The Free Intuitive Calculus Course Integrals
|
|
|
- Jeremy Hines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intuitive-Calculus.com Presents The Free Intuitive Calculus Course Integrals Day 19: Trigonometric Integrals By Pablo Antuna 013 All Rights Reserved. The Intuitive Calculus Course - By Pablo Antuna
2 Contents 1 Welcome Types of Trigonometric Integrals 3 3 First Case: Odd Powers of sinx or cosx 5 4 Second Case: Even Powers of sinx or cosx 7 5 Third Case: Integrals Involving tanx or secx 9 6 Fourth Case: Tricky Trigonometric Integrals 11 7 Exercises 13 8 Still To Come 14 1
3 1 Welcome Welcome to Day 19 of the Intuitive Online Calculus Course! The main purpose of this course is to give you the basic tools to succeed in calculus, whether you re in high school, college or self-studying calculus! Today we are going to learn how to solve trigonometric integrals.
4 Types of Trigonometric Integrals Our goal is to learn how to solve most trigonometric integrals. A goal of knowing how to solve all trigonometric integrals is not realistic, because there are some seemingly simple integrals that do no have simple functions as primitives. For example: sinx dx We are going to learn how to solve any integral that is solvable by hand. And to do that, it will be useful to classify trigonometric integrals into four cases. First Case: Integrals With Odd Powers of sinx or cosx For example: sin 3 xdx cos 4 x sin 3 x dx Second Case: Integrals With Only Even Powers of sinx or cosx For example: cos x dx Third case: Integrals Involving tanx or secx For example: tan 3 xdx 3
5 Fourth: Just Tricky Trigonometric Integrals For example: sinx cos 4 x + sin 4 x dx This last four case is for integrals that do not fit into any of the other cases. Now, let s solve an example of each of these. 4
6 3 First Case: Odd Powers of sinx or cosx Example 1 Let s solve the integral: sin 3 xdx Solution. We can write this integral as: sin 3 x dx = sin x sinx dx And use the identity: sin x = 1 cos x sin x sinx dx = (1 cos x ) sinx dx And we can break this up into two integrals: sinx dx cos x sinx dx The first integral can be solved directly, and the second one by substitution: u = cosx, sinx dx du dx = sinx cos x sinx dx = = cosx u. ( du ) dx.dx cos x sinx 5
7 That is: cosx + u. du dx. dx = cosx + u du cosx + u3 3 + C = cosx + cos3 x + C 3 sin 3 x dx = cosx + cos3 x 3 + C 6
8 4 Second Case: Even Powers of sinx or cosx Example Let s solve the integral: cos x dx Solution. When we have even powers of sinx or cosx, the trick is to use the following trig identity: cosx = cos(x + x) = cos x sin x That is: cosx = cos x 1 = 1 sin x cos x = 1 + cosx sin x = 1 cosx Using the first of these identities in our integral: 1 + cosx cos x dx = dx And we can now solve this integral by substitution: 1 + cosx u = x, du dx = 1 + cosu dx =. ( ) 1.du dx.dx 1 7
9 And we get: 1 + cosu. du 1 + cosu 4 dx. dx = du 4 And this integral is solved easily: 1 + cosu du = 1 du + 1 cos udu = u 4 sinu 4 + C And now we replace back u = x: cos x dx = x sinx 4 + C 8
10 5 Third Case: Integrals Involving tanx or secx Example 3 Let s solve the integral: tan 3 x dx Solution. We want to use the identity: And the fact that: 1 + tan x = sec x d dx (tanx) = sec x So, we write this integral as: tan 3 x dx = tan x tanx dx And replace tan x = sec x 1: (sec tan x tanx dx = 1 ) tanx dx = = tan x tanx sec x dx tanx dx sinx tanx sec x dx cosx dx 9
11 And we can solve both of these integrals by substitution: = u. u = tanx, v = cosx, du dx = sec x dv dx = sinx sinx tanx sec x dx cosx dx du dx.dx 1 v. ( dv ) dx.dx tanx sec x 1 cosx u. du 1 dx. dx + v.dv dx. dx dv udu + v = u + lnv + C And we substitute back u = tanx and v = cosx: tan 3 x dx = tan x + lncosx + C sinx 10
12 6 Fourth Case: Tricky Trigonometric Integrals Example 3 Let s solve the integral: sinx cos 4 x + sin 4 x dx Solution. In this case we can only guess what trigonometric identity will do the trick. So, first of all, we recognize that the denominator looks somewhat like a perfect square. For example, we have that: ( cos x + sin x ) = cos 4 x + sin x cos x + sin 4 x = 1 So: cos 4 x + sin 4 x = 1 sin x cos x = 1 sin x Here we used the identities: And: cos x + sin x = 1 sinx = sinx cosx sin x Replacing this in our integral: sinx cos 4 x + sin 4 x dx = sinx 1 sin x = sin x cos x dx = sinx sin x dx 11
13 Now, this looks a little more familiar. We can try the substitution: u = x, sinx sinx dx = du dx = sinu sin u. ( ) 1.du dx.dx 1 So, we must solve the integral: sinu sinu.1.du dx. dx = sinu sin u.du Now, what comes to mind, is using sin u = 1 cos u: sinu sin u.du = sinu 1 + cos u du = sinu 1 + cos u du And now we try the substitution: v = cosu, sinu 1 + cos u du = = dv du = sinu ( v. dv 1 + v dv du And this integral is solved directly, since (arctanv) = 1 dv 1 + v = arctanv + C And now, we substitute back v = cos u = cos x: ). du 1+v : sinx cos 4 x + sin 4 dx = arctancosx + C x 1
14 7 Exercises Solve the integrals: 1. cos 3 xdx. sin xdx 3. sin 4 xdx 4. cos 4 x sin 3 x dx dx 5. (this one is tricky!) (1 + cosx) 13
15 8 Still To Come Day 0: Introduction to Definite Integrals Day 1: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 14
Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS : Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Integrals / 7 The Substitution Method Idea: To replace a relatively
Section 5.5 More Integration Formula (The Substitution Method) 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS : Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Integrals / 7 The Substitution Method Idea: To replace a relatively
Math 226 Calculus Spring 2016 Exam 2V1
 Math 6 Calculus Spring 6 Exam V () (35 Points) Evaluate the following integrals. (a) (7 Points) tan 5 (x) sec 3 (x) dx (b) (8 Points) cos 4 (x) dx Math 6 Calculus Spring 6 Exam V () (Continued) Evaluate
Math 6 Calculus Spring 6 Exam V () (35 Points) Evaluate the following integrals. (a) (7 Points) tan 5 (x) sec 3 (x) dx (b) (8 Points) cos 4 (x) dx Math 6 Calculus Spring 6 Exam V () (Continued) Evaluate
The goal of today is to determine what u-substitution to use for trigonometric integrals. The most common substitutions are the following:
 Trigonometric Integrals The goal of today is to determine what u-substitution to use for trigonometric integrals. The most common substitutions are the following: Substitution u sinx u cosx u tanx u secx
Trigonometric Integrals The goal of today is to determine what u-substitution to use for trigonometric integrals. The most common substitutions are the following: Substitution u sinx u cosx u tanx u secx
Section 4.4. Using the Fundamental Theorem. Difference Equations to Differential Equations
 Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 4.4 Using the Fundamental Theorem As we saw in Section 4.3, using the Fundamental Theorem of Integral Calculus reduces the problem of evaluating a
Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 4.4 Using the Fundamental Theorem As we saw in Section 4.3, using the Fundamental Theorem of Integral Calculus reduces the problem of evaluating a
MAT137 - Term 2, Week 5
 MAT137 - Term 2, Week 5 Test 3 is tomorrow, February 3, at 4pm. See the course website for details. Today we will: Talk more about integration by parts. Talk about integrating certain combinations of trig
MAT137 - Term 2, Week 5 Test 3 is tomorrow, February 3, at 4pm. See the course website for details. Today we will: Talk more about integration by parts. Talk about integrating certain combinations of trig
Change of Variables: Indefinite Integrals
 Change of Variables: Indefinite Integrals Mathematics 11: Lecture 39 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 29, 2007 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Change of Variables: Indefinite Integrals November
Change of Variables: Indefinite Integrals Mathematics 11: Lecture 39 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 29, 2007 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Change of Variables: Indefinite Integrals November
If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy. du du. If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u
 Section 3 4B The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then f (u) u The Chain Rule with the Power
Section 3 4B The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then f (u) u The Chain Rule with the Power
Using this definition, it is possible to define an angle of any (positive or negative) measurement by recognizing how its terminal side is obtained.
 Angle in Standard Position With the Cartesian plane, we define an angle in Standard Position if it has its vertex on the origin and one of its sides ( called the initial side ) is always on the positive
Angle in Standard Position With the Cartesian plane, we define an angle in Standard Position if it has its vertex on the origin and one of its sides ( called the initial side ) is always on the positive
Example. Evaluate. 3x 2 4 x dx.
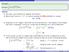 3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy. du du. If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u
 Section 3 4B Lecture The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u The Chain Rule
Section 3 4B Lecture The Chain Rule If y = f (u) is a differentiable function of u and u = g(x) is a differentiable function of x then dy dx = dy du du dx or If y = f (u) then y = f (u) u The Chain Rule
Mathematics 1161: Final Exam Study Guide
 Mathematics 1161: Final Exam Study Guide 1. The Final Exam is on December 10 at 8:00-9:45pm in Hitchcock Hall (HI) 031 2. Take your BuckID to the exam. The use of notes, calculators, or other electronic
Mathematics 1161: Final Exam Study Guide 1. The Final Exam is on December 10 at 8:00-9:45pm in Hitchcock Hall (HI) 031 2. Take your BuckID to the exam. The use of notes, calculators, or other electronic
Study 5.5, # 1 5, 9, 13 27, 35, 39, 49 59, 63, 69, 71, 81. Class Notes: Prof. G. Battaly, Westchester Community College, NY Homework.
 Goals: 1. Recognize an integrand that is the derivative of a composite function. 2. Generalize the Basic Integration Rules to include composite functions. 3. Use substitution to simplify the process of
Goals: 1. Recognize an integrand that is the derivative of a composite function. 2. Generalize the Basic Integration Rules to include composite functions. 3. Use substitution to simplify the process of
16 Inverse Trigonometric Functions
 6 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Concepts: Restricting the Domain of the Trigonometric Functions The Inverse Sine Function The Inverse Cosine Function The Inverse Tangent Function Using the Inverse Trigonometric
6 Inverse Trigonometric Functions Concepts: Restricting the Domain of the Trigonometric Functions The Inverse Sine Function The Inverse Cosine Function The Inverse Tangent Function Using the Inverse Trigonometric
Section 4.8 Anti Derivative and Indefinite Integrals 2 Lectures. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 4.8 Anti Derivative and Indefinite Integrals 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) 1 / 28 Indefinite Integral Given a function f, if F is a function such that
Section 4.8 Anti Derivative and Indefinite Integrals 2 Lectures College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) 1 / 28 Indefinite Integral Given a function f, if F is a function such that
Chapter 6. Techniques of Integration. 6.1 Differential notation
 Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Chapter 6. Techniques of Integration. 6.1 Differential notation
 Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Applied Calculus I. Lecture 29
 Applied Calculus I Lecture 29 Integrals of trigonometric functions We shall continue learning substitutions by considering integrals involving trigonometric functions. Integrals of trigonometric functions
Applied Calculus I Lecture 29 Integrals of trigonometric functions We shall continue learning substitutions by considering integrals involving trigonometric functions. Integrals of trigonometric functions
1 Lecture 39: The substitution rule.
 Lecture 39: The substitution rule. Recall the chain rule and restate as the substitution rule. u-substitution, bookkeeping for integrals. Definite integrals, changing limits. Symmetry-integrating even
Lecture 39: The substitution rule. Recall the chain rule and restate as the substitution rule. u-substitution, bookkeeping for integrals. Definite integrals, changing limits. Symmetry-integrating even
Handout 1. Research shows that students learn when they MAKE MISTAKES and not when they get it right. SO MAKE MISTAKES, because MISTAKES ARE GOOD!
 Handout Research shows that students learn when they MAKE MISTAKES and not when they get it right. SO MAKE MISTAKES, because MISTAKES ARE GOOD! Review:. The Substitution Rule Indefinite f (g()) g ()d =
Handout Research shows that students learn when they MAKE MISTAKES and not when they get it right. SO MAKE MISTAKES, because MISTAKES ARE GOOD! Review:. The Substitution Rule Indefinite f (g()) g ()d =
M152: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review
 M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
Integration 1/10. Integration. Student Guidance Centre Learning Development Service
 Integration / Integration Student Guidance Centre Learning Development Service lds@qub.ac.uk Integration / Contents Introduction. Indefinite Integration....................... Definite Integration.......................
Integration / Integration Student Guidance Centre Learning Development Service lds@qub.ac.uk Integration / Contents Introduction. Indefinite Integration....................... Definite Integration.......................
Inverse Trig Functions
 6.6i Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Sine Function Does g(x) = sin(x) have an inverse? What restriction would we need to make so that at least a piece of this function has an inverse? Given f (x)
6.6i Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Sine Function Does g(x) = sin(x) have an inverse? What restriction would we need to make so that at least a piece of this function has an inverse? Given f (x)
Lecture 25: The Sine and Cosine Functions. tan(x) 1+y
 Lecture 5: The Sine Cosine Functions 5. Denitions We begin b dening functions s : c : ; i! R ; i! R b Note that 8 >< q tan(x) ; if x s(x) + tan (x) ; >: ; if x 8 >< q ; if x c(x) + tan (x) ; >: 0; if x.
Lecture 5: The Sine Cosine Functions 5. Denitions We begin b dening functions s : c : ; i! R ; i! R b Note that 8 >< q tan(x) ; if x s(x) + tan (x) ; >: ; if x 8 >< q ; if x c(x) + tan (x) ; >: 0; if x.
5, tan = 4. csc = Simplify: 3. Simplify: 4. Factor and simplify: cos x sin x cos x
 Precalculus Final Review 1. Given the following values, evaluate (if possible) the other four trigonometric functions using the fundamental trigonometric identities or triangles csc = - 3 5, tan = 4 3.
Precalculus Final Review 1. Given the following values, evaluate (if possible) the other four trigonometric functions using the fundamental trigonometric identities or triangles csc = - 3 5, tan = 4 3.
Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from the Greek word meaning measurement of triangles Angles are typically labeled with Greek letters
 Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from the Greek word meaning measurement of triangles Angles are typically labeled with Greek letters α( alpha), β ( beta), θ ( theta) as well as upper case letters A,B,
Trigonometry Trigonometry comes from the Greek word meaning measurement of triangles Angles are typically labeled with Greek letters α( alpha), β ( beta), θ ( theta) as well as upper case letters A,B,
Integration by Parts
 Calculus 2 Lia Vas Integration by Parts Using integration by parts one transforms an integral of a product of two functions into a simpler integral. Divide the initial function into two parts called u
Calculus 2 Lia Vas Integration by Parts Using integration by parts one transforms an integral of a product of two functions into a simpler integral. Divide the initial function into two parts called u
CK- 12 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1
 14.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine 1. A.,1 B. (, 1) C. 3,0 D. 11 1, 6 E. (, 1) F. G. H. 11, 4 7, 1 11, 3. 3. 5 9,,,,,,, 4 4 4 4 3 5 3, and, 3 3 CK- 1 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1 4.ans-1401-01 5.
14.1 Graphing Sine and Cosine 1. A.,1 B. (, 1) C. 3,0 D. 11 1, 6 E. (, 1) F. G. H. 11, 4 7, 1 11, 3. 3. 5 9,,,,,,, 4 4 4 4 3 5 3, and, 3 3 CK- 1 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1 4.ans-1401-01 5.
f(x) g(x) = [f (x)g(x) dx + f(x)g (x)dx
 Chapter 7 is concerned with all the integrals that can t be evaluated with simple antidifferentiation. Chart of Integrals on Page 463 7.1 Integration by Parts Like with the Chain Rule substitutions with
Chapter 7 is concerned with all the integrals that can t be evaluated with simple antidifferentiation. Chart of Integrals on Page 463 7.1 Integration by Parts Like with the Chain Rule substitutions with
Techniques of Integration
 5 Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives
5 Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives
I can complete a table of values using a calculator.
 Starter 1) True or false? cos (x) = 1 + sin (x) Why? 2 2 2) Solve 1 + 4sin(x) = 3 for 0 < x < 360 Today we are learning... Sketching Trigonometric Graphs How to sketch a variety of trigonometric graphs.
Starter 1) True or false? cos (x) = 1 + sin (x) Why? 2 2 2) Solve 1 + 4sin(x) = 3 for 0 < x < 360 Today we are learning... Sketching Trigonometric Graphs How to sketch a variety of trigonometric graphs.
Practice Problems: Integration by Parts
 Practice Problems: Integration by Parts Answers. (a) Neither term will get simpler through differentiation, so let s try some choice for u and dv, and see how it works out (we can always go back and try
Practice Problems: Integration by Parts Answers. (a) Neither term will get simpler through differentiation, so let s try some choice for u and dv, and see how it works out (we can always go back and try
University Calculus I. Worksheet # 8 Mar b. sin tan e. sin 2 sin 1 5. b. tan. c. sec sin 1 ( x )) cos 1 ( x )) f. csc. c.
 MATH 6 WINTER 06 University Calculus I Worksheet # 8 Mar. 06-0 The topic covered by this worksheet is: Derivative of Inverse Functions and the Inverse Trigonometric functions. SamplesolutionstoallproblemswillbeavailableonDL,
MATH 6 WINTER 06 University Calculus I Worksheet # 8 Mar. 06-0 The topic covered by this worksheet is: Derivative of Inverse Functions and the Inverse Trigonometric functions. SamplesolutionstoallproblemswillbeavailableonDL,
Integration by Substitution
 Integration by Substitution Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University Abstract This handout contains material on a very important integration method called integration by substitution. Substitution
Integration by Substitution Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University Abstract This handout contains material on a very important integration method called integration by substitution. Substitution
Math 106: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS
 Math 6: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS INTEGRATION TIPS Substitution: usually let u a function that s inside another function, especially if du (possibly off by a multiplying constant) is also present
Math 6: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS INTEGRATION TIPS Substitution: usually let u a function that s inside another function, especially if du (possibly off by a multiplying constant) is also present
Algebra 2/Trig AIIT.17 Trig Identities Notes. Name: Date: Block:
 Algebra /Trig AIIT.7 Trig Identities Notes Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Trigonometric Identities When two trig expressions can be proven to be equal to each other, the statement is called a trig identity
Algebra /Trig AIIT.7 Trig Identities Notes Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Trigonometric Identities When two trig expressions can be proven to be equal to each other, the statement is called a trig identity
PRE-CALCULUS TRIG APPLICATIONS UNIT Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions
 What is an Identity? PRE-CALCULUS TRIG APPLICATIONS UNIT Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions What is it used for? The Reciprocal Identities: sin θ = cos θ = tan θ = csc θ = sec θ = ctn θ = The Quotient
What is an Identity? PRE-CALCULUS TRIG APPLICATIONS UNIT Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions What is it used for? The Reciprocal Identities: sin θ = cos θ = tan θ = csc θ = sec θ = ctn θ = The Quotient
secθ 1 cosθ The pythagorean identities can also be expressed as radicals
 Basic Identities Section Objectives: Students will know how to use fundamental trigonometric identities to evaluate trigonometric functions and simplify trigonometric expressions. We use trig. identities
Basic Identities Section Objectives: Students will know how to use fundamental trigonometric identities to evaluate trigonometric functions and simplify trigonometric expressions. We use trig. identities
Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry
 Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Using Fundamental Identities Verifying Trigonometric Identities Solving Trigonometric Equations Sum and Difference Formulas
Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 Section 5 Using Fundamental Identities Verifying Trigonometric Identities Solving Trigonometric Equations Sum and Difference Formulas
Welcome to AP Calculus!!!
 Welcome to AP Calculus!!! In preparation for next year, you need to complete this summer packet. This packet reviews & expands upon the concepts you studied in Algebra II and Pre-calculus. Make sure you
Welcome to AP Calculus!!! In preparation for next year, you need to complete this summer packet. This packet reviews & expands upon the concepts you studied in Algebra II and Pre-calculus. Make sure you
Chapter 7 Notes, Stewart 7e. 7.1 Integration by Parts Trigonometric Integrals Evaluating sin m xcos n (x)dx...
 Contents 7.1 Integration by Parts........................................ 2 7.2 Trigonometric Integrals...................................... 8 7.2.1 Evaluating sin m xcos n (x)dx..............................
Contents 7.1 Integration by Parts........................................ 2 7.2 Trigonometric Integrals...................................... 8 7.2.1 Evaluating sin m xcos n (x)dx..............................
f(x) = lim x 0 + x = lim f(x) =
 Infinite Limits Having discussed in detail its as x ±, we would like to discuss in more detail its where f(x) ±. Once again we would like to emphasize that ± are not numbers, so if we write f(x) = we are
Infinite Limits Having discussed in detail its as x ±, we would like to discuss in more detail its where f(x) ±. Once again we would like to emphasize that ± are not numbers, so if we write f(x) = we are
b n x n + b n 1 x n b 1 x + b 0
 Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
Calculus II Practice Test 1 Problems: , 6.5, Page 1 of 10
 Calculus II Practice Test Problems: 6.-6.3, 6.5, 7.-7.3 Page of This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on the actual test. To prepare for the test: review homework,
Calculus II Practice Test Problems: 6.-6.3, 6.5, 7.-7.3 Page of This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on the actual test. To prepare for the test: review homework,
NOTES 10: ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY
 NOTES 0: ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON 0. USING FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC INDENTITIES Reciprocal Identities sin csc cos sec
NOTES 0: ANALYTIC TRIGONOMETRY Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON 0. USING FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES FUNDAMENTAL TRIGONOMETRIC INDENTITIES Reciprocal Identities sin csc cos sec
Math 111 lecture for Friday, Week 10
 Math lecture for Friday, Week Finding antiderivatives mean reversing the operation of taking derivatives. Today we ll consider reversing the chain rule and the product rule. Substitution technique. Recall
Math lecture for Friday, Week Finding antiderivatives mean reversing the operation of taking derivatives. Today we ll consider reversing the chain rule and the product rule. Substitution technique. Recall
Trigonometric integrals by basic methods
 Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter : Integration methods Section 7 Trigonometric integrals by basic methods What you need to know already: Integrals of basic trigonometric functions. Basic trigonometric
Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter : Integration methods Section 7 Trigonometric integrals by basic methods What you need to know already: Integrals of basic trigonometric functions. Basic trigonometric
MATH 101: PRACTICE MIDTERM 2
 MATH : PRACTICE MIDTERM INSTRUCTOR: PROF. DRAGOS GHIOCA March 7, Duration of examination: 7 minutes This examination includes pages and 6 questions. You are responsible for ensuring that your copy of the
MATH : PRACTICE MIDTERM INSTRUCTOR: PROF. DRAGOS GHIOCA March 7, Duration of examination: 7 minutes This examination includes pages and 6 questions. You are responsible for ensuring that your copy of the
Section 6.2 Integration by Parts
 Section 6 Integration by Parts AP E XC II Version 0 Authors Gregory Hartman, PhD Department of Applied Mathema cs Virginia Military Ins tute Brian Heinold, PhD Department of Mathema cs and Computer Science
Section 6 Integration by Parts AP E XC II Version 0 Authors Gregory Hartman, PhD Department of Applied Mathema cs Virginia Military Ins tute Brian Heinold, PhD Department of Mathema cs and Computer Science
Section: I. u 4 du. (9x + 1) + C, 3
 EXAM 3 MAT 168 Calculus II Fall 18 Name: Section: I All answers must include either supporting work or an eplanation of your reasoning. MPORTANT: These elements are considered main part of the answer and
EXAM 3 MAT 168 Calculus II Fall 18 Name: Section: I All answers must include either supporting work or an eplanation of your reasoning. MPORTANT: These elements are considered main part of the answer and
DRAFT - Math 102 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 Math02 - Term72 - Guides and Exercises - DRAFT 7 Techniques of Integration A summery for the most important integrals that we have learned so far: 7. Integration by Parts The Product Rule states that if
Math02 - Term72 - Guides and Exercises - DRAFT 7 Techniques of Integration A summery for the most important integrals that we have learned so far: 7. Integration by Parts The Product Rule states that if
CHAIN RULE: DAY 2 WITH TRIG FUNCTIONS. Section 2.4A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised /30/2018 1:44 AM 2.4A: Chain Rule Day 2 1
 CHAIN RULE: DAY WITH TRIG FUNCTIONS Section.4A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 018 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 7/30/018 1:44 AM.4A: Chain Rule Day 1 THE CHAIN RULE A. d dx f g x = f g x g x B. If f(x) is a differentiable
CHAIN RULE: DAY WITH TRIG FUNCTIONS Section.4A Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 018 viet.dang@humbleisd.net 7/30/018 1:44 AM.4A: Chain Rule Day 1 THE CHAIN RULE A. d dx f g x = f g x g x B. If f(x) is a differentiable
Honors AP Calculus BC Trig Integration Techniques 13 December 2013
 Honors AP Calculus BC Name: Trig Integration Techniques 13 December 2013 Integration Techniques Antidifferentiation Substitutiion (antidifferentiation of the Chain rule) Integration by Parts (antidifferentiation
Honors AP Calculus BC Name: Trig Integration Techniques 13 December 2013 Integration Techniques Antidifferentiation Substitutiion (antidifferentiation of the Chain rule) Integration by Parts (antidifferentiation
WeBWorK, Problems 2 and 3
 WeBWorK, Problems 2 and 3 7 dx 2. Evaluate x ln(6x) This can be done using integration by parts or substitution. (Most can not). However, it is much more easily done using substitution. This can be written
WeBWorK, Problems 2 and 3 7 dx 2. Evaluate x ln(6x) This can be done using integration by parts or substitution. (Most can not). However, it is much more easily done using substitution. This can be written
Calculus II Practice Test Problems for Chapter 7 Page 1 of 6
 Calculus II Practice Test Problems for Chapter 7 Page of 6 This is a set of practice test problems for Chapter 7. This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on
Calculus II Practice Test Problems for Chapter 7 Page of 6 This is a set of practice test problems for Chapter 7. This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities. Math 30-1 R 3. (Revisit, Review and Revive)
 SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
SESSION 6 Trig. Equations and Identities Math 30-1 R 3 (Revisit, Review and Revive) 1 P a g e 2 P a g e Mathematics 30-1 Learning Outcomes Specific Outcome 5: Solve, algebraically and graphically, first
Grade: The remainder of this page has been left blank for your workings. VERSION E. Midterm E: Page 1 of 12
 First Name: Student-No: Last Name: Section: Grade: The remainder of this page has been left blank for your workings. Midterm E: Page of Indefinite Integrals. 9 marks Each part is worth 3 marks. Please
First Name: Student-No: Last Name: Section: Grade: The remainder of this page has been left blank for your workings. Midterm E: Page of Indefinite Integrals. 9 marks Each part is worth 3 marks. Please
a x a y = a x+y a x a = y ax y (a x ) r = a rx and log a (xy) = log a (x) + log a (y) log a ( x y ) = log a(x) log a (y) log a (x r ) = r log a (x).
 You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves. Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts
 Week #7: Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts 1 Week 7 The Indefinite Integral The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, b a f(x) dx =
Week #7: Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts 1 Week 7 The Indefinite Integral The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, b a f(x) dx =
5.5. The Substitution Rule
 INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
a. y= 5x 2 +2x 3 d. 2x+5=10 b. y= 3 x 2 c. y= 1 x 3 Learning Goal QUIZ Trigonometric Identities. OH nooooooo! Class Opener: March 17, 2015
 DAY 48 March 16/17, 2015 OH nooooooo! Class Opener: Find D and R: a. y= 5x 2 +2x 3 b. y= 3 x 2 c. y= 1 x 3 +2 d. 2x+5=10 Nov 14 2:45 PM Learning Goal 5.1.-5.2. QUIZ Trigonometric Identities. Mar 13 11:56
DAY 48 March 16/17, 2015 OH nooooooo! Class Opener: Find D and R: a. y= 5x 2 +2x 3 b. y= 3 x 2 c. y= 1 x 3 +2 d. 2x+5=10 Nov 14 2:45 PM Learning Goal 5.1.-5.2. QUIZ Trigonometric Identities. Mar 13 11:56
Pre-Calculus Spring Final Exam Review Guide
 Pre-Calculus Spring Final Exam Review Guide The Final Exam will cover: Chapter 4, Chapter 5, Polar Graphing, Solving systems of equations with Matrices (part of section 7.3), Partial Fraction Decomposition
Pre-Calculus Spring Final Exam Review Guide The Final Exam will cover: Chapter 4, Chapter 5, Polar Graphing, Solving systems of equations with Matrices (part of section 7.3), Partial Fraction Decomposition
AB 1: Find lim. x a.
 AB 1: Find lim x a f ( x) AB 1 Answer: Step 1: Find f ( a). If you get a zero in the denominator, Step 2: Factor numerator and denominator of f ( x). Do any cancellations and go back to Step 1. If you
AB 1: Find lim x a f ( x) AB 1 Answer: Step 1: Find f ( a). If you get a zero in the denominator, Step 2: Factor numerator and denominator of f ( x). Do any cancellations and go back to Step 1. If you
4181H Problem Set 10 Selected Solutions. Chapter 15. = lim. (by L Hôpital s Rule) (0) = lim. x 2, = lim x 3 ( sin x)x + cos x cos x = lim
 48H Problem Set 0 Selected Solutions Chapter 5 # 3(a From the definition of the derivative we have sin f f( f(0 (0 sin 0 0 0 0 = cos (by L Hôpital s Rule = sin (by L Hôpital s Rule = 0 (b From the definition
48H Problem Set 0 Selected Solutions Chapter 5 # 3(a From the definition of the derivative we have sin f f( f(0 (0 sin 0 0 0 0 = cos (by L Hôpital s Rule = sin (by L Hôpital s Rule = 0 (b From the definition
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
Unit 6 Trigonometric Identities
 Unit 6 Trigonometric Identities Prove trigonometric identities Solve trigonometric equations Prove trigonometric identities, using: Reciprocal identities Quotient identities Pythagorean identities Sum
Unit 6 Trigonometric Identities Prove trigonometric identities Solve trigonometric equations Prove trigonometric identities, using: Reciprocal identities Quotient identities Pythagorean identities Sum
Math 1552: Integral Calculus Final Exam Study Guide, Spring 2018
 Math 55: Integral Calculus Final Exam Study Guide, Spring 08 PART : Concept Review (Note: concepts may be tested on the exam in the form of true/false or short-answer questions.). Complete each statement
Math 55: Integral Calculus Final Exam Study Guide, Spring 08 PART : Concept Review (Note: concepts may be tested on the exam in the form of true/false or short-answer questions.). Complete each statement
Find all of the real numbers x that satisfy the algebraic equation:
 Appendix C: Factoring Algebraic Expressions Factoring algebraic equations is the reverse of expanding algebraic expressions discussed in Appendix B. Factoring algebraic equations can be a great help when
Appendix C: Factoring Algebraic Expressions Factoring algebraic equations is the reverse of expanding algebraic expressions discussed in Appendix B. Factoring algebraic equations can be a great help when
Chapter 8 Integration Techniques and Improper Integrals
 Chapter 8 Integration Techniques and Improper Integrals 8.1 Basic Integration Rules 8.2 Integration by Parts 8.4 Trigonometric Substitutions 8.5 Partial Fractions 8.6 Numerical Integration 8.7 Integration
Chapter 8 Integration Techniques and Improper Integrals 8.1 Basic Integration Rules 8.2 Integration by Parts 8.4 Trigonometric Substitutions 8.5 Partial Fractions 8.6 Numerical Integration 8.7 Integration
Prelim 2 Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 90 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck!
 April 4, Prelim Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Trigonometric Formulas sin x sin x cos x cos (u + v) cos
April 4, Prelim Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Trigonometric Formulas sin x sin x cos x cos (u + v) cos
Chapter 5 Notes. 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities
 Chapter 5 Notes 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities 1. Simplify each expression to its lowest terms. Write the answer to part as the product of factors. (a) sin x csc x cot x ( 1+ sinσ + cosσ ) (c) 1 tanx
Chapter 5 Notes 5.1 Using Fundamental Identities 1. Simplify each expression to its lowest terms. Write the answer to part as the product of factors. (a) sin x csc x cot x ( 1+ sinσ + cosσ ) (c) 1 tanx
There are some trigonometric identities given on the last page.
 MA 114 Calculus II Fall 2015 Exam 4 December 15, 2015 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: No books or notes may be used. Turn off all your electronic devices and do not wear ear-plugs during
MA 114 Calculus II Fall 2015 Exam 4 December 15, 2015 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: No books or notes may be used. Turn off all your electronic devices and do not wear ear-plugs during
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 23 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 23 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative
The definition, and some continuity laws. Types of discontinuities. The Squeeze Theorem. Two special limits. The IVT and EVT.
 MAT137 - Week 5 The deadline to drop to MAT135 is tomorrow. (Details on course website.) The deadline to let us know you have a scheduling conflict with Test 1 is also tomorrow. (Details on the course
MAT137 - Week 5 The deadline to drop to MAT135 is tomorrow. (Details on course website.) The deadline to let us know you have a scheduling conflict with Test 1 is also tomorrow. (Details on the course
and verify that it satisfies the differential equation:
 MOTIVATION: Chapter One: Basic and Review Why study differential equations? Suppose we know how a certain quantity changes with time (for example, the temperature of coffee in a cup, the number of people
MOTIVATION: Chapter One: Basic and Review Why study differential equations? Suppose we know how a certain quantity changes with time (for example, the temperature of coffee in a cup, the number of people
Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals
 Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation. The substitution
MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B Calculus Section 1: - Integration.
 MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B 2007. For use in Dr Chris Tisdell s lectures: Tues 11 + Thur 10 in KBT Calculus Section 1: - Integration. 1. Motivation 2. What you should already know 3. Useful integrals 4. Integrals
MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B 2007. For use in Dr Chris Tisdell s lectures: Tues 11 + Thur 10 in KBT Calculus Section 1: - Integration. 1. Motivation 2. What you should already know 3. Useful integrals 4. Integrals
Calculus for Engineers II - Sample Problems on Integrals Manuela Kulaxizi
 Calculus for Engineers II - Sample Problems on Integrals Manuela Kulaxizi Question : Solve the following integrals:. π sin x. x 4 3. 4. sinh 8 x cosh x sin x cos 7 x 5. x 5 ln x 6. 8x + 6 3x + x 7. 8..
Calculus for Engineers II - Sample Problems on Integrals Manuela Kulaxizi Question : Solve the following integrals:. π sin x. x 4 3. 4. sinh 8 x cosh x sin x cos 7 x 5. x 5 ln x 6. 8x + 6 3x + x 7. 8..
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture. Dr. Abdulla Eid. College of Science. MATHS 101: Calculus I
 Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 1 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative of
Section 3.6 The chain rule 1 Lecture College of Science MATHS 101: Calculus I (University of Bahrain) Logarithmic Differentiation 1 / 1 Motivation Goal: We want to derive rules to find the derivative of
One of the powerful themes in trigonometry is that the entire subject emanates from a very simple idea: locating a point on the unit circle.
 2.24 Tanz and the Reciprocals Derivatives of Other Trigonometric Functions One of the powerful themes in trigonometry is that the entire subject emanates from a very simple idea: locating a point on the
2.24 Tanz and the Reciprocals Derivatives of Other Trigonometric Functions One of the powerful themes in trigonometry is that the entire subject emanates from a very simple idea: locating a point on the
In this chapter we study several functions that are useful in calculus and other areas of mathematics.
 Calculus 5 7 Special functions In this chapter we study several functions that are useful in calculus and other areas of mathematics. 7. Hyperbolic trigonometric functions The functions we study in this
Calculus 5 7 Special functions In this chapter we study several functions that are useful in calculus and other areas of mathematics. 7. Hyperbolic trigonometric functions The functions we study in this
Chapter 1. Functions 1.3. Trigonometric Functions
 1.3 Trigonometric Functions 1 Chapter 1. Functions 1.3. Trigonometric Functions Definition. The number of radians in the central angle A CB within a circle of radius r is defined as the number of radius
1.3 Trigonometric Functions 1 Chapter 1. Functions 1.3. Trigonometric Functions Definition. The number of radians in the central angle A CB within a circle of radius r is defined as the number of radius
Techniques of Integration
 0 Techniques of Integration ½¼º½ ÈÓÛ Ö Ó Ò Ò Ó Ò Functions consisting of products of the sine and cosine can be integrated by using substitution and trigonometric identities. These can sometimes be tedious,
0 Techniques of Integration ½¼º½ ÈÓÛ Ö Ó Ò Ò Ó Ò Functions consisting of products of the sine and cosine can be integrated by using substitution and trigonometric identities. These can sometimes be tedious,
The Relation between the Integral and the Derivative Graphs. Unit #10 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals
 Graphs of Antiderivatives - Unit #0 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation.
Graphs of Antiderivatives - Unit #0 : Graphs of Antiderivatives, Substitution Integrals Goals: Relationship between the graph of f(x) and its anti-derivative F (x) The guess-and-check method for anti-differentiation.
MAS113 CALCULUS II SPRING 2008, QUIZ 4 SOLUTIONS
 MAS113 CALCULUS II SPRING 8, QUIZ 4 SOLUTIONS Quiz 4a Solutions 1 Find the area of the surface obtained by rotating the curve y = x 3 /6 + 1/x, 1/ x 1 about the x-axis. We have y = x / 1/x. Therefore,
MAS113 CALCULUS II SPRING 8, QUIZ 4 SOLUTIONS Quiz 4a Solutions 1 Find the area of the surface obtained by rotating the curve y = x 3 /6 + 1/x, 1/ x 1 about the x-axis. We have y = x / 1/x. Therefore,
5 Integrals reviewed Basic facts U-substitution... 4
 Contents 5 Integrals reviewed 5. Basic facts............................... 5.5 U-substitution............................. 4 6 Integral Applications 0 6. Area between two curves.......................
Contents 5 Integrals reviewed 5. Basic facts............................... 5.5 U-substitution............................. 4 6 Integral Applications 0 6. Area between two curves.......................
Math 180, Final Exam, Fall 2012 Problem 1 Solution
 Math 80, Final Exam, Fall 0 Problem Solution. Find the derivatives of the following functions: (a) ln(ln(x)) (b) x 6 + sin(x) e x (c) tan(x ) + cot(x ) (a) We evaluate the derivative using the Chain Rule.
Math 80, Final Exam, Fall 0 Problem Solution. Find the derivatives of the following functions: (a) ln(ln(x)) (b) x 6 + sin(x) e x (c) tan(x ) + cot(x ) (a) We evaluate the derivative using the Chain Rule.
f(g(x)) g (x) dx = f(u) du.
 1. Techniques of Integration Section 8-IT 1.1. Basic integration formulas. Integration is more difficult than derivation. The derivative of every rational function or trigonometric function is another
1. Techniques of Integration Section 8-IT 1.1. Basic integration formulas. Integration is more difficult than derivation. The derivative of every rational function or trigonometric function is another
Math 106: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS
 Math 6: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS INTEGRATION TIPS Substitution: usually let u a function that s inside another function, especially if du (possibly off by a multiplying constant) is also present
Math 6: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS INTEGRATION TIPS Substitution: usually let u a function that s inside another function, especially if du (possibly off by a multiplying constant) is also present
Math 5 Trigonometry Chapter 4 Test Fall 08 Name Show work for credit. Write all responses on separate paper. Do not use a calculator.
 Math 5 Trigonometry Chapter Test Fall 08 Name Show work for credit. Write all responses on separate paper. Do not use a calculator. 23 1. Consider an arclength of t = travelled counter-clockwise around
Math 5 Trigonometry Chapter Test Fall 08 Name Show work for credit. Write all responses on separate paper. Do not use a calculator. 23 1. Consider an arclength of t = travelled counter-clockwise around
Main topics for the First Midterm
 Main topics for the First Midterm Midterm 2 will cover Sections 7.7-7.9, 8.1-8.5, 9.1-9.2, 11.1-11.2. This is roughly the material from the first five homeworks and and three quizzes. In particular, I
Main topics for the First Midterm Midterm 2 will cover Sections 7.7-7.9, 8.1-8.5, 9.1-9.2, 11.1-11.2. This is roughly the material from the first five homeworks and and three quizzes. In particular, I
Solutions to Math 41 Final Exam December 10, 2012
 Solutions to Math 4 Final Exam December,. ( points) Find each of the following limits, with justification. If there is an infinite limit, then explain whether it is or. x ln(t + ) dt (a) lim x x (5 points)
Solutions to Math 4 Final Exam December,. ( points) Find each of the following limits, with justification. If there is an infinite limit, then explain whether it is or. x ln(t + ) dt (a) lim x x (5 points)
x 2 = 1 Clearly, this equation is not true for all real values of x. Nevertheless, we can solve it by taking careful steps:
 Sec. 01 notes Solving Trig Equations: The Easy Ones Main Idea We are now ready to discuss the solving of trigonometric equations. Recall that, generally speaking, identities are equations which hold true
Sec. 01 notes Solving Trig Equations: The Easy Ones Main Idea We are now ready to discuss the solving of trigonometric equations. Recall that, generally speaking, identities are equations which hold true
Solutions to Exam 1, Math Solution. Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists. Recall that (f 1 ) (a) =
 Solutions to Exam, Math 56 The function f(x) e x + x 3 + x is one-to-one (there is no need to check this) What is (f ) ( + e )? Solution Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists
Solutions to Exam, Math 56 The function f(x) e x + x 3 + x is one-to-one (there is no need to check this) What is (f ) ( + e )? Solution Because f(x) is one-to-one, we know the inverse function exists
7.2 Trigonometric Integrals
 7.2 1 7.2 Trigonometric Integrals Products of Powers of Sines and Cosines We wish to evaluate integrals of the form: sin m x cos n xdx where m and n are nonnegative integers. Recall the double angle formulas
7.2 1 7.2 Trigonometric Integrals Products of Powers of Sines and Cosines We wish to evaluate integrals of the form: sin m x cos n xdx where m and n are nonnegative integers. Recall the double angle formulas
TAMU 2009 Freshman-Sophomore Math Contest
 TAMU 29 Freshman-Sophomore Math Contest First-year student version There are five problems, each worth 2% of your total score. This is not an examination, and a good score, even a winning score, can be
TAMU 29 Freshman-Sophomore Math Contest First-year student version There are five problems, each worth 2% of your total score. This is not an examination, and a good score, even a winning score, can be
Practice Exam I. Summer Term I Kostadinov. MA124 Calculus II Boston University
 student: Practice Exam I Problem 1: Find the derivative of the functions T 1 (x), T 2 (x), T 3 (x). State the reason of your answers. a) T 1 (x) = x 2t dt 2 b) T 2 (x) = e x ln(t2 )dt c) T 3 (x) = x 2
student: Practice Exam I Problem 1: Find the derivative of the functions T 1 (x), T 2 (x), T 3 (x). State the reason of your answers. a) T 1 (x) = x 2t dt 2 b) T 2 (x) = e x ln(t2 )dt c) T 3 (x) = x 2
Math 250 Skills Assessment Test
 Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
2.5 The Chain Rule Brian E. Veitch
 2.5 The Chain Rule This is our last ifferentiation rule for this course. It s also one of the most use. The best way to memorize this (along with the other rules) is just by practicing until you can o
2.5 The Chain Rule This is our last ifferentiation rule for this course. It s also one of the most use. The best way to memorize this (along with the other rules) is just by practicing until you can o
3 Algebraic Methods. we can differentiate both sides implicitly to obtain a differential equation involving x and y:
 3 Algebraic Methods b The first appearance of the equation E Mc 2 in Einstein s handwritten notes. So far, the only general class of differential equations that we know how to solve are directly integrable
3 Algebraic Methods b The first appearance of the equation E Mc 2 in Einstein s handwritten notes. So far, the only general class of differential equations that we know how to solve are directly integrable
Math 152 Take Home Test 1
 Math 5 Take Home Test Due Monday 5 th October (5 points) The following test will be done at home in order to ensure that it is a fair and representative reflection of your own ability in mathematics I
Math 5 Take Home Test Due Monday 5 th October (5 points) The following test will be done at home in order to ensure that it is a fair and representative reflection of your own ability in mathematics I
