SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS
|
|
|
- Claud Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SuperCDMS: Recent Results for low-mass WIMPS David G. Cerdeño Institute for Theoretical Physics Universidad Autónoma de Madrid for the SuperCDMS Collaboration
2 Hints for low-mass WIMPs in direct detection experiments CDMS II Ge DAMA/LIBRA XENON S CDMSlite CoGeNT LUX CDMS II Si CRESST II CDMS II Ge EDELWEISS (LT) CDMS II Si: Phys.Rev.Le. (03) 530 CDMSlite: Phys.Rev.Le. (04) 0430
3 Particle Physics models provide candidates for light DM Among other possibilities: Supersymmetry neutralino in the MSSM or NMSSM sneutrino in extended models Asymmetric DM Are these theoretical predictions within the reach of our detectors? Sneutrino DM (Cerdeño, Peiró, Robles) It is an appealing window of the DM parameter space that is essential to explore 3
4 The search for low-mass WIMPs is challenging The signal is expected at very low recoil energies Favours light targets Low-threshold searches Ge is relatively heavy so the threshold has to be just above the noise to be sensitive to 5 GeV WIMPs WIMP scatters / kg / d in Ge SuperCDMS! analysis range lower recoil energy! =! sensitivity to lighter WIMPs trigger threshold.6 kevnr Backgrounds are more difficult to discriminate (this is not a background free search) 4
5 SuperCDMS at SOUDAN Operational since March 0 izip interleaved Z-sensitive Ionization & Phonon detectors Instrumented on both sides with charge+ 4 phonon sensors 3 Diameter.5 cm Thick 9.0 kg Ge (5 izips x 600g) Data for this analysis: 577 kg-days taken from Mar 0 July 03 7 izips with lowest trigger threshold Side Side 5
6 izip discrimination of surface events In the new izips the ionization lines (±V) are interleaved with phonon sensors (0V) on a ~mm pitch Bulk events: charges (e,h) drift to both sides of the crystal Surface events: charges (e,h) drift to only one side of the crystal e - h + e - h + Z-PARTITION: The resulting symmetry/asymmetry in charge collection in sides and 6
7 izip discrimination of surface events In the new izips the ionization lines (±V) are interleaved with phonon sensors (0V) on a ~mm pitch Bulk events: charges (e,h) drift to both sides of the crystal Surface events: charges (e,h) drift to only one side of the crystal Sidewalls Surface events on the sides of the detector leave more energy in the outer sensors. Z-PARTITION: The resulting symmetry/asymmetry in charge collection in sides and RADIAL PARTITION: division of energy between inner and outer sensors 7
8 The rejection of surface events with the new izips using Z-partition has been demonstrated with data from exposure to betas from Pb sources In ~800 live hours, no events leaked into the 8-5 kev signal region Rejection at >.7x -5 This could allow a background free search for 5 yr of operation in SNOLAB (~0 kg) Appl.Phys.Lett. 3 (03) 645 (the low threshold analysis corresponds to smaller energies and some leakage is expected) 8
9 Measurement of the recoil energy V IonizaYon Energy [kev] 5 - Ionization for nuclear recoils, measured from 5 Cf data: Detector: TZ C.L. < 68% 68% < C.L. < 95% 95% < C.L. < 99% C.L. > 99% Measurement Lindhard Best fit Measured Lindhard Best Fit ptnf [kev] Total phonon energy [kev] prompt phonons Luke phonons Total phonon energy = E total = E luke + E recoil E total is measured with phonons NR equivalent energy = E total E Luke NR E Luke NR estimated from mean NR ionization, varies with E total 9
10 Sources of background Bulk electron recoils Compton background.3 kev activation line Yield = Ionization/phonon helps discriminating NR from ER Sidewall & surface events betas and x-rays from Pb, Bi, recoils from 06 Pb, outer radial Comptons, ejected electrons from Compton scattering Z-Partition and Radial partition define a fiducial volume Neutrons (cosmogenic & radiogenic) Use active and passive shielding. Simulation determines remaining irreducible rate
11 Analysis: Selection criteria and efficiencies We carry out a blind analysis, with all singles in energy range following 5 Cf calibration due to activation removed from study, except data Data Quality: Reject periods with poor detector performance Remove misreconstructed and noisy pulses Measure efficiency with pulse MC Quality + Thresholds Trigger and analysis threshold: Select periods with stable well-defined trigger threshold Measure efficiency from 33 Ba calibration data Preselection: Single-detector scatter Remove events coincident with muon veto Ionization fiducial volume Ionization and phonon partitions consistent with NR Boosted Decision Tree: Optimised cut on the phonon fiducial volume and ionization yield at low energy Efficiency estimated from fraction of 5 Cf passing + Preselection + BDT Efficiencies: measured for neutrons from 5 Cf. Corrected for multiple scattering with Geant4
12 ecision Tree DT inputs [kev] [kev] gy [kev] 3 rgy [kev] 3 tition artition 0.4 partition 0.4 Number Number of of events events Number of of events events simulation" ents reweighted ev WIMP Boosted Decision Tree (BDT) Number of events Boosted Decision Tree 5 5 Total phonon energy [kev] Total phonon energy [kev] total total phonon phonon energy energy [kev] [kev] Number of events Inputs (per detector) Number Number of events of events Number of of events / 0.04 / Number of events Ionization energy [kev] ionization energy [kev] Boosted Decision Tree BDT inputs summed over detectors summed over detectors BDT BDT inputs BDT output inputs Number of events Number of events ionization energy [kev] Ionization energy ionization energy [kev] 5 Total phonon energy total phonon energy [kev] Number of events Number of events GeV GeV WIMP" summed WIMP" -4 over # = 6 x -4 cm cm detectors Number of events / 0.04 BDT output Output 5 Total phonon energy [kev] total phonon energy [kev] Number of events / 0.04 BD BD summed over dete summed over dete GeV WIMP" # = 6 x -4 cm BDT score BDT score per BDT score Construction: BDT per detector" Construction: BDT per detector" Optimization: set cuts 0. Vertical 0. phonon Vertical phonon to WIMP ( GeV)" phonon z-partition Radial phonon WIMP (-0.4GeV)" -0. Radial 0 phonon Optimization: 0.4 set cuts phonon r-partition phonon Vertical r-partition simultaneously phonon to minimize Vertical phonon phonon z-partition WIMP ( GeV)" phonon z-partition simultaneously Sidewall WIMP to minimize (06Pb" GeV)" Sidewall 06Pb" Background model: pulse expected simulation" 90% CL upper limit from" from" Sidewall 06Pb" expected 90% Sidewall CL upper!" 06Pb" limit Background model: pulse simulation" Signal Background Sidewall!" model: model: 5 Cf NR pulse events on WIMP-nucleon simulation" reweighted cross from" Face!" from" Pb Sidewall!" on WIMP-nucleon Sidewall cross!" Pb Signal model: 5 to Signal Face!" match model: 5, 7,, 5 Cf NR events Background: reweighted Modelled Cf and NR 5 events section with simulated GeV WIMP reweighted Face!" data Pb on sidebands section Pb.3 Face kev!" to match 5, 7,, and 5 GeV and line" to.3 WIMP match kev calibration. line" 5, 7,, and 5 GeV WIMP.3 kev line"!! Gammas.3 kev line"! Gammas Gammas Gammas WIMP Signal: Modelled with NR data from 5 Cf, then rescaled for WIMPs with mass 5, 7,, 5 GeV
13 Unblinding: Before BDT cut Events passing all the cuts prior to applying BDT Ionization energy [kev] 4 3 Lindhard nuclear-recoil energy [kevnr] kev line Approx NR band 0 Outer radial events Total phonon energy [kev] 3
14 Unblinding: After BDT cut candidates ( expected) Ionization energy [kev] 4 3 Lindhard nuclear-recoil energy [kevnr] Total phonon energy [kev] 4
15 Unblinding: After BDT cut candidates ( expected) Ionization energy [kev] 4 3 Lindhard nuclear-recoil energy [kevnr] % CL intervals for WIMPS with m=5 GeV m=7 GeV m= GeV m=5 GeV Total phonon energy [kev] 5
16 Post-unblinding discussion Events are high in quality. Only the lowest energy candidate looks like spurious noise For most of the detectors there is good agreement with predicted background GeV BDT P-value = 0.4 6
17 Post-unblinding discussion Events are high in quality. Only the lowest energy candidate looks like spurious noise For most of the detectors there is good agreement with predicted background However, T5Z3 observes the 3 highest-energy events (Poisson p-value is 0.04%) Events passing BDT range Range of counts of counts with p>0.05 with p-value>0.05! σ background expectation expectation observed observed shorted ionization guard 0 TZ TZ TZ T4Z T4Z3 T5Z T5Z3 Detector $ T5Z3 has a shorted ionization guard. This may have affected the background model performance. Additional studies are undergoing. 7
18 New limit for low-mass WIMPs 90% C.L. optimal interval method (no background subtraction) systematics (efficiency, energy scale, trigger efficiency) This work arxiv: Difference with expectation due to events in T5Z3 8
19 Conclusions First result using the background rejection capability of SuperCDMS 7 izips analysed (threshold.6 kev nr) Exposure: 577 kg day σ SI >. x -6 pb at 8 GeV New limit for WIMPs with masses in the range 4-6 GeV This work (below 4 GeV CDMSlite dominates) arxiv: CoGeNT interpretation of WIMP signal disfavoured in model-independent way CDMS-II (Si) disfavoured assuming standard WIMP interactions and for the standard halo model. High threshold analysis of SuperCDMS ongoing SuperCDMS Soudan detectors are a vast improvement over CDMS II 9
20 SuperCDMS-SNOLAB (with ~0 kg Ge and ~kg Si) will extend the sensitivity by over an order of magnitude with an excellent coverage of the light mass window. Si lite Ge lite Si Ge 0
21 The SuperCDMS collaboration
22 Extra material & Backup slides
23 Limit without T5Z3 The limit extracted without T5Z3 only differs for m> GeV and is approx. a factor better This work This work without T5Z3 3
24 candidates that pass all the cuts 4
25 Efficiencies 5
26 SuperCDMS Soudan 6
27 CDMSlite Amplification of the Luke-Neganov phonons V EQ = N eh ε = IonisaYon energy prompt phonons Luke phonons ε = 3 ev (in Ge) = (e- h) pair creayon mean energy Erecoil = E. of prompt phonons E Luke = V e Neh Ptot = Erecoil + ELuke If the bias voltage is increased, the work done in drifting charge carriers, ELuke, increases The signal is amplified, allowing a substantial reduction in energy threshold and a better energy resolution The phonon instrumentation thus measures the ionization energy (no signal is used from the ionization channels) à No Yield-based discrimination of electron and nuclear recoils 7
28 CDMSlite data taking Data were taken in three periods in 0 with 33 Ba calibration data interspersed throughout There were two neutron exposures ( 5 Cf) to determine energy scale and monitor stability August, and August 3 One izip was used, IT5Z 0.6 kg Selected for its low trigger threshold and low leakage current Signal gain at operating voltage of 69 V was 4 E T = E r ( + ev ) b ε γ Average excitation energy per charge pair ε γ = 3 ev. Raw exposure is 5 live days, 9.6 kg days Optimized based on a flat extrapolation of known electron recoil backgrounds in the -7 kev window 8
29 CDMSlite low-energy spectrum and efficiency Event selection criteria Recoil spectrum of WIMP search events Not coincident with signals in the muon veto Single detector energy depositions 7 evee Not consistent with high frequency noise ( glitches ) Not consistent with low frequency noise (microphonics) Time periods selected with low leakage and where the gain could be well calibrated Exposure =.3 live days = 6.3 kg day The spectrum shows features at.36 kev and.3 kev due to K- and L- shell electron captures in 7 Ge. The energy resolution of the.3 kev line is 43 ev (σ). 9
30 CDMSlite Spectrum of nuclear recoils E nr = E ee ( + ev b ε γ ) ( + ev b ε γ Y (E nr )) Resulting NR spectrum The yield is not measured: use theoretical (Lindhard) model 84 evnr A number of experiments have measured nuclear recoils in germanium over the relevant energy range. 30
31 CDMSlite Results This analysis limits new WIMP parameter space for low masses and rules out portions of CDMS II and CoGeNT contours The choice of a different model for the yield affects the reconstruction of the nuclear recoil energy and thus the interpretation as a limit on the WIMP-nucleon cross-section 3
32 Resulting experimental situation for low-energy WIMPs DAMA CoGeNT (03) CDMS II Si (03) DAMA 3
33 izip discrimination of surface events In the new izips the ionization lines (±V) are interleaved with phonon sensors (0V) on a ~mm pitch Bulk events: charges (e,h) drift to both sides of the crystal e - Surface events: h + charges (e,h) drift to only one side of the crystal e - h + The resulting symmetry/asymmetry in charge collection is an extremely effective discriminant for surface events 33
34 Pb izip calibration ~900 live hours in T3Z with a Pb Source β γ source on side 06Pb 7,55 electrons 6,58 06Pb recoils No events leaking into the signal region (8-5 kev) For 300 kg yr (00 kg Ge SNOLAB) the estimated leakage is < 0.6 events 90% cl 3 γ e-! 5Cf (n)! 06Pb! (a) (b) FIG. 3. (color online) All panels show the same data from 900 live hours of detector T3Z with the (Ionization threshold kevee) (c) Pb source facing side. Clearly 34 visible are the symmetric charge events (large blue dots) in the interior of the crystal, and the events that fail the symmetric charge cut
35 CDMS II 4.6 kg Ge (9 x 40 g). kg Si ( x 6g) 3 Diameter cm Thick SuperCDMS Soudan 9.0 kg Ge (5 x 600g) 3 Diameter.5 cm Thick charge + 4 phonon charge + charge 4 phonon + 4 phonon 35
Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS
 Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS SuperCDMS Science Coordinator Syracuse University arxiv: 1304.4279 1304.3706 1203.1309 A New Order 0.01% Visible H, He 0.5% ENERGY Metals Dark Matter
Searches for Low-Mass WIMPs with CDMS II and SuperCDMS SuperCDMS Science Coordinator Syracuse University arxiv: 1304.4279 1304.3706 1203.1309 A New Order 0.01% Visible H, He 0.5% ENERGY Metals Dark Matter
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search. Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration
 SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: A G2 Dark Matter Search Ben Loer, Fermilab Center for Particle Astrophysics On behalf of the SuperCDMS Collaboration A bit of background Astronomical data at all scales indicates dark
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project
 Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Recent results from the second CDMSlite run and overview of SuperCDMS SNOLAB project SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory/Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Menlo Park, CA 94025,
Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment
 Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Kevin A. McCarthy Massachusetts Institute of Technology On behalf of the SuperCDMS and CDMS Collaborations
Dark Matter Search Results from the Silicon Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Experiment Kevin A. McCarthy Massachusetts Institute of Technology On behalf of the SuperCDMS and CDMS Collaborations
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches
 Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Precision Measurement Of Nuclear Recoil Ionization Yields For Low Mass Wimp Searches Tarek Saab University of Florida Tali Figueroa Northwestern University Calibration of Low Energy Particle Detectors
Search for Inelastic Dark Matter with the CDMS experiment. Sebastian Arrenberg Universität Zürich Doktorierendenseminar 2010 Zürich,
 Search for Inelastic Dark Matter with the CDMS experiment Sebastian Arrenberg Universität Zürich Doktorierendenseminar 2010 Zürich, 30.08.2010 The CDMS experiment - 19 Ge and 11 Si semiconductor detectors
Search for Inelastic Dark Matter with the CDMS experiment Sebastian Arrenberg Universität Zürich Doktorierendenseminar 2010 Zürich, 30.08.2010 The CDMS experiment - 19 Ge and 11 Si semiconductor detectors
Quenchings in crystals!
 Quenchings in crystals! Why are they important? Some Models Light Quenching (few comments) Ionization Quenching Measurements Jules Gascon! (IPNLyon, Université Lyon 1 + CNRS/IN2P3)! Quenching! Background
Quenchings in crystals! Why are they important? Some Models Light Quenching (few comments) Ionization Quenching Measurements Jules Gascon! (IPNLyon, Université Lyon 1 + CNRS/IN2P3)! Quenching! Background
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: Goals, Design, and Status. Sunil Golwala Caltech DM /02/19
 SuperCDMS SNOLAB: Goals, Design, and Status Caltech DM2016 2016/02/19 SuperCDMS SNOLAB Science Goals - [ ] HV detectors: lowest masses - ( ) - - - [ ] [ / ] SuperCDMS SNOLAB/DM2016 2 SuperCDMS SNOLAB Science
SuperCDMS SNOLAB: Goals, Design, and Status Caltech DM2016 2016/02/19 SuperCDMS SNOLAB Science Goals - [ ] HV detectors: lowest masses - ( ) - - - [ ] [ / ] SuperCDMS SNOLAB/DM2016 2 SuperCDMS SNOLAB Science
DarkSide new results and prospects
 DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
DarkSide new results and prospects Stefano Davini - INFN Genova on behalf of the DarkSide collaboration La Thuile, March 20, 2018 The DarkSide WIMP-argon program at LNGS 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
The Direct Search for Dark Matter
 picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
picture: Thomas Tuchan The Direct Search for Dark Matter with special emphasis on the XENON project Rafael F. Lang Purdue University rafael@purdue.edu IPMU Tokyo, March 8, 2013 1 baryon fraction Dark Matter
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches
 Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
Technical Specifications and Requirements on Direct detection for Dark Matter Searches Jin Li THU/IHEP Symposium of the Sino-German GDT Cooperation 04/08/2013 Tübingen Outline Introduction Direct detection
The CDMS-II Dark Matter Search and SuperCDMS
 The CDMS-II Dark Matter Search and SuperCDMS R. W. Ogburn IV Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA For the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) currently sets
The CDMS-II Dark Matter Search and SuperCDMS R. W. Ogburn IV Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA For the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search (CDMS) currently sets
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results
 A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
A survey of recent dark matter direct detection results I where we stand II recent results (CDMS, XENON10, etc) III DAMA results IV a bit about modulation V issues with DAMA results VI what to look for
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012](/thumbs/75/71468977.jpg) Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:1201.3685v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012 M. Pyle 1 D.A. Bauer 2 B. Cabrera 1 J. Hall 2 R.W. Schnee 4 R. Basu Thakur
Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:1201.3685v1 [astro-ph.im] 18 Jan 2012 M. Pyle 1 D.A. Bauer 2 B. Cabrera 1 J. Hall 2 R.W. Schnee 4 R. Basu Thakur
Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results
 Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results Outline I. Leading spin-independent measurements II. Leading spin-depending measurements III. Low Mass WIMP searches IV. Discussion on Calibration 43 Current
Direct Detection Lecture 2: Current Results Outline I. Leading spin-independent measurements II. Leading spin-depending measurements III. Low Mass WIMP searches IV. Discussion on Calibration 43 Current
ANAIS: Status and prospects
 LSC Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc ANAIS: Status and prospects Miguel Ángel Oliván on behalf of the ANAIS team Universidad de Zaragoza Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc RICAP 2014 Roma International
LSC Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc ANAIS: Status and prospects Miguel Ángel Oliván on behalf of the ANAIS team Universidad de Zaragoza Laboratorio Subterráneo de Canfranc RICAP 2014 Roma International
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III
 The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
The EDELWEISS DM search Phase II to Phase III Adam Cox Karlsruhe Institute for Technology (KIT) on behalf of the EDELWEISS Collaboration CEA, Saclay (IRFU and IRAMIS) IPNL (CNRS/IN2P3 and Université de
Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector. David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012
 Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012 LZ Construction 2 Background Sources Ti cryostats 1500 kg
Background Characterization and Rejection in the LZ Detector David Malling Brown University IDM 2012 July 25, 2012 LZ Construction 2 Background Sources Ti cryostats 1500 kg
CDMS-II to SuperCDMS
 CDMS-II to SuperCDMS WIMP search at a zeptobarn Tobias Bruch University of Zürich 5 th Patras Workshop on Axions,WIMPs and WISPs University of Durham, 13 July 2009 CDMS-II 5 Tower setup 5 Towers a 6 detectors
CDMS-II to SuperCDMS WIMP search at a zeptobarn Tobias Bruch University of Zürich 5 th Patras Workshop on Axions,WIMPs and WISPs University of Durham, 13 July 2009 CDMS-II 5 Tower setup 5 Towers a 6 detectors
Light Dark Matter and XENON100. For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University
 Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Light Dark Matter and XENON100 For the XENON100 Collaboration Rafael F. Lang Columbia University rafael.lang@astro.columbia.edu The XENON Collaboration ~60 scientists from 12 institutions: University of
Direct dark matter search with XMASS. K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration
 Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
Direct dark matter search with XMASS K. Abe for the XMASS collaboration Outline XMASS experiment. Single phase liquid xenon detector Many targets were searched with XMASS. WIMP search fiducialized volume.
Chapter 12. Dark Matter
 Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal 128 Chapter 12 Dark Matter Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal Baryonic Dark Matter Brightness & Rotation Curve of NGC3198 Brightness Rotation Curve measured expected
Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal 128 Chapter 12 Dark Matter Karl-Heinz Kampert Univ. Wuppertal Baryonic Dark Matter Brightness & Rotation Curve of NGC3198 Brightness Rotation Curve measured expected
The XENON1T experiment
 The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
The XENON1T experiment Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science For the XENON collaboration 1 The XENON1T experiment Direct detection with xenon The XENON project XENON1T/nT 2 Quick introduction and
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments
 Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
Measurement of 39 Ar in Underground Argon for Dark Matter Experiments Jingke Xu Princeton University June 7 th, 2013 1 Evidences for Dark Matter Rotation Curve Gravitational Lensing CMB Power Spectrum
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector
 XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
XMASS: a large single-phase liquid-xenon detector Katsuki Hiraide, the university of Tokyo for the XMASS Collaboration October 3 rd, 2016 IPRD16@Siena, Italy 1 XMASS project XMASS: a multi purpose experiment
Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search
 Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search KIT Institute Centre for Particle Nuclear and Physics Astroparticle Physics KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of
Status of the EDELWEISS Dark Matter search KIT Institute Centre for Particle Nuclear and Physics Astroparticle Physics KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Research Center of
Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T
 Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T Marco Selvi INFN - Sezione di Bologna (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Feb 19 th 016, UCLA Dark Matter 016 1 Outline Description of the detector;
Background and sensitivity predictions for XENON1T Marco Selvi INFN - Sezione di Bologna (on behalf of the XENON collaboration) Feb 19 th 016, UCLA Dark Matter 016 1 Outline Description of the detector;
Search for low-mass WIMPs with Spherical Detectors : NEWS-LSM and NEWS-SNO
 Search for low-mass WIMPs with Spherical Detectors : NEWS-LSM and NEWS-SNO G. Gerbier 1 for the NEWS collaboration 2, 1 Queen s University, Physics Department, Kingston, Canada 2 New Experiments With Spheres
Search for low-mass WIMPs with Spherical Detectors : NEWS-LSM and NEWS-SNO G. Gerbier 1 for the NEWS collaboration 2, 1 Queen s University, Physics Department, Kingston, Canada 2 New Experiments With Spheres
Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration. Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016
 Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016 The DarkSide program 2 Double Phase Liquid Argon TPC, a staged approach:
Paolo Agnes Laboratoire APC, Université Paris 7 on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration Dark Matter 2016 UCLA 17th - 19th February 2016 The DarkSide program 2 Double Phase Liquid Argon TPC, a staged approach:
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 24 Jun 2004
 LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
LATEST RESULTS OF THE EDELWEISS EXPERIMENT arxiv:astro-ph/46537v 24 Jun 24 V. SANGLARD for the Edelweiss collaboration Institut de Physique Nucléaire de Lyon, 4 rue Enrico Fermi, 69622 Villeurbanne, France
New Physics Results from DarkSide-50. Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide-50 Collaboration Feb
 New Physics Results from DarkSide5 Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide5 Collaboration Feb. 8 Lake Louise Winter Institute 8 DETECTOR DARKSIDE 5 Radonfree (Rn levels < 5 mbq/m )
New Physics Results from DarkSide5 Masayuki Wada Princeton University on behalf of the DarkSide5 Collaboration Feb. 8 Lake Louise Winter Institute 8 DETECTOR DARKSIDE 5 Radonfree (Rn levels < 5 mbq/m )
UCLA Dark Matter 2014 Symposium. Origins and Distributions of the Backgrounds. 15 min
 S. Fiorucci Brown University UCLA Dark Matter 2014 Symposium Origins and Distributions of the Backgrounds 15 min What is a signal for LUX? Nuclear recoil Single scatter Signal Low energy, typically < 25
S. Fiorucci Brown University UCLA Dark Matter 2014 Symposium Origins and Distributions of the Backgrounds 15 min What is a signal for LUX? Nuclear recoil Single scatter Signal Low energy, typically < 25
CDMS and SuperCDMS. SLAC Summer Institute - CDMS. August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS
 CDMS and SuperCDMS SLAC Summer Institute August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS CDMS-II science results - less than 1 evt / kg of Ge / month Status of CDMS-II 5-Tower
CDMS and SuperCDMS SLAC Summer Institute August 2, 2007 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS CDMS-II science results - less than 1 evt / kg of Ge / month Status of CDMS-II 5-Tower
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search
 Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
Sensitivity and Backgrounds of the LUX Dark Matter Search 1 LUX Goal: Direct Detection of Dark Matter WMAP 5-year data (2008) gives matter densities (Ω) based on best fit to Λ-CDM cosmological model: Ω
David Reyna Belkis Cabrera-Palmer AAP2010, Japan
 David Reyna Belkis Cabrera-Palmer AAP2010, Japan Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin Company, for the United States Department of Energy s National Nuclear
David Reyna Belkis Cabrera-Palmer AAP2010, Japan Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin Company, for the United States Department of Energy s National Nuclear
Ge and Dark Matter Searches: CDEX, present and future
 Ge and Dark Matter Searches: CDEX, present and future -Ge detectors at LN temperature Lin, Shin-Ted / Sichuan University On behalf of CDEX Collaboration Oct. 19, 2015 (Materials Provided by Prof. Qian
Ge and Dark Matter Searches: CDEX, present and future -Ge detectors at LN temperature Lin, Shin-Ted / Sichuan University On behalf of CDEX Collaboration Oct. 19, 2015 (Materials Provided by Prof. Qian
XENON100. Marc Schumann. Physik Institut, Universität Zürich. IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th,
 XENON100 Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Why WIMP search with Xenon? efficient, fast scintillator (178nm)
XENON100 Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich IDM 2010, Montpellier, July 26 th, 2010 www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/ Why WIMP search with Xenon? efficient, fast scintillator (178nm)
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter
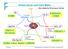 Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
Direkte Suche nach Dark Matter WIMP über elastische Streuung an Kernen HDMS Ge 10% energy Ionization Ge, Si Edelweiss, CDMS liquid Xe Zeplin-2, US-Xenon NaI, liqu.xe Target Light 1% energy fastest no surface
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment
 The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
The Search for Dark Matter with the XENON Experiment Elena Aprile Columbia University Paris TPC Workshop December 19, 2008 World Wide Dark Matter Searches Yangyang KIMS Homestake LUX SNOLAB DEAP/CLEAN
Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment. Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH
 Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH The XENON dark matter search program Target Volume 62 kg Total
Background Studies for the XENON100 Experiment Alexander Kish Physics Institute, University of Zürich Doktorandenseminar August 30, 2010 UZH The XENON dark matter search program Target Volume 62 kg Total
TWO-PHASE DETECTORS USING THE NOBLE LIQUID XENON. Henrique Araújo Imperial College London
 TWO-PHASE DETECTORS USING THE NOBLE LIQUID XENON Henrique Araújo Imperial College London Oxford University 18 th October 2016 OUTLINE Two-phase xenon for (dark) radiation detection Instrumenting a liquid
TWO-PHASE DETECTORS USING THE NOBLE LIQUID XENON Henrique Araújo Imperial College London Oxford University 18 th October 2016 OUTLINE Two-phase xenon for (dark) radiation detection Instrumenting a liquid
The EDELWEISS III Experiment Status
 Quentin ARNAUD for the Edelweiss Collaboration The EDELWEISS III Experiment Status Les Rencontres de Moriond 2014 Cosmology Session 27/03/2014 Dark Matter Search Evidences for Dark Matter Galaxy Clusters
Quentin ARNAUD for the Edelweiss Collaboration The EDELWEISS III Experiment Status Les Rencontres de Moriond 2014 Cosmology Session 27/03/2014 Dark Matter Search Evidences for Dark Matter Galaxy Clusters
Status of the XENON100 Dark Matter Search
 Status of the XENON Dark Matter Search Guillaume Plante Columbia University on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Exploring Low-Mass Dark Matter Candidates - PITT PACC - November 146, 211 XENON Collaboration
Status of the XENON Dark Matter Search Guillaume Plante Columbia University on behalf of the XENON Collaboration Exploring Low-Mass Dark Matter Candidates - PITT PACC - November 146, 211 XENON Collaboration
Recent Results from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search. Bruno Serfass - UC Berkeley on behalf of the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations
 Recent Results from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Bruno Serfass - UC Berkeley on behalf of the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations CDMS/SuperCDMS Collaborations DOE NSF California Institute of Technology
Recent Results from the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search Bruno Serfass - UC Berkeley on behalf of the CDMS and SuperCDMS collaborations CDMS/SuperCDMS Collaborations DOE NSF California Institute of Technology
Ricochet Proposal and Current Efforts. Alexander F. Leder
 Ricochet Proposal and Current Efforts A Talk Outline Divided into three sections: 1. Introduction and Motivation 2. Ricochet Proposal 3. Neutron Monitoring at MIT Research Reactor Part I: Introduction
Ricochet Proposal and Current Efforts A Talk Outline Divided into three sections: 1. Introduction and Motivation 2. Ricochet Proposal 3. Neutron Monitoring at MIT Research Reactor Part I: Introduction
COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection
 COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB Rencontres de Moriond 2013 La Thuille, Italy; March 9-16, 2013 COUPP bubble chambers Target material: superheated CF 3 I spin-dependent/independent
COUPP: Bubble Chambers for Dark Matter Detection Eric Vázquez Jáuregui SNOLAB Rencontres de Moriond 2013 La Thuille, Italy; March 9-16, 2013 COUPP bubble chambers Target material: superheated CF 3 I spin-dependent/independent
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector. WIMP Search. Mani Tripathi, INPAC Meeting. Berkeley, May 5, 2007
 LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
LUX: A Large Underground Xenon detector WIMP Search Mani Tripathi INPAC Meeting Berkeley, New Collaboration Groups formerly in XENON10: Case Western, Brown, Livermore Natl. Lab (major fraction of the US
DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO
 Search for Dark Matter WIMPs: SuperCDMS Soudan Soudan and SNOLAB leading to GEODM at DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO - September 17, 2009 Blas Cabrera - Stanford
Search for Dark Matter WIMPs: SuperCDMS Soudan Soudan and SNOLAB leading to GEODM at DUSEL NATIONAL LAB ROLE ESSENTIAL FOR SNOLAB AND DUSEL EXPERIMENTS SLUO - September 17, 2009 Blas Cabrera - Stanford
Edelweiss-II : status and first results A new generation of background-free bolometers for WIMP search
 Edelweiss-II : status and first results A new generation of background-free bolometers for WIMP search From EDWI to EDW II New ID detectors Some current results Outlook G. Gerbier CEA Saclay, IRFU, France
Edelweiss-II : status and first results A new generation of background-free bolometers for WIMP search From EDWI to EDW II New ID detectors Some current results Outlook G. Gerbier CEA Saclay, IRFU, France
Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE
 Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE Kyungeun E. Lim (on behalf of the CUORE collaboration) Oct. 30. 015, APS Division of Nuclear Physics meeting, Santa Fe, NM The CUORE Experiment CUORE
Search for Low Energy Events with CUORE-0 and CUORE Kyungeun E. Lim (on behalf of the CUORE collaboration) Oct. 30. 015, APS Division of Nuclear Physics meeting, Santa Fe, NM The CUORE Experiment CUORE
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search
 Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
Results from 730 kg days of the CRESST-II Dark Matter Search Federica Petricca on behalf of the CRESST collaboration: Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, München TU München University of Oxford Universität
Dark anti-atoms. Quentin Wallemacq IFPA, AGO Dept., University of Liège. CosPa Meeting 19 th of November 2014
 Dark anti-atoms Quentin Wallemacq IFPA, AGO Dept., University of Liège CosPa Meeting 19 th of November 2014 Q. Wallemacq, J.R. Cudell, arxiv:1411.3178 Introduction The status of direct-search experiments
Dark anti-atoms Quentin Wallemacq IFPA, AGO Dept., University of Liège CosPa Meeting 19 th of November 2014 Q. Wallemacq, J.R. Cudell, arxiv:1411.3178 Introduction The status of direct-search experiments
No combined analysis of all experiments available
 Compatibility between DAMA-CDMS CDMS-Edelweiss-Xenon10 - KIMS? No combined analysis of all experiments available However, some trivial considerations: * for m χ 25 GeV capture on DAMA is dominated by the
Compatibility between DAMA-CDMS CDMS-Edelweiss-Xenon10 - KIMS? No combined analysis of all experiments available However, some trivial considerations: * for m χ 25 GeV capture on DAMA is dominated by the
Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments
 Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX, USA E-mail: cooley@physics.smu.edu The past year has yielded several new results from the direct detection
Overview of Direct Detection Dark Matter Experiments Southern Methodist University Dallas, TX, USA E-mail: cooley@physics.smu.edu The past year has yielded several new results from the direct detection
DARWIN. Marc Schumann. U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19,
 DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Dark Matter Searches: Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions
DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg PATRAS 2017 Thessaloniki, May 19, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Dark Matter Searches: Status spin-independent WIMP-nucleon interactions
Direct Detection of! sub-gev Dark Matter
 Direct Detection of! sub-gev Dark Matter Rouven Essig C.N. Yang Institute for Theoretical Physics, Stony Brook Sackler Conference, Harvard, May 18, 2014 An ongoing program Direct Detection of sub-gev Dark
Direct Detection of! sub-gev Dark Matter Rouven Essig C.N. Yang Institute for Theoretical Physics, Stony Brook Sackler Conference, Harvard, May 18, 2014 An ongoing program Direct Detection of sub-gev Dark
The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100
 The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100 Symmetries and Fundamental Interactions 01 05 September 2014 Chiemsee Fraueninsel Boris Bauermeister on behalf of the XENON collaboration Boris.Bauermeister@uni-mainz.de
The Neutron/WIMP Acceptance In XENON100 Symmetries and Fundamental Interactions 01 05 September 2014 Chiemsee Fraueninsel Boris Bauermeister on behalf of the XENON collaboration Boris.Bauermeister@uni-mainz.de
Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors
 Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors Complementarity between Dark Matter Searches & Collider Experiments Miniworkshop before SUSY06 at Irvine -
Direct Detection in the next five years: Experimental challenges and Phonon Mediated Detectors Complementarity between Dark Matter Searches & Collider Experiments Miniworkshop before SUSY06 at Irvine -
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background
 Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
Cryodetectors, CRESST and Background A cryogenic detector for Dark Matter with heat (phonon) readout and light (scintillation) readout MPI, TUM, Oxford, Tübingen, LNGS What we re looking for: M W imp =
The XENON Project. M. Selvi The XENON project
 The XENON Project M. Selvi Assemblea di Sezione 2011 Dark matter in the Universe Dark matter properties: what we know Direct WIMP search Direct WIMP search Direct WIMP detection Why Xenon? A double-phase
The XENON Project M. Selvi Assemblea di Sezione 2011 Dark matter in the Universe Dark matter properties: what we know Direct WIMP search Direct WIMP search Direct WIMP detection Why Xenon? A double-phase
Supporting Online Material for
 Originally published 11 February 21; corrected 26 March 21 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1186112/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Dark Matter Search Results from the CDMS II Experiment
Originally published 11 February 21; corrected 26 March 21 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1186112/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Dark Matter Search Results from the CDMS II Experiment
Latest results of EDELWEISS II
 Latest results of EDELWEISS II Ana Torrentó CEA/IRFU/SPP Saclay Rencontres de Moriond 2011 «EW and Unified Theories» WIMP search Motivated by the «WIMP miracle» Very small rate of WIMPnucleus scattering
Latest results of EDELWEISS II Ana Torrentó CEA/IRFU/SPP Saclay Rencontres de Moriond 2011 «EW and Unified Theories» WIMP search Motivated by the «WIMP miracle» Very small rate of WIMPnucleus scattering
DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run
 DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run Yann Guardincerri on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration August 27th, 2014 1 / 21 DarkSide Direct detection search for WIMP dark
DarkSide-50: performance and results from the first atmospheric argon run Yann Guardincerri on behalf of the DarkSide Collaboration August 27th, 2014 1 / 21 DarkSide Direct detection search for WIMP dark
Results from CRESST and CDMS
 Results from CRESST and CDMS Syracuse University CDMS Thanks to Federica Petricca & Franz Proebst of CRESST for sharing slides and information November 14, 2011 CRESST target: CRESST Target Material scintillating
Results from CRESST and CDMS Syracuse University CDMS Thanks to Federica Petricca & Franz Proebst of CRESST for sharing slides and information November 14, 2011 CRESST target: CRESST Target Material scintillating
Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS
 Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS TeV 2006, Madison - August 30, 2006 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS Summary of current status of Direct
Latest Results on Direct Detection of Dark Matter WIMPs - CDMS & SuperCDMS TeV 2006, Madison - August 30, 2006 Blas Cabrera Co-Spokesperson CDMS & Spokesperson SuperCDMS Summary of current status of Direct
The COSINUS project. development of new NaI- based detectors for dark ma6er search. STATUS report Karoline Schäffner
 The COSINUS project development of new NaI- based detectors for dark ma6er search STATUS report 2016 Karoline Schäffner SCATTERING SCENARIO Dark matter particles scatter off nuclei elastically coherently:
The COSINUS project development of new NaI- based detectors for dark ma6er search STATUS report 2016 Karoline Schäffner SCATTERING SCENARIO Dark matter particles scatter off nuclei elastically coherently:
DAMIC DARK MATTER IN CCD
 1 DAMIC DARK MATTER IN CCD ROMAIN GAIOR (LPNHE PARIS) DARK MATTER DAY (APC 2016/12/01) MOTIVATION! A. Aguilar-Arevalo et al. (DAMIC Collaboration) Phys. Rev. D 94, 082006 DAMIC (2016) Super CDMS Si HV
1 DAMIC DARK MATTER IN CCD ROMAIN GAIOR (LPNHE PARIS) DARK MATTER DAY (APC 2016/12/01) MOTIVATION! A. Aguilar-Arevalo et al. (DAMIC Collaboration) Phys. Rev. D 94, 082006 DAMIC (2016) Super CDMS Si HV
Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program
 Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli PM2018-14th Pisa Meeting on Advanced Detectors DM direct detection WIMP χ Low mass
Darkside and the future Liquid Argon Dark Matter program Giuliana Fiorillo Università di Napoli Federico II & INFN Napoli PM2018-14th Pisa Meeting on Advanced Detectors DM direct detection WIMP χ Low mass
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter
 Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Down-to-earth searches for cosmological dark matter Carter Hall, University of Maryland October 19, 2016 Astrophysical evidence for dark matter Galaxy cluster collisions Rotation curves Ω 380,000 years
Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE
 Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE Marco Vignati University of Rome La Sapienza & INFN Rome on behalf of the CUORE collaboration Panic 11, July 5, MIT 988 TeO crystals Ton scale bolometric
Direct Dark Matter and Axion Detection with CUORE Marco Vignati University of Rome La Sapienza & INFN Rome on behalf of the CUORE collaboration Panic 11, July 5, MIT 988 TeO crystals Ton scale bolometric
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter
 Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
Direct Search for Dark Matter Direct Dark Matter Search Dark Matter in the Universe Ω = 0.23 non-baryonic not neutrinos physics beyond the standard model thermal relics from Big Bang weakly interacting
After LUX: The LZ Program. David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011
 After LUX: The LZ Program David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011 The LZ Program LZ LUX-ZEPLIN LUX (14 U.S. institutions) + new collaborators from ZEPLIN, other
After LUX: The LZ Program David Malling, Simon Fiorucci Brown University APS DPF Conference August 10, 2011 The LZ Program LZ LUX-ZEPLIN LUX (14 U.S. institutions) + new collaborators from ZEPLIN, other
WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT
 WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT P.L. BRINK, L. BAUDIS, B. CABRERA, J.P. CASTLE, C. CHANG AND T. SAAB Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94350, USA R. J. GAITSKELL
WIMP EXCLUSION RESULTS FROM THE CDMS EXPERIMENT P.L. BRINK, L. BAUDIS, B. CABRERA, J.P. CASTLE, C. CHANG AND T. SAAB Department of Physics, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94350, USA R. J. GAITSKELL
Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches
 Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches Klaus Eitel, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, KCETA, IK KIT University of the State of Baden-Württemberg and National Large-scale Research
Dark Matter -- Astrophysical Evidences and Terrestrial Searches Klaus Eitel, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, KCETA, IK KIT University of the State of Baden-Württemberg and National Large-scale Research
Collaborazione DAMA & INR-Kiev. XCVIII Congresso SIF Napoli, 18 Settembre F. Cappella
 Collaborazione DAMA & INR-Kiev http://people.roma2.infn.it/dama XCVIII Congresso SIF Napoli, 18 Settembre 2012 F. Cappella Based on the study of the correlation between the Earth motion in the galactic
Collaborazione DAMA & INR-Kiev http://people.roma2.infn.it/dama XCVIII Congresso SIF Napoli, 18 Settembre 2012 F. Cappella Based on the study of the correlation between the Earth motion in the galactic
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments
 Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
Status of Dark Matter Detection Experiments Debasish Majumdar Astroparticle Physics and Cosmology Division Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata WIMP Hunting Going beyond gravity, three ways to detect
The CUTE Facility. Ryan Underwood Queen s University, TRIUMF WNPPC 2019
 The CUTE Facility Ryan Underwood Queen s University, TRIUMF WNPPC 2019 Dark Matter Strong evidence for a nonluminous, gravitationally interacting kind of matter; Dark Matter Interaction with normal matter
The CUTE Facility Ryan Underwood Queen s University, TRIUMF WNPPC 2019 Dark Matter Strong evidence for a nonluminous, gravitationally interacting kind of matter; Dark Matter Interaction with normal matter
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX
 Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Direct Detection of Dark Matter with LUX we are a collaboration of 50+ scientists, please see http://lux.brown.edu for more information Peter Sorensen Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory DNP October
Direct Dark Matter Searches
 Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
Direct Dark Matter Searches Marc Schumann Physik Institut, Universität Zürich What is? Invisibles12, GGI Florence, June 27th 2012 marc.schumann@physik.uzh.ch www.physik.uzh.ch/groups/groupbaudis/xenon/
BubXe: a liquid xenon bubble chamber for Dark Matter detection!
 BubXe: a liquid xenon bubble chamber for Dark Matter detection Jeremy Mock, on behalf of Cecilia Levy and Matthew Szydagis SUNY Albany Direct DM Search Today 3 detection channels (light, charge, heat):
BubXe: a liquid xenon bubble chamber for Dark Matter detection Jeremy Mock, on behalf of Cecilia Levy and Matthew Szydagis SUNY Albany Direct DM Search Today 3 detection channels (light, charge, heat):
Dark Matter Detection with XENON100 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future
 Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
Dark Matter Detection with XENON0 Accomplishments, Challenges and the Future http://xenon.astro.columbia.edu Kaixuan Ni Columbia University TeV Particle Astrophysics IHEP, Beijing, Sep.4-8, 008 The Challenges
DARWIN. Marc Schumann. U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15,
 DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017
DARWIN Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017 marc.schumann@physik.uni-freiburg.de www.app.uni-freiburg.de 1 Marc Schumann U Freiburg LAUNCH 17 Heidelberg, September 15, 2017
Search for double electron capture on 124 Xe with the XMASS-I detector
 Search for double electron capture on 124 Xe with the XMASS-I detector KATSUKI HIRAIDE (ICRR, THE UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO) SEPTEMBER 7 TH, 2015 TAUP2015 1 124 Xe 2n double electron capture Natural xenon contains
Search for double electron capture on 124 Xe with the XMASS-I detector KATSUKI HIRAIDE (ICRR, THE UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO) SEPTEMBER 7 TH, 2015 TAUP2015 1 124 Xe 2n double electron capture Natural xenon contains
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases
 Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
Direct dark matter search using liquid noble gases Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia marrodan@physik.uzh.ch Physik Institut Universität Zürich Texas Symposium 2010, Heidelberg, 09.11.2010 Teresa Marrodán Undagoitia
What is the probability that direct detection experiments have observed Dark Matter?
 Prepared for submission to JCAP arxiv:1410.6160v2 [astro-ph.co] 17 Nov 2014 What is the probability that direct detection experiments have observed Dark Matter? Nassim Bozorgnia a,b and Thomas Schwetz
Prepared for submission to JCAP arxiv:1410.6160v2 [astro-ph.co] 17 Nov 2014 What is the probability that direct detection experiments have observed Dark Matter? Nassim Bozorgnia a,b and Thomas Schwetz
DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS SUMMARY OF RECENT ACHIEVEMENTS AND EFFORTS
 DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update María Luisa Sarsa (Universidad de Zaragoza) On behalf of ANAIS & ROSEBUD Collaborations OUTLINE ANAIS INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS
DARK MATTER SEARCHES AT CANFRANC: ANAIS AND ROSEBUD: an update María Luisa Sarsa (Universidad de Zaragoza) On behalf of ANAIS & ROSEBUD Collaborations OUTLINE ANAIS INTRODUCTION AND EXPERIMENTAL GOALS
Search for Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with CDMS and XENON
 Search for Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with CDMS and XENON Elena Aprile 1,2, Laura Baudis 3,4, Blas Cabrera 5,6 1 Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University,
Search for Weakly Interacting Massive Particles with CDMS and XENON Elena Aprile 1,2, Laura Baudis 3,4, Blas Cabrera 5,6 1 Physics Department and Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory, Columbia University,
Sensitivity of sodium iodide cryogenic scintillation-phonon detectors to WIMP signals
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Sensitivity of sodium iodide cryogenic scintillation-phonon detectors to WIMP signals To cite this article: M Clark et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Sensitivity of sodium iodide cryogenic scintillation-phonon detectors to WIMP signals To cite this article: M Clark et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Dark Matter Search. Dark Matter
 Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Cryogenic Detectors Direct Search Matter in the Universe - Composition ν too light => most of the is cold Ωmat = 0.27 0.04 u d of so far unknown weakly interacting, massive particles WIMPs normal baryonic
Dark Matter. and TPC Technologies
 Dark Matter and TPC Technologies The Physics Case for WIMPs Status of the Field:event by event discrimination Elements of a roadmap Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute for
Dark Matter and TPC Technologies The Physics Case for WIMPs Status of the Field:event by event discrimination Elements of a roadmap Bernard Sadoulet Dept. of Physics /LBNL UC Berkeley UC Institute for
Nuclear Recoil Scintillation and Ionization Yields in Liquid Xenon
 Nuclear Recoil Scintillation and Ionization Yields in Liquid Xenon Dan McKinsey Yale University Physics Department February, 011 Indirect and Direct Detection of Dark Matter Aspen Center of Physics Energy
Nuclear Recoil Scintillation and Ionization Yields in Liquid Xenon Dan McKinsey Yale University Physics Department February, 011 Indirect and Direct Detection of Dark Matter Aspen Center of Physics Energy
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST
 Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Esperimenti bolometrici al Gran Sasso: CUORE e CRESST Marco Vignati 24 Ottobre 2011 0νDBD in Theory Nuclear process: (A,Z) (A,Z+2) + 2 e - Can only happen if lepton number is not conserved. The decay probability
Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination
 Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination Results from DEAP-1 and Status of DEAP-3600 Pierre Gorel for the DEAP collaboration University of Alberta Dark matter Experiment
Search for Dark Matter with Liquid Argon and Pulse Shape Discrimination Results from DEAP-1 and Status of DEAP-3600 Pierre Gorel for the DEAP collaboration University of Alberta Dark matter Experiment
Dark Matter Search * in China
 Dark Matter Search * in China Jianglai Liu 刘江来 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Member of the PandaX collaboration * Disclaimer: focused on direct detection The 7th Workshop on Hadron Physics in China and
Dark Matter Search * in China Jianglai Liu 刘江来 Shanghai Jiao Tong University Member of the PandaX collaboration * Disclaimer: focused on direct detection The 7th Workshop on Hadron Physics in China and
Looking for WIMPs A Review
 Looking for WIMPs A Review Beatriz E. Burrola Gabilondo There is currently a race to find out what dark matter actually is. Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) are a strong candidate for dark
Looking for WIMPs A Review Beatriz E. Burrola Gabilondo There is currently a race to find out what dark matter actually is. Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs) are a strong candidate for dark
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors. David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011
 Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
Background Modeling and Materials Screening for the LUX and LZ Detectors David Malling Brown University LUX Collaboration AARM Meeting February 2011 1 Summary LUX screening program limits background contributions
DETECTOR RESPONSE TO LOW ENERGY NUCLEAR RECOILS. D Ann Barker and D.-M. Mei University of South Dakota
 DETECTOR RESPONSE TO LOW ENERGY NUCLEAR RECOILS D Ann Barker and D.-M. Mei University of South Dakota 11/11/11 D. Barker AARM Minneapolis, MN 2 Low Energy WIMP Induced Nuclear Recoils WIMP WIMP Elastic
DETECTOR RESPONSE TO LOW ENERGY NUCLEAR RECOILS D Ann Barker and D.-M. Mei University of South Dakota 11/11/11 D. Barker AARM Minneapolis, MN 2 Low Energy WIMP Induced Nuclear Recoils WIMP WIMP Elastic
Status of DM Direct Detection. Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science
 Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Status of DM Direct Detection Ranny Budnik Weizmann Institute of Science DM evidence on one slide Thermal freeze out of dark matter in the standard cosmological model Weakly Interacting Massive Particles
Factors Affecting Detector Performance Goals and Alternative Photo-detectors
 XENON Experiment - SAGENAP Factors Affecting Detector Performance Goals and Alternative Photo-detectors Department of Physics Brown University Source at http://gaitskell.brown.edu Gaitskell Review WIMP
XENON Experiment - SAGENAP Factors Affecting Detector Performance Goals and Alternative Photo-detectors Department of Physics Brown University Source at http://gaitskell.brown.edu Gaitskell Review WIMP
