Run For Your Life! Can you escape an volcanic eruption?
|
|
|
- Ariel McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Run For Your Life! Can you escape an volcanic eruption? Date: Directions : Using the information provided determine the speed of the flow resulting from each volcanic eruption, and the four other things we ll compare them to. Hawaii Kīlauea volcano lava flow moves at a speed of mph which is meters per second. A pyroclastic flow such as Guatemala s Fuego Volcano can move at an average of mph which is meters per second. Helpful Hint: The boxes below either give you the information in the video, have information in the video that you can use to calculate the speed, is given to you, or you can find by measuring yourself. The box in the upper right-hand corner has a proportion you can format to help you solve. You can also use the Google search bar to help you convert your measurements into meters per second as needed. Resource by Brian Soash
2 *Round any calculations to the nearest hundredth Determine the speed of Bertie the world s fastest tortoise in meters per second from the following video. Determine Usain Bolt s speed in meters per second from the following video. Convert the average US Interstate speed limit of 65 mph to meters per second. Calculate your own speed by measuring out a ten-meter distance or greater and having a friend or classmate time you.
3 Slope-Intercept Form Slope-intercept form is a form of linear equation that describes the starting point of a graph based on its placement on the y-axis and the rate of change of its equation. It s widely used and appreciated because it makes it fairly easy to graph linear functions by easily identifying the y-intercept as a point to start your graph and then using the slope to determine the next points. Each variable in the equations represents a different component of your graph the following way. Slope-Intercept Equations Example: A deer running from the volcanic eruption 2,000m from the volcano at 697 meters a minute would have a slope-intercept form equation of y=697x+2000.
4 Slope-Intercept Form Equations For The Characters And Volcanoes Kīlauea Slope Intercept Form Equation Tortoise Equation Average Vehicle Equation Fuego Slope Intercept Form Equation 100m world record holder equation YOUR Equation Compare the flows: Lava and pyroclastic flows as we know are made of different things and have a large difference in speed. Use page 1 of your graph paper to graph the slope-intercept equations of each flow to compare both rates visually. Try this: Be sure to start from your y-intercept and then plug in the safe distance of 5,000m to calculate how long it will take each flow to reach the safe distance. *Observation: If you were only given the graph of the two equations how would you know which one was moving faster?
5 *Analyze: If you expanded these graphs to a four quadrant graph the only place they would intersect would be at your point (0,0) as they do on your graph now. What does the origin in this situation represent? Why is this the only place these two graphs will ever intersect? Kīlauea Using the graph paper page provided let s determine whether or not the tortoise, Usain Bolt, a car on a US Highway, or YOU could outrun Kīlauea s lava flow with a 1,000m head start to a safe distance 5,000m away. Graph Kīlauea s lava flow and each of the 4 other equations you re comparing it to on the graph paper. Be sure to use a different color or type of line for each of your equations, then label them in the key provided. REMEMBER: Assume both you and the lava travel at the exact same speed for the entire time and would only travel in one, even, straight and uninterrupted line to the safe location 5,000m away. *Observe: Out of the four other equations graphed, which one(s) if any were able to make it to the safety of 5,000m away before the lava flow reached there? *Observe: Were there any that make it to the 5,000m mark on your graph paper? If so, what would it mean for that character? Why do you think this was the case? Use evidence from your graph or equation to justify your claim.
6 *Analyze: How were you able to interpret this from the graph? Fuego Using the graph paper page and some calculations let s determine if you could make it to your safe point 5,000m away with your previous 1,000m head start. If not, we ll find out how much of a head start you would need to reach the safe distance of 5,000m away from the volcano before Fuego s pyroclastic flow could make it there. Graph Fuego s pyroclastic flow and each of the 4 other equations you re comparing it to on the graph paper. Be sure to use the same color or types of lines associated with the equation as you did on your previous graph. REMEMBER: Assume both you and the rest of the characters as well as the pyroclastic flow travel at the exact same speed for the entire time and would only travel in one, even, straight and uninterrupted line to the safe location 5,000m away. *Observe: Out of the four other equations graphed, which one(s) if any were able to make it to the safety of 5,000m away before the pyroclastic flow?
7 *Analyze: How were you able to interpret this from the graph? Fuego Part Two Pyroclastic flows as you ve discovered are especially deadly. Due to their high rate of speed they ve been known to cause some of the most well-known instances of volcanic eruptions that have resulted in the greatest loss of human life. Mount Tambora in 1815 resulted in the loss of at least 10,000 Indonesians. Krakatoa s eruption in 1883, also in Indonesia, resulted in the loss of over 35,000 lives as a result of pyroclastic flows and accompanying tsunamis. Mount Vesuvius eruption in 79 AD, which although not the deadliest, is one of the most well-known examples of the destruction of pyroclastic flows and volcanic eruptions. Vesuvius quickly covered both the town and its victims in ash preserving the remains of both in the process. What type of headstart would it take for our 4 characters to survive and make it to the safe distance 5,000m away?
8 *Round all calculations to the nearest hundredth. World s Fastest Tortoise Usain Bolt Head Start Needed: Head Start Needed: Average Car On The Interstate You Head Start Needed: Head Start Needed:
9 Reflection: A) Quite a few people live in a community very close to some volcanoes. Based on what you ve seen from these two different, but very real situations if you were in charge of these areas would you allow people to develop communities near or at the base of a volcano? Create a claim and justify your decision using the evidence from the graphs and calculations you created above. I think that people (Circle one) SHOULD / SHOULDN T be allowed to develop communities near the based of the volcano because... List at least 3 pieces of evidence from the resource, graph, or your calculations from the activity above: 1) 2) 3) Explain how each piece of evidence supports your claim below: The Reasoning For Evidence #1 The Reasoning For Evidence #2 The Reasoning For Evidence #3
10 B) You re the Governor of a state that wants to develop a community on land at the base of an active volcano that hasn t been previously developed. The law in your state says that currently, it s illegal to build a town within 10 miles of a volcano. The developers think you should repeal the law and allow them to build due to a new Volcano Siren that s been developed that will warn that says it can warn the community 15 minutes before an eruption. As governor what is your decision? Use the chart below to plan your response and then put it together in written form below on the next page. Claim: Section Evidence Reasoning Decision
11 Decision (continued) Section 4 Distinguished 3 Proficient 2 Developing 1 Beginning Claim The claim is clearly stated. The claim directly references the situation described. The claim is clearly stated. Claim directly correlates to the situation described. The claim is stated, but is not clear. The claim does not directly correlate to the situation described. No claim is made. Evidence 3 or more pieces of evidence are cited from the activity in support of the claim. 3 pieces of evidence are used from the activity and are not cited. Less than 3 pieces of evidence are used from the activity. Pieces of evidence are used, but they are not supportive of the claim or are not from the activity. Reasoning Reasoning clearly justifies the claim and clearly elaborates on all of the pieces of evidence previously provided. There are no spelling or grammar issues in the section. Reasoning clearly justifies the claim. The reasoning elaborates on only some pieces of evidence cited. Reasoning does not directly or clearly support the claim or the evidence stated in the No reasoning is provided or is incoherent.
Welcome to GCSE Geography. Where will it take us today?
 Welcome to GCSE Geography Where will it take us today? Topic 1.2: global hazards 1.2a: What processes occur @ plate boundaries aiii) How the movement of tectonic plates causes volcanoes 06/12/2018 Think
Welcome to GCSE Geography Where will it take us today? Topic 1.2: global hazards 1.2a: What processes occur @ plate boundaries aiii) How the movement of tectonic plates causes volcanoes 06/12/2018 Think
PHYSICS LAB: CONSTANT MOTION
 PHYSICS LAB: CONSTANT MOTION Introduction Experimentation is fundamental to physics (and all science, for that matter) because it allows us to prove or disprove our hypotheses about how the physical world
PHYSICS LAB: CONSTANT MOTION Introduction Experimentation is fundamental to physics (and all science, for that matter) because it allows us to prove or disprove our hypotheses about how the physical world
Released Science Inquiry Task Encounter with an Active Volcano Grade 11
 Date: Your Name: Released Science Inquiry Task Encounter with an Active Volcano 2016 Grade 11 Directions: Science You will be reading a story and analyzing the data provided to answer a set of questions.
Date: Your Name: Released Science Inquiry Task Encounter with an Active Volcano 2016 Grade 11 Directions: Science You will be reading a story and analyzing the data provided to answer a set of questions.
PHYSICS LAB: CONSTANT MOTION
 PHYSICS LAB: CONSTANT MOTION Introduction Experimentation is fundamental to physics (and all science, for that matter) because it allows us to prove or disprove our hypotheses about how the physical world
PHYSICS LAB: CONSTANT MOTION Introduction Experimentation is fundamental to physics (and all science, for that matter) because it allows us to prove or disprove our hypotheses about how the physical world
1. The graph of a quadratic function is shown. Each square is one unit.
 1. The graph of a quadratic function is shown. Each square is one unit. a. What is the vertex of the function? b. If the lead coefficient (the value of a) is 1, write the formula for the function in vertex
1. The graph of a quadratic function is shown. Each square is one unit. a. What is the vertex of the function? b. If the lead coefficient (the value of a) is 1, write the formula for the function in vertex
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration?
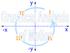 Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Which car/s is/are undergoing an acceleration? Which car experiences the greatest acceleration? Match a Graph Consider the position-time graphs below. Each one of the 3 lines on the position-time graph
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0.
 Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Position, Speed and Velocity Position is a variable that gives your location relative to an origin. The origin is the place where position equals 0. The position of this car at 50 cm describes where the
Section 2. Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: What Goes Up and What Comes Down. What Do You See? What Do You Think?
 Thrills and Chills Section Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: What Goes Up and What Comes Down Florida Next Generation Sunshine State Standards: Additional Benchmarks met in Section SC.91.N..4
Thrills and Chills Section Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy: What Goes Up and What Comes Down Florida Next Generation Sunshine State Standards: Additional Benchmarks met in Section SC.91.N..4
Volcanoes. Introduction
 Volcanoes Introduction Display Slide V-0 Explain that a volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are
Volcanoes Introduction Display Slide V-0 Explain that a volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are
Econ A Math Survival Guide
 Econ 101 - A Math Survival Guide T.J. Rakitan Teaching Assistant, Summer Session II, 013 1 Introduction The introductory study of economics relies on two major ways of thinking about the world: qualitative
Econ 101 - A Math Survival Guide T.J. Rakitan Teaching Assistant, Summer Session II, 013 1 Introduction The introductory study of economics relies on two major ways of thinking about the world: qualitative
Earthquakes and Society
 CHAPTER 8 SECTION 3 Earthquakes Earthquakes and Society BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Can scientists predict when earthquakes will happen? Why
CHAPTER 8 SECTION 3 Earthquakes Earthquakes and Society BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Can scientists predict when earthquakes will happen? Why
MLK Day!!! Solving Equations with Radicals Day 1. Practice. Solving Equations with Radicals Day 2. Practice. Applications of Radicals.
 Name Algebra 2 Agenda Period Week.3 Objective Stamp Grade Monday January 8, 206 MLK Day!!! Tuesday January 9, 206 Solving Equations with Radicals Day Practice Wednesday January 20, 206 Solving Equations
Name Algebra 2 Agenda Period Week.3 Objective Stamp Grade Monday January 8, 206 MLK Day!!! Tuesday January 9, 206 Solving Equations with Radicals Day Practice Wednesday January 20, 206 Solving Equations
Honors Physics / Unit 01 / CVPM. Name:
 Name: Constant Velocity Model The front of each model packet should serve as a storehouse for things you ll want to be able to quickly look up later. We will usually try to give you some direction on a
Name: Constant Velocity Model The front of each model packet should serve as a storehouse for things you ll want to be able to quickly look up later. We will usually try to give you some direction on a
Lesson 3A: How Fast Are You Moving?
 Lesson 3A: How Fast Are You Moving? 3.1 Observe and represent Decide on a starting point. You will need 2 cars (or other moving objects). For each car, you will mark its position at each second. Make sure
Lesson 3A: How Fast Are You Moving? 3.1 Observe and represent Decide on a starting point. You will need 2 cars (or other moving objects). For each car, you will mark its position at each second. Make sure
How do Volcanoes change the Earth s surface?
 How do Volcanoes change the Earth s surface? Volcanoes In the Earth s mantle, there are pockets of hot, liquid-like rocks and gases called magma. As heat and pressure builds up in these pockets (chambers)
How do Volcanoes change the Earth s surface? Volcanoes In the Earth s mantle, there are pockets of hot, liquid-like rocks and gases called magma. As heat and pressure builds up in these pockets (chambers)
June To Advanced Placement Calculus Student,
 June 2018 To Advanced Placement Calculus Student, I congratulate you on accepting the challenge of taking the Advanced Placement Calculus course at Northwestern. I have prepared this packet to give you
June 2018 To Advanced Placement Calculus Student, I congratulate you on accepting the challenge of taking the Advanced Placement Calculus course at Northwestern. I have prepared this packet to give you
Point of intersection
 Name: Date: Period: Exploring Systems of Linear Equations, Part 1 Learning Goals Define a system of linear equations and a solution to a system of linear equations. Identify whether a system of linear
Name: Date: Period: Exploring Systems of Linear Equations, Part 1 Learning Goals Define a system of linear equations and a solution to a system of linear equations. Identify whether a system of linear
Math Review Problems Exam 2
 14.1 The graph shows distance from home as a function of time for Laura s trip to the mall. Write a brief description of her trip that explains all features of the graph. A. distance from home A B C D
14.1 The graph shows distance from home as a function of time for Laura s trip to the mall. Write a brief description of her trip that explains all features of the graph. A. distance from home A B C D
Constructive & Destructive Forces
 Constructive & Destructive Forces Intro: Constructive Forces Processes that create landforms. Destructive Forces Processes that destroy landforms. Intro: Constructive Forces Volcanoes Deposition Landslides
Constructive & Destructive Forces Intro: Constructive Forces Processes that create landforms. Destructive Forces Processes that destroy landforms. Intro: Constructive Forces Volcanoes Deposition Landslides
Describing Mo tion. Speed and Velocity. What is speed?
 CHAPTER 1 LESSON 2 Describing Mo tion Speed and Velocity Key Concepts What is speed? How can you use a dis tance-time graph to calculate average speed? What are ways velocity can change? What do you think?
CHAPTER 1 LESSON 2 Describing Mo tion Speed and Velocity Key Concepts What is speed? How can you use a dis tance-time graph to calculate average speed? What are ways velocity can change? What do you think?
Also, when Cascade volcanoes do erupt, high-speed avalanches of pyroclastic flows
 INTRODUCTION A volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are built by surface accumulation of their eruptive
INTRODUCTION A volcano is a vent through which molten rock escapes to the Earth s surface. Unlike other mountains, which are pushed up from below, volcanoes are built by surface accumulation of their eruptive
LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION
 Name Date Partners L02-1 LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise To learn how to use a motion detector and gain more familiarity
Name Date Partners L02-1 LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise To learn how to use a motion detector and gain more familiarity
+ 37,500. Discuss with your group how do you THINK you would represent 40 degrees below 0 as an integer?
 6.1 Integers *I can use positive and negative numbers to show amounts in real-world situations and explain what the number 0 means in those situations. *I can recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating
6.1 Integers *I can use positive and negative numbers to show amounts in real-world situations and explain what the number 0 means in those situations. *I can recognize opposite signs of numbers as indicating
Acceleration Worksheet Definitions: velocity: speed in a given direction acceleration: the rate at which the velocity is changing
 Name: Period: Date: / / Acceleration Worksheet Definitions: velocity: speed in a given direction acceleration: the rate at which the velocity is changing Acceleration Notes: 1. What are the three things
Name: Period: Date: / / Acceleration Worksheet Definitions: velocity: speed in a given direction acceleration: the rate at which the velocity is changing Acceleration Notes: 1. What are the three things
Chapter: Basic Physics-Motion
 Chapter: Basic Physics-Motion The Big Idea Speed represents how quickly an object is moving through space. Velocity is speed with a direction, making it a vector quantity. If an object s velocity changes
Chapter: Basic Physics-Motion The Big Idea Speed represents how quickly an object is moving through space. Velocity is speed with a direction, making it a vector quantity. If an object s velocity changes
Predicting and Preparing for Volcanoes
 Predicting and Preparing for Volcanoes Prediction methods for volcanic eruptions are more reliable than those for earthquakes. Some volcanoes such as Mount Etna in Italy are monitored all of the time because
Predicting and Preparing for Volcanoes Prediction methods for volcanic eruptions are more reliable than those for earthquakes. Some volcanoes such as Mount Etna in Italy are monitored all of the time because
Epicenter - a point, directly above the true center of disturbance, from which the shock waves of an earthquake apparently radiate.
 Name: Date: Period: Earthquakes Epicenter - a point, directly above the true center of disturbance, from which the shock waves of an earthquake apparently radiate. Define each of the following terms in
Name: Date: Period: Earthquakes Epicenter - a point, directly above the true center of disturbance, from which the shock waves of an earthquake apparently radiate. Define each of the following terms in
Part II: Succession Stations
 Part II: Succession Stations Station 1: Mount St. Helens - Before and After Mount St. Helens is a volcano in the Cascade Mountain range in Washington state. For many years, it was dormant. Then, at 8:32
Part II: Succession Stations Station 1: Mount St. Helens - Before and After Mount St. Helens is a volcano in the Cascade Mountain range in Washington state. For many years, it was dormant. Then, at 8:32
Math 4: Advanced Algebra Ms. Sheppard-Brick A Quiz Review Learning Targets
 5A Quiz Review Learning Targets 4.4 5.5 Key Facts Graphing one-variable inequalities (ex. x < 4 ) o Perform algebra steps to get x alone! If you multiply or divide by a negative number, you must flip the
5A Quiz Review Learning Targets 4.4 5.5 Key Facts Graphing one-variable inequalities (ex. x < 4 ) o Perform algebra steps to get x alone! If you multiply or divide by a negative number, you must flip the
Name Period. Algebra 2 Agenda. Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade
 Name Period Algebra Agenda Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade Monday January 3, 07 Tuesday January 4, 07 Wednesday January 5, 07 Thursday January 6, 07 Friday January 7, 07 Solving Equations with Radicals
Name Period Algebra Agenda Week 3.4 Objective Summary Grade Monday January 3, 07 Tuesday January 4, 07 Wednesday January 5, 07 Thursday January 6, 07 Friday January 7, 07 Solving Equations with Radicals
Geology Rocks Minerals Earthquakes Natural Resources. Meteorology. Oceanography. Astronomy. Weather Storms Warm fronts Cold fronts
 Geology Rocks Minerals Earthquakes Natural Resources Meteorology Weather Storms Warm fronts Cold fronts Oceanography Mid ocean ridges Tsunamis Astronomy Space Stars Planets Moon Prologue 1 Prologue I.
Geology Rocks Minerals Earthquakes Natural Resources Meteorology Weather Storms Warm fronts Cold fronts Oceanography Mid ocean ridges Tsunamis Astronomy Space Stars Planets Moon Prologue 1 Prologue I.
Comparing linear and exponential growth
 Januar 16, 2009 Comparing Linear and Exponential Growth page 1 Comparing linear and exponential growth How does exponential growth, which we ve been studing this week, compare to linear growth, which we
Januar 16, 2009 Comparing Linear and Exponential Growth page 1 Comparing linear and exponential growth How does exponential growth, which we ve been studing this week, compare to linear growth, which we
Unit 1 Science Models & Graphing
 Name: Date: 9/18 Period: Unit 1 Science Models & Graphing Essential Questions: What do scientists mean when they talk about models? How can we get equations from graphs? Objectives Explain why models are
Name: Date: 9/18 Period: Unit 1 Science Models & Graphing Essential Questions: What do scientists mean when they talk about models? How can we get equations from graphs? Objectives Explain why models are
What kind of number is? Write the number in scientific notation ,000
 Chapter 1: 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 Chapter 2: 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Chapter 3: 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4 Chapter 4: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.5, 4.7 Chapter 5: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.6, 5.7 Chapter 6: 6.1 1.1 What kind of number
Chapter 1: 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 Chapter 2: 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Chapter 3: 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4 Chapter 4: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.5, 4.7 Chapter 5: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.6, 5.7 Chapter 6: 6.1 1.1 What kind of number
Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration (CE )
 Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration 3 (CE ) Field Notebook Module 1: Introduction to Volcanoes Investigation 1: Volcanic Hazards and Benefits Table of Contents Folder 1: Mount Vesuvius, Italy... 3 Folder 2:
Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration 3 (CE ) Field Notebook Module 1: Introduction to Volcanoes Investigation 1: Volcanic Hazards and Benefits Table of Contents Folder 1: Mount Vesuvius, Italy... 3 Folder 2:
Landforms from Volcanoes
 Landforms from Volcanoes Lesson Concept Link Volcanoes are classified by how they are formed (quiet or explosive eruption) and the resulting land formation (shield, cinder cone, or composite/stratovolcano).
Landforms from Volcanoes Lesson Concept Link Volcanoes are classified by how they are formed (quiet or explosive eruption) and the resulting land formation (shield, cinder cone, or composite/stratovolcano).
Alex s Guide to Word Problems and Linear Equations Following Glencoe Algebra 1
 Alex s Guide to Word Problems and Linear Equations Following Glencoe Algebra 1 What is a linear equation? It sounds fancy, but linear equation means the same thing as a line. In other words, it s an equation
Alex s Guide to Word Problems and Linear Equations Following Glencoe Algebra 1 What is a linear equation? It sounds fancy, but linear equation means the same thing as a line. In other words, it s an equation
Lesson 7: Slopes and Functions: Speed and Velocity
 Lesson 7: Slopes and Functions: Speed and Velocity 7.1 Observe and Represent Another way of comparing trend lines is by calculating the slope of each line and comparing the numerical values of the slopes.
Lesson 7: Slopes and Functions: Speed and Velocity 7.1 Observe and Represent Another way of comparing trend lines is by calculating the slope of each line and comparing the numerical values of the slopes.
Earthquake Investigation
 Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Lesson 3: Working With Linear Relations Day 3 Unit 1 Linear Relations
 (A) Lesson Context BIG PICTURE of this UNIT: CONTEXT of this LESSON: mastery with algebraic manipulations/calculations involving linear relations proficiency in working with graphic and numeric representations
(A) Lesson Context BIG PICTURE of this UNIT: CONTEXT of this LESSON: mastery with algebraic manipulations/calculations involving linear relations proficiency in working with graphic and numeric representations
This lesson examines the average and
 NATIONAL MATH + SCIENCE INITIATIVE Mathematics 5 4 1 5 4 1 1 4 5 1 4 5 LEVEL Algebra or Math in a unit on quadratic functions MODULE/CONNECTION TO AP* Rate of Change: Average and Instantaneous *Advanced
NATIONAL MATH + SCIENCE INITIATIVE Mathematics 5 4 1 5 4 1 1 4 5 1 4 5 LEVEL Algebra or Math in a unit on quadratic functions MODULE/CONNECTION TO AP* Rate of Change: Average and Instantaneous *Advanced
Lesson 3-2: Solving Linear Systems Algebraically
 Yesterday we took our first look at solving a linear system. We learned that a linear system is two or more linear equations taken at the same time. Their solution is the point that all the lines have
Yesterday we took our first look at solving a linear system. We learned that a linear system is two or more linear equations taken at the same time. Their solution is the point that all the lines have
LAB: FORCE AND MOTION
 LAB: FORCE AND MOTION Introduction In this lab we will apply a force to a cart and look at the motion that results. Therefore, we are asking the question: "How does the motion depend on the force?" More
LAB: FORCE AND MOTION Introduction In this lab we will apply a force to a cart and look at the motion that results. Therefore, we are asking the question: "How does the motion depend on the force?" More
=.55 = = 5.05
 MAT1193 4c Definition of derivative With a better understanding of limits we return to idea of the instantaneous velocity or instantaneous rate of change. Remember that in the example of calculating the
MAT1193 4c Definition of derivative With a better understanding of limits we return to idea of the instantaneous velocity or instantaneous rate of change. Remember that in the example of calculating the
Physics 6A Lab Experiment 6
 Biceps Muscle Model Physics 6A Lab Experiment 6 Introduction This lab will begin with some warm-up exercises to familiarize yourself with the theory, as well as the experimental setup. Then you ll move
Biceps Muscle Model Physics 6A Lab Experiment 6 Introduction This lab will begin with some warm-up exercises to familiarize yourself with the theory, as well as the experimental setup. Then you ll move
Determining the relationship between the summit and Pu u Ō ō on Kilauea
 Name: Determining the relationship between the summit and Pu u Ō ō on Kilauea After completing this activity, you will be able to: 1. summarize the physical events that produce the data volcanologists
Name: Determining the relationship between the summit and Pu u Ō ō on Kilauea After completing this activity, you will be able to: 1. summarize the physical events that produce the data volcanologists
Name Hour. Environmental Science Semester 2 Study Guide. Plate Tectonics. 1. Explain sea floor spreading.
 Name Hour Environmental Science Semester 2 Study Guide Plate Tectonics 1. Explain sea floor spreading. 2. Describe Wegener s idea of continental drift. 3. List 5 pieces of evidence to support the idea
Name Hour Environmental Science Semester 2 Study Guide Plate Tectonics 1. Explain sea floor spreading. 2. Describe Wegener s idea of continental drift. 3. List 5 pieces of evidence to support the idea
Lesson 1.2 Position Time Graphs
 Lesson 1.2 Position Time Graphs Be able to explain the motion represented in a position time graph Be able to calculate the avg. vel, x, and t for portions of a position time graph. Be able to draw a position
Lesson 1.2 Position Time Graphs Be able to explain the motion represented in a position time graph Be able to calculate the avg. vel, x, and t for portions of a position time graph. Be able to draw a position
Calculus Jeopardy Sample
 In the purchased version, the game board has 6 categories and is interactive, allowing you to click on category and money amount to see the answers. In this sample just scroll through the document. www.mastermathmentor.com
In the purchased version, the game board has 6 categories and is interactive, allowing you to click on category and money amount to see the answers. In this sample just scroll through the document. www.mastermathmentor.com
Living Near a Volcano
 living near a volcano Grade Level 3-5 Grade Level 3-5 (1) 15 minute prep lesson (3) 45 minute lessons Lesson overview: Is it possible to build a volcano-safe home? In this lesson, students will learn about
living near a volcano Grade Level 3-5 Grade Level 3-5 (1) 15 minute prep lesson (3) 45 minute lessons Lesson overview: Is it possible to build a volcano-safe home? In this lesson, students will learn about
11.4 The Rock Cycle. Rocks and Soils. Objective. Materials. Teacher Tip. Directed Instruction. Content. Introduction
 11.4 The Rock Cycle Rocks and Soils Objective Students will explain orally how rocks change form through the rock cycle. Materials Blackline Master 11.4A Discover: The Rock Cycle Blackline Master 11.4B
11.4 The Rock Cycle Rocks and Soils Objective Students will explain orally how rocks change form through the rock cycle. Materials Blackline Master 11.4A Discover: The Rock Cycle Blackline Master 11.4B
Natural Disasters. Why Are There Earthquakes? 197 words. The Power of the Earth 221 words. Big Waves! 188 words
 ARTICLE-A-DAY Natural Disasters 6 Articles Check articles you have read: Why Are There Earthquakes? 197 words The Power of the Earth 221 words Big Waves! 188 words The Volcano That Keeps Erupting 228 words
ARTICLE-A-DAY Natural Disasters 6 Articles Check articles you have read: Why Are There Earthquakes? 197 words The Power of the Earth 221 words Big Waves! 188 words The Volcano That Keeps Erupting 228 words
3.4 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing
 www.ck1.org Chapter 3. Quadratic Equations and Quadratic Functions 3.4 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square Learning objectives Complete the square of a quadratic expression. Solve quadratic
www.ck1.org Chapter 3. Quadratic Equations and Quadratic Functions 3.4 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square Learning objectives Complete the square of a quadratic expression. Solve quadratic
February 29 th March 4 th
 February 29 th March 4 th Unit 7: Introduction to Functions Jump Start Table A: Bags of candy ( ) Cost ( ) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 $1.25 $2.50 $3.75 $5.00 $6.25 $7.50 $8.75 $10.00 Table B: Number of seconds (
February 29 th March 4 th Unit 7: Introduction to Functions Jump Start Table A: Bags of candy ( ) Cost ( ) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 $1.25 $2.50 $3.75 $5.00 $6.25 $7.50 $8.75 $10.00 Table B: Number of seconds (
Physics 6A Lab Experiment 6
 Rewritten Biceps Lab Introduction This lab will be different from the others you ve done so far. First, we ll have some warmup exercises to familiarize yourself with some of the theory, as well as the
Rewritten Biceps Lab Introduction This lab will be different from the others you ve done so far. First, we ll have some warmup exercises to familiarize yourself with some of the theory, as well as the
Unit 3 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey
 HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
e with water and gases.
 Top deck 2 Assessment test Listening Unit 1 (Level 1) Listening test Part 1 1 3.09 Listen to the radio interview and match the sentence halves. Write a e on the line. There is one answer you do not need.
Top deck 2 Assessment test Listening Unit 1 (Level 1) Listening test Part 1 1 3.09 Listen to the radio interview and match the sentence halves. Write a e on the line. There is one answer you do not need.
Volcanoes Shake and Bake Indoor Activity
 Mount St Helens National Volcanic Monument Teacher s Corner 2011 Gifford Pinchot National Forest USDA Forest Service Volcanoes Shake and Bake Indoor Activity Time Commitment: Trail: Location: 45 minutes
Mount St Helens National Volcanic Monument Teacher s Corner 2011 Gifford Pinchot National Forest USDA Forest Service Volcanoes Shake and Bake Indoor Activity Time Commitment: Trail: Location: 45 minutes
Cite power of ten and abbreviation associated with metric prefixes: nano-, micro-, milli-, centi-, kilo-, mega-, and giga-.
 Reading: Chapter 1 Objectives/HW: The student will be able to: HW: 1 Define and identify significant digits. 1, 2 2 Use the rules of significant digits to determine the correct number of 3 6 significant
Reading: Chapter 1 Objectives/HW: The student will be able to: HW: 1 Define and identify significant digits. 1, 2 2 Use the rules of significant digits to determine the correct number of 3 6 significant
Recitation Questions 1D Motion (part 1)
 Recitation Questions 1D Motion (part 1) 18 January Question 1: Two runners (This problem is simple, but it has the same template as most of the problems that you ll be doing for this unit. Take note of
Recitation Questions 1D Motion (part 1) 18 January Question 1: Two runners (This problem is simple, but it has the same template as most of the problems that you ll be doing for this unit. Take note of
Lesson 2-4: Average vs. Instantaneous Velocity (Revisiting the Tortoise and Hare) Period: Date:
 Name: Period: Date: For this assignment: Re-read the Tortoise vs. the Hare story (2-1) All the needed information is on this assignment or in the reading Every question requires you to go back to previous
Name: Period: Date: For this assignment: Re-read the Tortoise vs. the Hare story (2-1) All the needed information is on this assignment or in the reading Every question requires you to go back to previous
Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST **
 Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST ** 1. What is a force? A push or a pull on an object. Forces have size and direction.
Physical Science Forces and Motion Study Guide ** YOU MUST ALSO USE THE NOTES PROVIDED IN CLASS TO PREPARE FOR THE TEST ** 1. What is a force? A push or a pull on an object. Forces have size and direction.
ALGEBRA 1 SUMMER MATH CALENDAR STUDENT NAME:
 ALGEBRA 1 SUMMER MATH CALENDAR STUDENT NAME: All students should also be spending at least 30 minutes a week on Moby Max. To access Moby Max, sign into your Office 365 account, go to the open app launcher
ALGEBRA 1 SUMMER MATH CALENDAR STUDENT NAME: All students should also be spending at least 30 minutes a week on Moby Max. To access Moby Max, sign into your Office 365 account, go to the open app launcher
Describe the layers of the Earth Understand what plates are and how they move
 Lesson links Lesson 1 layers of the earth and plate boundaries Lesson 2 How and why a volcano erupts Lesson 3 The impacts of a volcanic eruption Mt St Helen s (learning Milestone) Lesson 4 How an earthquake
Lesson links Lesson 1 layers of the earth and plate boundaries Lesson 2 How and why a volcano erupts Lesson 3 The impacts of a volcanic eruption Mt St Helen s (learning Milestone) Lesson 4 How an earthquake
Methods and Tools of Physics
 Methods and Tools of Physics Order of Magnitude Estimation: Essential idea: Scientists aim towards designing experiments that can give a true value from their measurements, but due to the limited precision
Methods and Tools of Physics Order of Magnitude Estimation: Essential idea: Scientists aim towards designing experiments that can give a true value from their measurements, but due to the limited precision
7.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 7.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Learn how to solve a sstem of linear equations b graphing Learn how to model a real-life situation using a sstem of linear equations With an equation, an
7.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Learn how to solve a sstem of linear equations b graphing Learn how to model a real-life situation using a sstem of linear equations With an equation, an
M1-Lesson 8: Bell Curves and Standard Deviation
 M1-Lesson 8: Bell Curves and Standard Deviation 1. Read over the description of a bell curve and then mark the picture with the characteristics of the curve. Which characteristic was confusing for you?
M1-Lesson 8: Bell Curves and Standard Deviation 1. Read over the description of a bell curve and then mark the picture with the characteristics of the curve. Which characteristic was confusing for you?
Summer Solutions Common Core Mathematics 8. Common Core. Mathematics. Help Pages
 8 Common Core Mathematics 6 6 Vocabulary absolute value additive inverse property adjacent angles the distance between a number and zero on a number line. Example: the absolute value of negative seven
8 Common Core Mathematics 6 6 Vocabulary absolute value additive inverse property adjacent angles the distance between a number and zero on a number line. Example: the absolute value of negative seven
Lesson 5: Solving Linear Systems Problem Solving Assignment solutions
 Write inequalities to represent the following problem, and then solve to answer the question. 1. The Rent-A-Lemon Car Rental Company charges $60 a day to rent a car and an additional $0.40 per mile. Alex
Write inequalities to represent the following problem, and then solve to answer the question. 1. The Rent-A-Lemon Car Rental Company charges $60 a day to rent a car and an additional $0.40 per mile. Alex
Math 8 Honors Coordinate Geometry part 1 Unit Updated July 29, 2016
 Reviewing the basics The number line A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number lines. The top left one includes only positive whole numbers,
Reviewing the basics The number line A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number lines. The top left one includes only positive whole numbers,
AP Calculus. Applications of Derivatives. Table of Contents
 AP Calculus 2015 11 03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Related Rates Linear Motion Linear Approximation & Differentials L'Hopital's Rule Horizontal Tangents 1 Related
AP Calculus 2015 11 03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Related Rates Linear Motion Linear Approximation & Differentials L'Hopital's Rule Horizontal Tangents 1 Related
Physics #1 - Motion Notebook
 Name Hour Group # Test Date Physics #1 - Motion Notebook Physics #1 - LEARNING Targets Physics #1 Vocabulary: You re The Scientist #1 Getting to Know a Physicist! You will research a physicist and create
Name Hour Group # Test Date Physics #1 - Motion Notebook Physics #1 - LEARNING Targets Physics #1 Vocabulary: You re The Scientist #1 Getting to Know a Physicist! You will research a physicist and create
General Physics. Linear Motion. Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha
 General Physics Linear Motion Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha High Throw How high can a human throw something? Mechanics The study of motion Kinematics Description
General Physics Linear Motion Life is in infinite motion; at the same time it is motionless. Debasish Mridha High Throw How high can a human throw something? Mechanics The study of motion Kinematics Description
Processes and Impact of Natural Hazards
 The Big Island of Hawaii is the largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is also home to a very active volcano. The Kilauea volcano has been active since 1983. The lava that flows from the Kilauea volcano has
The Big Island of Hawaii is the largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is also home to a very active volcano. The Kilauea volcano has been active since 1983. The lava that flows from the Kilauea volcano has
Day 5 Notes: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Particle Motion, and Average Value
 AP Calculus Unit 6 Basic Integration & Applications Day 5 Notes: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Particle Motion, and Average Value b (1) v( t) dt p( b) p( a), where v(t) represents the velocity and
AP Calculus Unit 6 Basic Integration & Applications Day 5 Notes: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, Particle Motion, and Average Value b (1) v( t) dt p( b) p( a), where v(t) represents the velocity and
Bellringer Day In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules?
 Bellringer Day 01 1. In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules? Lab Safety Video Lab Safety Map See if you can identify the lab safety equipment around the room. You can discuss
Bellringer Day 01 1. In your opinion, what are the five most important lab safety rules? Lab Safety Video Lab Safety Map See if you can identify the lab safety equipment around the room. You can discuss
The line that passes through the point A ( and parallel to the vector v = (a, b, c) has parametric equations:,,
 Vectors: Lines in Space A straight line can be determined by any two points in space. A line can also be determined by specifying a point on it and a direction. The direction would be a non-zero parallel
Vectors: Lines in Space A straight line can be determined by any two points in space. A line can also be determined by specifying a point on it and a direction. The direction would be a non-zero parallel
Not all eruptions are the same. Sometimes, there is a huge explosion. The hot magma shoots
 Natural Disasters A natural disaster is an event that happens in nature. It is an event that can cause a lot of damage. Volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis are all natural disasters. Volcanoes A volcano
Natural Disasters A natural disaster is an event that happens in nature. It is an event that can cause a lot of damage. Volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis are all natural disasters. Volcanoes A volcano
Transportation Costs (or Trucker s Dilemma) Math 1050 College Algebra Project
 Name Carlos Vega Date 03/11/16 Transportation Costs (or Trucker s Dilemma) Math 1050 College Algebra Project A truck driving 260 miles over a flat interstate at a constant rate of 50 miles per hour gets
Name Carlos Vega Date 03/11/16 Transportation Costs (or Trucker s Dilemma) Math 1050 College Algebra Project A truck driving 260 miles over a flat interstate at a constant rate of 50 miles per hour gets
Pre-Calculus Module 4
 Pre-Calculus Module 4 4 th Nine Weeks Table of Contents Precalculus Module 4 Unit 9 Rational Functions Rational Functions with Removable Discontinuities (1 5) End Behavior of Rational Functions (6) Rational
Pre-Calculus Module 4 4 th Nine Weeks Table of Contents Precalculus Module 4 Unit 9 Rational Functions Rational Functions with Removable Discontinuities (1 5) End Behavior of Rational Functions (6) Rational
Conceptual Explanations: Simultaneous Equations Distance, rate, and time
 Conceptual Explanations: Simultaneous Equations Distance, rate, and time If you travel 30 miles per hour for 4 hours, how far do you go? A little common sense will tell you that the answer is 120 miles.
Conceptual Explanations: Simultaneous Equations Distance, rate, and time If you travel 30 miles per hour for 4 hours, how far do you go? A little common sense will tell you that the answer is 120 miles.
3/24/2016. Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016
 Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
Geology 12 Mr. M. Gauthier 24 March 2016 Introduction: Mt. St. Helens Before 1980 Mt. St Helens, in Southern Washington State, had not erupted since 1857 On March 27,1980 minor ashand eruptions were due
LAB 7. Lab 7. Formation of Geologic Features: How Can We Explain the Growth of the Hawaiian Archipelago Over the Past 100 Million Years?
 LAB 7 Lab Handout Lab 7. Formation of Geologic Features: How Can We Explain the Growth of the Hawaiian Archipelago Over the Past 100 Million Years? Introduction Scientists use the theory of plate tectonics
LAB 7 Lab Handout Lab 7. Formation of Geologic Features: How Can We Explain the Growth of the Hawaiian Archipelago Over the Past 100 Million Years? Introduction Scientists use the theory of plate tectonics
Beadle Plasticus Evolution Teacher Information
 STO-125 Beadle Plasticus Evolution Teacher Information Summary Students model the effects of two different environments on the frequencies of characteristics in a simulated Beadle population. Core Concepts
STO-125 Beadle Plasticus Evolution Teacher Information Summary Students model the effects of two different environments on the frequencies of characteristics in a simulated Beadle population. Core Concepts
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere. Volcanic Activity
 Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Goal 2.1 Forces in the Lithosphere Volcanic Activity Lesson 3 Volcanoes, Part 1 Think About It What happens when you shake a can of soda and then open it? Focus Question How does the composition of magma
Name: Problem Possible Score Number Points Total 140
 Name: Math Xa Final Examination Part II Thursday, January 20, 2005 Please circle your section: Thomas Judson Angela Vierling-Claassen David Harvey Ben Weinkove Jennie Schiffman (CA) Connie Zong (CA) Margaret
Name: Math Xa Final Examination Part II Thursday, January 20, 2005 Please circle your section: Thomas Judson Angela Vierling-Claassen David Harvey Ben Weinkove Jennie Schiffman (CA) Connie Zong (CA) Margaret
Volcanic Hazards: Airborne Debris
 Activity 4 Volcanic Hazards: Airborne Debris Goals In this activity you will: Understand why ash from volcanic eruptions can affect a much larger region than lava, pyroclastic flows, or lahars. Define
Activity 4 Volcanic Hazards: Airborne Debris Goals In this activity you will: Understand why ash from volcanic eruptions can affect a much larger region than lava, pyroclastic flows, or lahars. Define
Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Academic Standards Mathematics
 6 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compare and order positive and negative integers*, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. They find multiples*
6 th GRADE Archdiocese of Washington Catholic Schools Standard 1 - Number Sense Students compare and order positive and negative integers*, decimals, fractions, and mixed numbers. They find multiples*
PLC Papers Created For:
 PLC Papers Created For: Year 11 Topic Practice Paper: Solving Quadratics (Graphically) Quadratic equations (graphical methods) 1 Grade 6 Objective: Find approximate solutions to quadratic equations using
PLC Papers Created For: Year 11 Topic Practice Paper: Solving Quadratics (Graphically) Quadratic equations (graphical methods) 1 Grade 6 Objective: Find approximate solutions to quadratic equations using
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES. ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra I Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES ALGEBRA I Part II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra I Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
Chapter 6. Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 6 Systems of Equations and Inequalities 6.1 Solve Linear Systems by Graphing I can graph and solve systems of linear equations. CC.9-12.A.CED.2, CC.9-12.A.CED.3, CC.9-12.A.REI.6 What is a system
Chapter 6 Systems of Equations and Inequalities 6.1 Solve Linear Systems by Graphing I can graph and solve systems of linear equations. CC.9-12.A.CED.2, CC.9-12.A.CED.3, CC.9-12.A.REI.6 What is a system
1.6 The Tortoise and the Hare A Solidify Understanding Task
 29 1.6 The Tortoise and the Hare A Solidify Understanding Task In the children s story of the tortoise and the hare, the hare mocks the tortoise for being slow. The tortoise replies, Slow and steady wins
29 1.6 The Tortoise and the Hare A Solidify Understanding Task In the children s story of the tortoise and the hare, the hare mocks the tortoise for being slow. The tortoise replies, Slow and steady wins
Ch 3 Exam Review. Plot the ordered pairs on the rectangular coordinate system provided. 3) A(1, 3), B(-5, 3)
 Ch 3 Exam Review Note: These are only a sample of the type of problems that may appear on the exam. Keep in mind, anything covered in class can be covered on the exam. Solve the problem. 1) This bar graph
Ch 3 Exam Review Note: These are only a sample of the type of problems that may appear on the exam. Keep in mind, anything covered in class can be covered on the exam. Solve the problem. 1) This bar graph
Mathematical Reasoning Understanding Pre-Algebra: Middle School Mathematics. Table of Contents. Introduction... ii
 Mathematical Reasoning Understanding Pre-Algebra: Middle School Mathematics Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... ii Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Family of Numbers...1-14 Family
Mathematical Reasoning Understanding Pre-Algebra: Middle School Mathematics Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... ii Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 Chapter 4 Family of Numbers...1-14 Family
The slope, m, compares the change in y-values to the change in x-values. Use the points (2, 4) and (6, 6) to determine the slope.
 LESSON Relating Slope and -intercept to Linear Equations UNDERSTAND The slope of a line is the ratio of the line s vertical change, called the rise, to its horizontal change, called the run. You can find
LESSON Relating Slope and -intercept to Linear Equations UNDERSTAND The slope of a line is the ratio of the line s vertical change, called the rise, to its horizontal change, called the run. You can find
GRE Workshop Quantitative Reasoning. February 13 and 20, 2018
 GRE Workshop Quantitative Reasoning February 13 and 20, 2018 Overview Welcome and introduction Tonight: arithmetic and algebra 6-7:15 arithmetic 7:15 break 7:30-8:45 algebra Time permitting, we ll start
GRE Workshop Quantitative Reasoning February 13 and 20, 2018 Overview Welcome and introduction Tonight: arithmetic and algebra 6-7:15 arithmetic 7:15 break 7:30-8:45 algebra Time permitting, we ll start
DMA 50 Worksheet #1 Introduction to Graphs: Analyzing, Interpreting, and Creating Graphs
 DMA 0 Worksheet #1 Introduction to Graphs: Analzing, Interpreting, and Creating Graphs A graph will be given followed b a set of questions to answer. Show our work. The bar graph below shows the number
DMA 0 Worksheet #1 Introduction to Graphs: Analzing, Interpreting, and Creating Graphs A graph will be given followed b a set of questions to answer. Show our work. The bar graph below shows the number
Name Date Period. Worksheet 1.5 Continuity on Intervals & IVT. Show all work. No Calculator (unless stated otherwise) Short Answer
 Name Date Period Worksheet 1.5 Continuity on Intervals & IVT Show all work. No Calculator (unless stated otherwise) Short Answer 1. A piece of the graph of (a) Sketch a graph of f ( x). x, x 1 f( x) =
Name Date Period Worksheet 1.5 Continuity on Intervals & IVT Show all work. No Calculator (unless stated otherwise) Short Answer 1. A piece of the graph of (a) Sketch a graph of f ( x). x, x 1 f( x) =
5E's. View the video clip:
 5E's TEKS 8.10 (C) identify the role of the oceans in the formation of weather systems such as hurricanes Engage View the video clip: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h9vpwmtnozc What is a hurricane? How
5E's TEKS 8.10 (C) identify the role of the oceans in the formation of weather systems such as hurricanes Engage View the video clip: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h9vpwmtnozc What is a hurricane? How
The New Madrid Earthquakes on :
 RESOURCES Important Earthquakes in History Where, sequence of events, additional hazards, $ amount of property damage, death and injury toll, interesting fact and/or inspirational stories, other earthquakes
RESOURCES Important Earthquakes in History Where, sequence of events, additional hazards, $ amount of property damage, death and injury toll, interesting fact and/or inspirational stories, other earthquakes
