Homogenization of random Hamilton Jacobi Bellman Equations
|
|
|
- Sylvia Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Probabiliy, Geomery and Inegrable Sysems MSRI Publicaions Volume 55, 28 Homogenizaion of random Hamilon Jacobi Bellman Equaions S. R. SRINIVASA VARADHAN ABSTRACT. We consider nonlinear parabolic equaions of Hamilon Jacobi Bellman ype. The Lagrangian is assumed o be convex, bu wih a spaial dependence which is saionary and random. Rescaling in space and ime produces a similar equaion wih a rapidly varying spaial dependence and a small viscosiy erm. Moivaed by corresponding resuls for he linear ellipic equaion wih small viscosiy, we seek o find he limiing behavior of he soluion of he Cauchy (final value) problem in erms of a homogenized problem, described by a convex funcion of he gradien of he soluion. The main idea is o use he principle of dynamic programming o wrie a variaional formula for he soluion in erms of soluions of linear problems. We hen show ha asympoically i is enough o resric he opimizaion o a subclass, one for which he asympoic behavior can be fully analyzed. The paper oulines hese seps and refers o he recenly published work of Kosygina, Rezakhanlou and he auhor for full deails. Homogenizaion is a heory abou approximaing soluions of a differenial equaion wih rapidly varying coefficiens by a soluion of a consan coefficien differenial equaion of a similar naure. The simples example of is kind is he soluion u " of he equaion u " D x 2 a u " xx " I u".; x/ D f.x/ on Œ;. The funcion a. / is assumed o be uniformly posiive, coninuous and periodic of period. The limi u of u " exiss and solves he equaion u D Na 2 u xxi u.; x/ D f.x/ where Na is he harmonic mean dx Na D : a.x/ 397
2 398 S. R. SRINIVASA VARADHAN Alhough his is a resul abou soluions of PDE s i can be viewed as a limi heorem in probabiliy. If we consider he Markov process x./ wih generaor 2 a.x/d2 x saring from a ime, as! he limiing disribuion of y./ D x./ p Gaussian wih mean and variance Na. The acual variance of y./ is E a.x.s// ds : The resul on he convergence of u " o u is seen o follow from an ergodic heorem of he ype lim a.x.s// ds D Na:! From he heory of Markov processes one can see an ergodic heorem of his ype wih Na D a.x/.x/ dx; where.x/ is he normalized invarian measure on Œ; wih end poins idenified. This is seen o be dx.x/ D a.x/ a.x/ ; so ha dx Na D a.x/.x/ dx D : a.x/ We can consider he siuaion where a.x/ D a.x;!/ is a random process, saionary wih respec o ranslaions in x. We can formally consider a probabiliy space. ; ; P/, and an ergodic acion x of on. We also have a funcion a.!/ saisfying < c a.!/ C <. The saionary process a.x;!/ is given by a.x;!/ D a. x!/. Now he soluion u " of is u ".; x;!/ D 2 a.x;!/u" xx.; x;!/i u".; x;!/ D f.x/ can be shown o converge again, in probabiliy, o he nonrandom soluion u of u.; x/ D Na 2 u xx.; x/i u ".; x/ D f.x/ wih Na D a.!/ dp :
3 HOMOGENIATION OF RANDOM HAMILTON JACOBI BELLMAN EQUATIONS 399 This is also an ergodic heorem for a.!.s// ds; bu he acual Markov process!./ for which he ergodic heorem is proved is one ha akes values in wih generaor L D 2 a.!/d2 ; where D is he generaor of he ranslaion group x on. The invarian measure is seen o be dq D Na a.!/ dp; where Na D a.x/ dp : We will ry o adap his ype of approach o some nonlinear problems of Hamilon-Jacobi Bellman ype. One par of he work ha we ouline here was done joinly wih Elena Kosygina and Fraydoun Rezakhanlou and has appeared in prin [Kosygina e al. 26], while anoher par, carried ou wih Kosygina, has been submied for publicaion. The problems we wish o consider are of he form u " C " x 2 u" C H " ; ru" ;! D I u.t; x/ D f.x/ for Œ; T d. Here f is a coninuous funcion wih a mos linear growh.. ; ; P/ is a probabiliy space on which d acs ergodically as measure preserving ransformaions x. H.; p;!/ is a funcion on d which is a convex funcion of p for every! and H.x; p;!/ D H.; p; x!/. I saisfies some bounds and some addiional regulariy. The problem is o prove ha u "! u as "!, where u is a soluion of u C H.ru/ D I u.t; x/ D f.x/ for some convex funcion H.p/ of p and deermine i. The analysis consiss of several seps. We migh as well assume T D and concenrae on u ".; ;!/. Firs we noe ha, by rescaling, he problem can be reduced o he behavior of lim! u.; ;!/; where u is he soluion in Œ; d, of u s C 2u C H.x; ru;!/i u.; x/ D f x :
4 4 S. R. SRINIVASA VARADHAN The second sep is o use he principle of dynamic programming o wrie a variaional formula for u.s; x;!/. Denoe by L. x!; q/ he convex dual L.x; q;!/ D sup p hp; qi H.x; p;!/ Le b.s; x/ be a funcion b W Œ; d! d. Le B denoe he space all such bounded funcions. For each b 2 B, we consider he linear equaion vs b C 2 vb C hb.s; x/; rv b x i L. x!; b.s; x// D ; v.; x/ D f I hen he soluion u.s; x/ is sup b v b.s; x/. If we denoe by Q b he Markov process wih generaor L b s D 2 C hb.s; x/; ri saring from.; /, hen v b.; ;!/ D E Qb f. x./ / L.x.s/; b.s; x.s//;!/ ds and u D sup v b b2b The hird sep is o consider a subclass of B of he form b.; x/ D c. x!/ wih c W! d chosen from a reasonable class C. The soluion v b wih his choice of b.; x/ D b.x/ D c. x!/ will be denoed by v c. We will show ha for our choice of C, he limi lim! vc.; ;!/ D g.c/ will exis for every c 2 C. I hen follows ha lim inf! u.; / sup g.c/: c2c Given c here is a Markov process Q c;! on saring from! wih generaor A c D 2 C hc.!/; ri: Here r is he infiniesimal generaor of he d acion f x g and D r r. This process can be consruced by solving dx./ D c. x./!/ d C ˇ./I x./ D Then one lifs i o by defining!./ D x./!. Such a process wih generaor A c could have an invarian densiy P c and i could (alhough i is unlikely) be muually absoluely coninuous wih respec o P, having densiy c. c will be a weak soluion of 2 c D r c. / c:
5 HOMOGENIATION OF RANDOM HAMILTON JACOBI BELLMAN EQUATIONS 4 We can hen expec g.c/ D f c.!/ dp c L!; c.!/ dp c : In general he exisence of such a for a given c is nearly impossible o prove. On he oher hand for a given finding a c is easy. For insance, will do. More generally one can have c D r 2 c D r 2 C c ; so long as r c D. So pairs.c; / such ha 2 c D r c. / c exis. Our class C will be hose for which exiss. I is no hard o show, using he ergodiciy of f x g acion, ha is unique for a given c when i exiss and he Markov process wih generaor A c is ergodic wih dp c D cdp as invarian measure. We will denoe by C he class of pairs.c; / saisfying he above relaion. So we have a lower bound where lim inf! I.m/ D uc.; / sup m2 d Œf.m/ inf c; W.c; /2C R c dpdm I.m/ L.c.!/;!/ dp Now we urn o proving upper bounds. Fix 2 d. If we had a nice es funcion W.x;!/ such ha for almos all! jw.x;!/ h; xij o.jxj/ and 2W C H.x; rw;!/ Then, by convex dualiy wih QW D W.x;!/.s /, we have QW s C 2 QW C hb.s; x/; r QW i L.b.s; x/;!/ : If H./ is defined as H./ D inff W W exissg
6 42 S. R. SRINIVASA VARADHAN hen under some conrol on he growh of L, i is no hard o deduce ha wih f.x/ D h; xi, lim sup! u.; ;!/ H./ If we can prove ha H./ D sup m Œh; mi I.m/; we are done. We would mach he upper and lower bounds. We reduce his o a minmax equals maxmin heorem. sup m Œh; mi I.m/ D sup hc.!/; i L.c.!/;!/ dp.c; /2C D sup inf hc.!/; i C A c W L.c.!/;!/ dp.c; / W D inf hc.!/; i C A c W L.c.!/;!/ dp W.c; / D inf W 2 W C H. C rw;!/ dp D inf W sup! D H./: 2 W C H. C rw;!/ dp While W may no exis, rw will exis. We can inegrae on d, hen ergodic heorem will yield an esimae of he form W.x/ D o.jxj/ and h; xi C W.x/ will work as a es funcion. There are some echnical deails on he issues of growh and regulariy. The deails have appeared in [Kosygina e al. 26] along wih addiional references. Similar resuls on he homogenizaion of random Hamilon Jacobi Bellman equaions have been obained by Lions and Souganidis [25], using differen mehods. Now we examine he ime dependen case. If we replace d acion by dc acion wih.; x/ denoing ime and space, hen he saionary processes H and L are space ime processes. The lower bound works more or less in he same manner. In addiion o r we now have D he derivaive in he ime direcion. The!./ process is he space-ime process. Is consrucion for a given c is slighly differen. We sar wih b.; x/ D c. ;x!/ and consruc a diffusion on d corresponding o he ime dependen generaor A c s D 2 C hb.s; x/; ri
7 HOMOGENIATION OF RANDOM HAMILTON JACOBI BELLMAN EQUATIONS 43 and hen lif i by!.s/ D s;x.s/!. The invarian densiies are soluions of D C 2 D r c : The lower bound works he same way. Bu for obaining he upper bound, a es funcion W has o be consruced ha saisfies W C 2W C H.; x; rw;!/ H./ In he ime independen case here was a lower bound on he growh of he convex funcion H ha provided esimaes on rw. Here one has o work much harder in order o conrol in some manner W. The deails will appear in [Kosygina and Varadhan 28]. References [Kosygina and Varadhan 28] E. Kosygina and S. R. S. Varadhan, Homogenizaion of Hamilon Jacobi Bellman equaions wih respec o ime-space shifs in a saionary ergodic medium, Comm. Pure Appl. Mah. 6:6 (28). [Kosygina e al. 26] E. Kosygina, F. Rezakhanlou, and S. R. S. Varadhan, Sochasic homogenizaion of Hamilon Jacobi Bellman equaions, Comm. Pure Appl. Mah. 59: (26), [Lions and Souganidis 25] P.-L. Lions and P. E. Souganidis, Homogenizaion of viscous Hamilon Jacobi equaions in saionary ergodic media, Comm. Parial Differenial Equaions 3:-3 (25), S. R. SRINIVASA VARADHAN COURANT INSTITUTE NEW YORK UNIVERSITY 25 MERCER STREET NEW YORK, NY 2 UNITED STATES varadhan@cims.nyu.edu
8
Hamilton- J acobi Equation: Explicit Formulas In this lecture we try to apply the method of characteristics to the Hamilton-Jacobi equation: u t
 M ah 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecure 1 0 O c. 7, 2 0 0 9 Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Explici Formulas In his lecure we ry o apply he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u + H D u, x = 0 in R n
M ah 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecure 1 0 O c. 7, 2 0 0 9 Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Explici Formulas In his lecure we ry o apply he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u + H D u, x = 0 in R n
Hamilton- J acobi Equation: Weak S olution We continue the study of the Hamilton-Jacobi equation:
 M ah 5 7 Fall 9 L ecure O c. 4, 9 ) Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Weak S oluion We coninue he sudy of he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: We have shown ha u + H D u) = R n, ) ; u = g R n { = }. ). In general we canno
M ah 5 7 Fall 9 L ecure O c. 4, 9 ) Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Weak S oluion We coninue he sudy of he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: We have shown ha u + H D u) = R n, ) ; u = g R n { = }. ). In general we canno
Vanishing Viscosity Method. There are another instructive and perhaps more natural discontinuous solutions of the conservation law
 Vanishing Viscosiy Mehod. There are anoher insrucive and perhaps more naural disconinuous soluions of he conservaion law (1 u +(q(u x 0, he so called vanishing viscosiy mehod. This mehod consiss in viewing
Vanishing Viscosiy Mehod. There are anoher insrucive and perhaps more naural disconinuous soluions of he conservaion law (1 u +(q(u x 0, he so called vanishing viscosiy mehod. This mehod consiss in viewing
An Introduction to Malliavin calculus and its applications
 An Inroducion o Malliavin calculus and is applicaions Lecure 5: Smoohness of he densiy and Hörmander s heorem David Nualar Deparmen of Mahemaics Kansas Universiy Universiy of Wyoming Summer School 214
An Inroducion o Malliavin calculus and is applicaions Lecure 5: Smoohness of he densiy and Hörmander s heorem David Nualar Deparmen of Mahemaics Kansas Universiy Universiy of Wyoming Summer School 214
2. Nonlinear Conservation Law Equations
 . Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
. Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
MATH 4330/5330, Fourier Analysis Section 6, Proof of Fourier s Theorem for Pointwise Convergence
 MATH 433/533, Fourier Analysis Secion 6, Proof of Fourier s Theorem for Poinwise Convergence Firs, some commens abou inegraing periodic funcions. If g is a periodic funcion, g(x + ) g(x) for all real x,
MATH 433/533, Fourier Analysis Secion 6, Proof of Fourier s Theorem for Poinwise Convergence Firs, some commens abou inegraing periodic funcions. If g is a periodic funcion, g(x + ) g(x) for all real x,
Uniqueness of solutions to quadratic BSDEs. BSDEs with convex generators and unbounded terminal conditions
 Recalls and basic resuls on BSDEs Uniqueness resul Links wih PDEs On he uniqueness of soluions o quadraic BSDEs wih convex generaors and unbounded erminal condiions IRMAR, Universié Rennes 1 Châeau de
Recalls and basic resuls on BSDEs Uniqueness resul Links wih PDEs On he uniqueness of soluions o quadraic BSDEs wih convex generaors and unbounded erminal condiions IRMAR, Universié Rennes 1 Châeau de
Hamilton Jacobi equations
 Hamilon Jacobi equaions Inoducion o PDE The rigorous suff from Evans, mosly. We discuss firs u + H( u = 0, (1 where H(p is convex, and superlinear a infiniy, H(p lim p p = + This by comes by inegraion
Hamilon Jacobi equaions Inoducion o PDE The rigorous suff from Evans, mosly. We discuss firs u + H( u = 0, (1 where H(p is convex, and superlinear a infiniy, H(p lim p p = + This by comes by inegraion
Math 527 Lecture 6: Hamilton-Jacobi Equation: Explicit Formulas
 Mah 527 Lecure 6: Hamilon-Jacobi Equaion: Explici Formulas Sep. 23, 2 Mehod of characerisics. We r o appl he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u +Hx, Du = in R n, u = g on R n =. 2 To
Mah 527 Lecure 6: Hamilon-Jacobi Equaion: Explici Formulas Sep. 23, 2 Mehod of characerisics. We r o appl he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u +Hx, Du = in R n, u = g on R n =. 2 To
THE WAVE EQUATION. part hand-in for week 9 b. Any dilation v(x, t) = u(λx, λt) of u(x, t) is also a solution (where λ is constant).
 THE WAVE EQUATION 43. (S) Le u(x, ) be a soluion of he wave equaion u u xx = 0. Show ha Q43(a) (c) is a. Any ranslaion v(x, ) = u(x + x 0, + 0 ) of u(x, ) is also a soluion (where x 0, 0 are consans).
THE WAVE EQUATION 43. (S) Le u(x, ) be a soluion of he wave equaion u u xx = 0. Show ha Q43(a) (c) is a. Any ranslaion v(x, ) = u(x + x 0, + 0 ) of u(x, ) is also a soluion (where x 0, 0 are consans).
THE MYSTERY OF STOCHASTIC MECHANICS. Edward Nelson Department of Mathematics Princeton University
 THE MYSTERY OF STOCHASTIC MECHANICS Edward Nelson Deparmen of Mahemaics Princeon Universiy 1 Classical Hamilon-Jacobi heory N paricles of various masses on a Euclidean space. Incorporae he masses in he
THE MYSTERY OF STOCHASTIC MECHANICS Edward Nelson Deparmen of Mahemaics Princeon Universiy 1 Classical Hamilon-Jacobi heory N paricles of various masses on a Euclidean space. Incorporae he masses in he
An Introduction to Backward Stochastic Differential Equations (BSDEs) PIMS Summer School 2016 in Mathematical Finance.
 1 An Inroducion o Backward Sochasic Differenial Equaions (BSDEs) PIMS Summer School 2016 in Mahemaical Finance June 25, 2016 Chrisoph Frei cfrei@ualbera.ca This inroducion is based on Touzi [14], Bouchard
1 An Inroducion o Backward Sochasic Differenial Equaions (BSDEs) PIMS Summer School 2016 in Mahemaical Finance June 25, 2016 Chrisoph Frei cfrei@ualbera.ca This inroducion is based on Touzi [14], Bouchard
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories and the nonlinear conservation law
 Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Math 2214 Solution Test 1A Spring 2016
 Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1A Spring 016 sec Problem 1: Wha is he larges -inerval for which ( 4) = has a guaraneed + unique soluion for iniial value (-1) = 3 according o he Exisence Uniqueness Theorem? Soluion
Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1A Spring 016 sec Problem 1: Wha is he larges -inerval for which ( 4) = has a guaraneed + unique soluion for iniial value (-1) = 3 according o he Exisence Uniqueness Theorem? Soluion
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics. Fokker-Planck Equation. Time Evolution
 Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Solutions to Assignment 1
 MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
THE SINE INTEGRAL. x dt t
 THE SINE INTEGRAL As one learns in elemenary calculus, he limi of sin(/ as vanishes is uniy. Furhermore he funcion is even and has an infinie number of zeros locaed a ±n for n1,,3 Is plo looks like his-
THE SINE INTEGRAL As one learns in elemenary calculus, he limi of sin(/ as vanishes is uniy. Furhermore he funcion is even and has an infinie number of zeros locaed a ±n for n1,,3 Is plo looks like his-
Math Final Exam Solutions
 Mah 246 - Final Exam Soluions Friday, July h, 204 () Find explici soluions and give he inerval of definiion o he following iniial value problems (a) ( + 2 )y + 2y = e, y(0) = 0 Soluion: In normal form,
Mah 246 - Final Exam Soluions Friday, July h, 204 () Find explici soluions and give he inerval of definiion o he following iniial value problems (a) ( + 2 )y + 2y = e, y(0) = 0 Soluion: In normal form,
EXERCISES FOR SECTION 1.5
 1.5 Exisence and Uniqueness of Soluions 43 20. 1 v c 21. 1 v c 1 2 4 6 8 10 1 2 2 4 6 8 10 Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler s mehod wih = 0.1. Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler
1.5 Exisence and Uniqueness of Soluions 43 20. 1 v c 21. 1 v c 1 2 4 6 8 10 1 2 2 4 6 8 10 Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler s mehod wih = 0.1. Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler
t 2 B F x,t n dsdt t u x,t dxdt
 Evoluion Equaions For 0, fixed, le U U0, where U denoes a bounded open se in R n.suppose ha U is filled wih a maerial in which a conaminan is being ranspored by various means including diffusion and convecion.
Evoluion Equaions For 0, fixed, le U U0, where U denoes a bounded open se in R n.suppose ha U is filled wih a maerial in which a conaminan is being ranspored by various means including diffusion and convecion.
The Asymptotic Behavior of Nonoscillatory Solutions of Some Nonlinear Dynamic Equations on Time Scales
 Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-5321 Volume 1 Number 1 (2006, pp. 103 112 c Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm The Asympoic Behavior of Nonoscillaory Soluions
Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-5321 Volume 1 Number 1 (2006, pp. 103 112 c Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm The Asympoic Behavior of Nonoscillaory Soluions
Module 2 F c i k c s la l w a s o s f dif di fusi s o i n
 Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 15 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 15 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 15 Nov 2016](/thumbs/90/102217337.jpg) arxiv:6.599v [mah.ca] 5 Nov 26 Counerexamples on Jumarie s hree basic fracional calculus formulae for non-differeniable coninuous funcions Cheng-shi Liu Deparmen of Mahemaics Norheas Peroleum Universiy
arxiv:6.599v [mah.ca] 5 Nov 26 Counerexamples on Jumarie s hree basic fracional calculus formulae for non-differeniable coninuous funcions Cheng-shi Liu Deparmen of Mahemaics Norheas Peroleum Universiy
u(x) = e x 2 y + 2 ) Integrate and solve for x (1 + x)y + y = cos x Answer: Divide both sides by 1 + x and solve for y. y = x y + cos x
 . 1 Mah 211 Homework #3 February 2, 2001 2.4.3. y + (2/x)y = (cos x)/x 2 Answer: Compare y + (2/x) y = (cos x)/x 2 wih y = a(x)x + f(x)and noe ha a(x) = 2/x. Consequenly, an inegraing facor is found wih
. 1 Mah 211 Homework #3 February 2, 2001 2.4.3. y + (2/x)y = (cos x)/x 2 Answer: Compare y + (2/x) y = (cos x)/x 2 wih y = a(x)x + f(x)and noe ha a(x) = 2/x. Consequenly, an inegraing facor is found wih
Ends of the moduli space of Higgs bundles. Frederik Witt
 Universiy of Münser The Geomery, Topology and Physics of Moduli Spaces of Higgs Bundles, Singapore, NUS 6h of Augus 2014 based on arxiv:1405.5765 [mah.dg] join wih R. Mazzeo (Sanford) J. Swoboda (Bonn)
Universiy of Münser The Geomery, Topology and Physics of Moduli Spaces of Higgs Bundles, Singapore, NUS 6h of Augus 2014 based on arxiv:1405.5765 [mah.dg] join wih R. Mazzeo (Sanford) J. Swoboda (Bonn)
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
d 1 = c 1 b 2 - b 1 c 2 d 2 = c 1 b 3 - b 1 c 3
 and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
MA 366 Review - Test # 1
 MA 366 Review - Tes # 1 Fall 5 () Resuls from Calculus: differeniaion formulas, implici differeniaion, Chain Rule; inegraion formulas, inegraion b pars, parial fracions, oher inegraion echniques. (1) Order
MA 366 Review - Tes # 1 Fall 5 () Resuls from Calculus: differeniaion formulas, implici differeniaion, Chain Rule; inegraion formulas, inegraion b pars, parial fracions, oher inegraion echniques. (1) Order
Tracking Adversarial Targets
 A. Proofs Proof of Lemma 3. Consider he Bellman equaion λ + V π,l x, a lx, a + V π,l Ax + Ba, πax + Ba. We prove he lemma by showing ha he given quadraic form is he unique soluion of he Bellman equaion.
A. Proofs Proof of Lemma 3. Consider he Bellman equaion λ + V π,l x, a lx, a + V π,l Ax + Ba, πax + Ba. We prove he lemma by showing ha he given quadraic form is he unique soluion of he Bellman equaion.
Stochastic Model for Cancer Cell Growth through Single Forward Mutation
 Journal of Modern Applied Saisical Mehods Volume 16 Issue 1 Aricle 31 5-1-2017 Sochasic Model for Cancer Cell Growh hrough Single Forward Muaion Jayabharahiraj Jayabalan Pondicherry Universiy, jayabharahi8@gmail.com
Journal of Modern Applied Saisical Mehods Volume 16 Issue 1 Aricle 31 5-1-2017 Sochasic Model for Cancer Cell Growh hrough Single Forward Muaion Jayabharahiraj Jayabalan Pondicherry Universiy, jayabharahi8@gmail.com
On a Fractional Stochastic Landau-Ginzburg Equation
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 4, 1, no. 7, 317-35 On a Fracional Sochasic Landau-Ginzburg Equaion Nguyen Tien Dung Deparmen of Mahemaics, FPT Universiy 15B Pham Hung Sree, Hanoi, Vienam dungn@fp.edu.vn
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 4, 1, no. 7, 317-35 On a Fracional Sochasic Landau-Ginzburg Equaion Nguyen Tien Dung Deparmen of Mahemaics, FPT Universiy 15B Pham Hung Sree, Hanoi, Vienam dungn@fp.edu.vn
Algorithmic Trading: Optimal Control PIMS Summer School
 Algorihmic Trading: Opimal Conrol PIMS Summer School Sebasian Jaimungal, U. Torono Álvaro Carea,U. Oxford many hanks o José Penalva,(U. Carlos III) Luhui Gan (U. Torono) Ryan Donnelly (Swiss Finance Insiue,
Algorihmic Trading: Opimal Conrol PIMS Summer School Sebasian Jaimungal, U. Torono Álvaro Carea,U. Oxford many hanks o José Penalva,(U. Carlos III) Luhui Gan (U. Torono) Ryan Donnelly (Swiss Finance Insiue,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 10, October ISSN
 Inernaional Journal of Scienific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 10, Ocober-2013 900 FUZZY MEAN RESIDUAL LIFE ORDERING OF FUZZY RANDOM VARIABLES J. EARNEST LAZARUS PIRIYAKUMAR 1, A. YAMUNA 2 1.
Inernaional Journal of Scienific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 10, Ocober-2013 900 FUZZY MEAN RESIDUAL LIFE ORDERING OF FUZZY RANDOM VARIABLES J. EARNEST LAZARUS PIRIYAKUMAR 1, A. YAMUNA 2 1.
Dual Representation as Stochastic Differential Games of Backward Stochastic Differential Equations and Dynamic Evaluations
 arxiv:mah/0602323v1 [mah.pr] 15 Feb 2006 Dual Represenaion as Sochasic Differenial Games of Backward Sochasic Differenial Equaions and Dynamic Evaluaions Shanjian Tang Absrac In his Noe, assuming ha he
arxiv:mah/0602323v1 [mah.pr] 15 Feb 2006 Dual Represenaion as Sochasic Differenial Games of Backward Sochasic Differenial Equaions and Dynamic Evaluaions Shanjian Tang Absrac In his Noe, assuming ha he
6. Stochastic calculus with jump processes
 A) Trading sraegies (1/3) Marke wih d asses S = (S 1,, S d ) A rading sraegy can be modelled wih a vecor φ describing he quaniies invesed in each asse a each insan : φ = (φ 1,, φ d ) The value a of a porfolio
A) Trading sraegies (1/3) Marke wih d asses S = (S 1,, S d ) A rading sraegy can be modelled wih a vecor φ describing he quaniies invesed in each asse a each insan : φ = (φ 1,, φ d ) The value a of a porfolio
Heavy Tails of Discounted Aggregate Claims in the Continuous-time Renewal Model
 Heavy Tails of Discouned Aggregae Claims in he Coninuous-ime Renewal Model Qihe Tang Deparmen of Saisics and Acuarial Science The Universiy of Iowa 24 Schae er Hall, Iowa Ciy, IA 52242, USA E-mail: qang@sa.uiowa.edu
Heavy Tails of Discouned Aggregae Claims in he Coninuous-ime Renewal Model Qihe Tang Deparmen of Saisics and Acuarial Science The Universiy of Iowa 24 Schae er Hall, Iowa Ciy, IA 52242, USA E-mail: qang@sa.uiowa.edu
ON THE NUMBER OF FAMILIES OF BRANCHING PROCESSES WITH IMMIGRATION WITH FAMILY SIZES WITHIN RANDOM INTERVAL
 ON THE NUMBER OF FAMILIES OF BRANCHING PROCESSES ITH IMMIGRATION ITH FAMILY SIZES ITHIN RANDOM INTERVAL Husna Hasan School of Mahemaical Sciences Universii Sains Malaysia, 8 Minden, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
ON THE NUMBER OF FAMILIES OF BRANCHING PROCESSES ITH IMMIGRATION ITH FAMILY SIZES ITHIN RANDOM INTERVAL Husna Hasan School of Mahemaical Sciences Universii Sains Malaysia, 8 Minden, Pulau Pinang, Malaysia
14 Autoregressive Moving Average Models
 14 Auoregressive Moving Average Models In his chaper an imporan parameric family of saionary ime series is inroduced, he family of he auoregressive moving average, or ARMA, processes. For a large class
14 Auoregressive Moving Average Models In his chaper an imporan parameric family of saionary ime series is inroduced, he family of he auoregressive moving average, or ARMA, processes. For a large class
4 Sequences of measurable functions
 4 Sequences of measurable funcions 1. Le (Ω, A, µ) be a measure space (complee, afer a possible applicaion of he compleion heorem). In his chaper we invesigae relaions beween various (nonequivalen) convergences
4 Sequences of measurable funcions 1. Le (Ω, A, µ) be a measure space (complee, afer a possible applicaion of he compleion heorem). In his chaper we invesigae relaions beween various (nonequivalen) convergences
Oscillation of an Euler Cauchy Dynamic Equation S. Huff, G. Olumolode, N. Pennington, and A. Peterson
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE FOURTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS May 4 7, 00, Wilmingon, NC, USA pp 0 Oscillaion of an Euler Cauchy Dynamic Equaion S Huff, G Olumolode,
PROCEEDINGS OF THE FOURTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS May 4 7, 00, Wilmingon, NC, USA pp 0 Oscillaion of an Euler Cauchy Dynamic Equaion S Huff, G Olumolode,
Omega-limit sets and bounded solutions
 arxiv:3.369v [mah.gm] 3 May 6 Omega-limi ses and bounded soluions Dang Vu Giang Hanoi Insiue of Mahemaics Vienam Academy of Science and Technology 8 Hoang Quoc Vie, 37 Hanoi, Vienam e-mail: dangvugiang@yahoo.com
arxiv:3.369v [mah.gm] 3 May 6 Omega-limi ses and bounded soluions Dang Vu Giang Hanoi Insiue of Mahemaics Vienam Academy of Science and Technology 8 Hoang Quoc Vie, 37 Hanoi, Vienam e-mail: dangvugiang@yahoo.com
Ann. Funct. Anal. 2 (2011), no. 2, A nnals of F unctional A nalysis ISSN: (electronic) URL:
 Ann. Func. Anal. 2 2011, no. 2, 34 41 A nnals of F uncional A nalysis ISSN: 2008-8752 elecronic URL: www.emis.de/journals/afa/ CLASSIFICAION OF POSIIVE SOLUIONS OF NONLINEAR SYSEMS OF VOLERRA INEGRAL EQUAIONS
Ann. Func. Anal. 2 2011, no. 2, 34 41 A nnals of F uncional A nalysis ISSN: 2008-8752 elecronic URL: www.emis.de/journals/afa/ CLASSIFICAION OF POSIIVE SOLUIONS OF NONLINEAR SYSEMS OF VOLERRA INEGRAL EQUAIONS
Properties Of Solutions To A Generalized Liénard Equation With Forcing Term
 Applied Mahemaics E-Noes, 8(28), 4-44 c ISSN 67-25 Available free a mirror sies of hp://www.mah.nhu.edu.w/ amen/ Properies Of Soluions To A Generalized Liénard Equaion Wih Forcing Term Allan Kroopnick
Applied Mahemaics E-Noes, 8(28), 4-44 c ISSN 67-25 Available free a mirror sies of hp://www.mah.nhu.edu.w/ amen/ Properies Of Soluions To A Generalized Liénard Equaion Wih Forcing Term Allan Kroopnick
Lecture 10: The Poincaré Inequality in Euclidean space
 Deparmens of Mahemaics Monana Sae Universiy Fall 215 Prof. Kevin Wildrick n inroducion o non-smooh analysis and geomery Lecure 1: The Poincaré Inequaliy in Euclidean space 1. Wha is he Poincaré inequaliy?
Deparmens of Mahemaics Monana Sae Universiy Fall 215 Prof. Kevin Wildrick n inroducion o non-smooh analysis and geomery Lecure 1: The Poincaré Inequaliy in Euclidean space 1. Wha is he Poincaré inequaliy?
arxiv:math-ph/ v1 1 Jan 1998
 Journal of Nonlinear Mahemaical Physics 1998, V.5, N 1, 8 1. Leer Classical and Nonclassical Symmeries of a Generalied Boussinesq Equaion M.L. GANDARIAS and M.S. BRUZON arxiv:mah-ph/980106v1 1 Jan 1998
Journal of Nonlinear Mahemaical Physics 1998, V.5, N 1, 8 1. Leer Classical and Nonclassical Symmeries of a Generalied Boussinesq Equaion M.L. GANDARIAS and M.S. BRUZON arxiv:mah-ph/980106v1 1 Jan 1998
dy dx = xey (a) y(0) = 2 (b) y(1) = 2.5 SOLUTION: See next page
 Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
= ( ) ) or a system of differential equations with continuous parametrization (T = R
 XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
Convergence of the Neumann series in higher norms
 Convergence of he Neumann series in higher norms Charles L. Epsein Deparmen of Mahemaics, Universiy of Pennsylvania Version 1.0 Augus 1, 003 Absrac Naural condiions on an operaor A are given so ha he Neumann
Convergence of he Neumann series in higher norms Charles L. Epsein Deparmen of Mahemaics, Universiy of Pennsylvania Version 1.0 Augus 1, 003 Absrac Naural condiions on an operaor A are given so ha he Neumann
Example on p. 157
 Example 2.5.3. Le where BV [, 1] = Example 2.5.3. on p. 157 { g : [, 1] C g() =, g() = g( + ) [, 1), var (g) = sup g( j+1 ) g( j ) he supremum is aken over all he pariions of [, 1] (1) : = < 1 < < n =
Example 2.5.3. Le where BV [, 1] = Example 2.5.3. on p. 157 { g : [, 1] C g() =, g() = g( + ) [, 1), var (g) = sup g( j+1 ) g( j ) he supremum is aken over all he pariions of [, 1] (1) : = < 1 < < n =
1 st order ODE Initial Condition
 Mah-33 Chapers 1-1 s Order ODE Sepember 1, 17 1 1 s order ODE Iniial Condiion f, sandard form LINEAR NON-LINEAR,, p g differenial form M x dx N x d differenial form is equivalen o a pair of differenial
Mah-33 Chapers 1-1 s Order ODE Sepember 1, 17 1 1 s order ODE Iniial Condiion f, sandard form LINEAR NON-LINEAR,, p g differenial form M x dx N x d differenial form is equivalen o a pair of differenial
23.5. Half-Range Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Differential Equations
 Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Fractional Method of Characteristics for Fractional Partial Differential Equations
 Fracional Mehod of Characerisics for Fracional Parial Differenial Equaions Guo-cheng Wu* Modern Teile Insiue, Donghua Universiy, 188 Yan-an ilu Road, Shanghai 51, PR China Absrac The mehod of characerisics
Fracional Mehod of Characerisics for Fracional Parial Differenial Equaions Guo-cheng Wu* Modern Teile Insiue, Donghua Universiy, 188 Yan-an ilu Road, Shanghai 51, PR China Absrac The mehod of characerisics
Finish reading Chapter 2 of Spivak, rereading earlier sections as necessary. handout and fill in some missing details!
 MAT 257, Handou 6: Ocober 7-2, 20. I. Assignmen. Finish reading Chaper 2 of Spiva, rereading earlier secions as necessary. handou and fill in some missing deails! II. Higher derivaives. Also, read his
MAT 257, Handou 6: Ocober 7-2, 20. I. Assignmen. Finish reading Chaper 2 of Spiva, rereading earlier secions as necessary. handou and fill in some missing deails! II. Higher derivaives. Also, read his
Unit Root Time Series. Univariate random walk
 Uni Roo ime Series Univariae random walk Consider he regression y y where ~ iid N 0, he leas squares esimae of is: ˆ yy y y yy Now wha if = If y y hen le y 0 =0 so ha y j j If ~ iid N 0, hen y ~ N 0, he
Uni Roo ime Series Univariae random walk Consider he regression y y where ~ iid N 0, he leas squares esimae of is: ˆ yy y y yy Now wha if = If y y hen le y 0 =0 so ha y j j If ~ iid N 0, hen y ~ N 0, he
Empirical Process Theory
 Empirical Process heory 4.384 ime Series Analysis, Fall 27 Reciaion by Paul Schrimpf Supplemenary o lecures given by Anna Mikusheva Ocober 7, 28 Reciaion 7 Empirical Process heory Le x be a real-valued
Empirical Process heory 4.384 ime Series Analysis, Fall 27 Reciaion by Paul Schrimpf Supplemenary o lecures given by Anna Mikusheva Ocober 7, 28 Reciaion 7 Empirical Process heory Le x be a real-valued
Homework 10 (Stats 620, Winter 2017) Due Tuesday April 18, in class Questions are derived from problems in Stochastic Processes by S. Ross.
 Homework (Sas 6, Winer 7 Due Tuesday April 8, in class Quesions are derived from problems in Sochasic Processes by S. Ross.. A sochasic process {X(, } is said o be saionary if X(,..., X( n has he same
Homework (Sas 6, Winer 7 Due Tuesday April 8, in class Quesions are derived from problems in Sochasic Processes by S. Ross.. A sochasic process {X(, } is said o be saionary if X(,..., X( n has he same
MATH 5720: Gradient Methods Hung Phan, UMass Lowell October 4, 2018
 MATH 5720: Gradien Mehods Hung Phan, UMass Lowell Ocober 4, 208 Descen Direcion Mehods Consider he problem min { f(x) x R n}. The general descen direcions mehod is x k+ = x k + k d k where x k is he curren
MATH 5720: Gradien Mehods Hung Phan, UMass Lowell Ocober 4, 208 Descen Direcion Mehods Consider he problem min { f(x) x R n}. The general descen direcions mehod is x k+ = x k + k d k where x k is he curren
di Bernardo, M. (1995). A purely adaptive controller to synchronize and control chaotic systems.
 di ernardo, M. (995). A purely adapive conroller o synchronize and conrol chaoic sysems. hps://doi.org/.6/375-96(96)8-x Early version, also known as pre-prin Link o published version (if available):.6/375-96(96)8-x
di ernardo, M. (995). A purely adapive conroller o synchronize and conrol chaoic sysems. hps://doi.org/.6/375-96(96)8-x Early version, also known as pre-prin Link o published version (if available):.6/375-96(96)8-x
Math 334 Test 1 KEY Spring 2010 Section: 001. Instructor: Scott Glasgow Dates: May 10 and 11.
 1 Mah 334 Tes 1 KEY Spring 21 Secion: 1 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Daes: Ma 1 and 11. Do NOT wrie on his problem saemen bookle, excep for our indicaion of following he honor code jus below. No credi will be
1 Mah 334 Tes 1 KEY Spring 21 Secion: 1 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Daes: Ma 1 and 11. Do NOT wrie on his problem saemen bookle, excep for our indicaion of following he honor code jus below. No credi will be
Elements of Stochastic Processes Lecture II Hamid R. Rabiee
 Sochasic Processes Elemens of Sochasic Processes Lecure II Hamid R. Rabiee Overview Reading Assignmen Chaper 9 of exbook Furher Resources MIT Open Course Ware S. Karlin and H. M. Taylor, A Firs Course
Sochasic Processes Elemens of Sochasic Processes Lecure II Hamid R. Rabiee Overview Reading Assignmen Chaper 9 of exbook Furher Resources MIT Open Course Ware S. Karlin and H. M. Taylor, A Firs Course
L p -L q -Time decay estimate for solution of the Cauchy problem for hyperbolic partial differential equations of linear thermoelasticity
 ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LIV.2 99) L p -L q -Time decay esimae for soluion of he Cauchy problem for hyperbolic parial differenial equaions of linear hermoelasiciy by Jerzy Gawinecki Warszawa) Absrac.
ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LIV.2 99) L p -L q -Time decay esimae for soluion of he Cauchy problem for hyperbolic parial differenial equaions of linear hermoelasiciy by Jerzy Gawinecki Warszawa) Absrac.
Innova Junior College H2 Mathematics JC2 Preliminary Examinations Paper 2 Solutions 0 (*)
 Soluion 3 x 4x3 x 3 x 0 4x3 x 4x3 x 4x3 x 4x3 x x 3x 3 4x3 x Innova Junior College H Mahemaics JC Preliminary Examinaions Paper Soluions 3x 3 4x 3x 0 4x 3 4x 3 0 (*) 0 0 + + + - 3 3 4 3 3 3 3 Hence x or
Soluion 3 x 4x3 x 3 x 0 4x3 x 4x3 x 4x3 x 4x3 x x 3x 3 4x3 x Innova Junior College H Mahemaics JC Preliminary Examinaions Paper Soluions 3x 3 4x 3x 0 4x 3 4x 3 0 (*) 0 0 + + + - 3 3 4 3 3 3 3 Hence x or
Ordinary Differential Equations
 Lecure 22 Ordinary Differenial Equaions Course Coordinaor: Dr. Suresh A. Karha, Associae Professor, Deparmen of Civil Engineering, IIT Guwahai. In naure, mos of he phenomena ha can be mahemaically described
Lecure 22 Ordinary Differenial Equaions Course Coordinaor: Dr. Suresh A. Karha, Associae Professor, Deparmen of Civil Engineering, IIT Guwahai. In naure, mos of he phenomena ha can be mahemaically described
Chapter 6. Systems of First Order Linear Differential Equations
 Chaper 6 Sysems of Firs Order Linear Differenial Equaions We will only discuss firs order sysems However higher order sysems may be made ino firs order sysems by a rick shown below We will have a sligh
Chaper 6 Sysems of Firs Order Linear Differenial Equaions We will only discuss firs order sysems However higher order sysems may be made ino firs order sysems by a rick shown below We will have a sligh
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
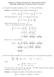 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
23.2. Representing Periodic Functions by Fourier Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Couplage du principe des grandes déviations et de l homogénisation dans le cas des EDP paraboliques: (le cas constant)
 Couplage du principe des grandes déviaions e de l homogénisaion dans le cas des EDP paraboliques: (le cas consan) Alioune COULIBALY U.F.R Sciences e Technologie Universié Assane SECK de Ziguinchor Probabilié
Couplage du principe des grandes déviaions e de l homogénisaion dans le cas des EDP paraboliques: (le cas consan) Alioune COULIBALY U.F.R Sciences e Technologie Universié Assane SECK de Ziguinchor Probabilié
Some Basic Information about M-S-D Systems
 Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Robust estimation based on the first- and third-moment restrictions of the power transformation model
 h Inernaional Congress on Modelling and Simulaion, Adelaide, Ausralia, 6 December 3 www.mssanz.org.au/modsim3 Robus esimaion based on he firs- and hird-momen resricions of he power ransformaion Nawaa,
h Inernaional Congress on Modelling and Simulaion, Adelaide, Ausralia, 6 December 3 www.mssanz.org.au/modsim3 Robus esimaion based on he firs- and hird-momen resricions of he power ransformaion Nawaa,
Math 23 Spring Differential Equations. Final Exam Due Date: Tuesday, June 6, 5pm
 Mah Spring 6 Differenial Equaions Final Exam Due Dae: Tuesday, June 6, 5pm Your name (please prin): Insrucions: This is an open book, open noes exam. You are free o use a calculaor or compuer o check your
Mah Spring 6 Differenial Equaions Final Exam Due Dae: Tuesday, June 6, 5pm Your name (please prin): Insrucions: This is an open book, open noes exam. You are free o use a calculaor or compuer o check your
Undetermined coefficients for local fractional differential equations
 Available online a www.isr-publicaions.com/jmcs J. Mah. Compuer Sci. 16 (2016), 140 146 Research Aricle Undeermined coefficiens for local fracional differenial equaions Roshdi Khalil a,, Mohammed Al Horani
Available online a www.isr-publicaions.com/jmcs J. Mah. Compuer Sci. 16 (2016), 140 146 Research Aricle Undeermined coefficiens for local fracional differenial equaions Roshdi Khalil a,, Mohammed Al Horani
Lipschitz stability for a coefficient inverse problem for the non-stationary transport equation via Carleman estimate
 Lipschiz sabiliy for a coefficien inverse problem for he non-saionary ranspor equaion via Carleman esimae Michael V. Klibanov Sergey E. Pamyanykh Deparmen of Mahemaics Saisics, The Universiy of Norh Carolina
Lipschiz sabiliy for a coefficien inverse problem for he non-saionary ranspor equaion via Carleman esimae Michael V. Klibanov Sergey E. Pamyanykh Deparmen of Mahemaics Saisics, The Universiy of Norh Carolina
t is a basis for the solution space to this system, then the matrix having these solutions as columns, t x 1 t, x 2 t,... x n t x 2 t...
 Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
(1) (2) Differentiation of (1) and then substitution of (3) leads to. Therefore, we will simply consider the second-order linear system given by (4)
 Phase Plane Analysis of Linear Sysems Adaped from Applied Nonlinear Conrol by Sloine and Li The general form of a linear second-order sysem is a c b d From and b bc d a Differeniaion of and hen subsiuion
Phase Plane Analysis of Linear Sysems Adaped from Applied Nonlinear Conrol by Sloine and Li The general form of a linear second-order sysem is a c b d From and b bc d a Differeniaion of and hen subsiuion
ME 391 Mechanical Engineering Analysis
 Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Class Meeting # 10: Introduction to the Wave Equation
 MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
Two Coupled Oscillators / Normal Modes
 Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
dt = C exp (3 ln t 4 ). t 4 W = C exp ( ln(4 t) 3) = C(4 t) 3.
 Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Some Regularity Properties of Three Dimensional Incompressible Magnetohydrodynamic Flows
 Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mahemaics. ISSN 973-78 Volume 3, Number 7 (7), pp. 339-335 Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com Some Regulariy Properies of Three Dimensional Incompressible
Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mahemaics. ISSN 973-78 Volume 3, Number 7 (7), pp. 339-335 Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com Some Regulariy Properies of Three Dimensional Incompressible
Theory of! Partial Differential Equations!
 hp://www.nd.edu/~gryggva/cfd-course/! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 011! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
hp://www.nd.edu/~gryggva/cfd-course/! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 011! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules: The Schrodinger equation. Hilary Term 2008 Dr Grant Ritchie
 e Quanum eory of Aoms and Molecules: e Scrodinger equaion Hilary erm 008 Dr Gran Ricie An equaion for maer waves? De Broglie posulaed a every paricles as an associaed wave of waveleng: / p Wave naure of
e Quanum eory of Aoms and Molecules: e Scrodinger equaion Hilary erm 008 Dr Gran Ricie An equaion for maer waves? De Broglie posulaed a every paricles as an associaed wave of waveleng: / p Wave naure of
( ) a system of differential equations with continuous parametrization ( T = R + These look like, respectively:
 XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
Harnack inequalities and Gaussian estimates for a class of hypoelliptic operators
 Harnack inequaliies and Gaussian esimaes for a class of hypoellipic operaors Sergio Polidoro Diparimeno di Maemaica, Universià di Bologna Absrac We announce some resuls obained in a recen sudy [14], concerning
Harnack inequaliies and Gaussian esimaes for a class of hypoellipic operaors Sergio Polidoro Diparimeno di Maemaica, Universià di Bologna Absrac We announce some resuls obained in a recen sudy [14], concerning
MA Study Guide #1
 MA 66 Su Guide #1 (1) Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Firs Order Linear Equaion (FOL): + p() = g() Soluion : = 1 µ() [ ] µ()g() + C, where µ() = e p() II. Separable Equaion (SEP): dx = h(x) g()
MA 66 Su Guide #1 (1) Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Firs Order Linear Equaion (FOL): + p() = g() Soluion : = 1 µ() [ ] µ()g() + C, where µ() = e p() II. Separable Equaion (SEP): dx = h(x) g()
( ) ( ) if t = t. It must satisfy the identity. So, bulkiness of the unit impulse (hyper)function is equal to 1. The defining characteristic is
 UNIT IMPULSE RESPONSE, UNIT STEP RESPONSE, STABILITY. Uni impulse funcion (Dirac dela funcion, dela funcion) rigorously defined is no sricly a funcion, bu disribuion (or measure), precise reamen requires
UNIT IMPULSE RESPONSE, UNIT STEP RESPONSE, STABILITY. Uni impulse funcion (Dirac dela funcion, dela funcion) rigorously defined is no sricly a funcion, bu disribuion (or measure), precise reamen requires
Theory of! Partial Differential Equations-I!
 hp://users.wpi.edu/~grear/me61.hml! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions-I! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 010! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
hp://users.wpi.edu/~grear/me61.hml! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions-I! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 010! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS
 European Scienific Journal Sepember 214 /SPECIAL/ ediion Vol.3 ISSN: 1857 7881 (Prin) e - ISSN 1857-7431 CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS Berrabah Faima Zohra, MA Universiy of sidi bel abbes/ Algeria
European Scienific Journal Sepember 214 /SPECIAL/ ediion Vol.3 ISSN: 1857 7881 (Prin) e - ISSN 1857-7431 CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS Berrabah Faima Zohra, MA Universiy of sidi bel abbes/ Algeria
MA 214 Calculus IV (Spring 2016) Section 2. Homework Assignment 1 Solutions
 MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
12: AUTOREGRESSIVE AND MOVING AVERAGE PROCESSES IN DISCRETE TIME. Σ j =
 1: AUTOREGRESSIVE AND MOVING AVERAGE PROCESSES IN DISCRETE TIME Moving Averages Recall ha a whie noise process is a series { } = having variance σ. The whie noise process has specral densiy f (λ) = of
1: AUTOREGRESSIVE AND MOVING AVERAGE PROCESSES IN DISCRETE TIME Moving Averages Recall ha a whie noise process is a series { } = having variance σ. The whie noise process has specral densiy f (λ) = of
1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx.
![1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx. 1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx.](/thumbs/71/65799522.jpg) . Use Simpson s rule wih n 4 o esimae an () +. Soluion: Since we are using 4 seps, 4 Thus we have [ ( ) f() + 4f + f() + 4f 3 [ + 4 4 6 5 + + 4 4 3 + ] 5 [ + 6 6 5 + + 6 3 + ]. 5. Our funcion is f() +.
. Use Simpson s rule wih n 4 o esimae an () +. Soluion: Since we are using 4 seps, 4 Thus we have [ ( ) f() + 4f + f() + 4f 3 [ + 4 4 6 5 + + 4 4 3 + ] 5 [ + 6 6 5 + + 6 3 + ]. 5. Our funcion is f() +.
A remark on the H -calculus
 A remark on he H -calculus Nigel J. Kalon Absrac If A, B are secorial operaors on a Hilber space wih he same domain range, if Ax Bx A 1 x B 1 x, hen i is a resul of Auscher, McInosh Nahmod ha if A has
A remark on he H -calculus Nigel J. Kalon Absrac If A, B are secorial operaors on a Hilber space wih he same domain range, if Ax Bx A 1 x B 1 x, hen i is a resul of Auscher, McInosh Nahmod ha if A has
Echocardiography Project and Finite Fourier Series
 Echocardiography Projec and Finie Fourier Series 1 U M An echocardiagram is a plo of how a porion of he hear moves as he funcion of ime over he one or more hearbea cycles If he hearbea repeas iself every
Echocardiography Projec and Finie Fourier Series 1 U M An echocardiagram is a plo of how a porion of he hear moves as he funcion of ime over he one or more hearbea cycles If he hearbea repeas iself every
Chapter 3 Boundary Value Problem
 Chaper 3 Boundary Value Problem A boundary value problem (BVP) is a problem, ypically an ODE or a PDE, which has values assigned on he physical boundary of he domain in which he problem is specified. Le
Chaper 3 Boundary Value Problem A boundary value problem (BVP) is a problem, ypically an ODE or a PDE, which has values assigned on he physical boundary of he domain in which he problem is specified. Le
On Gronwall s Type Integral Inequalities with Singular Kernels
 Filoma 31:4 (217), 141 149 DOI 1.2298/FIL17441A Published by Faculy of Sciences and Mahemaics, Universiy of Niš, Serbia Available a: hp://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filoma On Gronwall s Type Inegral Inequaliies
Filoma 31:4 (217), 141 149 DOI 1.2298/FIL17441A Published by Faculy of Sciences and Mahemaics, Universiy of Niš, Serbia Available a: hp://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filoma On Gronwall s Type Inegral Inequaliies
A Sharp Existence and Uniqueness Theorem for Linear Fuchsian Partial Differential Equations
 A Sharp Exisence and Uniqueness Theorem for Linear Fuchsian Parial Differenial Equaions Jose Ernie C. LOPE Absrac This paper considers he equaion Pu = f, where P is he linear Fuchsian parial differenial
A Sharp Exisence and Uniqueness Theorem for Linear Fuchsian Parial Differenial Equaions Jose Ernie C. LOPE Absrac This paper considers he equaion Pu = f, where P is he linear Fuchsian parial differenial
Optima and Equilibria for Traffic Flow on a Network
 Opima and Equilibria for Traffic Flow on a Nework Albero Bressan Deparmen of Mahemaics, Penn Sae Universiy bressan@mah.psu.edu Albero Bressan (Penn Sae) Opima and equilibria for raffic flow 1 / 1 A Traffic
Opima and Equilibria for Traffic Flow on a Nework Albero Bressan Deparmen of Mahemaics, Penn Sae Universiy bressan@mah.psu.edu Albero Bressan (Penn Sae) Opima and equilibria for raffic flow 1 / 1 A Traffic
