Unexpected facets of the Yang Baxter equation
|
|
|
- Dorothy Cook
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unexpected facets of the Yang Baxter equation Victoria LEBED (ab)c = a(bc) = z 1 (y 1 xy)z= (z 1 y 1 z)(z 1 xz)(z 1 yz) TCD, Octobre 2016
2 1 Yang Baxter equation: basics Data: vectorspacev, ff:v 2 V 2. Yang-Baxter equation(ybe) ff 1 ff 2 ff 1 =ff 2 ff 1 ff 2 :V 3 V 3 ff 1 =ff Id V,ff 2 =Id V ff
3 1 Yang Baxter equation: basics Data: vectorspacev, ff:v 2 V 2. Yang-Baxter equation(ybe) ff 1 ff 2 ff 1 =ff 2 ff 1 ff 2 :V 3 V 3 ff 1 =ff Id V,ff 2 =Id V ff Avatars: factorization condition for the dispersion matrix in the 1-dim. n-body problem(mcguire& Yang 60 ); condition for the partition function in an exactly solvable lattice model(onsager 44; Baxter 70 );
4 1 Yang Baxter equation: basics Data: vectorspacev, ff:v 2 V 2. Yang-Baxter equation(ybe) ff 1 ff 2 ff 1 =ff 2 ff 1 ff 2 :V 3 V 3 ff 1 =ff Id V,ff 2 =Id V ff Avatars: factorization condition for the dispersion matrix in the 1-dim. n-body problem(mcguire& Yang 60 ); condition for the partition function in an exactly solvable lattice model(onsager 44; Baxter 70 ); quantum inverse scattering method for completely integrable systems(faddeev et al. 79); factorisable S-matrices in 2-dim. quantum field theory (Zamolodchikov 79); R-matricesinquantumgroups(Drinfel 0 d80 ); C algebras(woronowicz80 );...
5 1 Yang Baxter equation: basics Data: vectorspacev, ff:v 2 V 2. Yang-Baxter equation(ybe) ff 1 ff 2 ff 1 =ff 2 ff 1 ff 2 :V 3 V 3 ff Avatars: 1 =ff Id V,ff 2 =Id V ff braid equation in low-dimensional topology ff YBE = Reidemeister III move
6 2 Braided sets Data: sets, ff:sˆ2 Sˆ2. Set-theoreticYBE(Drinfel 0 d 90) ff 1 ff 2 ff 1 =ff 2 ff 1 ff 2 :Sˆ3 Sˆ3 ff Solutions are called braided sets. 1 =ffˆid S,ff 2 =Id Sˆff
7 2 Braided sets Data: sets, ff:sˆ2 Sˆ2. Set-theoreticYBE(Drinfel 0 d 90) ff 1 ff 2 ff 1 =ff 2 ff 1 ff 2 :Sˆ3 Sˆ3 ff Solutions are called braided sets. 1 =ffˆid S,ff 2 =Id Sˆff braided sets linearise deform general solutions
8 2 Braided sets Data: sets, ff:sˆ2 Sˆ2. Set-theoreticYBE(Drinfel 0 d 90) ff 1 ff 2 ff 1 =ff 2 ff 1 ff 2 :Sˆ3 Sˆ3 ff Solutions are called braided sets. 1 =ffˆid S,ff 2 =Id Sˆff linearise deform braided sets Examples: ff(x;y)=(x;y); ff(x;y)=(y;x) R-matrices; general solutions
9 2 Braided sets Data: sets, ff:sˆ2 Sˆ2. Set-theoreticYBE(Drinfel 0 d 90) ff 1 ff 2 ff 1 =ff 2 ff 1 ff 2 :Sˆ3 Sˆ3 ff Solutions are called braided sets. braided sets Examples: ff(x;y)=(x;y); ff(x;y)=(y;x) linearise deform R-matrices; Liealgebra (V; []),centralelement12v, ff(x y)=y x+ h1 [x;y]. 1 =ffˆid S,ff 2 =Id Sˆff YBEforff Jacobiidentityfor [] general solutions
10 3 Self-distributivity sets,binaryoperation, ff(x;y)=(y;x y) YBEforff self-distributivityfor Self-distributivity: (x y) z=(x z) (y z)
11 3 Self-distributivity sets,binaryoperation, ff(x;y)=(y;x y) YBEforff self-distributivityfor Self-distributivity: (x y) z=(x z) (y z) Examples: groupswithx y=y 1 xyyieldaquandle: (SD) & 8y;x7 x yisabijection & x x=x; z 1 (y 1 xy)z=(z 1 y 1 z)(z 1 xz)(z 1 yz)
12 3 Self-distributivity sets,binaryoperation, ff(x;y)=(y;x y) YBEforff self-distributivityfor Self-distributivity: (x y) z=(x z) (y z) Examples: groupswithx y=y 1 xyyieldaquandle: (SD) & 8y;x7 x yisabijection & x x=x; z 1 (y 1 xy)z=(z 1 y 1 z)(z 1 xz)(z 1 yz) abeliangroups,t:s S, a b=ta+(1 t)b.
13 3 Self-distributivity sets,binaryoperation, ff(x;y)=(y;x y) YBEforff self-distributivityfor Self-distributivity: (x y) z=(x z) (y z) Examples: groupswithx y=y 1 xyyieldaquandle: (SD) & 8y;x7 x yisabijection & x x=x; z 1 (y 1 xy)z=(z 1 y 1 z)(z 1 xz)(z 1 yz) abeliangroups,t:s S, a b=ta+(1 t)b. Applications: invariants of knots and knotted surfaces (Joyce&Matveev 82);
14 (S; )-colourings c y x y of knot diagrams: b a x y cf. Wirtinger presentation ofı 1 (R 3 \K): p
15 (S; )-colourings c y x y of knot diagrams: b a x y Proposition: (S; )isaquandle = #{(S; )-colouringsofdiagrams } c b c (a b) c isaknotinvariant. c b c (a c) (b c) a b RIII a c a b c a b c
16 (S; )-colourings c y x y of knot diagrams: b a x y Proposition: (S; )isaquandle = #{(S; )-colouringsofdiagrams } Example: (Z 3 ;a b=2b a) isaknotinvariant.
17 (S; )-colourings c y x y of knot diagrams: b a x y Proposition: (S; )isaquandle = #{(S; )-colouringsofdiagrams } Example: (Z 3 ;a b=2b a) isaknotinvariant. 3 colourings 9 colourings
18 3 Self-distributivity sets,binaryoperation, ff(x;y)=(y;x y) YBEforff self-distributivityfor Self-distributivity: (x y) z=(x z) (y z) Applications: invariants of knots and knotted surfaces (Joyce&Matveev 82); atotalorderonbraidgroups(dehornoy 91);
19 3 Self-distributivity sets,binaryoperation, ff(x;y)=(y;x y) YBEforff self-distributivityfor Self-distributivity: (x y) z=(x z) (y z) Applications: invariants of knots and knotted surfaces (Joyce&Matveev 82); atotalorderonbraidgroups(dehornoy 91); Hopf algebra classification(andruskiewitsch Graña 03).
20 4 More examples of braided sets monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y); YBEforff associativityfor
21 4 More examples of braided sets monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y); YBEforff associativityfor monoidfactorizationg=hk, S=H[K, ff(x;y)=(h;k),h2h,k2k,hk=xy;
22 4 More examples of braided sets monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y); YBEforff associativityfor monoidfactorizationg=hk, S=H[K, ff(x;y)=(h;k),h2h,k2k,hk=xy; lattice (S; V ; W ), ff(x;y)=(x V y;x W y).
23 4 More examples of braided sets monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y); YBEforff associativityfor monoidfactorizationg=hk, S=H[K, ff(x;y)=(h;k),h2h,k2k,hk=xy; lattice (S; V ; W ), ff(x;y)=(x V y;x W y). All these braidings are idempotent: ffff = ff.
24 5 Universal enveloping constructions Universal enveloping monoids: Mon(S;ff)=hS xy=y 0 x 0 wheneverff(x;y)=(y 0 ;x 0 )i U. e. (semi)groups and algebras are defined similarly. methods braided sets groups& algebras
25 5 Universal enveloping constructions Universal enveloping monoids: Mon(S;ff)=hS xy=y 0 x 0 wheneverff(x;y)=(y 0 ;x 0 )i U. e. (semi)groups and algebras are defined similarly. braided sets methods examples groups& algebras Theorem: (S;ff)a nice finitebraidedset,ff 2 =Id = Mon(S; ff) is of I-type, cancellative, Ore; Grp(S; ff) is solvable, Garside; k Mon(S; ff) is Koszul, noetherian, Cohen Macaulay, Artin Schelter regular (Manin, Gateva-Ivanova& Van den Bergh, Etingof Schedler Soloviev, Jespers Okniński, Chouraqui ).
26 Example: S={a;b}, aa ff bb; ab ff; ba ff; Grp(S;ff)=ha;b a 2 =b 2 i=:g.
27 Example: S={a;b}, aa ff bb; ab ff; ba ff; Grp(S;ff)=ha;b a 2 =b 2 i=:g. RealisationbyEuclideantransformationsofR 2 : b a 0 b=a 0 ba 0 a=a0 b a 2 =b 2
28 Example: S={a;b}, aa ff bb; ab ff; ba ff; Grp(S;ff)=ha;b a 2 =b 2 i=:g. RealisationbyEuclideantransformationsofR 2 : b a 0 b=a 0 ba 0 a=a0 b a 2 =b 2 R 2 =G =Kleinbottle:
29 5 Universal enveloping constructions Universal enveloping monoids: Mon(S;ff)=hS xy=y 0 x 0 wheneverff(x;y)=(y 0 ;x 0 )i Examples: monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y), S Mon(S;ff) = 1S =1 Mon ;
30 5 Universal enveloping constructions Universal enveloping monoids: Mon(S;ff)=hS xy=y 0 x 0 wheneverff(x;y)=(y 0 ;x 0 )i Examples: monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y), S Mon(S;ff) = 1S =1 Mon ; Liealgebra (V; [];1), ff(x y)=y x+ h1 [x;y], UEA(V; []) kmon(s;ff) = 1=1Mon.
31 6 Representations Mon(S;ff)=hS xy=y 0 x 0 wheneverff(x;y)=(y 0 ;x 0 )i Representations of (S; ff) := representations of k Mon(S; ff), i.e. vectorspacesmwithmˆs M s.t. (m x) y = (m y 0 ) x 0 = ff m x y m x y
32 6 Representations Mon(S;ff)=hS xy=y 0 x 0 wheneverff(x;y)=(y 0 ;x 0 )i Representations of (S; ff) := representations of k Mon(S; ff), i.e. vectorspacesmwithmˆs M s.t. (m x) y = (m y 0 ) x 0 = ff m x y m x y Examples: trivialrep.: M=k;m x=m; M=kMon(S;ff);m x=mx; usual reps for monoids, Lie algebras, self-distributive structures.
33 7 A cohomology theory? A cohomology theory for YBE solutions should: 1)Describedeformations: ff 0 ff 0 + hff 1 + h 2 ff 2 +.
34 7 A cohomology theory? A cohomology theory for YBE solutions should: 1)Describedeformations: ff 0 ff 0 + hff 1 + h 2 ff 2 +. Difficult! Pioneers: Freyd Yetter 89, Eisermann 05.
35 7 A cohomology theory? A cohomology theory for YBE solutions should: 1)Describedeformations: ff 0 ff 0 + hff 1 + h 2 ff 2 +. Difficult! Pioneers: Freyd Yetter 89, Eisermann 05. First approximation: diagonal deformations ff q (x;y)=q!(x;y) ff(x;y);!:sˆs Z:!a2-cocycle = ff q aybesolution.
36 7 A cohomology theory? A cohomology theory for YBE solutions should: 1)Describedeformations: ff 0 ff 0 + hff 1 + h 2 ff 2 +. Difficult! Pioneers: Freyd Yetter 89, Eisermann 05. First approximation: diagonal deformations ff q (x;y)=q!(x;y) ff(x;y);!:sˆs Z:!a2-cocycle = ff q aybesolution. 2) Yield knot and knotted surface invariants: (S;ff)-coloureddiagram (D;C) &!:SˆS Z Boltzmannweight B! (C) =!(x;y)!(x;y): y 0 x x 0 y x y y 0 x 0!a2-cocycle = aknotinvariantgivenby {B! (C) Cisa(S;ff)-colouringofD}:
37 7 A cohomology theory? A cohomology theory for YBE solutions should: 3) Unify cohomology theories for associative structures, Lie algebras, self-distributive structures etc. + explain parallels between them, + suggest theories for new structures.
38 7 A cohomology theory? A cohomology theory for YBE solutions should: 3) Unify cohomology theories for associative structures, Lie algebras, self-distributive structures etc. + explain parallels between them, + suggest theories for new structures. 4)ComputethecohomologyofkMon(S;ff).
39 8 Braided cohomology Data: braidedset (S;ff) & bimodulemoverit.
40 8 Braided cohomology Data: braidedset (S;ff) & bimodulemoverit. Construction: C n (S;ff;M)=Maps(Sˆn ;M), d n = n+1 i=1 ( 1)i 1 (d n;i l d n;i r ):C n C n+1, d n;i l f: x 0 i f(x0 1:::x 0 i 1 x i+1:::x n+1 ) x 0 i x0 1:::x 0 i 1 x i+1:::x n+1 ff 1 ff i 1 x 1 :::x n+1 f ff ff x 1 ::: x i :::x n+1
41 8 Braided cohomology Data: braidedset (S;ff) & bimodulemoverit. Construction: C n (S;ff;M)=Maps(Sˆn ;M), d n = n+1 i=1 ( 1)i 1 (d n;i l d n;i r ):C n C n+1, d n;i l f: x 0 i f(x0 1:::x 0 i 1 x i+1:::x n+1 ) x 0 i x0 1:::x 0 i 1 x i+1:::x n+1 ff 1 ff i 1 x 1 :::x n+1 f ff ff x 1 ::: x i :::x n+1 Theorem: d n+1 d n =0;
42 8 Braided cohomology Data: braidedset (S;ff) & bimodulemoverit. Construction: C n (S;ff;M)=Maps(Sˆn ;M), d n = n+1 i=1 ( 1)i 1 (d n;i l d n;i r ):C n C n+1, d n;i l f: x 0 i f(x0 1:::x 0 i 1 x i+1:::x n+1 ) x 0 i x0 1:::x 0 i 1 x i+1:::x n+1 ff 1 ff i 1 x 1 :::x n+1 f ff ff x 1 ::: x i :::x n+1 Theorem: d n+1 d n =0; H n (S;ff;M)=Kerd n =Imd n 1 isthenthcohomologygroupof (S;ff)withcoefficientsinM;
43 8 Braided cohomology Data: braidedset (S;ff) & bimodulemoverit. Construction: C n (S;ff;M)=Maps(Sˆn ;M), d n = n+1 i=1 ( 1)i 1 (d n;i l d n;i r ):C n C n+1, d n;i l f: x 0 i f(x0 1:::x 0 i 1 x i+1:::x n+1 ) x 0 i x0 1:::x 0 i 1 x i+1:::x n+1 ff 1 ff i 1 x 1 :::x n+1 f ff ff x 1 ::: x i :::x n+1 Theorem: d n+1 d n =0; H n (S;ff;M)=Kerd n =Imd n 1 isthenthcohomologygroupof (S;ff)withcoefficientsinM; for nice M,acupproduct :H n H m H n+m ;
44 8 Braided cohomology Data: braidedset (S;ff) & bimodulemoverit. Construction: C n (S;ff;M)=Maps(Sˆn ;M), d n = n+1 i=1 ( 1)i 1 (d n;i l d n;i r ):C n C n+1, d n;i l f: x 0 i f(x0 1:::x 0 i 1 x i+1:::x n+1 ) x 0 i x0 1:::x 0 i 1 x i+1:::x n+1 ff 1 ff i 1 x 1 :::x n+1 f ff ff x 1 ::: x i :::x n+1 Theorem: d n+1 d n =0; H n (S;ff;M)=Kerd n =Imd n 1 isthenthcohomologygroupof (S;ff)withcoefficientsinM; for nice M,acupproduct :H n H m H n+m ; other good properties.
45 9 Agoodtheory? 1)&2) For!2C 2 (S;ff;Z), d 2!=0 =!yieldsboltzmannweights & diagonal deformations,!=d 1 =!yieldstrivial...
46 9 Agoodtheory? 1)&2) For!2C 2 (S;ff;Z), d 2!=0 =!yieldsboltzmannweights & diagonal deformations,!=d 1 =!yieldstrivial... 3) Unifies classical cohomology theories. Example: monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y), d n;i l f: :::x i 2 x i 1 x i x i+1 ::: ffi 1
47 9 Agoodtheory? 1)&2) For!2C 2 (S;ff;Z), d 2!=0 =!yieldsboltzmannweights & diagonal deformations,!=d 1 =!yieldstrivial... 3) Unifies classical cohomology theories. Example: monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y), d n;i l f: :::x i 2 x i 1 x i x i+1 ::: ffi 1 :::x i 2 1(x i 1 x i )x i+1 ::: ffi 2
48 9 Agoodtheory? 1)&2) For!2C 2 (S;ff;Z), d 2!=0 =!yieldsboltzmannweights & diagonal deformations,!=d 1 =!yieldstrivial... 3) Unifies classical cohomology theories. Example: monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y), d n;i l f: :::x i 2 x i 1 x i x i+1 ::: ffi 1 :::x i 2 1(x i 1 x i )x i+1 ::: ffi 2 :::1x i 2 (x i 1 x i )x i+1 ::: :::
49 9 Agoodtheory? 1)&2) For!2C 2 (S;ff;Z), d 2!=0 =!yieldsboltzmannweights & diagonal deformations,!=d 1 =!yieldstrivial... 3) Unifies classical cohomology theories. Example: monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y), d n;i l f: :::x i 2 x i 1 x i x i+1 ::: ffi 1 :::x i 2 1(x i 1 x i )x i+1 ::: ffi 2 :::1x i 2 (x i 1 x i )x i+1 ::: ::: 1x 1 :::x i 2 (x i 1 x i )x i+1 :::
50 9 Agoodtheory? 1)&2) For!2C 2 (S;ff;Z), d 2!=0 =!yieldsboltzmannweights & diagonal deformations,!=d 1 =!yieldstrivial... 3) Unifies classical cohomology theories. Example: monoid (S; ;1), ff(x;y)=(1;x y), d n;i l f: :::x i 2 x i 1 x i x i+1 ::: ffi 1 :::x i 2 1(x i 1 x i )x i+1 ::: ffi 2 :::1x i 2 (x i 1 x i )x i+1 ::: ::: 1x 1 :::x i 2 (x i 1 x i )x i+1 ::: f(:::x i 2 (x i 1 x i )x i+1 :::).
51 9 Agoodtheory? 4) Quantum symmetriser QS: braided cohomology of (S;ff)withcoefsinM QS Hochschildcohomologyof kmon(s;ff)withcoefsinm
52 9 Agoodtheory? 4) Quantum symmetriser QS: braided cohomology of (S;ff)withcoefsinM cup product QS Hochschildcohomologyof kmon(s;ff)withcoefsinm cup product
53 9 Agoodtheory? 4) Quantum symmetriser QS: braided cohomology of (S;ff)withcoefsinM cup product smaller complexes QS Hochschildcohomologyof kmon(s;ff)withcoefsinm cup product tools
54 9 Agoodtheory? 4) Quantum symmetriser QS: braided cohomology of (S;ff)withcoefsinM cup product smaller complexes QS Hochschildcohomologyof kmon(s;ff)withcoefsinm cup product tools QS is an isomorphism when ffff=idandchark=0(farinati&garcía-galofre 16); ffff=ff(l. 16).
55 9 Agoodtheory? 4) Quantum symmetriser QS: braided cohomology of (S;ff)withcoefsinM cup product smaller complexes QS Hochschildcohomologyof kmon(s;ff)withcoefsinm cup product tools QS is an isomorphism when ffff=idandchark=0(farinati&garcía-galofre 16); ffff=ff(l. 16). Applications: factorizable groups, Young tableaux.
56 9 Agoodtheory? 4) Quantum symmetriser QS: braided cohomology of (S;ff)withcoefsinM cup product smaller complexes QS Hochschildcohomologyof kmon(s;ff)withcoefsinm cup product tools QS is an isomorphism when ffff=idandchark=0(farinati&garcía-galofre 16); ffff=ff(l. 16). Applications: factorizable groups, Young tableaux. Openproblem: HowfarisQSfrombeinganisoingeneral?
On set-theoretic solutions to the Yang-Baxter equation. Victoria LEBED (Nantes) with Leandro VENDRAMIN (Buenos Aires)
 On set-theoretic solutions to the Yang-Baxter equation Victoria LEBED (Nantes) with Leandro VENDRAMIN (Buenos Aires) Turin, January 2016 1 Yang-Baxter equation X: vector space, ff : X 2 X 2. Yang-Baxter
On set-theoretic solutions to the Yang-Baxter equation Victoria LEBED (Nantes) with Leandro VENDRAMIN (Buenos Aires) Turin, January 2016 1 Yang-Baxter equation X: vector space, ff : X 2 X 2. Yang-Baxter
Skew braces. Leandro Vendramin Joint work with Agata Smoktunowicz. Universidad de Buenos Aires
 Skew braces Leandro Vendramin Joint work with Agata Smoktunowicz Universidad de Buenos Aires Groups, rings and the Yang Baxter equation Spa, Belgium June 2017 In 1992 Drinfeld propose to study set-theoretical
Skew braces Leandro Vendramin Joint work with Agata Smoktunowicz Universidad de Buenos Aires Groups, rings and the Yang Baxter equation Spa, Belgium June 2017 In 1992 Drinfeld propose to study set-theoretical
Unexpected facets of the Yang-Baxter equation
 Unexpected facets of the Yang-Baxter equation Victoria LEBED University of Nantes Utrecht, September 29, 2015 1 Yang-Baxter equation Avectorspace V(oranobjectinany monoidal category) σ: V 2 V 2 Yang-Baxter
Unexpected facets of the Yang-Baxter equation Victoria LEBED University of Nantes Utrecht, September 29, 2015 1 Yang-Baxter equation Avectorspace V(oranobjectinany monoidal category) σ: V 2 V 2 Yang-Baxter
Groups, Group rings and the Yang-Baxter equation. International Workshop Groups, Rings, Lie and Hopf Algebras.III
 Groups, Group rings and the Yang-Baxter equation International Workshop Groups, Rings, Lie and Hopf Algebras.III August 12 18, 2012 Bonne Bay Marine Station Memorial University of Newfoundland Eric Jespers
Groups, Group rings and the Yang-Baxter equation International Workshop Groups, Rings, Lie and Hopf Algebras.III August 12 18, 2012 Bonne Bay Marine Station Memorial University of Newfoundland Eric Jespers
I. Braces. On some connections between set-theoretic solutions of the Yang-Baxter equation, matrices and noncommutative rings. Agata Smoktunowicz
 On some connections between set-theoretic solutions of the Yang-Baxter equation, matrices and noncommutative rings I. Braces Agata Smoktunowicz 18-24 June 2017, Spa, Belgium. Groups, Rings, and the Yang-Baxter
On some connections between set-theoretic solutions of the Yang-Baxter equation, matrices and noncommutative rings I. Braces Agata Smoktunowicz 18-24 June 2017, Spa, Belgium. Groups, Rings, and the Yang-Baxter
Finitely presented algebras defined by homogeneous semigroup relations
 Finitely presented algebras defined by homogeneous semigroup relations Aachen, March 2010 Plan of the talk 1. motivating problems 2. algebras defined by homogeneous semigroup presentations 3. special classes
Finitely presented algebras defined by homogeneous semigroup relations Aachen, March 2010 Plan of the talk 1. motivating problems 2. algebras defined by homogeneous semigroup presentations 3. special classes
Grade 8 Factorisation
 ID : ae-8-factorisation [1] Grade 8 Factorisation For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Find factors of following polynomial A) y 2-2xy + 3y - 6x B) 3y 2-12xy - 2y + 8x
ID : ae-8-factorisation [1] Grade 8 Factorisation For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Find factors of following polynomial A) y 2-2xy + 3y - 6x B) 3y 2-12xy - 2y + 8x
Homework 1/Solutions. Graded Exercises
 MTH 310-3 Abstract Algebra I and Number Theory S18 Homework 1/Solutions Graded Exercises Exercise 1. Below are parts of the addition table and parts of the multiplication table of a ring. Complete both
MTH 310-3 Abstract Algebra I and Number Theory S18 Homework 1/Solutions Graded Exercises Exercise 1. Below are parts of the addition table and parts of the multiplication table of a ring. Complete both
Radical Rings, Quantum Groups, and Theory of the Unknot
 Radical Rings, Quantum Groups, and Theory of the Unknot Wolfgang Rump In this talk, I will throw a bridge from radical rings to a variety of quantum-like mathematical structures related to Sklyanin algebras,
Radical Rings, Quantum Groups, and Theory of the Unknot Wolfgang Rump In this talk, I will throw a bridge from radical rings to a variety of quantum-like mathematical structures related to Sklyanin algebras,
arxiv: v1 [math.ra] 18 Dec 2013
![arxiv: v1 [math.ra] 18 Dec 2013 arxiv: v1 [math.ra] 18 Dec 2013](/thumbs/88/116250167.jpg) arxiv:1312.5142v1 [math.ra] 18 Dec 2013 A family of solutions of the Yang-Baxter equation David Bachiller Abstract Ferran Cedó A new method to construct involutive non-degenerate set-theoretic solutions
arxiv:1312.5142v1 [math.ra] 18 Dec 2013 A family of solutions of the Yang-Baxter equation David Bachiller Abstract Ferran Cedó A new method to construct involutive non-degenerate set-theoretic solutions
BINOMIAL SKEW POLYNOMIAL RINGS, ARTIN-SCHELTER REGULARITY, AND BINOMIAL SOLUTIONS OF THE YANG-BAXTER EQUATION. Tatiana Gateva-Ivanova
 Serdica Math. J. 30 (2004), 431 470 BINOMIAL SKEW POLYNOMIAL RINGS, ARTIN-SCHELTER REGULARITY, AND BINOMIAL SOLUTIONS OF THE YANG-BAXTER EQUATION Tatiana Gateva-Ivanova Communicated by V. Drensky Abstract.
Serdica Math. J. 30 (2004), 431 470 BINOMIAL SKEW POLYNOMIAL RINGS, ARTIN-SCHELTER REGULARITY, AND BINOMIAL SOLUTIONS OF THE YANG-BAXTER EQUATION Tatiana Gateva-Ivanova Communicated by V. Drensky Abstract.
Matched pairs approach to set theoretic solutions of the Yang Baxter equation
 Journal of Algebra 319 (2008) 1462 1529 www.elsevier.com/locate/jalgebra Matched pairs approach to set theoretic solutions of the Yang Baxter equation Tatiana Gateva-Ivanova a,b, Shahn Majid c, a Institute
Journal of Algebra 319 (2008) 1462 1529 www.elsevier.com/locate/jalgebra Matched pairs approach to set theoretic solutions of the Yang Baxter equation Tatiana Gateva-Ivanova a,b, Shahn Majid c, a Institute
arxiv: v1 [math.qa] 26 Mar 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.qa] 26 Mar 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.qa] 26 Mar 2017](/thumbs/76/73289840.jpg) BRACES AND SYMMETRIC GROUPS WITH SPECIAL CONDITIONS arxiv:1703.08766v1 [math.qa] 26 Mar 2017 FERRAN CEDÓ, TATIANA GATEVA-IVANOVA, AGATA SMOKTUNOWICZ Abstract. We study symmetric groups and left braces
BRACES AND SYMMETRIC GROUPS WITH SPECIAL CONDITIONS arxiv:1703.08766v1 [math.qa] 26 Mar 2017 FERRAN CEDÓ, TATIANA GATEVA-IVANOVA, AGATA SMOKTUNOWICZ Abstract. We study symmetric groups and left braces
Deformations of a noncommutative surface of dimension 4
 Deformations of a noncommutative surface of dimension 4 Sue Sierra University of Edinburgh Homological Methods in Algebra and Geometry, AIMS Ghana 2016 In this talk, I will describe the work of my student
Deformations of a noncommutative surface of dimension 4 Sue Sierra University of Edinburgh Homological Methods in Algebra and Geometry, AIMS Ghana 2016 In this talk, I will describe the work of my student
QUADRATIC PBW-ALGEBRAS, YANG-BAXTER EQUATION AND ARTIN-SCHELTER REGULARITY
 Available at: http://publications.ictp.it IC/2010/07 United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization and International Atomic Energy Agency THE ABDUS SALAM INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL
Available at: http://publications.ictp.it IC/2010/07 United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization and International Atomic Energy Agency THE ABDUS SALAM INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR THEORETICAL
A Survey of Quandles with some recent developments
 A Survey of Quandles with some recent developments University of South Florida QQQ 2016 Knots and their diagrams Overview of knot diagrams and Quandles A knot is the image of a smooth embeding S 1 R 3
A Survey of Quandles with some recent developments University of South Florida QQQ 2016 Knots and their diagrams Overview of knot diagrams and Quandles A knot is the image of a smooth embeding S 1 R 3
Loop Groups and Lie 2-Algebras
 Loop Groups and Lie 2-Algebras Alissa S. Crans Joint work with: John Baez Urs Schreiber & Danny Stevenson in honor of Ross Street s 60th birthday July 15, 2005 Lie 2-Algebras A 2-vector space L is a category
Loop Groups and Lie 2-Algebras Alissa S. Crans Joint work with: John Baez Urs Schreiber & Danny Stevenson in honor of Ross Street s 60th birthday July 15, 2005 Lie 2-Algebras A 2-vector space L is a category
On finite simple braces
 Jan Okniński University of Warsaw Lecce, September 2017 Plan of the talk 1. set theoretic solutions and braces 2. three important results 3. matched products and simple braces 4. asymmetric products and
Jan Okniński University of Warsaw Lecce, September 2017 Plan of the talk 1. set theoretic solutions and braces 2. three important results 3. matched products and simple braces 4. asymmetric products and
Lectures on Quantum Groups
 Lectures in Mathematical Physics Lectures on Quantum Groups Pavel Etingof and Olivier Schiffinann Second Edition International Press * s. c *''.. \ir.ik,!.'..... Contents Introduction ix 1 Poisson algebras
Lectures in Mathematical Physics Lectures on Quantum Groups Pavel Etingof and Olivier Schiffinann Second Edition International Press * s. c *''.. \ir.ik,!.'..... Contents Introduction ix 1 Poisson algebras
The Knot Quandle. Steven Read
 The Knot Quandle Steven Read Abstract A quandle is a set with two operations that satisfy three conditions. For example, there is a quandle naturally associated to any group. It turns out that one can
The Knot Quandle Steven Read Abstract A quandle is a set with two operations that satisfy three conditions. For example, there is a quandle naturally associated to any group. It turns out that one can
arxiv: v2 [math.gr] 5 Apr 2016
![arxiv: v2 [math.gr] 5 Apr 2016 arxiv: v2 [math.gr] 5 Apr 2016](/thumbs/81/84412086.jpg) COHOMOLOGY AND EXTENSIONS OF BRACES arxiv:1601.01633v2 [math.gr] 5 Apr 2016 VICTORIA LEBED AND LEANDRO VENDRAMIN Abstract. Braces and linear cycle sets are algebraic structures playing a major role in
COHOMOLOGY AND EXTENSIONS OF BRACES arxiv:1601.01633v2 [math.gr] 5 Apr 2016 VICTORIA LEBED AND LEANDRO VENDRAMIN Abstract. Braces and linear cycle sets are algebraic structures playing a major role in
REVIEW. Evaluation of the Applicants
 REVIEW By: Regarding: Vesselin Drensky, D.Sc. Full Member of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Full Professor at the Institute of Mathematics and Informatics of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences The application
REVIEW By: Regarding: Vesselin Drensky, D.Sc. Full Member of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Full Professor at the Institute of Mathematics and Informatics of the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences The application
DISTRIBUTIVE PRODUCTS AND THEIR HOMOLOGY
 DISTRIBUTIVE PRODUCTS AND THEIR HOMOLOGY Abstract. We develop a theory of sets with distributive products (called shelves and multi-shelves) and of their homology. We relate the shelf homology to the rack
DISTRIBUTIVE PRODUCTS AND THEIR HOMOLOGY Abstract. We develop a theory of sets with distributive products (called shelves and multi-shelves) and of their homology. We relate the shelf homology to the rack
Skew Calabi-Yau algebras and homological identities
 Skew Calabi-Yau algebras and homological identities Manuel L. Reyes Bowdoin College Joint international AMS-RMS meeting Alba Iulia, Romania June 30, 2013 (joint work with Daniel Rogalski and James J. Zhang)
Skew Calabi-Yau algebras and homological identities Manuel L. Reyes Bowdoin College Joint international AMS-RMS meeting Alba Iulia, Romania June 30, 2013 (joint work with Daniel Rogalski and James J. Zhang)
CHAPTER 2 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA
 CHAPTER 2 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Basic Operations 2.3 Boolean Expressions and Truth Tables 2.4 Basic Theorems 2.5 Commutative, Associative,
CHAPTER 2 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA This chapter in the book includes: Objectives Study Guide 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Basic Operations 2.3 Boolean Expressions and Truth Tables 2.4 Basic Theorems 2.5 Commutative, Associative,
Knot semigroups: a new algebraic approach to knots and braids
 Knot semigroups: a new algebraic approach to knots and braids Alexei Vernitski University of Essex On the picture: the logo of a shopping centre in Colchester presents what in this talk we shall treat
Knot semigroups: a new algebraic approach to knots and braids Alexei Vernitski University of Essex On the picture: the logo of a shopping centre in Colchester presents what in this talk we shall treat
Class 8 Factorisation
 ID : in-8-factorisation [1] Class 8 Factorisation For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Find factors of following polynomial A) xy - 7y + 9x - 63 B) xy - 5y + 6x - 30
ID : in-8-factorisation [1] Class 8 Factorisation For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer the questions (1) Find factors of following polynomial A) xy - 7y + 9x - 63 B) xy - 5y + 6x - 30
Two Posts to Fill On School Board
 Y Y 9 86 4 4 qz 86 x : ( ) z 7 854 Y x 4 z z x x 4 87 88 Y 5 x q x 8 Y 8 x x : 6 ; : 5 x ; 4 ( z ; ( ) ) x ; z 94 ; x 3 3 3 5 94 ; ; ; ; 3 x : 5 89 q ; ; x ; x ; ; x : ; ; ; ; ; ; 87 47% : () : / : 83
Y Y 9 86 4 4 qz 86 x : ( ) z 7 854 Y x 4 z z x x 4 87 88 Y 5 x q x 8 Y 8 x x : 6 ; : 5 x ; 4 ( z ; ( ) ) x ; z 94 ; x 3 3 3 5 94 ; ; ; ; 3 x : 5 89 q ; ; x ; x ; ; x : ; ; ; ; ; ; 87 47% : () : / : 83
Artin-Schelter regular algebras and the Steenrod algebra
 Artin-Schelter regular algebras and the Steenrod algebra J. H. Palmieri and J. J. Zhang University of Washington Los Angeles, 10 October 2010 Exercise Let A(1) be the sub-hopf algebra of the mod 2 Steenrod
Artin-Schelter regular algebras and the Steenrod algebra J. H. Palmieri and J. J. Zhang University of Washington Los Angeles, 10 October 2010 Exercise Let A(1) be the sub-hopf algebra of the mod 2 Steenrod
Quandles and universal algebra
 Quandles and universal algebra Quandles and knots, and groups, and universal algebra David Stanovský Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic Novi Sad, June 2017 David Stanovský (Prague) Quandles, knots,
Quandles and universal algebra Quandles and knots, and groups, and universal algebra David Stanovský Charles University, Prague, Czech Republic Novi Sad, June 2017 David Stanovský (Prague) Quandles, knots,
Prove proposition 68. It states: Let R be a ring. We have the following
 Theorem HW7.1. properties: Prove proposition 68. It states: Let R be a ring. We have the following 1. The ring R only has one additive identity. That is, if 0 R with 0 +b = b+0 = b for every b R, then
Theorem HW7.1. properties: Prove proposition 68. It states: Let R be a ring. We have the following 1. The ring R only has one additive identity. That is, if 0 R with 0 +b = b+0 = b for every b R, then
Ajourney intothegreenbook
 Ajourney intothegreenook Victori LEBED, Trinity College Dulin Alger dys 2017, Cen 1 An exotic xiom for clssicl structures Self-distriutivity: ( ) c = ( c) ( c) 1 Mituhis Tkski, fresh Jpnese mths PhD in
Ajourney intothegreenook Victori LEBED, Trinity College Dulin Alger dys 2017, Cen 1 An exotic xiom for clssicl structures Self-distriutivity: ( ) c = ( c) ( c) 1 Mituhis Tkski, fresh Jpnese mths PhD in
A Note on UNAR LA-Semigroup
 Punjab University Journal of Mathematics (ISSN 1016-2526) Vol. 50(3)(2018) pp. 113-121 A Note on UNAR LA-Semigroup Muhammad Rashad Department of Mathematics, University of Malakand, Pakistan, Email: rashad@uom.edu.pk
Punjab University Journal of Mathematics (ISSN 1016-2526) Vol. 50(3)(2018) pp. 113-121 A Note on UNAR LA-Semigroup Muhammad Rashad Department of Mathematics, University of Malakand, Pakistan, Email: rashad@uom.edu.pk
' Liberty and Umou Ono and Inseparablo "
 3 5? #< q 8 2 / / ) 9 ) 2 ) > < _ / ] > ) 2 ) ) 5 > x > [ < > < ) > _ ] ]? <
3 5? #< q 8 2 / / ) 9 ) 2 ) > < _ / ] > ) 2 ) ) 5 > x > [ < > < ) > _ ] ]? <
ON GRADED MORITA EQUIVALENCES FOR AS-REGULAR ALGEBRAS KENTA UEYAMA
 ON GRADED MORITA EQUIVALENCES FOR AS-REGULAR ALGEBRAS KENTA UEYAMA Abstract. One of the most active projects in noncommutative algebraic geometry is to classify AS-regular algebras. The motivation of this
ON GRADED MORITA EQUIVALENCES FOR AS-REGULAR ALGEBRAS KENTA UEYAMA Abstract. One of the most active projects in noncommutative algebraic geometry is to classify AS-regular algebras. The motivation of this
Opinion Template. Recommended length: two to three pages OPINION
 Opinion Template Recommended length: two to three pages OPINION By: Regarding: Candidate 1: Professor Azniv Kirkor Kasparian, PhD, Section of Algebra, Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Kliment
Opinion Template Recommended length: two to three pages OPINION By: Regarding: Candidate 1: Professor Azniv Kirkor Kasparian, PhD, Section of Algebra, Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Kliment
1. A polynomial p(x) in one variable x is an algebraic expression in x of the form
 POLYNOMIALS Important Points 1. A polynomial p(x) in one variable x is an algebraic expression in x of the form p(x) = a nx n +a n-1x n-1 + a 2x 2 +a 1x 1 +a 0x 0 where a 0, a 1, a 2 a n are constants
POLYNOMIALS Important Points 1. A polynomial p(x) in one variable x is an algebraic expression in x of the form p(x) = a nx n +a n-1x n-1 + a 2x 2 +a 1x 1 +a 0x 0 where a 0, a 1, a 2 a n are constants
arxiv: v1 [math.ra] 5 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.ra] 5 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.ra] 5 Dec 2018](/thumbs/91/106736876.jpg) THE STRUCTURE MONOID AND ALGEBRA OF A NON-DEGENERATE SET-THEORETIC SOLUTION OF THE YANG BAXTER EQUATION ERIC JESPERS, LUKASZ KUBAT, AND ARNE VAN ANTWERPEN arxiv:1812.02026v1 [math.ra] 5 Dec 2018 Abstract.
THE STRUCTURE MONOID AND ALGEBRA OF A NON-DEGENERATE SET-THEORETIC SOLUTION OF THE YANG BAXTER EQUATION ERIC JESPERS, LUKASZ KUBAT, AND ARNE VAN ANTWERPEN arxiv:1812.02026v1 [math.ra] 5 Dec 2018 Abstract.
Non-equilibrium statistical mechanics Stochastic dynamics, Markov process, Integrable systems Quantum groups, Yang-Baxter equation,
 (Mon) Non-equilibrium statistical mechanics Stochastic dynamics, Markov process, Integrable systems Quantum groups, Yang-Baxter equation, Integrable Markov process Spectral problem of the Markov matrix:
(Mon) Non-equilibrium statistical mechanics Stochastic dynamics, Markov process, Integrable systems Quantum groups, Yang-Baxter equation, Integrable Markov process Spectral problem of the Markov matrix:
LOWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL. ^Jberxy and (Jmott Oao M d Ccmsparftble. %m >ai ruv GEEAT INDUSTRIES
 ? (») /»» 9 F ( ) / ) /»F»»»»»# F??»»» Q ( ( »»» < 3»» /» > > } > Q ( Q > Z F 5
? (») /»» 9 F ( ) / ) /»F»»»»»# F??»»» Q ( ( »»» < 3»» /» > > } > Q ( Q > Z F 5
Question: 1. Use suitable identities to find the following products:
 CH-2 Polynomial Question: 1. Use suitable identities to find the following products: (i) (x + 4) (x + 10) Solution:- (x+4)(x+10) = x 2 +10x+4x+4 x 10 = x 2 +14x+40 (ii) (x + 8) (x 10) Solution: x 2-10x+8x-80
CH-2 Polynomial Question: 1. Use suitable identities to find the following products: (i) (x + 4) (x + 10) Solution:- (x+4)(x+10) = x 2 +10x+4x+4 x 10 = x 2 +14x+40 (ii) (x + 8) (x 10) Solution: x 2-10x+8x-80
A brief introduction to pre-lie algebras
 Chern Institute of Mathematics, Nankai University Vasteras, November 16, 2016 Outline What is a pre-lie algebra? Examples of pre-lie algebras Pre-Lie algebras and classical Yang-Baxter equation Pre-Lie
Chern Institute of Mathematics, Nankai University Vasteras, November 16, 2016 Outline What is a pre-lie algebra? Examples of pre-lie algebras Pre-Lie algebras and classical Yang-Baxter equation Pre-Lie
Axioms of Kleene Algebra
 Introduction to Kleene Algebra Lecture 2 CS786 Spring 2004 January 28, 2004 Axioms of Kleene Algebra In this lecture we give the formal definition of a Kleene algebra and derive some basic consequences.
Introduction to Kleene Algebra Lecture 2 CS786 Spring 2004 January 28, 2004 Axioms of Kleene Algebra In this lecture we give the formal definition of a Kleene algebra and derive some basic consequences.
Modular Categories and Applications I
 I Modular Categories and Applications I Texas A&M University U. South Alabama, November 2009 Outline I 1 Topological Quantum Computation 2 Fusion Categories Ribbon and Modular Categories Fusion Rules and
I Modular Categories and Applications I Texas A&M University U. South Alabama, November 2009 Outline I 1 Topological Quantum Computation 2 Fusion Categories Ribbon and Modular Categories Fusion Rules and
A DARK GREY P O N T, with a Switch Tail, and a small Star on the Forehead. Any
 Y Y Y X X «/ YY Y Y ««Y x ) & \ & & } # Y \#$& / Y Y X» \\ / X X X x & Y Y X «q «z \x» = q Y # % \ & [ & Z \ & { + % ) / / «q zy» / & / / / & x x X / % % ) Y x X Y $ Z % Y Y x x } / % «] «] # z» & Y X»
Y Y Y X X «/ YY Y Y ««Y x ) & \ & & } # Y \#$& / Y Y X» \\ / X X X x & Y Y X «q «z \x» = q Y # % \ & [ & Z \ & { + % ) / / «q zy» / & / / / & x x X / % % ) Y x X Y $ Z % Y Y x x } / % «] «] # z» & Y X»
Introduction to the Yang-Baxter Equation with Open Problems
 Axioms 2012, 1, 33-37; doi:10.3390/axioms1010033 Communication OPEN ACCESS axioms ISSN 2075-1680 www.mdpi.com/journal/axioms/ Introduction to the Yang-Baxter Equation with Open Problems Florin Nichita
Axioms 2012, 1, 33-37; doi:10.3390/axioms1010033 Communication OPEN ACCESS axioms ISSN 2075-1680 www.mdpi.com/journal/axioms/ Introduction to the Yang-Baxter Equation with Open Problems Florin Nichita
OWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 Y \»< - } Y Y Y & #»»» q ] q»»»>) & - - - } ) x ( - { Y» & ( x - (» & )< - Y X - & Q Q» 3 - x Q Y 6 \Y > Y Y X 3 3-9 33 x - - / - -»- --
Y \»< - } Y Y Y & #»»» q ] q»»»>) & - - - } ) x ( - { Y» & ( x - (» & )< - Y X - & Q Q» 3 - x Q Y 6 \Y > Y Y X 3 3-9 33 x - - / - -»- --
Yang-Baxterization of the BH algebra.
 DIAS STP 94 18 Revised version Yang-Baxterization of the BH algebra. arxiv:hep-th/9405098v1 16 May 1994 G.A.T.F.da Costa Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies 10 Burlington Road,Dublin 4,Ireland. May 14,1994
DIAS STP 94 18 Revised version Yang-Baxterization of the BH algebra. arxiv:hep-th/9405098v1 16 May 1994 G.A.T.F.da Costa Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies 10 Burlington Road,Dublin 4,Ireland. May 14,1994
The Maschke Theorem for L-R-smash Products
 139ò16Ï ê Æ? Ð Vol.39, No.6 2010c12 ADVANCES IN MATHEMATICS Dec., 2010 The Maschke Theorem for L-R-smash Products NIU Ruifang, ZHOU Xiaoyan, WANG Yong, ZHANG Liangyun (Dept. of Math., Nanjing Agricultural
139ò16Ï ê Æ? Ð Vol.39, No.6 2010c12 ADVANCES IN MATHEMATICS Dec., 2010 The Maschke Theorem for L-R-smash Products NIU Ruifang, ZHOU Xiaoyan, WANG Yong, ZHANG Liangyun (Dept. of Math., Nanjing Agricultural
Connected Sums of Simplicial Complexes
 Connected Sums of Simplicial Complexes Tomoo Matsumura 1 W. Frank Moore 2 1 KAIST 2 Department of Mathematics Wake Forest University October 15, 2011 Let R,S,T be commutative rings, and let V be a T -module.
Connected Sums of Simplicial Complexes Tomoo Matsumura 1 W. Frank Moore 2 1 KAIST 2 Department of Mathematics Wake Forest University October 15, 2011 Let R,S,T be commutative rings, and let V be a T -module.
Algebraic Expressions
 Algebraic Expressions 1. Expressions are formed from variables and constants. 2. Terms are added to form expressions. Terms themselves are formed as product of factors. 3. Expressions that contain exactly
Algebraic Expressions 1. Expressions are formed from variables and constants. 2. Terms are added to form expressions. Terms themselves are formed as product of factors. 3. Expressions that contain exactly
FOURIER - SATO TRANSFORM BRAID GROUP ACTIONS, AND FACTORIZABLE SHEAVES. Vadim Schechtman. Talk at
 , BRAID GROUP ACTIONS, AND FACTORIZABLE SHEAVES Vadim Schechtman Talk at Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe, Kashiwa-no-ha, October 2014 This is a report on a joint work with
, BRAID GROUP ACTIONS, AND FACTORIZABLE SHEAVES Vadim Schechtman Talk at Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe, Kashiwa-no-ha, October 2014 This is a report on a joint work with
Boolean Algebra. Sungho Kang. Yonsei University
 Boolean Algebra Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outline Set, Relations, and Functions Partial Orders Boolean Functions Don t Care Conditions Incomplete Specifications 2 Set Notation $09,3/#0,9 438 v V Element
Boolean Algebra Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outline Set, Relations, and Functions Partial Orders Boolean Functions Don t Care Conditions Incomplete Specifications 2 Set Notation $09,3/#0,9 438 v V Element
DEFORMATIONS OF (BI)TENSOR CATEGORIES
 DEFORMATIONS OF (BI)TENSOR CATEGORIES Louis Crane and David N. Yetter Department of Mathematics Kansas State University Manhattan, KS 66506 arxiv:q-alg/9612011v1 5 Dec 1996 1 Introduction In [1], a new
DEFORMATIONS OF (BI)TENSOR CATEGORIES Louis Crane and David N. Yetter Department of Mathematics Kansas State University Manhattan, KS 66506 arxiv:q-alg/9612011v1 5 Dec 1996 1 Introduction In [1], a new
Unitary Solutions to the Yang-Baxter. Equation in Dimension Four
 arxiv:quant-ph/02050 v3 Aug 2003 Unitary Solutions to the Yang-Baxter Equation in Dimension Four H. A. Dye Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Computer Science University of Illinois at Chicago
arxiv:quant-ph/02050 v3 Aug 2003 Unitary Solutions to the Yang-Baxter Equation in Dimension Four H. A. Dye Department of Mathematics, Statistics, and Computer Science University of Illinois at Chicago
1 Hilbert function. 1.1 Graded rings. 1.2 Graded modules. 1.3 Hilbert function
 1 Hilbert function 1.1 Graded rings Let G be a commutative semigroup. A commutative ring R is called G-graded when it has a (weak direct sum decomposition R = i G R i (that is, the R i are additive subgroups,
1 Hilbert function 1.1 Graded rings Let G be a commutative semigroup. A commutative ring R is called G-graded when it has a (weak direct sum decomposition R = i G R i (that is, the R i are additive subgroups,
The quandle map E passes to a bijection form (Aut(X),H, z) to X. This completes the proof.
 Quandles and Groups This example is due to Joyce [?] and Matveev[?]. Let G be a group, H a subgroup, s : G G an automorphism such that for each h H s(h) =h. Define a binary operation s = on G by, a b =
Quandles and Groups This example is due to Joyce [?] and Matveev[?]. Let G be a group, H a subgroup, s : G G an automorphism such that for each h H s(h) =h. Define a binary operation s = on G by, a b =
Math 203A - Solution Set 1
 Math 203A - Solution Set 1 Problem 1. Show that the Zariski topology on A 2 is not the product of the Zariski topologies on A 1 A 1. Answer: Clearly, the diagonal Z = {(x, y) : x y = 0} A 2 is closed in
Math 203A - Solution Set 1 Problem 1. Show that the Zariski topology on A 2 is not the product of the Zariski topologies on A 1 A 1. Answer: Clearly, the diagonal Z = {(x, y) : x y = 0} A 2 is closed in
THE CLASSICAL HOM-YANG-BAXTER EQUATION AND HOM-LIE BIALGEBRAS. Donald Yau
 International Electronic Journal of Algebra Volume 17 (2015) 11-45 THE CLASSICAL HOM-YANG-BAXTER EQUATION AND HOM-LIE BIALGEBRAS Donald Yau Received: 25 January 2014 Communicated by A. Çiğdem Özcan Abstract.
International Electronic Journal of Algebra Volume 17 (2015) 11-45 THE CLASSICAL HOM-YANG-BAXTER EQUATION AND HOM-LIE BIALGEBRAS Donald Yau Received: 25 January 2014 Communicated by A. Çiğdem Özcan Abstract.
Lecture 4: Least Squares (LS) Estimation
 ME 233, UC Berkeley, Spring 2014 Xu Chen Lecture 4: Least Squares (LS) Estimation Background and general solution Solution in the Gaussian case Properties Example Big picture general least squares estimation:
ME 233, UC Berkeley, Spring 2014 Xu Chen Lecture 4: Least Squares (LS) Estimation Background and general solution Solution in the Gaussian case Properties Example Big picture general least squares estimation:
The graded module category of a generalized Weyl algebra
 The graded module category of a generalized Weyl algebra Final Defense Robert Won Advised by: Daniel Rogalski May 2, 2016 1 / 39 Overview 1 Graded rings and things 2 Noncommutative is not commutative 3
The graded module category of a generalized Weyl algebra Final Defense Robert Won Advised by: Daniel Rogalski May 2, 2016 1 / 39 Overview 1 Graded rings and things 2 Noncommutative is not commutative 3
Categorifying quantum knot invariants
 Categorifying quantum knot invariants Ben Webster U. of Oregon November 26, 2010 Ben Webster (U. of Oregon) Categorifying quantum knot invariants November 26, 2010 1 / 26 This talk is online at http://pages.uoregon.edu/bwebster/rims-iii.pdf.
Categorifying quantum knot invariants Ben Webster U. of Oregon November 26, 2010 Ben Webster (U. of Oregon) Categorifying quantum knot invariants November 26, 2010 1 / 26 This talk is online at http://pages.uoregon.edu/bwebster/rims-iii.pdf.
Quantizations and classical non-commutative non-associative algebras
 Journal of Generalized Lie Theory and Applications Vol. (008), No., 35 44 Quantizations and classical non-commutative non-associative algebras Hilja Lisa HURU and Valentin LYCHAGIN Department of Mathematics,
Journal of Generalized Lie Theory and Applications Vol. (008), No., 35 44 Quantizations and classical non-commutative non-associative algebras Hilja Lisa HURU and Valentin LYCHAGIN Department of Mathematics,
ROUQUIER COMPLEXES DONGKWAN KIM
 ROUQUIER COMPLEXES DONGKWAN KIM 1. Rouquier complexes 1.1. Setup. In this talk k is a field of characteristic 0. Let (W, S) be a Coxeter group with S = n
ROUQUIER COMPLEXES DONGKWAN KIM 1. Rouquier complexes 1.1. Setup. In this talk k is a field of characteristic 0. Let (W, S) be a Coxeter group with S = n
12. Stresses and Strains
 12. Stresses and Strains Finite Element Method Differential Equation Weak Formulation Approximating Functions Weighted Residuals FEM - Formulation Classification of Problems Scalar Vector 1-D T(x) u(x)
12. Stresses and Strains Finite Element Method Differential Equation Weak Formulation Approximating Functions Weighted Residuals FEM - Formulation Classification of Problems Scalar Vector 1-D T(x) u(x)
Evaluation of sl N -foams. Workshop on Quantum Topology Lille
 Evaluation of sl N -foams Louis-Hadrien Robert Emmanuel Wagner Workshop on Quantum Topology Lille a b a a + b b a + b b + c c a a + b + c a b a a + b b a + b b + c c a a + b + c Definition (R. Wagner,
Evaluation of sl N -foams Louis-Hadrien Robert Emmanuel Wagner Workshop on Quantum Topology Lille a b a a + b b a + b b + c c a a + b + c a b a a + b b a + b b + c c a a + b + c Definition (R. Wagner,
A = A(f) = k x 1,...,x n /(f = f ij x i x j )
 Noncommutative Algebraic Geometry Shanghai September 12-16, 211 Calabi-Yau algebras linked to Poisson algebras Roland Berger (Saint-Étienne, France (jointly Anne Pichereau Calabi-Yau algebras viewed as
Noncommutative Algebraic Geometry Shanghai September 12-16, 211 Calabi-Yau algebras linked to Poisson algebras Roland Berger (Saint-Étienne, France (jointly Anne Pichereau Calabi-Yau algebras viewed as
LOWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 Y -» $ 5 Y 7 Y Y -Y- Q x Q» 75»»/ q } # ]»\ - - $ { Q» / X x»»- 3 q $ 9 ) Y q - 5 5 3 3 3 7 Q q - - Q _»»/Q Y - 9 - - - )- [ X 7» -» - )»? / /? Q Y»» # X Q» - -?» Q ) Q \ Q - - - 3? 7» -? #»»» 7 - / Q
Y -» $ 5 Y 7 Y Y -Y- Q x Q» 75»»/ q } # ]»\ - - $ { Q» / X x»»- 3 q $ 9 ) Y q - 5 5 3 3 3 7 Q q - - Q _»»/Q Y - 9 - - - )- [ X 7» -» - )»? / /? Q Y»» # X Q» - -?» Q ) Q \ Q - - - 3? 7» -? #»»» 7 - / Q
Atiyah classes and homotopy algebras
 Atiyah classes and homotopy algebras Mathieu Stiénon Workshop on Lie groupoids and Lie algebroids Kolkata, December 2012 Atiyah (1957): obstruction to existence of holomorphic connections Rozansky-Witten
Atiyah classes and homotopy algebras Mathieu Stiénon Workshop on Lie groupoids and Lie algebroids Kolkata, December 2012 Atiyah (1957): obstruction to existence of holomorphic connections Rozansky-Witten
Graded Calabi-Yau Algebras actions and PBW deformations
 Actions on Graded Calabi-Yau Algebras actions and PBW deformations Q. -S. Wu Joint with L. -Y. Liu and C. Zhu School of Mathematical Sciences, Fudan University International Conference at SJTU, Shanghai
Actions on Graded Calabi-Yau Algebras actions and PBW deformations Q. -S. Wu Joint with L. -Y. Liu and C. Zhu School of Mathematical Sciences, Fudan University International Conference at SJTU, Shanghai
Conjugacy in epigroups
 October 2018 Conjugacy in epigroups António Malheiro (CMA/FCT/NOVA University of Lisbon) @ the York semigroup (joint work with João Araújo, Michael Kinyon, Janusz Konieczny) Acknowledgement: This work
October 2018 Conjugacy in epigroups António Malheiro (CMA/FCT/NOVA University of Lisbon) @ the York semigroup (joint work with João Araújo, Michael Kinyon, Janusz Konieczny) Acknowledgement: This work
L bor y nnd Union One nnd Inseparable. LOW I'LL, MICHIGAN. WLDNHSDA Y. JULY ), I8T. liuwkll NATIdiNAI, liank
 G k y $5 y / >/ k «««# ) /% < # «/» Y»««««?# «< >«>» y k»» «k F 5 8 Y Y F G k F >«y y
G k y $5 y / >/ k «««# ) /% < # «/» Y»««««?# «< >«>» y k»» «k F 5 8 Y Y F G k F >«y y
Factorisations of the Garside element in the dual braid monoids
 Factorisations of the Garside element in the dual braid monoids Vivien Ripoll École Normale Supérieure Département de Mathématiques et Applications 30 June 2010 Journées Garside Caen 1 Dual braid monoids
Factorisations of the Garside element in the dual braid monoids Vivien Ripoll École Normale Supérieure Département de Mathématiques et Applications 30 June 2010 Journées Garside Caen 1 Dual braid monoids
MATH 433 Applied Algebra Lecture 22: Semigroups. Rings.
 MATH 433 Applied Algebra Lecture 22: Semigroups. Rings. Groups Definition. A group is a set G, together with a binary operation, that satisfies the following axioms: (G1: closure) for all elements g and
MATH 433 Applied Algebra Lecture 22: Semigroups. Rings. Groups Definition. A group is a set G, together with a binary operation, that satisfies the following axioms: (G1: closure) for all elements g and
Quantum Groups and Link Invariants
 Quantum Groups and Link Invariants Jenny August April 22, 2016 1 Introduction These notes are part of a seminar on topological field theories at the University of Edinburgh. In particular, this lecture
Quantum Groups and Link Invariants Jenny August April 22, 2016 1 Introduction These notes are part of a seminar on topological field theories at the University of Edinburgh. In particular, this lecture
LEFT SEMI-BRACES AND SOLUTIONS OF THE YANG-BAXTER EQUATION arxiv: v1 [math.gr] 27 Feb 2018
![LEFT SEMI-BRACES AND SOLUTIONS OF THE YANG-BAXTER EQUATION arxiv: v1 [math.gr] 27 Feb 2018 LEFT SEMI-BRACES AND SOLUTIONS OF THE YANG-BAXTER EQUATION arxiv: v1 [math.gr] 27 Feb 2018](/thumbs/89/98141702.jpg) LEFT SEMI-BRACES AND SOLUTIONS OF THE YANG-BAXTER EQUATION arxiv:1802.09993v1 [math.gr] 27 Feb 2018 ERIC JESPERS AND ARNE VAN ANTWERPEN Abstract. Let r : X 2 X 2 be a set-theoretic solution of the Yang-Baxter
LEFT SEMI-BRACES AND SOLUTIONS OF THE YANG-BAXTER EQUATION arxiv:1802.09993v1 [math.gr] 27 Feb 2018 ERIC JESPERS AND ARNE VAN ANTWERPEN Abstract. Let r : X 2 X 2 be a set-theoretic solution of the Yang-Baxter
An introduction to calculus of functors
 An introduction to calculus of functors Ismar Volić Wellesley College International University of Sarajevo May 28, 2012 Plan of talk Main point: One can use calculus of functors to answer questions about
An introduction to calculus of functors Ismar Volić Wellesley College International University of Sarajevo May 28, 2012 Plan of talk Main point: One can use calculus of functors to answer questions about
LOWHLL #WEEKLY JOURNAL.
 # F 7 F --) 2 9 Q - Q - - F - x $ 2 F? F \ F q - x q - - - - )< - -? - F - - Q z 2 Q - x -- - - - 3 - % 3 3 - - ) F x - \ - - - - - q - q - - - - -z- < F 7-7- - Q F 2 F - F \x -? - - - - - z - x z F -
# F 7 F --) 2 9 Q - Q - - F - x $ 2 F? F \ F q - x q - - - - )< - -? - F - - Q z 2 Q - x -- - - - 3 - % 3 3 - - ) F x - \ - - - - - q - q - - - - -z- < F 7-7- - Q F 2 F - F \x -? - - - - - z - x z F -
Higher-Dimensional Algebra VI: Lie 2-Algebras
 Higher-Dimensional Algebra VI: Lie 2-Algebras John C. Baez Department of Mathematics, University of California Riverside, California 92521 USA Alissa S. Crans Department of Mathematics, Loyola Marymount
Higher-Dimensional Algebra VI: Lie 2-Algebras John C. Baez Department of Mathematics, University of California Riverside, California 92521 USA Alissa S. Crans Department of Mathematics, Loyola Marymount
Research Article Rota-Baxter Operators on 3-Dimensional Lie Algebras and the Classical R-Matrices
 Hindawi Advances in Mathematical Physics Volume 07, Article ID 680, 7 pages https://doi.org/0.55/07/680 Research Article Rota-Baxter Operators on 3-Dimensional Lie Algebras and the Classical R-Matrices
Hindawi Advances in Mathematical Physics Volume 07, Article ID 680, 7 pages https://doi.org/0.55/07/680 Research Article Rota-Baxter Operators on 3-Dimensional Lie Algebras and the Classical R-Matrices
Involutive Yang-Baxter Groups
 Involutive Yang-Baxter Groups Ferran Cedó, Eric Jespers and Ángel del Río Abstract In 1992 Drinfeld posed the question of finding the set theoretic solutions of the Yang-Baxter equation. Recently, Gateva-Ivanova
Involutive Yang-Baxter Groups Ferran Cedó, Eric Jespers and Ángel del Río Abstract In 1992 Drinfeld posed the question of finding the set theoretic solutions of the Yang-Baxter equation. Recently, Gateva-Ivanova
Nichols algebras. Leandro Vendramin. Philipps-Universität Marburg Fachbereich Mathematik und Informatik Marburg, Germany
 Nichols algebras Leandro Vendramin Philipps-Universität Marburg Fachbereich Mathematik und Informatik Marburg, Germany Séminaire Lotharingien de Combinatoire 69 Strobl, September 2012 Let (V, c) be a braided
Nichols algebras Leandro Vendramin Philipps-Universität Marburg Fachbereich Mathematik und Informatik Marburg, Germany Séminaire Lotharingien de Combinatoire 69 Strobl, September 2012 Let (V, c) be a braided
Noncommutative motives and their applications
 MSRI 2013 The classical theory of pure motives (Grothendieck) V k category of smooth projective varieties over a field k; morphisms of varieties (Pure) Motives over k: linearization and idempotent completion
MSRI 2013 The classical theory of pure motives (Grothendieck) V k category of smooth projective varieties over a field k; morphisms of varieties (Pure) Motives over k: linearization and idempotent completion
Math 203A - Solution Set 1
 Math 203A - Solution Set 1 Problem 1. Show that the Zariski topology on A 2 is not the product of the Zariski topologies on A 1 A 1. Answer: Clearly, the diagonal Z = {(x, y) : x y = 0} A 2 is closed in
Math 203A - Solution Set 1 Problem 1. Show that the Zariski topology on A 2 is not the product of the Zariski topologies on A 1 A 1. Answer: Clearly, the diagonal Z = {(x, y) : x y = 0} A 2 is closed in
Research Statement. Noncommutative Algebra. Noncommut. Invariant Theory. struct. thms. [32, 33] Poisson. Algebras
![Research Statement. Noncommutative Algebra. Noncommut. Invariant Theory. struct. thms. [32, 33] Poisson. Algebras Research Statement. Noncommutative Algebra. Noncommut. Invariant Theory. struct. thms. [32, 33] Poisson. Algebras](/thumbs/94/118544766.jpg) Research Statement My research interest is Noncommutative Algebra, which has motivating contexts in noncommutative geometry, number theory, combinatorics, and mathematical physics. Below is the mindmap
Research Statement My research interest is Noncommutative Algebra, which has motivating contexts in noncommutative geometry, number theory, combinatorics, and mathematical physics. Below is the mindmap
SEMIRINGS SATISFYING PROPERTIES OF DISTRIBUTIVE TYPE
 proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 82, Number 3, July 1981 SEMIRINGS SATISFYING PROPERTIES OF DISTRIBUTIVE TYPE ARIF KAYA AND M. SATYANARAYANA Abstract. Any distributive lattice admits
proceedings of the american mathematical society Volume 82, Number 3, July 1981 SEMIRINGS SATISFYING PROPERTIES OF DISTRIBUTIVE TYPE ARIF KAYA AND M. SATYANARAYANA Abstract. Any distributive lattice admits
2x (x 2 + y 2 + 1) 2 2y. (x 2 + y 2 + 1) 4. 4xy. (1, 1)(x 1) + (1, 1)(y + 1) (1, 1)(x 1)(y + 1) 81 x y y + 7.
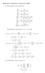 Homework 8 Solutions, November 007. (1 We calculate some derivatives: f x = f y = x (x + y + 1 y (x + y + 1 x = (x + y + 1 4x (x + y + 1 4 y = (x + y + 1 4y (x + y + 1 4 x y = 4xy (x + y + 1 4 Substituting
Homework 8 Solutions, November 007. (1 We calculate some derivatives: f x = f y = x (x + y + 1 y (x + y + 1 x = (x + y + 1 4x (x + y + 1 4 y = (x + y + 1 4y (x + y + 1 4 x y = 4xy (x + y + 1 4 Substituting
Multivariable Calculus and Matrix Algebra-Summer 2017
 Multivariable Calculus and Matrix Algebra-Summer 017 Homework 4 Solutions Note that the solutions below are for the latest version of the problems posted. For those of you who worked on an earlier version
Multivariable Calculus and Matrix Algebra-Summer 017 Homework 4 Solutions Note that the solutions below are for the latest version of the problems posted. For those of you who worked on an earlier version
Chapter 2 : Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates
 Chapter 2 : Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates By Electrical Engineering Department College of Engineering King Saud University 1431-1432 2.1. Basic Definitions 2.2. Basic Theorems and Properties of Boolean
Chapter 2 : Boolean Algebra and Logic Gates By Electrical Engineering Department College of Engineering King Saud University 1431-1432 2.1. Basic Definitions 2.2. Basic Theorems and Properties of Boolean
Linear Algebra Review
 Linear Algebra Review ORIE 4741 September 1, 2017 Linear Algebra Review September 1, 2017 1 / 33 Outline 1 Linear Independence and Dependence 2 Matrix Rank 3 Invertible Matrices 4 Norms 5 Projection Matrix
Linear Algebra Review ORIE 4741 September 1, 2017 Linear Algebra Review September 1, 2017 1 / 33 Outline 1 Linear Independence and Dependence 2 Matrix Rank 3 Invertible Matrices 4 Norms 5 Projection Matrix
COURSE SUMMARY FOR MATH 508, WINTER QUARTER 2017: ADVANCED COMMUTATIVE ALGEBRA
 COURSE SUMMARY FOR MATH 508, WINTER QUARTER 2017: ADVANCED COMMUTATIVE ALGEBRA JAROD ALPER WEEK 1, JAN 4, 6: DIMENSION Lecture 1: Introduction to dimension. Define Krull dimension of a ring A. Discuss
COURSE SUMMARY FOR MATH 508, WINTER QUARTER 2017: ADVANCED COMMUTATIVE ALGEBRA JAROD ALPER WEEK 1, JAN 4, 6: DIMENSION Lecture 1: Introduction to dimension. Define Krull dimension of a ring A. Discuss
Integrable spin systems and four-dimensional gauge theory
 Integrable spin systems and four-dimensional gauge theory Based on 1303.2632 and joint work with Robbert Dijkgraaf, Edward Witten and Masahito Yamizaki Perimeter Institute of theoretical physics Waterloo,
Integrable spin systems and four-dimensional gauge theory Based on 1303.2632 and joint work with Robbert Dijkgraaf, Edward Witten and Masahito Yamizaki Perimeter Institute of theoretical physics Waterloo,
Irreducible representations of the plactic monoid of rank four
 Lukasz Kubat (joint work with Ferran Cedó and Jan Okniński) Institute of Mathematics University of Warsaw Groups, Rings and the Yang Baxter equation Spa, June 23, 2017 Plan of the talk 1 Background Plactic
Lukasz Kubat (joint work with Ferran Cedó and Jan Okniński) Institute of Mathematics University of Warsaw Groups, Rings and the Yang Baxter equation Spa, June 23, 2017 Plan of the talk 1 Background Plactic
PREPOISSON ALGEBRAS MARCELO AGUIAR
 PREPOISSON ALGEBRAS MARCELO AGUIAR Abstract. A definition of prepoisson algebras is proposed, combining structures of prelie and zinbiel algebra on the same vector space. It is shown that a prepoisson
PREPOISSON ALGEBRAS MARCELO AGUIAR Abstract. A definition of prepoisson algebras is proposed, combining structures of prelie and zinbiel algebra on the same vector space. It is shown that a prepoisson
THE QUANTUM DOUBLE AS A HOPF ALGEBRA
 THE QUANTUM DOUBLE AS A HOPF ALGEBRA In this text we discuss the generalized quantum double construction. treatment of the results described without proofs in [2, Chpt. 3, 3]. We give several exercises
THE QUANTUM DOUBLE AS A HOPF ALGEBRA In this text we discuss the generalized quantum double construction. treatment of the results described without proofs in [2, Chpt. 3, 3]. We give several exercises
Q SON,' (ESTABLISHED 1879L
 ( < 5(? Q 5 9 7 00 9 0 < 6 z 97 ( # ) $ x 6 < ( ) ( ( 6( ( ) ( $ z 0 z z 0 ) { ( % 69% ( ) x 7 97 z ) 7 ) ( ) 6 0 0 97 )( 0 x 7 97 5 6 ( ) 0 6 ) 5 ) 0 ) 9%5 z» 0 97 «6 6» 96? 0 96 5 0 ( ) ( ) 0 x 6 0
( < 5(? Q 5 9 7 00 9 0 < 6 z 97 ( # ) $ x 6 < ( ) ( ( 6( ( ) ( $ z 0 z z 0 ) { ( % 69% ( ) x 7 97 z ) 7 ) ( ) 6 0 0 97 )( 0 x 7 97 5 6 ( ) 0 6 ) 5 ) 0 ) 9%5 z» 0 97 «6 6» 96? 0 96 5 0 ( ) ( ) 0 x 6 0
PROBLEMS, MATH 214A. Affine and quasi-affine varieties
 PROBLEMS, MATH 214A k is an algebraically closed field Basic notions Affine and quasi-affine varieties 1. Let X A 2 be defined by x 2 + y 2 = 1 and x = 1. Find the ideal I(X). 2. Prove that the subset
PROBLEMS, MATH 214A k is an algebraically closed field Basic notions Affine and quasi-affine varieties 1. Let X A 2 be defined by x 2 + y 2 = 1 and x = 1. Find the ideal I(X). 2. Prove that the subset
Integrable Spin Systems From Four Dimensions
 Integrable Spin Systems From Four Dimensions Edward Witten Monte Verita, July 2, 2017 A few years ago, Kevin Costello introduced a new approach to integrable spin systems in two dimensions starting from
Integrable Spin Systems From Four Dimensions Edward Witten Monte Verita, July 2, 2017 A few years ago, Kevin Costello introduced a new approach to integrable spin systems in two dimensions starting from
arxiv: v4 [math.qa] 2 Jan 2017
![arxiv: v4 [math.qa] 2 Jan 2017 arxiv: v4 [math.qa] 2 Jan 2017](/thumbs/78/77187012.jpg) SET-THEORETIC SOLUTIONS OF THE YANG-BAXTER EQUATION, BRACES AND SYMMETRIC GROUPS arxiv:1507.02602v4 [math.qa] 2 Jan 2017 TATIANA GATEVA-IVANOVA Abstract. We involve simultaneously the theory of matched
SET-THEORETIC SOLUTIONS OF THE YANG-BAXTER EQUATION, BRACES AND SYMMETRIC GROUPS arxiv:1507.02602v4 [math.qa] 2 Jan 2017 TATIANA GATEVA-IVANOVA Abstract. We involve simultaneously the theory of matched
Subfactors and Modular Tensor Categories
 UNSW Topological matter, strings, K-theory and related areas University of Adelaide September 2016 Outline Motivation What is a modular tensor category? Where do modular tensor categories come from? Some
UNSW Topological matter, strings, K-theory and related areas University of Adelaide September 2016 Outline Motivation What is a modular tensor category? Where do modular tensor categories come from? Some
