Anomalous dimensions, Mottness, Bose metals, and holography. D. Dalidovich G. La Nave G. Vanacore. Wednesday, January 18, 17
|
|
|
- Lora Clara Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anomalous dimensions, Mottness, Bose metals, and holography D. Dalidovich G. La Nave G. Vanacore
2 Anomalous dimensions, Mottness, Bose metals, and holography 1 p 2 (p 2 ) d U d/2 Fermi liquids D. Dalidovich G. La Nave G. Vanacore
3 = d ln g(l) d ln L = d 2 no metals for d apple 2
4 = d ln g(l) d ln L = d 2 no metals for d apple 2 2D MIT 2D IST Kravchenko 1995 Goldman 1989
5 = d ln g(l) d ln L = d 2 no metals for d apple 2 2D MIT 2D IST? Kravchenko 1995 Goldman 1989
6 = d ln g(l) d ln L = d 2 no metals for d apple 2 2D MIT 2D IST? Kravchenko 1995 unresolved? Goldman 1989
7 insulator-superconductor transition = h/4e 2
8 insulator-superconductor transition insulator = h/4e 2
9 insulator-superconductor transition insulator = h/4e 2 superconductor
10 phase-only critical bosons X H = E C p 2 X + J i i hiji cos( i i! i g c g = E C /J
11 phase-only critical bosons X H = E C p 2 X + J i i hiji cos( i i! i g c hni i6=0 h i i6=0 g = E C /J
12 phase-only critical bosons X H = E C p 2 X + J i i hiji cos( i i! i g c hni i6=0 h i i6=0 g = E C /J vortex-particle duality (MPAF 1990)
13 phase-only critical bosons X H = E C p 2 X + J i i hiji cos( i i! i g c hni i6=0 h i i6=0 g = E C /J vortex-particle duality (MPAF 1990)
14 insulator-superconductor transition =# h 4e 2
15 insulator-superconductor transition =# h 4e 2 g c g = E C /J
16 insulator-superconductor transition =# h 4e 2 #=1 g c =0 g = E C /J
17 insulator-superconductor transition =# h 4e 2 #=1 g c #=0 =0 g = E C /J =0
18 insulator-superconductor transition =# h 4e 2 #=1 #=1 g c #=0 =0 g = E C /J =0
19 insulator-superconductor transition =# h 4e 2 #=1 #=1 g c #=0 =0 g = E C /J G(k,!) =k d/2! F k z =0 anomalous dimension
20 does this theory really work?
21 non-universality of c?
22 is a metallic phase for bosons possible?
23 is a metallic phase for bosons possible?
24 is a metallic phase for bosons possible? 1989
25 is a metallic phase for bosons possible?
26 is a metallic phase for bosons possible?
27 metal below H c2 activated region shifts to lower T as H increases
28 metal below H c2 mason/kapitulnik activated region (2000) shifts to lower T as H increases
29 not a refrigeration artifact
30 not a refrigeration artifact bose metal
31 not a refrigeration artifact bose metal / (H H SM ) 3
32 phases disrupting superconductivity dissipation (Kapitulnik)
33 phases disrupting superconductivity dissipation (Kapitulnik) Bose-Hubbard model (disordered) disorder-localised insulator (shortrange hopping)
34
35 is a Bose metal possible?
36 is a Bose metal possible? dc =lim T!0 lim!!0 (!, T)
37 is a Bose metal possible? dc =lim T!0 lim!!0 (!, T) collision-dominated transport Damle/Sachdev (hydrodynamic regime)
38 X H = E C p 2 X + J i i hiji cos( i j ) T T BKT m / T m<t m T g = E c /J
39 X H = E C p 2 X + J i i hiji cos( i j ) T T BKT m / T =? m<t m T g = E c /J
40 qp collisions n / e m/t
41 qp collisions n / e m/t / e m/t
42 qp collisions n / e m/t / e m/t / n O(1)
43 qp collisions n / e m/t / e m/t / n O(1) = 2 e 2 h
44 the insulator is a metal
45 the insulator is a metal but it is fragile 1! 1 +
46 the insulator is a metal but it is fragile 1! 1 +! 0
47 dissipation Z Z apple r + ie F [ ] = d 2 r d apple r ie ~ ~ A(~r, ) (~r, ) ~ ~ A(~r, ) (~r, ) +apple (~r, ) 2 + m 2 (~r, ) 2o + L dis 127,000 hits
48 dissipation Z Z apple r + ie F [ ] = d 2 r d apple r ie ~ ~ A(~r, ) (~r, ) ~ ~ A(~r, ) (~r, ) +apple (~r, ) 2 + m 2 (~r, ) 2o + L dis L dis = X ~k,!n! n ( ~ k,! n ) 2 ohmic dissipation 127,000 hits
49 but conductivity diverges at low T 4 =(e 2 /h)exp UT applet < /apple
50 but conductivity diverges at low T 4 =(e 2 /h)exp UT applet < /apple dissipation alone is not enough
51 disorder H = E C i 2 X hi,ji J ij cos( i j ) P (J ij )=1/ p 2 J 2 exp (J ij J 0 ) 2 /2J 2
52 disorder H = E C i 2 X hi,ji J ij cos( i j ) P (J ij )=1/ p 2 J 2 exp (J ij J 0 ) 2 /2J 2 3-phases
53 disorder H = E C i 2 X hi,ji J ij cos( i j ) P (J ij )=1/ p 2 J 2 exp (J ij J 0 ) 2 /2J 2 3-phases phase glass paramagnet superconductor
54 ln[z] = lim n!0 ([Z n ] 1)/n S i = (cos i, sin i )
55 ln[z] = lim n!0 ([Z n ] 1)/n S i = (cos i, sin i ) Q ab µ ( ~ k, ~ k 0,, 0 )=hs a µ( ~ k, )S b ( ~ k 0, 0 )i D( 0 1 )= lim n!0 Mn hqaa µµ( ~ k, ~ k 0,, 0 )i Edwards-Anderson order parameter
56 ln[z] = lim n!0 ([Z n ] 1)/n S i = (cos i, sin i ) Q ab µ ( ~ k, ~ k 0,, 0 )=hs a µ( ~ k, )S b ( ~ k 0, 0 )i D( 0 1 )= lim n!0 Mn hqaa µµ( ~ k, ~ k 0,, 0 )i Edwards-Anderson order parameter a µ( ~ k, ) =hs a µ( ~ k, )i SC order
57 F[,Q]=F SG (Q)+ X 1 applet Z d d x Z d 1 d 2 a,b,µ, free energy (k 2 +! n 2 + m 2 ) a,µ,k,! n X a µ(x, 1 ) +U Z d X a,µ a µ( ~ k,! n ) 2 b (x, 2 )Q ab µ (x, 1, 2 ) aµ (x, ) a 2 µ(x, ) Q ab µ ( ~ k,! 1,! 2 )= (2 ) d d (k) µ [D(! 1 )!1 +! 2,0 ab +!1,0! 2,0q ab. D(!) =! /apple
58 F[,Q]=F SG (Q)+ X 1 applet Z d d x Z d 1 d 2 a,b,µ, free energy (k 2 +! n 2 + m 2 ) a,µ,k,! n X a µ(x, 1 ) +U Z d X a,µ a µ( ~ k,! n ) 2 b (x, 2 )Q ab µ (x, 1, 2 ) [ aµ (x, ) new term a 2 µ(x, ) Q ab µ ( ~ k,! 1,! 2 )= (2 ) d d (k) µ [D(! 1 )!1 +! 2,0 ab +!1,0! 2,0q ab. D(!) =! /apple
59 similar problem F gauss = X a, ~ k,! n (k 2 +! 2 n +! n + m 2 ) a ( ~ k,! n ) 2 q X a,b, ~ k,! n! n,0 a ( ~ k,! n )[ b ( ~ k,! n )] new term propagator is replica offdiagonal G (0) ab (~ k,! n )=G 0 ( ~ k,! n ) ab + G 2 0( ~ k,! n )q!n,0
60 conductivity (! =0,T! 0) = 2 3 q EA m 4 e 2 h
61 conductivity (! =0,T! 0) = 2 3 q EA m 4 e 2 h / (g g c ) 2z
62 conductivity (! =0,T! 0) = 2 3 q EA m 4 e 2 h / (g g c ) 2z experiments: / (H H SM ) 3
63 is a phase glass stiff? F / s k 2?
64 energy landscape
65 energy landscape s 6=0
66 energy landscape s 6=0
67 energy landscape s 6=0 s =0
68
69 No
70 F gauss = X bose metal a, ~ k,! n (k 2 +! 2 n +! n + m 2 ) a ( ~ k,! n ) 2 q X a,b, ~ k,! n! n,0 a ( ~ k,! n )[ b ( ~ k,! n )] glassy physics
71 IST G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k z anomalous dimension
72 disorder holographically IST G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k z anomalous dimension
73 disorder holographically IST G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k z Z S = S 0 + d d xg(x)o(x) anomalous dimension
74 disorder holographically P [g(x)] / e 1 2f R d d xg(x) 2 IST G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k z Z S = S 0 + d d xg(x)o(x) anomalous dimension
75 disorder holographically P [g(x)] / e 1 2f R d d xg(x) 2 IST G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k z Z S = S 0 + d d xg(x)o(x) anomalous dimension 1 2 (@ µ ) 2 + m 2 2
76 disorder holographically P [g(x)] / e 1 2f R d d xg(x) 2 IST G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k z Z S = S 0 + d d xg(x)o(x) anomalous dimension Z d d x 0 (x)o(x) 1 2 (@ µ ) 2 + m 2 2
77 disorder holographically P [g(x)] / e 1 2f R d d xg(x) 2 IST G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k z Z S = S 0 + d d xg(x)o(x) anomalous dimension Z d d x 0 (x)o(x) 1 2 (@ µ ) 2 + m 2 2 [O] =d/2+
78 disorder holographically P [g(x)] / e 1 2f R d d xg(x) 2 IST G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k z Z S = S 0 + d d xg(x)o(x) anomalous dimension Z d d x 0 (x)o(x) 1 2 (@ µ ) 2 + m 2 2 [O] =d/2+
79 disorder holographically P [g(x)] / e 1 2f R d d xg(x) 2 IST G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k z Z S = S 0 + d d xg(x)o(x) anomalous dimension Z d d x 0 (x)o(x) 1 2 (@ µ ) 2 + m 2 2 [O] =d/2+ [O] <d Harris criterion
80 disorder holographically P [g(x)] / e 1 2f R d d xg(x) 2 IST G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k z Z S = S 0 + d d xg(x)o(x) anomalous dimension Z d d x 0 (x)o(x) 1 2 (@ µ ) 2 + m 2 2 [O] =d/2+ [O] <d Harris criterion are these anomalous dimensions related?
81 G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k µ
82 G(k,!) =k d/2 F! k µ anomalous dimension O/@ µ
83 use Caffarelli-Silvestre extension theorem (2006) g(x, 0) = f(x) xg + a zg 2 zg lim za z!0 = C d, ( r) f = 1 a 2
84 lim za z!0 C d, ( r) f x
85 lim za z!0 C d, ( r) f x
86 lim za z!0 C d, ( r) f x g(z =0,x)=f(x) = 1 a 2
87 BDHM(P) apple (x 1 ) (x n ) Z bulk[ ] =0 lim z n h (x 1,z) (x n,z)i bulk z!0 z d non-normalizable mode
88 BDHM(P) apple (x 1 ) (x n ) Z bulk[ ] =0 lim z n h (x 1,z) (x n,z)i bulk z!0 z d non-normalizable mode Heemskerk/Polchinski holographic renormalization z (x, `) = (x) IR UV z = ` z = x
89 Z bulk [ ]= Z D Z D z>`e S z>` Z D z<`e S z<`
90 Z Z Z bulk [ ]= D Z Z bulk [ ]= D z>`e S z>` } Z D z<`e S z<` } D IR[ ; `] UV[, ;, `]
91 Z Z Z bulk [ ]= D Z Z bulk [ ]= D z>`e S z>` } Z D z<`e S z<` } D IR[ ; `] UV[, ;, `] n-point function n-insertions of lim `!0
92 Z apple lim `!0 D IR (x 1 ) (x n ) UV[ ] =0
93 Z apple lim `!0 D IR (x 1 ) (x n ) UV[ ] =0 lim ` n `!0 Z D IR (x 1 ) (x n ) UV[ ] =0
94 Z apple lim `!0 D IR (x 1 ) (x n ) UV[ ] =0 lim ` n `!0 Z D IR (x 1 ) (x n ) UV[ ] =0 operator identity (P): O = C O lim z!0 z (x, z)
95 O = C O lim z!0 z (x, z)
96 use conjugate momentum O = C O lim z!0 z (x, z) = C O lim z!0 z z (x, z)
97 use conjugate momentum O = C O lim z!0 z (x, z) = C O lim z!0 z z (x, z) + m 2 =0 = Fz d 2 + Gz d 2 +, F,G 2C 1 (H), F = 0 + O(z 2 ), G = g 0 + O(z 2 )
98 use conjugate momentum O = C O lim z!0 z (x, z) = C O lim z!0 z z (x, z) + m 2 =0 = Fz d 2 + Gz d 2 +, F,G 2C 1 (H), F = 0 + O(z 2 ), G = g 0 + O(z 2 ) O(x) =2 g 0
99 solves massive scalar eom
100 solves massive scalar eom g = z d/2 solves CS extension problem p d2 +4m 2 := 2
101 solves massive scalar eom g = z d/2 solves CS extension problem p d2 +4m 2 := 2 O =( ) 0 the O for massive scalar field
102 independent of interactions Z (`)= ( )= Z S bulk [ ] <y<`= D d d x Z ` <y<` e S bulk[ ] <y<` dy y d+1 y 2 2 (@ y ) 2 + r x 2 + V ( )
103 independent of interactions Z (`)= ( )= Z S bulk [ ] <y<`= D d d x Z ` <y<` e S bulk[ ] <y<` dy y d+1 y 2 2 (@ y ) 2 + r x 2 + V ( ) z = y/`
104 independent of interactions Z (`)= ( )= Z S bulk [ ] <y<`= D d d x Z ` <y<` e S bulk[ ] <y<` dy y d+1 y 2 2 (@ y ) 2 + r x 2 + V ( ) S bulk [ ] /`<z<1 = 1`d Z d d x Z 1 /` dz z d+1 z = y/` z 2 2 (@ z ) 2 z2`2 + 2 r x 2 + V ( )
105 independent of interactions Z (`)= ( )= Z S bulk [ ] <y<`= D d d x Z ` <y<` e S bulk[ ] <y<` dy y d+1 y 2 2 (@ y ) 2 + r x 2 + V ( ) S bulk [ ] /`<z<1 = 1`d Z d d x Z 1 /` dz z d+1 z = y/` z 2 2 (@ z ) 2 z2`2 + 2 r x 2 + V ( )
106 independent of interactions Z (`)= ( )= Z S bulk [ ] <y<`= D d d x Z ` <y<` e S bulk[ ] <y<` dy y d+1 y 2 2 (@ y ) 2 + r x 2 + V ( ) S bulk [ ] /`<z<1 = 1`d Z d d x Z 1 /` dz z d+1 z = y/` z 2 2 (@ z ) 2 z2`2 + 2 r x 2 + V ( )
107 independent of interactions Z (`)= ( )= Z S bulk [ ] <y<`= D d d x Z ` <y<` e S bulk[ ] <y<` dy y d+1 y 2 2 (@ y ) 2 + r x 2 + V ( ) S bulk [ ] /`<z<1 = 1`d Z d d x Z 1 /` dz z d+1 z = y/` z 2 2 (@ z ) 2 z2`2 + 2 r x 2 + V ( ) saddle point is exact
108 independent of interactions Z (`)= ( )= Z S bulk [ ] <y<`= D d d x Z ` <y<` e S bulk[ ] <y<` dy y d+1 y 2 2 (@ y ) 2 + r x 2 + V ( ) S bulk [ ] /`<z<1 = 1`d Z d d x Z 1 /` dz z d+1 z = y/` z 2 2 (@ z ) 2 z2`2 + 2 r x 2 + V ( ) saddle point is exact = Fy d 2 + Gy d 2 +, F = 0 + O(y 2 ), G =( 0) + O(y 2 )
109 independent of interactions Z (`)= ( )= Z S bulk [ ] <y<`= D d d x Z ` <y<` e S bulk[ ] <y<` dy y d+1 y 2 2 (@ y ) 2 + r x 2 + V ( ) S bulk [ ] /`<z<1 = 1`d Z d d x Z 1 /` dz z d+1 z = y/` z 2 2 (@ z ) 2 z2`2 + 2 r x 2 + V ( ) saddle point is exact = Fy d 2 + Gy d 2 +, F = 0 + O(y 2 ), G =( 0) + O(y 2 ) same asymptotics!
110 boundary `action = Z 0( ) 0 + S int S int = f Z d d x nx O i (x)! 2 + Z d d x nx (O i (x)) 2 i=1 i=1 Fujita, et al. 2008
111 boundary `action Z = 0( ) 0 + S int S int = f Z d d x nx O i (x)! 2 + Z d d x nx (O i (x)) 2 i=1 i=1 ho(k)iho( k)i = fg(k) G(k)) 2 Fujita, et al glassy order
112 boundary `action Z = 0( ) 0 + S int S int = f Z d d x nx O i (x)! 2 + Z d d x nx (O i (x)) 2 i=1 i=1 ho(k)iho( k)i = fg(k) G(k)) 2 Fujita, et al glassy order
113 IMT Phys. Rev. Lett. 109, (2012)
114
115
116 holographic construction strong interaction +disorder (Mott physics)
117 holographic construction strong interaction +disorder (Mott physics) probe fermions [ (r, k,!)] = m k
118 holographic construction strong interaction +disorder (Mott physics) probe fermions [ (r, k,!)] = m k
119 Mott-like physics S probe (, ) = Z d d x p gi ( M D M m + )
120 Mott-like physics S probe (, ) = Z d d x p gi ( M D M m + ) what is hidden here?
121 Mott-like physics S probe (, ) = Z d d x p gi ( M D M m + ) what is hidden here? consider p gi (D m ipf µ µ )
122 Mott-like physics S probe (, ) = Z d d x p gi ( M D M m + ) what is hidden here? one possibility consider p gi (D m ipf µ µ )
123 AdS 2 ±(r,!, k) / r ±m kl p changes scaling dimension m 2 k = m 2 + pe d ± kl 2 r 0 e d =1/ p 2d(d 1) increasing p should change the spectral weight at 0
124 How is the spectrum modified? P=0 Fermi surface peak
125 How is the spectrum modified? P P=0 Fermi surface peak
126 How is the spectrum modified? P P= <p< > kf > 1/2 <! / k k F =! / (k k F ) 2 k F `Fermi Liquid Fermi surface peak
127 How is the spectrum modified? P P=0 Fermi surface peak
128 How is the spectrum modified? P P=0 p = 0.53 kf =1/2 MFL 0.53 <p<1/ p 6 1/2 > kf > 0 <! = =! / (k k F ) 1/(2 k F ) NFL Fermi surface peak
129 How is the spectrum modified? ST P P=0 p = 0.53 kf =1/2 MFL 0.53 <p<1/ p 6 1/2 > kf > 0 <! = =! / (k k F ) 1/(2 k F ) NFL Fermi surface peak
130 How is the spectrum modified? ST P P=0 Fermi surface peak
131 How is the spectrum modified? ST P>4.2 P P=0 Fermi surface peak
132 How is the spectrum modified? ST P>4.2 P P=0 Fermi surface peak Edalati,Leigh, PP PRL, 106 (2011)
133 How is the spectrum modified? ST P>4.2 P P=0 Fermi surface peak Edalati,Leigh, PP PRL, 106 (2011) dynamical spectral weight transfer
134 Schwarzschild/AdS G. Vanacore, PRD 2014
135 chiral symmetry and Pauli term
136 chiral symmetry and Pauli term! e i 5
137 chiral symmetry and Pauli term! e i 5 X breaks chiral symmetry if { 5,X}6=0
138 chiral symmetry and Pauli term! e i 5 X breaks chiral symmetry if { 5,X}6=0 { 5, µ F µ }6=0 Pauli term breaks chiral symmetry
139 chiral symmetry and Pauli term! e i 5 X breaks chiral symmetry if { 5,X}6=0 { 5, µ F µ }6=0 Pauli term breaks chiral symmetry mass generation scenario
140 Reissner-Nordstrom/AdS hep-th: Alsup,Siopsis, Eletherios p! p poles! zeros
141 Reissner-Nordstrom/AdS hep-th: Alsup,Siopsis, Eletherios p! p poles! zeros
142 Flow equations u 2p f(u)@ u ± = 2(mL)u ± +[v (u) k]+[v + (u) ± k] 2 ±, v ± (u) = 1 p! + Qq(1 u 2 d ) ± Qpu 2 d. f(u)
143 Flow equations u 2p f(u)@ u ± = 2(mL)u ± +[v (u) k]+[v + (u) ± k] 2 ±, v ± (u) = 1 p! + Qq(1 u 2 d ) ± Qpu 2 d. f(u) ±! ± 1/ ± p! k! p k
144 Flow equations u 2p f(u)@ u ± = 2(mL)u ± +[v (u) k]+[v + (u) ± k] 2 ±, v ± (u) = 1 p! + Qq(1 u 2 d ) ± Qpu 2 d. f(u) ±! ± 1/ ± p! k! p k u 2p f(u)@ u ± = +2(mL)u ± [v (u) k] [v + (u) ± k] 2 ±,
145 Flow equations u 2p f(u)@ u ± = 2(mL)u ± +[v (u) k]+[v + (u) ± k] 2 ±, v ± (u) = 1 p! + Qq(1 u 2 d ) ± Qpu 2 d. f(u) ±! ± 1/ ± p! k! p k u 2p f(u)@ u ± = +2(mL)u ± [v (u) k] [v + (u) ± k] 2 ±, Green functions are -inverses of one another!!
146 Flow equations u 2p f(u)@ u ± = 2(mL)u ± +[v (u) k]+[v + (u) ± k] 2 ±, v ± (u) = 1 p! + Qq(1 u 2 d ) ± Qpu 2 d. f(u) ±! ± 1/ ± p! k! p k u 2p f(u)@ u ± = +2(mL)u ± [v (u) k] [v + (u) ± k] 2 ±, Green functions are -inverses of one another!! 1 DetG R (!, k; m, p) = DetG R (!, k; m, p)
147 Schwarzschild/AdS
148 Q q
149 why is this an insulator? Q q
150 why is this an insulator? Q q who stole the charge?
151 why is this an insulator? Q q who stole the charge? p F µ µ
152 why is this an insulator? Q q who stole the charge? p F µ µ fermion back reaction is important!!
153 Q q
154 Q q two forces
155 Q q two forces Coulomb repulsion between Q, q gravity
156
157
158
159
160 q b q c q d
161 Q q
162 if q<q c gravity wins Q q
163 if Q q<q c q<q c Q q gravity wins infall to black hole
164 Mott Insulator if Q q<q c q<q c Q q gravity wins infall to black hole
165 Mott Insulator if Fermi surfaces exist Q q<q c q<q c Q q gravity wins infall to black hole
166 Mott Insulator if Fermi surfaces exist Q q<q c q<q c Q q gravity wins infall to black hole n charge = n rh + n q
167 Mott Insulator if Fermi surfaces exist Q q<q c q<q c Q q gravity wins infall to black hole n charge = n rh + n q zeros: composite stuff
168 Mott Insulator if Fermi surfaces exist Q q<q c q<q c Q q gravity wins infall to black hole n charge = n rh + n q zeros: composite stuff poles
169 Mott Insulator if Fermi surfaces exist Q q<q c q<q c Q q gravity wins infall to black hole n charge = n rh + n q No Luttinger `Theorem zeros: composite stuff poles
170 disorder include random electric field perturbatively in metric
171 disorder include random electric field perturbatively in metric?
`Anomalous dimensions for conserved currents from holographic dilatonic models to superconductivity. Gabriele La Nave. Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE)
 `Anomalous dimensions for conserved currents from holographic dilatonic models to superconductivity Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Gabriele La Nave Kridsangaphong Limtragool Pippard s problem J s 6= c 4 2
`Anomalous dimensions for conserved currents from holographic dilatonic models to superconductivity Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Gabriele La Nave Kridsangaphong Limtragool Pippard s problem J s 6= c 4 2
Do Cuprates Harbor Extra Dimensions?
 Do Cuprates Harbor Extra Dimensions? Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Gabriele La Nave Kridsangaphong Limtragool How would such dimensions be detected? Do they obey the standard electricity and magnetism? standard
Do Cuprates Harbor Extra Dimensions? Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Gabriele La Nave Kridsangaphong Limtragool How would such dimensions be detected? Do they obey the standard electricity and magnetism? standard
`Anomalous dimensions for conserved currents and Noether s Second Theorem
 `Anomalous dimensions for conserved currents and Noether s Second Theorem Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Gabriele La Nave Kridsangaphong Limtragool 0 no order Mott insulator x strange metal: experimental facts
`Anomalous dimensions for conserved currents and Noether s Second Theorem Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Gabriele La Nave Kridsangaphong Limtragool 0 no order Mott insulator x strange metal: experimental facts
Unparticles in High T_c Superconductors
 Unparticles in High T_c Superconductors Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Kiaran dave Charlie Kane Brandon Langley J. A. Hutasoit Correlated Electron Matter Correlated Electron Matter What is carrying the current?
Unparticles in High T_c Superconductors Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Kiaran dave Charlie Kane Brandon Langley J. A. Hutasoit Correlated Electron Matter Correlated Electron Matter What is carrying the current?
Optical Conductivity in the Cuprates: from Mottness to Scale Invariance
 Optical Conductivity in the Cuprates: from Mottness to Scale Invariance Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Brandon Langley Garrett Vanacore Kridsangaphong Limtragool N e ( ) = 2mV cell e 2 Z 0 (!)d! optical
Optical Conductivity in the Cuprates: from Mottness to Scale Invariance Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Brandon Langley Garrett Vanacore Kridsangaphong Limtragool N e ( ) = 2mV cell e 2 Z 0 (!)d! optical
Detecting unparticles and anomalous dimensions in the Strange Metal
 Detecting unparticles and anomalous dimensions in the Strange Metal Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Andreas Karch Brandon Langley Garrett Vanacore Kridsangaphong Limtragool Gabriele La Nave Drude metal Drude
Detecting unparticles and anomalous dimensions in the Strange Metal Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Andreas Karch Brandon Langley Garrett Vanacore Kridsangaphong Limtragool Gabriele La Nave Drude metal Drude
Optical Conductivity in the Cuprates from holography and unparticles
 Optical Conductivity in the Cuprates from holography and unparticles Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Brandon Langley Garrett Vanacore Kridsangaphong Limtragool Properties all particles share? charge fixed mass!
Optical Conductivity in the Cuprates from holography and unparticles Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Brandon Langley Garrett Vanacore Kridsangaphong Limtragool Properties all particles share? charge fixed mass!
Holography and Mottness: a Discrete Marriage
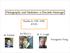 Holography and Mottness: a Discrete Marriage Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Ka Wai Lo M. Edalati R. G. Leigh Seungmin Hong Mott Problem Mott Problem + # + Mott Problem + # + σ(ω) Ω -1 cm -1 VO 2 T=360 K T=295
Holography and Mottness: a Discrete Marriage Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Ka Wai Lo M. Edalati R. G. Leigh Seungmin Hong Mott Problem Mott Problem + # + Mott Problem + # + σ(ω) Ω -1 cm -1 VO 2 T=360 K T=295
Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE)
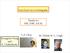 From Fermi Arcs to Holography Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Seungmin Hong and S. Chakraborty T.-P. Choy M. Edalati R. G. Leigh Fermi Arcs P. Johnson, PRL 2011 Na-CCOC (Shen, Science 2006) La-Bi2201 (Meng,
From Fermi Arcs to Holography Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Seungmin Hong and S. Chakraborty T.-P. Choy M. Edalati R. G. Leigh Fermi Arcs P. Johnson, PRL 2011 Na-CCOC (Shen, Science 2006) La-Bi2201 (Meng,
Holography and Mottness: a Discrete Marriage
 Holography and Mottness: a Discrete Marriage Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Ka Wai Lo M. Edalati R. G. Leigh Mott Problem emergent gravity Mott Problem What interacting problems can we solve in quantum mechanics?
Holography and Mottness: a Discrete Marriage Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Ka Wai Lo M. Edalati R. G. Leigh Mott Problem emergent gravity Mott Problem What interacting problems can we solve in quantum mechanics?
Unparticles and Emergent Mottness
 Unparticles and Emergent Mottness Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Kiaran dave Charlie Kane Brandon Langley J. A. Hutasoit Correlated Electron Matter Correlated Electron Matter What is carrying the current?
Unparticles and Emergent Mottness Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Kiaran dave Charlie Kane Brandon Langley J. A. Hutasoit Correlated Electron Matter Correlated Electron Matter What is carrying the current?
Autocorrelators in models with Lifshitz scaling
 Autocorrelators in models with Lifshitz scaling Lárus Thorlacius based on V. Keränen & L.T.: Class. Quantum Grav. 29 (202) 94009 arxiv:50.nnnn (to appear...) International workshop on holography and condensed
Autocorrelators in models with Lifshitz scaling Lárus Thorlacius based on V. Keränen & L.T.: Class. Quantum Grav. 29 (202) 94009 arxiv:50.nnnn (to appear...) International workshop on holography and condensed
Is Strongly Correlated Electron Matter Full of Unparticles? Kiaran dave Charlie Kane Brandon Langley
 Is Strongly Correlated Electron Matter Full of Unparticles? Kiaran dave Charlie Kane Brandon Langley Correlated Matter Correlated Matter What is carrying the current? current-carrying excitations? current-carrying
Is Strongly Correlated Electron Matter Full of Unparticles? Kiaran dave Charlie Kane Brandon Langley Correlated Matter Correlated Matter What is carrying the current? current-carrying excitations? current-carrying
Quantum criticality of Fermi surfaces
 Quantum criticality of Fermi surfaces Subir Sachdev Physics 268br, Spring 2018 HARVARD Quantum criticality of Ising-nematic ordering in a metal y Occupied states x Empty states A metal with a Fermi surface
Quantum criticality of Fermi surfaces Subir Sachdev Physics 268br, Spring 2018 HARVARD Quantum criticality of Ising-nematic ordering in a metal y Occupied states x Empty states A metal with a Fermi surface
Conference on Superconductor-Insulator Transitions May 2009
 2035-10 Conference on Superconductor-Insulator Transitions 18-23 May 2009 Phase transitions in strongly disordered magnets and superconductors on Bethe lattice L. Ioffe Rutgers, the State University of
2035-10 Conference on Superconductor-Insulator Transitions 18-23 May 2009 Phase transitions in strongly disordered magnets and superconductors on Bethe lattice L. Ioffe Rutgers, the State University of
Holographic Lattices
 Holographic Lattices Jerome Gauntlett with Aristomenis Donos Christiana Pantelidou Holographic Lattices CFT with a deformation by an operator that breaks translation invariance Why? Translation invariance
Holographic Lattices Jerome Gauntlett with Aristomenis Donos Christiana Pantelidou Holographic Lattices CFT with a deformation by an operator that breaks translation invariance Why? Translation invariance
Is Strongly Correlated Electron Matter Full of Unparticles? Kiaran dave Charlie Kane Brandon Langley
 Is Strongly Correlated Electron Matter Full of Unparticles? Kiaran dave Charlie Kane Brandon Langley 2=3 goal 2 = 3 Properties all particles share? Properties all particles share? charge fixed mass! Properties
Is Strongly Correlated Electron Matter Full of Unparticles? Kiaran dave Charlie Kane Brandon Langley 2=3 goal 2 = 3 Properties all particles share? Properties all particles share? charge fixed mass! Properties
Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE)
 Mottness and Holography: A Discrete Marriage Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Seungmin Hong M. Edalati R. G. Leigh emergent gravity spectral weight transfer 2-particle probe spectral weight transfer spectral
Mottness and Holography: A Discrete Marriage Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Seungmin Hong M. Edalati R. G. Leigh emergent gravity spectral weight transfer 2-particle probe spectral weight transfer spectral
Entanglement, holography, and strange metals
 Entanglement, holography, and strange metals PCTS, Princeton, October 26, 2012 Subir Sachdev Talk online at sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD Liza Huijse Max Metlitski Brian Swingle Complex entangled
Entanglement, holography, and strange metals PCTS, Princeton, October 26, 2012 Subir Sachdev Talk online at sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD Liza Huijse Max Metlitski Brian Swingle Complex entangled
Complex entangled states of quantum matter, not adiabatically connected to independent particle states. Compressible quantum matter
 Complex entangled states of quantum matter, not adiabatically connected to independent particle states Gapped quantum matter Z2 Spin liquids, quantum Hall states Conformal quantum matter Graphene, ultracold
Complex entangled states of quantum matter, not adiabatically connected to independent particle states Gapped quantum matter Z2 Spin liquids, quantum Hall states Conformal quantum matter Graphene, ultracold
Holographic Metals. Valentina Giangreco Marotta Puletti Chalmers Institute of Technology. XIII Marcel Grossmann Meeting Stockholm, July 5th, 2012
 Holographic Metals Valentina Giangreco Marotta Puletti Chalmers Institute of Technology XIII Marcel Grossmann Meeting Stockholm, July 5th, 2012 in collaboration with S. Nowling, L. Thorlacius, and T. Zingg
Holographic Metals Valentina Giangreco Marotta Puletti Chalmers Institute of Technology XIII Marcel Grossmann Meeting Stockholm, July 5th, 2012 in collaboration with S. Nowling, L. Thorlacius, and T. Zingg
The Hubbard model in cold atoms and in the high-tc cuprates
 The Hubbard model in cold atoms and in the high-tc cuprates Daniel E. Sheehy Aspen, June 2009 Sheehy@LSU.EDU What are the key outstanding problems from condensed matter physics which ultracold atoms and
The Hubbard model in cold atoms and in the high-tc cuprates Daniel E. Sheehy Aspen, June 2009 Sheehy@LSU.EDU What are the key outstanding problems from condensed matter physics which ultracold atoms and
Holographic Lattices
 Holographic Lattices Jerome Gauntlett with Aristomenis Donos Christiana Pantelidou Holographic Lattices CFT with a deformation by an operator that breaks translation invariance Why? Translation invariance
Holographic Lattices Jerome Gauntlett with Aristomenis Donos Christiana Pantelidou Holographic Lattices CFT with a deformation by an operator that breaks translation invariance Why? Translation invariance
Holography with Shape Dynamics
 . 1/ 11 Holography with Henrique Gomes Physics, University of California, Davis July 6, 2012 In collaboration with Tim Koslowski Outline 1 Holographic dulaities 2 . 2/ 11 Holographic dulaities Ideas behind
. 1/ 11 Holography with Henrique Gomes Physics, University of California, Davis July 6, 2012 In collaboration with Tim Koslowski Outline 1 Holographic dulaities 2 . 2/ 11 Holographic dulaities Ideas behind
Optical Conductivity in the Cuprates from Holography and Unparticles
 Optical Conductivity in the Cuprates from Holography and Unparticles Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Brandon Langley Garrett Vanacore Kridsangaphong Limtragool Drude conductivity n e 2 1 m 1 i! (!) =C! 2 3
Optical Conductivity in the Cuprates from Holography and Unparticles Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Brandon Langley Garrett Vanacore Kridsangaphong Limtragool Drude conductivity n e 2 1 m 1 i! (!) =C! 2 3
Emergent Quantum Criticality
 (Non-)Fermi Liquids and Emergent Quantum Criticality from gravity Hong Liu Massachusetts setts Institute te of Technology HL, John McGreevy, David Vegh, 0903.2477 Tom Faulkner, HL, JM, DV, to appear Sung-Sik
(Non-)Fermi Liquids and Emergent Quantum Criticality from gravity Hong Liu Massachusetts setts Institute te of Technology HL, John McGreevy, David Vegh, 0903.2477 Tom Faulkner, HL, JM, DV, to appear Sung-Sik
Holography of compressible quantum states
 Holography of compressible quantum states New England String Meeting, Brown University, November 18, 2011 sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD Liza Huijse Max Metlitski Brian Swingle Compressible quantum
Holography of compressible quantum states New England String Meeting, Brown University, November 18, 2011 sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD Liza Huijse Max Metlitski Brian Swingle Compressible quantum
Strongly correlated Cooper pair insulators and superfluids
 Strongly correlated Cooper pair insulators and superfluids Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Acknowledgments Collaborators Subir Sachdev Eun-Gook Moon Anton Burkov Arun Paramekanti Affiliations and
Strongly correlated Cooper pair insulators and superfluids Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Acknowledgments Collaborators Subir Sachdev Eun-Gook Moon Anton Burkov Arun Paramekanti Affiliations and
Holographic vortex pair annihilation in superfluid turbulence
 Holographic vortex pair annihilation in superfluid turbulence Vrije Universiteit Brussel and International Solvay Institutes Based mainly on arxiv:1412.8417 with: Yiqiang Du and Yu Tian(UCAS,CAS) Chao
Holographic vortex pair annihilation in superfluid turbulence Vrije Universiteit Brussel and International Solvay Institutes Based mainly on arxiv:1412.8417 with: Yiqiang Du and Yu Tian(UCAS,CAS) Chao
Gauge/Gravity Duality: Applications to Condensed Matter Physics. Johanna Erdmenger. Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg
 Gauge/Gravity Duality: Applications to Condensed Matter Physics. Johanna Erdmenger Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg 1 New Gauge/Gravity Duality group at Würzburg University Permanent members 2 Gauge/Gravity
Gauge/Gravity Duality: Applications to Condensed Matter Physics. Johanna Erdmenger Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg 1 New Gauge/Gravity Duality group at Würzburg University Permanent members 2 Gauge/Gravity
Contents. 1.1 Prerequisites and textbooks Physical phenomena and theoretical tools The path integrals... 9
 Preface v Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Prerequisites and textbooks......................... 1 1.2 Physical phenomena and theoretical tools................. 5 1.3 The path integrals..............................
Preface v Chapter 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Prerequisites and textbooks......................... 1 1.2 Physical phenomena and theoretical tools................. 5 1.3 The path integrals..............................
Testing Mottness/unparticles and anomalous dimensions in the Cuprates
 Testing Mottness/unparticles and anomalous dimensions in the Cuprates Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Brandon Langley Garrett Vanacore Kridsangaphong Limtragool / at what is strange about the strange metal?
Testing Mottness/unparticles and anomalous dimensions in the Cuprates Thanks to: NSF, EFRC (DOE) Brandon Langley Garrett Vanacore Kridsangaphong Limtragool / at what is strange about the strange metal?
Purely electronic transport in dirty boson insulators
 Purely electronic transport in dirty boson insulators Markus Müller Ann. Phys. (Berlin) 18, 849 (2009). Discussions with M. Feigel man, M.P.A. Fisher, L. Ioffe, V. Kravtsov, Abdus Salam International Center
Purely electronic transport in dirty boson insulators Markus Müller Ann. Phys. (Berlin) 18, 849 (2009). Discussions with M. Feigel man, M.P.A. Fisher, L. Ioffe, V. Kravtsov, Abdus Salam International Center
Unaprticles: MEELS, ARPES and the Strange Metal
 Unaprticles: MEELS, ARPES and the Strange Metal K. Limtragool Chandan Setty Chandan Setty Zhidong Leong Zhidong Leong Bikash Padhi strange metal: experimental facts T-linear resistivity (!) =C! 2 3 L xy
Unaprticles: MEELS, ARPES and the Strange Metal K. Limtragool Chandan Setty Chandan Setty Zhidong Leong Zhidong Leong Bikash Padhi strange metal: experimental facts T-linear resistivity (!) =C! 2 3 L xy
Quantum matter and gauge-gravity duality
 Quantum matter and gauge-gravity duality 2013 Arnold Sommerfeld School, Munich, August 5-9, 2013 Subir Sachdev Talk online at sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD " k Dirac semi-metal " k Insulating antiferromagnet
Quantum matter and gauge-gravity duality 2013 Arnold Sommerfeld School, Munich, August 5-9, 2013 Subir Sachdev Talk online at sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD " k Dirac semi-metal " k Insulating antiferromagnet
Examples of Lifshitz topological transition in interacting fermionic systems
 Examples of Lifshitz topological transition in interacting fermionic systems Joseph Betouras (Loughborough U. Work in collaboration with: Sergey Slizovskiy (Loughborough, Sam Carr (Karlsruhe/Kent and Jorge
Examples of Lifshitz topological transition in interacting fermionic systems Joseph Betouras (Loughborough U. Work in collaboration with: Sergey Slizovskiy (Loughborough, Sam Carr (Karlsruhe/Kent and Jorge
Dynamical mean field approach to correlated lattice systems in and out of equilibrium
 Dynamical mean field approach to correlated lattice systems in and out of equilibrium Philipp Werner University of Fribourg, Switzerland Kyoto, December 2013 Overview Dynamical mean field approximation
Dynamical mean field approach to correlated lattice systems in and out of equilibrium Philipp Werner University of Fribourg, Switzerland Kyoto, December 2013 Overview Dynamical mean field approximation
Holographic transport with random-field disorder. Andrew Lucas
 Holographic transport with random-field disorder Andrew Lucas Harvard Physics Quantum Field Theory, String Theory and Condensed Matter Physics: Orthodox Academy of Crete September 1, 2014 Collaborators
Holographic transport with random-field disorder Andrew Lucas Harvard Physics Quantum Field Theory, String Theory and Condensed Matter Physics: Orthodox Academy of Crete September 1, 2014 Collaborators
Is there a de Almeida-Thouless line in finite-dimensional spin glasses? (and why you should care)
 Is there a de Almeida-Thouless line in finite-dimensional spin glasses? (and why you should care) Peter Young Talk at MPIPKS, September 12, 2013 Available on the web at http://physics.ucsc.edu/~peter/talks/mpipks.pdf
Is there a de Almeida-Thouless line in finite-dimensional spin glasses? (and why you should care) Peter Young Talk at MPIPKS, September 12, 2013 Available on the web at http://physics.ucsc.edu/~peter/talks/mpipks.pdf
Recent Developments in Holographic Superconductors. Gary Horowitz UC Santa Barbara
 Recent Developments in Holographic Superconductors Gary Horowitz UC Santa Barbara Outline 1) Review basic ideas behind holographic superconductors 2) New view of conductivity and the zero temperature limit
Recent Developments in Holographic Superconductors Gary Horowitz UC Santa Barbara Outline 1) Review basic ideas behind holographic superconductors 2) New view of conductivity and the zero temperature limit
MOTTNESS AND STRONG COUPLING
 MOTTNESS AND STRONG COUPLING ROB LEIGH UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS Rutgers University April 2008 based on various papers with Philip Phillips and Ting-Pong Choy PRL 99 (2007) 046404 PRB 77 (2008) 014512 PRB
MOTTNESS AND STRONG COUPLING ROB LEIGH UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS Rutgers University April 2008 based on various papers with Philip Phillips and Ting-Pong Choy PRL 99 (2007) 046404 PRB 77 (2008) 014512 PRB
Under The Dome. Doped holographic superconductors with broken translational symmetry
 Prepared for submission to JHEP Under The Dome arxiv:1510.06363v1 [hep-th] 21 Oct 2015 Doped holographic superconductors with broken translational symmetry Matteo Baggioli, a,b Mikhail Goykhman c a Institut
Prepared for submission to JHEP Under The Dome arxiv:1510.06363v1 [hep-th] 21 Oct 2015 Doped holographic superconductors with broken translational symmetry Matteo Baggioli, a,b Mikhail Goykhman c a Institut
Boson Vortex duality. Abstract
 Boson Vortex duality Subir Sachdev Department of Physics, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 0238, USA and Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, Waterloo, Ontario N2L 2Y5, Canada (Dated:
Boson Vortex duality Subir Sachdev Department of Physics, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 0238, USA and Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, Waterloo, Ontario N2L 2Y5, Canada (Dated:
Quantum phase transitions in condensed matter
 Quantum phase transitions in condensed matter The 8th Asian Winter School on Strings, Particles, and Cosmology, Puri, India January 11-18, 2014 Subir Sachdev Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD
Quantum phase transitions in condensed matter The 8th Asian Winter School on Strings, Particles, and Cosmology, Puri, India January 11-18, 2014 Subir Sachdev Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD
QCD and Instantons: 12 Years Later. Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State
 QCD and Instantons: 12 Years Later Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State 1 ESQGP: A man ahead of his time 2 Instanton Liquid: Pre-History 1975 (Polyakov): The instanton solution r 2 2 E + B A a µ(x) = 2
QCD and Instantons: 12 Years Later Thomas Schaefer North Carolina State 1 ESQGP: A man ahead of his time 2 Instanton Liquid: Pre-History 1975 (Polyakov): The instanton solution r 2 2 E + B A a µ(x) = 2
Mott metal-insulator transition on compressible lattices
 Mott metal-insulator transition on compressible lattices Markus Garst Universität zu Köln T p in collaboration with : Mario Zacharias (Köln) Lorenz Bartosch (Frankfurt) T c Mott insulator p c T metal pressure
Mott metal-insulator transition on compressible lattices Markus Garst Universität zu Köln T p in collaboration with : Mario Zacharias (Köln) Lorenz Bartosch (Frankfurt) T c Mott insulator p c T metal pressure
Applications of AdS/CFT correspondence to cold atom physics
 Applications of AdS/CFT correspondence to cold atom physics Sergej Moroz in collaboration with Carlos Fuertes ITP, Heidelberg Outline Basics of AdS/CFT correspondence Schrödinger group and correlation
Applications of AdS/CFT correspondence to cold atom physics Sergej Moroz in collaboration with Carlos Fuertes ITP, Heidelberg Outline Basics of AdS/CFT correspondence Schrödinger group and correlation
Topological order in the pseudogap metal
 HARVARD Topological order in the pseudogap metal High Temperature Superconductivity Unifying Themes in Diverse Materials 2018 Aspen Winter Conference Aspen Center for Physics Subir Sachdev January 16,
HARVARD Topological order in the pseudogap metal High Temperature Superconductivity Unifying Themes in Diverse Materials 2018 Aspen Winter Conference Aspen Center for Physics Subir Sachdev January 16,
The Higgs particle in condensed matter
 The Higgs particle in condensed matter Assa Auerbach, Technion N. H. Lindner and A. A, Phys. Rev. B 81, 054512 (2010) D. Podolsky, A. A, and D. P. Arovas, Phys. Rev. B 84, 174522 (2011)S. Gazit, D. Podolsky,
The Higgs particle in condensed matter Assa Auerbach, Technion N. H. Lindner and A. A, Phys. Rev. B 81, 054512 (2010) D. Podolsky, A. A, and D. P. Arovas, Phys. Rev. B 84, 174522 (2011)S. Gazit, D. Podolsky,
Elementary/Composite Mixing in Randall-Sundrum Models
 Elementary/Composite Mixing in Randall-Sundrum Models Brian Batell University of Minnesota with Tony Gherghetta - arxiv:0706.0890 - arxiv:0710.1838 Cornell 1/30/08 5D Warped Dimension = 4D Strong Dynamics
Elementary/Composite Mixing in Randall-Sundrum Models Brian Batell University of Minnesota with Tony Gherghetta - arxiv:0706.0890 - arxiv:0710.1838 Cornell 1/30/08 5D Warped Dimension = 4D Strong Dynamics
Solvable model for a dynamical quantum phase transition from fast to slow scrambling
 Solvable model for a dynamical quantum phase transition from fast to slow scrambling Sumilan Banerjee Weizmann Institute of Science Designer Quantum Systems Out of Equilibrium, KITP November 17, 2016 Work
Solvable model for a dynamical quantum phase transition from fast to slow scrambling Sumilan Banerjee Weizmann Institute of Science Designer Quantum Systems Out of Equilibrium, KITP November 17, 2016 Work
Floquet Superconductor in Holography
 Floquet Superconductor in Holography Takaaki Ishii (Utrecht) arxiv:1804.06785 [hep-th] w/ Keiju Murata 11 June 2018, Nonperturbative QCD Paris Motivations Holography in time dependent systems To understand
Floquet Superconductor in Holography Takaaki Ishii (Utrecht) arxiv:1804.06785 [hep-th] w/ Keiju Murata 11 June 2018, Nonperturbative QCD Paris Motivations Holography in time dependent systems To understand
dynamics of broken symmetry
 dynamics of broken symmetry Julian Sonner, MIT Simons Symposium - Quantum Entanglement Caneel Bay, USVI a physics connection in paradise 1957: J. R. Oppenheimer purchases small plot of land in Hawksnest
dynamics of broken symmetry Julian Sonner, MIT Simons Symposium - Quantum Entanglement Caneel Bay, USVI a physics connection in paradise 1957: J. R. Oppenheimer purchases small plot of land in Hawksnest
Wilsonian and large N theories of quantum critical metals. Srinivas Raghu (Stanford)
 Wilsonian and large N theories of quantum critical metals Srinivas Raghu (Stanford) Collaborators and References R. Mahajan, D. Ramirez, S. Kachru, and SR, PRB 88, 115116 (2013). A. Liam Fitzpatrick, S.
Wilsonian and large N theories of quantum critical metals Srinivas Raghu (Stanford) Collaborators and References R. Mahajan, D. Ramirez, S. Kachru, and SR, PRB 88, 115116 (2013). A. Liam Fitzpatrick, S.
Metal-insulator Transition by Holographic Charge Density Waves
 Metal-insulator Transition by Holographic Charge Density Waves Chao Niu (IHEP, CAS) Based mainly on arxiv:1404.0777 with: Yi Ling, Jianpin Wu, Zhuoyu Xian and Hongbao Zhang (May 9, 2014) Outlines 1. Introduction
Metal-insulator Transition by Holographic Charge Density Waves Chao Niu (IHEP, CAS) Based mainly on arxiv:1404.0777 with: Yi Ling, Jianpin Wu, Zhuoyu Xian and Hongbao Zhang (May 9, 2014) Outlines 1. Introduction
Fermi liquid theory Can we apply the free fermion approximation to a real metal? Phys540.nb Strong interaction vs.
 Phys540.nb 7 Fermi liquid theory.. Can we apply the free fermion approximation to a real metal? Can we ignore interactions in a real metal? Experiments says yes (free fermion models work very well), but
Phys540.nb 7 Fermi liquid theory.. Can we apply the free fermion approximation to a real metal? Can we ignore interactions in a real metal? Experiments says yes (free fermion models work very well), but
FRG approach to interacting fermions with partial bosonization: from weak to strong coupling
 FRG approach to interacting fermions with partial bosonization: from weak to strong coupling Talk at conference ERG08, Heidelberg, June 30, 2008 Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt collaborators: Lorenz
FRG approach to interacting fermions with partial bosonization: from weak to strong coupling Talk at conference ERG08, Heidelberg, June 30, 2008 Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt collaborators: Lorenz
Strange metal from local quantum chaos
 Strange metal from local quantum chaos John McGreevy (UCSD) hello based on work with Daniel Ben-Zion (UCSD) 2017-08-26 Compressible states of fermions at finite density The metallic states that we understand
Strange metal from local quantum chaos John McGreevy (UCSD) hello based on work with Daniel Ben-Zion (UCSD) 2017-08-26 Compressible states of fermions at finite density The metallic states that we understand
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter. Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti)
 Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Field Theory Description of Topological States of Matter Andrea Cappelli INFN, Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Topological States of Matter System with bulk gap but non-trivial at energies below
Holographic Q-Lattices and Metal-Insulator Transitions
 Holographic Q-Lattices and Metal-Insulator Transitions Jerome Gauntlett Aristomenis Donos Holographic tools provide a powerful framework for investigating strongly coupled systems using weakly coupled
Holographic Q-Lattices and Metal-Insulator Transitions Jerome Gauntlett Aristomenis Donos Holographic tools provide a powerful framework for investigating strongly coupled systems using weakly coupled
Holographic Kondo and Fano Resonances
 Holographic Kondo and Fano Resonances Andy O Bannon Disorder in Condensed Matter and Black Holes Lorentz Center, Leiden, the Netherlands January 13, 2017 Credits Johanna Erdmenger Würzburg Carlos Hoyos
Holographic Kondo and Fano Resonances Andy O Bannon Disorder in Condensed Matter and Black Holes Lorentz Center, Leiden, the Netherlands January 13, 2017 Credits Johanna Erdmenger Würzburg Carlos Hoyos
Theory of Quantum Matter: from Quantum Fields to Strings
 Theory of Quantum Matter: from Quantum Fields to Strings Salam Distinguished Lectures The Abdus Salam International Center for Theoretical Physics Trieste, Italy January 27-30, 2014 Subir Sachdev Talk
Theory of Quantum Matter: from Quantum Fields to Strings Salam Distinguished Lectures The Abdus Salam International Center for Theoretical Physics Trieste, Italy January 27-30, 2014 Subir Sachdev Talk
Preface Introduction to the electron liquid
 Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Quantum critical dynamics: CFT, Monte Carlo & holography. William Witczak-Krempa Perimeter Institute
 Quantum critical dynamics: CFT, Monte Carlo & holography William Witczak-Krempa Perimeter Institute Toronto, HEP seminar, Jan. 12 2015 S. Sachdev @Harvard / PI E. Sorensen @McMaster E. Katz @Boston U.
Quantum critical dynamics: CFT, Monte Carlo & holography William Witczak-Krempa Perimeter Institute Toronto, HEP seminar, Jan. 12 2015 S. Sachdev @Harvard / PI E. Sorensen @McMaster E. Katz @Boston U.
Glueballs at finite temperature from AdS/QCD
 Light-Cone 2009: Relativistic Hadronic and Particle Physics Instituto de Física Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro Glueballs at finite temperature from AdS/QCD Alex S. Miranda Work done in collaboration
Light-Cone 2009: Relativistic Hadronic and Particle Physics Instituto de Física Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro Glueballs at finite temperature from AdS/QCD Alex S. Miranda Work done in collaboration
Entanglement, holography, and strange metals
 Entanglement, holography, and strange metals University of Cologne, June 8, 2012 Subir Sachdev Lecture at the 100th anniversary Solvay conference, Theory of the Quantum World, chair D.J. Gross. arxiv:1203.4565
Entanglement, holography, and strange metals University of Cologne, June 8, 2012 Subir Sachdev Lecture at the 100th anniversary Solvay conference, Theory of the Quantum World, chair D.J. Gross. arxiv:1203.4565
Quantum phase transitions in condensed matter
 Quantum phase transitions in condensed matter The 8th Asian Winter School on Strings, Particles, and Cosmology, Puri, India January 11-18, 2014 Subir Sachdev Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD
Quantum phase transitions in condensed matter The 8th Asian Winter School on Strings, Particles, and Cosmology, Puri, India January 11-18, 2014 Subir Sachdev Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD
Holographic Wilsonian Renormalization Group
 Holographic Wilsonian Renormalization Group JiYoung Kim May 0, 207 Abstract Strongly coupled systems are difficult to study because the perturbation of the systems does not work with strong couplings.
Holographic Wilsonian Renormalization Group JiYoung Kim May 0, 207 Abstract Strongly coupled systems are difficult to study because the perturbation of the systems does not work with strong couplings.
Quantum oscillations & black hole ringing
 Quantum oscillations & black hole ringing Sean Hartnoll Harvard University Work in collaboration with Frederik Denef : 0901.1160. Frederik Denef and Subir Sachdev : 0908.1788, 0908.2657. Sept. 09 ASC,
Quantum oscillations & black hole ringing Sean Hartnoll Harvard University Work in collaboration with Frederik Denef : 0901.1160. Frederik Denef and Subir Sachdev : 0908.1788, 0908.2657. Sept. 09 ASC,
Disordered metals without quasiparticles, and charged black holes
 HARVARD Disordered metals without quasiparticles, and charged black holes String Theory: Past and Present (SpentaFest) International Center for Theoretical Sciences, Bengaluru January 11-13, 2017 Subir
HARVARD Disordered metals without quasiparticles, and charged black holes String Theory: Past and Present (SpentaFest) International Center for Theoretical Sciences, Bengaluru January 11-13, 2017 Subir
Metals without quasiparticles
 Metals without quasiparticles A. Review of Fermi liquid theory B. A non-fermi liquid: the Ising-nematic quantum critical point C. Fermi surfaces and gauge fields Metals without quasiparticles A. Review
Metals without quasiparticles A. Review of Fermi liquid theory B. A non-fermi liquid: the Ising-nematic quantum critical point C. Fermi surfaces and gauge fields Metals without quasiparticles A. Review
A Holographic Model of the Kondo Effect (Part 1)
 A Holographic Model of the Kondo Effect (Part 1) Andy O Bannon Quantum Field Theory, String Theory, and Condensed Matter Physics Kolymbari, Greece September 1, 2014 Credits Based on 1310.3271 Johanna Erdmenger
A Holographic Model of the Kondo Effect (Part 1) Andy O Bannon Quantum Field Theory, String Theory, and Condensed Matter Physics Kolymbari, Greece September 1, 2014 Credits Based on 1310.3271 Johanna Erdmenger
Nanoelectronics 14. [( ) k B T ] 1. Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics. Quick Review over the Last Lecture.
![Nanoelectronics 14. [( ) k B T ] 1. Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics. Quick Review over the Last Lecture. Nanoelectronics 14. [( ) k B T ] 1. Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics. Quick Review over the Last Lecture.](/thumbs/85/92941616.jpg) Nanoelectronics 14 Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics 09:00 Tuesday, 27/February/2018 (P/T 005) Quick Review over the Last Lecture Function Fermi-Dirac distribution f ( E) = 1 exp E µ [( ) k B
Nanoelectronics 14 Atsufumi Hirohata Department of Electronics 09:00 Tuesday, 27/February/2018 (P/T 005) Quick Review over the Last Lecture Function Fermi-Dirac distribution f ( E) = 1 exp E µ [( ) k B
Conductor Insulator Quantum
 Conductor Insulator Quantum Phase Transitions Edited by Vladimir Dobrosavljevic, Nandini Trivedi, James M. Valles, Jr. OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of abbreviations List of contributors xiv xvi
Conductor Insulator Quantum Phase Transitions Edited by Vladimir Dobrosavljevic, Nandini Trivedi, James M. Valles, Jr. OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of abbreviations List of contributors xiv xvi
Magnetic-field-tuned superconductor-insulator transition in underdoped La 2-x Sr x CuO 4
 Magnetic-field-tuned superconductor-insulator transition in underdoped La 2-x Sr x CuO 4 Dragana Popović National High Magnetic Field Laboratory Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, USA Collaborators
Magnetic-field-tuned superconductor-insulator transition in underdoped La 2-x Sr x CuO 4 Dragana Popović National High Magnetic Field Laboratory Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL, USA Collaborators
Probing Holographic Superfluids with Solitons
 Probing Holographic Superfluids with Solitons Sean Nowling Nordita GGI Workshop on AdS4/CFT3 and the Holographic States of Matter work in collaboration with: V. Keränen, E. Keski-Vakkuri, and K.P. Yogendran
Probing Holographic Superfluids with Solitons Sean Nowling Nordita GGI Workshop on AdS4/CFT3 and the Holographic States of Matter work in collaboration with: V. Keränen, E. Keski-Vakkuri, and K.P. Yogendran
Superconducting fluctuations, interactions and disorder : a subtle alchemy
 Les défis actuels de la supraconductivité Dautreppe 2011 Superconducting fluctuations, interactions and disorder : a subtle alchemy Claude Chapelier, Benjamin Sacépé, Thomas Dubouchet INAC-SPSMS-LaTEQS,
Les défis actuels de la supraconductivité Dautreppe 2011 Superconducting fluctuations, interactions and disorder : a subtle alchemy Claude Chapelier, Benjamin Sacépé, Thomas Dubouchet INAC-SPSMS-LaTEQS,
UNIVERSAL BOUNDS ON DIFFUSION
 9th Crete Regional Meeting in String Theory UNIVERSAL BOUNDS ON DIFFUSION with B. Gouteraux, E. Kiritsis and W.Li +... Matteo Baggioli UOC & Crete Center for Theoretical Physics Is there a miminum (Planckian)
9th Crete Regional Meeting in String Theory UNIVERSAL BOUNDS ON DIFFUSION with B. Gouteraux, E. Kiritsis and W.Li +... Matteo Baggioli UOC & Crete Center for Theoretical Physics Is there a miminum (Planckian)
Quantum critical transport, duality, and M-theory
 Quantum critical transport, duality, and M-theory hep-th/0701036 Christopher Herzog (Washington) Pavel Kovtun (UCSB) Subir Sachdev (Harvard) Dam Thanh Son (Washington) Talks online at http://sachdev.physics.harvard.edu
Quantum critical transport, duality, and M-theory hep-th/0701036 Christopher Herzog (Washington) Pavel Kovtun (UCSB) Subir Sachdev (Harvard) Dam Thanh Son (Washington) Talks online at http://sachdev.physics.harvard.edu
HIGHER SPIN DUALITY from THERMOFIELD DOUBLE QFT. AJ+Kenta Suzuki+Jung-Gi Yoon Workshop on Double Field Theory ITS, ETH Zurich, Jan 20-23,2016
 HIGHER SPIN DUALITY from THERMOFIELD DOUBLE QFT AJ+Kenta Suzuki+Jung-Gi Yoon Workshop on Double Field Theory ITS, ETH Zurich, Jan 20-23,2016 Overview } Construction of AdS HS Gravity from CFT } Simplest
HIGHER SPIN DUALITY from THERMOFIELD DOUBLE QFT AJ+Kenta Suzuki+Jung-Gi Yoon Workshop on Double Field Theory ITS, ETH Zurich, Jan 20-23,2016 Overview } Construction of AdS HS Gravity from CFT } Simplest
Quantum Choreography: Exotica inside Crystals
 Quantum Choreography: Exotica inside Crystals U. Toronto - Colloquia 3/9/2006 J. Alicea, O. Motrunich, T. Senthil and MPAF Electrons inside crystals: Quantum Mechanics at room temperature Quantum Theory
Quantum Choreography: Exotica inside Crystals U. Toronto - Colloquia 3/9/2006 J. Alicea, O. Motrunich, T. Senthil and MPAF Electrons inside crystals: Quantum Mechanics at room temperature Quantum Theory
Analog Duality. Sabine Hossenfelder. Nordita. Sabine Hossenfelder, Nordita Analog Duality 1/29
 Analog Duality Sabine Hossenfelder Nordita Sabine Hossenfelder, Nordita Analog Duality 1/29 Dualities A duality, in the broadest sense, identifies two theories with each other. A duality is especially
Analog Duality Sabine Hossenfelder Nordita Sabine Hossenfelder, Nordita Analog Duality 1/29 Dualities A duality, in the broadest sense, identifies two theories with each other. A duality is especially
On higher-spin gravity in three dimensions
 On higher-spin gravity in three dimensions Jena, 6 November 2015 Stefan Fredenhagen Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin und Max-Planck-Institut für Gravitationsphysik Higher spins Gauge theories are a success
On higher-spin gravity in three dimensions Jena, 6 November 2015 Stefan Fredenhagen Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin und Max-Planck-Institut für Gravitationsphysik Higher spins Gauge theories are a success
A Holographic Realization of Ferromagnets
 A Holographic Realization of Ferromagnets Masafumi Ishihara ( AIMR, Tohoku University) Collaborators: Koji Sato ( AIMR, Tohoku University) Naoto Yokoi Eiji Saitoh ( IMR, Tohoku University) ( AIMR, IMR,
A Holographic Realization of Ferromagnets Masafumi Ishihara ( AIMR, Tohoku University) Collaborators: Koji Sato ( AIMR, Tohoku University) Naoto Yokoi Eiji Saitoh ( IMR, Tohoku University) ( AIMR, IMR,
General relativity and the cuprates
 General relativity and the cuprates Gary T. Horowitz and Jorge E. Santos Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA 93106, U.S.A. E-mail: gary@physics.ucsb.edu, jss55@physics.ucsb.edu
General relativity and the cuprates Gary T. Horowitz and Jorge E. Santos Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA 93106, U.S.A. E-mail: gary@physics.ucsb.edu, jss55@physics.ucsb.edu
R. Citro. In collaboration with: A. Minguzzi (LPMMC, Grenoble, France) E. Orignac (ENS, Lyon, France), X. Deng & L. Santos (MP, Hannover, Germany)
 Phase Diagram of interacting Bose gases in one-dimensional disordered optical lattices R. Citro In collaboration with: A. Minguzzi (LPMMC, Grenoble, France) E. Orignac (ENS, Lyon, France), X. Deng & L.
Phase Diagram of interacting Bose gases in one-dimensional disordered optical lattices R. Citro In collaboration with: A. Minguzzi (LPMMC, Grenoble, France) E. Orignac (ENS, Lyon, France), X. Deng & L.
Strongly Correlated Physics With Ultra-Cold Atoms
 Strongly Correlated Physics With Ultra-Cold Atoms Predrag Nikolić Rice University Acknowledgments Collaborators Subir Sachdev Eun-Gook Moon Anton Burkov Arun Paramekanti Sponsors W.M.Keck Program in Quantum
Strongly Correlated Physics With Ultra-Cold Atoms Predrag Nikolić Rice University Acknowledgments Collaborators Subir Sachdev Eun-Gook Moon Anton Burkov Arun Paramekanti Sponsors W.M.Keck Program in Quantum
QCD and a Holographic Model of Hadrons
 QCD and a Holographic Model of Hadrons M. Stephanov U. of Illinois at Chicago AdS/QCD p.1/18 Motivation and plan Large N c : planar diagrams dominate resonances are infinitely narrow Effective theory in
QCD and a Holographic Model of Hadrons M. Stephanov U. of Illinois at Chicago AdS/QCD p.1/18 Motivation and plan Large N c : planar diagrams dominate resonances are infinitely narrow Effective theory in
ɛ(k) = h2 k 2 2m, k F = (3π 2 n) 1/3
 4D-XY Quantum Criticality in Underdoped High-T c cuprates M. Franz University of British Columbia franz@physics.ubc.ca February 22, 2005 In collaboration with: A.P. Iyengar (theory) D.P. Broun, D.A. Bonn
4D-XY Quantum Criticality in Underdoped High-T c cuprates M. Franz University of British Columbia franz@physics.ubc.ca February 22, 2005 In collaboration with: A.P. Iyengar (theory) D.P. Broun, D.A. Bonn
can be moved in energy/momentum but not individually destroyed; in general: topological Fermi surfaces
 nodes protected against gapping can be moved in energy/momentum but not individually destroyed; in general: topological Fermi surfaces physical realization: stacked 2d topological insulators C=1 3d top
nodes protected against gapping can be moved in energy/momentum but not individually destroyed; in general: topological Fermi surfaces physical realization: stacked 2d topological insulators C=1 3d top
Topological order in quantum matter
 HARVARD Topological order in quantum matter Stanford University Subir Sachdev November 30, 2017 Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu Mathias Scheurer Wei Wu Shubhayu Chatterjee arxiv:1711.09925 Michel
HARVARD Topological order in quantum matter Stanford University Subir Sachdev November 30, 2017 Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu Mathias Scheurer Wei Wu Shubhayu Chatterjee arxiv:1711.09925 Michel
Quantum Cluster Methods (CPT/CDMFT)
 Quantum Cluster Methods (CPT/CDMFT) David Sénéchal Département de physique Université de Sherbrooke Sherbrooke (Québec) Canada Autumn School on Correlated Electrons Forschungszentrum Jülich, Sept. 24,
Quantum Cluster Methods (CPT/CDMFT) David Sénéchal Département de physique Université de Sherbrooke Sherbrooke (Québec) Canada Autumn School on Correlated Electrons Forschungszentrum Jülich, Sept. 24,
Lattice modulation experiments with fermions in optical lattices and more
 Lattice modulation experiments with fermions in optical lattices and more Nonequilibrium dynamics of Hubbard model Ehud Altman Weizmann Institute David Pekker Harvard University Rajdeep Sensarma Harvard
Lattice modulation experiments with fermions in optical lattices and more Nonequilibrium dynamics of Hubbard model Ehud Altman Weizmann Institute David Pekker Harvard University Rajdeep Sensarma Harvard
Large N fermionic tensor models in d = 2
 Large N fermionic tensor models in d = 2 Sylvain Carrozza Quantum spacetime and the Renormalization roup 2018 Bad Honnef Sylvain Carrozza Large N fermionic tensor models Bad Honnef 20/6/2018 1 / 17 Context
Large N fermionic tensor models in d = 2 Sylvain Carrozza Quantum spacetime and the Renormalization roup 2018 Bad Honnef Sylvain Carrozza Large N fermionic tensor models Bad Honnef 20/6/2018 1 / 17 Context
Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators
 Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators Satoshi Fujimoto Dept. Phys., Kyoto University Collaborator: Ken Shiozaki
Topological Electromagnetic and Thermal Responses of Time-Reversal Invariant Superconductors and Chiral-Symmetric band insulators Satoshi Fujimoto Dept. Phys., Kyoto University Collaborator: Ken Shiozaki
Dark energy and nonlocal gravity
 Dark energy and nonlocal gravity Michele Maggiore Vacuum 2015, Barcelona based on Jaccard, MM, Mitsou, PRD 2013, 1305.3034 MM, PRD 2014, 1307.3898 Foffa, MM, Mitsou, PLB 2014, 1311.3421 Foffa, MM, Mitsou,
Dark energy and nonlocal gravity Michele Maggiore Vacuum 2015, Barcelona based on Jaccard, MM, Mitsou, PRD 2013, 1305.3034 MM, PRD 2014, 1307.3898 Foffa, MM, Mitsou, PLB 2014, 1311.3421 Foffa, MM, Mitsou,
J. McGreevy, arxiv Wednesday, April 18, 2012
 r J. McGreevy, arxiv0909.0518 Consider the metric which transforms under rescaling as x i ζx i t ζ z t ds ζ θ/d ds. This identifies z as the dynamic critical exponent (z = 1 for relativistic quantum critical
r J. McGreevy, arxiv0909.0518 Consider the metric which transforms under rescaling as x i ζx i t ζ z t ds ζ θ/d ds. This identifies z as the dynamic critical exponent (z = 1 for relativistic quantum critical
Disordered Ultracold Gases
 Disordered Ultracold Gases 1. Ultracold Gases: basic physics 2. Methods: disorder 3. Localization and Related Measurements Brian DeMarco, University of Illinois bdemarco@illinois.edu Localization & Related
Disordered Ultracold Gases 1. Ultracold Gases: basic physics 2. Methods: disorder 3. Localization and Related Measurements Brian DeMarco, University of Illinois bdemarco@illinois.edu Localization & Related
Quark matter and the high-density frontier. Mark Alford Washington University in St. Louis
 Quark matter and the high-density frontier Mark Alford Washington University in St. Louis Outline I Quarks at high density Confined, quark-gluon plasma, color superconducting II Color superconducting phases
Quark matter and the high-density frontier Mark Alford Washington University in St. Louis Outline I Quarks at high density Confined, quark-gluon plasma, color superconducting II Color superconducting phases
Holographic superconductors
 Holographic superconductors Sean Hartnoll Harvard University Work in collaboration with Chris Herzog and Gary Horowitz : 0801.1693, 0810.1563. Frederik Denef : 0901.1160. Frederik Denef and Subir Sachdev
Holographic superconductors Sean Hartnoll Harvard University Work in collaboration with Chris Herzog and Gary Horowitz : 0801.1693, 0810.1563. Frederik Denef : 0901.1160. Frederik Denef and Subir Sachdev
