Handout 1. Research shows that students learn when they MAKE MISTAKES and not when they get it right. SO MAKE MISTAKES, because MISTAKES ARE GOOD!
|
|
|
- Mildred Rogers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Handout Research shows that students learn when they MAKE MISTAKES and not when they get it right. SO MAKE MISTAKES, because MISTAKES ARE GOOD! Review:. The Substitution Rule Indefinite f (g()) g ()d = f(u)du Definite b a f (g()) g ()d = g(b) g(a) f(u)du Parameters: f must be continuous on the range of u = g() and either g () is continous on the interval [a,b] (Definite Case) or g() is differentiable (Indefinite Case).. Useful Integrals sec ()d = tan() + C sec()tan()d = sec() + C cosh()d = sinh() + C sinh()d = cosh() + C ( a d = ) sin + C a + a d = ( ) a tan + C a cot()d = ln sin() + C tan()d = ln sec() + C a d = a ln(a) + C d = ln + C 3. Even and Odd Functions A function f is even if f( ) = f() for every in the domain of f. Eamples:, 4, cos() over R. A function f is odd if f( ) = f() for every in the domain of f. Eamples:, 3, sin() over R. 4. Eamples: Notes: The purpose of the Substitution Rule is to convert an unfamiliar integral into one that is familiar. The trick to using the rule successfully is to look for a function, possibly composed within another function, with its derivative laying around. For instance, in the integral ( in the book) sin(ln()) d, we see the natural log sitting inside the sine function, and its derivative laying below it. So we might try using Substitution as follows: Let u = ln() then du = d and we have sin(ln()) d = = [ ] sin ([ ln()]) d sin([u])[du] = cos([u]) + C = cos([ln()]) + C
2 Eample II: Number 36 in book. Hint: Which of the above integrals does it look like? + 4 d Eample III: Number 48 in the book d
3 5. Integration by Parts Reversing the product rule Let f and g be differentiable functions, then the product rule states d d [f()g()] = Integrating both sides and splitting the integral implies: f()g() = If we let u = f(), and v = g() then du = f ()d, and dv = g ()d. With a little rearranging we get udv = uv vdu 6. Eamples: Notes: The trick to using Int. by Parts efficiently is a wise choice of u and dv. That wise choice comes down to intuitively choosing your u as the function that will simplify and eventually go away after repeated differentiation (like k for some natural number k), and a dv that wont get too messy when you integrate it (you have to know how to integrate it of course). Sometimes we use integration by parts on single functions that we don t know the integral of, but we know their derivatives as the following eample shows. Let u = sin () and dv = d, then du = and v =. Thus, 0 sin ()d = [ sin () ] 0 d Using U-sub with u = and du = we get, [ π 0 ] () (0) π ( ) d = π 0 du u [ ] u = π 0 [ 0] = π 0 Eample V: Number 5 in the book. Hint: Try using U-Sub first. e ( + ) d 3
4 Eample VI: Hint: You might have to use Int. by Parts more than once and look for patterns. e sinh()d 4
5 Name: In Class Eercises: Write only your solutions on this paper. No Scratch Work! Work in groups of no more than 3.. Independently (Everyone in the group has their own problems) reverse engineer (create) two distinct integrals (not constant multiples of each other) that can be solved using a substitution involving tan( ). Then show their solutions. 5
6 . As a group (everyone creates the same problem) reverse engineer an integral that can be solved using two different substitutions and show its solution. 6
7 3. Independently solve the following integrals. Hint: After using Integration by Parts use the Fundamental Trig Id. sin () + cos () =. a.) cos ()d Hint: Use the Fundamental Trig Id., then U-Sub (Int. by parts is not strictly necessary). b.) cos 3 ()d 7
8 4.) As a group develop a rule for calculating the integral cos n ()d when n N and bigger than. Hint: Try it for n = 4 and n = 5, then look for patterns from 3a and 3b. You might even choose to break it up into two rules, one for when n is even and the other when n is odd, though this is not necessary. 8
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals 8. Basic Integration Rules In this section we will review various integration strategies. Strategies: I. Separate
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals 8. Basic Integration Rules In this section we will review various integration strategies. Strategies: I. Separate
Methods of Integration
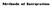 Methods of Integration Essential Formulas k d = k +C sind = cos +C n d = n+ n + +C cosd = sin +C e d = e +C tand = ln sec +C d = ln +C cotd = ln sin +C + d = tan +C lnd = ln +C secd = ln sec + tan +C cscd
Methods of Integration Essential Formulas k d = k +C sind = cos +C n d = n+ n + +C cosd = sin +C e d = e +C tand = ln sec +C d = ln +C cotd = ln sin +C + d = tan +C lnd = ln +C secd = ln sec + tan +C cscd
11.4. Differentiating ProductsandQuotients. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Differentiating ProductsandQuotients 11.4 Introduction We have seen, in the first three Sections, how standard functions like n, e a, sin a, cos a, ln a may be differentiated. In this Section we see how
Differentiating ProductsandQuotients 11.4 Introduction We have seen, in the first three Sections, how standard functions like n, e a, sin a, cos a, ln a may be differentiated. In this Section we see how
The Free Intuitive Calculus Course Integrals
 Intuitive-Calculus.com Presents The Free Intuitive Calculus Course Integrals Day 19: Trigonometric Integrals By Pablo Antuna 013 All Rights Reserved. The Intuitive Calculus Course - By Pablo Antuna Contents
Intuitive-Calculus.com Presents The Free Intuitive Calculus Course Integrals Day 19: Trigonometric Integrals By Pablo Antuna 013 All Rights Reserved. The Intuitive Calculus Course - By Pablo Antuna Contents
TImath.com Calculus. Topic: Techniques of Integration Derive the formula for integration by parts and use it to compute integrals
 Integration by Parts ID: 985 Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In previous activities, students have eplored the differential calculus through investigations of the methods of first principles,
Integration by Parts ID: 985 Time required 45 minutes Activity Overview In previous activities, students have eplored the differential calculus through investigations of the methods of first principles,
Math 112 Section 10 Lecture notes, 1/7/04
 Math 11 Section 10 Lecture notes, 1/7/04 Section 7. Integration by parts To integrate the product of two functions, integration by parts is used when simpler methods such as substitution or simplifying
Math 11 Section 10 Lecture notes, 1/7/04 Section 7. Integration by parts To integrate the product of two functions, integration by parts is used when simpler methods such as substitution or simplifying
Math 222, Exam I, September 17, 2002 Answers
 Math, Exam I, September 7, 00 Answers I. (5 points.) (a) Evaluate (6x 5 x 4 7x + 3/x 5 + 4e x + 7 x ). Answer: (6x 5 x 4 7x + 3/x 5 + 4e x + 7 x ) = = x 6 + x 3 3 7x + 3 ln x 5x + 4ex + 7x ln 7 + C. Answer:
Math, Exam I, September 7, 00 Answers I. (5 points.) (a) Evaluate (6x 5 x 4 7x + 3/x 5 + 4e x + 7 x ). Answer: (6x 5 x 4 7x + 3/x 5 + 4e x + 7 x ) = = x 6 + x 3 3 7x + 3 ln x 5x + 4ex + 7x ln 7 + C. Answer:
Spring 2018 Exam 1 MARK BOX HAND IN PART PIN: 17
 problem MARK BOX points HAND IN PART -3 653x5 5 NAME: Solutions 5 6 PIN: 7 % INSTRUCTIONS This exam comes in two parts. () HAND IN PART. Hand in only this part. () STATEMENT OF MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS.
problem MARK BOX points HAND IN PART -3 653x5 5 NAME: Solutions 5 6 PIN: 7 % INSTRUCTIONS This exam comes in two parts. () HAND IN PART. Hand in only this part. () STATEMENT OF MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS.
Campus Academic Resource Program Chain Rule
 This handout will: Provide a strategy to identify composite functions Provide a strategy to find chain rule by using a substitution method. Identifying Composite Functions This section will provide a strategy
This handout will: Provide a strategy to identify composite functions Provide a strategy to find chain rule by using a substitution method. Identifying Composite Functions This section will provide a strategy
Math F15 Rahman
 Math - 9 F5 Rahman Week3 7.3 Hyperbolic Functions Hyperbolic functions are similar to trigonometric functions, and have the following definitions: sinh x = (ex e x ) cosh x = (ex + e x ) tanh x = sinh
Math - 9 F5 Rahman Week3 7.3 Hyperbolic Functions Hyperbolic functions are similar to trigonometric functions, and have the following definitions: sinh x = (ex e x ) cosh x = (ex + e x ) tanh x = sinh
Trigonometric integrals by basic methods
 Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter : Integration methods Section 7 Trigonometric integrals by basic methods What you need to know already: Integrals of basic trigonometric functions. Basic trigonometric
Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter : Integration methods Section 7 Trigonometric integrals by basic methods What you need to know already: Integrals of basic trigonometric functions. Basic trigonometric
MA 242 Review Exponential and Log Functions Notes for today s class can be found at
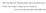 MA 242 Review Exponential and Log Functions Notes for today s class can be found at www.xecu.net/jacobs/index242.htm Example: If y = x n If y = x 2 then then dy dx = nxn 1 dy dx = 2x1 = 2x Power Function
MA 242 Review Exponential and Log Functions Notes for today s class can be found at www.xecu.net/jacobs/index242.htm Example: If y = x n If y = x 2 then then dy dx = nxn 1 dy dx = 2x1 = 2x Power Function
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.3 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Sec. 5.3: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Fundamental
EXACT EQUATIONS AND INTEGRATING FACTORS
 MAP- EXACT EQUATIONS AND INTEGRATING FACTORS First-order Differential Equations for Which We Can Find Eact Solutions Stu the patterns carefully. The first step of any solution is correct identification
MAP- EXACT EQUATIONS AND INTEGRATING FACTORS First-order Differential Equations for Which We Can Find Eact Solutions Stu the patterns carefully. The first step of any solution is correct identification
Example. Evaluate. 3x 2 4 x dx.
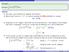 3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
3x 2 4 x 3 + 4 dx. Solution: We need a new technique to integrate this function. Notice that if we let u x 3 + 4, and we compute the differential du of u, we get: du 3x 2 dx Going back to our integral,
Math3B Exam #02 Solution Fall 2017
 . Integrate. a) 8 MathB Eam # Solution Fall 7 e d b) ln e e d . Integrate. 6 d . Integrate. sin cos d 4. Use Simpsons Rule with n 6 to approimate sin d. Then use integration to get the eact value. 6 6
. Integrate. a) 8 MathB Eam # Solution Fall 7 e d b) ln e e d . Integrate. 6 d . Integrate. sin cos d 4. Use Simpsons Rule with n 6 to approimate sin d. Then use integration to get the eact value. 6 6
6.1 Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus
 6. Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus 6. ANTIDERIVATIVES AND SLOPE FIELDS Indefinite Integrals In the previous chapter we dealt with definite integrals. Definite integrals had limits of integration.
6. Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Calculus 6. ANTIDERIVATIVES AND SLOPE FIELDS Indefinite Integrals In the previous chapter we dealt with definite integrals. Definite integrals had limits of integration.
Calculus II Practice Test Problems for Chapter 7 Page 1 of 6
 Calculus II Practice Test Problems for Chapter 7 Page of 6 This is a set of practice test problems for Chapter 7. This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on
Calculus II Practice Test Problems for Chapter 7 Page of 6 This is a set of practice test problems for Chapter 7. This is in no way an inclusive set of problems there can be other types of problems on
MA1131 Lecture 15 (2 & 3/12/2010) 77. dx dx v + udv dx. (uv) = v du dx dx + dx dx dx
 MA3 Lecture 5 ( & 3//00) 77 0.3. Integration by parts If we integrate both sides of the proct rule we get d (uv) dx = dx or uv = d (uv) = dx dx v + udv dx v dx dx + v dx dx + u dv dx dx u dv dx dx This
MA3 Lecture 5 ( & 3//00) 77 0.3. Integration by parts If we integrate both sides of the proct rule we get d (uv) dx = dx or uv = d (uv) = dx dx v + udv dx v dx dx + v dx dx + u dv dx dx u dv dx dx This
HAND IN PART. Prof. Girardi Math 142 Spring Exam 1. NAME: key
 HAND IN PART Prof. Girardi Math 4 Spring 4..4 Exam MARK BOX problem points 7 % NAME: key PIN: INSTRUCTIONS The mark box above indicates the problems along with their points. Check that your copy of the
HAND IN PART Prof. Girardi Math 4 Spring 4..4 Exam MARK BOX problem points 7 % NAME: key PIN: INSTRUCTIONS The mark box above indicates the problems along with their points. Check that your copy of the
How to Find Limits. Yilong Yang. October 22, The General Guideline 1
 How to Find Limits Yilong Yang October 22, 204 Contents The General Guideline 2 Put Fractions Together and Factorization 2 2. Why put fractions together..................................... 2 2.2 Formula
How to Find Limits Yilong Yang October 22, 204 Contents The General Guideline 2 Put Fractions Together and Factorization 2 2. Why put fractions together..................................... 2 2.2 Formula
FUNCTIONS OF ONE VARIABLE FUNCTION DEFINITIONS
 Page of 6 FUNCTIONS OF ONE VARIABLE FUNCTION DEFINITIONS 6. HYPERBOLIC FUNCTIONS These functions which are defined in terms of e will be seen later to be related to the trigonometic functions via comple
Page of 6 FUNCTIONS OF ONE VARIABLE FUNCTION DEFINITIONS 6. HYPERBOLIC FUNCTIONS These functions which are defined in terms of e will be seen later to be related to the trigonometic functions via comple
Integration. Section 8: Using partial fractions in integration
 Integration Section 8: Using partial fractions in integration Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on Using partial fractions in integration Putting all the integration techniques together
Integration Section 8: Using partial fractions in integration Notes and Eamples These notes contain subsections on Using partial fractions in integration Putting all the integration techniques together
In this note we will evaluate the limits of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0. f(x)
 L Hôpital s Rule In this note we will evaluate the its of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0 f() Suppose a f() = 0 and a g() = 0. Then a g() the indeterminate
L Hôpital s Rule In this note we will evaluate the its of some indeterminate forms using L Hôpital s Rule. Indeterminate Forms and 0 0 f() Suppose a f() = 0 and a g() = 0. Then a g() the indeterminate
Prelim 2 Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 90 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck!
 April 4, Prelim Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Trigonometric Formulas sin x sin x cos x cos (u + v) cos
April 4, Prelim Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Trigonometric Formulas sin x sin x cos x cos (u + v) cos
1 Introduction; Integration by Parts
 1 Introduction; Integration by Parts September 11-1 Traditionally Calculus I covers Differential Calculus and Calculus II covers Integral Calculus. You have already seen the Riemann integral and certain
1 Introduction; Integration by Parts September 11-1 Traditionally Calculus I covers Differential Calculus and Calculus II covers Integral Calculus. You have already seen the Riemann integral and certain
INTEGRATION 1. SIX STANDARD INTEGRALS
 . sin c a a INTEGRATION. SIX STANDARD INTEGRALS. a tan a c a. log e a a c. log e a a c 5. a a log e c a a 6. a a log e c a a Note: Integrals - appear on the Standard Sheet of Integrals. Integrals 5 and
. sin c a a INTEGRATION. SIX STANDARD INTEGRALS. a tan a c a. log e a a c. log e a a c 5. a a log e c a a 6. a a log e c a a Note: Integrals - appear on the Standard Sheet of Integrals. Integrals 5 and
Chapter 5: Integrals
 Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.5 The Substitution Rule (u-substitution) Sec. 5.5: The Substitution Rule We know how to find the derivative of any combination of functions Sum rule Difference rule Constant
Chapter 5: Integrals Section 5.5 The Substitution Rule (u-substitution) Sec. 5.5: The Substitution Rule We know how to find the derivative of any combination of functions Sum rule Difference rule Constant
VII. Techniques of Integration
 VII. Techniques of Integration Integration, unlike differentiation, is more of an art-form than a collection of algorithms. Many problems in applied mathematics involve the integration of functions given
VII. Techniques of Integration Integration, unlike differentiation, is more of an art-form than a collection of algorithms. Many problems in applied mathematics involve the integration of functions given
MATH 1010E University Mathematics Lecture Notes (week 8) Martin Li
 MATH 1010E University Mathematics Lecture Notes (week 8) Martin Li 1 L Hospital s Rule Another useful application of mean value theorems is L Hospital s Rule. It helps us to evaluate its of indeterminate
MATH 1010E University Mathematics Lecture Notes (week 8) Martin Li 1 L Hospital s Rule Another useful application of mean value theorems is L Hospital s Rule. It helps us to evaluate its of indeterminate
4.317 d 4 y. 4 dx d 2 y dy. 20. dt d 2 x. 21. y 3y 3y y y 6y 12y 8y y (4) y y y (4) 2y y 0. d 4 y 26.
 38 CHAPTER 4 HIGHER-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS sstems are also able, b means of their dsolve commands, to provide eplicit solutions of homogeneous linear constant-coefficient differential equations.
38 CHAPTER 4 HIGHER-ORDER DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS sstems are also able, b means of their dsolve commands, to provide eplicit solutions of homogeneous linear constant-coefficient differential equations.
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER DIFFERENTIATION 4 (Products and quotients) & (Logarithmic differentiation) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 104 DIFFERENTIATION 4 (Products and quotients) & (Logarithmic differentiation) by AJHobson 1041 Products 1042 Quotients 1043 Logarithmic differentiation 1044 Exercises 1045 Answers
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 104 DIFFERENTIATION 4 (Products and quotients) & (Logarithmic differentiation) by AJHobson 1041 Products 1042 Quotients 1043 Logarithmic differentiation 1044 Exercises 1045 Answers
Chapter 6 Differential Equations and Mathematical Modeling. 6.1 Antiderivatives and Slope Fields
 Chapter 6 Differential Equations and Mathematical Modeling 6. Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Def: An equation of the form: = y ln x which contains a derivative is called a Differential Equation. In this
Chapter 6 Differential Equations and Mathematical Modeling 6. Antiderivatives and Slope Fields Def: An equation of the form: = y ln x which contains a derivative is called a Differential Equation. In this
Techniques of Integration: I
 October 1, 217 We had the tenth breakfast yesterday morning: If you d like to propose a future event (breakfast, lunch, dinner), please let me know. Techniques of Integration To evaluate number), we might
October 1, 217 We had the tenth breakfast yesterday morning: If you d like to propose a future event (breakfast, lunch, dinner), please let me know. Techniques of Integration To evaluate number), we might
dx. Ans: y = tan x + x2 + 5x + C
 Chapter 7 Differential Equations and Mathematical Modeling If you know one value of a function, and the rate of change (derivative) of the function, then yu can figure out many things about the function.
Chapter 7 Differential Equations and Mathematical Modeling If you know one value of a function, and the rate of change (derivative) of the function, then yu can figure out many things about the function.
C6-2 Differentiation 3
 chain, product and quotient rules C6- Differentiation Pre-requisites: C6- Estimate Time: 8 hours Summary Learn Solve Revise Answers Summary The chain rule is used to differentiate a function of a function.
chain, product and quotient rules C6- Differentiation Pre-requisites: C6- Estimate Time: 8 hours Summary Learn Solve Revise Answers Summary The chain rule is used to differentiate a function of a function.
MTH 133 Solutions to Exam 2 April 19, Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 12.
 MTH 33 Solutions to Exam 2 April 9, 207 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through
MTH 33 Solutions to Exam 2 April 9, 207 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through
y sin n x dx cos x sin n 1 x n 1 y sin n 2 x cos 2 x dx y sin n xdx cos x sin n 1 x n 1 y sin n 2 x dx n 1 y sin n x dx
 SECTION 7. INTEGRATION BY PARTS 57 EXAPLE 6 Prove the reduction formula N Equation 7 is called a reduction formula because the eponent n has been reduced to n and n. 7 sin n n cos sinn n n sin n where
SECTION 7. INTEGRATION BY PARTS 57 EXAPLE 6 Prove the reduction formula N Equation 7 is called a reduction formula because the eponent n has been reduced to n and n. 7 sin n n cos sinn n n sin n where
Assignment 13 Assigned Mon Oct 4
 Assignment 3 Assigned Mon Oct 4 We refer to the integral table in the back of the book. Section 7.5, Problem 3. I don t see this one in the table in the back of the book! But it s a very easy substitution
Assignment 3 Assigned Mon Oct 4 We refer to the integral table in the back of the book. Section 7.5, Problem 3. I don t see this one in the table in the back of the book! But it s a very easy substitution
Integration by Parts
 Calculus 2 Lia Vas Integration by Parts Using integration by parts one transforms an integral of a product of two functions into a simpler integral. Divide the initial function into two parts called u
Calculus 2 Lia Vas Integration by Parts Using integration by parts one transforms an integral of a product of two functions into a simpler integral. Divide the initial function into two parts called u
Calculus Integration
 Calculus Integration By Norhafizah Md Sarif & Norazaliza Mohd Jamil Faculty of Instrial Science & Technology norhafizah@ump.e.my, norazaliza@ump.e.my Description Aims This chapter is aimed to : 1. introce
Calculus Integration By Norhafizah Md Sarif & Norazaliza Mohd Jamil Faculty of Instrial Science & Technology norhafizah@ump.e.my, norazaliza@ump.e.my Description Aims This chapter is aimed to : 1. introce
Integration: Using the chain rule in reverse
 Mathematics Learning Centre Integration: Using the chain rule in reverse Mary Barnes c 999 University of Syney Mathematics Learning Centre, University of Syney Using the Chain Rule in Reverse Recall that
Mathematics Learning Centre Integration: Using the chain rule in reverse Mary Barnes c 999 University of Syney Mathematics Learning Centre, University of Syney Using the Chain Rule in Reverse Recall that
5.5. The Substitution Rule
 INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
INTEGRALS 5 INTEGRALS 5.5 The Substitution Rule In this section, we will learn: To substitute a new variable in place of an existing expression in a function, making integration easier. INTRODUCTION Due
CALCULUS I. Integrals. Paul Dawkins
 CALCULUS I Integrals Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... ii Integrals... Introduction... Indefinite Integrals... Computing Indefinite Integrals... Substitution Rule for Indefinite Integrals... More
CALCULUS I Integrals Paul Dawkins Table of Contents Preface... ii Integrals... Introduction... Indefinite Integrals... Computing Indefinite Integrals... Substitution Rule for Indefinite Integrals... More
Integration by parts Integration by parts is a direct reversal of the product rule. By integrating both sides, we get:
 Integration by parts Integration by parts is a direct reversal of the proct rule. By integrating both sides, we get: u dv dx x n sin mx dx (make u = x n ) dx = uv v dx dx When to use integration by parts
Integration by parts Integration by parts is a direct reversal of the proct rule. By integrating both sides, we get: u dv dx x n sin mx dx (make u = x n ) dx = uv v dx dx When to use integration by parts
Practice Differentiation Math 120 Calculus I Fall 2015
 . x. Hint.. (4x 9) 4x + 9. Hint. Practice Differentiation Math 0 Calculus I Fall 0 The rules of differentiation are straightforward, but knowing when to use them and in what order takes practice. Although
. x. Hint.. (4x 9) 4x + 9. Hint. Practice Differentiation Math 0 Calculus I Fall 0 The rules of differentiation are straightforward, but knowing when to use them and in what order takes practice. Although
Outline. 1 Integration by Substitution: The Technique. 2 Integration by Substitution: Worked Examples. 3 Integration by Parts: The Technique
 MS2: IT Mathematics Integration Two Techniques of Integration John Carroll School of Mathematical Sciences Dublin City University Integration by Substitution: The Technique Integration by Substitution:
MS2: IT Mathematics Integration Two Techniques of Integration John Carroll School of Mathematical Sciences Dublin City University Integration by Substitution: The Technique Integration by Substitution:
MTH 133 Exam 2 November 16th, Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 12.
 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through 2. Show all your work on the standard response
Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through 2. Show all your work on the standard response
2 (x 2 + a 2 ) x 2. is easy. Do this first.
 MAC 3 INTEGRATION BY PARTS General Remark: Unless specified otherwise, you will solve the following problems using integration by parts, combined, if necessary with simple substitutions We will not explicitly
MAC 3 INTEGRATION BY PARTS General Remark: Unless specified otherwise, you will solve the following problems using integration by parts, combined, if necessary with simple substitutions We will not explicitly
Section: I. u 4 du. (9x + 1) + C, 3
 EXAM 3 MAT 168 Calculus II Fall 18 Name: Section: I All answers must include either supporting work or an eplanation of your reasoning. MPORTANT: These elements are considered main part of the answer and
EXAM 3 MAT 168 Calculus II Fall 18 Name: Section: I All answers must include either supporting work or an eplanation of your reasoning. MPORTANT: These elements are considered main part of the answer and
7.3 Hyperbolic Functions Hyperbolic functions are similar to trigonometric functions, and have the following
 Math 2-08 Rahman Week3 7.3 Hyperbolic Functions Hyperbolic functions are similar to trigonometric functions, and have the following definitions: sinh x = 2 (ex e x ) cosh x = 2 (ex + e x ) tanh x = sinh
Math 2-08 Rahman Week3 7.3 Hyperbolic Functions Hyperbolic functions are similar to trigonometric functions, and have the following definitions: sinh x = 2 (ex e x ) cosh x = 2 (ex + e x ) tanh x = sinh
Integration by inverse substitution
 Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter : Integration methods Section 9 Integration by inverse substitution by using the sine function What you need to know already: How to integrate through basic
Roberto s Notes on Integral Calculus Chapter : Integration methods Section 9 Integration by inverse substitution by using the sine function What you need to know already: How to integrate through basic
6.6 Substitution with All Basic Forms
 670 CHAPTER 6. BASIC INTEGRATION 6.6 Substitution with All Basic Forms In this section we will add to our forms for substitution and recall some rather general guidelines for substitution. Ecept for our
670 CHAPTER 6. BASIC INTEGRATION 6.6 Substitution with All Basic Forms In this section we will add to our forms for substitution and recall some rather general guidelines for substitution. Ecept for our
Calculus II. Calculus II tends to be a very difficult course for many students. There are many reasons for this.
 Preface Here are my online notes for my Calculus II course that I teach here at Lamar University. Despite the fact that these are my class notes they should be accessible to anyone wanting to learn Calculus
Preface Here are my online notes for my Calculus II course that I teach here at Lamar University. Despite the fact that these are my class notes they should be accessible to anyone wanting to learn Calculus
Math 205, Winter 2018, Assignment 3
 Math 05, Winter 08, Assignment 3 Solutions. Calculate the following integrals. Show your steps and reasoning. () a) ( + + )e = ( + + )e ( + )e = ( + + )e ( + )e + e = ( )e + e + c = ( + )e + c This uses
Math 05, Winter 08, Assignment 3 Solutions. Calculate the following integrals. Show your steps and reasoning. () a) ( + + )e = ( + + )e ( + )e = ( + + )e ( + )e + e = ( )e + e + c = ( + )e + c This uses
Section 6.2 Integration by Parts
 Section 6 Integration by Parts AP E XC II Version 0 Authors Gregory Hartman, PhD Department of Applied Mathema cs Virginia Military Ins tute Brian Heinold, PhD Department of Mathema cs and Computer Science
Section 6 Integration by Parts AP E XC II Version 0 Authors Gregory Hartman, PhD Department of Applied Mathema cs Virginia Military Ins tute Brian Heinold, PhD Department of Mathema cs and Computer Science
MTH 133 Solutions to Exam 2 November 15, Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 13.
 MTH 33 Solutions to Exam 2 November 5, 207 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through
MTH 33 Solutions to Exam 2 November 5, 207 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 28 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 4 - CALCULUS TUTORIAL 2 - INTEGRATION
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 8 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME - CALCULUS TUTORIAL - INTEGRATION CONTENTS Be able to apply calculus Differentiation: review of standard derivatives, differentiation
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE UNIT 8 FURTHER MATHEMATICS FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME - CALCULUS TUTORIAL - INTEGRATION CONTENTS Be able to apply calculus Differentiation: review of standard derivatives, differentiation
In last semester, we have seen some examples about it (See Tutorial Note #13). Try to have a look on that. Here we try to show more technique.
 MATH202 Introduction to Analysis (2007 Fall and 2008 Spring) Tutorial Note #4 Part I: Cauchy Sequence Definition (Cauchy Sequence): A sequence of real number { n } is Cauchy if and only if for any ε >
MATH202 Introduction to Analysis (2007 Fall and 2008 Spring) Tutorial Note #4 Part I: Cauchy Sequence Definition (Cauchy Sequence): A sequence of real number { n } is Cauchy if and only if for any ε >
A1. Let r > 0 be constant. In this problem you will evaluate the following integral in two different ways: r r 2 x 2 dx
 Math 6 Summer 05 Homework 5 Solutions Drew Armstrong Book Problems: Chap.5 Eercises, 8, Chap 5. Eercises 6, 0, 56 Chap 5. Eercises,, 6 Chap 5.6 Eercises 8, 6 Chap 6. Eercises,, 30 Additional Problems:
Math 6 Summer 05 Homework 5 Solutions Drew Armstrong Book Problems: Chap.5 Eercises, 8, Chap 5. Eercises 6, 0, 56 Chap 5. Eercises,, 6 Chap 5.6 Eercises 8, 6 Chap 6. Eercises,, 30 Additional Problems:
Andrew s handout. 1 Trig identities. 1.1 Fundamental identities. 1.2 Other identities coming from the Pythagorean identity
 Andrew s handout Trig identities. Fundamental identities These are the most fundamental identities, in the sense that ou should probabl memorize these and use them to derive the rest (or, if ou prefer,
Andrew s handout Trig identities. Fundamental identities These are the most fundamental identities, in the sense that ou should probabl memorize these and use them to derive the rest (or, if ou prefer,
Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 12.
 MTH 33 Exam 2 November 4th, 208 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through 2. Show
MTH 33 Exam 2 November 4th, 208 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through 2. Show
Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 12.
 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through 2. Show all your work on the standard response
Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through 2. Show all your work on the standard response
Integration by Substitution
 Integration by Substitution Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University Abstract This handout contains material on a very important integration method called integration by substitution. Substitution
Integration by Substitution Dr. Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University Abstract This handout contains material on a very important integration method called integration by substitution. Substitution
5.2. November 30, 2012 Mrs. Poland. Verifying Trigonometric Identities
 5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Verifying Identities by Working With One Side Verifying Identities by Working With Both Sides November 30, 2012 Mrs. Poland Objective #4: Students will be able to
5.2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Verifying Identities by Working With One Side Verifying Identities by Working With Both Sides November 30, 2012 Mrs. Poland Objective #4: Students will be able to
Worksheet Week 7 Section
 Worksheet Week 7 Section 8.. 8.4. This worksheet is for improvement of your mathematical writing skill. Writing using correct mathematical epression and steps is really important part of doing math. Please
Worksheet Week 7 Section 8.. 8.4. This worksheet is for improvement of your mathematical writing skill. Writing using correct mathematical epression and steps is really important part of doing math. Please
Math 106: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS
 Math 6: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS INTEGRATION TIPS Substitution: usually let u a function that s inside another function, especially if du (possibly off by a multiplying constant) is also present
Math 6: Review for Exam II - SOLUTIONS INTEGRATION TIPS Substitution: usually let u a function that s inside another function, especially if du (possibly off by a multiplying constant) is also present
67. (a) Use a computer algebra system to find the partial fraction CAS. 68. (a) Find the partial fraction decomposition of the function CAS
 SECTION 7.5 STRATEGY FOR INTEGRATION 483 6. 2 sin 2 2 cos CAS 67. (a) Use a computer algebra sstem to find the partial fraction decomposition of the function 62 63 Find the area of the region under the
SECTION 7.5 STRATEGY FOR INTEGRATION 483 6. 2 sin 2 2 cos CAS 67. (a) Use a computer algebra sstem to find the partial fraction decomposition of the function 62 63 Find the area of the region under the
1. The following problems are not related: (a) (15 pts, 5 pts ea.) Find the following limits or show that they do not exist: arcsin(x)
 APPM 5 Final Eam (5 pts) Fall. The following problems are not related: (a) (5 pts, 5 pts ea.) Find the following limits or show that they do not eist: (i) lim e (ii) lim arcsin() (b) (5 pts) Find and classify
APPM 5 Final Eam (5 pts) Fall. The following problems are not related: (a) (5 pts, 5 pts ea.) Find the following limits or show that they do not eist: (i) lim e (ii) lim arcsin() (b) (5 pts) Find and classify
4181H Problem Set 10 Selected Solutions. Chapter 15. = lim. (by L Hôpital s Rule) (0) = lim. x 2, = lim x 3 ( sin x)x + cos x cos x = lim
 48H Problem Set 0 Selected Solutions Chapter 5 # 3(a From the definition of the derivative we have sin f f( f(0 (0 sin 0 0 0 0 = cos (by L Hôpital s Rule = sin (by L Hôpital s Rule = 0 (b From the definition
48H Problem Set 0 Selected Solutions Chapter 5 # 3(a From the definition of the derivative we have sin f f( f(0 (0 sin 0 0 0 0 = cos (by L Hôpital s Rule = sin (by L Hôpital s Rule = 0 (b From the definition
Math RE - Calculus I Trigonometry Limits & Derivatives Page 1 of 8. x = 1 cos x. cos x 1 = lim
 Math 0-0-RE - Calculus I Trigonometry Limits & Derivatives Page of 8 Trigonometric Limits It has been shown in class that: lim 0 sin lim 0 sin lim 0 cos cos 0 lim 0 cos lim 0 + cos + To evaluate trigonometric
Math 0-0-RE - Calculus I Trigonometry Limits & Derivatives Page of 8 Trigonometric Limits It has been shown in class that: lim 0 sin lim 0 sin lim 0 cos cos 0 lim 0 cos lim 0 + cos + To evaluate trigonometric
Methods of Integration
 Methods of Integration Professor D. Olles January 8, 04 Substitution The derivative of a composition of functions can be found using the chain rule form d dx [f (g(x))] f (g(x)) g (x) Rewriting the derivative
Methods of Integration Professor D. Olles January 8, 04 Substitution The derivative of a composition of functions can be found using the chain rule form d dx [f (g(x))] f (g(x)) g (x) Rewriting the derivative
Chapter 2 Overview: Anti-Derivatives. As noted in the introduction, Calculus is essentially comprised of four operations.
 Chapter Overview: Anti-Derivatives As noted in the introduction, Calculus is essentially comprised of four operations. Limits Derivatives Indefinite Integrals (or Anti-Derivatives) Definite Integrals There
Chapter Overview: Anti-Derivatives As noted in the introduction, Calculus is essentially comprised of four operations. Limits Derivatives Indefinite Integrals (or Anti-Derivatives) Definite Integrals There
Integration 1/10. Integration. Student Guidance Centre Learning Development Service
 Integration / Integration Student Guidance Centre Learning Development Service lds@qub.ac.uk Integration / Contents Introduction. Indefinite Integration....................... Definite Integration.......................
Integration / Integration Student Guidance Centre Learning Development Service lds@qub.ac.uk Integration / Contents Introduction. Indefinite Integration....................... Definite Integration.......................
Fall 2018 Exam 1 NAME:
 MARK BOX problem points 0 20 HAND IN PART -8 40=8x5 9 0 NAME: 0 0 PIN: 0 2 0 % 00 INSTRUCTIONS This exam comes in two parts. () HAND IN PART. Hand in only this part. (2) STATEMENT OF MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS.
MARK BOX problem points 0 20 HAND IN PART -8 40=8x5 9 0 NAME: 0 0 PIN: 0 2 0 % 00 INSTRUCTIONS This exam comes in two parts. () HAND IN PART. Hand in only this part. (2) STATEMENT OF MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS.
MATH 1220 Midterm 1 Thurs., Sept. 20, 2007
 MATH 220 Midterm Thurs., Sept. 20, 2007 Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the eam and nothing else. Calculators
MATH 220 Midterm Thurs., Sept. 20, 2007 Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the eam and nothing else. Calculators
Fall 2017 Exam 1 MARK BOX HAND IN PART NAME: PIN:
 problem MARK BOX points HAND IN PART 0 30 1-10 50=10x5 11 10 1 10 NAME: PIN: % 100 INSTRUCTIONS This exam comes in two parts. (1) HAND IN PART. Hand in only this part. () STATEMENT OF MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS.
problem MARK BOX points HAND IN PART 0 30 1-10 50=10x5 11 10 1 10 NAME: PIN: % 100 INSTRUCTIONS This exam comes in two parts. (1) HAND IN PART. Hand in only this part. () STATEMENT OF MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS.
Chapter 6. Techniques of Integration. 6.1 Differential notation
 Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Spring 2018 Exam 1 MARK BOX HAND IN PART NAME: PIN:
 problem MARK BOX points HAND IN PART - 65=x5 4 5 5 6 NAME: PIN: % INSTRUCTIONS This exam comes in two parts. () HAND IN PART. Hand in only this part. () STATEMENT OF MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS. Do not hand
problem MARK BOX points HAND IN PART - 65=x5 4 5 5 6 NAME: PIN: % INSTRUCTIONS This exam comes in two parts. () HAND IN PART. Hand in only this part. () STATEMENT OF MULTIPLE CHOICE PROBLEMS. Do not hand
6.5 Second Trigonometric Rules
 662 CHAPTER 6. BASIC INTEGRATION 6.5 Second Trigonometric Rules We first looked at the simplest trigonometric integration rules those arising from the derivatives of the trignometric functions in Section
662 CHAPTER 6. BASIC INTEGRATION 6.5 Second Trigonometric Rules We first looked at the simplest trigonometric integration rules those arising from the derivatives of the trignometric functions in Section
Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 12.
 MTH 33 Exam 2 April th, 208 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through 2. Show all
MTH 33 Exam 2 April th, 208 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through 2. Show all
The goal of today is to determine what u-substitution to use for trigonometric integrals. The most common substitutions are the following:
 Trigonometric Integrals The goal of today is to determine what u-substitution to use for trigonometric integrals. The most common substitutions are the following: Substitution u sinx u cosx u tanx u secx
Trigonometric Integrals The goal of today is to determine what u-substitution to use for trigonometric integrals. The most common substitutions are the following: Substitution u sinx u cosx u tanx u secx
STEP Support Programme. Pure STEP 3 Solutions
 STEP Support Programme Pure STEP 3 Solutions S3 Q6 Preparation Completing the square on gives + + y, so the centre is at, and the radius is. First draw a sketch of y 4 3. This has roots at and, and you
STEP Support Programme Pure STEP 3 Solutions S3 Q6 Preparation Completing the square on gives + + y, so the centre is at, and the radius is. First draw a sketch of y 4 3. This has roots at and, and you
Chapter 6. Techniques of Integration. 6.1 Differential notation
 Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Chapter 6 Techniques of Integration In this chapter, we expand our repertoire for antiderivatives beyond the elementary functions discussed so far. A review of the table of elementary antiderivatives (found
Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages 1 through 13.
 MTH 33 Solutions to Exam November th, 08 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through
MTH 33 Solutions to Exam November th, 08 Name: Section: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS Fill in your name, etc. on this first page. Without fully opening the exam, check that you have pages through
CALCULUS: Graphical,Numerical,Algebraic by Finney,Demana,Watts and Kennedy Chapter 3: Derivatives 3.3: Derivative of a function pg.
 CALCULUS: Graphical,Numerical,Algebraic b Finne,Demana,Watts and Kenned Chapter : Derivatives.: Derivative of a function pg. 116-16 What ou'll Learn About How to find the derivative of: Functions with
CALCULUS: Graphical,Numerical,Algebraic b Finne,Demana,Watts and Kenned Chapter : Derivatives.: Derivative of a function pg. 116-16 What ou'll Learn About How to find the derivative of: Functions with
Friday 09/15/2017 Midterm I 50 minutes
 Fa 17: MATH 2924 040 Differential and Integral Calculus II Noel Brady Friday 09/15/2017 Midterm I 50 minutes Name: Student ID: Instructions. 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Do not write on back of exam sheets.
Fa 17: MATH 2924 040 Differential and Integral Calculus II Noel Brady Friday 09/15/2017 Midterm I 50 minutes Name: Student ID: Instructions. 1. Attempt all questions. 2. Do not write on back of exam sheets.
CHAPTER 7: TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION
 CHAPTER 7: TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION DAVID GLICKENSTEIN. Introduction This semester we will be looking deep into the recesses of calculus. Some of the main topics will be: Integration: we will learn how
CHAPTER 7: TECHNIQUES OF INTEGRATION DAVID GLICKENSTEIN. Introduction This semester we will be looking deep into the recesses of calculus. Some of the main topics will be: Integration: we will learn how
11.5. The Chain Rule. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 The Chain Rule 11.5 Introduction In this Section we will see how to obtain the derivative of a composite function (often referred to as a function of a function ). To do this we use the chain rule. This
The Chain Rule 11.5 Introduction In this Section we will see how to obtain the derivative of a composite function (often referred to as a function of a function ). To do this we use the chain rule. This
Chapter 7 Notes, Stewart 7e. 7.1 Integration by Parts Trigonometric Integrals Evaluating sin m xcos n (x)dx...
 Contents 7.1 Integration by Parts........................................ 2 7.2 Trigonometric Integrals...................................... 8 7.2.1 Evaluating sin m xcos n (x)dx..............................
Contents 7.1 Integration by Parts........................................ 2 7.2 Trigonometric Integrals...................................... 8 7.2.1 Evaluating sin m xcos n (x)dx..............................
Integration by parts (product rule backwards)
 Integration by parts (product rule backwards) The product rule states Integrating both sides gives f(x)g(x) = d dx f(x)g(x) = f(x)g (x) + f (x)g(x). f(x)g (x)dx + Letting f(x) = u, g(x) = v, and rearranging,
Integration by parts (product rule backwards) The product rule states Integrating both sides gives f(x)g(x) = d dx f(x)g(x) = f(x)g (x) + f (x)g(x). f(x)g (x)dx + Letting f(x) = u, g(x) = v, and rearranging,
MAT 271 Recitation. MAT 271 Recitation. Sections 7.1 and 7.2. Lindsey K. Gamard, ASU SoMSS. 30 August 2013
 MAT 271 Recitation Sections 7.1 and 7.2 Lindsey K. Gamard, ASU SoMSS 30 August 2013 Agenda Today s agenda: 1. Review 2. Review Section 7.2 (Trigonometric Integrals) 3. (If time) Start homework in pairs
MAT 271 Recitation Sections 7.1 and 7.2 Lindsey K. Gamard, ASU SoMSS 30 August 2013 Agenda Today s agenda: 1. Review 2. Review Section 7.2 (Trigonometric Integrals) 3. (If time) Start homework in pairs
PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND LOGS
 PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND LOGS Calculus Lesson- Derivatives of Eponentials and Logs Name: Date: Objective: to learn how to find the derivative of an eponential or logarithmic function Finding
PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND LOGS Calculus Lesson- Derivatives of Eponentials and Logs Name: Date: Objective: to learn how to find the derivative of an eponential or logarithmic function Finding
Calculus Differentiation Norhafizah Md Sarif Faculty of Industrial Science & Technology
 Calculus Differentiation By Norhafizah Md Sarif Faculty of Industrial Science & Technology norhafizah@ump.edu.my Description Aims This chapter is aimed to : 1. introduce the concept of integration. evaluate
Calculus Differentiation By Norhafizah Md Sarif Faculty of Industrial Science & Technology norhafizah@ump.edu.my Description Aims This chapter is aimed to : 1. introduce the concept of integration. evaluate
Mathematics 104 Fall Term 2006 Solutions to Final Exam. sin(ln t) dt = e x sin(x) dx.
 Mathematics 14 Fall Term 26 Solutions to Final Exam 1. Evaluate sin(ln t) dt. Solution. We first make the substitution t = e x, for which dt = e x. This gives sin(ln t) dt = e x sin(x). To evaluate the
Mathematics 14 Fall Term 26 Solutions to Final Exam 1. Evaluate sin(ln t) dt. Solution. We first make the substitution t = e x, for which dt = e x. This gives sin(ln t) dt = e x sin(x). To evaluate the
MATH 250 TOPIC 11 LIMITS. A. Basic Idea of a Limit and Limit Laws. Answers to Exercises and Problems
 Math 5 T-Limits Page MATH 5 TOPIC LIMITS A. Basic Idea of a Limit and Limit Laws B. Limits of the form,, C. Limits as or as D. Summary for Evaluating Limits Answers to Eercises and Problems Math 5 T-Limits
Math 5 T-Limits Page MATH 5 TOPIC LIMITS A. Basic Idea of a Limit and Limit Laws B. Limits of the form,, C. Limits as or as D. Summary for Evaluating Limits Answers to Eercises and Problems Math 5 T-Limits
192 Calculus and Structures
 9 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER PRODUCT, QUOTIENT, CHAIN RULE, AND TRIG FUNCTIONS Calculus and Structures 9 Copyright Chapter PRODUCT, QUTIENT, CHAIN RULE AND TRIG FUNTIONS. NEW FUNCTIONS FROM OLD ONES
9 Calculus and Structures CHAPTER PRODUCT, QUOTIENT, CHAIN RULE, AND TRIG FUNCTIONS Calculus and Structures 9 Copyright Chapter PRODUCT, QUTIENT, CHAIN RULE AND TRIG FUNTIONS. NEW FUNCTIONS FROM OLD ONES
1 Exponential Functions Limit Derivative Integral... 5
 Contents Eponential Functions 3. Limit................................................. 3. Derivative.............................................. 4.3 Integral................................................
Contents Eponential Functions 3. Limit................................................. 3. Derivative.............................................. 4.3 Integral................................................
1 Functions and Inverses
 October, 08 MAT86 Week Justin Ko Functions and Inverses Definition. A function f : D R is a rule that assigns each element in a set D to eactly one element f() in R. The set D is called the domain of f.
October, 08 MAT86 Week Justin Ko Functions and Inverses Definition. A function f : D R is a rule that assigns each element in a set D to eactly one element f() in R. The set D is called the domain of f.
