Research Article Weak Solutions in Elasticity of Dipolar Porous Materials
|
|
|
- Nickolas Carter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume 2008, Article ID , 8 pages doi: /2008/ Research Article Weak Solutions in Elasticity of Dipolar Porous Materials Marin Marin Department of Mathematics, University of rasov, rasov, Romania Correspondence should be addressed to Marin Marin, m.marin@unitbv.ro Received 25 March 2008; Accepted 17 July 2008 Recommended by K. R. Rajagopal The main aim of our study is to use some general results from the general theory of elliptic equations in order to obtain some qualitative results in a concrete and very applicative situation. In fact, we will prove the existence and uniqueness of the generalized solutions for the boundary value problems in elasticity of initially stressed bodies with voids porous materials. Copyright q 2008 Marin Marin. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 1. Introduction The theories of porous materials represent a material length scale and are quite sufficient for a large number of the solid mechanics applications. In the following, we restrict our attention to the behavior of the porous solids in which the matrix material is elastic and the interstices are voids of material. The intended applications of this theory are to the geological materials, like rocks and soils and to the manufactured porous materials. The plane of the paper is the following one. In the beginning, we write down the basic equations and conditions of the mixed boundary value problem within context of linear theory of initially stressed bodies with voids, as in the papers of 1, 2. Then, we accommodate some general results from the paper 3, and the book 4, in order to obtain the existence and uniqueness of a weak solution of the formulated problem. For convenience, the notations chosen are almost identical to those of 2, asic equations Let be an open region of three-dimensional Euclidean space R 3 occupied by our porous material at time t 0. We assume that the boundary of the domain, denoted by, is a closed, bounded and pice-wise smooth surface which allows us the application of the
2 2 Mathematical Problems in Engineering divergence theorem. A fixed system of rectangular Cartesian axes is used and we adopt the Cartesian tensor notations. The points in are denoted by x i or x. The variable t is the time and t 0,t 0. We will employ the usual summation over repeated subscripts while subscripts preceded by a comma denote the partial differentiation with respect to the spatial argument. We also use a superposed dot to denote the partial differentiation with respect to t. The Latin indices are understood to range over the integers 1, 2, 3. In the following, we designate by n i the components of the outward unit normal to the surface. The closure of domain, denoted by, means. Also, the spatial argument and the time argument of a function will be omitted when there is no likelihood of confusion. The behavior of initially stressed bodies with voids is characterized by the following kinematic variables: u i u i x, t, ϕ jk ϕ jk x, t, σ σ x, t, x, t 0,t 0 ). 2.1 In our study, we analyze an anisotropic and homogeneous initially stressed elastic solid with voids. We restrict our considerations to the Elastostatics, so that the basic equations become as follows. i The equations of equilibrium is as follows: ( ) τij η ij,j ρf i 0, μ ijk,i η jk u j,i M ik ϕ ki M ji ϕ kr,i N ijr ρg jk 0; 2.2 ii the balance of the equilibrated forces is as follows: h i,i g ρl 0; 2.3 iii the constitutive equations are as follows: τ ij u j,k P ki C ijmn ε mn G mnij κ mn F mnrij χ mnr a ij σ d ijk σ,k, η ij ϕ jk M ik ϕ jk,r N rik G ijmn ε mn ijmn κ mn D ijmnr χ mnr b ij σ e ijk σ,k, μ ijk u j,r N irk F ijkmn ε mn D mnijk κ mn A ijkmnr χ mnr c ijk σ f ijkm σ,m, 2.4 h i d mni ε mn e mni κ mn f mnri χ mnr d i σ g ij σ,j, g a mn ε mn b mn κ mn c mnr χ mnr ξσ d i σ,i ; iv the geometric equations are ε ij 1 2( uj,i u i,j ), κij u j,i ϕ ij, χ ijk ϕ jk,i, σ ν ν In the above equations we have used the following notations: i ρ the constant mass density; ii u i the components of the displacement field;
3 Marin Marin 3 iii ϕ jk the components of the dipolar displacement field; iv ν the volume distribution function which in the reference state is ν 0 ; v σ a measure of volume change of the bulk material resulting from void compaction or distension; vi τ ij, η ij, μ ij the components of the stress tensors; vii h i the components of the equilibrated stress; viii F i the components of body force per unit mass; ix G jk the components of dipolar body force per unit mass; x L the extrinsic equilibrated body force; xi g the intrinsic equilibrated body force; xii ε ij, κ ij, χ ijk the kinematic characteristics of the strain tensors; xiii C ijmn, ijmn,...,d ijm, E ijm,...,a ij, b ij, c ijk, d i, ξ represent the characteristic functions of the material the constitutive coefficients and they obey to the following symmetry relations C ijmn C mnij C ijnm, ijmn mnij, G ijmn G ijnm, F ijkmn F ijknm, A ijkmnr A mnrijk, a ij a ji, P ij P ji, g ij g ji. 2.6 The physical significances of the functions L and h i are presented in the works 6, 7. The prescribed functions P ij, M ij and N ijk from 2.2 and 2.3 satisfy the following equations: ( ) Pij M ij,j 0, N ijk,i P jk Existence and uniqueness theorems In the main section of our paper, we will accommodate some theoretical results from the theory of elliptic equations in order to derive the existence and the uniqueness of a generalized solution of the mixed boundary-value problem in the context of initially stressed bodies with voids. Throughout this section, we assume that is a Lipschitz region of the Euclidian threedimensional space R 3. We use the following notations: W W 1,2 ] 13, W0 W 1,2 0 ]13, 3.1 with the convention that A 13 A A A, the Cartesian product is considered to be of 13-times. Also, W k,m is the familiar Sobolev space. With other words, W is defined as the space of all u u i,ϕ ij,σ, where u i, ϕ ij, σ W 1,2 with the norm 3 u 2 W σ 2 W 1,2 3 ( 3 ) ui 2 W 1,2 ϕij W 1,2 i 1 For clarity and simplification in presentation, we consider the following regularity hypotheses on the considered functions: j 1 i 1
4 4 Mathematical Problems in Engineering i all the constitutive coefficients are functions of class C 2 on ; ii the body loads F i,g jk,andh are continuous functions on. The ordered array u i,ϕ jk,σ is an admissible process on provided u i, ϕ jk, σ C 1 C 2. Also, the ordered array of functions τ ij,η ij,μ ijk,h i is an admissible system of stress on if τ ij, η ij, μ ijk, h i C 1 C 0 and τ ij,i, η ij,i, μ ijk,k, h k,k, h C 0. Let S u S t C be a disjunct decomposition of, where C is a set of surface measure and S u and S t are either empty or open in. Assume the following boundary conditions: u i ũ i, ϕ jk ϕ jk σ σ on S u, t i ( ) τ ij η ij nj t i, μ jk μ ijk n i μ jk, h h i n i h on S t, 3.3 where the functions ũ i, ϕ jk, σ, t i, μ jk,and h are prescribed, ũ i, ϕ jk, σ W 1,2 S u,and t i, μ jk, h L 2 S t.also,wedefinev as a subspace of the space W of all functions u u i,ϕ ij,σ which satisfy the boundary conditions: u i 0, ϕ ij 0, σ 0 on S u. 3.4 On the product space W W, we consider a bilinear form A v, u, defined by { A v, u Cijmn ε mn u ε ij v G mnij εij v κ mn u ε ij u κ mn v ] F mnrij εij v χ mnr u ε ij u χ mn v ] ijmn κ ij v κ mn u D ijmnr κij v χ mnr u κ ij u χ mn v ] A ijkmnr χ ijk v χ mnr u P ki u j,k v j,i M ik u j,i ψ jk v j,i ϕ jk N rik u j,k ψ jk,r v j,k ϕ jk,r a ij εij v σ ε ij u γ ] b ij κij v σ κ ij u γ ] c ijk χijk v σ χ ij u γ ] d ijk εij v σ,k ε ij u γ,k ] e ijk κij v σ,k κ ij u γ,k ] f ijkm χijk v σ,m χ ijk u γ,m ] 3.5 d i σγ,i γσ,i ] gij σ,i γ,j ξσγ } dv, where u ( u i,ϕ ij,σ ), v ( v i,ψ ij,γ ), ε ij u 1 2( uj,i u i,j ), ε ij v 2( 1 ) vj,i v i,j, κij u u j,i ϕ ij, κ ij v v j,i ψ ij, χ ijk u ϕ jk,i, χ ijk v ψ jk,i. 3.6 We assume that the constitutive coefficients are bounded measurable functions in which satisfy the symmetries 2.6. Then, by using relations 3.5 and 2.6 it is easy to deduce that A v, u A u, v. 3.7
5 Marin Marin 5 Also, by using symmetries 2.6 into 3.5, itresultsin A u, u Cijmn ε mn u ε ij v 2G mnij ε ij u κ mn u ijmn κ ij u κ mn u 2F mnrij ε ij u χ mnr u 2D ijmnr κ ij u χ mnr u A ijkmnr χ ijk u χ mnr u P ki u j,k u j,i 2M ik u j,i ϕ jk 2N rik u j,i ϕ jk,r 2a ij ε ij u σ 2b ij κ ij u σ 2c ijk χ ijk u σ 3.8 and thus 2d ijk ε ij u σ,k 2e ijk κ ij u σ,k 2f ijkm χ ijk u σ,m 2d i σγ,i g ij σ,i σ,j ξσ 2] dv, A u, u 2 UdV, 3.9 where U ρe is the internal energy density associated to u. We suppose that U is a positive definite quadratic form, that is, there exists a positive constant c such that C ijmn x ij x mn 2G ijmn x ij y mn 2F ijmnr x ij z mnr ijmn y ij y mn 2D ijmnr y ij z mnr A ijkmnr z ijk z mn P ki x ji x jk 2M ik x ji y jk 2N rik x ji z jkr 2a ij x ij w 2b ij y ij w 2c ijk z ij w 2d ijk x ij ω k 2e ijk y ij ω k f ijkm z ijk ω m 2d i wω i g ijk ω i ω j ξw 2 c ( x ij x ij y ij x ij z ijk z ijk ω i ω i w 2), for all x ij, y ij, z ijk, ω i,andw. Now, we introduce the functionals f v and g v by f v ρ ( F i v i G jk ψ jk Lγ ) dv, v W, g v ( t i v i μ jk ψ jk hγ ) da, v W, S t 3.11 where v v i,ψ jk,γ W and ρ, F i, G jk, L L 2. Let v ũ i, ϕ jk, γ W be such that ũ i, ϕ jk, γ on S u may by obtained by means of embedding the space W 1,2 into the space L 2 S u. The element v u i,ϕ jk,σ W is called weak (or generalized) solution of the boundary value problem, if u ũ V, A u, u f u g v 3.12
6 6 Mathematical Problems in Engineering hold for each v V. In the above relations, we used the spaces L 2 and L 2 S u which represent, as it is well known, the space of real functions which are square-integrable on, respectively, on S u. It follows from 3.10 and 3.8 that A v, v 2c εij v ε ij v κ ij v κ ij v χ ijk v χ ijk v γ i γ i γ 2] dv, 3.13 for any v v i,ψ jk,γ W. Let us consider the operators N k v, k 1, 2,...,49, mapping the space W into the space L 2, defined by N i v ε 1i v, N 3 i v ε 2i v, N 6 i v ε 2i v, N 9 i v κ 1i v, N 12 i v κ 1i v, N 15 i v κ 1i v, N 18 i v χ 11i v, N 21 i v χ 12i v, N 24 i v χ 13i v, N 27 i v χ 21i v, N 30 i v χ 22i v, N 33 i v χ 23i v, N 36 i v χ 31i v, N 39 i v χ 32i v, N 42 i v χ 33i v, N 45 i v σ,i v, N 49 v σ v i 1, 2, It is easy to see that, in fact, the operators N k v, k 1, 2,...,49, defined above, have the following general form: m N k v n kr αd α v r, p α, 3.15 r 1 α k r where n kr α are bounded and measurable functions on. Also, we have used the notation D α for the multi-indices derivative, that is, D α x α xα 2 2 xα 3 3 y definition, the operators N k v, k 1, 2,...,49 form a coercive system of operators on Wif for each v W the following inequality takes place: 49 k 1 α N k v 2 13 L 2 v r 2 L 2 c 1 v 2 W, c 1 > r 1 In this inequality, the constant c 1 does not depend on v and the norms L2 and W represent the usual norms in the spaces L 2 and W, respectively. In the following theorem, we indicate a necessary and sufficient condition for a system of operators to be a coercive system. Theorem 3.1. Let n psα be constant for α k s. Then the system of operators N p v is coercive on W if and only if the rank of the matrix ( Nps ξ ) ( ) n psα ξ α 3.18 α k s is equal to m for each ξ C 3, ξ / 0,whereC 3 is the notation for the complex three-dimensional space, and ξ α ξ α 1 1 ξα 2 2 ξα
7 Marin Marin 7 The demonstration of this result can be find in 4. In the following, we assume that for each v W, we have 49 A v, v c 2 Nk v 2 L 2, c 2 > 0, 3.20 k 1 where the constant c 2 does not depend on v. We denote by P the following set: { 49 P v V : Nk v } 2 L 2 0, 3.21 k 1 and by V/P the factor-space of classes ṽ, where having the norm ṽ { v p, v V, p P }, ṽ V/P inf p P v p W In the following theorem, it is indicated a necessary and sufficient condition for the existence of a weak solution of the boundary-value problem. Theorem 3.2. Let A v, u ṽ, ũ define a bilinear form for each ṽ, ũ W/P, whereu ũ and v ṽ. If it is supposed that the inequalities 3.17 and 3.20 hold, then a necessary and sufficient condition for the existence of a weak solution of the boundary value problem is p P f p g p Moreover, the weak solution, u W, satisfies the following inequality: where c 3 is a real positive constant. Further, one has for each ṽ W/P. ũ u W/P c ( m 3 W fil2 i 1 )1/2 ( m gil2 S i 1 )1/2], 3.25 A ( ṽ, ṽ ) c 4 ṽ W/P, c 4 > 0, 3.26 For the prove of this result, see 3. In the following, we intend to apply the above two results in order to obtain the existence of a weak solution for the boundary value problem formulated in the context of theory of initially stressed elastic solids with voids. Theorem 3.3. Let P {0}. Then there exists one and only one weak solution u W of our boundaryvalue problem.
8 8 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Proof. Clearly, from 3.13 and 3.14 we immediately obtain The matrix 3.20 has the rank 13 for each ξ C 3, ξ / 0. Thus by Theorem 3.1 we conclude that the system of N k operators, defined in 3.14, is coercive on the space W. According to definition 3.21 of P, we have that ε ij v 0,κ ij v 0, χ ijk v 0, γ i v 0, ψ 0 for each v P, v v i,ψ jk,ψ. So, we deduce that P reduces to P { v v i,ψ jk,γ V : v i a i ε ijk b j x k,ψ jk ε jks b s,γ c }, 3.27 where a i and b i and c are arbitrary constants and ε ijk is the alternating symbol. We will consider two distinct cases. First, we suppose that the set S u is nonempty. Then the set P reduces to P {0}, and therefore, condition 3.24 is satisfied. y using Theorem 3.2, we immediately obtain the desired result. In the second case, we assume that S u is an empty set. Then we have the following result. Theorem 3.4. The necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of a weak solution u W of the boundary-value problem for elastic dipolar bodies with stretch, are given by ρf i dv t i da 0, 3.28 ( ) ( ) ρε ijk xj F k G jk dv ε ijk xj t k μ jk da 0, where ε ijk is the alternating symbol. Proof. In this case, the boundary value problem P is given by 3.27, where a i, b i,andc are arbitrary constants such that we can apply, once again, Theorem 3.2 to obtain the above result. 4. Conclusion For the considered initial-boundary value problem the basic results still valid. Now, for different particular cases, the solution can be found because it exists and is unique. References 1 D. Ieşan, Thermoelastic stresses in initially stressed bodies with microstructure, Thermal Stresses, vol. 4, no. 3-4, pp , M. Marin, Sur l existence et l unicité danslathermoélasticité des milieux micropolaires, Comptes Rendus de l Académie des Sciences. Serie II, vol. 321, no. 12, pp , I. Hlaváček and J. Nečas, On inequalities of Korn s type. I: boundary-value problems for elliptic system of partial differential equations, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, vol. 36, no. 4, pp , I. Nečas, Les Méthodes Directes en Théorie des Équations Elliptiques, Academia, Prague, Czech Republic, M. Marin, On the nonlinear theory of micropolar bodies with voids, Applied Mathematics, vol. 2007, Article ID 15745, 11 pages, M. A. Goodman and S. C. Cowin, A continuum theory for granular materials, Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, vol. 44, no. 4, pp , J. W. Nunziato and S. C. Cowin, Linear elastic materials with void, Elasticity, vol. 13, pp , 1983.
9 Advances in Operations Research Advances in Decision Sciences Applied Mathematics Algebra Probability and Statistics The Scientific World Journal International Differential Equations Submit your manuscripts at International Advances in Combinatorics Mathematical Physics Complex Analysis International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Mathematical Problems in Engineering Mathematics Discrete Mathematics Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Function Spaces Abstract and Applied Analysis International Stochastic Analysis Optimization
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 49-58
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No. 2-2017 Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 49-58 THERMOELASTICITY WITH FRACTIONAL ORDER STRAIN FOR DIPOLAR MATERIALS WITH VOIDS
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No. 2-2017 Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 49-58 THERMOELASTICITY WITH FRACTIONAL ORDER STRAIN FOR DIPOLAR MATERIALS WITH VOIDS
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 83-90
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No. 1-2017 Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 83-90 GENERALIZED MICROPOLAR THERMOELASTICITY WITH FRACTIONAL ORDER STRAIN Adina
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No. 1-2017 Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 83-90 GENERALIZED MICROPOLAR THERMOELASTICITY WITH FRACTIONAL ORDER STRAIN Adina
INTERNAL STATE VARIABLES IN DIPOLAR THERMOELASTIC BODIES
 Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 43 1 14, 15 6 INTERNAL STATE VARIALES IN DIPOLAR THERMOELASTIC ODIES M. Marin a, S. R. Mahmoud b c, and G. Stan a Received 7 : 1 : 1 : Accepted 3
Hacettepe Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Volume 43 1 14, 15 6 INTERNAL STATE VARIALES IN DIPOLAR THERMOELASTIC ODIES M. Marin a, S. R. Mahmoud b c, and G. Stan a Received 7 : 1 : 1 : Accepted 3
On temporal behaviour of solutions in Thermoelasticity of porous micropolar bodies
 DOI: 1.2478/auom-214-14 An. Şt. Univ. Ovidius Constanţa Vol. 22(1),214, 169 188 On temporal behaviour of solutions in Thermoelasticity of porous micropolar bodies Marin Marin and Olivia Florea Abstract
DOI: 1.2478/auom-214-14 An. Şt. Univ. Ovidius Constanţa Vol. 22(1),214, 169 188 On temporal behaviour of solutions in Thermoelasticity of porous micropolar bodies Marin Marin and Olivia Florea Abstract
Effect of internal state variables in thermoelasticity of microstretch bodies
 DOI: 10.1515/auom-016-0057 An. Şt. Univ. Ovidius Constanţa Vol. 43,016, 41 57 Effect of internal state variables in thermoelasticity of microstretch bodies Marin Marin and Sorin Vlase Abstract First, we
DOI: 10.1515/auom-016-0057 An. Şt. Univ. Ovidius Constanţa Vol. 43,016, 41 57 Effect of internal state variables in thermoelasticity of microstretch bodies Marin Marin and Sorin Vlase Abstract First, we
On some exponential decay estimates for porous elastic cylinders
 Arch. Mech., 56, 3, pp. 33 46, Warszawa 004 On some exponential decay estimates for porous elastic cylinders S. CHIRIȚĂ Faculty of Mathematics, University of Iaşi, 6600 Iaşi, Romania. In this paper we
Arch. Mech., 56, 3, pp. 33 46, Warszawa 004 On some exponential decay estimates for porous elastic cylinders S. CHIRIȚĂ Faculty of Mathematics, University of Iaşi, 6600 Iaşi, Romania. In this paper we
Basic results for porous dipolar elastic materials
 asic results for porous dipolar elastic materials MARIN MARIN Department of Mathematics, University of rasov Romania, e-mail: m.marin@unitbv.ro Abstract. This paper is concerned with the nonlinear theory
asic results for porous dipolar elastic materials MARIN MARIN Department of Mathematics, University of rasov Romania, e-mail: m.marin@unitbv.ro Abstract. This paper is concerned with the nonlinear theory
Qualitative results on mixed problem of micropolar bodies with microtemperatures
 Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 12, Issue 2 December 2017, pp. 776 789 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal AAM Qualitative results on
Available at http://pvamu.edu/aam Appl. Appl. Math. ISSN: 1932-9466 Vol. 12, Issue 2 December 2017, pp. 776 789 Applications and Applied Mathematics: An International Journal AAM Qualitative results on
Chapter 3 Stress, Strain, Virtual Power and Conservation Principles
 Chapter 3 Stress, Strain, irtual Power and Conservation Principles 1 Introduction Stress and strain are key concepts in the analytical characterization of the mechanical state of a solid body. While stress
Chapter 3 Stress, Strain, irtual Power and Conservation Principles 1 Introduction Stress and strain are key concepts in the analytical characterization of the mechanical state of a solid body. While stress
Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity
 Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research of the Polish Academy
Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research of the Polish Academy
Generalized Korn s inequality and conformal Killing vectors
 Generalized Korn s inequality and conformal Killing vectors arxiv:gr-qc/0505022v1 4 May 2005 Sergio Dain Max-Planck-Institut für Gravitationsphysik Am Mühlenberg 1 14476 Golm Germany February 4, 2008 Abstract
Generalized Korn s inequality and conformal Killing vectors arxiv:gr-qc/0505022v1 4 May 2005 Sergio Dain Max-Planck-Institut für Gravitationsphysik Am Mühlenberg 1 14476 Golm Germany February 4, 2008 Abstract
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by: [University of Salerno] On: 4 November 8 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 73997733] Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and
This article was downloaded by: [University of Salerno] On: 4 November 8 Access details: Access Details: [subscription number 73997733] Publisher Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England and
On vibrations in thermoelasticity without energy dissipation for micropolar bodies
 Marin and Baleanu Boundary Value Problems 206 206: DOI 0.86/s366-06-0620-9 R E S E A R C H Open Access On vibrations in thermoelasticity without energy dissipation for micropolar bodies Marin Marin * and
Marin and Baleanu Boundary Value Problems 206 206: DOI 0.86/s366-06-0620-9 R E S E A R C H Open Access On vibrations in thermoelasticity without energy dissipation for micropolar bodies Marin Marin * and
Research Article Dispersion of Love Waves in a Composite Layer Resting on Monoclinic Half-Space
 Applied Mathematics Volume 011, Article ID 71349, 9 pages doi:10.1155/011/71349 Research Article Dispersion of Love Waves in a Composite Layer Resting on Monoclinic Half-Space Sukumar Saha BAS Division,
Applied Mathematics Volume 011, Article ID 71349, 9 pages doi:10.1155/011/71349 Research Article Dispersion of Love Waves in a Composite Layer Resting on Monoclinic Half-Space Sukumar Saha BAS Division,
Stress of a spatially uniform dislocation density field
 Stress of a spatially uniform dislocation density field Amit Acharya November 19, 2018 Abstract It can be shown that the stress produced by a spatially uniform dislocation density field in a body comprising
Stress of a spatially uniform dislocation density field Amit Acharya November 19, 2018 Abstract It can be shown that the stress produced by a spatially uniform dislocation density field in a body comprising
Structural Continuous Dependence in Micropolar Porous Bodies
 Copyright 15 Tech Science Press CMC, vol.45, no., pp.17-15, 15 Structural Continuous Dependence in Micropolar Porous odies M. Marin 1,, A.M. Abd-Alla 3,4, D. Raducanu 1 and S.M. Abo-Dahab 3,5 Abstract:
Copyright 15 Tech Science Press CMC, vol.45, no., pp.17-15, 15 Structural Continuous Dependence in Micropolar Porous odies M. Marin 1,, A.M. Abd-Alla 3,4, D. Raducanu 1 and S.M. Abo-Dahab 3,5 Abstract:
Mathematical Preliminaries
 Mathematical Preliminaries Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMAZ G. ZIELIŃKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Table of Contents Vectors, tensors, and index notation. Generalization of the concept
Mathematical Preliminaries Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMAZ G. ZIELIŃKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Table of Contents Vectors, tensors, and index notation. Generalization of the concept
ON THE ANALYSIS OF A VISCOPLASTIC CONTACT PROBLEM WITH TIME DEPENDENT TRESCA S FRIC- TION LAW
 Electron. J. M ath. Phys. Sci. 22, 1, 1,47 71 Electronic Journal of Mathematical and Physical Sciences EJMAPS ISSN: 1538-263X www.ejmaps.org ON THE ANALYSIS OF A VISCOPLASTIC CONTACT PROBLEM WITH TIME
Electron. J. M ath. Phys. Sci. 22, 1, 1,47 71 Electronic Journal of Mathematical and Physical Sciences EJMAPS ISSN: 1538-263X www.ejmaps.org ON THE ANALYSIS OF A VISCOPLASTIC CONTACT PROBLEM WITH TIME
Research Article Propagation of Plane Waves in a Thermally Conducting Mixture
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 211, Article ID 31816, 12 pages doi:1.542/211/31816 Research Article Propagation of Plane Waves in a Thermally Conducting Mixture
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 211, Article ID 31816, 12 pages doi:1.542/211/31816 Research Article Propagation of Plane Waves in a Thermally Conducting Mixture
A short review of continuum mechanics
 A short review of continuum mechanics Professor Anette M. Karlsson, Department of Mechanical ngineering, UD September, 006 This is a short and arbitrary review of continuum mechanics. Most of this material
A short review of continuum mechanics Professor Anette M. Karlsson, Department of Mechanical ngineering, UD September, 006 This is a short and arbitrary review of continuum mechanics. Most of this material
Uniqueness in thermoelasticity of porous media with microtemperatures
 Arch. Mech., 61, 5, pp. 371 382, Warszawa 29 Uniqueness in thermoelasticity of porous media with microtemperatures R. QUINTANILLA Department of Applied Mathematics II UPC Terrassa, Colom 11, 8222 Terrassa,
Arch. Mech., 61, 5, pp. 371 382, Warszawa 29 Uniqueness in thermoelasticity of porous media with microtemperatures R. QUINTANILLA Department of Applied Mathematics II UPC Terrassa, Colom 11, 8222 Terrassa,
Research Article Localization and Perturbations of Roots to Systems of Polynomial Equations
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 653914, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/653914 Research Article Localization and Perturbations of Roots to Systems of Polynomial Equations
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 653914, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/653914 Research Article Localization and Perturbations of Roots to Systems of Polynomial Equations
Basic concepts to start Mechanics of Materials
 Basic concepts to start Mechanics of Materials Georges Cailletaud Centre des Matériaux Ecole des Mines de Paris/CNRS Notations Notations (maths) (1/2) A vector v (element of a vectorial space) can be seen
Basic concepts to start Mechanics of Materials Georges Cailletaud Centre des Matériaux Ecole des Mines de Paris/CNRS Notations Notations (maths) (1/2) A vector v (element of a vectorial space) can be seen
Other state variables include the temperature, θ, and the entropy, S, which are defined below.
 Chapter 3 Thermodynamics In order to complete the formulation we need to express the stress tensor T and the heat-flux vector q in terms of other variables. These expressions are known as constitutive
Chapter 3 Thermodynamics In order to complete the formulation we need to express the stress tensor T and the heat-flux vector q in terms of other variables. These expressions are known as constitutive
Linearized theory of elasticity
 Linearized theory of elasticity Arie Verhoeven averhoev@win.tue.nl CASA Seminar, May 24, 2006 Seminar: Continuum mechanics 1 Stress and stress principles Bart Nowak March 8 2 Strain and deformation Mark
Linearized theory of elasticity Arie Verhoeven averhoev@win.tue.nl CASA Seminar, May 24, 2006 Seminar: Continuum mechanics 1 Stress and stress principles Bart Nowak March 8 2 Strain and deformation Mark
Elements of Continuum Elasticity. David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II February 25, 2004
 Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
VECTORS, TENSORS AND INDEX NOTATION
 VECTORS, TENSORS AND INDEX NOTATION Enrico Nobile Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Architettura Università degli Studi di Trieste, 34127 TRIESTE March 5, 2018 Vectors & Tensors, E. Nobile March 5, 2018 1 /
VECTORS, TENSORS AND INDEX NOTATION Enrico Nobile Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Architettura Università degli Studi di Trieste, 34127 TRIESTE March 5, 2018 Vectors & Tensors, E. Nobile March 5, 2018 1 /
KINEMATICS OF CONTINUA
 KINEMATICS OF CONTINUA Introduction Deformation of a continuum Configurations of a continuum Deformation mapping Descriptions of motion Material time derivative Velocity and acceleration Transformation
KINEMATICS OF CONTINUA Introduction Deformation of a continuum Configurations of a continuum Deformation mapping Descriptions of motion Material time derivative Velocity and acceleration Transformation
16.21 Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 2003 Unit #5 - Constitutive Equations
 6.2 Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 2003 Unit #5 - Constitutive quations Constitutive quations For elastic materials: If the relation is linear: Û σ ij = σ ij (ɛ) = ρ () ɛ ij σ ij =
6.2 Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 2003 Unit #5 - Constitutive quations Constitutive quations For elastic materials: If the relation is linear: Û σ ij = σ ij (ɛ) = ρ () ɛ ij σ ij =
Vectors. January 13, 2013
 Vectors January 13, 2013 The simplest tensors are scalars, which are the measurable quantities of a theory, left invariant by symmetry transformations. By far the most common non-scalars are the vectors,
Vectors January 13, 2013 The simplest tensors are scalars, which are the measurable quantities of a theory, left invariant by symmetry transformations. By far the most common non-scalars are the vectors,
A.1 Appendix on Cartesian tensors
 1 Lecture Notes on Fluid Dynamics (1.63J/2.21J) by Chiang C. Mei, February 6, 2007 A.1 Appendix on Cartesian tensors [Ref 1] : H Jeffreys, Cartesian Tensors; [Ref 2] : Y. C. Fung, Foundations of Solid
1 Lecture Notes on Fluid Dynamics (1.63J/2.21J) by Chiang C. Mei, February 6, 2007 A.1 Appendix on Cartesian tensors [Ref 1] : H Jeffreys, Cartesian Tensors; [Ref 2] : Y. C. Fung, Foundations of Solid
Research Article Finite Element Formulation of Forced Vibration Problem of a Prestretched Plate Resting on a Rigid Foundation
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 7, Article ID 5636, 1 pages doi:1.1155/7/5636 Research Article Finite Element Formulation of Forced Vibration Problem of a Prestretched
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 7, Article ID 5636, 1 pages doi:1.1155/7/5636 Research Article Finite Element Formulation of Forced Vibration Problem of a Prestretched
Mathematical Background
 CHAPTER ONE Mathematical Background This book assumes a background in the fundamentals of solid mechanics and the mechanical behavior of materials, including elasticity, plasticity, and friction. A previous
CHAPTER ONE Mathematical Background This book assumes a background in the fundamentals of solid mechanics and the mechanical behavior of materials, including elasticity, plasticity, and friction. A previous
. D CR Nomenclature D 1
 . D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
. D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
In this section, thermoelasticity is considered. By definition, the constitutive relations for Gradθ. This general case
 Section.. Thermoelasticity In this section, thermoelasticity is considered. By definition, the constitutive relations for F, θ, Gradθ. This general case such a material depend only on the set of field
Section.. Thermoelasticity In this section, thermoelasticity is considered. By definition, the constitutive relations for F, θ, Gradθ. This general case such a material depend only on the set of field
Research Article Quasilinearization Technique for Φ-Laplacian Type Equations
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 0, Article ID 975760, pages doi:0.55/0/975760 Research Article Quasilinearization Technique for Φ-Laplacian Type Equations Inara Yermachenko and
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 0, Article ID 975760, pages doi:0.55/0/975760 Research Article Quasilinearization Technique for Φ-Laplacian Type Equations Inara Yermachenko and
LECTURE # 0 BASIC NOTATIONS AND CONCEPTS IN THE THEORY OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (PDES)
 LECTURE # 0 BASIC NOTATIONS AND CONCEPTS IN THE THEORY OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (PDES) RAYTCHO LAZAROV 1 Notations and Basic Functional Spaces Scalar function in R d, d 1 will be denoted by u,
LECTURE # 0 BASIC NOTATIONS AND CONCEPTS IN THE THEORY OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS (PDES) RAYTCHO LAZAROV 1 Notations and Basic Functional Spaces Scalar function in R d, d 1 will be denoted by u,
Professor Terje Haukaas University of British Columbia, Vancouver Notation
 Notation This document establishes the notation that is employed throughout these notes. It is intended as a look-up source during the study of other documents and software on this website. As a general
Notation This document establishes the notation that is employed throughout these notes. It is intended as a look-up source during the study of other documents and software on this website. As a general
Introduction to Continuum Mechanics
 Introduction to Continuum Mechanics I-Shih Liu Instituto de Matemática Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro 2018 Contents 1 Notations and tensor algebra 1 1.1 Vector space, inner product........................
Introduction to Continuum Mechanics I-Shih Liu Instituto de Matemática Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro 2018 Contents 1 Notations and tensor algebra 1 1.1 Vector space, inner product........................
Nonsimple material problems addressed by the Lagrange s identity
 Marin et al.oundary Value Problems 23, 23:35 R E S E A R C H Open Access Nonsimple material problems addressed by the Lagrange s identity Marin I Marin *, Ravi P Agarwal 2 and SR Mahmoud 3,4 * Correspondence:
Marin et al.oundary Value Problems 23, 23:35 R E S E A R C H Open Access Nonsimple material problems addressed by the Lagrange s identity Marin I Marin *, Ravi P Agarwal 2 and SR Mahmoud 3,4 * Correspondence:
1.4 LECTURE 4. Tensors and Vector Identities
 16 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA 1.3.2 Triple Product The triple product of three vectors A, B and C is defined by In tensor notation it is A ( B C ) = [ A, B, C ] = A ( B C ) i, j,k=1 ε i jk A i B j C k =
16 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA 1.3.2 Triple Product The triple product of three vectors A, B and C is defined by In tensor notation it is A ( B C ) = [ A, B, C ] = A ( B C ) i, j,k=1 ε i jk A i B j C k =
Niiranen, Jarkko; Khakalo, Sergei; Balobanov, Viacheslav Strain gradient elasticity theories in lattice structure modelling
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Niiranen, Jarkko; Khakalo, Sergei;
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is an electronic reprint of the original article. This reprint may differ from the original in pagination and typographic detail. Niiranen, Jarkko; Khakalo, Sergei;
Thermodynamics for fluid flow in porous structures
 Communications to SIMAI Congress, ISSN 1827-9015, Vol. 1 (2006) DOI: 10.1685/CSC06105 Thermodynamics for fluid flow in porous structures M.E. Malaspina University of Messina, Department of Mathematics
Communications to SIMAI Congress, ISSN 1827-9015, Vol. 1 (2006) DOI: 10.1685/CSC06105 Thermodynamics for fluid flow in porous structures M.E. Malaspina University of Messina, Department of Mathematics
Theory of PDE Homework 2
 Theory of PDE Homework 2 Adrienne Sands April 18, 2017 In the following exercises we assume the coefficients of the various PDE are smooth and satisfy the uniform ellipticity condition. R n is always an
Theory of PDE Homework 2 Adrienne Sands April 18, 2017 In the following exercises we assume the coefficients of the various PDE are smooth and satisfy the uniform ellipticity condition. R n is always an
LECTURE 1: SOURCES OF ERRORS MATHEMATICAL TOOLS A PRIORI ERROR ESTIMATES. Sergey Korotov,
 LECTURE 1: SOURCES OF ERRORS MATHEMATICAL TOOLS A PRIORI ERROR ESTIMATES Sergey Korotov, Institute of Mathematics Helsinki University of Technology, Finland Academy of Finland 1 Main Problem in Mathematical
LECTURE 1: SOURCES OF ERRORS MATHEMATICAL TOOLS A PRIORI ERROR ESTIMATES Sergey Korotov, Institute of Mathematics Helsinki University of Technology, Finland Academy of Finland 1 Main Problem in Mathematical
Research Article Solving the Matrix Nearness Problem in the Maximum Norm by Applying a Projection and Contraction Method
 Advances in Operations Research Volume 01, Article ID 357954, 15 pages doi:10.1155/01/357954 Research Article Solving the Matrix Nearness Problem in the Maximum Norm by Applying a Projection and Contraction
Advances in Operations Research Volume 01, Article ID 357954, 15 pages doi:10.1155/01/357954 Research Article Solving the Matrix Nearness Problem in the Maximum Norm by Applying a Projection and Contraction
Research Article The Solution Set Characterization and Error Bound for the Extended Mixed Linear Complementarity Problem
 Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 219478, 15 pages doi:10.1155/2012/219478 Research Article The Solution Set Characterization and Error Bound for the Extended Mixed Linear Complementarity
Journal of Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 219478, 15 pages doi:10.1155/2012/219478 Research Article The Solution Set Characterization and Error Bound for the Extended Mixed Linear Complementarity
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow
 Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research
NONLINEAR CONTINUUM FORMULATIONS CONTENTS
 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM FORMULATIONS CONTENTS Introduction to nonlinear continuum mechanics Descriptions of motion Measures of stresses and strains Updated and Total Lagrangian formulations Continuum shell
NONLINEAR CONTINUUM FORMULATIONS CONTENTS Introduction to nonlinear continuum mechanics Descriptions of motion Measures of stresses and strains Updated and Total Lagrangian formulations Continuum shell
Continuum mechanics V. Constitutive equations. 1. Constitutive equation: definition and basic axioms
 Continuum mechanics office Math 0.107 ales.janka@unifr.ch http://perso.unifr.ch/ales.janka/mechanics Mars 16, 2011, Université de Fribourg 1. Constitutive equation: definition and basic axioms Constitutive
Continuum mechanics office Math 0.107 ales.janka@unifr.ch http://perso.unifr.ch/ales.janka/mechanics Mars 16, 2011, Université de Fribourg 1. Constitutive equation: definition and basic axioms Constitutive
MATH45061: SOLUTION SHEET 1 V
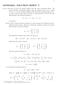 1 MATH4561: SOLUTION SHEET 1 V 1.) a.) The faces of the cube remain aligned with the same coordinate planes. We assign Cartesian coordinates aligned with the original cube (x, y, z), where x, y, z 1. The
1 MATH4561: SOLUTION SHEET 1 V 1.) a.) The faces of the cube remain aligned with the same coordinate planes. We assign Cartesian coordinates aligned with the original cube (x, y, z), where x, y, z 1. The
Symmetry and Properties of Crystals (MSE638) Stress and Strain Tensor
 Symmetry and Properties of Crystals (MSE638) Stress and Strain Tensor Somnath Bhowmick Materials Science and Engineering, IIT Kanpur April 6, 2018 Tensile test and Hooke s Law Upto certain strain (0.75),
Symmetry and Properties of Crystals (MSE638) Stress and Strain Tensor Somnath Bhowmick Materials Science and Engineering, IIT Kanpur April 6, 2018 Tensile test and Hooke s Law Upto certain strain (0.75),
A matrix over a field F is a rectangular array of elements from F. The symbol
 Chapter MATRICES Matrix arithmetic A matrix over a field F is a rectangular array of elements from F The symbol M m n (F ) denotes the collection of all m n matrices over F Matrices will usually be denoted
Chapter MATRICES Matrix arithmetic A matrix over a field F is a rectangular array of elements from F The symbol M m n (F ) denotes the collection of all m n matrices over F Matrices will usually be denoted
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 1 June 2006 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 76 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM MECHANICS Attempt FOUR questions. There are SIX questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 1 June 2006 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 76 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM MECHANICS Attempt FOUR questions. There are SIX questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
Research Article New Oscillation Criteria for Second-Order Neutral Delay Differential Equations with Positive and Negative Coefficients
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2010, Article ID 564068, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2010/564068 Research Article New Oscillation Criteria for Second-Order Neutral Delay Differential Equations with Positive
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2010, Article ID 564068, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2010/564068 Research Article New Oscillation Criteria for Second-Order Neutral Delay Differential Equations with Positive
Basic Principles of Weak Galerkin Finite Element Methods for PDEs
 Basic Principles of Weak Galerkin Finite Element Methods for PDEs Junping Wang Computational Mathematics Division of Mathematical Sciences National Science Foundation Arlington, VA 22230 Polytopal Element
Basic Principles of Weak Galerkin Finite Element Methods for PDEs Junping Wang Computational Mathematics Division of Mathematical Sciences National Science Foundation Arlington, VA 22230 Polytopal Element
2. Conservation Equations for Turbulent Flows
 2. Conservation Equations for Turbulent Flows Coverage of this section: Review of Tensor Notation Review of Navier-Stokes Equations for Incompressible and Compressible Flows Reynolds & Favre Averaging
2. Conservation Equations for Turbulent Flows Coverage of this section: Review of Tensor Notation Review of Navier-Stokes Equations for Incompressible and Compressible Flows Reynolds & Favre Averaging
Elements of Rock Mechanics
 Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
Elements of Rock Mechanics Stress and strain Creep Constitutive equation Hooke's law Empirical relations Effects of porosity and fluids Anelasticity and viscoelasticity Reading: Shearer, 3 Stress Consider
Research Article A Two-Grid Method for Finite Element Solutions of Nonlinear Parabolic Equations
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 212, Article ID 391918, 11 pages doi:1.1155/212/391918 Research Article A Two-Grid Method for Finite Element Solutions of Nonlinear Parabolic Equations Chuanjun Chen
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 212, Article ID 391918, 11 pages doi:1.1155/212/391918 Research Article A Two-Grid Method for Finite Element Solutions of Nonlinear Parabolic Equations Chuanjun Chen
1.3 LECTURE 3. Vector Product
 12 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Example. Let L be a line x x 1 a = y y 1 b = z z 1 c passing through a point P 1 and parallel to the vector N = a i +b j +c k. The equation of the plane passing through the
12 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Example. Let L be a line x x 1 a = y y 1 b = z z 1 c passing through a point P 1 and parallel to the vector N = a i +b j +c k. The equation of the plane passing through the
Some results on the spatial behaviour in linear porous elasticity
 Arch. Mech., 57, 1, pp. 43 65, Warszawa 005 Some results on the spatial behaviour in linear porous elasticity M. CIARLETTA 1, S. CHIRIȚĂ, F. PASSARELLA 1 (1) Department of Information Engineering and Applied
Arch. Mech., 57, 1, pp. 43 65, Warszawa 005 Some results on the spatial behaviour in linear porous elasticity M. CIARLETTA 1, S. CHIRIȚĂ, F. PASSARELLA 1 (1) Department of Information Engineering and Applied
A direct evaluation of the Fabric Tensor in anisotropic porous media
 A direct evaluation of the Fabric Tensor in anisotropic porous media Maria Cristina Pernice 1, Luciano Nunziante 1, Massimiliano Fraldi 1,2 1 Department of Structural Engineering, University of Naples
A direct evaluation of the Fabric Tensor in anisotropic porous media Maria Cristina Pernice 1, Luciano Nunziante 1, Massimiliano Fraldi 1,2 1 Department of Structural Engineering, University of Naples
Weak Convergence Methods for Energy Minimization
 Weak Convergence Methods for Energy Minimization Bo Li Department of Mathematics University of California, San Diego E-mail: bli@math.ucsd.edu June 3, 2007 Introduction This compact set of notes present
Weak Convergence Methods for Energy Minimization Bo Li Department of Mathematics University of California, San Diego E-mail: bli@math.ucsd.edu June 3, 2007 Introduction This compact set of notes present
Research Article Uniqueness of Weak Solutions to an Electrohydrodynamics Model
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2012, Article ID 864186, 14 pages doi:10.1155/2012/864186 Research Article Uniqueness of Weak Solutions to an Electrohydrodynamics Model Yong Zhou 1 and Jishan Fan
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2012, Article ID 864186, 14 pages doi:10.1155/2012/864186 Research Article Uniqueness of Weak Solutions to an Electrohydrodynamics Model Yong Zhou 1 and Jishan Fan
Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science School of Mathematics
 Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science School of Mathematics JS & SS Mathematics SS Theoretical Physics SS TSM Mathematics Module MA3429: Differential Geometry I Trinity Term 2018???, May??? SPORTS
Faculty of Engineering, Mathematics and Science School of Mathematics JS & SS Mathematics SS Theoretical Physics SS TSM Mathematics Module MA3429: Differential Geometry I Trinity Term 2018???, May??? SPORTS
Plane waves in a rotating generalized thermo-elastic solid with voids
 MultiCraft International Journal of Engineering, Science and Technology Vol. 3, No. 2, 2011, pp. 34-41 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY www.ijest-ng.com 2011 MultiCraft Limited.
MultiCraft International Journal of Engineering, Science and Technology Vol. 3, No. 2, 2011, pp. 34-41 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY www.ijest-ng.com 2011 MultiCraft Limited.
(2) 2. (3) 2 Using equation (3), the material time derivative of the Green-Lagrange strain tensor can be obtained as: 1 = + + +
 LAGRANGIAN FORMULAION OF CONINUA Review of Continuum Kinematics he reader is referred to Belytscho et al. () for a concise review of the continuum mechanics concepts used here. he notation followed here
LAGRANGIAN FORMULAION OF CONINUA Review of Continuum Kinematics he reader is referred to Belytscho et al. () for a concise review of the continuum mechanics concepts used here. he notation followed here
Research Article Some New Fixed-Point Theorems for a (ψ, φ)-pair Meir-Keeler-Type Set-Valued Contraction Map in Complete Metric Spaces
 Applied Mathematics Volume 2011, Article ID 327941, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2011/327941 Research Article Some New Fixed-Point Theorems for a (ψ, φ)-pair Meir-Keeler-Type Set-Valued Contraction Map in Complete
Applied Mathematics Volume 2011, Article ID 327941, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2011/327941 Research Article Some New Fixed-Point Theorems for a (ψ, φ)-pair Meir-Keeler-Type Set-Valued Contraction Map in Complete
A Recursive Trust-Region Method for Non-Convex Constrained Minimization
 A Recursive Trust-Region Method for Non-Convex Constrained Minimization Christian Groß 1 and Rolf Krause 1 Institute for Numerical Simulation, University of Bonn. {gross,krause}@ins.uni-bonn.de 1 Introduction
A Recursive Trust-Region Method for Non-Convex Constrained Minimization Christian Groß 1 and Rolf Krause 1 Institute for Numerical Simulation, University of Bonn. {gross,krause}@ins.uni-bonn.de 1 Introduction
Chapter 3. Forces, Momentum & Stress. 3.1 Newtonian mechanics: a very brief résumé
 Chapter 3 Forces, Momentum & Stress 3.1 Newtonian mechanics: a very brief résumé In classical Newtonian particle mechanics, particles (lumps of matter) only experience acceleration when acted on by external
Chapter 3 Forces, Momentum & Stress 3.1 Newtonian mechanics: a very brief résumé In classical Newtonian particle mechanics, particles (lumps of matter) only experience acceleration when acted on by external
Research Article Strong Convergence of Parallel Iterative Algorithm with Mean Errors for Two Finite Families of Ćirić Quasi-Contractive Operators
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 01, Article ID 66547, 10 pages doi:10.1155/01/66547 Research Article Strong Convergence of Parallel Iterative Algorithm with Mean Errors for Two Finite Families of
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 01, Article ID 66547, 10 pages doi:10.1155/01/66547 Research Article Strong Convergence of Parallel Iterative Algorithm with Mean Errors for Two Finite Families of
OPTIMIZATION FOR THE BALANCE EQUATIONS
 OPTIMIZATION FOR THE BALANCE EQUATIONS REUVEN SEGEV Abstract. We present a framework for the analysis of optimization problems associated with balance equations on a given region Ω. As balance equations
OPTIMIZATION FOR THE BALANCE EQUATIONS REUVEN SEGEV Abstract. We present a framework for the analysis of optimization problems associated with balance equations on a given region Ω. As balance equations
This introductory chapter presents some basic concepts of continuum mechanics, symbols and notations for future reference.
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Elasticity This introductory chapter presents some basic concepts of continuum mechanics, symbols and notations for future reference. 1.1 Kinematics of finite deformations We
Chapter 1 Introduction to Elasticity This introductory chapter presents some basic concepts of continuum mechanics, symbols and notations for future reference. 1.1 Kinematics of finite deformations We
Research Article Nontrivial Solution for a Nonlocal Elliptic Transmission Problem in Variable Exponent Sobolev Spaces
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 21, Article ID 38548, 12 pages doi:1.1155/21/38548 Research Article Nontrivial Solution for a Nonlocal Elliptic Transmission Problem in Variable Exponent Sobolev Spaces
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 21, Article ID 38548, 12 pages doi:1.1155/21/38548 Research Article Nontrivial Solution for a Nonlocal Elliptic Transmission Problem in Variable Exponent Sobolev Spaces
2 A Model, Harmonic Map, Problem
 ELLIPTIC SYSTEMS JOHN E. HUTCHINSON Department of Mathematics School of Mathematical Sciences, A.N.U. 1 Introduction Elliptic equations model the behaviour of scalar quantities u, such as temperature or
ELLIPTIC SYSTEMS JOHN E. HUTCHINSON Department of Mathematics School of Mathematical Sciences, A.N.U. 1 Introduction Elliptic equations model the behaviour of scalar quantities u, such as temperature or
16.20 HANDOUT #2 Fall, 2002 Review of General Elasticity
 6.20 HANDOUT #2 Fall, 2002 Review of General Elasticity NOTATION REVIEW (e.g., for strain) Engineering Contracted Engineering Tensor Tensor ε x = ε = ε xx = ε ε y = ε 2 = ε yy = ε 22 ε z = ε 3 = ε zz =
6.20 HANDOUT #2 Fall, 2002 Review of General Elasticity NOTATION REVIEW (e.g., for strain) Engineering Contracted Engineering Tensor Tensor ε x = ε = ε xx = ε ε y = ε 2 = ε yy = ε 22 ε z = ε 3 = ε zz =
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017
 Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Duality method in limit analysis problem of non-linear elasticity
 Duality method in limit analysis problem of non-linear elasticity Igor A. Brigadnov Department of Computer Science North-Western State Technical University Millionnaya 5, St. Petersburg, 191186, Russia
Duality method in limit analysis problem of non-linear elasticity Igor A. Brigadnov Department of Computer Science North-Western State Technical University Millionnaya 5, St. Petersburg, 191186, Russia
THE STOKES SYSTEM R.E. SHOWALTER
 THE STOKES SYSTEM R.E. SHOWALTER Contents 1. Stokes System 1 Stokes System 2 2. The Weak Solution of the Stokes System 3 3. The Strong Solution 4 4. The Normal Trace 6 5. The Mixed Problem 7 6. The Navier-Stokes
THE STOKES SYSTEM R.E. SHOWALTER Contents 1. Stokes System 1 Stokes System 2 2. The Weak Solution of the Stokes System 3 3. The Strong Solution 4 4. The Normal Trace 6 5. The Mixed Problem 7 6. The Navier-Stokes
4.3 Momentum Balance Principles
 4.3 Momentum Balance Principles 4.3.1 Balance of linear angular momentum in spatial material description Consider a continuum body B with a set of particles occupying an arbitrary region Ω with boundary
4.3 Momentum Balance Principles 4.3.1 Balance of linear angular momentum in spatial material description Consider a continuum body B with a set of particles occupying an arbitrary region Ω with boundary
ON THE FOLIATION OF SPACE-TIME BY CONSTANT MEAN CURVATURE HYPERSURFACES
 ON THE FOLIATION OF SPACE-TIME BY CONSTANT MEAN CURVATURE HYPERSURFACES CLAUS GERHARDT Abstract. We prove that the mean curvature τ of the slices given by a constant mean curvature foliation can be used
ON THE FOLIATION OF SPACE-TIME BY CONSTANT MEAN CURVATURE HYPERSURFACES CLAUS GERHARDT Abstract. We prove that the mean curvature τ of the slices given by a constant mean curvature foliation can be used
Research Article Hyperbolically Bi-Lipschitz Continuity for 1/ w 2 -Harmonic Quasiconformal Mappings
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 569481, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2012/569481 Research Article Hyperbolically Bi-Lipschitz Continuity for 1/ w 2 -Harmonic Quasiconformal
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 569481, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2012/569481 Research Article Hyperbolically Bi-Lipschitz Continuity for 1/ w 2 -Harmonic Quasiconformal
Research Article Brézis-Wainger Inequality on Riemannian Manifolds
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 2008, Article ID 7596, 6 pages doi:0.55/2008/7596 Research Article Brézis-Wainger Inequality on Riemannian anifolds Przemysław
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 2008, Article ID 7596, 6 pages doi:0.55/2008/7596 Research Article Brézis-Wainger Inequality on Riemannian anifolds Przemysław
Mathematical Modeling. of Large Elastic-Plastic Deformations
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, 04, no. 60, 99 996 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/0.988/ams.04.447 Mathematical Modeling of Large Elastic-Plastic Deformations L. U. Sultanov Kazan
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, 04, no. 60, 99 996 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/0.988/ams.04.447 Mathematical Modeling of Large Elastic-Plastic Deformations L. U. Sultanov Kazan
Research Article Existence of Periodic Positive Solutions for Abstract Difference Equations
 Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 2011, Article ID 870164, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/870164 Research Article Existence of Periodic Positive Solutions for Abstract Difference Equations Shugui
Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society Volume 2011, Article ID 870164, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/870164 Research Article Existence of Periodic Positive Solutions for Abstract Difference Equations Shugui
Physics of Continuous media
 Physics of Continuous media Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Classical Mechanics 2012 October 26, 2012 Deformations of continuous media If a body is deformed, we say that the point which originally had
Physics of Continuous media Sourendu Gupta TIFR, Mumbai, India Classical Mechanics 2012 October 26, 2012 Deformations of continuous media If a body is deformed, we say that the point which originally had
Research Article New Examples of Einstein Metrics in Dimension Four
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2010, Article ID 716035, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2010/716035 Research Article New Examples of Einstein Metrics in Dimension Four Ryad Ghanam Department
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2010, Article ID 716035, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2010/716035 Research Article New Examples of Einstein Metrics in Dimension Four Ryad Ghanam Department
Research Article On Behavior of Solution of Degenerated Hyperbolic Equation
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 124936, 10 pages doi:10.5402/2012/124936 Research Article On Behavior of Solution of Degenerated Hyperbolic Equation
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 124936, 10 pages doi:10.5402/2012/124936 Research Article On Behavior of Solution of Degenerated Hyperbolic Equation
Research Article Some Generalizations of Fixed Point Results for Multivalued Contraction Mappings
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Mathematical Analysis Volume 2011, Article ID 924396, 13 pages doi:10.5402/2011/924396 Research Article Some Generalizations of Fixed Point Results for Multivalued
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Mathematical Analysis Volume 2011, Article ID 924396, 13 pages doi:10.5402/2011/924396 Research Article Some Generalizations of Fixed Point Results for Multivalued
Research Article Morita Equivalence of Brandt Semigroup Algebras
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 280636, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/280636 Research Article Morita Equivalence of Brandt Semigroup Algebras Maysam Maysami Sadr
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 280636, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2012/280636 Research Article Morita Equivalence of Brandt Semigroup Algebras Maysam Maysami Sadr
3D Elasticity Theory
 3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
Research Article Function Spaces with a Random Variable Exponent
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 211, Article I 17968, 12 pages doi:1.1155/211/17968 Research Article Function Spaces with a Random Variable Exponent Boping Tian, Yongqiang Fu, and Bochi Xu epartment
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 211, Article I 17968, 12 pages doi:1.1155/211/17968 Research Article Function Spaces with a Random Variable Exponent Boping Tian, Yongqiang Fu, and Bochi Xu epartment
Explicit algebraic Reynolds stress models for boundary layer flows
 1. Explicit algebraic models Two explicit algebraic models are here compared in order to assess their predictive capabilities in the simulation of boundary layer flow cases. The studied models are both
1. Explicit algebraic models Two explicit algebraic models are here compared in order to assess their predictive capabilities in the simulation of boundary layer flow cases. The studied models are both
PREPRINT 2010:23. A nonconforming rotated Q 1 approximation on tetrahedra PETER HANSBO
 PREPRINT 2010:23 A nonconforming rotated Q 1 approximation on tetrahedra PETER HANSBO Department of Mathematical Sciences Division of Mathematics CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF GOTHENBURG
PREPRINT 2010:23 A nonconforming rotated Q 1 approximation on tetrahedra PETER HANSBO Department of Mathematical Sciences Division of Mathematics CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF GOTHENBURG
Elastic Wave Theory. LeRoy Dorman Room 436 Ritter Hall Tel: Based on notes by C. R. Bentley. Version 1.
 Elastic Wave Theory LeRoy Dorman Room 436 Ritter Hall Tel: 4-2406 email: ldorman@ucsd.edu Based on notes by C. R. Bentley. Version 1.1, 20090323 1 Chapter 1 Tensors Elastic wave theory is concerned with
Elastic Wave Theory LeRoy Dorman Room 436 Ritter Hall Tel: 4-2406 email: ldorman@ucsd.edu Based on notes by C. R. Bentley. Version 1.1, 20090323 1 Chapter 1 Tensors Elastic wave theory is concerned with
Constitutive Equations
 Constitutive quations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and ngineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 0239 October 4, 2000 Introduction The modules on kinematics (Module
Constitutive quations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and ngineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 0239 October 4, 2000 Introduction The modules on kinematics (Module
Engineering Sciences 241 Advanced Elasticity, Spring Distributed Thursday 8 February.
 Engineering Sciences 241 Advanced Elasticity, Spring 2001 J. R. Rice Homework Problems / Class Notes Mechanics of finite deformation (list of references at end) Distributed Thursday 8 February. Problems
Engineering Sciences 241 Advanced Elasticity, Spring 2001 J. R. Rice Homework Problems / Class Notes Mechanics of finite deformation (list of references at end) Distributed Thursday 8 February. Problems
NIELINIOWA OPTYKA MOLEKULARNA
 NIELINIOWA OPTYKA MOLEKULARNA chapter 1 by Stanisław Kielich translated by:tadeusz Bancewicz http://zon8.physd.amu.edu.pl/~tbancewi Poznan,luty 2008 ELEMENTS OF THE VECTOR AND TENSOR ANALYSIS Reference
NIELINIOWA OPTYKA MOLEKULARNA chapter 1 by Stanisław Kielich translated by:tadeusz Bancewicz http://zon8.physd.amu.edu.pl/~tbancewi Poznan,luty 2008 ELEMENTS OF THE VECTOR AND TENSOR ANALYSIS Reference
i=1 α i. Given an m-times continuously
 1 Fundamentals 1.1 Classification and characteristics Let Ω R d, d N, d 2, be an open set and α = (α 1,, α d ) T N d 0, N 0 := N {0}, a multiindex with α := d i=1 α i. Given an m-times continuously differentiable
1 Fundamentals 1.1 Classification and characteristics Let Ω R d, d N, d 2, be an open set and α = (α 1,, α d ) T N d 0, N 0 := N {0}, a multiindex with α := d i=1 α i. Given an m-times continuously differentiable
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics
 Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Engineering Acoustics Session 1aEA: Thermoacoustics I 1aEA7. On discontinuity
Proceedings of Meetings on Acoustics Volume 19, 2013 http://acousticalsociety.org/ ICA 2013 Montreal Montreal, Canada 2-7 June 2013 Engineering Acoustics Session 1aEA: Thermoacoustics I 1aEA7. On discontinuity
