(2) 2. (3) 2 Using equation (3), the material time derivative of the Green-Lagrange strain tensor can be obtained as: 1 = + + +
|
|
|
- Charlene Mitchell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LAGRANGIAN FORMULAION OF CONINUA Review of Continuum Kinematics he reader is referred to Belytscho et al. () for a concise review of the continuum mechanics concepts used here. he notation followed here is also from this reference. Vectors and tensors are written in bold face and their Cartesian components are written in italics with subscripts.consider a body occupying a region Ω of space with boundary Γ at time t. his is called the reference configuration of the body. he position vector of a point in the body is X. In Cartesian coordinates, the vector is represented by its components X i. he motion of the body is described by the map φ, so that at time t, the position vector of the point X is x φ(x,t). he displacement of the point X is u and xx u. he deformation gradient tensor F is defined as: he Green-Lagrange strain tensor is defined as: x F X or F ui, j () E ( F F I ) or E ( Fi F j ) () where I is the identity matrix and is the Kronecer delta ( if ij, otherwise). Using the definition of the deformation gradient, the Green-Lagrange strain tensor may be written in terms of the displacements as: E ( ui, j uj, i u, iu, j ) (3) Using equation (3), the material time derivative of the Green-Lagrange strain tensor can be obtained as: E ( ui, j uji, ui, u, j ui, u, j) ( u ) u ( u ) u ( )( u ) u ( iu, j juj, i u, iu, j u, iu, j) i i,, j j i, ji, ip jq iq jp p, p, q Hence we obtain the strain rate-velocity relationship: E where B ( ip jq iq jp )( p u, p ) B u X q is the strain rate-velocity operator. he stress measure that is wor conjugate to the Green-Lagrange strain tensor is the second Piola-Kirchhoff stress S defined by the relation: (4) (5)
2 τ i FSn i j (6) where τ is the traction vector and n is the unit normal in the reference configuration. Γ u and Γ τ are the portions of the boundary with prescribed displacement and prescribed traction respectively. Continuum Plasticity Finite deformation plasticity can be formulated in several ways. hese are discussed in an excellent fashion by Simo and Ortiz (985). Of these, the material formulation is adopted here. Other formulations are equally applicable using appropriate inematic operators. he fundamental assumption of finite deformation plasticity is the multiplicative B decomposition of the deformation gradient tensor into plastic and elastic parts: e p F F F (7) where the elastic deformation F e is obtained by unloading the body to an intermediate configuration (Simo and Ortiz (985)). he material formulation then defines the following relationships:. he plastic Green-Lagrange strain tensor: p p p E F F I. he elastic Green-Lagrange strain tensor: 3. he elastic stress-strain relationship: (8) e p E E E (9) E e ψ ρ S where S is the second Piola-Kirchhoff stress tensor and ψ(s) is the complementary strain energy function per unit mass, assumed here to be quadratic so that ψ ( S ) AlSS l where A l is the inverse of the elasticity tensor and ρ is the mass density in the reference configuration. 4. he yield condition: so that the elastic domain is 5. he flow rule: as in equation (3) of Section. () Φ SF, () {, } C S Φ S F <. he Lagrangian formulation of the continuum is now presented. p E U C ()
3 Lagrangian Formulation It is proposed that the Lagrangian and dissipation density functions (i.e. per unit mass) and the action integral of the continuum are given respectively by: where J t L uu A J J J B u ρ (4) ϕ ( Ju, ) UC ( J) cuu i j (5) I ρ LdΩdt u Γ ρ u dω dt ρ J d dt J Ω (6) ρ f u dωdt τ u dγdt S dτ, the impulse of the second Piola-Kirchhoff stress tensor, S and c is the damping per unit mass. It is shown next that the governing equations of the continuum can be derived from this Lagrangian formulation as Euler-Lagrange Equations. Derivation of Euler-Lagrange Equations Consider the first integral of equation (6): l l ρ L dω dt ρ u u ρ A J J J B u dωdt (7) By integrating by parts in time, the first two terms of the integral on the right hand side can be written as follows: ρ uud Ω dt ρ u udωdt (8) ρ A J J dω dt ρ A J J dωdt (9) l l l l Consider now the integrand of the third term: Now J ( ) ( J ) J B u J u u ( ip jq iq jp )( p, p ), q ip jq iq jp pq Jqp J pq due to the symmetry of the second Piola- Kirchhoff stress tensor and hence of the impulse tensor J. Hence: (, ), (, ) JBu J pq p u p u q J i u i u, j ()
4 replacing the indices p and q by i and j respectively. Substituting, we have: Ω ( i, i ), j J B u d dt J u u dωdt Consider the following time integral: J u u dωdt, i, j ( ) J u u dωdt i, i, j () ( ) ( ) J u u dt J u u i, i, j i, i, j J u u dt J u u dt i, i, j, i, j he first term on the right hand side vanishes because u is prescribed at the beginning and end of the time interval in Hamilton s principle. Moreover, using the symmetry of J, the indices, i and j in the third term can be switched to obtain: ( ) ( ) J u u dt J u u dt J u u i, i, j i, i, j, j, i Since i u, i Fi, the deformation gradient: (, ) i i i ji i j dt () J u S F S F P (3) where P is the unsymmetric first Piola-Kirchhoff stress tensor. he second equality above follows from the symmetry of the second Piola-Kirchhoff stress tensor, S. Notice also that similar to equation (), the first integrand on the right hand side of equation () can be written as: (, ), J u u J B u i i j Substituting equations (), (3) and (4) in equation (), we have: (4) JBud Ω dt JBud Ωdt Pu dω dt (5) j, j Notice that the second integral of equation () cancels out the second integral of equation () in a fashion similar to the spatially discrete case of section 5.8. Now consider the spatial integral:
5 ( ), j P u dω P u dω P u dω j, j j j, j Ω Ω Ω PnudΓ P udω Γ j j j, j Ω where Γ is the boundary of the domain, n is the unit vector normal to the boundary and the second equality follows from Gauss theorem. Substituting equation (6) in equation (5), we have: j, j JBudΩ dt JBudΩ dt P udωdt Γ PnudΓdt j j Substituting equations (8), (9) and (7) in equation (6) and grouping terms containing u and J gives: ( Pn τ ) Γ ρu ρ Pj, j ρf udωdt u ρal J l ρ Bu Jd dt J Ω udγdt j j Let Γ u and Γ τ be the portions of the boundary with prescribed displacement and prescribed traction respectively. hen due to the arbitrariness of u everywhere but on Γ u, and due to the arbitrariness of J, we have: ρ ρ ρ u Pj, j f u ρ ρ Al Jl Bu J Pn u τ on Γ j j τ on Γ u (6) (7) (8) (9) Equation (9) is the equation of motion expressed in the reference configuration (see for example, Belytscho, Liu et al. ()), equation (3) is the equation of compatibility and equation (3) represents the boundary conditions. It has thus been demonstrated that the Lagrangian function, the dissipation function and the action integral of equations (4) -(6) determine the governing equations of the three dimensional continuum. (3) (3)
Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity. Dr.-Ing. Martin Ruess
 Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity Dr.-Ing. Martin Ruess geometry description Cartesian global coordinate system with base vectors of the Euclidian space orthonormal basis origin O point P domain of a deformable
Nonlinear Theory of Elasticity Dr.-Ing. Martin Ruess geometry description Cartesian global coordinate system with base vectors of the Euclidian space orthonormal basis origin O point P domain of a deformable
NONLINEAR CONTINUUM FORMULATIONS CONTENTS
 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM FORMULATIONS CONTENTS Introduction to nonlinear continuum mechanics Descriptions of motion Measures of stresses and strains Updated and Total Lagrangian formulations Continuum shell
NONLINEAR CONTINUUM FORMULATIONS CONTENTS Introduction to nonlinear continuum mechanics Descriptions of motion Measures of stresses and strains Updated and Total Lagrangian formulations Continuum shell
Review of fluid dynamics
 Chapter 2 Review of fluid dynamics 2.1 Preliminaries ome basic concepts: A fluid is a substance that deforms continuously under stress. A Material olume is a tagged region that moves with the fluid. Hence
Chapter 2 Review of fluid dynamics 2.1 Preliminaries ome basic concepts: A fluid is a substance that deforms continuously under stress. A Material olume is a tagged region that moves with the fluid. Hence
Other state variables include the temperature, θ, and the entropy, S, which are defined below.
 Chapter 3 Thermodynamics In order to complete the formulation we need to express the stress tensor T and the heat-flux vector q in terms of other variables. These expressions are known as constitutive
Chapter 3 Thermodynamics In order to complete the formulation we need to express the stress tensor T and the heat-flux vector q in terms of other variables. These expressions are known as constitutive
Elements of Continuum Elasticity. David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II February 25, 2004
 Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
You may not start to read the questions printed on the subsequent pages until instructed to do so by the Invigilator.
 MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 1 June 2006 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 76 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM MECHANICS Attempt FOUR questions. There are SIX questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
MATHEMATICAL TRIPOS Part III Thursday 1 June 2006 1.30 to 4.30 PAPER 76 NONLINEAR CONTINUUM MECHANICS Attempt FOUR questions. There are SIX questions in total. The questions carry equal weight. STATIONERY
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Strain Strain is the formal description of the change in shape of a
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 2: Continuum mechanics Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Strain Strain is the formal description of the change in shape of a
Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity
 Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research of the Polish Academy
Fundamentals of Linear Elasticity Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research of the Polish Academy
Engineering Sciences 241 Advanced Elasticity, Spring Distributed Thursday 8 February.
 Engineering Sciences 241 Advanced Elasticity, Spring 2001 J. R. Rice Homework Problems / Class Notes Mechanics of finite deformation (list of references at end) Distributed Thursday 8 February. Problems
Engineering Sciences 241 Advanced Elasticity, Spring 2001 J. R. Rice Homework Problems / Class Notes Mechanics of finite deformation (list of references at end) Distributed Thursday 8 February. Problems
Chapter 2: Fluid Dynamics Review
 7 Chapter 2: Fluid Dynamics Review This chapter serves as a short review of basic fluid mechanics. We derive the relevant transport equations (or conservation equations), state Newton s viscosity law leading
7 Chapter 2: Fluid Dynamics Review This chapter serves as a short review of basic fluid mechanics. We derive the relevant transport equations (or conservation equations), state Newton s viscosity law leading
16.21 Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 2005 Unit #8 Principle of Virtual Displacements
 6. Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 005 Unit #8 rinciple of irtual Displacements Raúl Radovitzky March 3, 005 rinciple of irtual Displacements Consider a body in equilibrium. We know
6. Techniques of Structural Analysis and Design Spring 005 Unit #8 rinciple of irtual Displacements Raúl Radovitzky March 3, 005 rinciple of irtual Displacements Consider a body in equilibrium. We know
Linearized theory of elasticity
 Linearized theory of elasticity Arie Verhoeven averhoev@win.tue.nl CASA Seminar, May 24, 2006 Seminar: Continuum mechanics 1 Stress and stress principles Bart Nowak March 8 2 Strain and deformation Mark
Linearized theory of elasticity Arie Verhoeven averhoev@win.tue.nl CASA Seminar, May 24, 2006 Seminar: Continuum mechanics 1 Stress and stress principles Bart Nowak March 8 2 Strain and deformation Mark
Chapter 0. Preliminaries. 0.1 Things you should already know
 Chapter 0 Preliminaries These notes cover the course MATH45061 (Continuum Mechanics) and are intended to supplement the lectures. The course does not follow any particular text, so you do not need to buy
Chapter 0 Preliminaries These notes cover the course MATH45061 (Continuum Mechanics) and are intended to supplement the lectures. The course does not follow any particular text, so you do not need to buy
4.3 Momentum Balance Principles
 4.3 Momentum Balance Principles 4.3.1 Balance of linear angular momentum in spatial material description Consider a continuum body B with a set of particles occupying an arbitrary region Ω with boundary
4.3 Momentum Balance Principles 4.3.1 Balance of linear angular momentum in spatial material description Consider a continuum body B with a set of particles occupying an arbitrary region Ω with boundary
AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS
 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS 1 / 57 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Dynamics of Continuous Systems These slides are based on the recommended textbook: M. Géradin and D. Rixen, Mechanical Vibrations: Theory
AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS 1 / 57 AA242B: MECHANICAL VIBRATIONS Dynamics of Continuous Systems These slides are based on the recommended textbook: M. Géradin and D. Rixen, Mechanical Vibrations: Theory
Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem
 CHAPTER 3 Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem 3.1 Introduction In the mathematical theory of elasticity, the principles of minimum potential energy and minimum complimentary energy are
CHAPTER 3 Analytical formulation of Modified Upper Bound theorem 3.1 Introduction In the mathematical theory of elasticity, the principles of minimum potential energy and minimum complimentary energy are
Basic Theorems in Dynamic Elasticity
 Basic Theorems in Dynamic Elasticity 1. Stress-Strain relationships 2. Equation of motion 3. Uniqueness and reciprocity theorems 4. Elastodynamic Green s function 5. Representation theorems Víctor M. CRUZ-ATIENZA
Basic Theorems in Dynamic Elasticity 1. Stress-Strain relationships 2. Equation of motion 3. Uniqueness and reciprocity theorems 4. Elastodynamic Green s function 5. Representation theorems Víctor M. CRUZ-ATIENZA
Conference in Honour of Jerry Ericksen s 90th Birthday
 On the K 13 problem in the Oseen-Frank theory of nematic liquid crystals Arghir Dani Zarnescu University of Sussex and Simion Stoilow Institute of the Romanian Academy joint work with Stuart Day (U of
On the K 13 problem in the Oseen-Frank theory of nematic liquid crystals Arghir Dani Zarnescu University of Sussex and Simion Stoilow Institute of the Romanian Academy joint work with Stuart Day (U of
Mechanics of materials Lecture 4 Strain and deformation
 Mechanics of materials Lecture 4 Strain and deformation Reijo Kouhia Tampere University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Design Wednesday 3 rd February, 206 of a continuum
Mechanics of materials Lecture 4 Strain and deformation Reijo Kouhia Tampere University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Design Wednesday 3 rd February, 206 of a continuum
Professor George C. Johnson. ME185 - Introduction to Continuum Mechanics. Midterm Exam II. ) (1) x
 Spring, 997 ME85 - Introduction to Continuum Mechanics Midterm Exam II roblem. (+ points) (a) Let ρ be the mass density, v be the velocity vector, be the Cauchy stress tensor, and b be the body force per
Spring, 997 ME85 - Introduction to Continuum Mechanics Midterm Exam II roblem. (+ points) (a) Let ρ be the mass density, v be the velocity vector, be the Cauchy stress tensor, and b be the body force per
A new closed-form model for isotropic elastic sphere including new solutions for the free vibrations problem
 A new closed-form model for isotropic elastic sphere including new solutions for the free vibrations problem E Hanukah Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa
A new closed-form model for isotropic elastic sphere including new solutions for the free vibrations problem E Hanukah Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa
Constitutive Relations
 Constitutive Relations Andri Andriyana, Ph.D. Centre de Mise en Forme des Matériaux, CEMEF UMR CNRS 7635 École des Mines de Paris, 06904 Sophia Antipolis, France Spring, 2008 Outline Outline 1 Review of
Constitutive Relations Andri Andriyana, Ph.D. Centre de Mise en Forme des Matériaux, CEMEF UMR CNRS 7635 École des Mines de Paris, 06904 Sophia Antipolis, France Spring, 2008 Outline Outline 1 Review of
Continuum mechanics V. Constitutive equations. 1. Constitutive equation: definition and basic axioms
 Continuum mechanics office Math 0.107 ales.janka@unifr.ch http://perso.unifr.ch/ales.janka/mechanics Mars 16, 2011, Université de Fribourg 1. Constitutive equation: definition and basic axioms Constitutive
Continuum mechanics office Math 0.107 ales.janka@unifr.ch http://perso.unifr.ch/ales.janka/mechanics Mars 16, 2011, Université de Fribourg 1. Constitutive equation: definition and basic axioms Constitutive
3 2 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) 3. a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1
 Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
Math Problem a- If A has eigenvalues λ =, λ = 1 and corresponding eigenvectors 1 3 6 Solve the initial value problem u ( t) = Au( t) with u (0) =. 3 1 u 1 =, u 1 3 = b- True or false and why 1. if A is
By drawing Mohr s circle, the stress transformation in 2-D can be done graphically. + σ x σ y. cos 2θ + τ xy sin 2θ, (1) sin 2θ + τ xy cos 2θ.
 Mohr s Circle By drawing Mohr s circle, the stress transformation in -D can be done graphically. σ = σ x + σ y τ = σ x σ y + σ x σ y cos θ + τ xy sin θ, 1 sin θ + τ xy cos θ. Note that the angle of rotation,
Mohr s Circle By drawing Mohr s circle, the stress transformation in -D can be done graphically. σ = σ x + σ y τ = σ x σ y + σ x σ y cos θ + τ xy sin θ, 1 sin θ + τ xy cos θ. Note that the angle of rotation,
CVEN 7511 Computational Mechanics of Solids and Structures
 CVEN 7511 Computational Mechanics of Solids and Structures Instructor: Kaspar J. Willam Original Version of Class Notes Chishen T. Lin Fall 1990 Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Continuum Mechanics Abstract In
CVEN 7511 Computational Mechanics of Solids and Structures Instructor: Kaspar J. Willam Original Version of Class Notes Chishen T. Lin Fall 1990 Chapter 1 Fundamentals of Continuum Mechanics Abstract In
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017
 Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
Mechanics PhD Preliminary Spring 2017 1. (10 points) Consider a body Ω that is assembled by gluing together two separate bodies along a flat interface. The normal vector to the interface is given by n
The Finite Element Method II
 [ 1 The Finite Element Method II Non-Linear finite element Use of Constitutive Relations Xinghong LIU Phd student 02.11.2007 [ 2 Finite element equilibrium equations: kinematic variables Displacement Strain-displacement
[ 1 The Finite Element Method II Non-Linear finite element Use of Constitutive Relations Xinghong LIU Phd student 02.11.2007 [ 2 Finite element equilibrium equations: kinematic variables Displacement Strain-displacement
Constitutive Relations
 Constitutive Relations Dr. Andri Andriyana Centre de Mise en Forme des Matériaux, CEMEF UMR CNRS 7635 École des Mines de Paris, 06904 Sophia Antipolis, France Spring, 2008 Outline Outline 1 Review of field
Constitutive Relations Dr. Andri Andriyana Centre de Mise en Forme des Matériaux, CEMEF UMR CNRS 7635 École des Mines de Paris, 06904 Sophia Antipolis, France Spring, 2008 Outline Outline 1 Review of field
On the Numerical Modelling of Orthotropic Large Strain Elastoplasticity
 63 Advances in 63 On the Numerical Modelling of Orthotropic Large Strain Elastoplasticity I. Karsaj, C. Sansour and J. Soric Summary A constitutive model for orthotropic yield function at large strain
63 Advances in 63 On the Numerical Modelling of Orthotropic Large Strain Elastoplasticity I. Karsaj, C. Sansour and J. Soric Summary A constitutive model for orthotropic yield function at large strain
Course No: (1 st version: for graduate students) Course Name: Continuum Mechanics Offered by: Chyanbin Hwu
 Course No: (1 st version: for graduate students) Course Name: Continuum Mechanics Offered by: Chyanbin Hwu 2011. 11. 25 Contents: 1. Introduction 1.1 Basic Concepts of Continuum Mechanics 1.2 The Need
Course No: (1 st version: for graduate students) Course Name: Continuum Mechanics Offered by: Chyanbin Hwu 2011. 11. 25 Contents: 1. Introduction 1.1 Basic Concepts of Continuum Mechanics 1.2 The Need
Chapter 3. Forces, Momentum & Stress. 3.1 Newtonian mechanics: a very brief résumé
 Chapter 3 Forces, Momentum & Stress 3.1 Newtonian mechanics: a very brief résumé In classical Newtonian particle mechanics, particles (lumps of matter) only experience acceleration when acted on by external
Chapter 3 Forces, Momentum & Stress 3.1 Newtonian mechanics: a very brief résumé In classical Newtonian particle mechanics, particles (lumps of matter) only experience acceleration when acted on by external
Classification of Prostate Cancer Grades and T-Stages based on Tissue Elasticity Using Medical Image Analysis. Supplementary Document
 Classification of Prostate Cancer Grades and T-Stages based on Tissue Elasticity Using Medical Image Analysis Supplementary Document Shan Yang, Vladimir Jojic, Jun Lian, Ronald Chen, Hongtu Zhu, Ming C.
Classification of Prostate Cancer Grades and T-Stages based on Tissue Elasticity Using Medical Image Analysis Supplementary Document Shan Yang, Vladimir Jojic, Jun Lian, Ronald Chen, Hongtu Zhu, Ming C.
ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda
 ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda Contents Preface xiii Part 1. ELEMENTS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS 1 Chapter 1. TENSOR PRELIMINARIES 3 1.1. Vectors 3 1.2. Second-Order Tensors 4 1.3. Eigenvalues and
ELASTOPLASTICITY THEORY by V. A. Lubarda Contents Preface xiii Part 1. ELEMENTS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS 1 Chapter 1. TENSOR PRELIMINARIES 3 1.1. Vectors 3 1.2. Second-Order Tensors 4 1.3. Eigenvalues and
2.3 BASIC EQUATIONS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS
 211 2.3 BASIC EQUATIONS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS Continuum mechanics is the study of how materials behave when subjected to external influences. External influences which affect the properties of a substance
211 2.3 BASIC EQUATIONS OF CONTINUUM MECHANICS Continuum mechanics is the study of how materials behave when subjected to external influences. External influences which affect the properties of a substance
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow
 Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research
Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamics: Elementary Viscous Flow Introductory Course on Multiphysics Modelling TOMASZ G. ZIELIŃSKI bluebox.ippt.pan.pl/ tzielins/ Institute of Fundamental Technological Research
4 Constitutive Theory
 ME338A CONTINUUM MECHANICS lecture notes 13 Tuesday, May 13, 2008 4.1 Closure Problem In the preceding chapter, we derived the fundamental balance equations: Balance of Spatial Material Mass ρ t + ρ t
ME338A CONTINUUM MECHANICS lecture notes 13 Tuesday, May 13, 2008 4.1 Closure Problem In the preceding chapter, we derived the fundamental balance equations: Balance of Spatial Material Mass ρ t + ρ t
Computational non-linear structural dynamics and energy-momentum integration schemes
 icccbe 2010 Nottingham University Press Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering W Tizani (Editor) Computational non-linear structural dynamics and energy-momentum
icccbe 2010 Nottingham University Press Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering W Tizani (Editor) Computational non-linear structural dynamics and energy-momentum
This introductory chapter presents some basic concepts of continuum mechanics, symbols and notations for future reference.
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Elasticity This introductory chapter presents some basic concepts of continuum mechanics, symbols and notations for future reference. 1.1 Kinematics of finite deformations We
Chapter 1 Introduction to Elasticity This introductory chapter presents some basic concepts of continuum mechanics, symbols and notations for future reference. 1.1 Kinematics of finite deformations We
Computer Fluid Dynamics E181107
 Computer Fluid Dynamics E181107 2181106 Transport equations, Navier Stokes equations Remark: foils with black background could be skipped, they are aimed to the more advanced courses Rudolf Žitný, Ústav
Computer Fluid Dynamics E181107 2181106 Transport equations, Navier Stokes equations Remark: foils with black background could be skipped, they are aimed to the more advanced courses Rudolf Žitný, Ústav
KINEMATICS OF CONTINUA
 KINEMATICS OF CONTINUA Introduction Deformation of a continuum Configurations of a continuum Deformation mapping Descriptions of motion Material time derivative Velocity and acceleration Transformation
KINEMATICS OF CONTINUA Introduction Deformation of a continuum Configurations of a continuum Deformation mapping Descriptions of motion Material time derivative Velocity and acceleration Transformation
A CONTINUUM MECHANICS PRIMER
 A CONTINUUM MECHANICS PRIMER On Constitutive Theories of Materials I-SHIH LIU Rio de Janeiro Preface In this note, we concern only fundamental concepts of continuum mechanics for the formulation of basic
A CONTINUUM MECHANICS PRIMER On Constitutive Theories of Materials I-SHIH LIU Rio de Janeiro Preface In this note, we concern only fundamental concepts of continuum mechanics for the formulation of basic
An Atomistic-based Cohesive Zone Model for Quasi-continua
 An Atomistic-based Cohesive Zone Model for Quasi-continua By Xiaowei Zeng and Shaofan Li Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, CA94720, USA Extended Abstract
An Atomistic-based Cohesive Zone Model for Quasi-continua By Xiaowei Zeng and Shaofan Li Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, CA94720, USA Extended Abstract
Physical Conservation and Balance Laws & Thermodynamics
 Chapter 4 Physical Conservation and Balance Laws & Thermodynamics The laws of classical physics are, for the most part, expressions of conservation or balances of certain quantities: e.g. mass, momentum,
Chapter 4 Physical Conservation and Balance Laws & Thermodynamics The laws of classical physics are, for the most part, expressions of conservation or balances of certain quantities: e.g. mass, momentum,
Constitutive Equations
 Constitutive quations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and ngineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 0239 October 4, 2000 Introduction The modules on kinematics (Module
Constitutive quations David Roylance Department of Materials Science and ngineering Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA 0239 October 4, 2000 Introduction The modules on kinematics (Module
3D Elasticity Theory
 3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
3D lasticity Theory Many structural analysis problems are analysed using the theory of elasticity in which Hooke s law is used to enforce proportionality between stress and strain at any deformation level.
Modeling of a soft link continuum formulation
 Modeling of a soft link continuum formulation Stanislao Grazioso Thursday 12 th April, 2018 Stanislao Grazioso Geometric Theory of Soft Robots Thursday 12 th April, 2018 1 / 38 Introduction Soft arm: 2D
Modeling of a soft link continuum formulation Stanislao Grazioso Thursday 12 th April, 2018 Stanislao Grazioso Geometric Theory of Soft Robots Thursday 12 th April, 2018 1 / 38 Introduction Soft arm: 2D
Natural States and Symmetry Properties of. Two-Dimensional Ciarlet-Mooney-Rivlin. Nonlinear Constitutive Models
 Natural States and Symmetry Properties of Two-Dimensional Ciarlet-Mooney-Rivlin Nonlinear Constitutive Models Alexei Cheviakov, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Univ. Saskatchewan, Canada Jean-François
Natural States and Symmetry Properties of Two-Dimensional Ciarlet-Mooney-Rivlin Nonlinear Constitutive Models Alexei Cheviakov, Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Univ. Saskatchewan, Canada Jean-François
FVM for Fluid-Structure Interaction with Large Structural Displacements
 FVM for Fluid-Structure Interaction with Large Structural Displacements Željko Tuković and Hrvoje Jasak Zeljko.Tukovic@fsb.hr, h.jasak@wikki.co.uk Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture
FVM for Fluid-Structure Interaction with Large Structural Displacements Željko Tuković and Hrvoje Jasak Zeljko.Tukovic@fsb.hr, h.jasak@wikki.co.uk Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture
CH.11. VARIATIONAL PRINCIPLES. Multimedia Course on Continuum Mechanics
 CH.11. ARIATIONAL PRINCIPLES Multimedia Course on Continuum Mechanics Overview Introduction Functionals Gâteaux Derivative Extreme of a Functional ariational Principle ariational Form of a Continuum Mechanics
CH.11. ARIATIONAL PRINCIPLES Multimedia Course on Continuum Mechanics Overview Introduction Functionals Gâteaux Derivative Extreme of a Functional ariational Principle ariational Form of a Continuum Mechanics
. D CR Nomenclature D 1
 . D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
. D CR Nomenclature D 1 Appendix D: CR NOMENCLATURE D 2 The notation used by different investigators working in CR formulations has not coalesced, since the topic is in flux. This Appendix identifies the
Elastic Wave Theory. LeRoy Dorman Room 436 Ritter Hall Tel: Based on notes by C. R. Bentley. Version 1.
 Elastic Wave Theory LeRoy Dorman Room 436 Ritter Hall Tel: 4-2406 email: ldorman@ucsd.edu Based on notes by C. R. Bentley. Version 1.1, 20090323 1 Chapter 1 Tensors Elastic wave theory is concerned with
Elastic Wave Theory LeRoy Dorman Room 436 Ritter Hall Tel: 4-2406 email: ldorman@ucsd.edu Based on notes by C. R. Bentley. Version 1.1, 20090323 1 Chapter 1 Tensors Elastic wave theory is concerned with
Nonlinear Equations for Finite-Amplitude Wave Propagation in Fiber-Reinforced Hyperelastic Media
 Nonlinear Equations for Finite-Amplitude Wave Propagation in Fiber-Reinforced Hyperelastic Media Alexei F. Cheviakov Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada
Nonlinear Equations for Finite-Amplitude Wave Propagation in Fiber-Reinforced Hyperelastic Media Alexei F. Cheviakov Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada
Continuum Mechanics and the Finite Element Method
 Continuum Mechanics and the Finite Element Method 1 Assignment 2 Due on March 2 nd @ midnight 2 Suppose you want to simulate this The familiar mass-spring system l 0 l y i X y i x Spring length before/after
Continuum Mechanics and the Finite Element Method 1 Assignment 2 Due on March 2 nd @ midnight 2 Suppose you want to simulate this The familiar mass-spring system l 0 l y i X y i x Spring length before/after
Introduction to Continuum Mechanics
 Introduction to Continuum Mechanics I-Shih Liu Instituto de Matemática Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro 2018 Contents 1 Notations and tensor algebra 1 1.1 Vector space, inner product........................
Introduction to Continuum Mechanics I-Shih Liu Instituto de Matemática Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro 2018 Contents 1 Notations and tensor algebra 1 1.1 Vector space, inner product........................
Variational principles in mechanics
 CHAPTER Variational principles in mechanics.1 Linear Elasticity n D Figure.1: A domain and its boundary = D [. Consider a domain Ω R 3 with its boundary = D [ of normal n (see Figure.1). The problem of
CHAPTER Variational principles in mechanics.1 Linear Elasticity n D Figure.1: A domain and its boundary = D [. Consider a domain Ω R 3 with its boundary = D [ of normal n (see Figure.1). The problem of
Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies
 Ch3-Stress-Equilibrium Page 1 Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies When structures / deformable bodies are acted upon by loads, they build up internal forces (stresses) within them to
Ch3-Stress-Equilibrium Page 1 Chapter 3: Stress and Equilibrium of Deformable Bodies When structures / deformable bodies are acted upon by loads, they build up internal forces (stresses) within them to
MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec05_300k-mp4
 MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec05_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
MITOCW MITRES2_002S10nonlinear_lec05_300k-mp4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources
NONLINEAR MECHANICAL SYSTEMS LAGRANGIAN AND HAMILTONIAN FORMULATIONS. Lagrangian formulation. Ek * (f,q) = 1 2 f t I(q) f
 NONLINEAR MECHANICAL SYSTEMS LAGRANGIAN AND HAMILTONIAN FORMULATIONS q f Lagrangian formulation Ek * (f,q) = 1 2 f t I(q) f generalized coordinates (displacement) generalized velocity (flow) Ek * (f,q)
NONLINEAR MECHANICAL SYSTEMS LAGRANGIAN AND HAMILTONIAN FORMULATIONS q f Lagrangian formulation Ek * (f,q) = 1 2 f t I(q) f generalized coordinates (displacement) generalized velocity (flow) Ek * (f,q)
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics. Final Examination December 17, 2004
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics Course: 8.09 Classical Mechanics Term: Fall 004 Final Examination December 17, 004 Instructions Do not start until you are told to do so. Solve
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics Course: 8.09 Classical Mechanics Term: Fall 004 Final Examination December 17, 004 Instructions Do not start until you are told to do so. Solve
Chapter 3 Stress, Strain, Virtual Power and Conservation Principles
 Chapter 3 Stress, Strain, irtual Power and Conservation Principles 1 Introduction Stress and strain are key concepts in the analytical characterization of the mechanical state of a solid body. While stress
Chapter 3 Stress, Strain, irtual Power and Conservation Principles 1 Introduction Stress and strain are key concepts in the analytical characterization of the mechanical state of a solid body. While stress
Draft:S Ghorai. 1 Body and surface forces. Stress Principle
 Stress Principle Body and surface forces Stress is a measure of force intensity, either within or on the bounding surface of a body subjected to loads. It should be noted that in continuum mechanics a
Stress Principle Body and surface forces Stress is a measure of force intensity, either within or on the bounding surface of a body subjected to loads. It should be noted that in continuum mechanics a
202 Index. failure, 26 field equation, 122 force, 1
 Index acceleration, 12, 161 admissible function, 155 admissible stress, 32 Airy's stress function, 122, 124 d'alembert's principle, 165, 167, 177 amplitude, 171 analogy, 76 anisotropic material, 20 aperiodic
Index acceleration, 12, 161 admissible function, 155 admissible stress, 32 Airy's stress function, 122, 124 d'alembert's principle, 165, 167, 177 amplitude, 171 analogy, 76 anisotropic material, 20 aperiodic
Stress of a spatially uniform dislocation density field
 Stress of a spatially uniform dislocation density field Amit Acharya November 19, 2018 Abstract It can be shown that the stress produced by a spatially uniform dislocation density field in a body comprising
Stress of a spatially uniform dislocation density field Amit Acharya November 19, 2018 Abstract It can be shown that the stress produced by a spatially uniform dislocation density field in a body comprising
Aircraft Structures Kirchhoff-Love Plates
 University of Liège erospace & Mechanical Engineering ircraft Structures Kirchhoff-Love Plates Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials CM3 http://www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be/ Chemin
University of Liège erospace & Mechanical Engineering ircraft Structures Kirchhoff-Love Plates Ludovic Noels Computational & Multiscale Mechanics of Materials CM3 http://www.ltas-cm3.ulg.ac.be/ Chemin
Mathematical Background
 CHAPTER ONE Mathematical Background This book assumes a background in the fundamentals of solid mechanics and the mechanical behavior of materials, including elasticity, plasticity, and friction. A previous
CHAPTER ONE Mathematical Background This book assumes a background in the fundamentals of solid mechanics and the mechanical behavior of materials, including elasticity, plasticity, and friction. A previous
Mechanics of solids and fluids -Introduction to continuum mechanics
 Mechanics of solids and fluids -Introduction to continuum mechanics by Magnus Ekh August 12, 2016 Introduction to continuum mechanics 1 Tensors............................. 3 1.1 Index notation 1.2 Vectors
Mechanics of solids and fluids -Introduction to continuum mechanics by Magnus Ekh August 12, 2016 Introduction to continuum mechanics 1 Tensors............................. 3 1.1 Index notation 1.2 Vectors
Chapter 1. Continuum mechanics review. 1.1 Definitions and nomenclature
 Chapter 1 Continuum mechanics review We will assume some familiarity with continuum mechanics as discussed in the context of an introductory geodynamics course; a good reference for such problems is Turcotte
Chapter 1 Continuum mechanics review We will assume some familiarity with continuum mechanics as discussed in the context of an introductory geodynamics course; a good reference for such problems is Turcotte
MATH45061: SOLUTION SHEET 1 V
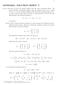 1 MATH4561: SOLUTION SHEET 1 V 1.) a.) The faces of the cube remain aligned with the same coordinate planes. We assign Cartesian coordinates aligned with the original cube (x, y, z), where x, y, z 1. The
1 MATH4561: SOLUTION SHEET 1 V 1.) a.) The faces of the cube remain aligned with the same coordinate planes. We assign Cartesian coordinates aligned with the original cube (x, y, z), where x, y, z 1. The
SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by
 SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring 2014 1. Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by u(x) = [cos(β)x 1 + sin(β)x 2 X 1 ]e 1 + [ sin(β)x 1 + cos(β)x 2 X 2 ]e
SEMM Mechanics PhD Preliminary Exam Spring 2014 1. Consider a two-dimensional rigid motion, whose displacement field is given by u(x) = [cos(β)x 1 + sin(β)x 2 X 1 ]e 1 + [ sin(β)x 1 + cos(β)x 2 X 2 ]e
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 83-90
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No. 1-2017 Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 83-90 GENERALIZED MICROPOLAR THERMOELASTICITY WITH FRACTIONAL ORDER STRAIN Adina
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol 10(59), No. 1-2017 Series III: Mathematics, Informatics, Physics, 83-90 GENERALIZED MICROPOLAR THERMOELASTICITY WITH FRACTIONAL ORDER STRAIN Adina
Optimal thickness of a cylindrical shell under dynamical loading
 Optimal thickness of a cylindrical shell under dynamical loading Paul Ziemann Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science, E.-M.-A. University Greifswald, Germany e-mail paul.ziemann@uni-greifswald.de
Optimal thickness of a cylindrical shell under dynamical loading Paul Ziemann Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science, E.-M.-A. University Greifswald, Germany e-mail paul.ziemann@uni-greifswald.de
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 3: The elastic wave equation
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 3: The elastic wave equation Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Equation of motion The equation of motion can be derived by considering
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 3: The elastic wave equation Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Equation of motion The equation of motion can be derived by considering
Discrete Analysis for Plate Bending Problems by Using Hybrid-type Penalty Method
 131 Bulletin of Research Center for Computing and Multimedia Studies, Hosei University, 21 (2008) Published online (http://hdl.handle.net/10114/1532) Discrete Analysis for Plate Bending Problems by Using
131 Bulletin of Research Center for Computing and Multimedia Studies, Hosei University, 21 (2008) Published online (http://hdl.handle.net/10114/1532) Discrete Analysis for Plate Bending Problems by Using
Useful Formulae ( )
 Appendix A Useful Formulae (985-989-993-) 34 Jeremić et al. A.. CHAPTER SUMMARY AND HIGHLIGHTS page: 35 of 536 A. Chapter Summary and Highlights A. Stress and Strain This section reviews small deformation
Appendix A Useful Formulae (985-989-993-) 34 Jeremić et al. A.. CHAPTER SUMMARY AND HIGHLIGHTS page: 35 of 536 A. Chapter Summary and Highlights A. Stress and Strain This section reviews small deformation
Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics
 Computational Biology Group (CoBi), D-BSSE, ETHZ Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil MSc Computational Biology 2015/16 7. Mai 2016 2 / 57 Contents 1 Introduction to Elastic Materials
Computational Biology Group (CoBi), D-BSSE, ETHZ Lecture 8: Tissue Mechanics Prof Dagmar Iber, PhD DPhil MSc Computational Biology 2015/16 7. Mai 2016 2 / 57 Contents 1 Introduction to Elastic Materials
A short review of continuum mechanics
 A short review of continuum mechanics Professor Anette M. Karlsson, Department of Mechanical ngineering, UD September, 006 This is a short and arbitrary review of continuum mechanics. Most of this material
A short review of continuum mechanics Professor Anette M. Karlsson, Department of Mechanical ngineering, UD September, 006 This is a short and arbitrary review of continuum mechanics. Most of this material
Continuum Mechanics Fundamentals
 Continuum Mechanics Fundamentals James R. Rice, notes for ES 220, 12 November 2009; corrections 9 December 2009 Conserved Quantities Let a conseved quantity have amount F per unit volume. Examples are
Continuum Mechanics Fundamentals James R. Rice, notes for ES 220, 12 November 2009; corrections 9 December 2009 Conserved Quantities Let a conseved quantity have amount F per unit volume. Examples are
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering
 Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
A Study on Numerical Solution to the Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equation
 A Study on Numerical Solution to the Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equation Zipeng Zhao May 2014 1 Introduction 1.1 Motivation One of the most important applications of finite differences lies in the field
A Study on Numerical Solution to the Incompressible Navier-Stokes Equation Zipeng Zhao May 2014 1 Introduction 1.1 Motivation One of the most important applications of finite differences lies in the field
Variational formulations for single-crystal strain-gradient plasticity at large deformations
 GAMM-Mitt. 36, No. 2, 149 160 (2013) / DOI 10.1002/gamm.201310009 Variational formulations for single-crystal strain-gradient plasticity at large deformations. D. Reddy 1, 1 University of Cape Town, Department
GAMM-Mitt. 36, No. 2, 149 160 (2013) / DOI 10.1002/gamm.201310009 Variational formulations for single-crystal strain-gradient plasticity at large deformations. D. Reddy 1, 1 University of Cape Town, Department
Symmetries and invariant solutions of mathematical models of plastic ow during linear friction welding
 Symmetries and invariant solutions of mathematical models of plastic ow during linear friction welding Artur Araslanov Ufa State Aviation Technical University, Ufa, Russia. Laboratory of Group Analysis
Symmetries and invariant solutions of mathematical models of plastic ow during linear friction welding Artur Araslanov Ufa State Aviation Technical University, Ufa, Russia. Laboratory of Group Analysis
Glossary. Glossary of Symbols. Glossary of Roman Symbols Glossary of Greek Symbols. Contents:
 Glossary Glossary of Symbols Contents: Glossary of Roman Symbols Glossary of Greek Symbols Glossary G-l Glossary of Roman Symbols The Euclidean norm or "two-norm." For a vector a The Mooney-Rivlin material
Glossary Glossary of Symbols Contents: Glossary of Roman Symbols Glossary of Greek Symbols Glossary G-l Glossary of Roman Symbols The Euclidean norm or "two-norm." For a vector a The Mooney-Rivlin material
Multiple integrals: Sufficient conditions for a local minimum, Jacobi and Weierstrass-type conditions
 Multiple integrals: Sufficient conditions for a local minimum, Jacobi and Weierstrass-type conditions March 6, 2013 Contents 1 Wea second variation 2 1.1 Formulas for variation........................
Multiple integrals: Sufficient conditions for a local minimum, Jacobi and Weierstrass-type conditions March 6, 2013 Contents 1 Wea second variation 2 1.1 Formulas for variation........................
Law of behavior very-rubber band: almost incompressible material
 Titre : Loi de comportement hyperélastique : matériau pres[...] Date : 25/09/2013 Page : 1/9 Law of behavior very-rubber band: almost incompressible material Summary: One describes here the formulation
Titre : Loi de comportement hyperélastique : matériau pres[...] Date : 25/09/2013 Page : 1/9 Law of behavior very-rubber band: almost incompressible material Summary: One describes here the formulation
Chapter 2. General concepts. 2.1 The Navier-Stokes equations
 Chapter 2 General concepts 2.1 The Navier-Stokes equations The Navier-Stokes equations model the fluid mechanics. This set of differential equations describes the motion of a fluid. In the present work
Chapter 2 General concepts 2.1 The Navier-Stokes equations The Navier-Stokes equations model the fluid mechanics. This set of differential equations describes the motion of a fluid. In the present work
Basic hydrodynamics. David Gurarie. 1 Newtonian fluids: Euler and Navier-Stokes equations
 Basic hydrodynamics David Gurarie 1 Newtonian fluids: Euler and Navier-Stokes equations The basic hydrodynamic equations in the Eulerian form consist of conservation of mass, momentum and energy. We denote
Basic hydrodynamics David Gurarie 1 Newtonian fluids: Euler and Navier-Stokes equations The basic hydrodynamic equations in the Eulerian form consist of conservation of mass, momentum and energy. We denote
Measurement of deformation. Measurement of elastic force. Constitutive law. Finite element method
 Deformable Bodies Deformation x p(x) Given a rest shape x and its deformed configuration p(x), how large is the internal restoring force f(p)? To answer this question, we need a way to measure deformation
Deformable Bodies Deformation x p(x) Given a rest shape x and its deformed configuration p(x), how large is the internal restoring force f(p)? To answer this question, we need a way to measure deformation
Solutions for Fundamentals of Continuum Mechanics. John W. Rudnicki
 Solutions for Fundamentals of Continuum Mechanics John W. Rudnicki December, 015 ii Contents I Mathematical Preliminaries 1 1 Vectors 3 Tensors 7 3 Cartesian Coordinates 9 4 Vector (Cross) Product 13 5
Solutions for Fundamentals of Continuum Mechanics John W. Rudnicki December, 015 ii Contents I Mathematical Preliminaries 1 1 Vectors 3 Tensors 7 3 Cartesian Coordinates 9 4 Vector (Cross) Product 13 5
Chapter 7. Kinematics. 7.1 Tensor fields
 Chapter 7 Kinematics 7.1 Tensor fields In fluid mechanics, the fluid flow is described in terms of vector fields or tensor fields such as velocity, stress, pressure, etc. It is important, at the outset,
Chapter 7 Kinematics 7.1 Tensor fields In fluid mechanics, the fluid flow is described in terms of vector fields or tensor fields such as velocity, stress, pressure, etc. It is important, at the outset,
Supplementary Technical Document
 Supplementary Technical Document Qi Guo, Xuchen Han, Chuyuan Fu, Theodore Gast, Rasmus Tamstorf, Joseph Teran 1 FEM Force computation We compute forces on the control points x p by fp KL = ΨS F KL,Etr
Supplementary Technical Document Qi Guo, Xuchen Han, Chuyuan Fu, Theodore Gast, Rasmus Tamstorf, Joseph Teran 1 FEM Force computation We compute forces on the control points x p by fp KL = ΨS F KL,Etr
BACKGROUNDS. Two Models of Deformable Body. Distinct Element Method (DEM)
 BACKGROUNDS Two Models of Deformable Body continuum rigid-body spring deformation expressed in terms of field variables assembly of rigid-bodies connected by spring Distinct Element Method (DEM) simple
BACKGROUNDS Two Models of Deformable Body continuum rigid-body spring deformation expressed in terms of field variables assembly of rigid-bodies connected by spring Distinct Element Method (DEM) simple
Nonlinear analysis in ADINA Structures
 Nonlinear analysis in ADINA Structures Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Topics presented Types of nonlinearities Materially nonlinear only Geometrically nonlinear analysis Deformation-dependent
Nonlinear analysis in ADINA Structures Theodore Sussman, Ph.D. ADINA R&D, Inc, 2016 1 Topics presented Types of nonlinearities Materially nonlinear only Geometrically nonlinear analysis Deformation-dependent
Duality, Dual Variational Principles
 Duality, Dual Variational Principles April 5, 2013 Contents 1 Duality 1 1.1 Legendre and Young-Fenchel transforms.............. 1 1.2 Second conjugate and convexification................ 4 1.3 Hamiltonian
Duality, Dual Variational Principles April 5, 2013 Contents 1 Duality 1 1.1 Legendre and Young-Fenchel transforms.............. 1 1.2 Second conjugate and convexification................ 4 1.3 Hamiltonian
7 The Navier-Stokes Equations
 18.354/12.27 Spring 214 7 The Navier-Stokes Equations In the previous section, we have seen how one can deduce the general structure of hydrodynamic equations from purely macroscopic considerations and
18.354/12.27 Spring 214 7 The Navier-Stokes Equations In the previous section, we have seen how one can deduce the general structure of hydrodynamic equations from purely macroscopic considerations and
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems. Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture ST1-19 November, 2015
 The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture ST1-19 November, 2015 Institute of Structural Engineering Method of Finite Elements II 1 Constitutive
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Lecture ST1-19 November, 2015 Institute of Structural Engineering Method of Finite Elements II 1 Constitutive
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analysis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design
 MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analsis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design Cornell Universit, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Materials Process Design and Control Laborator Sible School of Mechanical and Aerospace
MAE4700/5700 Finite Element Analsis for Mechanical and Aerospace Design Cornell Universit, Fall 2009 Nicholas Zabaras Materials Process Design and Control Laborator Sible School of Mechanical and Aerospace
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 MASSACHUSETTS NSTTUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MATERALS SCENCE AND ENGNEERNG CAMBRDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 39 3. MECHANCAL PROPERTES OF MATERALS PROBLEM SET SOLUTONS Reading Ashby, M.F., 98, Tensors: Notes
MASSACHUSETTS NSTTUTE OF TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MATERALS SCENCE AND ENGNEERNG CAMBRDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 39 3. MECHANCAL PROPERTES OF MATERALS PROBLEM SET SOLUTONS Reading Ashby, M.F., 98, Tensors: Notes
Internal Variables and Generalized Continuum Theories
 Internal Variables and Generalized Continuum Theories Arkadi Berezovski, Jüri Engelbrecht and Gérard A. Maugin Abstract The canonical thermomechanics on the material manifold is enriched by the introduction
Internal Variables and Generalized Continuum Theories Arkadi Berezovski, Jüri Engelbrecht and Gérard A. Maugin Abstract The canonical thermomechanics on the material manifold is enriched by the introduction
arxiv:q-bio/ v1 [q-bio.qm] 30 Nov 2003
![arxiv:q-bio/ v1 [q-bio.qm] 30 Nov 2003 arxiv:q-bio/ v1 [q-bio.qm] 30 Nov 2003](/thumbs/81/83376084.jpg) Material forces in the context of biotissue remodelling arxiv:q-bio/0312002v1 [q-bio.qm] 30 Nov 2003 K. Garikipati, H. Narayanan, E. M. Arruda, K. Grosh, S. Calve University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Material forces in the context of biotissue remodelling arxiv:q-bio/0312002v1 [q-bio.qm] 30 Nov 2003 K. Garikipati, H. Narayanan, E. M. Arruda, K. Grosh, S. Calve University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan
