. Note that if you think the given 1.2
 1) A two-story building frame is shown below. The mass of the frame is assumed to be lumped at the floor levels and the floor slabs are considered rigid. The floor masses and the story stiffnesses are
1) A two-story building frame is shown below. The mass of the frame is assumed to be lumped at the floor levels and the floor slabs are considered rigid. The floor masses and the story stiffnesses are
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction
 Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng. Professor Graduate School of Engineering Hiroshima University Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Chapter 1 : Introduction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng.
Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng. Professor Graduate School of Engineering Hiroshima University Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Chapter 1 : Introduction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng.
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives
 AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
Control of Earthquake Induced Vibrations in Asymmetric Buildings Using Passive Damping
 Control of Earthquake Induced Vibrations in Asymmetric Buildings Using Passive Damping Rakesh K. Goel, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo Abstract This paper summarizes the results
Control of Earthquake Induced Vibrations in Asymmetric Buildings Using Passive Damping Rakesh K. Goel, California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo Abstract This paper summarizes the results
Theory of Vibrations in Stewart Platforms
 Theory of Vibrations in Stewart Platforms J.M. Selig and X. Ding School of Computing, Info. Sys. & Maths. South Bank University London SE1 0AA, U.K. (seligjm@sbu.ac.uk) Abstract This article develops a
Theory of Vibrations in Stewart Platforms J.M. Selig and X. Ding School of Computing, Info. Sys. & Maths. South Bank University London SE1 0AA, U.K. (seligjm@sbu.ac.uk) Abstract This article develops a
Vibration Dynamics and Control
 Giancarlo Genta Vibration Dynamics and Control Spri ringer Contents Series Preface Preface Symbols vii ix xxi Introduction 1 I Dynamics of Linear, Time Invariant, Systems 23 1 Conservative Discrete Vibrating
Giancarlo Genta Vibration Dynamics and Control Spri ringer Contents Series Preface Preface Symbols vii ix xxi Introduction 1 I Dynamics of Linear, Time Invariant, Systems 23 1 Conservative Discrete Vibrating
Multi Linear Elastic and Plastic Link in SAP2000
 26/01/2016 Marco Donà Multi Linear Elastic and Plastic Link in SAP2000 1 General principles Link object connects two joints, i and j, separated by length L, such that specialized structural behaviour may
26/01/2016 Marco Donà Multi Linear Elastic and Plastic Link in SAP2000 1 General principles Link object connects two joints, i and j, separated by length L, such that specialized structural behaviour may
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations:
 TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING 2019 Mathematics of Oscillating Systems Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations: Undamped Free Vibration Q2. A 4 g mass is suspended by
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS EXAMPLES SPRING 2019 Mathematics of Oscillating Systems Q1. Find general solutions for the following differential equations: Undamped Free Vibration Q2. A 4 g mass is suspended by
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS SPRING 2019
 TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS SPRING 2019 1. Introduction 1.1 Overview 1.2 Degrees of freedom 1.3 Simple harmonic motion 2. Undamped free oscillation 2.1 Generalised mass-spring system: simple harmonic motion
TOPIC E: OSCILLATIONS SPRING 2019 1. Introduction 1.1 Overview 1.2 Degrees of freedom 1.3 Simple harmonic motion 2. Undamped free oscillation 2.1 Generalised mass-spring system: simple harmonic motion
This equation of motion may be solved either by differential equation method or by graphical method as discussed below:
 2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES
 LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
LECTURE 14: DEVELOPING THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR TWO-MASS VIBRATION EXAMPLES Figure 3.47 a. Two-mass, linear vibration system with spring connections. b. Free-body diagrams. c. Alternative free-body
Soil-Structure Interaction in Nonlinear Pushover Analysis of Frame RC Structures: Nonhomogeneous Soil Condition
 ABSTRACT: Soil-Structure Interaction in Nonlinear Pushover Analysis of Frame RC Structures: Nonhomogeneous Soil Condition G. Dok ve O. Kırtel Res. Assist., Department of Civil Engineering, Sakarya University,
ABSTRACT: Soil-Structure Interaction in Nonlinear Pushover Analysis of Frame RC Structures: Nonhomogeneous Soil Condition G. Dok ve O. Kırtel Res. Assist., Department of Civil Engineering, Sakarya University,
Foundation Engineering Dr. Priti Maheshwari Department Of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Roorkee
 Foundation Engineering Dr. Priti Maheshwari Department Of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Roorkee Module - 02 Lecture - 15 Machine Foundations - 3 Hello viewers, In the last class we
Foundation Engineering Dr. Priti Maheshwari Department Of Civil Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Roorkee Module - 02 Lecture - 15 Machine Foundations - 3 Hello viewers, In the last class we
Chapter 15. Oscillatory Motion
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion Part 2 Oscillations and Mechanical Waves Periodic motion is the repeating motion of an object in which it continues to return to a given position after a fixed time interval.
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion Part 2 Oscillations and Mechanical Waves Periodic motion is the repeating motion of an object in which it continues to return to a given position after a fixed time interval.
EMA 545 Final Exam - Prof. M. S. Allen Spring 2011
 EMA 545 Final Exam - Prof. M. S. Allen Spring 2011 Honor Pledge: On my honor, I pledge that this exam represents my own work, and that I have neither given nor received inappropriate aid in the preparation
EMA 545 Final Exam - Prof. M. S. Allen Spring 2011 Honor Pledge: On my honor, I pledge that this exam represents my own work, and that I have neither given nor received inappropriate aid in the preparation
Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams.
 Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
Outline of Continuous Systems. Introduction to Continuous Systems. Continuous Systems. Strings, Torsional Rods and Beams. Vibrations of Flexible Strings. Torsional Vibration of Rods. Bernoulli-Euler Beams.
two structural analysis (statics & mechanics) APPLIED ACHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: DR. ANNE NICHOLS SPRING 2017 lecture STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS
 APPLIED ACHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS DR. ANNE NICHOLS SPRING 2017 lecture two structural analysis (statics & mechanics) Analysis 1 Structural Requirements strength serviceability
APPLIED ACHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS DR. ANNE NICHOLS SPRING 2017 lecture two structural analysis (statics & mechanics) Analysis 1 Structural Requirements strength serviceability
Software Verification
 SAP000 EXAMPLE 6-00 LINK LINEAR LINK WITH RAMP LOADING PROBLEM DESCRIPTION In this example a ramp load is applied to an undamped single degree of freedom structure. The ramp loading has a finite rise time
SAP000 EXAMPLE 6-00 LINK LINEAR LINK WITH RAMP LOADING PROBLEM DESCRIPTION In this example a ramp load is applied to an undamped single degree of freedom structure. The ramp loading has a finite rise time
Name: Fall 2014 CLOSED BOOK
 Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
Name: Fall 2014 1. Rod AB with weight W = 40 lb is pinned at A to a vertical axle which rotates with constant angular velocity ω =15 rad/s. The rod position is maintained by a horizontal wire BC. Determine
Extended Application Of Time-Varying Observer For Rigid Rotors Unbalance Estimation During Acceleration
 MATEC Web of Conferences 67, 5 (8) IC4M & ICDES 8 https://doi.org/.5/matecconf/8675 Extended Application Of Time-Varying Observer For Rigid Rotors Unbalance Estimation During Acceleration Xunxing Yu,a,
MATEC Web of Conferences 67, 5 (8) IC4M & ICDES 8 https://doi.org/.5/matecconf/8675 Extended Application Of Time-Varying Observer For Rigid Rotors Unbalance Estimation During Acceleration Xunxing Yu,a,
a) Find the equation of motion of the system and write it in matrix form.
 .003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set Problem : Torsional Oscillator Two disks of radius r and r and mass m and m are mounted in series with steel shafts. The shaft between the base and m has length L
Periodic Motion. Periodic motion is motion of an object that. regularly repeats
 Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A special kind of periodic motion occurs in mechanical systems
Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A special kind of periodic motion occurs in mechanical systems
Use of Full Spectrum Cascade for Rotor Rub Identification
 Use of Full Spectrum Cascade for Rotor Rub Identification T. H. Patel 1, A. K. Darpe 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi 110016, India. 1 Research scholar, 2 Assistant
Use of Full Spectrum Cascade for Rotor Rub Identification T. H. Patel 1, A. K. Darpe 2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi 110016, India. 1 Research scholar, 2 Assistant
Chapter a. Spring constant, k : The change in the force per unit length change of the spring. b. Coefficient of subgrade reaction, k:
 Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
Principles of Soil Dynamics 3rd Edition Das SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/principles-soil-dynamics-3rd-editiondas-solutions-manual/ Chapter
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR.
 LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
Oscillatory Motion SHM
 Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion SHM Dr. Armen Kocharian Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion SHM Dr. Armen Kocharian Periodic Motion Periodic motion is motion of an object that regularly repeats The object returns to a given position after a fixed time interval A
COMPARISON BETWEEN 2D AND 3D ANALYSES OF SEISMIC STABILITY OF DETACHED BLOCKS IN AN ARCH DAM
 COMPARISON BETWEEN 2D AND 3D ANALYSES OF SEISMIC STABILITY OF DETACHED BLOCKS IN AN ARCH DAM Sujan MALLA 1 ABSTRACT The seismic safety of the 147 m high Gigerwald arch dam in Switzerland was assessed for
COMPARISON BETWEEN 2D AND 3D ANALYSES OF SEISMIC STABILITY OF DETACHED BLOCKS IN AN ARCH DAM Sujan MALLA 1 ABSTRACT The seismic safety of the 147 m high Gigerwald arch dam in Switzerland was assessed for
Modal analysis of shear buildings
 Modal analysis of shear buildings A comprehensive modal analysis of an arbitrary multistory shear building having rigid beams and lumped masses at floor levels is obtained. Angular frequencies (rad/sec),
Modal analysis of shear buildings A comprehensive modal analysis of an arbitrary multistory shear building having rigid beams and lumped masses at floor levels is obtained. Angular frequencies (rad/sec),
Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance
 NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance Basic principles Ioannis N. Psycharis Lecture 3 MDOF systems Equation of motion M u + C u + K u = M r x g(t) where:
NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF ATHENS Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance Basic principles Ioannis N. Psycharis Lecture 3 MDOF systems Equation of motion M u + C u + K u = M r x g(t) where:
Dynamic Analysis Using Response Spectrum Seismic Loading
 Dynamic Analysis Using Response Spectrum Seismic Loading Paleti Teja M.Tech (Structural Engineering) Department of Civil Engineering Jogaiah Institute of Technology & Sciences College of Engineering Kalagampudi,
Dynamic Analysis Using Response Spectrum Seismic Loading Paleti Teja M.Tech (Structural Engineering) Department of Civil Engineering Jogaiah Institute of Technology & Sciences College of Engineering Kalagampudi,
Evaluation of a Six-DOF Electrodynamic Shaker System
 Evaluation of a Six-DOF Electrodynamic Shaker System David O. Smallwood Consultant 9817 Pitt Pl. NE Albuquerque NM 87111 (55) 296-2931 Dan Gregory Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque NM 87185 (55)
Evaluation of a Six-DOF Electrodynamic Shaker System David O. Smallwood Consultant 9817 Pitt Pl. NE Albuquerque NM 87111 (55) 296-2931 Dan Gregory Sandia National Laboratories Albuquerque NM 87185 (55)
