AP Calculus. Applications of Derivatives. Table of Contents
|
|
|
- Emery Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AP Calculus Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Related Rates Linear Motion Linear Approximation & Differentials L'Hopital's Rule Horizontal Tangents 1
2 Related Rates Teacher Notes Return to Table of Contents Related Rates Related Rates is the application of implicit differentiation (which we learned in the previous unit) to real life situations. In simplest terms, related rates are problems in which you need to figure out how fast one variable is changing when given the rate of change of another variable at a specific point in time. Teacher Notes For example, if a spherical balloon is being filled with air at a rate of 20 ft 3 /min, how fast is the radius changing when the radius is 2 feet? 2
3 Recall: Implicit Differentiation Before we attempt a Related Rates example, let's practice a few implicit differentiation examples first. Differentiate each equation with respect to time, t. 1) Draw a picture. Label the picture with numbers if constant or variables if changing. 2) Identify which rate of change is given and which rate of change you are being asked to find. 3) Find a formula/equation that relates the variables whose rate of change you seek with one or more variables whose rate of change you know. 4) Implicitly differentiate with respect to time, t. 5) Plug in values you know. Helpful Steps for Solving Related Rates Problems 6) Solve for rate of change you are being asked for. 7) the question. Try to write your answer in a sentence to eliminate confusion. Teacher Notes 3
4 Step 3 Step 3 requires you to think of an equation to relate variables. Some questions on the AP Exam will provide the equation for you, but if not, think of: trigonometry similar triangles Pythagorean theorem common Geometry equations Let's take a look back at this example... Example If a spherical balloon is being filled with air at a rate of 20 ft 3 /min, how fast is the radius changing when the radius is 2 feet? 1) Draw and label a picture. 2) Identify the rates of change you know and seek. 3) Find a formula/equation. 4) Implicitly differentiate with respect to time, t. 5) Plug in values you know. 6) Solve for rate of change you are being asked for. 7) the question. 4
5 Why is it important to write a sentence for an answer? In the last question we answered the following: The radius is increasing at a rate of when the radius is 2 feet. On the AP Exam, Related Rates questions are graded very critically. Graders will not award points without proper vocabulary usage (i.e. increasing or decreasing rate of change), appropriate units, and the actual correct answer. Take time when formulating your answer to make sure it makes logical sense and includes all needed information. Hands On Related Rates Lab (OPTIONAL) Click here to go to the lab titled "Related Rates" Teacher Notes 5
6 Hands On Related Rates (OPTIONAL) Items needed: 2 students 1 long rope/cord/string (at least 15 feet for best display) masking tape STEP #1 Set up masking tape in a right angle classroom with enough room for each student to walk along the tape line. Teacher Notes Hands On Related Rates (OPTIONAL) STEP #2 Student A begins at the end of one piece of tape, and Student B begins in the corner. Each student holds one end of the rope until it is taught. A B 6
7 Hands On Related Rates (OPTIONAL) STEP #3 It is imperative that student B walks at a CONSTANT and slow pace forward while student A simple walks at whatever pace needed to keep the rope taught. The class should watch Student A's rate of change over the course of his/her path. It may take several attempts to observe the result. B A Example A balloon is rising straight up from a level ground and tracked by a range finder 500 feet from lift off point. At the moment the range finder's elevation reads the angle is increasing at a rate of 0.14 radians/ minute. How fast is the balloon rising at that moment? 7
8 Example A bag is tied to the top of a 5m ladder resting against a vertical wall. Supposed the ladder begins sliding down the wall in such a way that the foot of the ladder is moving away from the wall at a constant rate of 2m/s. How fast is the bag descending at the instant the foot of the ladder is 4m from the wall? Example CHALLENGE! Water is pouring into an inverted conical tank at 2 cubic meters per minute. The tank is a right circular cone with height 16 meters and base radius of 4 meters. How fast is the water level rising when the water in the tank is 5 meters deep? 8
9 1 A person 6 feet tall is walking away from a streetlight 20 feet high at the rate of 7 ft/sec. At what rate is the length of the person's shadow increasing? A The shadow is increasing at a rate of 3/7 ft/sec. B C D E The shadow is increasing at a rate of 7/3 ft/sec. The shadow is increasing at a rate of 14 ft/sec. The shadow is increasing at a rate of 3 ft/sec. The shadow is increasing at a rate of 7 ft/sec. 2 Water leaking onto a floor forms a circular pool. The radius of the pool increases at a rate of 4 cm/min. How fast is the area of the pool increasing when the radius is 5 cm? A B C D E The area of the circle is increasing at a rate of when the radius is 5cm. The area of the circle is increasing at a rate of when the radius is 5cm. The area of the circle is increasing at a rate of when the radius is 5cm. The area of the circle is increasing at a rate of when the radius is 5cm. The area of the circle is increasing at a rate of when the radius is 5cm. cm 2 /min cm 2 /min cm 2 /min cm 2 /min cm 2 /min 9
10 3 Calculator OK Two people are 50 feet apart. One of them starts walking north at a rate so that the angle formed between them is changing at a constant rate of 0.01 rad/min. At what rate is the distance between the two people changing when radians? A B C D E The distance between the people is increasing at a rate of ft/min when radians The distance between the people is increasing at a rate of ft/min when radians The distance between the people is increasing at a rate of 0.01 ft/min when radians The distance between the people is increasing at a rate of ft/min when radians The distance between the people is increasing at a rate of 0.05 ft/min when radians 4 A trough of water is 8 meters long and its ends are in the shape of isosceles triangles whose width is 5 meters and height is 2 meters. If water is being pumped in at a constant rate of 6 m 3 /sec. At what rate is the height of the water changing when the water has a height of 120 cm? A B C D E The height of the water is increasing at a rate of 0.3 m/sec when the water is 120cm high. The height of the water is increasing at a rate of 6 m/sec when the water is 120cm high. The height of the water is increasing at a rate of 0.25 m/sec when the water is 120cm high. The height of the water is increasing at a rate of 40 m/sec when the water is 120cm high. The height of the water is increasing at a rate of 20 m/sec when the water is 120cm high. 10
11 5 The sides of the rectangle pictured increase in such a way that and. At the instant where x=4 and y=3, what is the value of y x z A B C D E 6 If the base, b, of a triangle is increasing at a rate of 3 inches per minute while it's height, h, is decreasing at a rate of 3 inches per minute, which of the following must be true about the area, A, of the triangle? A B C D E A is always increasing. A is always decreasing. A is decreasing only when b < h. A is decreasing only when b > h. A remains constant. 11
12 The minute hand of a certain clock is 4 in. long. Starting from the moment that the hand is pointing straight up, how fast is the area of the sector that is swept out by the hand increasing at any instant during the next revolution of the hand? Note: Area of a sector Linear Motion Return to Table of Contents 12
13 Linear Motion Another useful application of derivatives is to describe the linear motion of an object in two dimensions, either left and right, or up and down. This is a concept where calculus is extremely applicable. We will revisit this topic again in the next unit involving graphing, and again in the unit about integrals! Position, Velocity & Acceleration A remarkable relationship exists among the position of an object, the velocity of an object and the acceleration of an object. First... let's review what each of these words mean. Position Velocity Acceleration Teacher Notes 13
14 Are Velocity and Speed the Same Thing? Although you may hear velocity and speed interchanged often in common conversation, they are, in fact, 2 distinct quantities. Sometimes they are equivalent to each other, but this depends on the direction of the object. Velocity is a vector quantity meaning it has both magnitude and direction. Teacher Notes For example, if the velocity of an object is 3 feet per second, then that object is moving backwards or to the left (direction) at a rate of 3 feet per second (magnitude). Distance vs. Position Similarly, there is a difference between distance and position. Distance is how far something has traveled in total; distance is a quantity. Whereas position is the location of an object compared to a reference point; position is a distance with a direction. 14
15 Typical Notation for Linear Motion Problems is the notation for our position function is the notation for our velocity function is the notation for our acceleration function Example Consider driving your car along the highway. The time it takes you to travel from mile marker 27 to mile marker 105 is an hour and a half. How fast were you driving? 15
16 Average Velocity vs. Instantaneous Velocity We know that the average velocity can be found by dividing the distance traveled by the time; however, how can we find the instantaneous velocity (how fast you are traveling at a specific moment in time)? Because we are interested in the instantaneous rate of change of a position, we are able to take the derivative of the position function and find the instantaneous velocity. Note: This requires a position function to be given. Position, Velocity & Acceleration Therefore, if given a position function, x, as a function of t. The velocity of the object is given by: Furthermore, the acceleration of the object is: is also commonly used for position Teacher Notes 16
17 Example A race car is driven down a straight road such that after seconds it is feet from its origin. a) Find the instantaneous velocity after 8 seconds. b) What is the car's acceleration? Example A spring is pulled to 6 inches below its resting state and bounces up and down. Its position is modeled by. a) Find its velocity and acceleration at time t. b) Find the spring's velocity and acceleration after seconds. 17
18 Example A dynamite blast shoots a rock straight up into the air. Its height at any given time is feet after t seconds. a) How high does the rock travel? b) What is the velocity and speed of the rock when it is 256 feet above ground? c) What is the acceleration at any time, t? d) When does the rock hit the ground? One More Reminder! What is the difference between: Average Velocity Instantaneous Velocity Teacher Notes 18
19 7 A particle moves along the x axis so that at any time t>0 seconds its velocity is given by m/s. What is the acceleration of the particle at time? A B C D E 8 A particle moves along the x axis so that at any time t>0 minutes its position is given by. For what values of t is the particle at rest? A B C D E No values only only only 19
20 9 The position of a particle moving along a straight line at any time t is given by. What is the acceleration of the particle when t=4? A B C D E 10 A mouse runs through a straight pipe such that his position at any time is inches. Find the average velocity during the first 5 seconds. A B C D E 20
21 11 An object moves along the x axis so that at time t>0 its position is given by meters. Find the speed of the object at t=3 seconds. A B C D E A rock thrown vertically upward from the surface of the moon at a velocity of 24m/s reaches a height of meters in t seconds. Find the rock's acceleration as a function of time. 21
22 A rock thrown vertically upward from the surface of the moon at a velocity of 24m/s reaches a height of meters in t seconds. Find the rock's average velocity during the first 3 sec. A rock thrown vertically upward from the surface of the moon at a velocity of 24m/s reaches a height of meters in t seconds. Find the rock's instantaneous velocity at t=3 sec. 22
23 Linear Approximation & Differentials Return to Table of Contents Linear Approximation In the last unit we explored what it meant for a differentiable function to be "locally linear". Also in the previous unit, we discussed how to find the equation of a tangent line to a function. In this section, we will expand on those ideas and how they become useful in a topic called Linear Approximation. 23
24 What is the Purpose of Linear Approximation? Let's consider the graph of Zoomed in If asked to evaluate we could quickly conclude the answer is 3. However, if asked to evaluate, we know the answer is near 3 but don't have a very accurate estimate. Linear approximation allows us to better estimate this value using a tangent line. Linear Approximation Observe the black tangent line to the function at x=9. If we write the equation of the tangent line at x=9, we can then use this line and substitute 8.9 into our equation to find an approximation for f(8.9). Again, it won't be exact, but will be much closer than just saying 3. 24
25 To Find the Linear Approximation: not whole whole whole whole not whole Teacher Notes For the sake of understanding we will refer to as the "whole" number (i.e. x=9), and as the "not whole" number (i.e. x=8.9) Example Practice: Use linear approximation to approximate the value of f(8.9). 25
26 Example, Continued Is our approximation greater than or less than the actual value of f(8.9)? Why or why not? Teacher Notes Example Given, approximate. 26
27 Example Given, approximate. Given Approximate 27
28 12 For the previous question, is the approximation of greater than or less than the actual value? You may look at a graph of the function to decide. Recall A Greater than B Less than Given and approximate the value of 28
29 Given Approximate Find the approximate value of using linear approximation. 29
30 Given and approximate the value of Approximate the value of 30
31 Differentials So far we have been discussing and, but sometimes in calculus we are interested in only. We call this the differential. The process is fairly simple given we already know how to find. This is called differential form. Differentials Let's try an example: Find the differential. 31
32 Practice Now let's practice with given values to substitute... Given find when and vs. Note the difference between and. If we calculate both, we can then compare the values to calculate the percentage change or approximation error. 32
33 Example The radius of a circle increases from 10 cm to 10.1 cm. Use to estimate the increase in the circle's Area,. Compare this estimate with the true change,, and find the approximation error. Find the differential if 33
34 Find the differential if 13 Find and evaluate for the given values of and. A B C D E F 34
35 14 Find and evaluate for the given values of and. A B C D E F Given,, and calculate the estimated change. 35
36 Given,, and calculate the true change. Given,, and calculate the approximation error. 36
37 L'Hopital's Rule Return to Table of Contents L'Hopital's Rule One additional application of derivatives actually applies to solving limit questions! 37
38 L'Hopital's Rule (pronounced "Lho pee talls") Guillaume de L'Hopital was a french mathematicion from the 17th century. He is known most commonly for his work calculating limits involving indeterminate forms and. L'Hopital was the first to publish this notion, but gives credit to the Bernoulli brothers for their work in this area. Cool Fact! In the 17th and 18th centuries, the name was commonly spelled "L'Hospital", however, French spellings have been altered and the silent 's' has been dropped. Indeterminate Form Recall from the limits unit when we woud try to substitute our value into the limit expression and it would result in either or, known as indeterminate forms. As we know, upon substitution, this results in and indeterminate form, and our previous method was to factor, reduce and substitute again. 38
39 L'Hopital discovered an alternative way of dealing with these limits! L'HOPITAL'S RULE Suppose you have one of the following cases: or Teacher Notes Then, L'Hopital's Rule What does this mean? You now have an alternative method for calculating these indeterminate limits. Why didn't you learn this method earlier? You didn't know how to find a derivative yet! 39
40 Example Let's try L'Hopital's Rule on our previous example: Example Evaluate the following limit: 40
41 Evaluate the following limit: Example Note: L'Hopital's Rule can be applied more than one time, if needed. Important Fact to Remember: ONLY use L'Hopital's Rule on quotients that result in an indeterminate form upon substitution. Using the rule on other limits may, and often will, result in incorrect answers. 41
42 15 Evaluate the following limit: A B C D E 16 Evaluate the following limit: A B C D E 42
43 17 Evaluate the following limit: A B C D E 18 Evaluate the following limit: A B C D E Hint: Sometimes it is helpful to rewrite before applying L'Hopital's Rule. 43
44 19 Evaluate the following limit: A B C D E Horizontal Tangents Return to Table of Contents 44
45 Tangent Lines Recall what it means to be tangent to a function. We could draw an infinite amount of tangent lines below; however, looking at the ones given what observations can you make about the black tangent lines? Teacher Notes Horizontal Tangents Do you think there is a way to find out where the horizontal tangents are occurring aside from just estimating? Teacher Notes 45
46 Let's try an example... Example At what x value(s) does the following function have a horizontal tangent line? Example At what point(s) does the following function have a horizontal tangent line? ***Note the alternative wording. Pay attention on the AP Exam! Some questions will only ask for the x value, but if you are asked at what point(s) the function has horizontal tangent lines, you need both the x and y coordinates. 46
47 Example At what x value(s) does the following function have a horizontal tangent line? 20 At what x value(s) does the following function have a horizontal tangent line? A D B C E F G No Horizontal Tangents 47
48 21 At what x value(s) does the following function have a horizontal tangent line? A D B C E F G No Horizontal Tangents At what point(s) does the following function have a horizontal tangent line? 48
49 22 At what x value(s) does the following function have a horizontal tangent line? A D B C E F G No Horizontal Tangents 23 At what x value(s) does the following function have a horizontal tangent line? A D B C E F G No Horizontal Tangents 49
50 At what point(s) does the following function have a horizontal tangent line? 24 At what x value(s) does the following function have a horizontal tangent line? A D B C E F G No Horizontal Tangents 50
AP Calculus. Slide 1 / 101. Slide 2 / 101. Slide 3 / 101. Applications of Derivatives. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 101 Slide 2 / 101 AP Calculus Applications of Derivatives 2015-11-03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 101 Related Rates Linear Motion Linear
Slide 1 / 101 Slide 2 / 101 AP Calculus Applications of Derivatives 2015-11-03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 101 Related Rates Linear Motion Linear
AP Calculus. Related Rates. Related Rates. Slide 1 / 101 Slide 2 / 101. Slide 4 / 101. Slide 3 / 101. Slide 4 (Answer) / 101.
 Slide 1 / 101 Slide 2 / 101 P alculus pplications of erivatives 2015-11-03 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 101 Slide 4 / 101 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Related Rates Linear Motion
Slide 1 / 101 Slide 2 / 101 P alculus pplications of erivatives 2015-11-03 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 101 Slide 4 / 101 Table of ontents click on the topic to go to that section Related Rates Linear Motion
Implicit Differentiation
 Week 6. Implicit Differentiation Let s say we want to differentiate the equation of a circle: y 2 + x 2 =9 Using the techniques we know so far, we need to write the equation as a function of one variable
Week 6. Implicit Differentiation Let s say we want to differentiate the equation of a circle: y 2 + x 2 =9 Using the techniques we know so far, we need to write the equation as a function of one variable
AP Calculus AB Chapter 4 Packet Implicit Differentiation. 4.5: Implicit Functions
 4.5: Implicit Functions We can employ implicit differentiation when an equation that defines a function is so complicated that we cannot use an explicit rule to find the derivative. EXAMPLE 1: Find dy
4.5: Implicit Functions We can employ implicit differentiation when an equation that defines a function is so complicated that we cannot use an explicit rule to find the derivative. EXAMPLE 1: Find dy
Section 4.1: Related Rates
 1 Section 4.1: Related Rates Practice HW from Stewart Textbook (not to hand in) p. 67 # 1-19 odd, 3, 5, 9 In a related rates problem, we want to compute the rate of change of one quantity in terms of the
1 Section 4.1: Related Rates Practice HW from Stewart Textbook (not to hand in) p. 67 # 1-19 odd, 3, 5, 9 In a related rates problem, we want to compute the rate of change of one quantity in terms of the
Guidelines for implicit differentiation
 Guidelines for implicit differentiation Given an equation with x s and y s scattered, to differentiate we use implicit differentiation. Some informal guidelines to differentiate an equation containing
Guidelines for implicit differentiation Given an equation with x s and y s scattered, to differentiate we use implicit differentiation. Some informal guidelines to differentiate an equation containing
4.1 & 4.2 Student Notes Using the First and Second Derivatives. for all x in D, where D is the domain of f. The number f()
 4.1 & 4. Student Notes Using the First and Second Derivatives Definition A function f has an absolute maximum (or global maximum) at c if f ( c) f ( x) for all x in D, where D is the domain of f. The number
4.1 & 4. Student Notes Using the First and Second Derivatives Definition A function f has an absolute maximum (or global maximum) at c if f ( c) f ( x) for all x in D, where D is the domain of f. The number
6.2 Related Rates Name: Notes
 Calculus Write your questions and thoughts here! 6.2 Related Rates Name: Notes Guidelines to solving related rate problems 1. Draw a picture. 2. Make a list of all known and unknown rates and quantities.
Calculus Write your questions and thoughts here! 6.2 Related Rates Name: Notes Guidelines to solving related rate problems 1. Draw a picture. 2. Make a list of all known and unknown rates and quantities.
4.1 Implicit Differentiation
 4.1 Implicit Differentiation Learning Objectives A student will be able to: Find the derivative of variety of functions by using the technique of implicit differentiation. Consider the equation We want
4.1 Implicit Differentiation Learning Objectives A student will be able to: Find the derivative of variety of functions by using the technique of implicit differentiation. Consider the equation We want
Related Rates STEP 1 STEP 2:
 Related Rates You can use derivative analysis to determine how two related quantities also have rates of change which are related together. I ll lead off with this example. 3 Ex) A spherical ball is being
Related Rates You can use derivative analysis to determine how two related quantities also have rates of change which are related together. I ll lead off with this example. 3 Ex) A spherical ball is being
4.6 Related Rates Notes RELATED RATES PROBLEMS --- IT S AS EASY AS 1 2-3!
 4.6 Related Rates Notes RELATED RATES PROBLEMS --- IT S AS EASY AS 1 2-3! 1) Draw a picture. Label all variables and constant values. Identify the given rate of change, the rate to be found, and when to
4.6 Related Rates Notes RELATED RATES PROBLEMS --- IT S AS EASY AS 1 2-3! 1) Draw a picture. Label all variables and constant values. Identify the given rate of change, the rate to be found, and when to
Chapter 3.4 Practice Problems
 EXPECTED SKILLS: Chapter.4 Practice Problems Be able to solve related rates problems. It may be helpful to remember the following strategy:. Read the problem carefully. 2. Draw a diagram, if possible,
EXPECTED SKILLS: Chapter.4 Practice Problems Be able to solve related rates problems. It may be helpful to remember the following strategy:. Read the problem carefully. 2. Draw a diagram, if possible,
with dt. with 2. If x = u, find an equation relating du dt
 MATH 2250 Royal Section 3.10: Related Rates EXPANDED VERSION In this section, we consider two (or more) dependent variables that depend on a third variable (the independent variable). Usually, the independent
MATH 2250 Royal Section 3.10: Related Rates EXPANDED VERSION In this section, we consider two (or more) dependent variables that depend on a third variable (the independent variable). Usually, the independent
Name Date Class. Logarithmic/Exponential Differentiation and Related Rates Review AP Calculus. Find dy. dx. 1. y 4 x. y 6. 3e x.
 Name Date Class Find dy d. Logarithmic/Eponential Differentiation and Related Rates Review AP Calculus 1. y 4. 1 y ln. y ln 1 4. y log9 1 5. e y 6. y log 7. y e 8. e y e 4 1 1 9. y e e 10. 1 y ln 1 e 11.
Name Date Class Find dy d. Logarithmic/Eponential Differentiation and Related Rates Review AP Calculus 1. y 4. 1 y ln. y ln 1 4. y log9 1 5. e y 6. y log 7. y e 8. e y e 4 1 1 9. y e e 10. 1 y ln 1 e 11.
Related Rates. 2. List the relevant quantities in the problem and assign them appropriate variables. Then write down all the information given.
 Calculus 1 Lia Vas Related Rates The most important reason for a non-mathematics major to learn mathematics is to be able to apply it to problems from other disciplines or real life. In this section, we
Calculus 1 Lia Vas Related Rates The most important reason for a non-mathematics major to learn mathematics is to be able to apply it to problems from other disciplines or real life. In this section, we
AP Calculus Related Rates Worksheet
 AP Calculus Related Rates Worksheet 1. A small balloon is released at a point 150 feet from an observer, who is on level ground. If the balloon goes straight up at a rate of 8 feet per second, how fast
AP Calculus Related Rates Worksheet 1. A small balloon is released at a point 150 feet from an observer, who is on level ground. If the balloon goes straight up at a rate of 8 feet per second, how fast
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES If we are pumping air into a balloon, both the volume and the radius of the balloon are increasing and their rates of increase are related to each other. However,
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES If we are pumping air into a balloon, both the volume and the radius of the balloon are increasing and their rates of increase are related to each other. However,
Chapter 8: Radical Functions
 Chapter 8: Radical Functions Chapter 8 Overview: Types and Traits of Radical Functions Vocabulary:. Radical (Irrational) Function an epression whose general equation contains a root of a variable and possibly
Chapter 8: Radical Functions Chapter 8 Overview: Types and Traits of Radical Functions Vocabulary:. Radical (Irrational) Function an epression whose general equation contains a root of a variable and possibly
Days 3 & 4 Notes: Related Rates
 AP Calculus Unit 4 Applications of the Derivative Part 1 Days 3 & 4 Notes: Related Rates Implicitly differentiate the following formulas with respect to time. State what each rate in the differential equation
AP Calculus Unit 4 Applications of the Derivative Part 1 Days 3 & 4 Notes: Related Rates Implicitly differentiate the following formulas with respect to time. State what each rate in the differential equation
APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS
 APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS PROBLEM SET #1 Related Rates ***Calculators Allowed*** 1. An oil tanker spills oil that spreads in a circular pattern whose radius increases at the rate of
APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES UNIT PROBLEM SETS PROBLEM SET #1 Related Rates ***Calculators Allowed*** 1. An oil tanker spills oil that spreads in a circular pattern whose radius increases at the rate of
Unit 5 ICM/AB Applications of the Derivative Fall Nov 10 Learn Velocity and Acceleration: HW p P ,103 p.
 Unit 5 ICM/AB Applications of the Derivative Fall 2016 Nov 4 Learn Optimization, New PS up on Optimization, HW pg. 216 3,5,17,19,21,23,25,27,29,33,39,41,49,50 a,b,54 Nov 7 Continue on HW from Nov 4 and
Unit 5 ICM/AB Applications of the Derivative Fall 2016 Nov 4 Learn Optimization, New PS up on Optimization, HW pg. 216 3,5,17,19,21,23,25,27,29,33,39,41,49,50 a,b,54 Nov 7 Continue on HW from Nov 4 and
Section 3.8 Related Rates
 Section 3.8 Related Rates Read and re-read the problem until you understand it. Draw and label a picture which gives the relevant information (if possible). Introduce notation. Assign a symbol to every
Section 3.8 Related Rates Read and re-read the problem until you understand it. Draw and label a picture which gives the relevant information (if possible). Introduce notation. Assign a symbol to every
Calculus 437 Semester 1 Review Chapters 1, 2, and 3 January 2016
 Name: Class: Date: Calculus 437 Semester 1 Review Chapters 1, 2, and 3 January 2016 Short Answer 1. Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether calculus is required.
Name: Class: Date: Calculus 437 Semester 1 Review Chapters 1, 2, and 3 January 2016 Short Answer 1. Decide whether the following problem can be solved using precalculus, or whether calculus is required.
Chapter 3.5: Related Rates
 Expected Skills: Chapter.5: Related Rates Be able to solve related rates problems. It may be helpful to remember the following strategy:. Read the problem carefully. 2. Draw a diagram, if possible, representing
Expected Skills: Chapter.5: Related Rates Be able to solve related rates problems. It may be helpful to remember the following strategy:. Read the problem carefully. 2. Draw a diagram, if possible, representing
Implicit Differentiation
 Implicit Differentiation Much of our algebraic study of mathematics has dealt with functions. In pre-calculus, we talked about two different types of equations that relate x and y explicit and implicit.
Implicit Differentiation Much of our algebraic study of mathematics has dealt with functions. In pre-calculus, we talked about two different types of equations that relate x and y explicit and implicit.
Math Exam 02 Review
 Math 10350 Exam 02 Review 1. A differentiable function g(t) is such that g(2) = 2, g (2) = 1, g (2) = 1/2. (a) If p(t) = g(t)e t2 find p (2) and p (2). (Ans: p (2) = 7e 4 ; p (2) = 28.5e 4 ) (b) If f(t)
Math 10350 Exam 02 Review 1. A differentiable function g(t) is such that g(2) = 2, g (2) = 1, g (2) = 1/2. (a) If p(t) = g(t)e t2 find p (2) and p (2). (Ans: p (2) = 7e 4 ; p (2) = 28.5e 4 ) (b) If f(t)
p144 Section 2.6: Related Rates Find a related rate Use related rates to solve real life problems
 1 2 p144 Section 2.6: Related Rates Find a related rate Use related rates to solve real life problems Finding Related Rates We have used the chain rule to find dy/dx implicitly, but you can also use the
1 2 p144 Section 2.6: Related Rates Find a related rate Use related rates to solve real life problems Finding Related Rates We have used the chain rule to find dy/dx implicitly, but you can also use the
p144 Section 2.6: Related Rates Find a related rate Use related rates to solve real life problems
 p144 Section 2.6: Related Rates Find a related rate Use related rates to solve real life problems Finding Related Rates We have used the chain rule to find dy/dx implicitly, but you can also use the chain
p144 Section 2.6: Related Rates Find a related rate Use related rates to solve real life problems Finding Related Rates We have used the chain rule to find dy/dx implicitly, but you can also use the chain
Analyzing Functions. Implicit Functions and Implicit Differentiation
 Analyzing Functions Implicit Functions and Implicit Differentiation In mathematics, an implicit function is a generalization of the concept of a function in which the dependent variable, say, has not been
Analyzing Functions Implicit Functions and Implicit Differentiation In mathematics, an implicit function is a generalization of the concept of a function in which the dependent variable, say, has not been
Solve for an unknown rate of change using related rates of change.
 Objectives: Solve for an unknown rate of change using related rates of change. 1. Draw a diagram. 2. Label your diagram, including units. If a quantity in the diagram is not changing, label it with a number.
Objectives: Solve for an unknown rate of change using related rates of change. 1. Draw a diagram. 2. Label your diagram, including units. If a quantity in the diagram is not changing, label it with a number.
Compute the rate of change of one quantity in terms of the rate of change of another quantity.
 3.10 Related Rates Compute the rate of change of one quantity in terms of the rate of change of another quantity. Example 1: If x 2 y x + 4 = 0 and dx/dt = 3, find dy/dt when x = 1. Example 2: Air is being
3.10 Related Rates Compute the rate of change of one quantity in terms of the rate of change of another quantity. Example 1: If x 2 y x + 4 = 0 and dx/dt = 3, find dy/dt when x = 1. Example 2: Air is being
a right triangle), we see that x 200 or equivalently x = 200 tan θ. The rate at which the ray of light moves along the shore is
 Example 1: A revolving beacon in a lighthouse makes one revolution every 15 seconds. The beacon is 00 ft from the nearest point P on a straight shoreline. Find the rate at which a ray from the light moves
Example 1: A revolving beacon in a lighthouse makes one revolution every 15 seconds. The beacon is 00 ft from the nearest point P on a straight shoreline. Find the rate at which a ray from the light moves
Math 2413 t2rsu14. Name: 06/06/ Find the derivative of the following function using the limiting process.
 Name: 06/06/014 Math 413 trsu14 1. Find the derivative of the following function using the limiting process. f( x) = 4x + 5x. Find the derivative of the following function using the limiting process. f(
Name: 06/06/014 Math 413 trsu14 1. Find the derivative of the following function using the limiting process. f( x) = 4x + 5x. Find the derivative of the following function using the limiting process. f(
To conduct the experiment, each person in your group should be given a role:
 Varying Motion NAME In this activity, your group of 3 will collect data based on one person s motion. From this data, you will create graphs comparing displacement, velocity, and acceleration to time.
Varying Motion NAME In this activity, your group of 3 will collect data based on one person s motion. From this data, you will create graphs comparing displacement, velocity, and acceleration to time.
dy dx dx dx as a BC Calculus 1 The Chain Rule is notation for a which says that we have the
 2.4 2.6 BC Calculus 1 The Chain Rule dy is notation for a which says that we have the for an expression set equal to (the dependent variable), where the variable is x. This is read dee why, dee or the
2.4 2.6 BC Calculus 1 The Chain Rule dy is notation for a which says that we have the for an expression set equal to (the dependent variable), where the variable is x. This is read dee why, dee or the
1 The Derivative and Differrentiability
 1 The Derivative and Differrentiability 1.1 Derivatives and rate of change Exercise 1 Find the equation of the tangent line to f (x) = x 2 at the point (1, 1). Exercise 2 Suppose that a ball is dropped
1 The Derivative and Differrentiability 1.1 Derivatives and rate of change Exercise 1 Find the equation of the tangent line to f (x) = x 2 at the point (1, 1). Exercise 2 Suppose that a ball is dropped
Unit #5 : Implicit Differentiation, Related Rates. Goals: Introduce implicit differentiation. Study problems involving related rates.
 Unit #5 : Implicit Differentiation, Related Rates Goals: Introduce implicit differentiation. Study problems involving related rates. Textbook reading for Unit #5 : Study Sections 3.7, 4.6 Unit 5 - Page
Unit #5 : Implicit Differentiation, Related Rates Goals: Introduce implicit differentiation. Study problems involving related rates. Textbook reading for Unit #5 : Study Sections 3.7, 4.6 Unit 5 - Page
Derivatives and Rates of Change
 Sec.1 Derivatives and Rates of Change A. Slope of Secant Functions rise Recall: Slope = m = = run Slope of the Secant Line to a Function: Examples: y y = y1. From this we are able to derive: x x x1 m y
Sec.1 Derivatives and Rates of Change A. Slope of Secant Functions rise Recall: Slope = m = = run Slope of the Secant Line to a Function: Examples: y y = y1. From this we are able to derive: x x x1 m y
AP Calculus AB Semester 1 Practice Final
 Class: Date: AP Calculus AB Semester 1 Practice Final Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the limit (if it exists). lim x x + 4 x a. 6
Class: Date: AP Calculus AB Semester 1 Practice Final Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the limit (if it exists). lim x x + 4 x a. 6
Related Rates In each related rate problem there can be variations in the details. The problems, however, have the same general structure.
 Lab 6 Math 111 Spring 019 Related Rates In each related rate problem there can be variations in the details. The problems, however, have the same general structure. I. Relating Quantities: Independent
Lab 6 Math 111 Spring 019 Related Rates In each related rate problem there can be variations in the details. The problems, however, have the same general structure. I. Relating Quantities: Independent
DRAFT - Math 101 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 The Derivative of Polynomial and Exponential Functions In this section we learn how to differentiate constant functions, power functions, polynomials, and exponential functions.
3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 The Derivative of Polynomial and Exponential Functions In this section we learn how to differentiate constant functions, power functions, polynomials, and exponential functions.
Math 1710 Final Review 1 1
 Math 7 Final Review. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove 3 (2 2 +)=4. 2. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove +7 2 + =3. 3. Use the ɛ-δ definition of it to prove (32 +5 ) = 3. 4. Prove that if f() =
Math 7 Final Review. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove 3 (2 2 +)=4. 2. Use the ɛ δ definition of it to prove +7 2 + =3. 3. Use the ɛ-δ definition of it to prove (32 +5 ) = 3. 4. Prove that if f() =
College Calculus Final Review
 College Calculus Final Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the following limit. (Hint: Use the graph to calculate the limit.)
College Calculus Final Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the following limit. (Hint: Use the graph to calculate the limit.)
Final Exam Review / AP Calculus AB
 Chapter : Final Eam Review / AP Calculus AB Use the graph to find each limit. 1) lim f(), lim f(), and lim π - π + π f 5 4 1 y - - -1 - - -4-5 ) lim f(), - lim f(), and + lim f 8 6 4 y -4 - - -1-1 4 5-4
Chapter : Final Eam Review / AP Calculus AB Use the graph to find each limit. 1) lim f(), lim f(), and lim π - π + π f 5 4 1 y - - -1 - - -4-5 ) lim f(), - lim f(), and + lim f 8 6 4 y -4 - - -1-1 4 5-4
3.8 Exponential Growth and Decay
 3.8 Exponential Growth and Decay Suppose the rate of change of y with respect to t is proportional to y itself. So there is some constant k such that dy dt = ky The only solution to this equation is an
3.8 Exponential Growth and Decay Suppose the rate of change of y with respect to t is proportional to y itself. So there is some constant k such that dy dt = ky The only solution to this equation is an
AP Calculus. Derivatives.
 1 AP Calculus Derivatives 2015 11 03 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Rate of Change Slope of a Curve (Instantaneous ROC) Derivative Rules: Power, Constant, Sum/Difference Higher Order Derivatives Derivatives
1 AP Calculus Derivatives 2015 11 03 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Rate of Change Slope of a Curve (Instantaneous ROC) Derivative Rules: Power, Constant, Sum/Difference Higher Order Derivatives Derivatives
UNIT 2 SIMPLE APPLICATION OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS
 Calculus UNIT 2 SIMPLE APPLICATION OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS Structure 2.0 Introduction 2.1 Objectives 2.2 Rate of Change of Quantities 2.3 Increasing and Decreasing Function 2.4 Maima and Minima of Functions
Calculus UNIT 2 SIMPLE APPLICATION OF DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS Structure 2.0 Introduction 2.1 Objectives 2.2 Rate of Change of Quantities 2.3 Increasing and Decreasing Function 2.4 Maima and Minima of Functions
4.5 Linearization Calculus 4.5 LINEARIZATION. Notecards from Section 4.5: Linearization; Differentials. Linearization
 4.5 Linearization Calculus 4.5 LINEARIZATION Notecards from Section 4.5: Linearization; Differentials Linearization The goal of linearization is to approximate a curve with a line. Why? Because it s easier
4.5 Linearization Calculus 4.5 LINEARIZATION Notecards from Section 4.5: Linearization; Differentials Linearization The goal of linearization is to approximate a curve with a line. Why? Because it s easier
AP Calculus AB. Slide 1 / 175. Slide 2 / 175. Slide 3 / 175. Integration. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 175 Slide 2 / 175 AP Calculus AB Integration 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 175 Riemann Sums Trapezoid Approximation Area Under
Slide 1 / 175 Slide 2 / 175 AP Calculus AB Integration 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Slide 3 / 175 Riemann Sums Trapezoid Approximation Area Under
Math3A Exam #02 Solution Fall 2017
 Math3A Exam #02 Solution Fall 2017 1. Use the limit definition of the derivative to find f (x) given f ( x) x. 3 2. Use the local linear approximation for f x x at x0 8 to approximate 3 8.1 and write your
Math3A Exam #02 Solution Fall 2017 1. Use the limit definition of the derivative to find f (x) given f ( x) x. 3 2. Use the local linear approximation for f x x at x0 8 to approximate 3 8.1 and write your
A = 1 2 ab da dt = 1 da. We can find how fast the area is growing at 3 seconds by plugging everything into that differentiated equation: da
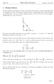 1 Related Rates In most related rates problems, we have an equation that relates a bunch of quantities that are changing over time. For example, suppose we have a right triangle whose base and height are
1 Related Rates In most related rates problems, we have an equation that relates a bunch of quantities that are changing over time. For example, suppose we have a right triangle whose base and height are
Math 2250, Spring 2017, Practice Sheet for Exam 2
 Math 2250, Spring 2017, Practice Sheet for Exam 2 (1) Find the derivative of the function f(x) = xx (x 2 4) 5 (x 1) 3 e xp x + e x (2) Solve for dy dx x 2 4y 2 =sin(xy) (3) Solve for dx dt given that e
Math 2250, Spring 2017, Practice Sheet for Exam 2 (1) Find the derivative of the function f(x) = xx (x 2 4) 5 (x 1) 3 e xp x + e x (2) Solve for dy dx x 2 4y 2 =sin(xy) (3) Solve for dx dt given that e
Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA123 exams.
 Word problems Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA3 exams. Max-min problems []. A field has the shape of a rectangle with
Word problems Chapter 7: Practice/review problems The collection of problems listed below contains questions taken from previous MA3 exams. Max-min problems []. A field has the shape of a rectangle with
AP Calculus AB. Integration. Table of Contents
 AP Calculus AB Integration 2015 11 24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Riemann Sums Trapezoid Approximation Area Under a Curve (The Definite Integral) Antiderivatives
AP Calculus AB Integration 2015 11 24 www.njctl.org Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Riemann Sums Trapezoid Approximation Area Under a Curve (The Definite Integral) Antiderivatives
AP Calculus BC Chapter 4 AP Exam Problems A) 4 B) 2 C) 1 D) 0 E) 2 A) 9 B) 12 C) 14 D) 21 E) 40
 Extreme Values in an Interval AP Calculus BC 1. The absolute maximum value of x = f ( x) x x 1 on the closed interval, 4 occurs at A) 4 B) C) 1 D) 0 E). The maximum acceleration attained on the interval
Extreme Values in an Interval AP Calculus BC 1. The absolute maximum value of x = f ( x) x x 1 on the closed interval, 4 occurs at A) 4 B) C) 1 D) 0 E). The maximum acceleration attained on the interval
Chapter: Basic Physics-Motion
 Chapter: Basic Physics-Motion The Big Idea Speed represents how quickly an object is moving through space. Velocity is speed with a direction, making it a vector quantity. If an object s velocity changes
Chapter: Basic Physics-Motion The Big Idea Speed represents how quickly an object is moving through space. Velocity is speed with a direction, making it a vector quantity. If an object s velocity changes
Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation
 2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
MATH1910Chapter2TestReview
 Class: Date: MATH1910Chapter2TestReview Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the slope m of the line tangent to the graph of the function
Class: Date: MATH1910Chapter2TestReview Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the slope m of the line tangent to the graph of the function
( ) as a fraction. If both numerator and denominator are
 A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptotes What you are finding: You can be asked to find lim f x x a (H.A.) problem is asking you find lim f x x ( ) and lim f x x ( ). ( ) or lim f x x ± ( ). Typically, a horizontal
A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptotes What you are finding: You can be asked to find lim f x x a (H.A.) problem is asking you find lim f x x ( ) and lim f x x ( ). ( ) or lim f x x ± ( ). Typically, a horizontal
Math 1131Q Section 10
 Math 1131Q Section 10 Section 3.9 and 3.10 Oct 19, 2010 Find the derivative of ln 3 5 e 2 ln 3 5 e 2 = ln 3 + ln 5/2 + ln e 2 = 3 ln + ( 5 ) ln + 2 2 (ln 3 5 e 2 ) = 3 + 5 2 + 2 Find the derivative of
Math 1131Q Section 10 Section 3.9 and 3.10 Oct 19, 2010 Find the derivative of ln 3 5 e 2 ln 3 5 e 2 = ln 3 + ln 5/2 + ln e 2 = 3 ln + ( 5 ) ln + 2 2 (ln 3 5 e 2 ) = 3 + 5 2 + 2 Find the derivative of
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems
 Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Section MWF 12 1pm SR 117
 Math 1431 Section 12485 MWF 12 1pm SR 117 Dr. Melahat Almus almus@math.uh.edu http://www.math.uh.edu/~almus COURSE WEBSITE: http://www.math.uh.edu/~almus/1431_sp16.html Visit my website regularly for announcements
Math 1431 Section 12485 MWF 12 1pm SR 117 Dr. Melahat Almus almus@math.uh.edu http://www.math.uh.edu/~almus COURSE WEBSITE: http://www.math.uh.edu/~almus/1431_sp16.html Visit my website regularly for announcements
THE MOVING MAN: DISTANCE, DISPLACEMENT, SPEED & VELOCITY
 THE MOVING MAN: DISTANCE, DISPLACEMENT, SPEED & VELOCITY Background Remember graphs are not just an evil thing your teacher makes you create, they are a means of communication. Graphs are a way of communicating
THE MOVING MAN: DISTANCE, DISPLACEMENT, SPEED & VELOCITY Background Remember graphs are not just an evil thing your teacher makes you create, they are a means of communication. Graphs are a way of communicating
Applications of Derivatives
 Applications of Derivatives Big Ideas Connecting the graphs of f, f, f Differentiability Continuity Continuity Differentiability Critical values Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives: Hypothesis: If f is
Applications of Derivatives Big Ideas Connecting the graphs of f, f, f Differentiability Continuity Continuity Differentiability Critical values Mean Value Theorem for Derivatives: Hypothesis: If f is
Chapter 2 Derivatives
 Contents Chapter 2 Derivatives Motivation to Chapter 2 2 1 Derivatives and Rates of Change 3 1.1 VIDEO - Definitions................................................... 3 1.2 VIDEO - Examples and Applications
Contents Chapter 2 Derivatives Motivation to Chapter 2 2 1 Derivatives and Rates of Change 3 1.1 VIDEO - Definitions................................................... 3 1.2 VIDEO - Examples and Applications
Position, Velocity, Acceleration
 191 CHAPTER 7 Position, Velocity, Acceleration When we talk of acceleration we think of how quickly the velocity is changing. For example, when a stone is dropped its acceleration (due to gravity) is approximately
191 CHAPTER 7 Position, Velocity, Acceleration When we talk of acceleration we think of how quickly the velocity is changing. For example, when a stone is dropped its acceleration (due to gravity) is approximately
Chapter II.C Derivatives for Implicit Functions
 Chapter II.C Derivatives for Implicit Functions The first thing you may be asking after reading the title of this section is "What's an implicit function? " This is not unexpected since generally courses
Chapter II.C Derivatives for Implicit Functions The first thing you may be asking after reading the title of this section is "What's an implicit function? " This is not unexpected since generally courses
Implicit Differentiation, Related Rates. Goals: Introduce implicit differentiation. Study problems involving related rates.
 Unit #5 : Implicit Differentiation, Related Rates Goals: Introduce implicit differentiation. Study problems involving related rates. Tangent Lines to Relations - Implicit Differentiation - 1 Implicit Differentiation
Unit #5 : Implicit Differentiation, Related Rates Goals: Introduce implicit differentiation. Study problems involving related rates. Tangent Lines to Relations - Implicit Differentiation - 1 Implicit Differentiation
*Finding the tangent line at a point P boils down to finding the slope of the tangent line at point P.
 The Derivative & Tangent Line Problem *Finding the tangent line at a point P boils down to finding the slope of the tangent line at point P. 1 The Derivative & Tangent Line Problem We can approximate using
The Derivative & Tangent Line Problem *Finding the tangent line at a point P boils down to finding the slope of the tangent line at point P. 1 The Derivative & Tangent Line Problem We can approximate using
3.4 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing
 www.ck1.org Chapter 3. Quadratic Equations and Quadratic Functions 3.4 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square Learning objectives Complete the square of a quadratic expression. Solve quadratic
www.ck1.org Chapter 3. Quadratic Equations and Quadratic Functions 3.4 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square Learning objectives Complete the square of a quadratic expression. Solve quadratic
Math 131. Related Rates Larson Section 2.6
 Math 131. Related Rates Larson Section 2.6 There are many natural situations when there are related variables that are changing with respect to time. For example, a spherical balloon is being inflated
Math 131. Related Rates Larson Section 2.6 There are many natural situations when there are related variables that are changing with respect to time. For example, a spherical balloon is being inflated
AP Physics C 2015 Summer Assignment
 AP Physics C 2015 Summer Assignment College Board (the people in charge of AP exams) recommends students to only take AP Physics C if they have already taken a 1 st year physics course and are currently
AP Physics C 2015 Summer Assignment College Board (the people in charge of AP exams) recommends students to only take AP Physics C if they have already taken a 1 st year physics course and are currently
Name: Date: Period: Calculus Honors: 4-2 The Product Rule
 Name: Date: Period: Calculus Honors: 4- The Product Rule Warm Up: 1. Factor and simplify. 9 10 0 5 5 10 5 5. Find ' f if f How did you go about finding the derivative? Let s Eplore how to differentiate
Name: Date: Period: Calculus Honors: 4- The Product Rule Warm Up: 1. Factor and simplify. 9 10 0 5 5 10 5 5. Find ' f if f How did you go about finding the derivative? Let s Eplore how to differentiate
Chapter 27 AB Calculus Practice Test
 Chapter 7 AB Calculus Practice Test The Eam AP Calculus AB Eam SECTION I: Multiple-Choice Questions DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. At a Glance Total Time 1 hour and 45 minutes Number
Chapter 7 AB Calculus Practice Test The Eam AP Calculus AB Eam SECTION I: Multiple-Choice Questions DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO DO SO. At a Glance Total Time 1 hour and 45 minutes Number
All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.
 AP Calculus.5 Worksheet All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit. 1. Consider the function y = sin x. a) Find the equation of the tangent line when
AP Calculus.5 Worksheet All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit. 1. Consider the function y = sin x. a) Find the equation of the tangent line when
Related Rates Problems. of h.
 Basic Related Rates Problems 1. If V is the volume of a cube and x the length of an edge. Express dv What is dv in terms of dx. when x is 5 and dx = 2? 2. If V is the volume of a sphere and r is the radius.
Basic Related Rates Problems 1. If V is the volume of a cube and x the length of an edge. Express dv What is dv in terms of dx. when x is 5 and dx = 2? 2. If V is the volume of a sphere and r is the radius.
AP Calculus AB Chapter 2 Test Review #1
 AP Calculus AB Chapter Test Review # Open-Ended Practice Problems:. Nicole just loves drinking chocolate milk out of her special cone cup which has a radius of inches and a height of 8 inches. Nicole pours
AP Calculus AB Chapter Test Review # Open-Ended Practice Problems:. Nicole just loves drinking chocolate milk out of her special cone cup which has a radius of inches and a height of 8 inches. Nicole pours
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension
 PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
PHYSICS Kinematics in One Dimension August 13, 2012 www.njctl.org 1 Motion in One Dimension Return to Table of Contents 2 Distance We all know what the distance between two objects is... So what is it?
Calculus I - Lecture 14 - Related Rates
 Calculus I - Lecture 14 - Related Rates Lecture Notes: http://www.math.ksu.edu/ gerald/math220d/ Course Syllabus: http://www.math.ksu.edu/math220/spring-2014/indexs14.html Gerald Hoehn (based on notes
Calculus I - Lecture 14 - Related Rates Lecture Notes: http://www.math.ksu.edu/ gerald/math220d/ Course Syllabus: http://www.math.ksu.edu/math220/spring-2014/indexs14.html Gerald Hoehn (based on notes
Math 121: Final Exam Review Sheet
 Exam Information Math 11: Final Exam Review Sheet The Final Exam will be given on Thursday, March 1 from 10:30 am 1:30 pm. The exam is cumulative and will cover chapters 1.1-1.3, 1.5, 1.6,.1-.6, 3.1-3.6,
Exam Information Math 11: Final Exam Review Sheet The Final Exam will be given on Thursday, March 1 from 10:30 am 1:30 pm. The exam is cumulative and will cover chapters 1.1-1.3, 1.5, 1.6,.1-.6, 3.1-3.6,
Motion Section 3 Acceleration
 Section 3 Acceleration Review velocity Scan Use the checklist below to preview Section 3 of your book. Read all section titles. Read all boldfaced words. Read all graphs and equations. Look at all the
Section 3 Acceleration Review velocity Scan Use the checklist below to preview Section 3 of your book. Read all section titles. Read all boldfaced words. Read all graphs and equations. Look at all the
AP CALCULUS Summer Assignment 2014
 Name AP CALCULUS Summer Assignment 014 Welcome to AP Calculus. In order to complete the curriculum before the AP Exam in May, it is necessary to do some preparatory work this summer. The following assignment
Name AP CALCULUS Summer Assignment 014 Welcome to AP Calculus. In order to complete the curriculum before the AP Exam in May, it is necessary to do some preparatory work this summer. The following assignment
The volume of a sphere and the radius of the same sphere are related by the formula:
 Related Rates Today is a day in which we explore the behavior of derivatives rather than trying to get new formulas for derivatives. Example Let s ask the following question: Suppose that you are filling
Related Rates Today is a day in which we explore the behavior of derivatives rather than trying to get new formulas for derivatives. Example Let s ask the following question: Suppose that you are filling
Almost all of the questions involving Related Rates will require one of the following relationships to link together the various changing rates:
 Related Rates All quantities that we meet in every-day life change with time, this is especially true in scientific investigations. Related Rate problems are those in which an equation epresses some relationship
Related Rates All quantities that we meet in every-day life change with time, this is especially true in scientific investigations. Related Rate problems are those in which an equation epresses some relationship
PTF #AB 07 Average Rate of Change
 The average rate of change of f( ) over the interval following: 1. y dy d. f() b f() a b a PTF #AB 07 Average Rate of Change ab, can be written as any of the. Slope of the secant line through the points
The average rate of change of f( ) over the interval following: 1. y dy d. f() b f() a b a PTF #AB 07 Average Rate of Change ab, can be written as any of the. Slope of the secant line through the points
(a) At what rate is the circumference of the circle changing when the radius is 10 inches? =2inches per minute and we want to find. c =2 r.
 3.11 Related Rates Problem 1 The radius of a circle is increasing at a rate of 2 inches per minute. (a) At what rate is the circumference of the circle changing when the radius is 10 inches? We know: dr
3.11 Related Rates Problem 1 The radius of a circle is increasing at a rate of 2 inches per minute. (a) At what rate is the circumference of the circle changing when the radius is 10 inches? We know: dr
AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D
 AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D 1 Algebra Based Physics Kinematics in One Dimension 2015 08 25 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents: Kinematics Motion in One Dimension Position and Reference Frame Displacement
AP Physics 1 Kinematics 1D 1 Algebra Based Physics Kinematics in One Dimension 2015 08 25 www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents: Kinematics Motion in One Dimension Position and Reference Frame Displacement
Calculus 1st Semester Final Review
 Calculus st Semester Final Review Use the graph to find lim f ( ) (if it eists) 0 9 Determine the value of c so that f() is continuous on the entire real line if f ( ), c /, > 0 Find the limit: lim 6+
Calculus st Semester Final Review Use the graph to find lim f ( ) (if it eists) 0 9 Determine the value of c so that f() is continuous on the entire real line if f ( ), c /, > 0 Find the limit: lim 6+
Displacement and Total Distance Traveled
 Displacement and Total Distance Traveled We have gone over these concepts before. Displacement: This is the distance a particle has moved within a certain time - To find this you simply subtract its position
Displacement and Total Distance Traveled We have gone over these concepts before. Displacement: This is the distance a particle has moved within a certain time - To find this you simply subtract its position
More Differentiation Page 1
 More Differentiation Page 1 Directions: Solve the following problems using the available space for scratchwork. Indicate your answers on the front page. Do not spend too much time on any one problem. Note:
More Differentiation Page 1 Directions: Solve the following problems using the available space for scratchwork. Indicate your answers on the front page. Do not spend too much time on any one problem. Note:
Exam Review Sheets Combined
 Exam Review Sheets Combined Fall 2008 1 Fall 2007 Exam 1 1. For each part, if the statement is always true, circle the printed capital T. If the statement is sometimes false, circle the printed capital
Exam Review Sheets Combined Fall 2008 1 Fall 2007 Exam 1 1. For each part, if the statement is always true, circle the printed capital T. If the statement is sometimes false, circle the printed capital
V = π 3 r2 h. dv dt = π [ r 2dh dt r2. dv 3 dt +2rhdr dt
 9 Related Rates Related rates is the phrase used to describe the situation when two or more related variables are changing with respect to time. The rate of change, as mentioned earlier, is another expression
9 Related Rates Related rates is the phrase used to describe the situation when two or more related variables are changing with respect to time. The rate of change, as mentioned earlier, is another expression
5. Find the intercepts of the following equations. Also determine whether the equations are symmetric with respect to the y-axis or the origin.
 MATHEMATICS 1571 Final Examination Review Problems 1. For the function f defined by f(x) = 2x 2 5x find the following: a) f(a + b) b) f(2x) 2f(x) 2. Find the domain of g if a) g(x) = x 2 3x 4 b) g(x) =
MATHEMATICS 1571 Final Examination Review Problems 1. For the function f defined by f(x) = 2x 2 5x find the following: a) f(a + b) b) f(2x) 2f(x) 2. Find the domain of g if a) g(x) = x 2 3x 4 b) g(x) =
Name Date Period. Multiple Choice
 Name Date Period Worksheet 3.8 Related Rates Show all work. Calculator permitted. Show all set-ups and analysis. Report all answers to 3 decimals and avoid intermediate rounding error. Multiple Choice
Name Date Period Worksheet 3.8 Related Rates Show all work. Calculator permitted. Show all set-ups and analysis. Report all answers to 3 decimals and avoid intermediate rounding error. Multiple Choice
Math 103: Related Rates
 Math 103: Related Rates Ryan Blair University of Pennsylvania Thursday October 20, 2011 Ryan Blair (U Penn) Math 103: Related Rates Thursday October 20, 2011 1 / 9 Outline 1 Review 2 Related Rates Ryan
Math 103: Related Rates Ryan Blair University of Pennsylvania Thursday October 20, 2011 Ryan Blair (U Penn) Math 103: Related Rates Thursday October 20, 2011 1 / 9 Outline 1 Review 2 Related Rates Ryan
WeBWorK demonstration assignment
 WeBWorK demonstration assignment The main purpose of this WeBWorK set is to familiarize yourself with WeBWorK. Here are some hints on how to use WeBWorK effectively: After first logging into WeBWorK change
WeBWorK demonstration assignment The main purpose of this WeBWorK set is to familiarize yourself with WeBWorK. Here are some hints on how to use WeBWorK effectively: After first logging into WeBWorK change
MCV4U1 Worksheet 4.7. dh / dt if neither r nor h is constant?
 MCV4U1 Worksheet 4.7 This worksheet serves as an additional exercise to complement the lesson and the examples given. Worksheets may take more than one day to complete. If you are stuck, read again the
MCV4U1 Worksheet 4.7 This worksheet serves as an additional exercise to complement the lesson and the examples given. Worksheets may take more than one day to complete. If you are stuck, read again the
Welcome to Math 104. D. DeTurck. January 16, University of Pennsylvania. D. DeTurck Math A: Welcome 1 / 44
 Welcome to Math 104 D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 16, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Welcome 1 / 44 Welcome to the course Math 104 Calculus I Topics: Quick review of Math 103 topics,
Welcome to Math 104 D. DeTurck University of Pennsylvania January 16, 2018 D. DeTurck Math 104 002 2018A: Welcome 1 / 44 Welcome to the course Math 104 Calculus I Topics: Quick review of Math 103 topics,
AP Calculus AB Integration
 Slide 1 / 175 Slide 2 / 175 AP Calculus AB Integration 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 175 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Riemann Sums Trapezoid Approximation Area Under
Slide 1 / 175 Slide 2 / 175 AP Calculus AB Integration 2015-11-24 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 175 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Riemann Sums Trapezoid Approximation Area Under
AP CALCULUS BC Syllabus / Summer Assignment 2015
 AP CALCULUS BC Syllabus / Summer Assignment 015 Name Congratulations! You made it to BC Calculus! In order to complete the curriculum before the AP Exam in May, it is necessary to do some preparatory work
AP CALCULUS BC Syllabus / Summer Assignment 015 Name Congratulations! You made it to BC Calculus! In order to complete the curriculum before the AP Exam in May, it is necessary to do some preparatory work
