Graphene: : CERN on the desk. Mikhail Katsnelson
|
|
|
- Martha Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Graphene: : CERN on the desk Mikhail Katsnelson
2 Instead of epigraph You can get much further with a kind word and a gun than you can with a kind word alone (Al Capone) You can get much further with an insight from experiment and mathematics than you can with mathematics alone
3 Why graphene is interesting? Till 2004: a way to understand graphite, nanotubes, fullerenes + theoretical interest (Dirac point Wallace 1947, McClure 1956 ) Do we theoreticians need experimentalists?! Yes!!! (Klein tunneling, supercritical charge, ripples, new wave equation bilayer, new type of transport ) 1. Applications (modern electronics is 2D, bulk is ballast) 2. Prototype membrane (new drosophila for 2D statistical mechanics) 3. CERN on the desk (mimic high energy physics)
4 Massless Dirac fermions pseudospin sp 2 hybridization, π bands crossing the neutrality point Neglecting intervalley scattering: massless Dirac fermions Symmetry protected (T and I)
5 Outline Minimal conductivity problem and transport via evanescent waves Klein tunneling and inhomogeneities Gauge pseudomagnetic fields and strain engineering Relativistic collapse for supercritical charges
6 Quantum-Limited Resistivity E =0 ρ (kω) ρ max 10K no temperature dependence in the peak between 3 and 80K V g (V) zero-gap semiconductor Novoselov et al, Nature 2005 ρ max (h/4e 2 ) 2 15 devices 1 µ (cm 2 /Vs) 0 0 4,000 8,000
7 Problem of minimal conductivity At zero doping, zero temperature there is a finite minimal conductivity approximately e 2 /h per channel Two views: from the side of no disorder and from the side of strong disorder Amazing property of 2D massless particles: finite conductivity for ideal crystal no scattering, no current carriers! (Ludwig et al, PR B 1994)
8 Transport via evanescent waves MIK, EPJ B 51, 157 (2006) Conductance = e 2 /h Tr T per valley per spin T is the transmission probability matrix The wave functions of massless Dirac fermions at zero energy: x ± i y ψ ( x, y) = 0 ψ ( x y) = f ( x± iy) f ± ±, Boundary conditions determine the functions f
9 Transport via evanescent waves II f(y+l y ) = f(y) ψ 2πn L ( x, y) = exp i ( x ± iy) = 0, ± 1, ± 2,... ± n y Edge states near the top and bottom of the sample New type of electron transport: via evanescent waves different from both ballistic and diffusive
10 Transport via evanescent waves III Leads from doped graphene Conductivity per channel: The problem of missing pi(e) may be, no problem
11 Other geometries by conformal mapping (MIK and Guinea, PR B 2008; Rycerz, Recher and Wimmer, PR B 2010) Λ transforms the region to circular ring (Corbino geometry)
12 Aharonov-Bohm effect at zero doping MIK, EPL 89, (2009) Magnetic flux tube within the ring General shape (topologically equivalent to rings)
13 Chiral tunneling and Klein paradox MIK, Novoselov, Geim, Nat. Phys. 2, 620 (2006) Electronics: heterostructures (p-n-p junctions etc.) Classical particles: cannot propagate through potential barriers Quantum particles: can propagate (tunneling) but probability decays exponentially with barrier height and width Ultrarelativistic quantum particles: can propagate with the probability of order of unity (Klein paradox)
14 Klein paradox II Ultrarelativisic Nonrelativistic Tunnel effect: momentum and coordinate are complementary variables, kinetic and potential energy are not measurable simultaneously Relativistic case: even the coordinate itself is not measurable, particle-antiparticle antiparticle pair creation
15 Transmission probability Barrier width 100 nm Electron concentration outside barrier 0.5x10 12 Hole concentration inside barrier 1x10 12 (red) and 3x10 12 cm Klein paradox III 12 cm cm -2 cm -2 (blue)
16 Klein paradox IV Problem: graphene transistor can hardly be locked! Possible solution: use bilayer graphene: chiral fermions with parabolic spectrum no analogue in particle physics! Transmission for bilayer; parameters are the same as for previous slide
17 Semiclassical theory T. Tudorovskiy, K. Reijnders & MIK, 2011 One-dimensional potential Skipping tildas: the Hamiltonian
18 Semiclassical theory II Reduction to exact Schrödinger equations for complex potential Canonical operator, expansion in h plus comparison with exact solution for linear potential (McCann & Falko, 2006)
19 Semiclassical theory III Fabry-Perot resonances For nonsymmetric p-n-p junction 100% transmission only at normal incidence
20 Comparison with numerics Asymmetric barriers
21 Bilayer graphene Magic angles with 100% transmission always exist (numerics) Interesting and important theoretical problem (no obvious conservation law, etc.)
22 Klein tunneling: Experimental confirmation
23 Back scattering is forbidden for chiral fermions! Magic angle = 0 Nonuniversal magic angle for bilayer exists! Klein tunneling prevents localization Graphene Conventional semiconductors Electrons cannot be locked by random potential relief neither for single-layer layer nor for bilayer graphene absence of localization and minimal conductivity?!
24 Quantum-Limited Resistivity σ = neµ = e 2 h k F l Mott argument: σ e 2 h (in the absence of localization) l λ F
25 Inhomogeneities are unavoidable Freely suspended graphene membrane is corrugated Meyer et al, Nature 446, 60 (2007) 2D crystals in 3D space cannot be flat, due to bending instability Atomistic simulations of intrinsic ripples Fasolino, Los & MIK, Nature Mater. 6, 858 (2007)
26 Chemical bonds RT: tendency to formation of single and double bonds instead of equivalent conjugated bonds Bending for chemical reasons
27 Pseudomagnetic fields Nearest-neighbour approximation: changes of hopping integrals Vector potentials K and K points are shifted in opposite directions; Umklapp processes restore time-reversal symmetry
28 Ripples and puddles Gibertini, Tomadin, Polini, Fasolino & MIK, PR B 81, (2010)
29 Gauge fields from mechanics: back to Maxwell Electromagnetic fields as deformations in ether; gears and wheels Review: Vozmediano, MIK & Guinea, Phys. Rep. 496, 109 (2010)
30 Zero-field QHE by strain engineering F. Guinea, MIK & A. Geim, Nature Phys. 6, 30 (2010) Within elasticity theory (continuum limit) Pseudomagnetic field
31 Zero-field QHE by strain engineering II Homegeneous magnetic field Three-fold symmetry With normal forces only
32 Zero-field QHE by strain engineering III Graphene: deformations up to 25%; at 10% pseudomagnetic fields of order T. Can be a bit inhomogeneous Normal stress applied to three edges, size 1.4 µm DOS in the center (0.5 µm)
33 Experimental confirmation? Graphene on Pt(111) STM observation of pseudo-landau levels
34 Combination of strain and electric field: Haldane insulator state (T. Low, F. Guinea & MIK, 2011) Without inversion center combination of vector and scalar potential leads to gap opening Wrinkles plus modulated scalar potential at different angles to the wrinkilng direction
35 Relativistic collapse for supercritical Coulomb potential charges following Shytov, MIK & Levitov, PRL 99, ; (2007) Naive arguments: Radius of atom R, momentum ħ/r. Nonrelativistic case: E(R) ~ ħ 2 /mr 2 Ze 2 /R Minimum gives a size of atom. Relativistic case: E(R) ~ ħc*/r Ze 2 /R Either no bound state or fall on the center. Vacuum reconstruction at Z > 170
36 Supercritical charges II Superheavy nuclei Graphene: v c/300, α eff 1
37 Supercritical charges III β = Ze 2 /ћv F ε > ½ Klein tunneling Quasi-local states
38 Supercritical charges IV Interference of scattered wave and wave described electron fall to the centre leads to oscillations of electron density β = 0.6 Inset: oscillations for different charges
39 Supercritical charge V
40 Vacuum polarization effect and screening Dimensional analysis: induced charge density in undoped graphene n(r) = Aδ(r) + B/r 2 If B is not zero: logarithmically divergent induces charge and nullification of Coulomb potential predicted by Thomas Fermi theory MIK, PR B 74, (2006) Linear screening theory: constant dielectric function, screening charge focused at the coordinate origin (only first term)
41 Screening II N = 4 (two valleys, two spins) Large β: replacing the sum by an integral recover the Thomas-Fermi result RG analysis: supercritical charge is screened to β = ½ with a finite screening radius (similar to black hole horizon)
42 Conclusions and final remarks New type of transport in solids: quantum relativistic transport via evanscent waves Klein tunneling a key phenomenon for graphene physics and applications Gauge fields are real mechanical fields, one can manipulate them Vacuum reconstruction? QED with strong interaction
43 Main collaborators Andre Geim, Kostya Novoselov (Manchester) Annalisa Fasolino, Jan Los, Kostya Zakharchenko, Rafa Roldan, Timur Tudorovskiy, Shengjun Yuan, Koen Reijnders (Nijmegen) Leonya Levitov (MIT), Andrey Shytov (Exeter) Paco Guinea, Maria Vozmediano (Madrid) Marco Polini (Pisa), Misha Fogler (San Diego) Tony Low (Purdue Univ.)
From materials science to basic physics
 From materials science to basic physics Mikhail Katsnelson 1. Wave-particle duality in solids: itinerant vs localized behavior of electrons in correlated systems. How to understand ARPES data 2. Massless
From materials science to basic physics Mikhail Katsnelson 1. Wave-particle duality in solids: itinerant vs localized behavior of electrons in correlated systems. How to understand ARPES data 2. Massless
Atomic collapse in graphene
 Atomic collapse in graphene Andrey V. Shytov (BNL) Work done in collaboration with: L.S. Levitov MIT M.I. Katsnelson University of Nijmegen, Netherlands * Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 236801; ibid. 99, 246802
Atomic collapse in graphene Andrey V. Shytov (BNL) Work done in collaboration with: L.S. Levitov MIT M.I. Katsnelson University of Nijmegen, Netherlands * Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 236801; ibid. 99, 246802
Graphene: massless electrons in flatland.
 Graphene: massless electrons in flatland. Enrico Rossi Work supported by: University of Chile. Oct. 24th 2008 Collaorators CMTC, University of Maryland Sankar Das Sarma Shaffique Adam Euyuong Hwang Roman
Graphene: massless electrons in flatland. Enrico Rossi Work supported by: University of Chile. Oct. 24th 2008 Collaorators CMTC, University of Maryland Sankar Das Sarma Shaffique Adam Euyuong Hwang Roman
Quantum theory of real materials: From graphene to high-temperature superconductors. Mikhail Katsnelson
 Quantum theory of real materials: From graphene to high-temperature superconductors Mikhail Katsnelson Hamburg Prize for Theoretical Physics In Russian: a methaphor of honest, true rating Legend invented
Quantum theory of real materials: From graphene to high-temperature superconductors Mikhail Katsnelson Hamburg Prize for Theoretical Physics In Russian: a methaphor of honest, true rating Legend invented
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons
 Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics
 Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics 09 02 200802 2008 ME class Outline driving force for the carbon nanomaterial electronic properties of fullerene exploration of electronic carbon nanotube gold rush of
Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics 09 02 200802 2008 ME class Outline driving force for the carbon nanomaterial electronic properties of fullerene exploration of electronic carbon nanotube gold rush of
GRAPHENE the first 2D crystal lattice
 GRAPHENE the first 2D crystal lattice dimensionality of carbon diamond, graphite GRAPHENE realized in 2004 (Novoselov, Science 306, 2004) carbon nanotubes fullerenes, buckyballs what s so special about
GRAPHENE the first 2D crystal lattice dimensionality of carbon diamond, graphite GRAPHENE realized in 2004 (Novoselov, Science 306, 2004) carbon nanotubes fullerenes, buckyballs what s so special about
KAVLI v F. Curved graphene revisited. María A. H. Vozmediano. Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid CSIC
 KAVLI 2012 v F Curved graphene revisited María A. H. Vozmediano Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid CSIC Collaborators ICMM(Graphene group) http://www.icmm.csic.es/gtg/ A. Cano E. V. Castro J.
KAVLI 2012 v F Curved graphene revisited María A. H. Vozmediano Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid CSIC Collaborators ICMM(Graphene group) http://www.icmm.csic.es/gtg/ A. Cano E. V. Castro J.
Graphene and Quantum Hall (2+1)D Physics
 The 4 th QMMRC-IPCMS Winter School 8 Feb 2011, ECC, Seoul, Korea Outline 2 Graphene and Quantum Hall (2+1)D Physics Lecture 1. Electronic structures of graphene and bilayer graphene Lecture 2. Electrons
The 4 th QMMRC-IPCMS Winter School 8 Feb 2011, ECC, Seoul, Korea Outline 2 Graphene and Quantum Hall (2+1)D Physics Lecture 1. Electronic structures of graphene and bilayer graphene Lecture 2. Electrons
Electronic structure and properties of a few-layer black phosphorus Mikhail Katsnelson
 Electronic structure and properties of a few-layer black phosphorus Mikhail Katsnelson Main collaborators: Sasha Rudenko Shengjun Yuan Rafa Roldan Milton Pereira Sergey Brener Motivation Plenty of 2D materials
Electronic structure and properties of a few-layer black phosphorus Mikhail Katsnelson Main collaborators: Sasha Rudenko Shengjun Yuan Rafa Roldan Milton Pereira Sergey Brener Motivation Plenty of 2D materials
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions
 Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
3-month progress Report
 3-month progress Report Graphene Devices and Circuits Supervisor Dr. P.A Childs Table of Content Abstract... 1 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Graphene gold rush... 1 1.2 Properties of graphene... 3 1.3 Semiconductor
3-month progress Report Graphene Devices and Circuits Supervisor Dr. P.A Childs Table of Content Abstract... 1 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Graphene gold rush... 1 1.2 Properties of graphene... 3 1.3 Semiconductor
A BIT OF MATERIALS SCIENCE THEN PHYSICS
 GRAPHENE AND OTHER D ATOMIC CRYSTALS Andre Geim with many thanks to K. Novoselov, S. Morozov, D. Jiang, F. Schedin, I. Grigorieva, J. Meyer, M. Katsnelson A BIT OF MATERIALS SCIENCE THEN PHYSICS CARBON
GRAPHENE AND OTHER D ATOMIC CRYSTALS Andre Geim with many thanks to K. Novoselov, S. Morozov, D. Jiang, F. Schedin, I. Grigorieva, J. Meyer, M. Katsnelson A BIT OF MATERIALS SCIENCE THEN PHYSICS CARBON
Graphene A One-Atom-Thick Material for Microwave Devices
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 11, Number 1, 2008, 29 35 Graphene A One-Atom-Thick Material for Microwave Devices D. DRAGOMAN 1, M. DRAGOMAN 2, A. A. MÜLLER3 1 University
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 11, Number 1, 2008, 29 35 Graphene A One-Atom-Thick Material for Microwave Devices D. DRAGOMAN 1, M. DRAGOMAN 2, A. A. MÜLLER3 1 University
Effects of Interactions in Suspended Graphene
 Effects of Interactions in Suspended Graphene Ben Feldman, Andrei Levin, Amir Yacoby, Harvard University Broken and unbroken symmetries in the lowest LL: spin and valley symmetries. FQHE Discussions with
Effects of Interactions in Suspended Graphene Ben Feldman, Andrei Levin, Amir Yacoby, Harvard University Broken and unbroken symmetries in the lowest LL: spin and valley symmetries. FQHE Discussions with
Electronic properties of graphene. Jean-Noël Fuchs Laboratoire de Physique des Solides Université Paris-Sud (Orsay)
 Electronic properties of graphene Jean-Noël Fuchs Laboratoire de Physique des Solides Université Paris-Sud (Orsay) Cargèse, September 2012 3 one-hour lectures in 2 x 1,5h on electronic properties of graphene
Electronic properties of graphene Jean-Noël Fuchs Laboratoire de Physique des Solides Université Paris-Sud (Orsay) Cargèse, September 2012 3 one-hour lectures in 2 x 1,5h on electronic properties of graphene
& Dirac Fermion confinement Zahra Khatibi
 Graphene & Dirac Fermion confinement Zahra Khatibi 1 Outline: What is so special about Graphene? applications What is Graphene? Structure Transport properties Dirac fermions confinement Necessity External
Graphene & Dirac Fermion confinement Zahra Khatibi 1 Outline: What is so special about Graphene? applications What is Graphene? Structure Transport properties Dirac fermions confinement Necessity External
IS THERE ANY KLEIN PARADOX? LOOK AT GRAPHENE! D. Dragoman Univ. Bucharest, Physics Dept., P.O. Box MG-11, Bucharest,
 1 IS THERE ANY KLEIN PARADOX? LOOK AT GRAPHENE! D. Dragoman Univ. Bucharest, Physics Dept., P.O. Box MG-11, 077125 Bucharest, Romania, e-mail: danieladragoman@yahoo.com Abstract It is demonstrated that
1 IS THERE ANY KLEIN PARADOX? LOOK AT GRAPHENE! D. Dragoman Univ. Bucharest, Physics Dept., P.O. Box MG-11, 077125 Bucharest, Romania, e-mail: danieladragoman@yahoo.com Abstract It is demonstrated that
Transport properties through double-magnetic-barrier structures in graphene
 Chin. Phys. B Vol. 20, No. 7 (20) 077305 Transport properties through double-magnetic-barrier structures in graphene Wang Su-Xin( ) a)b), Li Zhi-Wen( ) a)b), Liu Jian-Jun( ) c), and Li Yu-Xian( ) c) a)
Chin. Phys. B Vol. 20, No. 7 (20) 077305 Transport properties through double-magnetic-barrier structures in graphene Wang Su-Xin( ) a)b), Li Zhi-Wen( ) a)b), Liu Jian-Jun( ) c), and Li Yu-Xian( ) c) a)
Quantum Confinement in Graphene
 Quantum Confinement in Graphene from quasi-localization to chaotic billards MMM dominikus kölbl 13.10.08 1 / 27 Outline some facts about graphene quasibound states in graphene numerical calculation of
Quantum Confinement in Graphene from quasi-localization to chaotic billards MMM dominikus kölbl 13.10.08 1 / 27 Outline some facts about graphene quasibound states in graphene numerical calculation of
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities
 Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
Impact of disorder and topology in two dimensional systems at low carrier densities A Thesis Submitted For the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in the Faculty of Science by Mohammed Ali Aamir Department
TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES
 TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES 1) Berry curvature in superlattice bands 2) Energy scales for Moire superlattices 3) Spin-Hall effect in graphene Leonid Levitov (MIT) @ ISSP U Tokyo MIT Manchester
TOPOLOGICAL BANDS IN GRAPHENE SUPERLATTICES 1) Berry curvature in superlattice bands 2) Energy scales for Moire superlattices 3) Spin-Hall effect in graphene Leonid Levitov (MIT) @ ISSP U Tokyo MIT Manchester
From graphene to Z2 topological insulator
 From graphene to Z2 topological insulator single Dirac topological AL mass U U valley WL ordinary mass or ripples WL U WL AL AL U AL WL Rashba Ken-Ichiro Imura Condensed-Matter Theory / Tohoku Univ. Dirac
From graphene to Z2 topological insulator single Dirac topological AL mass U U valley WL ordinary mass or ripples WL U WL AL AL U AL WL Rashba Ken-Ichiro Imura Condensed-Matter Theory / Tohoku Univ. Dirac
Relativistic magnetotransport in graphene
 Relativistic magnetotransport in graphene Markus Müller in collaboration with Lars Fritz (Harvard) Subir Sachdev (Harvard) Jörg Schmalian (Iowa) Landau Memorial Conference June 6, 008 Outline Relativistic
Relativistic magnetotransport in graphene Markus Müller in collaboration with Lars Fritz (Harvard) Subir Sachdev (Harvard) Jörg Schmalian (Iowa) Landau Memorial Conference June 6, 008 Outline Relativistic
Graphene: Quantum Transport via Evanescent Waves
 Graphene: Quantum Transport via Evanescent Waves Milan Holzäpfel 6 May 203 (slides from the talk with additional notes added in some places /7 Overview Quantum Transport: Landauer Formula Graphene: Introduction
Graphene: Quantum Transport via Evanescent Waves Milan Holzäpfel 6 May 203 (slides from the talk with additional notes added in some places /7 Overview Quantum Transport: Landauer Formula Graphene: Introduction
Electronic properties of Graphene and 2-D materials
 Electronic properties of Graphene and 2-D materials 2D materials background Carbon allotropes Graphene Structure and Band structure Electronic properties Electrons in a magnetic field Onsager relation
Electronic properties of Graphene and 2-D materials 2D materials background Carbon allotropes Graphene Structure and Band structure Electronic properties Electrons in a magnetic field Onsager relation
Scaling Anomaly and Atomic Collapse Collective Energy Propagation at Charge Neutrality
 Scaling Anomaly and Atomic Collapse Collective Energy Propagation at Charge Neutrality Leonid Levitov (MIT) Electron Interactions in Graphene FTPI, University of Minnesota 05/04/2013 Scaling symmetry:
Scaling Anomaly and Atomic Collapse Collective Energy Propagation at Charge Neutrality Leonid Levitov (MIT) Electron Interactions in Graphene FTPI, University of Minnesota 05/04/2013 Scaling symmetry:
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics
 Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
Chun Ning Lau (Jeanie) Graphene: Quantum Transport in a 2D Membrane
 Chun Ning Lau (Jeanie) Graphene: Quantum Transport in a 2D Membrane Grapheneʼs Double Identity Extraordinary Conductor 2D Elastic Membrane Novoselov et al Nature 2005; Zhang et al, Nature 2005. New model
Chun Ning Lau (Jeanie) Graphene: Quantum Transport in a 2D Membrane Grapheneʼs Double Identity Extraordinary Conductor 2D Elastic Membrane Novoselov et al Nature 2005; Zhang et al, Nature 2005. New model
Dirac matter: Magneto-optical studies
 Dirac matter: Magneto-optical studies Marek Potemski Laboratoire National des Champs Magnétiques Intenses Grenoble High Magnetic Field Laboratory CNRS/UGA/UPS/INSA/EMFL MOMB nd International Conference
Dirac matter: Magneto-optical studies Marek Potemski Laboratoire National des Champs Magnétiques Intenses Grenoble High Magnetic Field Laboratory CNRS/UGA/UPS/INSA/EMFL MOMB nd International Conference
Graphene - most two-dimensional system imaginable
 Graphene - most two-dimensional system imaginable A suspended sheet of pure graphene a plane layer of C atoms bonded together in a honeycomb lattice is the most two-dimensional system imaginable. A.J.
Graphene - most two-dimensional system imaginable A suspended sheet of pure graphene a plane layer of C atoms bonded together in a honeycomb lattice is the most two-dimensional system imaginable. A.J.
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Aug 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Aug 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Aug 2006](/thumbs/76/73692373.jpg) Chiral tunneling and the Klein paradox in graphene arxiv:cond-mat/0604323v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Aug 2006 M. I. Katsnelson, 1 K. S. Novoselov, 2 and A. K. Geim 2 1 Institute for Molecules and Materials,
Chiral tunneling and the Klein paradox in graphene arxiv:cond-mat/0604323v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Aug 2006 M. I. Katsnelson, 1 K. S. Novoselov, 2 and A. K. Geim 2 1 Institute for Molecules and Materials,
Mesoscopic physics: From low-energy nuclear [1] to relativistic [2] high-energy analogies
![Mesoscopic physics: From low-energy nuclear [1] to relativistic [2] high-energy analogies Mesoscopic physics: From low-energy nuclear [1] to relativistic [2] high-energy analogies](/thumbs/92/108493944.jpg) Mesoscopic physics: From low-energy nuclear [1] to relativistic [2] high-energy analogies Constantine Yannouleas and Uzi Landman School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology [1] Ch. 4 in Metal Clusters,
Mesoscopic physics: From low-energy nuclear [1] to relativistic [2] high-energy analogies Constantine Yannouleas and Uzi Landman School of Physics, Georgia Institute of Technology [1] Ch. 4 in Metal Clusters,
Coulomb Drag in Graphene
 Graphene 2017 Coulomb Drag in Graphene -Toward Exciton Condensation Philip Kim Department of Physics, Harvard University Coulomb Drag Drag Resistance: R D = V 2 / I 1 Onsager Reciprocity V 2 (B)/ I 1 =
Graphene 2017 Coulomb Drag in Graphene -Toward Exciton Condensation Philip Kim Department of Physics, Harvard University Coulomb Drag Drag Resistance: R D = V 2 / I 1 Onsager Reciprocity V 2 (B)/ I 1 =
ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE
 ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE J. González Instituto de Estructura de la Materia, CSIC, Spain 1985 1991 4 ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE Graphene has opened the way to understand the behaior of an
ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE J. González Instituto de Estructura de la Materia, CSIC, Spain 1985 1991 4 ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE Graphene has opened the way to understand the behaior of an
Theories of graphene. Reinhold Egger Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Kolloquium, Hamburg
 Theories of graphene Reinhold Egger Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Kolloquium, Hamburg 1. 5. 011 Graphene monolayer Mother of all-carbon materials (fullerenes, nanotubes, graphite): made of benzene
Theories of graphene Reinhold Egger Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Kolloquium, Hamburg 1. 5. 011 Graphene monolayer Mother of all-carbon materials (fullerenes, nanotubes, graphite): made of benzene
Engineering of quantum Hamiltonians by high-frequency laser fields Mikhail Katsnelson
 Engineering of quantum Hamiltonians by high-frequency laser fields Mikhail Katsnelson Main collaborators: Sasha Itin Clément Dutreix Zhenya Stepanov Theory of Condensed Matter group http://www.ru.nl/tcm
Engineering of quantum Hamiltonians by high-frequency laser fields Mikhail Katsnelson Main collaborators: Sasha Itin Clément Dutreix Zhenya Stepanov Theory of Condensed Matter group http://www.ru.nl/tcm
ELECTRONIC ENERGY DISPERSION AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES ON GRAPHENE AND CARBON NANOTUBES
 ELECTRONIC ENERGY DISPERSION AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES ON GRAPHENE AND CARBON NANOTUBES D. RACOLTA, C. ANDRONACHE, D. TODORAN, R. TODORAN Technical University of Cluj Napoca, North University Center of
ELECTRONIC ENERGY DISPERSION AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES ON GRAPHENE AND CARBON NANOTUBES D. RACOLTA, C. ANDRONACHE, D. TODORAN, R. TODORAN Technical University of Cluj Napoca, North University Center of
Dirac fermions in Graphite:
 Igor Lukyanchuk Amiens University, France, Yakov Kopelevich University of Campinas, Brazil Dirac fermions in Graphite: I. Lukyanchuk, Y. Kopelevich et al. - Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 166402 (2004) - Phys. Rev.
Igor Lukyanchuk Amiens University, France, Yakov Kopelevich University of Campinas, Brazil Dirac fermions in Graphite: I. Lukyanchuk, Y. Kopelevich et al. - Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 166402 (2004) - Phys. Rev.
LECTURES ON QUANTUM MECHANICS
 LECTURES ON QUANTUM MECHANICS GORDON BAYM Unitsersity of Illinois A II I' Advanced Bock Progrant A Member of the Perseus Books Group CONTENTS Preface v Chapter 1 Photon Polarization 1 Transformation of
LECTURES ON QUANTUM MECHANICS GORDON BAYM Unitsersity of Illinois A II I' Advanced Bock Progrant A Member of the Perseus Books Group CONTENTS Preface v Chapter 1 Photon Polarization 1 Transformation of
Topological Physics in Band Insulators. Gene Mele Department of Physics University of Pennsylvania
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators Gene Mele Department of Physics University of Pennsylvania A Brief History of Topological Insulators What they are How they were discovered Why they are important
Topological Physics in Band Insulators Gene Mele Department of Physics University of Pennsylvania A Brief History of Topological Insulators What they are How they were discovered Why they are important
Quantum Field Theory. Kerson Huang. Second, Revised, and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH. From Operators to Path Integrals
 Kerson Huang Quantum Field Theory From Operators to Path Integrals Second, Revised, and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA I vh Contents Preface XIII 1 Introducing Quantum Fields
Kerson Huang Quantum Field Theory From Operators to Path Integrals Second, Revised, and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA I vh Contents Preface XIII 1 Introducing Quantum Fields
Klein tunneling in graphene p-n-p junctions
 10.1149/1.3569920 The Electrochemical Society Klein tunneling in graphene p-n-p junctions E. Rossi 1,J.H.Bardarson 2,3,P.W.Brouwer 4 1 Department of Physics, College of William and Mary, Williamsburg,
10.1149/1.3569920 The Electrochemical Society Klein tunneling in graphene p-n-p junctions E. Rossi 1,J.H.Bardarson 2,3,P.W.Brouwer 4 1 Department of Physics, College of William and Mary, Williamsburg,
J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2)
 Part I - Mechanics J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) s α l θ g z x A uniform rod of length l and mass m moves in the x-z plane. One end of the rod is suspended from a straight
Part I - Mechanics J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) s α l θ g z x A uniform rod of length l and mass m moves in the x-z plane. One end of the rod is suspended from a straight
Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands
 Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands Thomas Dahm University of Bielefeld T. Paananen and T. Dahm, PRB 87, 195447 (2013) T. Paananen et al, New J. Phys. 16, 033019 (2014)
Topological Insulators and Ferromagnets: appearance of flat surface bands Thomas Dahm University of Bielefeld T. Paananen and T. Dahm, PRB 87, 195447 (2013) T. Paananen et al, New J. Phys. 16, 033019 (2014)
Physics of Semiconductors
 Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Physics of Semiconductors 13 th 2016.7.11 Shingo Katsumoto Department of Physics and Institute for Solid State Physics University of Tokyo Outline today Laughlin s justification Spintronics Two current
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum
 Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
Laughlin quasiparticle interferometer: Observation of Aharonov-Bohm superperiod and fractional statistics
 Laughlin quasiparticle interferometer: Observation of Aharonov-Bohm superperiod and fractional statistics F.E. Camino, W. Zhou and V.J. Goldman Stony Brook University Outline Exchange statistics in 2D,
Laughlin quasiparticle interferometer: Observation of Aharonov-Bohm superperiod and fractional statistics F.E. Camino, W. Zhou and V.J. Goldman Stony Brook University Outline Exchange statistics in 2D,
6. QED. Particle and Nuclear Physics. Dr. Tina Potter. Dr. Tina Potter 6. QED 1
 6. QED Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 6. QED 1 In this section... Gauge invariance Allowed vertices + examples Scattering Experimental tests Running of alpha Dr. Tina Potter
6. QED Particle and Nuclear Physics Dr. Tina Potter Dr. Tina Potter 6. QED 1 In this section... Gauge invariance Allowed vertices + examples Scattering Experimental tests Running of alpha Dr. Tina Potter
Nonlinear Optical Response of Massless Dirac Fermions in Graphene and Topological Materials
 Nonlinear Optical Response of Massless Dirac Fermions in Graphene and Topological Materials Alexey Belyanin Department of Physics and Astronomy Texas A&M University Zhongqu Long, Sultan Almutairi, Ryan
Nonlinear Optical Response of Massless Dirac Fermions in Graphene and Topological Materials Alexey Belyanin Department of Physics and Astronomy Texas A&M University Zhongqu Long, Sultan Almutairi, Ryan
Supplementary Figure 2 Photoluminescence in 1L- (black line) and 7L-MoS 2 (red line) of the Figure 1B with illuminated wavelength of 543 nm.
 PL (normalized) Intensity (arb. u.) 1 1 8 7L-MoS 1L-MoS 6 4 37 38 39 4 41 4 Raman shift (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure 1 Raman spectra of the Figure 1B at the 1L-MoS area (black line) and 7L-MoS area (red
PL (normalized) Intensity (arb. u.) 1 1 8 7L-MoS 1L-MoS 6 4 37 38 39 4 41 4 Raman shift (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure 1 Raman spectra of the Figure 1B at the 1L-MoS area (black line) and 7L-MoS area (red
CONTENTS. vii. CHAPTER 2 Operators 15
 CHAPTER 1 Why Quantum Mechanics? 1 1.1 Newtonian Mechanics and Classical Electromagnetism 1 (a) Newtonian Mechanics 1 (b) Electromagnetism 2 1.2 Black Body Radiation 3 1.3 The Heat Capacity of Solids and
CHAPTER 1 Why Quantum Mechanics? 1 1.1 Newtonian Mechanics and Classical Electromagnetism 1 (a) Newtonian Mechanics 1 (b) Electromagnetism 2 1.2 Black Body Radiation 3 1.3 The Heat Capacity of Solids and
Maxwell s equations. electric field charge density. current density
 Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
On topological aspects of 2D graphene like materials
 On topological aspects of 2D graphene like materials M. J. I. Khan *, Kamran Tahir *, S. Babar * Laboratory of theoretical and computational physics * Department of Physics, Bahauddin Zakariya University,
On topological aspects of 2D graphene like materials M. J. I. Khan *, Kamran Tahir *, S. Babar * Laboratory of theoretical and computational physics * Department of Physics, Bahauddin Zakariya University,
Magnetic field induced confinement-deconfinement transition in graphene quantum dots
 Magnetic field induced confinement-deconfinement transition in graphene quantum dots G. Giavaras, P. A. Maksym, and M. Roy Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, Leicester LE1 7RH,
Magnetic field induced confinement-deconfinement transition in graphene quantum dots G. Giavaras, P. A. Maksym, and M. Roy Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, Leicester LE1 7RH,
Mikhail Katsnelson. Theory of Condensed Matter Institute for Molecules and Materials RU
 Theory of carbon-based based magnetism Mikhail Katsnelson Theory of Condensed Matter Institute for Molecules and Materials RU Outline sp magnetism in general: why it is interesting? Defect-induced magnetism
Theory of carbon-based based magnetism Mikhail Katsnelson Theory of Condensed Matter Institute for Molecules and Materials RU Outline sp magnetism in general: why it is interesting? Defect-induced magnetism
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Dirac cones reshaped by interaction effects in suspended graphene D. C. Elias et al #1. Experimental devices Graphene monolayers were obtained by micromechanical cleavage of graphite on top of an oxidized
Dirac cones reshaped by interaction effects in suspended graphene D. C. Elias et al #1. Experimental devices Graphene monolayers were obtained by micromechanical cleavage of graphite on top of an oxidized
Graphene: carbon in two dimensions
 Graphene: carbon in two dimensions Carbon is one of the most intriguing elements in the Periodic Table. It forms many allotropes, some known from ancient times (diamond and graphite) and some discovered
Graphene: carbon in two dimensions Carbon is one of the most intriguing elements in the Periodic Table. It forms many allotropes, some known from ancient times (diamond and graphite) and some discovered
Graphene electronics
 Graphene electronics Alberto Morpurgo Main collaborators J. Oostinga, H. Heersche, P. Jarillo Herrero, S. Russo, M. Craciun, L. Vandersypen, S. Tarucha, R. Danneau, P. Hakkonen A simple tight-binding H
Graphene electronics Alberto Morpurgo Main collaborators J. Oostinga, H. Heersche, P. Jarillo Herrero, S. Russo, M. Craciun, L. Vandersypen, S. Tarucha, R. Danneau, P. Hakkonen A simple tight-binding H
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes
 Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Part I. Many-Body Systems and Classical Field Theory
 Part I. Many-Body Systems and Classical Field Theory 1. Classical and Quantum Mechanics of Particle Systems 3 1.1 Introduction. 3 1.2 Classical Mechanics of Mass Points 4 1.3 Quantum Mechanics: The Harmonic
Part I. Many-Body Systems and Classical Field Theory 1. Classical and Quantum Mechanics of Particle Systems 3 1.1 Introduction. 3 1.2 Classical Mechanics of Mass Points 4 1.3 Quantum Mechanics: The Harmonic
Suspended graphene: a bridge to the Dirac point.
 Suspended graphene: a bridge to the Dirac point. Xu Du, Ivan Skachko, Anthony Barker, Eva Y. Andrei Department of Physics & Astronomy, Rutgers the State University of New Jersey The recent discovery of
Suspended graphene: a bridge to the Dirac point. Xu Du, Ivan Skachko, Anthony Barker, Eva Y. Andrei Department of Physics & Astronomy, Rutgers the State University of New Jersey The recent discovery of
Graphene transistor. Seminar I a. Mentor: doc. dr. Tomaž Rejec. April Abstract
 Graphene transistor Seminar I a Jan Srpčič Mentor: doc. dr. Tomaž Rejec April 2015 Abstract The topic of this seminar is graphene and its possible applications in the field of electronics, most notably
Graphene transistor Seminar I a Jan Srpčič Mentor: doc. dr. Tomaž Rejec April 2015 Abstract The topic of this seminar is graphene and its possible applications in the field of electronics, most notably
Electronic states on the surface of graphite
 Electronic states on the surface of graphite Guohong Li, Adina Luican, Eva Y. Andrei * Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers Univsersity, Piscataway, NJ 08854, USA Elsevier use only: Received date
Electronic states on the surface of graphite Guohong Li, Adina Luican, Eva Y. Andrei * Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rutgers Univsersity, Piscataway, NJ 08854, USA Elsevier use only: Received date
Elastic properties of graphene
 Elastic properties of graphene M. I. Katsnelson P. Le Doussal B. Horowitz K. Wiese J. Gonzalez P. San-Jose V. Parente B. Amorim R. Roldan C. Gomez-Navarro J. Gomez G. Lopez-Polin F. Perez-Murano A. Morpurgo
Elastic properties of graphene M. I. Katsnelson P. Le Doussal B. Horowitz K. Wiese J. Gonzalez P. San-Jose V. Parente B. Amorim R. Roldan C. Gomez-Navarro J. Gomez G. Lopez-Polin F. Perez-Murano A. Morpurgo
Topological insulator part I: Phenomena
 Phys60.nb 5 Topological insulator part I: Phenomena (Part II and Part III discusses how to understand a topological insluator based band-structure theory and gauge theory) (Part IV discusses more complicated
Phys60.nb 5 Topological insulator part I: Phenomena (Part II and Part III discusses how to understand a topological insluator based band-structure theory and gauge theory) (Part IV discusses more complicated
Carbon nanotubes and Graphene
 16 October, 2008 Solid State Physics Seminar Main points 1 History and discovery of Graphene and Carbon nanotubes 2 Tight-binding approximation Dynamics of electrons near the Dirac-points 3 Properties
16 October, 2008 Solid State Physics Seminar Main points 1 History and discovery of Graphene and Carbon nanotubes 2 Tight-binding approximation Dynamics of electrons near the Dirac-points 3 Properties
Graphene Field effect transistors
 GDR Meso 2008 Aussois 8-11 December 2008 Graphene Field effect transistors Jérôme Cayssol CPMOH, UMR Université de Bordeaux-CNRS 1) Role of the contacts in graphene field effect transistors motivated by
GDR Meso 2008 Aussois 8-11 December 2008 Graphene Field effect transistors Jérôme Cayssol CPMOH, UMR Université de Bordeaux-CNRS 1) Role of the contacts in graphene field effect transistors motivated by
Black phosphorus: A new bandgap tuning knob
 Black phosphorus: A new bandgap tuning knob Rafael Roldán and Andres Castellanos-Gomez Modern electronics rely on devices whose functionality can be adjusted by the end-user with an external knob. A new
Black phosphorus: A new bandgap tuning knob Rafael Roldán and Andres Castellanos-Gomez Modern electronics rely on devices whose functionality can be adjusted by the end-user with an external knob. A new
V bg
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION a b µ (1 6 cm V -1 s -1 ) 1..8.4-3 - -1 1 3 mfp (µm) 1 8 4-3 - -1 1 3 Supplementary Figure 1: Mobility and mean-free path. a) Drude mobility calculated from four-terminal resistance
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION a b µ (1 6 cm V -1 s -1 ) 1..8.4-3 - -1 1 3 mfp (µm) 1 8 4-3 - -1 1 3 Supplementary Figure 1: Mobility and mean-free path. a) Drude mobility calculated from four-terminal resistance
Semiconductor Physics and Devices Chapter 3.
 Introduction to the Quantum Theory of Solids We applied quantum mechanics and Schrödinger s equation to determine the behavior of electrons in a potential. Important findings Semiconductor Physics and
Introduction to the Quantum Theory of Solids We applied quantum mechanics and Schrödinger s equation to determine the behavior of electrons in a potential. Important findings Semiconductor Physics and
From optical graphene to topological insulator
 From optical graphene to topological insulator Xiangdong Zhang Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), China zhangxd@bit.edu.cn Collaborator: Wei Zhong (PhD student, BNU) Outline Background: From solid
From optical graphene to topological insulator Xiangdong Zhang Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), China zhangxd@bit.edu.cn Collaborator: Wei Zhong (PhD student, BNU) Outline Background: From solid
Quantum transport through graphene nanostructures
 Quantum transport through graphene nanostructures S. Rotter, F. Libisch, L. Wirtz, C. Stampfer, F. Aigner, I. Březinová, and J. Burgdörfer Institute for Theoretical Physics/E136 December 9, 2009 Graphene
Quantum transport through graphene nanostructures S. Rotter, F. Libisch, L. Wirtz, C. Stampfer, F. Aigner, I. Březinová, and J. Burgdörfer Institute for Theoretical Physics/E136 December 9, 2009 Graphene
Physics of Low-Dimensional Semiconductor Structures
 Physics of Low-Dimensional Semiconductor Structures Edited by Paul Butcher University of Warwick Coventry, England Norman H. March University of Oxford Oxford, England and Mario P. Tosi Scuola Normale
Physics of Low-Dimensional Semiconductor Structures Edited by Paul Butcher University of Warwick Coventry, England Norman H. March University of Oxford Oxford, England and Mario P. Tosi Scuola Normale
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Dec 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Dec 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Dec 2006](/thumbs/80/81150486.jpg) Graphene: carbon in two dimensions arxiv:cond-mat/0612534v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Dec 2006 Mikhail I. Katsnelson 1 1 Institute for Molecules and Materials, Radboud University Nijmegen, 6525 ED Nijmegen,
Graphene: carbon in two dimensions arxiv:cond-mat/0612534v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 20 Dec 2006 Mikhail I. Katsnelson 1 1 Institute for Molecules and Materials, Radboud University Nijmegen, 6525 ED Nijmegen,
DEFECTS IN 2D MATERIALS: HOW WE TAUGHT ELECTRONIC SCREENING TO MACHINES
 DEFECTS IN 2D MATERIALS: HOW WE TAUGHT ELECTRONIC SCREENING TO MACHINES Johannes Lischner Imperial College London LISCHNER GROUP AT IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Theory and simulation of materials: focus on
DEFECTS IN 2D MATERIALS: HOW WE TAUGHT ELECTRONIC SCREENING TO MACHINES Johannes Lischner Imperial College London LISCHNER GROUP AT IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Theory and simulation of materials: focus on
Part 1. March 5, 2014 Quantum Hadron Physics Laboratory, RIKEN, Wako, Japan 2
 MAR 5, 2014 Part 1 March 5, 2014 Quantum Hadron Physics Laboratory, RIKEN, Wako, Japan 2 ! Examples of relativistic matter Electrons, protons, quarks inside compact stars (white dwarfs, neutron, hybrid
MAR 5, 2014 Part 1 March 5, 2014 Quantum Hadron Physics Laboratory, RIKEN, Wako, Japan 2 ! Examples of relativistic matter Electrons, protons, quarks inside compact stars (white dwarfs, neutron, hybrid
A. F. J. Levi 1 EE539: Engineering Quantum Mechanics. Fall 2017.
 A. F. J. Levi 1 Engineering Quantum Mechanics. Fall 2017. TTh 9.00 a.m. 10.50 a.m., VHE 210. Web site: http://alevi.usc.edu Web site: http://classes.usc.edu/term-20173/classes/ee EE539: Abstract and Prerequisites
A. F. J. Levi 1 Engineering Quantum Mechanics. Fall 2017. TTh 9.00 a.m. 10.50 a.m., VHE 210. Web site: http://alevi.usc.edu Web site: http://classes.usc.edu/term-20173/classes/ee EE539: Abstract and Prerequisites
The Physics of Nanoelectronics
 The Physics of Nanoelectronics Transport and Fluctuation Phenomena at Low Temperatures Tero T. Heikkilä Low Temperature Laboratory, Aalto University, Finland OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of symbols
The Physics of Nanoelectronics Transport and Fluctuation Phenomena at Low Temperatures Tero T. Heikkilä Low Temperature Laboratory, Aalto University, Finland OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of symbols
Quantum behavior of graphene transistors near the scaling limit
 Supplementary Information for Quantum behavior of graphene transistors near the scaling limit Yanqing Wu *, Vasili Perebeinos, Yu-ming Lin, Tony Low, Fengnian Xia and Phaedon Avouris * IBM Thomas J. Watson
Supplementary Information for Quantum behavior of graphene transistors near the scaling limit Yanqing Wu *, Vasili Perebeinos, Yu-ming Lin, Tony Low, Fengnian Xia and Phaedon Avouris * IBM Thomas J. Watson
Imaging electrostatically confined Dirac fermions in graphene
 Imaging electrostatically confined Dirac fermions in graphene quantum dots 3 4 5 Juwon Lee, Dillon Wong, Jairo Velasco Jr., Joaquin F. Rodriguez-Nieva, Salman Kahn, Hsin- Zon Tsai, Takashi Taniguchi, Kenji
Imaging electrostatically confined Dirac fermions in graphene quantum dots 3 4 5 Juwon Lee, Dillon Wong, Jairo Velasco Jr., Joaquin F. Rodriguez-Nieva, Salman Kahn, Hsin- Zon Tsai, Takashi Taniguchi, Kenji
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures
 Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface
 Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface Ilya Eremin Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Uni Bochum Work done in collaboration with: F. Nogueira
Proximity-induced magnetization dynamics, interaction effects, and phase transitions on a topological surface Ilya Eremin Theoretische Physik III, Ruhr-Uni Bochum Work done in collaboration with: F. Nogueira
QUANTUM MECHANICS. Franz Schwabl. Translated by Ronald Kates. ff Springer
 Franz Schwabl QUANTUM MECHANICS Translated by Ronald Kates Second Revised Edition With 122Figures, 16Tables, Numerous Worked Examples, and 126 Problems ff Springer Contents 1. Historical and Experimental
Franz Schwabl QUANTUM MECHANICS Translated by Ronald Kates Second Revised Edition With 122Figures, 16Tables, Numerous Worked Examples, and 126 Problems ff Springer Contents 1. Historical and Experimental
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II
 Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
Topological Physics in Band Insulators II Gene Mele University of Pennsylvania Topological Insulators in Two and Three Dimensions The canonical list of electric forms of matter is actually incomplete Conductor
Theory of carbon-based magnetism
 Theory of carbon-based magnetism Mikhail Katsnelson Theory of Condensed Matter Institute for Molecules and Materials RU Outline sp magnetism in general: why it is interesting? Defect-induced magnetism
Theory of carbon-based magnetism Mikhail Katsnelson Theory of Condensed Matter Institute for Molecules and Materials RU Outline sp magnetism in general: why it is interesting? Defect-induced magnetism
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Trilayer graphene is a semimetal with a gate-tuneable band overlap M. F. Craciun, S. Russo, M. Yamamoto, J. B. Oostinga, A. F. Morpurgo and S. Tarucha
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Trilayer graphene is a semimetal with a gate-tuneable band overlap M. F. Craciun, S. Russo, M. Yamamoto, J. B. Oostinga, A. F. Morpurgo and S. Tarucha
5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
NONLOCAL TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE: VALLEY CURRENTS, HYDRODYNAMICS AND ELECTRON VISCOSITY
 NONLOCAL TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE: VALLEY CURRENTS, HYDRODYNAMICS AND ELECTRON VISCOSITY Leonid Levitov (MIT) Frontiers of Nanoscience ICTP Trieste, August, 2015 Boris @ 60 2 Boris @ 60 3 Boris Blinks the
NONLOCAL TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE: VALLEY CURRENTS, HYDRODYNAMICS AND ELECTRON VISCOSITY Leonid Levitov (MIT) Frontiers of Nanoscience ICTP Trieste, August, 2015 Boris @ 60 2 Boris @ 60 3 Boris Blinks the
Quantum Hall effect. Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in I believe. WHY?? G xy = N e2 h.
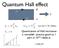 Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES
 PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES Jasprit Singh University of Michigan McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES Jasprit Singh University of Michigan McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal
The many forms of carbon
 The many forms of carbon Carbon is not only the basis of life, it also provides an enormous variety of structures for nanotechnology. This versatility is connected to the ability of carbon to form two
The many forms of carbon Carbon is not only the basis of life, it also provides an enormous variety of structures for nanotechnology. This versatility is connected to the ability of carbon to form two
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 6 Apr 2011
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 6 Apr 2011 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mtrl-sci] 6 Apr 2011](/thumbs/88/115458200.jpg) Melting of graphene: from two to one dimension K V Zakharchenko, Annalisa Fasolino, J H Los, M I Katsnelson 1 1 Radboud University of Nijmegen, Institute for Molecules and Materials, arxiv:1104.1130v1
Melting of graphene: from two to one dimension K V Zakharchenko, Annalisa Fasolino, J H Los, M I Katsnelson 1 1 Radboud University of Nijmegen, Institute for Molecules and Materials, arxiv:1104.1130v1
Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures
 B. Halperin Spin lecture 1 Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures Behavior of non-equilibrium spin populations. Spin relaxation and spin transport. How does one produce
B. Halperin Spin lecture 1 Spins and spin-orbit coupling in semiconductors, metals, and nanostructures Behavior of non-equilibrium spin populations. Spin relaxation and spin transport. How does one produce
Quantum Oscillations in Graphene in the Presence of Disorder
 WDS'9 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 97, 9. ISBN 978-8-778-- MATFYZPRESS Quantum Oscillations in Graphene in the Presence of Disorder D. Iablonskyi Taras Shevchenko National University of
WDS'9 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 97, 9. ISBN 978-8-778-- MATFYZPRESS Quantum Oscillations in Graphene in the Presence of Disorder D. Iablonskyi Taras Shevchenko National University of
Supplementary information for Tunneling Spectroscopy of Graphene-Boron Nitride Heterostructures
 Supplementary information for Tunneling Spectroscopy of Graphene-Boron Nitride Heterostructures F. Amet, 1 J. R. Williams, 2 A. G. F. Garcia, 2 M. Yankowitz, 2 K.Watanabe, 3 T.Taniguchi, 3 and D. Goldhaber-Gordon
Supplementary information for Tunneling Spectroscopy of Graphene-Boron Nitride Heterostructures F. Amet, 1 J. R. Williams, 2 A. G. F. Garcia, 2 M. Yankowitz, 2 K.Watanabe, 3 T.Taniguchi, 3 and D. Goldhaber-Gordon
Electron Interactions and Nanotube Fluorescence Spectroscopy C.L. Kane & E.J. Mele
 Electron Interactions and Nanotube Fluorescence Spectroscopy C.L. Kane & E.J. Mele Large radius theory of optical transitions in semiconducting nanotubes derived from low energy theory of graphene Phys.
Electron Interactions and Nanotube Fluorescence Spectroscopy C.L. Kane & E.J. Mele Large radius theory of optical transitions in semiconducting nanotubes derived from low energy theory of graphene Phys.
Maxwell s equations. based on S-54. electric field charge density. current density
 Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
Maxwell s equations based on S-54 Our next task is to find a quantum field theory description of spin-1 particles, e.g. photons. Classical electrodynamics is governed by Maxwell s equations: electric field
Topological Phases under Strong Magnetic Fields
 Topological Phases under Strong Magnetic Fields Mark O. Goerbig ITAP, Turunç, July 2013 Historical Introduction What is the common point between graphene, quantum Hall effects and topological insulators?...
Topological Phases under Strong Magnetic Fields Mark O. Goerbig ITAP, Turunç, July 2013 Historical Introduction What is the common point between graphene, quantum Hall effects and topological insulators?...
lattice that you cannot do with graphene! or... Antonio H. Castro Neto
 Theoretical Aspects What you can do with cold atomsof on agraphene honeycomb lattice that you cannot do with graphene! or... Antonio H. Castro Neto 2 Outline 1. Graphene for beginners 2. Fermion-Fermion
Theoretical Aspects What you can do with cold atomsof on agraphene honeycomb lattice that you cannot do with graphene! or... Antonio H. Castro Neto 2 Outline 1. Graphene for beginners 2. Fermion-Fermion
