CDMS and SuperCDMS. SLAC Summer Institute - CDMS. August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS
|
|
|
- Alison Marsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CDMS and SuperCDMS SLAC Summer Institute August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS CDMS-II science results - less than 1 evt / kg of Ge / month Status of CDMS-II 5-Tower run - target < 1 evt / kg of Ge / year SuperCDMS 25 kg experiment - Two SuperTowers at Soudan (DOE & NSF started FY07) - SuperCDMS 25 kg at SNOLab (review FY08 for FY09 start) EDELWEISS and CRESST status & plans leading to EUREKA Comparisons with liquid experiments: XENON, WArP, COUPP Conclusions Page 1
2 Composition of the Cosmos WMAP best fit Dark matter forms structure of universe WIMPs warm Page 2
3 Numerical simulations for DM Halos The phase-space structure of a dark-matter halo: Implications for dark-matter direct detection experiments, e.g., A. Helmi, S. White, and V. Springel PRD 66, (2002) Solar system moves with respect to zero mean velocity halo at 220 km/s Page 3
4 What is the dark matter? GUT monopoles L. Roszkowski Page 4
5 The Signal and Backgrounds Signal (WIMPs) Background (gammas) Nucleus Recoils E r Electron Recoils E r v/c E r 10 s KeV phonons v/c 0.3 ionization Neutrons also interact with nuclei, but mean free path a few cms Surface electrons from beta decay can mimic nuclear recoils χ 0 γ Page 5
6 Status of Direction Detection Search Cross-section [cm 2 ] (normalised to nucleon) DAMA Gaitskell,Mandic,Filippini CDMS Soudan XENON10 APS2007 CDMS Soudan Proj LUX 300kg Proj SuperCDMS SNOLab Proj KIMS CRESST EDELWEISS ZEPLIN II WARP 1 ev/kg/month 1 ev/kg/year 1 ev/10 kg/year 1 ev/ton/year WIMP Mass [GeV] Variety of techniques search for WIMP dark matter - interesting sensitivity Several have the potential to reach cm 2 soon and cm 2 in future Page 6
7 Discrimination strategies Most particle physics experience in MeV range Direct detection requires kev scale DAMA ZEPLIN I DEAP CLEAN CRESST Scintillation ~ 1 kev/γ Phonons 10 mev/ph ZEPLIN XENON WArP, ArDM Ionization ~ 10 ev/e Sub-K low threshold large mass >$$ CDMS EDELWEISS need both to confirm results Scintillation higher threshold & large fluctuations Noble liquids high threshold but large mass <$$ Page 7
8 CDMS Collaboration UC Berkeley, Stanford, LBNL, UC Santa Barbara, Case Western Reserve U, FNAL, Santa Clara U, NIST, U Colorado Denver, Brown U, U Minnesota, U Florida, Princeton Page 8
9 CDMS-II at Soudan (2090 mwe) At SUF 17 mwe 0.5 n/d/kg At Soudan 2090 mwe 0.6 n/y/kg At SNOLab 6060 mwe 1 n/y/ton Log 10 (Muon Flux) (m -2 s -1 ) Depth (meters water equivalent) Page 9
10 CDMS-II Soudan facility lead plastic scintillators outer polyethylene ancient lead inner polyethylene Page 10
11 Run 118 (1T) & Run 119 (2T) in Soudan Page 11
12 CDMS Active Background Rejection Detectors with excellent event-by-event background rejection Measured background rejection: % for EM backgrounds using charge/heat 99.4% for β s using pulse risetime as well Much better than expected in CDMS II proposal! Tower of 6 ZIPs Tower 1 4 Ge neutrons betas gammas gammas 2 Si betas Tower 2 2 Ge 4 Si neutrons Page 12
13 Really Cool Detectors: ZIPs z y x Z-sensitive Ionization and Phonon-mediated Measure ionization in low-field (~volts/cm) with segmented contacts to allow rejection of events near outer edge Q outer low-noise FET Q inner Page g Ge or 100 g Si crystal 1 cm thick x 7.5 cm diameter Photolithographic patterning Collect athermal phonons: Crystal lattice vibrations Speed of sound in crystal ~ 1 cm/ms results in measurable delays between the pulses of the 4 phonon channels => distinguish surface from bulk events 1 µ tungsten 380µ x 60µ aluminum fins
14 Model ZIP Detector Signal Charge & Phonon signals occur on a similar timescale Phonon pulse time of arrival allows for event position reconstruction 20 kev event in a Si & Ge ZIP Si ZIP Ge ZIP (EXCELLENT S/N FOR 20 KeV TRUE RECOIL ENERGY) Page 14
15 ZIP Phonon Position Sensitivity A Delay Plot D Am 241 : γ 14, 18, 20, 26, 60 kev Cd Al foil : γ 22 kev B C Page 15
16 Energy calibration of Ge ZIP with 133 Ba source Ionization energy in kev Phonon energy (prg) in kev Excellent agreement between data and Monte Carlo Page 16
17 Nuclear recoil calibration: Ge&Si ZIPs w/ 252 Cf Nuclear recoils in Ge ZIP Nuclear recoils in Si ZIP Excellent agreement between data and Monte Carlo Page 17
18 1.5 WIMP search data (5 Ge ZIPs ~53 kg-d) Prior to phonon pulse shape timing cuts 10.4 kev Gallium line 1.5 After timing cuts, which reject most electron recoils Z2/Z3/Z5/Z9/Z11 Ionization Yield Z2/Z3/Z5/Z9/Z Recoil Energy (kev) Ionization Yield candidate (barely) 1 near-miss Recoil Energy (kev) Background ESTIMATE: 0.37 ± 0.20 (sys.) ± 0.15 (stat.) electron recoils, 0.05 recoils from neutrons expected Page 18
19 Is the Candidate Event Just Background? Very likely so! Event occurred during run when its detector, Z11, suffered reduced ionization yield Worst run for this detector In hindsight, our cuts on bad data periods for single detectors weren t strict enough Some other detectors, without candidates, had similarly bad periods Will improve data quality screening for next run Ionization Yield Ba calibration for comparison Candidate time (hours) Automatic LED flash to reneutralize detectors Page 19
20 Improvements in Surface Event Rejection Significant improvements in our analysis of phonon timing information Surface event rejection improved by x3; kept pace with exposure increase! Cuts are set from calibration data (blind analysis) We still have more discrimination power available as needed Can continue to keep backgrounds < 1 event as more data accumulates This is the real strength of CDMS detectors! Surface Events Optimize background rejection versus nuclear recoil efficiency Neutron Efficiency Neutrons Chi-square (background pulse shape) - Chi-squared (neutron pulse shape) Page 20
21 How the detectors work Measure both heat and ionization produced Page 21
22 Develop detailed detector MC Compare signal collected in one quadrant versus x- y averaged over z for real ZIP T1Z5 (left) and simulated mzip (right) ZIP T1Z5 0.6 Simulated mzip Pa / Ptot Pa / Ptot y [cm] 2 0!2!4!4!3!2! x [cm] 4 0 y [cm] 2 0!2!4!4!3!2! x [cm] Page 22
23 Scientific reach of CDMS at Soudan DAMA ZEPLIN-1 SUSY Models Edelweiss CDMS II - Current new XENON10 preprint CDMS II -projected Page 23
24 Sensitivity issues for Ge and Xe limits at low mass very sensitive to threshold effects WIMP!Nucleon Cross!Section [cm 2 ] 10!42 10!43 10!44 10 kevr analysis threshold include 5-10 kevr CDMS II 2-Towers XENON10 preprint 4.5 kevr threshold with Q = 0.19 ~8 kevr threshold with variable Q WIMP Mass [GeV] limits at high mass robust Page 24
25 Spin Dependent WIMP limits Spin-sensitivity from 73 Ge (J=9/2, 7.7%) and 29 Si (J=1/2, 4.7%) n scattering p scattering CRESST I CDMS Si CDMS II Si DAMA/NaI PICASSO CRESST I CDMS II Ge PICASSO CDMS II Si ZEPLIN I CDMS II Ge DAMA/NaI NAIAD Majorana ν Super-K Majorana ν For further details see PRD D73, (2006) Page 25
26 Five Towers now in Soudan Tower 1: 4 Ge & 2 Si Tower 2: 2 Ge & 4 Si Tower 3: 4 Ge & 2 Si Tower 4: 4 Ge & 2 Si Tower 5: 5 Ge & 1 Si Page 26
27 Fermilab PAC - SuperCDMS Page 27 Blas Cabrera for SuperCDMS collaboration
28 Page 28
29 Proposal to DOE and NSF - May 06 SuperCDMS 25 kg Experiment The SuperCDMS Collaboration California Institute of Technology Case Western Reserve University Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory National Institute of Standards and Technology, Boulder Queen s University, Canada Santa Clara University Stanford University University of California at Berkeley University of California at Santa Barbara University of Colorado at Denver and Health Sciences Center University of Florida University of Minnesota Spokesperson: Blas Cabrera Co-spokesperon: Dan Akerib Project Manager: Dan Bauer Chair of Board: Bernard Sadoulet Page 29
30 Scientific reach of SuperCDMS 25 kg Explore very interesting region which is complementary to LHC SuperCDMS including 5 events for LCC2 25 kg Experiment Project Cross-section [cm 2 ] (normalised to nucleon) DAMA 1 Introduction WIMP Mass [GeV] CDMS II 2005 EDELWEISS ZEPLIN I CDMS II 2007 This proposal requests funding LCC2 for the Super- CDMS 25 kg Experiment that will improve sensitivity for directlcc1 detection of weakly-interacting massive particles (WIMPs) by 120 beyond the existing sensitivity. The proposed five-year program would (1) continue operation of the five CDMS II towers, (2) fabricate and operate at our existing Soudan facility two SuperTowers, and (3) 10 fabricate -48 and operate at a new SNOLAB facility seven SuperTowers. to nucleon) high discovery potential now DAMA EDELWEISS ZEPLIN I SuperCDMS 25kg CDMS II 2005 I 2007 Experiment Cross-section sensitivity CDMS II 2-T (2005) cm 2 CDMS II 5-T (2007) cm 2 SuperCDMS Detectors 2-ST at Soudan (2009) cm 2 SuperCDMS 25 kg 7-ST at SNOLAB (2012) cm 2 Table 1: WIMP-nucleon scattering cross-section goals for CDMS-II and for the proposed SuperCDMS 25 kg Experiment program (see Fig. 1). A WIMP mass of 60 GeV/c 2 is assumed with no background subtraction, where backgrounds are listed in Table 3. The ending dates are shown for completed and expected runs. in Table 1, the SuperCDMS 25 kg Experiment Page 30 program is complementary to explorations of supersymmetry and other physics beyond the Standard Model at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC),
31 Sensitivity reach with full bkgd analysis CDMS II T1 Jan 04 Current limit T1-2 Aug 04 no subtraction --- bkgd subtraction zero background CDMS 2007 SuperCDMS Soudan 2009 SuperCDMS 25kg 2012 x15 x120 SuperCDMS 150kg Page 31
32 SUF (17 mwe), Soudan (2090 mwe), & SNOLab (6060 mwe) At SUF 17 mwe 0.5 n/d/kg At Soudan 2090 mwe 0.6 n/y/kg At SNOLab 6060 mwe 1 n/y/ton Log 10 (Muon Flux) (m -2 s -1 ) Depth (meters water equivalent) Page 32
33 SuperCDMS is approved to be sited at SNOLab SuperCDMS at SNOLab We have received strong interest from Canadian collaborators - Queens... New lab space (under construction - ready in 2007) Sudbury, Ont. CA Sudbury Neutron Obs. Page 33
34 SuperCDMS in Expanded Ladder Lab SuperCDMS 25 kg Experiment Fermilab PAC - SuperCDMS Page 34 Blas Cabrera for SuperCDMS collaboration
35 ST1&2 Soudan -> SNOLab like Tower 1 SUF -> Soudan Tower 1 (4 Ge & 2 Si) at SUF (Stanford) then at Soudan 19 neutron events at SUF 0 events at Soudan Page 35
36 Baseline detector for SuperCDMS CDMS-II ZIPs: 3 dia x 1 cm => 0.25 kg of Ge Existing ZIPs SuperCDMS ZIPs: 3 dia x 1 => 0.64 kg of Ge ZIPs for SuperCDMS Page 36
37 1 thick ZIP processing at Stanford dedicated sputtering system (in use) 1 Substrate aligner (in use) - plan new dedicated unit 1 Substrate spinner (in use) dry etch (in use) Page 37
38 Data from UCB/Case TFs for Si 1 ZIP First data from 1 Si ZIP showing reconstructed location of 109 Cd events and spectrum Y Delay [μs] X Delay [μs] Number Q in [kevee] Yield Risetime [μs] neutrons Recoil [kev] Yield Page 38
39 Data from UCB/Case TFs for Ge 1 ZIP First data from 1 Ge ZIP showing 241 Am 60 kev gamma events in phonon vs charge Charge Number delay cut around source Phonon Q in [kevee] Page 39
40 Improved background rejection and reduction Background rejection 4 Analysis discrimination 2 Background reduction 5 Total Improvement = 40 Production rate per kg 5 Table 2: Targeted improvement factors over CDMS II advanced analysis levels (see Section 3.2) to achieve SuperCDMS 25 kg sensitivities with zero background from internal sources. The cosmogenic fast-neutron background is eliminated by the SNO- LAB overburden of 6000 mwe. to meet SuperCDMS 25 kg goals only need x20 actual Increase phonon collection area x2 and new H-a-Si electrodes suppress charge backdiffusion x2 Expect at least an additional x2 from advanced timing analyses Expect x2.5 from additional thickness and x2 from better control of Rn Need x20 of this x40 total for the SuperCDMS 25 kg target background Expect x2.5 from additional thickness and x2 from improved fabrication efficiency Page 40
41 Schematic of new SNObox Page 41
42 Status of Direction Detection Search Cross-section [cm 2 ] (normalised to nucleon) DAMA Gaitskell,Mandic,Filippini CDMS Soudan XENON10 APS2007 CDMS Soudan Proj LUX 300kg Proj SuperCDMS SNOLab Proj KIMS CRESST EDELWEISS ZEPLIN II WARP 1 ev/kg/month 1 ev/kg/year 1 ev/10 kg/year 1 ev/ton/year WIMP Mass [GeV] Variety of techniques search for WIMP dark matter - interesting sensitivity Several have the potential to reach cm 2 soon and cm 2 in future Page 42
43 Conclusion Soudan Towers 1&2 lead field by x10 - spin-independent limits PRL 2006 and spin dependent limits PRD RC XENON10 preprint now leads field by x2 at high mass Soudan Towers 1-5 will start mid-2006 and run through 2007 for an additional x10 improved sensitivity. We have a great horse race for discovering WIMPs Strong science case for ton scale direct detection major projects, as endorsed by Dark Matter SAG and P5. WE ARE APPROVED TO PROCEED WITH 2 OF 7 TOWERS FOR SuperCDMS 25 kg EXPERIMENT, AND REVIEWS DURING FY08 FOR APPROVAL OF REMAING 5 TOWERS. WE CAN HELP MAINTAIN US LEAD IN THIS RESEARCH WHICH IS COMPLEMENTARY TO LHC AND FUTURE ILC. Page 43
Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS
 Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS TeV 2006, Madison - August 30, 2006 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS Summary of current status of Direct
Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS TeV 2006, Madison - August 30, 2006 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS Summary of current status of Direct
Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors
 Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors Complementarity between Dark Matter Searches & Collider Experiments Miniworkshop before SUSY06 at Irvine -
Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors Complementarity between Dark Matter Searches & Collider Experiments Miniworkshop before SUSY06 at Irvine -
DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO
 Search for Dark Matter WIMPs: SuperCDMS Soudan Soudan and SNOLAB leading to GEODM at DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO - September 17, 2009 Blas Cabrera - Stanford
Search for Dark Matter WIMPs: SuperCDMS Soudan Soudan and SNOLAB leading to GEODM at DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO - September 17, 2009 Blas Cabrera - Stanford
SuperCDMS at SNOLAB. What is CDMS? Technical Progress. Collaboration. Funding. Schedule and Needs. Why is SuperCDMS 25 kg timely?
 What is CDMS? SuperCDMS at SNOLAB Why is SuperCDMS 25 kg timely? Technical Progress CDMS II running at Soudan (4.5 kg Ge) Detectors Cryogenics Backgrounds Electronics Infrastructure Collaboration Addition
What is CDMS? SuperCDMS at SNOLAB Why is SuperCDMS 25 kg timely? Technical Progress CDMS II running at Soudan (4.5 kg Ge) Detectors Cryogenics Backgrounds Electronics Infrastructure Collaboration Addition
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search. Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration
 SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT
 WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT P.L. BRINK, L. BAUDIS, B. CABRERA, J.P. CASTLE, C. CHANG AND T. SAAB Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94350, USA R. J. GAITSKELL
WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT P.L. BRINK, L. BAUDIS, B. CABRERA, J.P. CASTLE, C. CHANG AND T. SAAB Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94350, USA R. J. GAITSKELL
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector. WIMP Search. Mani Tripathi, INPAC Meeting. Berkeley, May 5, 2007
 LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment
 Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Kevin A. McCarthy Massachusetts Institute of Technology On behalf of the SuperCDMS and CDMS Collaborations
Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Kevin A. McCarthy Massachusetts Institute of Technology On behalf of the SuperCDMS and CDMS Collaborations
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Dark Matter Search. Dark Matter
 Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
The CDMS-II Dark Matter Search and SuperCDMS
 The CDMS-II Dark Matter Search and SuperCDMS R. W. Ogburn IV Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA For the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) currently sets
The CDMS-II Dark Matter Search and SuperCDMS R. W. Ogburn IV Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA For the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) currently sets
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX
 Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
CDMS-II to SuperCDMS
 CDMS-II to SuperCDMS WIMP search at a zeptobarn Tobias Bruch University of Zürich 5 th Patras Workshop on Axions,WIMPs and WISPs University of Durham, 13 July 2009 CDMS-II 5 Tower setup 5 Towers a 6 detectors
CDMS-II to SuperCDMS WIMP search at a zeptobarn Tobias Bruch University of Zürich 5 th Patras Workshop on Axions,WIMPs and WISPs University of Durham, 13 July 2009 CDMS-II 5 Tower setup 5 Towers a 6 detectors
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search
 Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment
 The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results
 A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
Present Status of the SuperCDMS program
 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 818 823 DOI 10.1007/s10909-008-9740-7 Present Status of the SuperCDMS program D.S. Akerib C.N. Bailey D.A. Bauer P.L. Brink R. Bunker B. Cabrera D.O. Caldwell J. Cooley P. Cushman
J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 818 823 DOI 10.1007/s10909-008-9740-7 Present Status of the SuperCDMS program D.S. Akerib C.N. Bailey D.A. Bauer P.L. Brink R. Bunker B. Cabrera D.O. Caldwell J. Cooley P. Cushman
The XENON1T experiment
 The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches
 Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project
 Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS
 Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS SuperCDMS Science Coordinator Syracuse University arxiv: 1304.4279 1304.3706 1203.1309 A New Order 0.01% Visible H, He 0.5% ENERGY Metals Dark Matter
Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS SuperCDMS Science Coordinator Syracuse University arxiv: 1304.4279 1304.3706 1203.1309 A New Order 0.01% Visible H, He 0.5% ENERGY Metals Dark Matter
SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS
 SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection
SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection
Chapter 12. Dark Matter
 Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal 128 Chapter 12 Dark Matter Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal Baryonic Dark Matter Brightness & Rotation Curve of NGC3198 Brightness Rotation Curve measured expected
Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal 128 Chapter 12 Dark Matter Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal Baryonic Dark Matter Brightness & Rotation Curve of NGC3198 Brightness Rotation Curve measured expected
Dark Matter. and TPC Technologies
 Dark Matter and TPC Technologies The Physics Case for WIMPs Status of the Field:event by event discrimination Elements of a roadmap Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute for
Dark Matter and TPC Technologies The Physics Case for WIMPs Status of the Field:event by event discrimination Elements of a roadmap Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute for
WIMP Direct Detection: an outlook
 WIMP Direct Detection: an outlook Particle Cosmology Non baryonic dark matter WIMPs: a generic consequence of new physics at TeV scale 1 Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute
WIMP Direct Detection: an outlook Particle Cosmology Non baryonic dark matter WIMPs: a generic consequence of new physics at TeV scale 1 Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Looking for WIMPs A Review
 Looking for WIMPs A Review Beatriz E. Burrola Gabilondo There is currently a race to find out what dark matter actually is. Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) are a strong candidate for dark
Looking for WIMPs A Review Beatriz E. Burrola Gabilondo There is currently a race to find out what dark matter actually is. Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) are a strong candidate for dark
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter
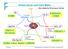 Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Status. Attila Dobi Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory June 10, 2015 WIN Heidelberg
 LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Status Attila Dobi Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory June 10, 2015 WIN-2015. Heidelberg 1 LZ = LUX + ZEPLIN 29 institutions currently About 160 people Continuing to expand internationally
LUX-ZEPLIN (LZ) Status Attila Dobi Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory June 10, 2015 WIN-2015. Heidelberg 1 LZ = LUX + ZEPLIN 29 institutions currently About 160 people Continuing to expand internationally
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
Dark Matter Searches. Marijke Haffke University of Zürich
 University of Zürich Structure Ι. Introduction - Dark Matter - WIMPs Ι Ι. ΙΙΙ. ΙV. V. Detection - Philosophy & Methods - Direct Detection Detectors - Scintillators - Bolometer - Liquid Noble Gas Detectors
University of Zürich Structure Ι. Introduction - Dark Matter - WIMPs Ι Ι. ΙΙΙ. ΙV. V. Detection - Philosophy & Methods - Direct Detection Detectors - Scintillators - Bolometer - Liquid Noble Gas Detectors
Dark Matter Detection with XENON100 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future
 Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
Search for Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with CDMS and XENON
 Search for Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with CDMS and XENON Elena Aprile 1,2, Laura Baudis 3,4, Blas Cabrera 5,6 1 Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University,
Search for Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with CDMS and XENON Elena Aprile 1,2, Laura Baudis 3,4, Blas Cabrera 5,6 1 Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University,
Axion search with Dark Matter detector
 Axion search with Dark Matter detector Paolo Beltrame Durham IPPP, 14th March 2016 1 Direct DM search Dark matter (DM) Milky Way s halo => flux on Earth ~ 10 5 cm -2 s -1 ρχ ~ 0.3 GeV/cm 3 and 100 GeV/c
Axion search with Dark Matter detector Paolo Beltrame Durham IPPP, 14th March 2016 1 Direct DM search Dark matter (DM) Milky Way s halo => flux on Earth ~ 10 5 cm -2 s -1 ρχ ~ 0.3 GeV/cm 3 and 100 GeV/c
Review of dark matter direct detection experiments
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 79, No. 5 journal of November 2012 physics pp. 1045 1057 Review of dark matter direct detection experiments RUPAK MAHAPATRA Department of Physics and Astronomy,
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 79, No. 5 journal of November 2012 physics pp. 1045 1057 Review of dark matter direct detection experiments RUPAK MAHAPATRA Department of Physics and Astronomy,
The Direct Search for Dark Matter
 picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments
 Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search
 Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search KIT Institute Centre for Particle Nuclear and Physics Astroparticle Physics KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of
Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search KIT Institute Centre for Particle Nuclear and Physics Astroparticle Physics KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of
Search for Inelastic Dark Matter with the CDMS experiment. Sebastian Arrenberg Universität Zürich Doktorierendenseminar 2010 Zürich,
 Search for Inelastic Dark Matter with the CDMS experiment Sebastian Arrenberg Universität Zürich Doktorierendenseminar 2010 Zürich, 30.08.2010 The CDMS experiment - 19 Ge and 11 Si semiconductor detectors
Search for Inelastic Dark Matter with the CDMS experiment Sebastian Arrenberg Universität Zürich Doktorierendenseminar 2010 Zürich, 30.08.2010 The CDMS experiment - 19 Ge and 11 Si semiconductor detectors
Status of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment
 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 800 805 DOI 10.1007/s10909-008-9741-6 Status of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Z. Ahmed D.S. Akerib M.J. Attisha C.N. Bailey L. Baudis D.A. Bauer P.L. Brink P.P.
J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 800 805 DOI 10.1007/s10909-008-9741-6 Status of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Z. Ahmed D.S. Akerib M.J. Attisha C.N. Bailey L. Baudis D.A. Bauer P.L. Brink P.P.
Light Dark Matter and XENON100. For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University
 Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment. 1 Abstract. 2 Introduction
 Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
Dark Matter Detection and the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory Columbia University New York, New York 10027 1 Abstract Observations on all fronts strongly
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 24 Jun 2004
 LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: Goals, Design, and Status. Sunil Golwala Caltech DM /02/19
 SuperCDMS SNOLAB: Goals, Design, and Status Caltech DM2016 2016/02/19 SuperCDMS SNOLAB Science Goals - [ ] HV detectors: lowest masses - ( ) - - - [ ] [ / ] SuperCDMS SNOLAB/DM2016 2 SuperCDMS SNOLAB Science
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: Goals, Design, and Status Caltech DM2016 2016/02/19 SuperCDMS SNOLAB Science Goals - [ ] HV detectors: lowest masses - ( ) - - - [ ] [ / ] SuperCDMS SNOLAB/DM2016 2 SuperCDMS SNOLAB Science
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors. David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011
 Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III
 The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches
 Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) : Status and future. Kipac SLAC April 2009
 The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) : Status and future Kipac SLAC April 2009 Department of Physics, Stanford University KIPAC associate member CDMS The CDMS Collaboration Caltech Z. Ahmed, S. Golwala,
The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) : Status and future Kipac SLAC April 2009 Department of Physics, Stanford University KIPAC associate member CDMS The CDMS Collaboration Caltech Z. Ahmed, S. Golwala,
Identification of the Surface Event Background in the CDMS II Experiment. Sunil Golwala for the CDMS II Collaboration Caltech August 21, 2008
 Identification of the Surface Event Background in the CDMS II Experiment Sunil Golwala for the CDMS II Collaboration Caltech August 21, 28 Surface Event Background in CDMS II Identification of Surface
Identification of the Surface Event Background in the CDMS II Experiment Sunil Golwala for the CDMS II Collaboration Caltech August 21, 28 Surface Event Background in CDMS II Identification of Surface
DARWIN. Marc Schumann. U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19,
 DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Dark Matter Searches: Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions
DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Dark Matter Searches: Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions
Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON. Kaixuan Ni (Columbia)
 Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON Kaixuan Ni (Columbia) University of Maryland, 11-25-2008 A well-known mystery for astronomers Fritz Zwicky, The Astrophysical Journal, 85
Shedding Light on Dark Matter from Deep Underground with XENON Kaixuan Ni (Columbia) University of Maryland, 11-25-2008 A well-known mystery for astronomers Fritz Zwicky, The Astrophysical Journal, 85
COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection
 COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB Rencontres de Moriond 2013 La Thuille, Italy; March 9-16, 2013 COUPP bubble chambers Target material: superheated CF 3 I spin-dependent/independent
COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB Rencontres de Moriond 2013 La Thuille, Italy; March 9-16, 2013 COUPP bubble chambers Target material: superheated CF 3 I spin-dependent/independent
Constraints on Low-Mass WIMP Signals from CDMS. Steven W. Leman (MIT) 18 March 2011 Rencontres de Moriond EW La Thuile, Valle d Aosta, Italy
 Constraints on Low-Mass WIMP Signals from CDMS Steven W. Leman (MIT) 18 March 2011 Rencontres de Moriond EW La Thuile, Valle d Aosta, Italy CDMS Members California Institute of Technology Z. Ahmed, J.
Constraints on Low-Mass WIMP Signals from CDMS Steven W. Leman (MIT) 18 March 2011 Rencontres de Moriond EW La Thuile, Valle d Aosta, Italy CDMS Members California Institute of Technology Z. Ahmed, J.
After LUX: The LZ Program. David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011
 After LUX: The LZ Program David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011 The LZ Program LZ LUX-ZEPLIN LUX (14 U.S. institutions) + new collaborators from ZEPLIN, other
After LUX: The LZ Program David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011 The LZ Program LZ LUX-ZEPLIN LUX (14 U.S. institutions) + new collaborators from ZEPLIN, other
Recent Results from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search. Bruno Serfass - UC Berkeley on behalf of the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations
 Recent Results from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Bruno Serfass - UC Berkeley on behalf of the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations CDMS/SuperCDMS Collaborations DOE NSF California Institute of Technology
Recent Results from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Bruno Serfass - UC Berkeley on behalf of the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations CDMS/SuperCDMS Collaborations DOE NSF California Institute of Technology
Direct Detection of Dark Matter. Lauren Hsu Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics TRISEP Summer School, June 10, 2014
 Direct Detection of Dark Matter Lauren Hsu Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics TRISEP Summer School, June 10, 2014 Direct Detection of Dark Matter Lecture 1 How to detect dark matter Lecture 2 Review
Direct Detection of Dark Matter Lauren Hsu Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics TRISEP Summer School, June 10, 2014 Direct Detection of Dark Matter Lecture 1 How to detect dark matter Lecture 2 Review
Direct Dark Matter Searches
 Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE
 Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE Kyungeun E. Lim (on behalf of the CUORE collaboration) Oct. 30. 015, APS Division of Nuclear Physics meeting, Santa Fe, NM The CUORE Experiment CUORE
Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE Kyungeun E. Lim (on behalf of the CUORE collaboration) Oct. 30. 015, APS Division of Nuclear Physics meeting, Santa Fe, NM The CUORE Experiment CUORE
CDMS. Vuk Mandic. 13. July 2010
 Dark Matter Direct Detection: CDMS Vuk Mandic University of Minnesota 13. July 2010 CDMS II Collaboration California Institute of Technology Z. Ahmed, J. Filippini, S.R. Golwala, D. Moore, R.W. Ogburn
Dark Matter Direct Detection: CDMS Vuk Mandic University of Minnesota 13. July 2010 CDMS II Collaboration California Institute of Technology Z. Ahmed, J. Filippini, S.R. Golwala, D. Moore, R.W. Ogburn
Status of DM Direct Detection. Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science
 Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe physics beyond the standard model how to detect Dark Matter particles Josef Jochum Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen Kepler
Direct Search for Dark Matter Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe physics beyond the standard model how to detect Dark Matter particles Josef Jochum Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen Kepler
Enectalí Figueroa-Feliciano
 School and Workshop on Dark Matter and Neutrino Detection Dark Matter Direct Detection Lecture 3 Enectalí Figueroa-Feliciano!113 Outline Lecture 1: The dark matter problem WIMP and WIMP-like DM detection
School and Workshop on Dark Matter and Neutrino Detection Dark Matter Direct Detection Lecture 3 Enectalí Figueroa-Feliciano!113 Outline Lecture 1: The dark matter problem WIMP and WIMP-like DM detection
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions
 Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
Measurements of liquid xenon s response to low-energy particle interactions Payam Pakarha Supervised by: Prof. L. Baudis May 5, 2013 1 / 37 Outline introduction Direct Dark Matter searches XENON experiment
The LZ Experiment Tom Shutt SLAC. SURF South Dakota
 The LZ Experiment Tom Shutt SLAC SURF South Dakota 1 LUX - ZEPLIN 31 Institutions, ~200 people 7 ton LXe TPC ( tons LXe total) University of Alabama University at Albany SUNY Berkeley Lab (LBNL), UC Berkeley
The LZ Experiment Tom Shutt SLAC SURF South Dakota 1 LUX - ZEPLIN 31 Institutions, ~200 people 7 ton LXe TPC ( tons LXe total) University of Alabama University at Albany SUNY Berkeley Lab (LBNL), UC Berkeley
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST
 Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Bubble Chambers for Direct Dark Matter Searches in COUPP
 Bubble Chambers for Direct Dark Matter Searches in COUPP Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB 8th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs and WISPs Chicago IL, USA; July 22, 2012 Eric Va zquez-ja uregui PATRAS 2012 July
Bubble Chambers for Direct Dark Matter Searches in COUPP Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB 8th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs and WISPs Chicago IL, USA; July 22, 2012 Eric Va zquez-ja uregui PATRAS 2012 July
DARWIN. Marc Schumann. U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15,
 DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017
DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017
Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results
 Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results Outline I. Leading spin-independent measurements II. Leading spin-depending measurements III. Low Mass WIMP searches IV. Discussion on Calibration 43 Current
Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results Outline I. Leading spin-independent measurements II. Leading spin-depending measurements III. Low Mass WIMP searches IV. Discussion on Calibration 43 Current
Towards One Tonne WIMP Direct Detectors: Have we got what it takes?
 Towards One Tonne WIMP Direct Detectors: Have we got what it takes? 000922 Center for Particle Astrophysics UC Berkeley source at http://cdms.berkeley.edu/gaitskell/ Gaitskell Future Reach / Lower limit
Towards One Tonne WIMP Direct Detectors: Have we got what it takes? 000922 Center for Particle Astrophysics UC Berkeley source at http://cdms.berkeley.edu/gaitskell/ Gaitskell Future Reach / Lower limit
Pushing the Limits: Dark Matter Search with SuperCDMS. Wolfgang Rau Queen s University Kingston For the SuperCDMS Collaboration
 Pushing the Limits: Dark Matter Search with Wolfgang Rau Queen s University Kingston For the Collaboration Dark Matter Velocity Observed Zwicky Expected (Kepler) Radius Rubin Luminous Matter (< 1 %) Ordinary
Pushing the Limits: Dark Matter Search with Wolfgang Rau Queen s University Kingston For the Collaboration Dark Matter Velocity Observed Zwicky Expected (Kepler) Radius Rubin Luminous Matter (< 1 %) Ordinary
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids
 Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Search with Noble Liquids Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich Recontres de Moriond 2012, Cosmology Session, La Thuile, March 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches
 Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches Klaus Eitel, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, KCETA, IK KIT University of the State of Baden-Württemberg and National Large-scale Research
Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches Klaus Eitel, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, KCETA, IK KIT University of the State of Baden-Württemberg and National Large-scale Research
Dark Matter Search * in China
 Dark Matter Search * in China Jianglai Liu 刘江来 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Member of the PandaX collaboration * Disclaimer: focused on direct detection The 7th Workshop on Hadron Physics in China and
Dark Matter Search * in China Jianglai Liu 刘江来 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Member of the PandaX collaboration * Disclaimer: focused on direct detection The 7th Workshop on Hadron Physics in China and
Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T
 Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T Jingkai Xia (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) On behalf of PandaX Collaboration August 2-5, Mini-Workshop@SJTU 2018/8/4 1 Outline Dark Matter direct
Recent results from PandaX- II and status of PandaX-4T Jingkai Xia (Shanghai Jiao Tong University) On behalf of PandaX Collaboration August 2-5, Mini-Workshop@SJTU 2018/8/4 1 Outline Dark Matter direct
PoS(VERTEX 2009)026. Dark Matter search with Ge detectors. Paul L. Brink 1
 Dark Matter search with Ge detectors Paul L. Brink 1 Dept. of Physics, Stanford University 382 Via Pueblo Mall, Stanford, CA 943405, USA E-mail: pbrink@stanford.edu The direct detection of Dark Matter,
Dark Matter search with Ge detectors Paul L. Brink 1 Dept. of Physics, Stanford University 382 Via Pueblo Mall, Stanford, CA 943405, USA E-mail: pbrink@stanford.edu The direct detection of Dark Matter,
First CDMS II Five-Tower Results. Sunil Golwala SLAC Summer Institute 2008 August 7, 2008
 First CDMS II Five-Tower Results Sunil Golwala SLAC Summer Institute 2008 August 7, 2008 Overview Why and how do we look for WIMP dark matter? Candidate WIMPs from particle physics The Cryogenic Dark Matter
First CDMS II Five-Tower Results Sunil Golwala SLAC Summer Institute 2008 August 7, 2008 Overview Why and how do we look for WIMP dark matter? Candidate WIMPs from particle physics The Cryogenic Dark Matter
No combined analysis of all experiments available
 Compatibility between DAMA-CDMS CDMS-Edelweiss-Xenon10 - KIMS? No combined analysis of all experiments available However, some trivial considerations: * for m χ 25 GeV capture on DAMA is dominated by the
Compatibility between DAMA-CDMS CDMS-Edelweiss-Xenon10 - KIMS? No combined analysis of all experiments available However, some trivial considerations: * for m χ 25 GeV capture on DAMA is dominated by the
Dark Matter Searches. Andrew Wagner SASS Presentation April 8, 2009
 Dark Matter Searches SASS Presentation April 8, 2009 Outline If its Dark how do we know its there? What could it be? (What is it?) How could it be directly detected? What are present limits set by two
Dark Matter Searches SASS Presentation April 8, 2009 Outline If its Dark how do we know its there? What could it be? (What is it?) How could it be directly detected? What are present limits set by two
Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment
 Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment by A. Lyashenko Yale University On behalf of LUX collaboration LUX Large Underground Xenon experiment LUX Collaboration: Yale, CWRU, UC Santa Barbara, Brown,
Current status of LUX Dark Matter Experiment by A. Lyashenko Yale University On behalf of LUX collaboration LUX Large Underground Xenon experiment LUX Collaboration: Yale, CWRU, UC Santa Barbara, Brown,
=> Ωmatter >> Ωbaryon
 Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Cryogenic Detectors CRESST Project Cosmic Microwave Background Matter-Density Ωmatter Anisotropy: Angular scale => geometry, Ωtot Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Cryogenic Detectors CRESST Project Cosmic Microwave Background Matter-Density Ωmatter Anisotropy: Angular scale => geometry, Ωtot Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN
 WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany XENON100 Rice University Houston, TX, USA http://xenon.physics.rice.edu 6th Patras Workshop Zurich July 7, 2010
WIMP Dark Matter Search with XENON and DARWIN Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany XENON100 Rice University Houston, TX, USA http://xenon.physics.rice.edu 6th Patras Workshop Zurich July 7, 2010
Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T
 Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T Marco Selvi INFN - Sezione di Bologna (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Feb 19 th 016, UCLA Dark Matter 016 1 Outline Description of the detector;
Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T Marco Selvi INFN - Sezione di Bologna (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Feb 19 th 016, UCLA Dark Matter 016 1 Outline Description of the detector;
Toward A Consistent Picture For CRESST, CoGeNT and DAMA. Chris Kelso Fermilab and University of Chicago Cosmology on the Beach Jan.
 Toward A Consistent Picture For CRESST, CoGeNT and DAMA Chris Kelso Fermilab and University of Chicago Cosmology on the Beach Jan. 19, 2012 How are we looking for dark matter? Current Direct Detection
Toward A Consistent Picture For CRESST, CoGeNT and DAMA Chris Kelso Fermilab and University of Chicago Cosmology on the Beach Jan. 19, 2012 How are we looking for dark matter? Current Direct Detection
Scalability of the SuperCDMS experiment
 Scalability of the SuperCDMS experiment Daniel Brandt dbrandt@slac.stanford.edu KIPAC, SLAC National Accelerator Lab Detecting dark matter The majority of the mass energy in the Universe is dark matter»
Scalability of the SuperCDMS experiment Daniel Brandt dbrandt@slac.stanford.edu KIPAC, SLAC National Accelerator Lab Detecting dark matter The majority of the mass energy in the Universe is dark matter»
Direct Detection of Dark Matter: Not Noble Gases
 Direct Detection of Dark Matter: Not Noble Gases Four broad classes of models Situation Feb 2016 Low mass, DAMA, PICO The immediate program US G2 + equivalent world wide Low temperature detectors The challenge
Direct Detection of Dark Matter: Not Noble Gases Four broad classes of models Situation Feb 2016 Low mass, DAMA, PICO The immediate program US G2 + equivalent world wide Low temperature detectors The challenge
arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 4 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 4 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.ins-det] 4 Nov 2017](/thumbs/89/101192102.jpg) arxiv:1711.01488v1 [physics.ins-det] 4 Nov 017 Current status and projected sensitivity of COSINE-0 WG Thompson, on behalf of the COSINE-0 Collaboration Department of Physics, Yale University, New Haven,
arxiv:1711.01488v1 [physics.ins-det] 4 Nov 017 Current status and projected sensitivity of COSINE-0 WG Thompson, on behalf of the COSINE-0 Collaboration Department of Physics, Yale University, New Haven,
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background
 Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments
 Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX, USA E-mail: cooley@physics.smu.edu The past year has yielded several new results from the direct detection
Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX, USA E-mail: cooley@physics.smu.edu The past year has yielded several new results from the direct detection
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012](/thumbs/75/71468977.jpg) Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:1201.3685v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012 M. Pyle 1 D.A. Bauer 2 B. Cabrera 1 J. Hall 2 R.W. Schnee 4 R. Basu Thakur
Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:1201.3685v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012 M. Pyle 1 D.A. Bauer 2 B. Cabrera 1 J. Hall 2 R.W. Schnee 4 R. Basu Thakur
DarkSide new results and prospects
 DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Direct dark matter search with XMASS. K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration
 Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids
 DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids Physik Institut, University of Zurich E-mail: laura.baudis@physik.uzh.ch DARWIN (DARk matter WImp search with Noble liquids) is an R&D and design study
DARWIN: dark matter WIMP search with noble liquids Physik Institut, University of Zurich E-mail: laura.baudis@physik.uzh.ch DARWIN (DARk matter WImp search with Noble liquids) is an R&D and design study
LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON
 LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON Cláudio Silva (LIP Coimbra) On behalf of the LUX Collaboration IDPASC Dark Matter Workshop 17 December 2011 1 THE LUX COLLABORATION Collaboration was formed in 2007 and fully funded
LARGE UNDERGROUND XENON Cláudio Silva (LIP Coimbra) On behalf of the LUX Collaboration IDPASC Dark Matter Workshop 17 December 2011 1 THE LUX COLLABORATION Collaboration was formed in 2007 and fully funded
Darkside-50, DarkSide-20k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon
 Darkside-5, DarkSide-2k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon Cristiano Galbiati Gran Sasso Science Institute and Princeton University The quest for dark matter with
Darkside-5, DarkSide-2k and the Global Collaboration to reach the Neutrino Floor with liquid argon Cristiano Galbiati Gran Sasso Science Institute and Princeton University The quest for dark matter with
DUSEL Initial Suite of Experiments (ISE) 1
 Dark Matter (WIMPS) Sensitivity 10^-44-10^-45 Noble Liquid (2 phase) 100 250 4100 LUX 300 proposal for Sanford Lab (2008) (Xe) CDMS Experiment in Soudan (running) Low Temperature Solid State 100 250 2000
Dark Matter (WIMPS) Sensitivity 10^-44-10^-45 Noble Liquid (2 phase) 100 250 4100 LUX 300 proposal for Sanford Lab (2008) (Xe) CDMS Experiment in Soudan (running) Low Temperature Solid State 100 250 2000
Ge and Dark Matter Searches: CDEX, present and future
 Ge and Dark Matter Searches: CDEX, present and future -Ge detectors at LN temperature Lin, Shin-Ted / Sichuan University On behalf of CDEX Collaboration Oct. 19, 2015 (Materials Provided by Prof. Qian
Ge and Dark Matter Searches: CDEX, present and future -Ge detectors at LN temperature Lin, Shin-Ted / Sichuan University On behalf of CDEX Collaboration Oct. 19, 2015 (Materials Provided by Prof. Qian
ANAIS: Status and prospects
 LSC Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc ANAIS: Status and prospects Miguel Ángel Oliván on behalf of the ANAIS team Universidad de Zaragoza Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc RICAP 2014 Roma International
LSC Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc ANAIS: Status and prospects Miguel Ángel Oliván on behalf of the ANAIS team Universidad de Zaragoza Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc RICAP 2014 Roma International
Low Background Experiments and Material Assay. Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016
 Low Background Experiments and Material Assay Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016 Outline How do we detect particles? Some interesting questions relating to particle physics How can particle detection
Low Background Experiments and Material Assay Tessa Johnson NSSC Summer School July 2016 Outline How do we detect particles? Some interesting questions relating to particle physics How can particle detection
David Reyna Belkis Cabrera-Palmer AAP2010, Japan
 David Reyna Belkis Cabrera-Palmer AAP2010, Japan Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin Company, for the United States Department of Energy s National Nuclear
David Reyna Belkis Cabrera-Palmer AAP2010, Japan Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin Company, for the United States Department of Energy s National Nuclear
Oak Ridge National Laboratory, TN. K. Scholberg, Duke University On behalf of the COHERENT collaboration August 2, 2017 DPF 2017, Fermilab
 Oak Ridge National Laboratory, TN K. Scholberg, Duke University On behalf of the COHERENT collaboration August 2, 2017 DPF 2017, Fermilab Coherent elastic neutrino-nucleus scattering (CEvNS) n + A n +
Oak Ridge National Laboratory, TN K. Scholberg, Duke University On behalf of the COHERENT collaboration August 2, 2017 DPF 2017, Fermilab Coherent elastic neutrino-nucleus scattering (CEvNS) n + A n +
