Main topics for the First Midterm
|
|
|
- Rosalyn Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Main topics for the First Midterm Midterm 2 will cover Sections , , , This is roughly the material from the first five homeworks and and three quizzes. In particular, I will expect you to know how to solve each problem from the homeworks and the quizzes. In addition, you will certainly need to know the material from Math Make sure you are comfortable with the following: Understand the material from Math In particular: Understand what an integral is, both intuitively (as a sum of infinitely small quantitites), and the actual definition (involving upper and lower sums). Make sure you understand the notations b f(x)dx and f(x)dx. In particular make sure a you understand why the first one is a number, and the second one is a function of x. Pay attention to which one you are asked to compute. If I ask you for a definite integral, your final answer should be a number, If I aks you for an indefinite integral, your final answer should be a function of x (or whatever the dummy variable is.) Know how to use the fundamental theorem of calculus to compute an integral by finding an antiderivative. Know how to use u-substitution to compute integrals. Make sure you are familiar with the forms for definite integrals and indefinite integrals. For definite integtals, remember that bounds change? (This can save you a lot of work by avoiding going back to the original variable.) For indefinite integrals, remember that you final answer should not be a function of u. Know the common trircks for u-substition (letting some complicated expression be u, letting u = x + a, finding a u that will make du appear in the integral, etc.) Don t forget that you also do simple things like u = ax + b, u doesn t have to be a complicated function of x in order to be useful. Have a look at section 8.1. Everything in there (except the hyperbolic functions) should seem pretty familiar to you by now. Know how to compute (f 1 ) (x) if f is one-to-one function. Remember that you can sometimes compute this (at least at specific points) without first finding f 1 (x) Know how to define ln x and exp(x), and know their basic properties. Know how to compute f (x) f(x) dx Trig Identities: A number of things we have covered this term involve trig functions, so you will need to know basic trig identities. These will be much more essential this term than they were the last term. 1
2 Know the simple identities like sin( x) = sin(x), cos x = sin( π 2 x), sin(π x) = sin x, etc. If you understand know the unit circle works, you won t need to memorize all of these. You should be able to come up with them on your own by just lookint at the picture. Know how to find the values of trig functions at certain special values (e.g. those you can get from or right triangles in terms of radians!) Know the Pythagorean identities: sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1 and 1 + tan 2 x = sec 2 x. They can help you integrare expressions of the form sin n (x) cos m (x) where at least one of n, m is odd.they are also usefull to expressions of the form tan n x sec m x where n is even or m is odd. Know how to take the derivatives of the basic trig functions. In particular, make sure know that (sin x) = cos x, (cos x) = sin x (remember these signs!) and (tan x) = sec 2 x = 1. Also, remember that you can ger the others with the quotient rule if you cos 2 x have forgotten them. Know how to use derivatives of trig functions to help you integrare expressions of the form sin n (x) cos m (x) where at least one of n, m is odd. They are also usefull to expressions of the form tan n x sec m x where n is even or m is odd. Know the double angle identities: sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x and cos(2x) = 2 cos 2 x 1 = 1 2 sin 2 x and the related half-angle formulas. Focus on how you can use these to integrate expressions of the form sin n x cos m x for n, m both even. It may also help to be somewhat familiar with the sum identities: sin(a+b) = sin a cos b+ cos a sin b, cos(a + b) = cos a cos b sin a sin b and the related product identities for sin a sin b, cos a cos b, sin a cos b. They are helpful in integrating experessions of the form: sin(nx) cos(mx), sin(nx) sin(mx), cos(nx) cos(mx). Inverse Trig Functions: Know how to define the basic inverse trig functions: arcsin and arctan (in particular, what are their domains and ranges?) Know how to define other inverse trig functions (e.g. arccos, arcsec etc.) in terms of these. Know how to compute certain values of these functions (if you know some value of a trig function, then you also know a value of the inverse trig function.) Know how to compute things like tan(arcsin x) of arcsin(sin x) (note that this is not always x) etc. If you can t immediately see how to do this with a trig identity, try drawing a picture. Most problems like this can be solved by drawing the init circle or an appropriate rignt triangle. Know how to take the derivatives of inverse trig functions (especially arcsin and arctan) Know how to use this to compute dx a 2 x 2 and dx x 2 +a 2 2
3 More generally, make sure you know how to compute things like dx or dx ax 2 +bx+c ax 2 +bx+c by completing the square (keep in mind that how you handle these will depend on whether the polynomial ax 2 + bx + c has real roots or not. Integration by Parts: Understand how the fundamental theorem of calculus and the product rule give the identity u(x)v (x)dx = u(x)v(x) u (x)v(x)dx. a Also know the definite version of this: u(x)v (x)dx = u(x)v(x) a b a u (x)v(x)dx. Remember that these are the limits for x, not for u or v. Know how to use this to sometimes compute f(x)g(x)dx - integrate one factor, and differentiate the other. If you are luck, the new integral will be easier to compute. If it is harder to compute, try the switching the derivative and the function. Remember that this often won t be as simple as memorizing a formula and plugging something in to get your answer. Integration by parts in useless if you can t figure out how to use if effectively. b There will sually be many different ways to break up your function into a product of two functions. Not all of them will be useful. Don t be afraid to try several things of your first guess doesn t work. Remember that there is always at least one way to break up a function as a product: f(x) = (1)f(x). Consider using this if f (x) is a much simple function than f(x), (e.g. f(x) = ln x, arcsin x, arctan x etc.) If using integration by parts doesn t immediately get you the answer, that doesn t mean you should give up on it. Did you end up with an integral which looks simpler? Consider using integration by parts again (e.g.. to compute x 2 e x dx). Maybe the integral you ended up with doesn t look any simpler. Can you find another way to relate if back to the original integral? Think about how we computed e x sin xdx: We used integration by parts twice and ended up with an equation we could solve for e x sin xdx. Don t forger about other techniques (like u-substitution) Is it possible that you could use u-substitution either before or after you use integration by parts? Products and Powers of Trig Functions: Know how to compute the integral sin n x cos m xdx for any m, n, Remember that if either m or n is odd, this is easy, simply use u substitution, with u = sin x, cos x and use the identity sin 2 x + cos 2 x = 1 to write the integral in the form f(u)du for some polynomial f. If m and n are both even, you can use the half-angle identities to decrease the exponents. Know how to hande something like sin(mx) cos(nx)dx (you can use the product identities) Also know how to deal with integrals involving other trig functions e.g. tan 3 xdx, sec 3 xdx. Remember the various tricks you can use, like u-substition, trig identities, and integration by parts. 3 b
4 Trig Substitution: Be familiar with the substitutions x = a sin u, x = a tan u, x = a sec u. How do they work? What is dx in each situation? When/why are they useful? (They are useful for simplifying expressions like a 2 x 2, a 2 + x 2, x 2 a 2 respectively.) What interval whould you pick u to lie in? For example, if you let x = a tan u, then you may take u ( π 2, π 2 ) in which case you will always have sec u > 0 and so x 2 + a 2 = a sec u. If you do this to compute an indefinite integral, then you will need to put the answer back in terms of x Make sure you know how to do this, Often simplifying your answer will involve computing things like sin(2 arctan x). Know how to do this (in this case you would want to first use a double angle identity and then a suitable right triangle.) Know what to do with other quadrativ functions. Any quadratic can be written in the form u 2 a 2, u 2 + a 2, a 2 u 2 by completing the square, Make sure you know how to do this and that you can use this to compute an integral involcing some quadratic function. Also keep in mind that an expression like a 2 x 2, a 2 + x 2, x 2 a 2 doesn t mean that you have to use trig substituion, Keep an eye for simpler approachs. You can compute x 4 x dx by setting x = 2 sin u, but is there something much 2 simpler you could do? Integrating Partial Fractions: Remeber that to use the partial fraction decomposition method, you first need a proper rational function. If the degree of the numerator is higher than the degree of the denominator, you will need to first divide the numerator by the denominator beore using the method. Also make sure that quadratics you end up with are really irreducible (for x 2 + bx + c you need b 2 4x < 0) Make absolutely sure that you know how to compute A (x a) dx and Bx+C dx for n (x 2 +bx+c) n x 2 + bx + c. If you don t know how to compute these integrals, then you won t be able to use this method. Remember, the first one is easy to compute. Just let u = x a, then you are left with du u Don t try to over complicate this. You don t need to complete the suare, or use n trig substitution of anything like that. This is the sort of things we were computing last term. The second one is harder. Your first step should be to complete the square. Then you are left with u du and 1 du. The first one of these can be done with a (u 2 +a 2 ) n (u 2 +a 2 ) n simple substition (let v = u 2 + a 2 ). The second one requires trig substitution at least of n > 1. In the case of Ax+B dx it will be useful the break the numerator into two parts x 2 +bx+c Ax + B = const.(x 2 + bx + c) + const. Why is this helpful? 4
5 Partial Fraction Decompostion: Know how to integrate a rational function (write it a sum of partial fractions, then integrate each partial fraction.) Remember that only proper rational fractions can be written as a sum of partial fractions. Know how to write a rational function P (x) r(x) r(x) Q(x) in the form p(x)+ Q(x) where Q(x) is proper. (This is just polynomial long division.) Know how to tell which partial fractions can appear in the decomposition of a given rational function. You can do this by factoring the denominator. A factor of (x a) n corresponds to A factor of (x 2 + bx + c) n corresponds to A 1 (x a) + A 2 (x a) A n (x a) n B 1 x + C 1 (x 2 + bx + c) + B 2x + C 2 (x 2 + bx + c) B nx + C n (x 2 + bx + c) n Remember, the numerator is always constant in the first case (and linear in the second case), regardless of the exponent n. If you have something like Bx+C, then (x a) 2 you have done something wrong. As a check: the number constants you introduce should always equal the degree of the denominator. If you have too many constants, you will not be able to solve for all of them. If you have too few, you will (probably) get a contradiction. If you set up things incorrectly, you will most likely get stuck. Be careful! One you have set things up, you will need to find the values of the constants. Your first step will (probably) be to clear up the denominatos by multiplying by the original denominator. There are two main methods for finding the constants: plugging in different values of x (think about whihc ones to use! What whill make your work easier?) or expanding and comparing the coefficients. Know how to use both of these. Also learn how to recognize which one will be less work. Also, be aware that you don t have to restrict yourselfto only using these Sometimes it must be useful to combine them. Maybe you can figure out a few of the coefficients by plugging in values of x, and then find the rest by expanding (before you expand, can you maybe factor out something like (x a) to make your life easier?). Don t be afriad to try other things, if they look like they might make things easier. You can use any method you want, as long as it works. Differential Equations: 5
6 Know what a differential equation is, and what it means to solve one. Know the difference between a geneal solution (i.e. any function that satisfies the equation) and a particular solution (i.e. one satisfying y(a) = b. Know how to find a particular solution if you know the general solution. Be sure to distinguish between the two types of diffential equations we studied. You won t be able to solve one type by using the method for the other type. Know how to solve a first order linear differential equation: y + p(x)y = q(x). (Multiply by an integrating factor e H(x), to turn the LHS into (e H(x) y). How do you figure out the appropriate H(x) to use? Really check that derivative of e H(x) y is exactly the LHS. If it is not, then you have done something incorectly. Note the plus sign in front of p(x). Know how to solve a separable differential equation (p(x) + q(y)y = 0). Sequences: Know how to tell when your equations is separable, often you will need to rewrite it. Remeber that you need to integrate both sides of an equation with respect to the same variable. Only because dy = y dx one of the integrals turn into integral for y. So pay attention to the integrating variable (differential.) Be careful with things like 1 xdx = ln x + C. Remember that g(x) = x is not differential at x = 0. Be aware that a separable differential equation has as solutions integral curves. They may or may not represent the graph of a function y = y(x). Thing about the curves y 2 + x 2 = C. Know what a sequence is both intuitively and the formal definition as a function. Know how to find the general term of a sequence by noticing the patern of the first few terms or using a recursive formula. Know how to prove your formula using a mathematical induction. Know what it means for a sequence to be increasing/decreasing or to be bounded above/below/both. Know how to show that a sequence is increasing by either checking the ratio a n+1 a n or calculating the derivative f (x) for a n = f(n). (In particular, know in which case which method to use). Know the order of increasing of the following expressions log n, n c, c n, n!. The Least Upper Bound Axiom: Know what it means for the number b to be an upper bound (or a least upper bound) for the set S. 6
7 Know (and understand) the statement of the least upper bound axiom. In particular, remember it applies to real numbers, not sets of rational numbers. Understand why an axiom is different from a theorem - its not something we can prove, its simply a basic property of the real numbers (like x+y = y +x or x(y +z) = xy +xz). It it wasn t true, then we we simply wouldn t be talking about the real numbers anymore. Understand what it is useful forl it gives us a way to show tat some real number exists without being able to explicitely find that number. We have been implicitly using it like this last quarter. If we didn t, we wouldn t even be able to talk about basic things like integrals. 7
Main topics for the Final Exam
 Main topics for the Final Exam The final will cover Sections 7.7-7.9, 8.1-8.5, 9.1-9.2, 11.1-11.7, 12.1-12.9. This is roughly the material from the fourteen homeworks and and six quizzes. In particular,
Main topics for the Final Exam The final will cover Sections 7.7-7.9, 8.1-8.5, 9.1-9.2, 11.1-11.7, 12.1-12.9. This is roughly the material from the fourteen homeworks and and six quizzes. In particular,
1.4 Techniques of Integration
 .4 Techniques of Integration Recall the following strategy for evaluating definite integrals, which arose from the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (see Section.3). To calculate b a f(x) dx. Find a function
.4 Techniques of Integration Recall the following strategy for evaluating definite integrals, which arose from the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus (see Section.3). To calculate b a f(x) dx. Find a function
Partial Fractions. June 27, In this section, we will learn to integrate another class of functions: the rational functions.
 Partial Fractions June 7, 04 In this section, we will learn to integrate another class of functions: the rational functions. Definition. A rational function is a fraction of two polynomials. For example,
Partial Fractions June 7, 04 In this section, we will learn to integrate another class of functions: the rational functions. Definition. A rational function is a fraction of two polynomials. For example,
DRAFT - Math 102 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 Math02 - Term72 - Guides and Exercises - DRAFT 7 Techniques of Integration A summery for the most important integrals that we have learned so far: 7. Integration by Parts The Product Rule states that if
Math02 - Term72 - Guides and Exercises - DRAFT 7 Techniques of Integration A summery for the most important integrals that we have learned so far: 7. Integration by Parts The Product Rule states that if
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration
 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
b n x n + b n 1 x n b 1 x + b 0
 Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
Math Partial Fractions Stewart 7.4 Integrating basic rational functions. For a function f(x), we have examined several algebraic methods for finding its indefinite integral (antiderivative) F (x) = f(x)
Main topics for the First Midterm Exam
 Main topics for the First Midterm Exam The final will cover Sections.-.0, 2.-2.5, and 4.. This is roughly the material from first three homeworks and three quizzes, in addition to the lecture on Monday,
Main topics for the First Midterm Exam The final will cover Sections.-.0, 2.-2.5, and 4.. This is roughly the material from first three homeworks and three quizzes, in addition to the lecture on Monday,
Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions
 Title Integration of Rational Functions by MATH 1700 MATH 1700 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 2 / 11 Rational functions A rational function is one of the form where P and Q are
Title Integration of Rational Functions by MATH 1700 MATH 1700 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 2 / 11 Rational functions A rational function is one of the form where P and Q are
CHAPTER 7: TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION
 CHAPTER 7: TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION DAVID GLICKENSTEIN. Introduction This semester we will be looking deep into the recesses of calculus. Some of the main topics will be: Integration: we will learn how
CHAPTER 7: TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION DAVID GLICKENSTEIN. Introduction This semester we will be looking deep into the recesses of calculus. Some of the main topics will be: Integration: we will learn how
Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions
 Title Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions MATH 1700 December 6, 2016 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions December 6, 2016 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions
Title Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions MATH 1700 December 6, 2016 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions December 6, 2016 1 / 11 Readings Readings Readings: Section 7.4 MATH 1700 Partial Fractions
Updated: January 16, 2016 Calculus II 7.4. Math 230. Calculus II. Brian Veitch Fall 2015 Northern Illinois University
 Math 30 Calculus II Brian Veitch Fall 015 Northern Illinois University Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions From algebra, we learned how to find common denominators so we can do something
Math 30 Calculus II Brian Veitch Fall 015 Northern Illinois University Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions From algebra, we learned how to find common denominators so we can do something
Calculus II Lecture Notes
 Calculus II Lecture Notes David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 206 edition Contents Contents 2 Review of Calculus I 5. Limits..................................... 7.2 Derivatives...................................3
Calculus II Lecture Notes David M. McClendon Department of Mathematics Ferris State University 206 edition Contents Contents 2 Review of Calculus I 5. Limits..................................... 7.2 Derivatives...................................3
MATH 250 TOPIC 13 INTEGRATION. 13B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules
 Math 5 Integration Topic 3 Page MATH 5 TOPIC 3 INTEGRATION 3A. Integration of Common Functions Practice Problems 3B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules Practice Problems 3C. Substitution Practice Problems
Math 5 Integration Topic 3 Page MATH 5 TOPIC 3 INTEGRATION 3A. Integration of Common Functions Practice Problems 3B. Constant, Sum, and Difference Rules Practice Problems 3C. Substitution Practice Problems
Review for Final Exam, MATH , Fall 2010
 Review for Final Exam, MATH 170-002, Fall 2010 The test will be on Wednesday December 15 in ILC 404 (usual class room), 8:00 a.m - 10:00 a.m. Please bring a non-graphing calculator for the test. No other
Review for Final Exam, MATH 170-002, Fall 2010 The test will be on Wednesday December 15 in ILC 404 (usual class room), 8:00 a.m - 10:00 a.m. Please bring a non-graphing calculator for the test. No other
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
Algebra & Trig Review
 Algebra & Trig Review 1 Algebra & Trig Review This review was originally written for my Calculus I class, but it should be accessible to anyone needing a review in some basic algebra and trig topics. The
Algebra & Trig Review 1 Algebra & Trig Review This review was originally written for my Calculus I class, but it should be accessible to anyone needing a review in some basic algebra and trig topics. The
Mathematics 136 Calculus 2 Everything You Need Or Want To Know About Partial Fractions (and maybe more!) October 19 and 21, 2016
 Mathematics 36 Calculus 2 Everything You Need Or Want To Know About Partial Fractions (and maybe more!) October 9 and 2, 206 Every rational function (quotient of polynomials) can be written as a polynomial
Mathematics 36 Calculus 2 Everything You Need Or Want To Know About Partial Fractions (and maybe more!) October 9 and 2, 206 Every rational function (quotient of polynomials) can be written as a polynomial
Review session Midterm 1
 AS.110.109: Calculus II (Eng) Review session Midterm 1 Yi Wang, Johns Hopkins University Fall 2018 7.1: Integration by parts Basic integration method: u-sub, integration table Integration By Parts formula
AS.110.109: Calculus II (Eng) Review session Midterm 1 Yi Wang, Johns Hopkins University Fall 2018 7.1: Integration by parts Basic integration method: u-sub, integration table Integration By Parts formula
How might we evaluate this? Suppose that, by some good luck, we knew that. x 2 5. x 2 dx 5
 8.4 1 8.4 Partial Fractions Consider the following integral. 13 2x (1) x 2 x 2 dx How might we evaluate this? Suppose that, by some good luck, we knew that 13 2x (2) x 2 x 2 = 3 x 2 5 x + 1 We could then
8.4 1 8.4 Partial Fractions Consider the following integral. 13 2x (1) x 2 x 2 dx How might we evaluate this? Suppose that, by some good luck, we knew that 13 2x (2) x 2 x 2 = 3 x 2 5 x + 1 We could then
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.5 The Substitution Rule (u-substitution) Sec. 5.5: The Substitution Rule We know how to find the derivative of any combination of functions Sum rule Difference rule Constant
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.5 The Substitution Rule (u-substitution) Sec. 5.5: The Substitution Rule We know how to find the derivative of any combination of functions Sum rule Difference rule Constant
Methods of Integration
 Methods of Integration Professor D. Olles January 8, 04 Substitution The derivative of a composition of functions can be found using the chain rule form d dx [f (g(x))] f (g(x)) g (x) Rewriting the derivative
Methods of Integration Professor D. Olles January 8, 04 Substitution The derivative of a composition of functions can be found using the chain rule form d dx [f (g(x))] f (g(x)) g (x) Rewriting the derivative
Solving Quadratic & Higher Degree Equations
 Chapter 7 Solving Quadratic & Higher Degree Equations Sec 1. Zero Product Property Back in the third grade students were taught when they multiplied a number by zero, the product would be zero. In algebra,
Chapter 7 Solving Quadratic & Higher Degree Equations Sec 1. Zero Product Property Back in the third grade students were taught when they multiplied a number by zero, the product would be zero. In algebra,
GEORGE ANDROULAKIS THE 7 INDETERMINATE FORMS OF LIMITS : usually we use L Hospital s rule. Two important such limits are lim
 MATH 4 (CALCULUS II) IN ORDER TO OBTAIN A PERFECT SCORE IN ANDROULAKIS MATH 4 CLASS YOU NEED TO MEMORIZE THIS HANDOUT AND SOLVE THE ASSIGNED HOMEWORK ON YOUR OWN GEORGE ANDROULAKIS TRIGONOMETRY θ sin(θ)
MATH 4 (CALCULUS II) IN ORDER TO OBTAIN A PERFECT SCORE IN ANDROULAKIS MATH 4 CLASS YOU NEED TO MEMORIZE THIS HANDOUT AND SOLVE THE ASSIGNED HOMEWORK ON YOUR OWN GEORGE ANDROULAKIS TRIGONOMETRY θ sin(θ)
M155 Exam 2 Concept Review
 M155 Exam 2 Concept Review Mark Blumstein DERIVATIVES Product Rule Used to take the derivative of a product of two functions u and v. u v + uv Quotient Rule Used to take a derivative of the quotient of
M155 Exam 2 Concept Review Mark Blumstein DERIVATIVES Product Rule Used to take the derivative of a product of two functions u and v. u v + uv Quotient Rule Used to take a derivative of the quotient of
8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition
 8.3 partial fraction decomposition 575 8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition Rational functions (polynomials divided by polynomials) and their integrals play important roles in mathematics and applications,
8.3 partial fraction decomposition 575 8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition Rational functions (polynomials divided by polynomials) and their integrals play important roles in mathematics and applications,
Solving Quadratic & Higher Degree Equations
 Chapter 9 Solving Quadratic & Higher Degree Equations Sec 1. Zero Product Property Back in the third grade students were taught when they multiplied a number by zero, the product would be zero. In algebra,
Chapter 9 Solving Quadratic & Higher Degree Equations Sec 1. Zero Product Property Back in the third grade students were taught when they multiplied a number by zero, the product would be zero. In algebra,
Partial Fractions. Calculus 2 Lia Vas
 Calculus Lia Vas Partial Fractions rational function is a quotient of two polynomial functions The method of partial fractions is a general method for evaluating integrals of rational function The idea
Calculus Lia Vas Partial Fractions rational function is a quotient of two polynomial functions The method of partial fractions is a general method for evaluating integrals of rational function The idea
Partial Fractions. (Do you see how to work it out? Substitute u = ax+b, so du = adx.) For example, 1 dx = ln x 7 +C, x 7
 Partial Fractions -4-209 Partial fractions is the opposite of adding fractions over a common denominator. It applies to integrals of the form P(x) dx, wherep(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Q(x) The idea
Partial Fractions -4-209 Partial fractions is the opposite of adding fractions over a common denominator. It applies to integrals of the form P(x) dx, wherep(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Q(x) The idea
Math 181, Exam 2, Study Guide 2 Problem 1 Solution. 1 + dx. 1 + (cos x)2 dx. 1 + cos2 xdx. = π ( 1 + cos π 2
 Math 8, Exam, Study Guide Problem Solution. Use the trapezoid rule with n to estimate the arc-length of the curve y sin x between x and x π. Solution: The arclength is: L b a π π + ( ) dy + (cos x) + cos
Math 8, Exam, Study Guide Problem Solution. Use the trapezoid rule with n to estimate the arc-length of the curve y sin x between x and x π. Solution: The arclength is: L b a π π + ( ) dy + (cos x) + cos
a x a y = a x+y a x a = y ax y (a x ) r = a rx and log a (xy) = log a (x) + log a (y) log a ( x y ) = log a(x) log a (y) log a (x r ) = r log a (x).
 You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
You should prepare the following topics for our final exam. () Pre-calculus. (2) Inverses. (3) Algebra of Limits. (4) Derivative Formulas and Rules. (5) Graphing Techniques. (6) Optimization (Maxima and
AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet
 Name Date Section AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the summer. It is meant to help you practice mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus
Name Date Section AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the summer. It is meant to help you practice mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus
Math Final Exam Review
 Math - Final Exam Review. Find dx x + 6x +. Name: Solution: We complete the square to see if this function has a nice form. Note we have: x + 6x + (x + + dx x + 6x + dx (x + + Note that this looks a lot
Math - Final Exam Review. Find dx x + 6x +. Name: Solution: We complete the square to see if this function has a nice form. Note we have: x + 6x + (x + + dx x + 6x + dx (x + + Note that this looks a lot
Partial Fractions. (Do you see how to work it out? Substitute u = ax + b, so du = a dx.) For example, 1 dx = ln x 7 + C, x x (x 3)(x + 1) = a
 Partial Fractions 7-9-005 Partial fractions is the opposite of adding fractions over a common denominator. It applies to integrals of the form P(x) dx, wherep(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Q(x) The idea
Partial Fractions 7-9-005 Partial fractions is the opposite of adding fractions over a common denominator. It applies to integrals of the form P(x) dx, wherep(x) and Q(x) are polynomials. Q(x) The idea
f(x) g(x) = [f (x)g(x) dx + f(x)g (x)dx
 Chapter 7 is concerned with all the integrals that can t be evaluated with simple antidifferentiation. Chart of Integrals on Page 463 7.1 Integration by Parts Like with the Chain Rule substitutions with
Chapter 7 is concerned with all the integrals that can t be evaluated with simple antidifferentiation. Chart of Integrals on Page 463 7.1 Integration by Parts Like with the Chain Rule substitutions with
3 Algebraic Methods. we can differentiate both sides implicitly to obtain a differential equation involving x and y:
 3 Algebraic Methods b The first appearance of the equation E Mc 2 in Einstein s handwritten notes. So far, the only general class of differential equations that we know how to solve are directly integrable
3 Algebraic Methods b The first appearance of the equation E Mc 2 in Einstein s handwritten notes. So far, the only general class of differential equations that we know how to solve are directly integrable
4.5 Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions
 4.5 Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions From algebra, we learned how to find common denominators so we can do something like this, 2 x + 1 + 3 x 3 = 2(x 3) (x + 1)(x 3) + 3(x + 1) (x
4.5 Integration of Rational Functions by Partial Fractions From algebra, we learned how to find common denominators so we can do something like this, 2 x + 1 + 3 x 3 = 2(x 3) (x + 1)(x 3) + 3(x + 1) (x
Review for the First Midterm Exam
 Review for the First Midterm Exam Thomas Morrell 5 pm, Sunday, 4 April 9 B9 Van Vleck Hall For the purpose of creating questions for this review session, I did not make an effort to make any of the numbers
Review for the First Midterm Exam Thomas Morrell 5 pm, Sunday, 4 April 9 B9 Van Vleck Hall For the purpose of creating questions for this review session, I did not make an effort to make any of the numbers
Solving Quadratic & Higher Degree Equations
 Chapter 9 Solving Quadratic & Higher Degree Equations Sec 1. Zero Product Property Back in the third grade students were taught when they multiplied a number by zero, the product would be zero. In algebra,
Chapter 9 Solving Quadratic & Higher Degree Equations Sec 1. Zero Product Property Back in the third grade students were taught when they multiplied a number by zero, the product would be zero. In algebra,
Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities Part I Review of Basic Equations Recall that an equation is an expression with an equal sign in the middle. Also recall that, if a question asks you to solve
Chapter 1 Review of Equations and Inequalities Part I Review of Basic Equations Recall that an equation is an expression with an equal sign in the middle. Also recall that, if a question asks you to solve
Final Exam Review Exercise Set A, Math 1551, Fall 2017
 Final Exam Review Exercise Set A, Math 1551, Fall 2017 This review set gives a list of topics that we explored throughout this course, as well as a few practice problems at the end of the document. A complete
Final Exam Review Exercise Set A, Math 1551, Fall 2017 This review set gives a list of topics that we explored throughout this course, as well as a few practice problems at the end of the document. A complete
Introduction. So, why did I even bother to write this?
 Introduction This review was originally written for my Calculus I class, but it should be accessible to anyone needing a review in some basic algebra and trig topics. The review contains the occasional
Introduction This review was originally written for my Calculus I class, but it should be accessible to anyone needing a review in some basic algebra and trig topics. The review contains the occasional
INTEGRATING RADICALS
 INTEGRATING RADICALS MATH 53, SECTION 55 (VIPUL NAIK) Corresponding material in the book: Section 8.4. What students should already know: The definitions of inverse trigonometric functions. The differentiation
INTEGRATING RADICALS MATH 53, SECTION 55 (VIPUL NAIK) Corresponding material in the book: Section 8.4. What students should already know: The definitions of inverse trigonometric functions. The differentiation
MATH 31B: BONUS PROBLEMS
 MATH 31B: BONUS PROBLEMS IAN COLEY LAST UPDATED: JUNE 8, 2017 7.1: 28, 38, 45. 1. Homework 1 7.2: 31, 33, 40. 7.3: 44, 52, 61, 71. Also, compute the derivative of x xx. 2. Homework 2 First, let me say
MATH 31B: BONUS PROBLEMS IAN COLEY LAST UPDATED: JUNE 8, 2017 7.1: 28, 38, 45. 1. Homework 1 7.2: 31, 33, 40. 7.3: 44, 52, 61, 71. Also, compute the derivative of x xx. 2. Homework 2 First, let me say
4.8 Partial Fraction Decomposition
 8 CHAPTER 4. INTEGRALS 4.8 Partial Fraction Decomposition 4.8. Need to Know The following material is assumed to be known for this section. If this is not the case, you will need to review it.. When are
8 CHAPTER 4. INTEGRALS 4.8 Partial Fraction Decomposition 4.8. Need to Know The following material is assumed to be known for this section. If this is not the case, you will need to review it.. When are
CALCULUS I. Review. Paul Dawkins
 CALCULUS I Review Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... ii Review... 1 Introduction... 1 Review : Functions... Review : Inverse Functions...1 Review : Trig Functions...0 Review : Solving Trig Equations...7
CALCULUS I Review Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... ii Review... 1 Introduction... 1 Review : Functions... Review : Inverse Functions...1 Review : Trig Functions...0 Review : Solving Trig Equations...7
Example. Evaluate. 3x 2 4 x dx.
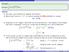 3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
Calculus II. Calculus II tends to be a very difficult course for many students. There are many reasons for this.
 Preface Here are my online notes for my Calculus II course that I teach here at Lamar University. Despite the fact that these are my class notes they should be accessible to anyone wanting to learn Calculus
Preface Here are my online notes for my Calculus II course that I teach here at Lamar University. Despite the fact that these are my class notes they should be accessible to anyone wanting to learn Calculus
CALCULUS I. Integrals. Paul Dawkins
 CALCULUS I Integrals Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... ii Integrals... Introduction... Indefinite Integrals... Computing Indefinite Integrals... Substitution Rule for Indefinite Integrals... More
CALCULUS I Integrals Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... ii Integrals... Introduction... Indefinite Integrals... Computing Indefinite Integrals... Substitution Rule for Indefinite Integrals... More
MA1131 Lecture 15 (2 & 3/12/2010) 77. dx dx v + udv dx. (uv) = v du dx dx + dx dx dx
 MA3 Lecture 5 ( & 3//00) 77 0.3. Integration by parts If we integrate both sides of the proct rule we get d (uv) dx = dx or uv = d (uv) = dx dx v + udv dx v dx dx + v dx dx + u dv dx dx u dv dx dx This
MA3 Lecture 5 ( & 3//00) 77 0.3. Integration by parts If we integrate both sides of the proct rule we get d (uv) dx = dx or uv = d (uv) = dx dx v + udv dx v dx dx + v dx dx + u dv dx dx u dv dx dx This
Math 230 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution
 Name: Math 30 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and
Name: Math 30 Mock Final Exam Detailed Solution Disclaimer: This mock exam is for practice purposes only. No graphing calulators TI-89 is allowed on this test. Be sure that all of your work is shown and
Assignment. Disguises with Trig Identities. Review Product Rule. Integration by Parts. Manipulating the Product Rule. Integration by Parts 12/13/2010
 Fitting Integrals to Basic Rules Basic Integration Rules Lesson 8.1 Consider these similar integrals Which one uses The log rule The arctangent rule The rewrite with long division principle Try It Out
Fitting Integrals to Basic Rules Basic Integration Rules Lesson 8.1 Consider these similar integrals Which one uses The log rule The arctangent rule The rewrite with long division principle Try It Out
Integrals. D. DeTurck. January 1, University of Pennsylvania. D. DeTurck Math A: Integrals 1 / 61
 Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Integrals D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 1, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Integrals 1 / 61 Integrals Start with dx this means a little bit of x or a little change in x If we add up
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections
 Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
Math 5a Reading Assignments for Sections 4.1 4.5 Due Dates for Reading Assignments Note: There will be a very short online reading quiz (WebWork) on each reading assignment due one hour before class on
5.5. The Substitution Rule
 INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
MATH 1130 Exam 1 Review Sheet
 MATH 1130 Exam 1 Review Sheet The Cartesian Coordinate Plane The Cartesian Coordinate Plane is a visual representation of the collection of all ordered pairs (x, y) where x and y are real numbers. This
MATH 1130 Exam 1 Review Sheet The Cartesian Coordinate Plane The Cartesian Coordinate Plane is a visual representation of the collection of all ordered pairs (x, y) where x and y are real numbers. This
Algebra Exam. Solutions and Grading Guide
 Algebra Exam Solutions and Grading Guide You should use this grading guide to carefully grade your own exam, trying to be as objective as possible about what score the TAs would give your responses. Full
Algebra Exam Solutions and Grading Guide You should use this grading guide to carefully grade your own exam, trying to be as objective as possible about what score the TAs would give your responses. Full
Albertson AP Calculus AB AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school.
 Albertson AP Calculus AB Name AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET 2015 DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the
Albertson AP Calculus AB Name AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER PACKET 2015 DUE DATE: The beginning of class on the last class day of the first week of school. This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the
(x + 3)(x 1) lim(x + 3) = 4. lim. (x 2)( x ) = (x 2)(x + 2) x + 2 x = 4. dt (t2 + 1) = 1 2 (t2 + 1) 1 t. f(x) = lim 3x = 6,
 Math 140 MT1 Sample C Solutions Tyrone Crisp 1 (B): First try direct substitution: you get 0. So try to cancel common factors. We have 0 x 2 + 2x 3 = x 1 and so the it as x 1 is equal to (x + 3)(x 1),
Math 140 MT1 Sample C Solutions Tyrone Crisp 1 (B): First try direct substitution: you get 0. So try to cancel common factors. We have 0 x 2 + 2x 3 = x 1 and so the it as x 1 is equal to (x + 3)(x 1),
Evaluating Limits Analytically. By Tuesday J. Johnson
 Evaluating Limits Analytically By Tuesday J. Johnson Suggested Review Topics Algebra skills reviews suggested: Evaluating functions Rationalizing numerators and/or denominators Trigonometric skills reviews
Evaluating Limits Analytically By Tuesday J. Johnson Suggested Review Topics Algebra skills reviews suggested: Evaluating functions Rationalizing numerators and/or denominators Trigonometric skills reviews
Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves. Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts
 Week #7: Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts 1 Week 7 The Indefinite Integral The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, b a f(x) dx =
Week #7: Substitutions and by Parts, Area Between Curves Goals: The Method of Substitution Areas Integration by Parts 1 Week 7 The Indefinite Integral The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, b a f(x) dx =
Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus. (Key contains solved problems)
 Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus (Key contains solved problems) Note: The purpose of this packet is to give you a review of basic skills. You are asked not to use the calculator, except on p. (8) and
Topics from Algebra and Pre-Calculus (Key contains solved problems) Note: The purpose of this packet is to give you a review of basic skills. You are asked not to use the calculator, except on p. (8) and
The definite integral gives the area under the curve. Simplest use of FTC1: derivative of integral is original function.
 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus EX. Given the graph of f, sketch the graph of x 0 f(t) dt. The definite integral gives the area under the curve. EX 2. Find the derivative of g(x) = x 0 + t 2 dt.
5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus EX. Given the graph of f, sketch the graph of x 0 f(t) dt. The definite integral gives the area under the curve. EX 2. Find the derivative of g(x) = x 0 + t 2 dt.
2.5 The Chain Rule Brian E. Veitch
 2.5 The Chain Rule This is our last ifferentiation rule for this course. It s also one of the most use. The best way to memorize this (along with the other rules) is just by practicing until you can o
2.5 The Chain Rule This is our last ifferentiation rule for this course. It s also one of the most use. The best way to memorize this (along with the other rules) is just by practicing until you can o
8.6 Partial Fraction Decomposition
 628 Systems of Equations and Matrices 8.6 Partial Fraction Decomposition This section uses systems of linear equations to rewrite rational functions in a form more palatable to Calculus students. In College
628 Systems of Equations and Matrices 8.6 Partial Fraction Decomposition This section uses systems of linear equations to rewrite rational functions in a form more palatable to Calculus students. In College
Integration by Substitution
 Integration by Substitution Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University Abstract This handout contains material on a very important integration method called integration by substitution. Substitution
Integration by Substitution Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University Abstract This handout contains material on a very important integration method called integration by substitution. Substitution
PARTIAL FRACTIONS AND POLYNOMIAL LONG DIVISION. The basic aim of this note is to describe how to break rational functions into pieces.
 PARTIAL FRACTIONS AND POLYNOMIAL LONG DIVISION NOAH WHITE The basic aim of this note is to describe how to break rational functions into pieces. For example 2x + 3 = + x 3 x +. The point is that we don
PARTIAL FRACTIONS AND POLYNOMIAL LONG DIVISION NOAH WHITE The basic aim of this note is to describe how to break rational functions into pieces. For example 2x + 3 = + x 3 x +. The point is that we don
IES Parque Lineal - 2º ESO
 UNIT5. ALGEBRA Contenido 1. Algebraic expressions.... 1 Worksheet: algebraic expressions.... 2 2. Monomials.... 3 Worksheet: monomials.... 5 3. Polynomials... 6 Worksheet: polynomials... 9 4. Factorising....
UNIT5. ALGEBRA Contenido 1. Algebraic expressions.... 1 Worksheet: algebraic expressions.... 2 2. Monomials.... 3 Worksheet: monomials.... 5 3. Polynomials... 6 Worksheet: polynomials... 9 4. Factorising....
MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B Calculus Section 1: - Integration.
 MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B 2007. For use in Dr Chris Tisdell s lectures: Tues 11 + Thur 10 in KBT Calculus Section 1: - Integration. 1. Motivation 2. What you should already know 3. Useful integrals 4. Integrals
MATH 1231 MATHEMATICS 1B 2007. For use in Dr Chris Tisdell s lectures: Tues 11 + Thur 10 in KBT Calculus Section 1: - Integration. 1. Motivation 2. What you should already know 3. Useful integrals 4. Integrals
Notes: Pythagorean Triples
 Math 5330 Spring 2018 Notes: Pythagorean Triples Many people know that 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2. Less commonly known are 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 and 7 2 + 24 2 = 25 2. Such a set of integers is called a Pythagorean Triple.
Math 5330 Spring 2018 Notes: Pythagorean Triples Many people know that 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2. Less commonly known are 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 and 7 2 + 24 2 = 25 2. Such a set of integers is called a Pythagorean Triple.
Generating Function Notes , Fall 2005, Prof. Peter Shor
 Counting Change Generating Function Notes 80, Fall 00, Prof Peter Shor In this lecture, I m going to talk about generating functions We ve already seen an example of generating functions Recall when we
Counting Change Generating Function Notes 80, Fall 00, Prof Peter Shor In this lecture, I m going to talk about generating functions We ve already seen an example of generating functions Recall when we
2t t dt.. So the distance is (t2 +6) 3/2
 Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
Math 8, Solutions to Review for the Final Exam Question : The distance is 5 t t + dt To work that out, integrate by parts with u t +, so that t dt du The integral is t t + dt u du u 3/ (t +) 3/ So the
Math ~ Exam #1 Review Guide* *This is only a guide, for your benefit, and it in no way replaces class notes, homework, or studying
 Math 1050 2 ~ Exam #1 Review Guide* *This is only a guide, for your benefit, and it in no way replaces class notes, homework, or studying General Tips for Studying: 1. Review this guide, class notes, the
Math 1050 2 ~ Exam #1 Review Guide* *This is only a guide, for your benefit, and it in no way replaces class notes, homework, or studying General Tips for Studying: 1. Review this guide, class notes, the
Hello Future Calculus Level One Student,
 Hello Future Calculus Level One Student, This assignment must be completed and handed in on the first day of class. This assignment will serve as the main review for a test on this material. The test will
Hello Future Calculus Level One Student, This assignment must be completed and handed in on the first day of class. This assignment will serve as the main review for a test on this material. The test will
8.4 Partial Fractions
 8.4 1 8.4 Partial Fractions Consider the following integral. (1) 13 2x x 2 x 2 dx How might we evaluate this? Suppose that, by some good luck, we knew that (2) 13 2x x 2 x 2 = 3 x 2 5 x+1 We could then
8.4 1 8.4 Partial Fractions Consider the following integral. (1) 13 2x x 2 x 2 dx How might we evaluate this? Suppose that, by some good luck, we knew that (2) 13 2x x 2 x 2 = 3 x 2 5 x+1 We could then
ABSTRACT VECTOR SPACES AND THE CONCEPT OF ISOMORPHISM. Executive summary
 ABSTRACT VECTOR SPACES AND THE CONCEPT OF ISOMORPHISM MATH 196, SECTION 57 (VIPUL NAIK) Corresponding material in the book: Sections 4.1 and 4.2. General stuff... Executive summary (1) There is an abstract
ABSTRACT VECTOR SPACES AND THE CONCEPT OF ISOMORPHISM MATH 196, SECTION 57 (VIPUL NAIK) Corresponding material in the book: Sections 4.1 and 4.2. General stuff... Executive summary (1) There is an abstract
Calculus Essentials Ebook
 Calculus Essentials Ebook Here you go. You ll never have to search endlessly through pages in your textbook just to find the key concepts ever again. Because staring at the same 3 pages and flipping back
Calculus Essentials Ebook Here you go. You ll never have to search endlessly through pages in your textbook just to find the key concepts ever again. Because staring at the same 3 pages and flipping back
Hi AP AB Calculus Class of :
 Hi AP AB Calculus Class of 2017 2018: In order to complete the syllabus that the College Board requires and to have sufficient time to review and practice for the exam, I am asking you to do a (mandatory)
Hi AP AB Calculus Class of 2017 2018: In order to complete the syllabus that the College Board requires and to have sufficient time to review and practice for the exam, I am asking you to do a (mandatory)
M152: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review
 M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
M52: Calculus II Midterm Exam Review Chapter 4. 4.2 : Mean Value Theorem. - Know the statement and idea of Mean Value Theorem. - Know how to find values of c making the theorem true. - Realize the importance
Chapter 6: The Definite Integral
 Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 6: The Definite Integral v v Sections: v 6.1 Estimating with Finite Sums v 6.5 Trapezoidal Rule v 6.2 Definite Integrals 6.3 Definite Integrals and Antiderivatives
Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 6: The Definite Integral v v Sections: v 6.1 Estimating with Finite Sums v 6.5 Trapezoidal Rule v 6.2 Definite Integrals 6.3 Definite Integrals and Antiderivatives
f(x 0 + h) f(x 0 ) h slope of secant line = m sec
 Derivatives Using limits, we can define the slope of a tangent line to a function. When given a function f(x), and given a point P (x 0, f(x 0 )) on f, if we want to find the slope of the tangent line
Derivatives Using limits, we can define the slope of a tangent line to a function. When given a function f(x), and given a point P (x 0, f(x 0 )) on f, if we want to find the slope of the tangent line
7.5 Partial Fractions and Integration
 650 CHPTER 7. DVNCED INTEGRTION TECHNIQUES 7.5 Partial Fractions and Integration In this section we are interested in techniques for computing integrals of the form P(x) dx, (7.49) Q(x) where P(x) and
650 CHPTER 7. DVNCED INTEGRTION TECHNIQUES 7.5 Partial Fractions and Integration In this section we are interested in techniques for computing integrals of the form P(x) dx, (7.49) Q(x) where P(x) and
Final Review Sheet. B = (1, 1 + 3x, 1 + x 2 ) then 2 + 3x + 6x 2
 Final Review Sheet The final will cover Sections Chapters 1,2,3 and 4, as well as sections 5.1-5.4, 6.1-6.2 and 7.1-7.3 from chapters 5,6 and 7. This is essentially all material covered this term. Watch
Final Review Sheet The final will cover Sections Chapters 1,2,3 and 4, as well as sections 5.1-5.4, 6.1-6.2 and 7.1-7.3 from chapters 5,6 and 7. This is essentially all material covered this term. Watch
MATH 124. Midterm 2 Topics
 MATH 124 Midterm 2 Topics Anything you ve learned in class (from lecture and homework) so far is fair game, but here s a list of some main topics since the first midterm that you should be familiar with:
MATH 124 Midterm 2 Topics Anything you ve learned in class (from lecture and homework) so far is fair game, but here s a list of some main topics since the first midterm that you should be familiar with:
MATHEMATICS Lecture. 4 Chapter.8 TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION By Dr. Mohammed Ramidh
 MATHEMATICS Lecture. 4 Chapter.8 TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION By TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION OVERVIEW The Fundamental Theorem connects antiderivatives and the definite integral. Evaluating the indefinite integral,
MATHEMATICS Lecture. 4 Chapter.8 TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION By TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION OVERVIEW The Fundamental Theorem connects antiderivatives and the definite integral. Evaluating the indefinite integral,
Summer Packet A Math Refresher For Students Entering IB Mathematics SL
 Summer Packet A Math Refresher For Students Entering IB Mathematics SL Name: PRECALCULUS SUMMER PACKET Directions: This packet is required if you are registered for Precalculus for the upcoming school
Summer Packet A Math Refresher For Students Entering IB Mathematics SL Name: PRECALCULUS SUMMER PACKET Directions: This packet is required if you are registered for Precalculus for the upcoming school
Finding Limits Analytically
 Finding Limits Analytically Most of this material is take from APEX Calculus under terms of a Creative Commons License In this handout, we explore analytic techniques to compute its. Suppose that f(x)
Finding Limits Analytically Most of this material is take from APEX Calculus under terms of a Creative Commons License In this handout, we explore analytic techniques to compute its. Suppose that f(x)
DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus
 DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This packet contains background skills you need to know for your AP Calculus. My suggestion is, you read the information and
DuVal High School Summer Review Packet AP Calculus Welcome to AP Calculus AB. This packet contains background skills you need to know for your AP Calculus. My suggestion is, you read the information and
MATH 1231 S2 2010: Calculus. Section 2: Techniques of integration.
 MATH 1231 S2 2010: Calculus For use in Dr Chris Tisdell s lectures Section 2: Techniques of integration. Created and compiled by Chris Tisdell S1: Motivation S2: What you should already know S3: Integrals
MATH 1231 S2 2010: Calculus For use in Dr Chris Tisdell s lectures Section 2: Techniques of integration. Created and compiled by Chris Tisdell S1: Motivation S2: What you should already know S3: Integrals
1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
 Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
x n cos 2x dx. dx = nx n 1 and v = 1 2 sin(2x). Andreas Fring (City University London) AS1051 Lecture Autumn / 36
 We saw in Example 5.4. that we sometimes need to apply integration by parts several times in the course of a single calculation. Example 5.4.4: For n let S n = x n cos x dx. Find an expression for S n
We saw in Example 5.4. that we sometimes need to apply integration by parts several times in the course of a single calculation. Example 5.4.4: For n let S n = x n cos x dx. Find an expression for S n
Calculus II (Fall 2015) Practice Problems for Exam 1
 Calculus II (Fall 15) Practice Problems for Exam 1 Note: Section divisions and instructions below are the same as they will be on the exam, so you will have a better idea of what to expect, though I will
Calculus II (Fall 15) Practice Problems for Exam 1 Note: Section divisions and instructions below are the same as they will be on the exam, so you will have a better idea of what to expect, though I will
1 Lesson 13: Methods of Integration
 Lesson 3: Methods of Integration Chapter 6 Material: pages 273-294 in the textbook: Lesson 3 reviews integration by parts and presents integration via partial fraction decomposition as the third of the
Lesson 3: Methods of Integration Chapter 6 Material: pages 273-294 in the textbook: Lesson 3 reviews integration by parts and presents integration via partial fraction decomposition as the third of the
Chapter 06: Analytic Trigonometry
 Chapter 06: Analytic Trigonometry 6.1: Inverse Trigonometric Functions The Problem As you recall from our earlier work, a function can only have an inverse function if it is oneto-one. Are any of our trigonometric
Chapter 06: Analytic Trigonometry 6.1: Inverse Trigonometric Functions The Problem As you recall from our earlier work, a function can only have an inverse function if it is oneto-one. Are any of our trigonometric
Algebra. Here are a couple of warnings to my students who may be here to get a copy of what happened on a day that you missed.
 This document was written and copyrighted by Paul Dawkins. Use of this document and its online version is governed by the Terms and Conditions of Use located at. The online version of this document is
This document was written and copyrighted by Paul Dawkins. Use of this document and its online version is governed by the Terms and Conditions of Use located at. The online version of this document is
Week 2 Techniques of Integration
 Week Techniques of Integration Richard Earl Mathematical Institute, Oxford, OX LB, October Abstract Integration by Parts. Substitution. Rational Functions. Partial Fractions. Trigonometric Substitutions.
Week Techniques of Integration Richard Earl Mathematical Institute, Oxford, OX LB, October Abstract Integration by Parts. Substitution. Rational Functions. Partial Fractions. Trigonometric Substitutions.
Math101, Sections 2 and 3, Spring 2008 Review Sheet for Exam #2:
 Math101, Sections 2 and 3, Spring 2008 Review Sheet for Exam #2: 03 17 08 3 All about lines 3.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System Know how to plot points in the rectangular coordinate system. Know the
Math101, Sections 2 and 3, Spring 2008 Review Sheet for Exam #2: 03 17 08 3 All about lines 3.1 The Rectangular Coordinate System Know how to plot points in the rectangular coordinate system. Know the
Course Notes for Calculus , Spring 2015
 Course Notes for Calculus 110.109, Spring 2015 Nishanth Gudapati In the previous course (Calculus 110.108) we introduced the notion of integration and a few basic techniques of integration like substitution
Course Notes for Calculus 110.109, Spring 2015 Nishanth Gudapati In the previous course (Calculus 110.108) we introduced the notion of integration and a few basic techniques of integration like substitution
Lesson 5b Solving Quadratic Equations
 Lesson 5b Solving Quadratic Equations In this lesson, we will continue our work with Quadratics in this lesson and will learn several methods for solving quadratic equations. The first section will introduce
Lesson 5b Solving Quadratic Equations In this lesson, we will continue our work with Quadratics in this lesson and will learn several methods for solving quadratic equations. The first section will introduce
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review
 Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
Mathematics 1 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Algebra Review c Trinity College 1 A note to the students from the lecturer: This course will be moving rather quickly, and it will be in your own best interests to
Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part)
 Fry Texas A&M University! Spring 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 8B-I! Page 79 Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part) Recall from geometry that if 2 corresponding triangles have 2 angles of
Fry Texas A&M University! Spring 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 8B-I! Page 79 Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part) Recall from geometry that if 2 corresponding triangles have 2 angles of
