Fourier Series. with the period 2π, given that sin nx and cos nx are period functions with the period 2π. Then we.
|
|
|
- Moses Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 . Definition We c the trigonometric series the series of the form + cos x+ b sin x+ cos x+ b sin x+ or more briefy + ( ncos nx+ bnsin nx) () n The constnts, n nd b, n ( n,, ) re coefficients of the series (Fourier coefficients). If the series () converges, its sum is periodic function with the period, given tht sin nx nd cos nx re period functions with the period. Then we f x f x+. obtin ( ) ( ). Computtion of the coefficients f Wht conditions needed to impose on ( ) converging to f ( x )? x so tht there exists trigonometric series Suppose tht the periodic function with the period of cn be represented by trigonometric series which converges to in the interv(, ); tht is, + ( ncos nx+ bnsin nx) () n Integrting both sides from to yieds dx dx + ncos nxdx bnsin nxdx + n Since, dx cos nxdx cos nxdx then, n n nd bnsin nxdx bn sin nxdx ( ) f x dx dx Before computing ndb, you need to recognize tht for integer n nd, Prepred by Mong Mr nd Ngov Simrong
2 If n, we obtin cos nx cos xdx cos nxsin xdx sin nxsin xdx nd if n, we obtin cos xdx sin x cos xdx ( II ) sin xdx For, mutipying both sides of () by cos x yieds cos x cos x+ ( ncos nxcos x+ bnsin nxcos x) n Integrting from to yieds cos xdx cos xdx n cos nx cos xdx bn sin nx cos xdx + + n Resuting from ( I ) nd (II) we obtin ( ) cos cos f x xdx xdx cos xdx Once gin, mutipying both sides of () by sin x yieds sin x sin x+ ( ncos nxsin x+ bnsin nxsin x) n sin xdx sin xdx n cos nxsin xdx bn sin nxsin xdx + + n From (I) nd (II) we obtin ( ) sin sin f x xdx b xdx b b sin xdx ( I ) Prepred by Mong Mr nd Ngov Simrong
3 3. Expnding functions into Exmpe: Given the periodic function with the period defined s x, < x. Find its Fourier series. x xdx x cos xdx sinx x sin xdx cos x b sin cos ( ) + x xdx x xdx + Then we obtin sin x sin x sin 3x + sin x + ( ) + 3 Exmpe: Given the periodic function with the period defined s foow x,for x x,for < x Find its Fourier series. Determining coefficients of Fourier: dx ( x) dx xdx + ( x) cos xdx x cos xdx + xsin x xsin x + sin xdx + cosx cosx +,for even ( cos ) 4,for odd sin xdx Prepred by Mong Mr nd Ngov Simrong 3
4 b ( x) sin xdx xsin xdx + Hence, we obtin the series 4 cos x cos 3x cos x cos( p+ ) x ( p + ) 4. Remr on expnding functions into Fourier series For ny re λ nd the periodic function ψ ( x) with the period, we hve λ+ ( x) dx ψ ( ) ψ x dx λ (The proof of this property is omitted) Exmpe: Expnd into Fourier series the periodic( ) function xover the interv x. soution: dx xdx Therefore, cos nxdx xcos nxdx xsinnx cosnx + n n b sin nxdx xsin nxdx xcosnx sinnx + n n n + sin nx n n Prepred by Mong Mr nd Ngov Simrong 4
5 . Fourier series of the even nd odd functions ψ x is n even function, we obtin If ( ) ( x) dx ψ ( ) ψ nd if the function ϕ ( x) is odd, then ϕ ( x) dx. x dx In the expnsion of n odd function into Fourier series, the product nd sin xis n even function. Therefore, f x dx f x cos xdx ( ) ( ) b sin xdx sin xdx cos xis odd If we expnd n even function the product sin xis n odd function nd cos x is n even function. Therefore, ( ) ( ) f x dx f x cos xdx b sin xdx Exmpe: Expnd the periodic function with the period defined by x, x We notice tht the function is n even one. Then, b f x sin xdx ( ) 3 x dx x dx 3 3 cos xdx x cos xdx ( ) x sinx xcosx 4cos sin x 3 + Therefore, we obtin ( ) 4 x + cos x 3 Exmpe: A periodic function with the period is defined s 4 Prepred by Mong Mr nd Ngov Simrong
6 Answer: if x < if x 4 sin x sin 3x sin x Fourier series of the function with period Let be period function with the period, different from in gener. Let expnd this ind of function into Fourier series. Ting x t, we obtin f t + cos t + b sin t where ( ) f t dt f t cos tdt b f t sin tdt Going bc to the previous vribe x: x x t, t dt dx then dx cos xdx b ( ) f x sin xdx Therefore, + cos x+ b sin x Exmpe: Find the Fourier coefficients corresponding to the function, < x < 3, < x < with period. Write the corresponding Fourier series. Since the period, then. Therefore, ( ) f x dx 3dx 3 cos xdx 3cos xdx Prepred by Mong Mr nd Ngov Simrong 6
7 3 x 3 x cos dx sin Thus, 3 nx b 3sin dx sin dx f ( ) 3 x 3 cos cos,if iseven 6,if is odd ( x) sin x sin x sin x Exercises.Expnd x, x.expnd x( x), x 3.Expnd in Fourier series in the interv (, ) f ( x) < < in Fourier series if the period is. < < in Fourier series if the period is. the function x, x x, < x f x x, in sine series. 4.Expnd the function ( ) in the interv [ ].Expnd the function xin the interv [ ], in cosine series. Prepred by Mong Mr nd Ngov Simrong 7
Suggested Solution to Assignment 5
 MATH 4 (5-6) prti diferenti equtions Suggested Soution to Assignment 5 Exercise 5.. () (b) A m = A m = = ( )m+ mπ x sin mπx dx = x mπ cos mπx + + 4( )m 4 m π. 4x cos mπx dx mπ x cos mπxdx = x mπ sin mπx
MATH 4 (5-6) prti diferenti equtions Suggested Soution to Assignment 5 Exercise 5.. () (b) A m = A m = = ( )m+ mπ x sin mπx dx = x mπ cos mπx + + 4( )m 4 m π. 4x cos mπx dx mπ x cos mπxdx = x mπ sin mπx
Ma 221 Eigenvalues and Fourier Series
 Ma Eigenvalues and Fourier Series Eigenvalue and Eigenfunction Examples Example Find the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions for y y 47 y y y5 Solution: The characteristic equation is r r 47 so r 44 447 6 Thus
Ma Eigenvalues and Fourier Series Eigenvalue and Eigenfunction Examples Example Find the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions for y y 47 y y y5 Solution: The characteristic equation is r r 47 so r 44 447 6 Thus
ENGI 9420 Lecture Notes 7 - Fourier Series Page 7.01
 ENGI 940 ecture Notes 7 - Fourier Series Pge 7.0 7. Fourier Series nd Fourier Trnsforms Fourier series hve multiple purposes, including the provision of series solutions to some liner prtil differentil
ENGI 940 ecture Notes 7 - Fourier Series Pge 7.0 7. Fourier Series nd Fourier Trnsforms Fourier series hve multiple purposes, including the provision of series solutions to some liner prtil differentil
AM1 Mathematical Analysis 1 Oct Feb Exercises Lecture 3. sin(x + h) sin x h cos(x + h) cos x h
 AM Mthemticl Anlysis Oct. Feb. Dte: October Exercises Lecture Exercise.. If h, prove the following identities hold for ll x: sin(x + h) sin x h cos(x + h) cos x h = sin γ γ = sin γ γ cos(x + γ) (.) sin(x
AM Mthemticl Anlysis Oct. Feb. Dte: October Exercises Lecture Exercise.. If h, prove the following identities hold for ll x: sin(x + h) sin x h cos(x + h) cos x h = sin γ γ = sin γ γ cos(x + γ) (.) sin(x
Online Multiple Choice Questions of EM-II of Unit-III
 Online Multiple Choice Questions of EM-II of Unit-III. The primitive period of a constant function is does not exist ANS: d. The constant function is an odd function an even function neither even nor odd
Online Multiple Choice Questions of EM-II of Unit-III. The primitive period of a constant function is does not exist ANS: d. The constant function is an odd function an even function neither even nor odd
Examples of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 10.3). The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case.
 s of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 1.3. The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem: Piecewise continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem:
s of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 1.3. The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem: Piecewise continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem:
PHYSICS 116C Homework 4 Solutions
 PHYSICS 116C Homework 4 Solutions 1. ( Simple hrmonic oscilltor. Clerly the eqution is of the Sturm-Liouville (SL form with λ = n 2, A(x = 1, B(x =, w(x = 1. Legendre s eqution. Clerly the eqution is of
PHYSICS 116C Homework 4 Solutions 1. ( Simple hrmonic oscilltor. Clerly the eqution is of the Sturm-Liouville (SL form with λ = n 2, A(x = 1, B(x =, w(x = 1. Legendre s eqution. Clerly the eqution is of
Math 201 Assignment #11
 Math 21 Assignment #11 Problem 1 (1.5 2) Find a formal solution to the given initial-boundary value problem. = 2 u x, < x < π, t > 2 u(, t) = u(π, t) =, t > u(x, ) = x 2, < x < π Problem 2 (1.5 5) Find
Math 21 Assignment #11 Problem 1 (1.5 2) Find a formal solution to the given initial-boundary value problem. = 2 u x, < x < π, t > 2 u(, t) = u(π, t) =, t > u(x, ) = x 2, < x < π Problem 2 (1.5 5) Find
PHYS 502 Lecture 3: Fourier Series
 PHYS 52 Lecture 3: Fourier Series Fourier Series Introduction In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a (possibly infinite) set of simple oscillating
PHYS 52 Lecture 3: Fourier Series Fourier Series Introduction In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a (possibly infinite) set of simple oscillating
Math 3150 HW 3 Solutions
 Math 315 HW 3 Solutions June 5, 18 3.8, 3.9, 3.1, 3.13, 3.16, 3.1 1. 3.8 Make graphs of the periodic extensions on the region x [ 3, 3] of the following functions f defined on x [, ]. Be sure to indicate
Math 315 HW 3 Solutions June 5, 18 3.8, 3.9, 3.1, 3.13, 3.16, 3.1 1. 3.8 Make graphs of the periodic extensions on the region x [ 3, 3] of the following functions f defined on x [, ]. Be sure to indicate
multiply both sides of eq. by a and projection overlap
 Fourier Series n x n x f xa ancos bncos n n periodic with period x consider n, sin x x x March. 3, 7 Any function with period can be represented with a Fourier series Examples (sawtooth) (square wave)
Fourier Series n x n x f xa ancos bncos n n periodic with period x consider n, sin x x x March. 3, 7 Any function with period can be represented with a Fourier series Examples (sawtooth) (square wave)
Abstract inner product spaces
 WEEK 4 Abstrct inner product spces Definition An inner product spce is vector spce V over the rel field R equipped with rule for multiplying vectors, such tht the product of two vectors is sclr, nd the
WEEK 4 Abstrct inner product spces Definition An inner product spce is vector spce V over the rel field R equipped with rule for multiplying vectors, such tht the product of two vectors is sclr, nd the
Physics 116C Solution of inhomogeneous ordinary differential equations using Green s functions
 Physics 6C Solution of inhomogeneous ordinry differentil equtions using Green s functions Peter Young November 5, 29 Homogeneous Equtions We hve studied, especilly in long HW problem, second order liner
Physics 6C Solution of inhomogeneous ordinry differentil equtions using Green s functions Peter Young November 5, 29 Homogeneous Equtions We hve studied, especilly in long HW problem, second order liner
Week 6 Lectures, Math 6451, Tanveer
 Fourier Series Week 6 Lectures, Math 645, Tanveer In the context of separation of variabe to find soutions of PDEs, we encountered or and in other cases f(x = f(x = a 0 + f(x = a 0 + b n sin nπx { a n
Fourier Series Week 6 Lectures, Math 645, Tanveer In the context of separation of variabe to find soutions of PDEs, we encountered or and in other cases f(x = f(x = a 0 + f(x = a 0 + b n sin nπx { a n
Chapter 28. Fourier Series An Eigenvalue Problem.
 Chpter 28 Fourier Series Every time I close my eyes The noise inside me mplifies I cn t escpe I relive every moment of the dy Every misstep I hve mde Finds wy it cn invde My every thought And this is why
Chpter 28 Fourier Series Every time I close my eyes The noise inside me mplifies I cn t escpe I relive every moment of the dy Every misstep I hve mde Finds wy it cn invde My every thought And this is why
c n φ n (x), 0 < x < L, (1) n=1
 SECTION : Fourier Series. MATH4. In section 4, we will study method clled Seprtion of Vribles for finding exct solutions to certin clss of prtil differentil equtions (PDEs. To do this, it will be necessry
SECTION : Fourier Series. MATH4. In section 4, we will study method clled Seprtion of Vribles for finding exct solutions to certin clss of prtil differentil equtions (PDEs. To do this, it will be necessry
The Product Rule state that if f and g are differentiable functions, then
 Chpter 6 Techniques of Integrtion 6. Integrtion by Prts Every differentition rule hs corresponding integrtion rule. For instnce, the Substitution Rule for integrtion corresponds to the Chin Rule for differentition.
Chpter 6 Techniques of Integrtion 6. Integrtion by Prts Every differentition rule hs corresponding integrtion rule. For instnce, the Substitution Rule for integrtion corresponds to the Chin Rule for differentition.
7.2 Trigonometric Integrals
 7.2 1 7.2 Trigonometric Integrals Products of Powers of Sines and Cosines We wish to evaluate integrals of the form: sin m x cos n xdx where m and n are nonnegative integers. Recall the double angle formulas
7.2 1 7.2 Trigonometric Integrals Products of Powers of Sines and Cosines We wish to evaluate integrals of the form: sin m x cos n xdx where m and n are nonnegative integers. Recall the double angle formulas
1 The Riemann Integral
 The Riemnn Integrl. An exmple leding to the notion of integrl (res) We know how to find (i.e. define) the re of rectngle (bse height), tringle ( (sum of res of tringles). But how do we find/define n re
The Riemnn Integrl. An exmple leding to the notion of integrl (res) We know how to find (i.e. define) the re of rectngle (bse height), tringle ( (sum of res of tringles). But how do we find/define n re
Summary: Method of Separation of Variables
 Physics 246 Electricity nd Mgnetism I, Fll 26, Lecture 22 1 Summry: Method of Seprtion of Vribles 1. Seprtion of Vribles in Crtesin Coordintes 2. Fourier Series Suggested Reding: Griffiths: Chpter 3, Section
Physics 246 Electricity nd Mgnetism I, Fll 26, Lecture 22 1 Summry: Method of Seprtion of Vribles 1. Seprtion of Vribles in Crtesin Coordintes 2. Fourier Series Suggested Reding: Griffiths: Chpter 3, Section
Chapter 5 Notes. 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities
 Chapter 5 Notes 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities 1. Simplify each expression to its lowest terms. Write the answer to part as the product of factors. (a) sin x csc x cot x ( 1+ sinσ + cosσ ) (c) 1 tanx
Chapter 5 Notes 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities 1. Simplify each expression to its lowest terms. Write the answer to part as the product of factors. (a) sin x csc x cot x ( 1+ sinσ + cosσ ) (c) 1 tanx
Review Sol. of More Long Answer Questions
 Review Sol. of More Long Answer Questions 1. Solve the integro-differential equation t y (t) e t v y(v)dv = t; y()=. (1) Solution. The key is to recognize the convolution: t e t v y(v) dv = e t y. () Now
Review Sol. of More Long Answer Questions 1. Solve the integro-differential equation t y (t) e t v y(v)dv = t; y()=. (1) Solution. The key is to recognize the convolution: t e t v y(v) dv = e t y. () Now
Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator
 Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator Recall the simple harmonic oscillator (e.g. mass-spring system) d 2 y dt 2 + ω2 0y = 0 Solution can be written in various ways: y(t) = Ae iω 0t y(t) = A cos
Periodic functions: simple harmonic oscillator Recall the simple harmonic oscillator (e.g. mass-spring system) d 2 y dt 2 + ω2 0y = 0 Solution can be written in various ways: y(t) = Ae iω 0t y(t) = A cos
k and v = v 1 j + u 3 i + v 2
 ORTHOGONAL FUNCTIONS AND FOURIER SERIES Orthogonl functions A function cn e considered to e generliztion of vector. Thus the vector concets like the inner roduct nd orthogonlity of vectors cn e extended
ORTHOGONAL FUNCTIONS AND FOURIER SERIES Orthogonl functions A function cn e considered to e generliztion of vector. Thus the vector concets like the inner roduct nd orthogonlity of vectors cn e extended
Fourier Series in Complex notation. cos(x) = eix + e ix 2. A n cos + B n sin l. i 2 B n. e inx=l + A n + ib n 2 8. ( 0 m 6= n. C n = 1 2l.
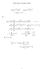 Fourier Series in Compex nottion sin(x) = eix e ix i = i eix e ix cos(x) = eix + e ix So So '(x) = A 1 0 + nx nx A n cos + B n sin = A 1 0 + e inx= + e inx= A n = A 0 + 1 = C n = C n 1 n= 1 A n ib n C
Fourier Series in Compex nottion sin(x) = eix e ix i = i eix e ix cos(x) = eix + e ix So So '(x) = A 1 0 + nx nx A n cos + B n sin = A 1 0 + e inx= + e inx= A n = A 0 + 1 = C n = C n 1 n= 1 A n ib n C
Math 124B January 24, 2012
 Mth 24B Jnury 24, 22 Viktor Grigoryn 5 Convergence of Fourier series Strting from the method of seprtion of vribes for the homogeneous Dirichet nd Neumnn boundry vue probems, we studied the eigenvue probem
Mth 24B Jnury 24, 22 Viktor Grigoryn 5 Convergence of Fourier series Strting from the method of seprtion of vribes for the homogeneous Dirichet nd Neumnn boundry vue probems, we studied the eigenvue probem
Fourier series
 11.1-11.2. Fourier series Yurii Lyubarskii, NTNU September 5, 2016 Periodic functions Function f defined on the whole real axis has period p if Properties f (t) = f (t + p) for all t R If f and g have
11.1-11.2. Fourier series Yurii Lyubarskii, NTNU September 5, 2016 Periodic functions Function f defined on the whole real axis has period p if Properties f (t) = f (t + p) for all t R If f and g have
MA 124 January 18, Derivatives are. Integrals are.
 MA 124 Jnury 18, 2018 Prof PB s one-minute introduction to clculus Derivtives re. Integrls re. In Clculus 1, we lern limits, derivtives, some pplictions of derivtives, indefinite integrls, definite integrls,
MA 124 Jnury 18, 2018 Prof PB s one-minute introduction to clculus Derivtives re. Integrls re. In Clculus 1, we lern limits, derivtives, some pplictions of derivtives, indefinite integrls, definite integrls,
DEFINITION The inner product of two functions f 1 and f 2 on an interval [a, b] is the number. ( f 1, f 2 ) b DEFINITION 11.1.
![DEFINITION The inner product of two functions f 1 and f 2 on an interval [a, b] is the number. ( f 1, f 2 ) b DEFINITION 11.1. DEFINITION The inner product of two functions f 1 and f 2 on an interval [a, b] is the number. ( f 1, f 2 ) b DEFINITION 11.1.](/thumbs/81/83893993.jpg) 398 CHAPTER 11 ORTHOGONAL FUNCTIONS AND FOURIER SERIES 11.1 ORTHOGONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW MATERIAL The notions of generlized vectors nd vector spces cn e found in ny liner lger text. INTRODUCTION The concepts
398 CHAPTER 11 ORTHOGONAL FUNCTIONS AND FOURIER SERIES 11.1 ORTHOGONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW MATERIAL The notions of generlized vectors nd vector spces cn e found in ny liner lger text. INTRODUCTION The concepts
Best Approximation. Chapter The General Case
 Chpter 4 Best Approximtion 4.1 The Generl Cse In the previous chpter, we hve seen how n interpolting polynomil cn be used s n pproximtion to given function. We now wnt to find the best pproximtion to given
Chpter 4 Best Approximtion 4.1 The Generl Cse In the previous chpter, we hve seen how n interpolting polynomil cn be used s n pproximtion to given function. We now wnt to find the best pproximtion to given
a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a In this section, we introduce a general formula for computing determinants.
 Section 9 The Lplce Expnsion In the lst section, we defined the determinnt of (3 3) mtrix A 12 to be 22 12 21 22 2231 22 12 21. In this section, we introduce generl formul for computing determinnts. Rewriting
Section 9 The Lplce Expnsion In the lst section, we defined the determinnt of (3 3) mtrix A 12 to be 22 12 21 22 2231 22 12 21. In this section, we introduce generl formul for computing determinnts. Rewriting
22. Periodic Functions and Fourier Series
 November 29, 2010 22-1 22. Periodic Functions and Fourier Series 1 Periodic Functions A real-valued function f(x) of a real variable is called periodic of period T > 0 if f(x + T ) = f(x) for all x R.
November 29, 2010 22-1 22. Periodic Functions and Fourier Series 1 Periodic Functions A real-valued function f(x) of a real variable is called periodic of period T > 0 if f(x + T ) = f(x) for all x R.
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration
 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
Math 3B: Lecture 9. Noah White. October 18, 2017
 Mth 3B: Lecture 9 Noh White October 18, 2017 The definite integrl Defintion The definite integrl of function f (x) is defined to be where x = b n. f (x) dx = lim n x n f ( + k x) k=1 Properties of definite
Mth 3B: Lecture 9 Noh White October 18, 2017 The definite integrl Defintion The definite integrl of function f (x) is defined to be where x = b n. f (x) dx = lim n x n f ( + k x) k=1 Properties of definite
More on Fourier Series
 More on Fourier Series R. C. Trinity University Partial Differential Equations Lecture 6.1 New Fourier series from old Recall: Given a function f (x, we can dilate/translate its graph via multiplication/addition,
More on Fourier Series R. C. Trinity University Partial Differential Equations Lecture 6.1 New Fourier series from old Recall: Given a function f (x, we can dilate/translate its graph via multiplication/addition,
Ma 221 Final Exam Solutions 5/14/13
 Ma 221 Final Exam Solutions 5/14/13 1. Solve (a) (8 pts) Solution: The equation is separable. dy dx exy y 1 y0 0 y 1e y dy e x dx y 1e y dy e x dx ye y e y dy e x dx ye y e y e y e x c The last step comes
Ma 221 Final Exam Solutions 5/14/13 1. Solve (a) (8 pts) Solution: The equation is separable. dy dx exy y 1 y0 0 y 1e y dy e x dx y 1e y dy e x dx ye y e y dy e x dx ye y e y e y e x c The last step comes
Section 7.1 Integration by Substitution
 Section 7. Integrtion by Substitution Evlute ech of the following integrls. Keep in mind tht using substitution my not work on some problems. For one of the definite integrls, it is not possible to find
Section 7. Integrtion by Substitution Evlute ech of the following integrls. Keep in mind tht using substitution my not work on some problems. For one of the definite integrls, it is not possible to find
HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 1910 Sections 7.9, 8.1 Fall 2016
 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 9 Sections 7.9, 8. Fll 6 Problem 7.9.33 Show tht for ny constnts M,, nd, the function yt) = )) t ) M + tnh stisfies the logistic eqution: y SOLUTION. Let Then nd Finlly, y = y M
HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 9 Sections 7.9, 8. Fll 6 Problem 7.9.33 Show tht for ny constnts M,, nd, the function yt) = )) t ) M + tnh stisfies the logistic eqution: y SOLUTION. Let Then nd Finlly, y = y M
Weighted SS(E) = w 2 1( y 1 y1) y n. w n. Wy W y 2 = Wy WAx 2. WAx = Wy. (WA) T WAx = (WA) T b
 6.8 - Applications of Inner Product Spaces Weighted Least-Squares Sometimes you want to get a least-squares solution to a problem where some of the data points are less reliable than others. In this case,
6.8 - Applications of Inner Product Spaces Weighted Least-Squares Sometimes you want to get a least-squares solution to a problem where some of the data points are less reliable than others. In this case,
`an cos nπx. n 1. L `b
 4 Fourier Series A periodic function on a range p,q may be decomposed into a sum of sinusoidal (sine or cosine) functions. This can be written as follows gpxq 1 2 a ` ř8 `b (4.1) The aim of this chapter
4 Fourier Series A periodic function on a range p,q may be decomposed into a sum of sinusoidal (sine or cosine) functions. This can be written as follows gpxq 1 2 a ` ř8 `b (4.1) The aim of this chapter
Mathematics Higher Block 3 Practice Assessment A
 Mthemtics Higher Block 3 Prctice Assessment A Red crefully 1. Clcultors my be used. 2. Full credit will be given only where the solution contins pproprite working. 3. Answers obtined from reding from scle
Mthemtics Higher Block 3 Prctice Assessment A Red crefully 1. Clcultors my be used. 2. Full credit will be given only where the solution contins pproprite working. 3. Answers obtined from reding from scle
Next, we ll use all of the tools we ve covered in our study of trigonometry to solve some equations.
 Section 6.3 - Solving Trigonometric Equations Next, we ll use all of the tools we ve covered in our study of trigonometry to solve some equations. These are equations from algebra: Linear Equation: Solve:
Section 6.3 - Solving Trigonometric Equations Next, we ll use all of the tools we ve covered in our study of trigonometry to solve some equations. These are equations from algebra: Linear Equation: Solve:
cos 3 (x) sin(x) dx 3y + 4 dy Math 1206 Calculus Sec. 5.6: Substitution and Area Between Curves
 Mth 126 Clculus Sec. 5.6: Substitution nd Are Between Curves I. U-Substitution for Definite Integrls A. Th m 6-Substitution in Definite Integrls: If g (x) is continuous on [,b] nd f is continuous on the
Mth 126 Clculus Sec. 5.6: Substitution nd Are Between Curves I. U-Substitution for Definite Integrls A. Th m 6-Substitution in Definite Integrls: If g (x) is continuous on [,b] nd f is continuous on the
Anti-derivatives/Indefinite Integrals of Basic Functions
 Anti-derivtives/Indefinite Integrls of Bsic Functions Power Rule: In prticulr, this mens tht x n+ x n n + + C, dx = ln x + C, if n if n = x 0 dx = dx = dx = x + C nd x (lthough you won t use the second
Anti-derivtives/Indefinite Integrls of Bsic Functions Power Rule: In prticulr, this mens tht x n+ x n n + + C, dx = ln x + C, if n if n = x 0 dx = dx = dx = x + C nd x (lthough you won t use the second
ES 111 Mathematical Methods in the Earth Sciences Lecture Outline 1 - Thurs 28th Sept 17 Review of trigonometry and basic calculus
 ES 111 Mthemticl Methods in the Erth Sciences Lecture Outline 1 - Thurs 28th Sept 17 Review of trigonometry nd bsic clculus Trigonometry When is it useful? Everywhere! Anything involving coordinte systems
ES 111 Mthemticl Methods in the Erth Sciences Lecture Outline 1 - Thurs 28th Sept 17 Review of trigonometry nd bsic clculus Trigonometry When is it useful? Everywhere! Anything involving coordinte systems
MATH 124B: HOMEWORK 2
 MATH 24B: HOMEWORK 2 Suggested due date: August 5th, 26 () Consider the geometric series ( ) n x 2n. (a) Does it converge pointwise in the interval < x
MATH 24B: HOMEWORK 2 Suggested due date: August 5th, 26 () Consider the geometric series ( ) n x 2n. (a) Does it converge pointwise in the interval < x
Convergence of Fourier Series
 MATH 454: Analysis Two James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University April, 8 MATH 454: Analysis Two Outline The Cos Family MATH 454: Analysis
MATH 454: Analysis Two James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University April, 8 MATH 454: Analysis Two Outline The Cos Family MATH 454: Analysis
FILTERING IN THE FREQUENCY DOMAIN
 1 FILTERING IN THE FREQUENCY DOMAIN Lecture 4 Spatial Vs Frequency domain 2 Spatial Domain (I) Normal image space Changes in pixel positions correspond to changes in the scene Distances in I correspond
1 FILTERING IN THE FREQUENCY DOMAIN Lecture 4 Spatial Vs Frequency domain 2 Spatial Domain (I) Normal image space Changes in pixel positions correspond to changes in the scene Distances in I correspond
Convergence of Fourier Series and Fejer s Theorem. Lee Ricketson
 Convergence of Fourier Series nd Fejer s Theorem Lee Ricketson My, 006 Abstrct This pper will ddress the Fourier Series of functions with rbitrry period. We will derive forms of the Dirichlet nd Fejer
Convergence of Fourier Series nd Fejer s Theorem Lee Ricketson My, 006 Abstrct This pper will ddress the Fourier Series of functions with rbitrry period. We will derive forms of the Dirichlet nd Fejer
Mutipy by r sin RT P to get sin R r r R + T sin (sin T )+ P P = (7) ffi So we hve P P ffi = m (8) choose m re so tht P is sinusoi. If we put this in b
 Topic 4: Lpce Eqution in Spheric Co-orintes n Mutipoe Expnsion Reing Assignment: Jckson Chpter 3.-3.5. Lpce Eqution in Spheric Coorintes Review of spheric por coorintes: x = r sin cos ffi y = r sin sin
Topic 4: Lpce Eqution in Spheric Co-orintes n Mutipoe Expnsion Reing Assignment: Jckson Chpter 3.-3.5. Lpce Eqution in Spheric Coorintes Review of spheric por coorintes: x = r sin cos ffi y = r sin sin
Geometrically Convex Function and Estimation of Remainder Terms in Taylor Series Expansion of some Functions
 Geometriclly Convex Function nd Estimtion of Reminder Terms in Tylor Series Expnsion of some Functions Xioming Zhng Ningguo Zheng December 21 25 Abstrct In this pper two integrl inequlities of geometriclly
Geometriclly Convex Function nd Estimtion of Reminder Terms in Tylor Series Expnsion of some Functions Xioming Zhng Ningguo Zheng December 21 25 Abstrct In this pper two integrl inequlities of geometriclly
1. The vibrating string problem revisited.
 Weeks 7 8: S eprtion of Vribes In the pst few weeks we hve expored the possibiity of soving first nd second order PDEs by trnsforming them into simper forms ( method of chrcteristics. Unfortuntey, this
Weeks 7 8: S eprtion of Vribes In the pst few weeks we hve expored the possibiity of soving first nd second order PDEs by trnsforming them into simper forms ( method of chrcteristics. Unfortuntey, this
Fourier Series. Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta
 1 Lecture Notes on Partial Differential Equations Chapter IV Fourier Series Ilyasse Aksikas Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta aksikas@ualberta.ca DEFINITIONS 2 Before
1 Lecture Notes on Partial Differential Equations Chapter IV Fourier Series Ilyasse Aksikas Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta aksikas@ualberta.ca DEFINITIONS 2 Before
NOTES 10: ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY
 NOTES 0: ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON 0. USING FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC INDENTITIES Reciprocal Identities sin csc cos sec
NOTES 0: ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON 0. USING FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC INDENTITIES Reciprocal Identities sin csc cos sec
Find all solutions cos 6. Find all solutions. 7sin 3t Find all solutions on the interval [0, 2 ) sin t 15cos t sin.
 7.1 Solving Trigonometric Equations with Identities In this section, we explore the techniques needed to solve more complex trig equations: By Factoring Using the Quadratic Formula Utilizing Trig Identities
7.1 Solving Trigonometric Equations with Identities In this section, we explore the techniques needed to solve more complex trig equations: By Factoring Using the Quadratic Formula Utilizing Trig Identities
MATH 261 MATH 261: Elementary Differential Equations MATH 261 FALL 2005 FINAL EXAM FALL 2005 FINAL EXAM EXAMINATION COVER PAGE Professor Moseley
 MATH 6 MATH 6: Elementary Differential Equations MATH 6 FALL 5 FINAL EXAM FALL 5 FINAL EXAM EXAMINATION COVER PAGE Professor Moseley PRINT NAME ( ) Last Name, First Name MI (What you wish to be called)
MATH 6 MATH 6: Elementary Differential Equations MATH 6 FALL 5 FINAL EXAM FALL 5 FINAL EXAM EXAMINATION COVER PAGE Professor Moseley PRINT NAME ( ) Last Name, First Name MI (What you wish to be called)
TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 CHAPTER 1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 CHAPTER 1 Set Lnguge & Nottion 3 CHAPTER 2 Functions 3 CHAPTER 3 Qudrtic Functions 4 CHAPTER 4 Indices & Surds 4 CHAPTER 5 Fctors of Polynomils 4 CHAPTER 6 Simultneous Equtions 4 CHAPTER
TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 CHAPTER 1 Set Lnguge & Nottion 3 CHAPTER 2 Functions 3 CHAPTER 3 Qudrtic Functions 4 CHAPTER 4 Indices & Surds 4 CHAPTER 5 Fctors of Polynomils 4 CHAPTER 6 Simultneous Equtions 4 CHAPTER
Reversing the Chain Rule. As we have seen from the Second Fundamental Theorem ( 4.3), the easiest way to evaluate an integral b
 Mth 32 Substitution Method Stewrt 4.5 Reversing the Chin Rule. As we hve seen from the Second Fundmentl Theorem ( 4.3), the esiest wy to evlute n integrl b f(x) dx is to find n ntiderivtive, the indefinite
Mth 32 Substitution Method Stewrt 4.5 Reversing the Chin Rule. As we hve seen from the Second Fundmentl Theorem ( 4.3), the esiest wy to evlute n integrl b f(x) dx is to find n ntiderivtive, the indefinite
Analysis II: Fourier Series
 .... Analysis II: Fourier Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American May 3, 011 K.Maruno (UT-Pan American) Analysis II May 3, 011 1 / 16 Fourier series were
.... Analysis II: Fourier Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American May 3, 011 K.Maruno (UT-Pan American) Analysis II May 3, 011 1 / 16 Fourier series were
Study # 1 11, 15, 19
 Goals: 1. Recognize Taylor Series. 2. Recognize the Maclaurin Series. 3. Derive Taylor series and Maclaurin series representations for known functions. Study 11.10 # 1 11, 15, 19 f (n) (c)(x c) n f(c)+
Goals: 1. Recognize Taylor Series. 2. Recognize the Maclaurin Series. 3. Derive Taylor series and Maclaurin series representations for known functions. Study 11.10 # 1 11, 15, 19 f (n) (c)(x c) n f(c)+
13.4. Integration by Parts. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Integrtion by Prts 13.4 Introduction Integrtion by Prts is technique for integrting products of functions. In this Section you will lern to recognise when it is pproprite to use the technique nd hve the
Integrtion by Prts 13.4 Introduction Integrtion by Prts is technique for integrting products of functions. In this Section you will lern to recognise when it is pproprite to use the technique nd hve the
An investigation of the comparative efficiency of the different methods in which π is calculated
 An investigation of the comparative efficiency of the different methods in which π is calculated Nouri Al-Othman arxiv:1310.5610v1 [math.ca] 17 Oct 013 October, 013 1 Abstract An investigation of the comparative
An investigation of the comparative efficiency of the different methods in which π is calculated Nouri Al-Othman arxiv:1310.5610v1 [math.ca] 17 Oct 013 October, 013 1 Abstract An investigation of the comparative
Euler-Maclaurin Summation Formula 1
 Jnury 9, Euler-Mclurin Summtion Formul Suppose tht f nd its derivtive re continuous functions on the closed intervl [, b]. Let ψ(x) {x}, where {x} x [x] is the frctionl prt of x. Lemm : If < b nd, b Z,
Jnury 9, Euler-Mclurin Summtion Formul Suppose tht f nd its derivtive re continuous functions on the closed intervl [, b]. Let ψ(x) {x}, where {x} x [x] is the frctionl prt of x. Lemm : If < b nd, b Z,
Improper Integrals, and Differential Equations
 Improper Integrls, nd Differentil Equtions October 22, 204 5.3 Improper Integrls Previously, we discussed how integrls correspond to res. More specificlly, we sid tht for function f(x), the region creted
Improper Integrls, nd Differentil Equtions October 22, 204 5.3 Improper Integrls Previously, we discussed how integrls correspond to res. More specificlly, we sid tht for function f(x), the region creted
Introduction and Review
 Chpter 6A Notes Pge of Introuction n Review Derivtives y = f(x) y x = f (x) Evlute erivtive t x = : y = x x= f f(+h) f() () = lim h h Geometric Interprettion: see figure slope of the line tngent to f t
Chpter 6A Notes Pge of Introuction n Review Derivtives y = f(x) y x = f (x) Evlute erivtive t x = : y = x x= f f(+h) f() () = lim h h Geometric Interprettion: see figure slope of the line tngent to f t
Fourier Sin and Cos Series and Least Squares Convergence
 Fourier and east Squares Convergence James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University May 7, 28 Outline et s look at the original Fourier sin
Fourier and east Squares Convergence James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University May 7, 28 Outline et s look at the original Fourier sin
PDE Notes. Paul Carnig. January ODE s vs PDE s 1
 PDE Notes Pul Crnig Jnury 2014 Contents 1 ODE s vs PDE s 1 2 Section 1.2 Het diffusion Eqution 1 2.1 Fourier s w of Het Conduction............................. 2 2.2 Energy Conservtion.....................................
PDE Notes Pul Crnig Jnury 2014 Contents 1 ODE s vs PDE s 1 2 Section 1.2 Het diffusion Eqution 1 2.1 Fourier s w of Het Conduction............................. 2 2.2 Energy Conservtion.....................................
Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 32: 10.2 Fourier Series
 Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 32: 1.2 Fourier Series Shawn D. Ryan Spring 212 Last Time: We studied the heat equation and the method of Separation of Variabes. We then used Separation
Lecture Notes for Math 251: ODE and PDE. Lecture 32: 1.2 Fourier Series Shawn D. Ryan Spring 212 Last Time: We studied the heat equation and the method of Separation of Variabes. We then used Separation
Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 2008
 Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 8 Contents Fourier Series. The coefficients........................................ Convergence......................................... 4.3 Convergence
Math 489AB A Very Brief Intro to Fourier Series Fall 8 Contents Fourier Series. The coefficients........................................ Convergence......................................... 4.3 Convergence
Fourier Series and Their Applications
 Fourier Series nd Their Applictions Rui iu My, 006 Abstrct Fourier series re of gret importnce in both theoreticl nd pplied mthemtics. For orthonorml fmilies of complex vlued functions {φ n}, Fourier Series
Fourier Series nd Their Applictions Rui iu My, 006 Abstrct Fourier series re of gret importnce in both theoreticl nd pplied mthemtics. For orthonorml fmilies of complex vlued functions {φ n}, Fourier Series
Review SOLUTIONS: Exam 2
 Review SOUTIONS: Exm. True or Flse? (And give short nswer ( If f(x is piecewise smooth on [, ], we cn find series representtion using either sine or cosine series. SOUTION: TRUE. If we use sine series,
Review SOUTIONS: Exm. True or Flse? (And give short nswer ( If f(x is piecewise smooth on [, ], we cn find series representtion using either sine or cosine series. SOUTION: TRUE. If we use sine series,
π π π π Trigonometry Homework Booklet 1. Convert 5.3 radians to degrees. A B C D Determine the period of 15
 Trigonometry Homework Booklet 1. Convert 5.3 radians to degrees. A. 0.09 B. 0.18 C. 151.83 D. 303.67. Determine the period of y = 6cos x + 8. 15 15 A. B. C. 15 D. 30 15 3. Determine the exact value of
Trigonometry Homework Booklet 1. Convert 5.3 radians to degrees. A. 0.09 B. 0.18 C. 151.83 D. 303.67. Determine the period of y = 6cos x + 8. 15 15 A. B. C. 15 D. 30 15 3. Determine the exact value of
Physics 250 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations
 Physics 25 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations Peter Young November 25, 27 Homogeneous Equations We have already discussed second order linear homogeneous differential equations, which
Physics 25 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations Peter Young November 25, 27 Homogeneous Equations We have already discussed second order linear homogeneous differential equations, which
Section Areas and Distances. Example 1: Suppose a car travels at a constant 50 miles per hour for 2 hours. What is the total distance traveled?
 Section 5. - Ares nd Distnces Exmple : Suppose cr trvels t constnt 5 miles per hour for 2 hours. Wht is the totl distnce trveled? Exmple 2: Suppose cr trvels 75 miles per hour for the first hour, 7 miles
Section 5. - Ares nd Distnces Exmple : Suppose cr trvels t constnt 5 miles per hour for 2 hours. Wht is the totl distnce trveled? Exmple 2: Suppose cr trvels 75 miles per hour for the first hour, 7 miles
Mathematics 1. (Integration)
 Mthemtics 1. (Integrtion) University of Debrecen 2018-2019 fll Definition Let I R be n open, non-empty intervl, f : I R be function. F : I R is primitive function of f if F is differentible nd F = f on
Mthemtics 1. (Integrtion) University of Debrecen 2018-2019 fll Definition Let I R be n open, non-empty intervl, f : I R be function. F : I R is primitive function of f if F is differentible nd F = f on
4 1-D Boundary Value Problems Heat Equation
 4 -D Boundary Vaue Probems Heat Equation The main purpose of this chapter is to study boundary vaue probems for the heat equation on a finite rod a x b. u t (x, t = ku xx (x, t, a < x < b, t > u(x, = ϕ(x
4 -D Boundary Vaue Probems Heat Equation The main purpose of this chapter is to study boundary vaue probems for the heat equation on a finite rod a x b. u t (x, t = ku xx (x, t, a < x < b, t > u(x, = ϕ(x
SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION. Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis
 SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis Fourier Series & Fourier Transforms Fourier Series Review of trigonometric identities Analysing the square wave Fourier Transform Transforms of some
SEISMIC WAVE PROPAGATION Lecture 2: Fourier Analysis Fourier Series & Fourier Transforms Fourier Series Review of trigonometric identities Analysing the square wave Fourier Transform Transforms of some
UNIFORM CONVERGENCE MA 403: REAL ANALYSIS, INSTRUCTOR: B. V. LIMAYE
 UNIFORM CONVERGENCE MA 403: REAL ANALYSIS, INSTRUCTOR: B. V. LIMAYE 1. Pointwise Convergence of Sequence Let E be set nd Y be metric spce. Consider functions f n : E Y for n = 1, 2,.... We sy tht the sequence
UNIFORM CONVERGENCE MA 403: REAL ANALYSIS, INSTRUCTOR: B. V. LIMAYE 1. Pointwise Convergence of Sequence Let E be set nd Y be metric spce. Consider functions f n : E Y for n = 1, 2,.... We sy tht the sequence
The Riemann Integral
 Deprtment of Mthemtics King Sud University 2017-2018 Tble of contents 1 Anti-derivtive Function nd Indefinite Integrls 2 3 4 5 Indefinite Integrls & Anti-derivtive Function Definition Let f : I R be function
Deprtment of Mthemtics King Sud University 2017-2018 Tble of contents 1 Anti-derivtive Function nd Indefinite Integrls 2 3 4 5 Indefinite Integrls & Anti-derivtive Function Definition Let f : I R be function
4.4 Areas, Integrals and Antiderivatives
 . res, integrls nd ntiderivtives 333. Ares, Integrls nd Antiderivtives This section explores properties of functions defined s res nd exmines some connections mong res, integrls nd ntiderivtives. In order
. res, integrls nd ntiderivtives 333. Ares, Integrls nd Antiderivtives This section explores properties of functions defined s res nd exmines some connections mong res, integrls nd ntiderivtives. In order
MTH301 Calculus II Solved Final Term Papers For Final Term Exam Preparation
 MTH301 Calculus II Solved Final Term Papers For Final Term Exam Preparation Question No: 1 Laplace transform of t is 1 s 1 s 2 e s s Question No: 2 Symmetric equation for the line through (1,3,5) and (2,-2,3)
MTH301 Calculus II Solved Final Term Papers For Final Term Exam Preparation Question No: 1 Laplace transform of t is 1 s 1 s 2 e s s Question No: 2 Symmetric equation for the line through (1,3,5) and (2,-2,3)
Math 8 Winter 2010 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions - 1. xcos 6xdx = 4. = x2 4
 Math 8 Winter 21 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions - 1 1 Evaluate xcos 2 3x Solution: First rewrite cos 2 3x using the half-angle formula: ( ) 1 + cos 6x xcos 2 3x = x = 1 x + 1 xcos 6x. 2 2 2 Now use
Math 8 Winter 21 Midterm 2 Review Problems Solutions - 1 1 Evaluate xcos 2 3x Solution: First rewrite cos 2 3x using the half-angle formula: ( ) 1 + cos 6x xcos 2 3x = x = 1 x + 1 xcos 6x. 2 2 2 Now use
APPLIED MATHEMATICS Part 4: Fourier Analysis
 APPLIED MATHEMATICS Part 4: Fourier Analysis Contents 1 Fourier Series, Integrals and Transforms 2 1.1 Periodic Functions. Trigonometric Series........... 3 1.2 Fourier Series..........................
APPLIED MATHEMATICS Part 4: Fourier Analysis Contents 1 Fourier Series, Integrals and Transforms 2 1.1 Periodic Functions. Trigonometric Series........... 3 1.2 Fourier Series..........................
The Fourier series for a 2π-periodic function
 The Fourier series for a 2π-periodic function Let f : ( π, π] R be a bounded piecewise continuous function which we continue to be a 2π-periodic function defined on R, i.e. f (x + 2π) = f (x), x R. The
The Fourier series for a 2π-periodic function Let f : ( π, π] R be a bounded piecewise continuous function which we continue to be a 2π-periodic function defined on R, i.e. f (x + 2π) = f (x), x R. The
CHAPTER 105 A NUMERICAL METHOD OF HARMONIC ANALYSIS
 CHAPTER 5 A NUMERICAL METHOD OF HARMONIC ANALYSIS EXERCISE 368 Pge 88. Determine the Fourier series to reresent the eriodic function given b the tble of vlues, u to nd including the third hrmonic nd ech
CHAPTER 5 A NUMERICAL METHOD OF HARMONIC ANALYSIS EXERCISE 368 Pge 88. Determine the Fourier series to reresent the eriodic function given b the tble of vlues, u to nd including the third hrmonic nd ech
Section 7.2 Addition and Subtraction Identities. In this section, we begin expanding our repertoire of trigonometric identities.
 Section 7. Addition and Subtraction Identities 47 Section 7. Addition and Subtraction Identities In this section, we begin expanding our repertoire of trigonometric identities. Identities The sum and difference
Section 7. Addition and Subtraction Identities 47 Section 7. Addition and Subtraction Identities In this section, we begin expanding our repertoire of trigonometric identities. Identities The sum and difference
8/19/16. Fourier Analysis. Fourier analysis: the dial tone phone. Fourier analysis: the dial tone phone
 Patrice Koehl Department of Biological Sciences National University of Singapore http://www.cs.ucdavis.edu/~koehl/teaching/bl5229 koehl@cs.ucdavis.edu Fourier analysis: the dial tone phone We use Fourier
Patrice Koehl Department of Biological Sciences National University of Singapore http://www.cs.ucdavis.edu/~koehl/teaching/bl5229 koehl@cs.ucdavis.edu Fourier analysis: the dial tone phone We use Fourier
The goal of today is to determine what u-substitution to use for trigonometric integrals. The most common substitutions are the following:
 Trigonometric Integrals The goal of today is to determine what u-substitution to use for trigonometric integrals. The most common substitutions are the following: Substitution u sinx u cosx u tanx u secx
Trigonometric Integrals The goal of today is to determine what u-substitution to use for trigonometric integrals. The most common substitutions are the following: Substitution u sinx u cosx u tanx u secx
10.12 INTRODUCTION TO FOURIER SERIES
 10.12 Fourier Series Contemporary Calculus 1 10.12 INTRODUCTION TO FOURIER SERIES When we discussed Maclaurin series in earlier sections we used information about the derivatives of a function f(x) to
10.12 Fourier Series Contemporary Calculus 1 10.12 INTRODUCTION TO FOURIER SERIES When we discussed Maclaurin series in earlier sections we used information about the derivatives of a function f(x) to
Mathematics for Engineers II. lectures. Power series, Fourier series
 Power series, Fourier series Power series, Taylor series It is a well-known fact, that 1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + = n=0 x n = 1 1 x if 1 < x < 1. On the left hand side of the equation there is sum containing
Power series, Fourier series Power series, Taylor series It is a well-known fact, that 1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + = n=0 x n = 1 1 x if 1 < x < 1. On the left hand side of the equation there is sum containing
Maths 381 The First Midterm Solutions
 Maths 38 The First Midterm Solutions As Given by Peter Denton October 8, 8 # From class, we have that If we make the substitution y = x 3/, we get # Once again, we use the fact that and substitute into
Maths 38 The First Midterm Solutions As Given by Peter Denton October 8, 8 # From class, we have that If we make the substitution y = x 3/, we get # Once again, we use the fact that and substitute into
Final Review, Math 1860 Thomas Calculus Early Transcendentals, 12 ed
 Finl Review, Mth 860 Thoms Clculus Erly Trnscendentls, 2 ed 6. Applictions of Integrtion: 5.6 (Review Section 5.6) Are between curves y = f(x) nd y = g(x), x b is f(x) g(x) dx nd similrly for x = f(y)
Finl Review, Mth 860 Thoms Clculus Erly Trnscendentls, 2 ed 6. Applictions of Integrtion: 5.6 (Review Section 5.6) Are between curves y = f(x) nd y = g(x), x b is f(x) g(x) dx nd similrly for x = f(y)
Mathematical MCQ for international students admitted to École polytechnique
 Mathematical MCQ for international students admitted to École polytechnique This multiple-choice questionnaire is intended for international students admitted to the first year of the engineering program
Mathematical MCQ for international students admitted to École polytechnique This multiple-choice questionnaire is intended for international students admitted to the first year of the engineering program
Power Series Solutions We use power series to solve second order differential equations
 Objectives Power Series Solutions We use power series to solve second order differential equations We use power series expansions to find solutions to second order, linear, variable coefficient equations
Objectives Power Series Solutions We use power series to solve second order differential equations We use power series expansions to find solutions to second order, linear, variable coefficient equations
Exam 3 Solutions. Multiple Choice Questions
 MA 4 Exam 3 Solutions Fall 26 Exam 3 Solutions Multiple Choice Questions. The average value of the function f (x) = x + sin(x) on the interval [, 2π] is: A. 2π 2 2π B. π 2π 2 + 2π 4π 2 2π 4π 2 + 2π 2.
MA 4 Exam 3 Solutions Fall 26 Exam 3 Solutions Multiple Choice Questions. The average value of the function f (x) = x + sin(x) on the interval [, 2π] is: A. 2π 2 2π B. π 2π 2 + 2π 4π 2 2π 4π 2 + 2π 2.
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department of Mathematics Semester 1, 2002/2003 MA1505 Math I Suggested Solutions to T. 3
 NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Deprtment of Mthemtics Semester, /3 MA55 Mth I Suggested Solutions to T. 3. Using the substitution method, or otherwise, find the following integrls. Solution. ) b) x sin(x
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Deprtment of Mthemtics Semester, /3 MA55 Mth I Suggested Solutions to T. 3. Using the substitution method, or otherwise, find the following integrls. Solution. ) b) x sin(x
CHAPTER 5: Analytic Trigonometry
 ) (Answers for Chapter 5: Analytic Trigonometry) A.5. CHAPTER 5: Analytic Trigonometry SECTION 5.: FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Left Side Right Side Type of Identity (ID) csc( x) sin x Reciprocal
) (Answers for Chapter 5: Analytic Trigonometry) A.5. CHAPTER 5: Analytic Trigonometry SECTION 5.: FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES Left Side Right Side Type of Identity (ID) csc( x) sin x Reciprocal
Math 3B Final Review
 Mth 3B Finl Review Written by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 9:45-10:45m SH 1607 Mth Lb Hours: TR 1-2pm Lst updted: 12/06/14 This is continution of the midterm review. Prctice problems
Mth 3B Finl Review Written by Victori Kl vtkl@mth.ucsb.edu SH 6432u Office Hours: R 9:45-10:45m SH 1607 Mth Lb Hours: TR 1-2pm Lst updted: 12/06/14 This is continution of the midterm review. Prctice problems
Grade: The remainder of this page has been left blank for your workings. VERSION D. Midterm D: Page 1 of 12
 First Name: Student-No: Last Name: Section: Grade: The remainder of this page has been left blank for your workings. Midterm D: Page of 2 Indefinite Integrals. 9 marks Each part is worth marks. Please
First Name: Student-No: Last Name: Section: Grade: The remainder of this page has been left blank for your workings. Midterm D: Page of 2 Indefinite Integrals. 9 marks Each part is worth marks. Please
1 + lim. n n+1. f(x) = x + 1, x 1. and we check that f is increasing, instead. Using the quotient rule, we easily find that. 1 (x + 1) 1 x (x + 1) 2 =
 Chapter 5 Sequences and series 5. Sequences Definition 5. (Sequence). A sequence is a function which is defined on the set N of natural numbers. Since such a function is uniquely determined by its values
Chapter 5 Sequences and series 5. Sequences Definition 5. (Sequence). A sequence is a function which is defined on the set N of natural numbers. Since such a function is uniquely determined by its values
