THIRD GRADE PAST LIFE
|
|
|
- Margaret Henry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THIRD GRADE PAST LIFE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
2 ROCK CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE CHEMISTRY WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing elements of the periodic table. LAB: Discovering properties of compounds. POST: Exploring why elements combine. MINERALS WEEK 2. PRE: Exploring the shapes of gems. LAB: Comparing mineral shapes. POST: Distinguishing the geometric shapes of minerals. WEEK 3. PRE: Distinguishing between crystalline and amorphous substances. LAB: Discovering that all minerals are not crystalline. POST: Exploring crystals. ROCKS WEEK 4. PRE: Exploring the etymology of sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic rocks. LAB: Contrasting different types of rocks. POST: Writing a creative essay on rocks. WEEK 5. PRE: Exploring agents of erosion. LAB: Analyzing different types of sands. POST: Comparing sand formed by wind and water. PAST LIFE WEEK 6. PRE: Comparing different modes of fossilization. LAB: Discovering information derived from organisms. POST: Observing fossil and living organisms. Math/Science Nucleus 1990,
3 ROCK CYCLE - PAST LIFE (3) PRE LAB OBJECTIVE: Students compare and distinguish different types of fossil preservation. 1. Comparing different ways a fossil can be preserved. 2. Distinguishing modes of preservation. VOCABULARY: alteration preservation MATERIALS: leaf chicken bone bark shell Fossils by P. Taylor BACKGROUND: Permineralization of dinosaur bone Fossils are the remains of plants and animals that lived long ago. The probability that an organism will be preserved as a fossil is very low. Geological processes such as erosion, weathering, sedimentation, and leaching constantly "attack" the fossil, and may destroy it before anyone sees it. There are two main types of fossil preservation. Most common is fossil preservation with alteration; the original organic material is partially to fully changed into new material. There are several types of preservation with alteration: A) carbonization, a chemical reaction where water transforms the organic material of plant or animal to a thin film of carbon. Nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen are driven off as gases, leaving an outline of the organism. Organisms often preserved by carbonization include fish, leaves and the woody tissues of plants. B) permineralization or petrifaction takes place in porous materials such as Carbonization Math/Science Nucleus 1990,
4 bones, plants and shells. The material is buried; later, groundwater percolates through its pore spaces. A solution, commonly supersaturated in either calcium carbonate or silica, precipitates minerals in the spaces. The original wood or shell like material preserved. C) recrystallization occurs when a solution or precipitate changes the internal physical structure of a fossil. Recrystallization changes the microstructure of the original Recrystallization minerals; they often reform as larger crystals. The composition of the mineral does not change, only the crystal structure. For example, many shells originally composed of calcium carbonate in the form of the mineral aragonite recrystallize into the more stable form of calcium carbonate called calcite. D) replacement involves the complete removal of original hard parts by solution and deposition of a new mineral in its place. The Petrified Forest in Arizona is an excellent example of this type of preservation. Here the original organic material (wood) has been wholly replaced by silica. The second type of fossil creation is direct preservation, the preservation of original organic materials as fossils. The most common directly preserved fossils are unaltered hard parts of a living organism, like shells, teeth, and bones. This material is unchanged, except for the removal of less stable organic matter. Other examples of this type of preservation include fossil corals, shells, sponges, microscopic fossils and a host of other organisms with hard parts. In rare circumstances, preservation of the soft parts of an organism may occur. An example is an insect which has become "stuck" in tree resin. When the resin fossilizes to form amber, it preserves the insect. This was the whole premise for the movie Jurassic Park. PROCEDURE: 1. Show the students different examples of living material, such as chicken bones, leaves, or tree bark. If you have a live animal in the classroom, you may also want to use it as an example. Ask the students what will remain after the organism dies. Lead them into a discussion about why hard parts such as shells or bones are more likely to be found in the fossil record then are the soft parts of an organism. 2. The Eyewitness Book on Fossils by P. Taylor has wonderful pictures of fossils for the students to examine. They will see examples of many of the modes of preservation presented above. Math/Science Nucleus 1990,
5 ROCK CYCLE -PAST LIFE (3) LAB OBJECTIVE: Students examine how organisms become fossils. 1. Exploring the present is the key to the past. 2. Discovering trace fossils. VOCABULARY: carbon coprolite trace fossil tracks MATERIALS: Rock Cycle - Past Life (3) model of lion and giraffe (optional) BACKGROUND: Trilobite The pre lab exercise introduced different types of fossil preservation. All of these are direct evidence of past life. Paleontologists can also study past life using indirect evidence about how the organisms lived. Types of indirect evidence include molds and casts, tracks and trails, burrows and borings, and coprolites. The formation of a mold and cast is a very common type of indirect preservation. After the remains of an organism have been buried and cemented within sediment, water percolating through the sediment dissolves or leaches out the fossil. This leaves a cavity in the rock, called a mold. A cast forms when the mold is filled up with another substance. In some cases minerals such as calcite or quartz precipitate in the mold; elsewhere loose sediment may fill it. The formation of a cast is similar to putting jello in a mold. When you remove the mold, you are looking at the cast of the mold. The other types of indirect evidence are collectively called trace fossils. A trace fossil gives a paleontologist some evidence of the organism s behavior. There are three main types of trace fossils. Tracks and trails are produced by an organism walking, crawling, foraging, or resting. Skinprint For example, dinosaur tracks provide information Math/Science Nucleus 1990,
6 about how large the dinosaur was, how fast it walked, and whether it walked alone or in a group. Burrows and borings are the tunnels or burrows left by organism digging into the ground, either on land or underwater. This may indicate whether the animal was feeding, dwelling, or just foraging. Finally, coprolites are fossilized animal excrement. They give some indication of the structure of the animal s gut, and sometimes provide clues to its diet. PROCEDURE: 1. Before lab, prepare sample collections for each student group, using the specimens in the Rock Cycle - Past Life (3) or other materials that you may have available. 2. Show the plastic lion and giraffe to the students. Ask them to name differences between the two animals, for example, the lion is a carnivore, while the giraffe is a herbivore. Tell the students that both animals presently live on the African Savannah. Have them then imagine that both creatures are no longer living; all that remains are their trace fossils. 3 Have the students predict what the fossil tracks of both animals would look like. Have them consider both running and walking tracks. The giraffe would leave hoof like impressions, compared to the paw prints of the lion. In general, the giraffe's prints would be further apart than the lion s tracks, because it is a bigger animal. Likewise, for both creatures, running tracks would have wider spacing than walking tracks. 4. Next ask the students to consider the coprolites of the two animals. How would they differ? You may wish to have them consider the coprolites of everyday animals, like cows and cats, as analogues. Note that the lion coprolite would probably have bone fragments, and the giraffe coprolite would not. 5. Have the students consider the skeletons of the lion and giraffe. How would they differ? For example, the giraffe, compared to the lion, would have longer neck bones (although the same number of bones as a lion), and larger bones in general. 6. Have students examine the fossils in the Rock Cycle - Past Life (3) kit. Introduce each of the specimens using the information below. Be sure to give them some information to guide their answers, but leave a great deal for them to determine. TRILOBITE - (from Morocco) These arthropods are now extinct, but the individual segments make it an obvious "bug." Trilobites are found in marine sedimentary rocks; they thus lived on the sea floor. The organisms were probably buried in mud after they died. The fossils are replacements of the original organism. Math/Science Nucleus 1990,
7 AMMONITE (from Morocco). This is related to the present day nautilus (Mollusca). Ammonites were squid-like animals that appear to have been predators. The animal lived in the outermost chamber of its shell. CRINOID STEM (from Morocco) - Crinoids belong to the same family of marine animals as do seastars and sand dollars. Crinoids were animals, but they lived attached to the sea floor. The top part of the organism had feathery tentacles, which trapped food. The fossil in the kit is actually part of the stem which connected this feathery top to the sea floor. Like the trilobite, this crinoid fossil is an example of replacement. IRREGULAR ECHINODERM (from Morocco). This is a "fat" sand dollar which would be related to sea biscuits. They like warm, shallow water. They burrow in the sandy mud, and tend to be preserved where they die. This is an example of replacement. SHARK TEETH (from Morocco). These are from several species of sharks that lived in the ancient Mediterranean Sea. Compare this with the present day shark jaw that is included in the kit. Sharks teeth will fall out as soon as the shark eats something, so there are always rows and rows of teeth to take the place of the fallen ones. You can see this within the shark jaw. ORTHOCERAS (from Morocco) Is an extinct organism related to the Ammonites and the present day nautilus (Mollusca). Unlike these creatures, Orthoceras had straight or linear chambers instead of a spiral shape. This organism swam in the water, much like an octopus or squid. 7. Have the students look at the coprolite and fossil fish samples. Have them try to determine how they became fossils. The coprolite is fossil dung from either a sloth or turtle (the sloth looks more like grapes, the turtle looks more like a swirl on an ice cream cone.) The coprolite is from a locality in the state of Washington. The coprolite was quickly buried by sand. It then slowly fossilized by replacement; the organic material was replaced by a variety of minerals. Ask students to name a modern animal today that is probably producing coprolites. A cat (in kitty litter) is a good example. The fossil fish is from an old lake bed near Green River, Wyoming. The fish died and settled to bottom of the lake. It was then buried with a layer of mud, and preserved by carbonization, especially the scales. Note that the impression of the backbone of the fish is also visible; this is a type of cast. Math/Science Nucleus 1990,
8 ROCK CYCLE - PAST LIFE (3) LAB PROBLEM: What information is available from fossil animals? PREDICTION: EXERCISE 1. Look at the fossils. Try and figure out what type of animal it was (guess) and how it became a fossil. Your teacher will give you some hints. Fossil Type of animal and fossilization trilobite ammonite shark teeth coral crinoid stem irregular echinoderm orthoceras EXERCISE 2. Look at the fossil that your teacher has on display. Draw them and try to guess how they became fossils. picture how it became a fossil coprolite fossil fish CONCLUSIONS: In how many ways can an organism become a fossil? Math/Science Nucleus 1990,
9 ROCK CYCLE - PAST LIFE (3) POST LAB OBJECTIVE: Students use the Internet to research. 1. Interpreting evidence from fossils. 2. Comparing modern day elephants with their extinct ancestors. VOCABULARY: mastodon mammoth prehistoric MATERIALS: Internet BACKGROUND: A wooly mammoth After the extinction of the dinosaurs 65 million years ago, prehistoric mammals dominated the Earth. Most of these animals are now extinct as well. Many of their descendants, however, can be easily recognized. Arsisnoitherium lived about 35 million years ago. It resembles a mix between a rhinoceros and an elephant. Zeuglodon was a large sea mammal that was 80 feet long. Imagine a dolphin or porpoise with large, sharp teeth. Hyracotherium was a small mammal that is thought to be the direct ancestor of the horse. Indricotherium, which stood 18 feet tall, is a giant ancestor of the rhinoceros. Smilodon, better known as the saber-toothed tiger or cat, is likely related to most large cats that now prowl the earth. Dinictis was small and slender, and is also probably related to the cheetah and other large cats. Moeritherium was smaller than its ancestor, the present day elephant. Platybelodon and the Woolly Mammoth are also related to the elephant. The mammoth was adapted to live in colder climates. Elephants are the largest living land mammals. Their ancestors included the Woolly Mammoth, the Columbia Mammoth, the Imperial Mammoth and the Mastodon. Today s elephants are adapted for warm climates, but their ancestors were adapted to both warm and cold climates. Frozen mummified mammoths have been found in Siberia and Alaska. Dimo, the complete carcass of a six-month-old baby mammoth, was discovered in Another mummified baby mammoth, less than three months old, was found in Siberia in Mastodons (Mammut americanum) are part of a group of extinct elephant-like mammals that first appeared during the early Miocene Epoch, about 20 million years ago. Math/Science Nucleus 1990,
10 They became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene Epoch, about 10,000 years ago. The Mastodons belong to same Order of mammals as the elephants, Order Proboscidea. PROCEDURE: 1. Use the background information to remind students that there are many types of extinct mammals. Tell them that we know these extinct animals only through their fossils. Have the students imagine what the fossil organisms looked like, by giving them clues from the background section. You may want them to draw a picture of what they think the mammal looked like. 2. Mastodons and mammoths were not the same type of animal. They are both related to the elephant, but have a number of important differences. Instruct the students to search the World Wide Web for information on mastodons and mammoths. Have them try to learn differences between these creatures. You may wish to suggest that they find pictures of each creature, and use them as a guide. Instruct students to make a list of the sites they searched, and to identify the sites that were most helpful. Useful sites include: 1) 2) 3) mastodon Math/Science Nucleus 1990,
Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification
 Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification page - INTRODUCTION The objectives of this exercise are to understand what fossils are, to recognize the different styles of fossil preservation,
Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification page - INTRODUCTION The objectives of this exercise are to understand what fossils are, to recognize the different styles of fossil preservation,
1 Looking at Fossils. What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils tell us about the history of life on earth?
 CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 1 Looking at Fossils California Science Standards 7.3.c, 7.4.c, 7.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 1 Looking at Fossils California Science Standards 7.3.c, 7.4.c, 7.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
Name Class Date. What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils tell us about the history of life on earth?
 CHAPTER 5 2 Looking at Fossils SECTION The Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils
CHAPTER 5 2 Looking at Fossils SECTION The Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils
Tales of the Past. Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education
 Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
Hard Parts of Organisms: Bones Shells Hard Parts of Insects Woody Material (trunks) Fossils provide evidence of how life has changed over time.
 PLEASE, PICK UP OUTLINE FROM THE FRONT TABLE! *recommend adding the extra stuff to the notes Fossus - means to dig up Fossils are preserved remains or traces of living things. Most fossils form when living
PLEASE, PICK UP OUTLINE FROM THE FRONT TABLE! *recommend adding the extra stuff to the notes Fossus - means to dig up Fossils are preserved remains or traces of living things. Most fossils form when living
Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past
 Table of Contents Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past Section : Section 2: Relative Ages of Rocks Section 3: Absolute Ages of Rocks Traces of the Distant Past Paleontologists, scientists who study fossils,
Table of Contents Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past Section : Section 2: Relative Ages of Rocks Section 3: Absolute Ages of Rocks Traces of the Distant Past Paleontologists, scientists who study fossils,
Looking at Fossils. Fossilized Organisms. Fossils in Rocks. Fossils in Amber
 1 Looking at Fossils Key Concept Fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. What You Will Learn Evidence of past life is preserved as fossils in sedimentary rock and
1 Looking at Fossils Key Concept Fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. What You Will Learn Evidence of past life is preserved as fossils in sedimentary rock and
NOTES 1. Fossils. The BIG Idea Rocks, fossils, and other types of natural evidence tell Earth s story.
 Name Period Date UNIT 6 NOTES 1 Fossils Objectives Identify and describe the types of fossils. Define fossils Explain fossil formation Explain how different kinds of fossils show traces of life from Earth
Name Period Date UNIT 6 NOTES 1 Fossils Objectives Identify and describe the types of fossils. Define fossils Explain fossil formation Explain how different kinds of fossils show traces of life from Earth
Fossils. Who studies fossils? How do fossils form? Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of living things.
 Fossils Essential Questions: What are fossils and how are they formed? What are the different kinds of fossils? What do fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time? Who studies fossils? Scientists
Fossils Essential Questions: What are fossils and how are they formed? What are the different kinds of fossils? What do fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time? Who studies fossils? Scientists
Earth s Changing Surface Chapter 4
 Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs. LAB 3: Fossils and Fossilization
 Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 3: Fossils and Fossilization The odds of an organism making it into the fossil record are not very good. Flesh rots away, hair falls out, bones are weathered and crumble,
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 3: Fossils and Fossilization The odds of an organism making it into the fossil record are not very good. Flesh rots away, hair falls out, bones are weathered and crumble,
Fossils. Presented by Kesler Science
 Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are fossils? 2. What are some different types of fossilization? 3. What is the difference between relative and absolute age? 4. What does the fossil
Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are fossils? 2. What are some different types of fossilization? 3. What is the difference between relative and absolute age? 4. What does the fossil
Body Fossils are preserved remains where an organism's body tissue, or parts thereof, become fossilized in an altered or actual state.
 TYPES OF FOSSILS By: Scott Marlowe Paleontology science essentially studies two principle fossil types: Body Fossils are preserved remains where an organism's body tissue, or parts thereof, become fossilized
TYPES OF FOSSILS By: Scott Marlowe Paleontology science essentially studies two principle fossil types: Body Fossils are preserved remains where an organism's body tissue, or parts thereof, become fossilized
Marquette County in the ICE AGE and before
 Marquette County in the ICE AGE and before Millions and millions of years ago, what we know as Marquette County was a giant sea that shifted and changed and left evidence of the animals and plants that
Marquette County in the ICE AGE and before Millions and millions of years ago, what we know as Marquette County was a giant sea that shifted and changed and left evidence of the animals and plants that
Chapter 6. Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal?
 Chapter 6 Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal? Fossils Fossils are the remains or traces of ancient life which have been preserved by natural causes in the Earth's crust. Fossils include both the remains
Chapter 6 Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal? Fossils Fossils are the remains or traces of ancient life which have been preserved by natural causes in the Earth's crust. Fossils include both the remains
There are actually 5 processes
 There are actually 5 processes )WEATHERING hen rocks are roken down nto sediment y Physical and hemical orces 2) ERODE - when sediment is CARRIED to a new location 3) DEPOSIT - when sediment is DROPPED
There are actually 5 processes )WEATHERING hen rocks are roken down nto sediment y Physical and hemical orces 2) ERODE - when sediment is CARRIED to a new location 3) DEPOSIT - when sediment is DROPPED
FoSSil Puzzler (1 Hour)
 FoSSil Puzzler (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 2 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW Students will examine and sketch various trace fossils from an unknown creature and then construct an image of the
FoSSil Puzzler (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 2 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW Students will examine and sketch various trace fossils from an unknown creature and then construct an image of the
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Geologic Change over Time. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of uniformitarianism states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of uniformitarianism states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Studying The Past. II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks?
 Studying The Past I. What is a Fossil? A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? A. To provide evidence of the past existence of
Studying The Past I. What is a Fossil? A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? A. To provide evidence of the past existence of
Lecture Title ( Fossils ) & Date. Main Ideas/Lecture Topics/Questions. Big Ideas or Chunking the Lecture
 Lecture Title ( Fossils ) & Date Main Ideas/Lecture Topics/Questions Big Ideas or Chunking the Lecture Fossil Trilobites Point of View #1 Natural selection provides a scientific explanation for the fossil
Lecture Title ( Fossils ) & Date Main Ideas/Lecture Topics/Questions Big Ideas or Chunking the Lecture Fossil Trilobites Point of View #1 Natural selection provides a scientific explanation for the fossil
Evolution Evidence of Change
 6 Evolution Evidence of Change lesson 1 Fossils and Evolution Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.e. Students know fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. Also
6 Evolution Evidence of Change lesson 1 Fossils and Evolution Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.e. Students know fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. Also
7.1 Life in the past. Fossil formation
 7 The drawing shows an artist s impression of a number of dinosaurs ancient reptiles that lived in eastern Australia about 100 million years ago. From your knowledge of modern-day animals, what evidence
7 The drawing shows an artist s impression of a number of dinosaurs ancient reptiles that lived in eastern Australia about 100 million years ago. From your knowledge of modern-day animals, what evidence
Focus on Fossils. Third - Fifth. Earth Science TEKS. Vocabulary
 Focus on Fossils Third - Fifth Earth Science TEKS Third Grade: 3.7A Fourth Grade: 4.7B Fifth Grade: 5.7A, 5.7D Vocabulary decomposition, deposition, erosion, extinct, fossil, paleontologist, relative dating,
Focus on Fossils Third - Fifth Earth Science TEKS Third Grade: 3.7A Fourth Grade: 4.7B Fifth Grade: 5.7A, 5.7D Vocabulary decomposition, deposition, erosion, extinct, fossil, paleontologist, relative dating,
Do Now HW due Friday 9/30
 Do Now HW due Friday 9/30 1. Describe the process of formation of a sedimentary rock. 2. Draw out the rock cycle clearly state how each rock type becomes another rock type. 3. Make a chart and compare
Do Now HW due Friday 9/30 1. Describe the process of formation of a sedimentary rock. 2. Draw out the rock cycle clearly state how each rock type becomes another rock type. 3. Make a chart and compare
Fun with Fossils. Ask a Fossil
 Fun with Fossils Have you ever found a rock that looks like a bone? Have you seen a rock with the print of a plant on it? These rocks are called fossils. They are made from living things. They have died
Fun with Fossils Have you ever found a rock that looks like a bone? Have you seen a rock with the print of a plant on it? These rocks are called fossils. They are made from living things. They have died
A Trip Through Geologic Time
 A Trip Through Geologic Time A Trip Through Geologic Time Review In: Have the same animals that live today always been on Earth? Illustrate and JUSTIFY. When finished with this In Question, show Ms. Johnson
A Trip Through Geologic Time A Trip Through Geologic Time Review In: Have the same animals that live today always been on Earth? Illustrate and JUSTIFY. When finished with this In Question, show Ms. Johnson
and Fuels OSSIIS Vocabulary Process Skill
 \ Vocabulary fossil, C22 amber, C22 fuel, C26 OSSIIS and Fuels Process Skill The objects captured in this piece of amber were once alive. Now they are fossils. Fossils tell us the story of life on Earth
\ Vocabulary fossil, C22 amber, C22 fuel, C26 OSSIIS and Fuels Process Skill The objects captured in this piece of amber were once alive. Now they are fossils. Fossils tell us the story of life on Earth
Clues to Earth s Past. Fossils and Geologic Time
 Clues to Earth s Past Fossils and Geologic Time Fossils A. Paleontologists study fossils and reconstruct the appearance of animals. Fossils B. Fossils remains, imprints, or traces of prehistoric organisms
Clues to Earth s Past Fossils and Geologic Time Fossils A. Paleontologists study fossils and reconstruct the appearance of animals. Fossils B. Fossils remains, imprints, or traces of prehistoric organisms
Clues to the Past. Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide
 Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Clues to the Past Grades 6-8 Educational Program Guide OAS Science Practices: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 Program Overview The Clues to the Past program will introduce students to several 300 million years old
Program Objectives. Fossil Casting 1. Science: Building with a Variety of Materials
 Fossil Casting 1 Program OVERVIEW Topic: Casting Theme: By using simple chemical reactions, we can create a cast of an original fossil for display. Program Description: In this popular program, each student
Fossil Casting 1 Program OVERVIEW Topic: Casting Theme: By using simple chemical reactions, we can create a cast of an original fossil for display. Program Description: In this popular program, each student
FOSSILS. Book G Chapter 4 Section 1
 FOSSILS Book G Chapter 4 Section 1 OVERVIEW Explain what fossils are and how most fossils form. Describe what fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time. Identify and describe different types
FOSSILS Book G Chapter 4 Section 1 OVERVIEW Explain what fossils are and how most fossils form. Describe what fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time. Identify and describe different types
11/5/2015. Creating a Time Scale - Relative Dating Principles. Creating a Time Scale - Relative Dating Principles. The Geologic Time Scale
 GEOL 110: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is the Geologic Time Scale important? Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth s history Without a time perspective, events have little meaning Chapter
GEOL 110: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is the Geologic Time Scale important? Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth s history Without a time perspective, events have little meaning Chapter
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck)
 The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
Determining the age of fossils
 Sea shells seem to be everywhere. Most of the time you will find them on beaches, but every now and then, you may find them far from the sea. For example, you may have found a shell stuck in a rock high
Sea shells seem to be everywhere. Most of the time you will find them on beaches, but every now and then, you may find them far from the sea. For example, you may have found a shell stuck in a rock high
PALEONTOLOGY - the study of the history of life as reflected in the fossil record
 Paleontology PALEONTOLOGY - the study of the history of life as reflected in the fossil record FOSSIL - remains or traces of organisms that lived in the geologic past and are preserved in the crust of
Paleontology PALEONTOLOGY - the study of the history of life as reflected in the fossil record FOSSIL - remains or traces of organisms that lived in the geologic past and are preserved in the crust of
Hot Sync. Materials Needed Today
 Materials Needed Today Please take these materials out of your backpack. Pencil Age of the Earth Research Assignment Hot Sync Tuesday 12/10/13 Answer the following questions in complete sentences on a
Materials Needed Today Please take these materials out of your backpack. Pencil Age of the Earth Research Assignment Hot Sync Tuesday 12/10/13 Answer the following questions in complete sentences on a
This lesson requires a collection of fossils for the students to examine. See the end notes for suggestions on where to obtain specimens.
 Science Unit: Lesson #4: Fossils What is a Fossil? School Year: 2015/2016 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: George T. Cunningham, Vancouver School District Kate Gregory
Science Unit: Lesson #4: Fossils What is a Fossil? School Year: 2015/2016 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Notes: George T. Cunningham, Vancouver School District Kate Gregory
Directed Reading. Section: The Fossil Record. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Fossil Record 1. For what geological information are fossils an important source? a. learning whether rock is sedimentary, igneous, or metamorphic b. finding
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Fossil Record 1. For what geological information are fossils an important source? a. learning whether rock is sedimentary, igneous, or metamorphic b. finding
What happened Before. reflect
 reflect Sea shells seem to be everywhere. Most of the time, you will find them on beaches. But every now and then, you might find them far from the sea. For example, you might find a shell stuck in a rock
reflect Sea shells seem to be everywhere. Most of the time, you will find them on beaches. But every now and then, you might find them far from the sea. For example, you might find a shell stuck in a rock
Lesson Eight The Meeting of the Dinosaurs Evidence Given by Dinosaur Footprints
 Lesson Eight The Meeting of the Dinosaurs Evidence Given by Dinosaur Footprints Summary During the first set of activities, students focused on the basics, learning about rocks, minerals, time, and fossils.
Lesson Eight The Meeting of the Dinosaurs Evidence Given by Dinosaur Footprints Summary During the first set of activities, students focused on the basics, learning about rocks, minerals, time, and fossils.
Ecology and Paleoecology. A brief review
 Ecology and Paleoecology A brief review Definitions Fossil assemblages Collection of fossils of organisms Lived in the same environment At the same time In the same rock record Diversity The measure of
Ecology and Paleoecology A brief review Definitions Fossil assemblages Collection of fossils of organisms Lived in the same environment At the same time In the same rock record Diversity The measure of
Objectives: Define Relative Age, Absolute Age
 S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
What we will learn about Fossils?
 The fossil Record What we will learn about Fossils? We will learn how fossils form? What types of fossils exist? How do scientists determine the age of fossils? What do fossils reveal to scientists? What
The fossil Record What we will learn about Fossils? We will learn how fossils form? What types of fossils exist? How do scientists determine the age of fossils? What do fossils reveal to scientists? What
The Environment and Change Over Time
 The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
The Environment and Change Over Time Fossil Evidence of Evolution What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if
Topic 7: Historical Geology
 Topic 7: Historical Geology (ES. 8 b, 9 a-e, 10 a-d, 12 a, b, e) ES.8 The student will investigate and understand geologic processes including plate tectonics. Key concepts include: b) processes (faulting,
Topic 7: Historical Geology (ES. 8 b, 9 a-e, 10 a-d, 12 a, b, e) ES.8 The student will investigate and understand geologic processes including plate tectonics. Key concepts include: b) processes (faulting,
FOSSIL "FUN"DAMENTALS
 NAME DATE PARTNER(S) FOSSIL "FUN"DAMENTALS You are taking a stroll on a beach in Calvert or southern Charles County when you come across a shark s tooth laying in the sand at the water s edge. You pick
NAME DATE PARTNER(S) FOSSIL "FUN"DAMENTALS You are taking a stroll on a beach in Calvert or southern Charles County when you come across a shark s tooth laying in the sand at the water s edge. You pick
Integrated Science. Geologic Time Notes. Section 1: Geologic Time
 Integrated Science Geologic Time Notes Section 1: Geologic Time To help in the analysis of Earth s rocks, geologists have divided the history of Earth into time units based upon the fossils contained in
Integrated Science Geologic Time Notes Section 1: Geologic Time To help in the analysis of Earth s rocks, geologists have divided the history of Earth into time units based upon the fossils contained in
Rock cycle diagram. Relative dating. Placing rocks and events in proper sequence of formation Deciphering Earth s history from clues in the rocks
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Module 9: Earth s History Topic 4 Content: Formation of Fossils Notes
 Introduction There are a variety of ways in which fossils can form. In this interactivity, click on each of the thumbnail images in the panel to explore the types of fossils and their formation. 1 Tar
Introduction There are a variety of ways in which fossils can form. In this interactivity, click on each of the thumbnail images in the panel to explore the types of fossils and their formation. 1 Tar
FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past
 FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past Fossils form when water replaces the cells of dead animals or plants with minerals. These minerals then petrify into rock to form the fossils we see in museums.
FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past Fossils form when water replaces the cells of dead animals or plants with minerals. These minerals then petrify into rock to form the fossils we see in museums.
NOTES: The Fossil Record and Geologic Time
 NOTES: The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Vocabulary: Paleontologist Fossil record extinct Relative dating Absolute dating Geologic time scale Objectives: What are fossils? How are they made? How do scientists
NOTES: The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Vocabulary: Paleontologist Fossil record extinct Relative dating Absolute dating Geologic time scale Objectives: What are fossils? How are they made? How do scientists
Studying The Past. II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks?
 Studying The Past I. What is a Fossil? A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? A. To provide evidence of the past existence of
Studying The Past I. What is a Fossil? A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? A. To provide evidence of the past existence of
Section 1 Darwin s theory
 Evolution Section 1 Darwin s theory EVOLUTION The gradual change in a species over time. 2 types EVOLUTION Microevolution: change within a species. Macroevolution: change of a species into a new species.
Evolution Section 1 Darwin s theory EVOLUTION The gradual change in a species over time. 2 types EVOLUTION Microevolution: change within a species. Macroevolution: change of a species into a new species.
Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11
 Correlation of rock layers Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Correlation of rock layers Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Earth Science 105. Geologic Time Chapter 11. Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Correlation of rock layers Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Correlation of rock layers Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
5 total items = 10 points
 Learning Activity Task Focus: Narrative Descriptive Task Title/Topic Fossils Guiding Question What can we learn about the past from fossils? Task Type Narrative Grade 4 Curriculum Connections Text Type
Learning Activity Task Focus: Narrative Descriptive Task Title/Topic Fossils Guiding Question What can we learn about the past from fossils? Task Type Narrative Grade 4 Curriculum Connections Text Type
2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale
 CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
CHAPTER 8 2 Eras of the Geologic Time Scale SECTION The History of Life on Earth BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What kinds of organisms evolved
Discovery Quest 2-3. Chaperone Guide
 Discovery Quest 2-3 Chaperone Guide Chaperone: Partner this guide with the 2-3 Discovery Quest Worksheet. This guide will help you lead students through the natural history exhibits of the Pink Palace
Discovery Quest 2-3 Chaperone Guide Chaperone: Partner this guide with the 2-3 Discovery Quest Worksheet. This guide will help you lead students through the natural history exhibits of the Pink Palace
Objectives. Vocabulary. Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch.
 The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch. Vocabulary geologic time scale eon era period
The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch. Vocabulary geologic time scale eon era period
Fossils, Fossils Everywhere
 Fossils, Fossils Everywhere Level: Grades 4 6 Standards: Explain how fossils provide evidence of the history of the Earth. (Michigan E.ST.04.31) Objectives: Materials: Time Consideration: Background: Learners
Fossils, Fossils Everywhere Level: Grades 4 6 Standards: Explain how fossils provide evidence of the history of the Earth. (Michigan E.ST.04.31) Objectives: Materials: Time Consideration: Background: Learners
Name: Period: Date: ID: A. Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank.
 Name: Period: _ Date: _ ID: A Unit 7 Practice Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank. 1. What term describes the movement of rock
Name: Period: _ Date: _ ID: A Unit 7 Practice Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank. 1. What term describes the movement of rock
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
 UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
3rd-4th Grade. The Fossilization Process Flip Chart
 3rd-4th Grade The Fossilization Process Flip Chart Step 1 Page 2 Step 1 Apologetics What are fossils? A fossil is any trace left by something that lived in the past. Animals, plants, and humans have all
3rd-4th Grade The Fossilization Process Flip Chart Step 1 Page 2 Step 1 Apologetics What are fossils? A fossil is any trace left by something that lived in the past. Animals, plants, and humans have all
Digging into the Past Pre-Visit Materials
 Digging into the Past Pre-Visit Materials Pre-Visit Activities Howard B. Owens Science Center Digging into the Past Pre-Visit The Pre-visit activities are linked to the pre-requisite skills and knowledge
Digging into the Past Pre-Visit Materials Pre-Visit Activities Howard B. Owens Science Center Digging into the Past Pre-Visit The Pre-visit activities are linked to the pre-requisite skills and knowledge
Sedimentary Rocks Reading with Questions (Pg. 3-6) Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification Video (Mr. White s website) Questions (Pg.
 Do At Least 2 Must Do All NAME: Kick Off Activity Comparing Sedimentary and Igneous Rocks (Pg. 2) The Foundation Sedimentary Rocks Reading with Questions (Pg. 3-6) Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification
Do At Least 2 Must Do All NAME: Kick Off Activity Comparing Sedimentary and Igneous Rocks (Pg. 2) The Foundation Sedimentary Rocks Reading with Questions (Pg. 3-6) Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification
Prehistoric Mammals. Sample
 Prehistoric Mammals Contents Teachers Notes. 4 Student Record Sheet... 6 Mammals for Little Ones... 7 Picturenary... 8 Make the Connection... 9 Fossicking Fossils... 10 Make a Good Impression... 11 A Mammoth
Prehistoric Mammals Contents Teachers Notes. 4 Student Record Sheet... 6 Mammals for Little Ones... 7 Picturenary... 8 Make the Connection... 9 Fossicking Fossils... 10 Make a Good Impression... 11 A Mammoth
RELATIVE VS. ABSOLUTE DATING
 Activity Overview BIG IDEA The only way to know anything of the ecology of the past is because of the wide variety of fossils that have been found. People tend to think of all fossils as dinosaurs, but
Activity Overview BIG IDEA The only way to know anything of the ecology of the past is because of the wide variety of fossils that have been found. People tend to think of all fossils as dinosaurs, but
The History of Life. Section 3-2. The Fossil Record
 The History of Life Section 3-2 The Fossil Record The History of Life Draw a line that has as many inches as you have years. Mark the years at every inch. For each year, record at least one major event
The History of Life Section 3-2 The Fossil Record The History of Life Draw a line that has as many inches as you have years. Mark the years at every inch. For each year, record at least one major event
Studying The Past. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks?
 I. What is a Fossil? Studying The Past A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? QQ#1 what is a fossil? Why are they important? A.
I. What is a Fossil? Studying The Past A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? QQ#1 what is a fossil? Why are they important? A.
Lesson Checkpoint: Name one animal that you know is extinct.
 FOSSILS AND EXTINCT ANIMALS Extinct Animals Many animals have become extinct over millions of years. Extinct means that no longer living on Earth. When a species is extinct, it means there aren t any animals
FOSSILS AND EXTINCT ANIMALS Extinct Animals Many animals have become extinct over millions of years. Extinct means that no longer living on Earth. When a species is extinct, it means there aren t any animals
Rock cycle diagram. Principle of Original Horizontality. Sediment is deposited horizontally
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Name Test Date Hour. forms that lived only during certain periods. abundant and widespread geographically. changes to the surface of Earth.
 Name Test Date Hour Earth Processes#3 - Notebook Earth s History LEARNING TARGETS I can explain the lack of evidence about the Precambrian Time. I can describe possible causes for the mass extinction in
Name Test Date Hour Earth Processes#3 - Notebook Earth s History LEARNING TARGETS I can explain the lack of evidence about the Precambrian Time. I can describe possible causes for the mass extinction in
Spilsbu Engag e Literacy Fo ssil Hunters
 Advance Fossil Hunters GRL S Nonfiction Word count: 3,304 Curriculum links: social science/archaeology; biography and autobiography; science and nature/fossils Text type: biography, informational text
Advance Fossil Hunters GRL S Nonfiction Word count: 3,304 Curriculum links: social science/archaeology; biography and autobiography; science and nature/fossils Text type: biography, informational text
Fossils ACTIVITY I: FOSSILIZATION. Activity 1 is for K 2 nd. Activities I and II are for 3 rd 5 th
 Fossils Activity 1 is for K 2 nd. Activities I and II are for 3 rd 5 th OVERVIEW How does a living thing become a fossil? The mysterious processes by which evidence of past life is preserved are explored
Fossils Activity 1 is for K 2 nd. Activities I and II are for 3 rd 5 th OVERVIEW How does a living thing become a fossil? The mysterious processes by which evidence of past life is preserved are explored
Fossils. Name Date Class. A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary
 Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Fossils: evidence of past life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
CRETACEOUS ALBERTA SCIENCE HALL. 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in
 Worksheet Level 3 p. 1 CRETACEOUS ALBERTA 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in 2. What type of dinosaur was found at this site, how many individuals were there, and what was their age range?
Worksheet Level 3 p. 1 CRETACEOUS ALBERTA 1. This exhibit is based on a discovery made in 2. What type of dinosaur was found at this site, how many individuals were there, and what was their age range?
Geologic Time. What is Age? Absolute Age The number of years since the rock formed. (150 million years old, 10 thousand years old.
 Geologic Time There are 2 kinds: What is Age? Absolute Age The number of years since the rock formed. (150 million years old, 10 thousand years old.) Relative Age The age compared to the ages of other
Geologic Time There are 2 kinds: What is Age? Absolute Age The number of years since the rock formed. (150 million years old, 10 thousand years old.) Relative Age The age compared to the ages of other
Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale
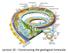 Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale Geologic Time Discovering the magnitude of the Earth s past was a momentous development in the history of humanity This discovery forever altered our perception
Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale Geologic Time Discovering the magnitude of the Earth s past was a momentous development in the history of humanity This discovery forever altered our perception
Online Fossil Lab Fossil Formation How Fossils Form 1. Describe the process in which fossils form.
 Name: Online Fossil Lab Fossil Formation How Fossils Form 1. Describe the process in which fossils form. Period: 2. What is a Mold? 3. What is a cast? Getting into the Fossil Record 4. What is the fossil
Name: Online Fossil Lab Fossil Formation How Fossils Form 1. Describe the process in which fossils form. Period: 2. What is a Mold? 3. What is a cast? Getting into the Fossil Record 4. What is the fossil
Final Revision G8 Biology ( ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Final Revision G8 Biology ( 2017-2018 ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A species is a group of similar organisms that A can mate with each
Final Revision G8 Biology ( 2017-2018 ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A species is a group of similar organisms that A can mate with each
MOR FOSSILS TEACHERS. Making a Fossil Activity Overview BIG IDEA
 Making a Fossil Activity Overview BIG IDEA OBJECTIVE BACKGROUND Not every organism that died, including dinosaurs, left behind a fossil. Explore fossilization with this activity. Students will follow a
Making a Fossil Activity Overview BIG IDEA OBJECTIVE BACKGROUND Not every organism that died, including dinosaurs, left behind a fossil. Explore fossilization with this activity. Students will follow a
Fascinating Fossils Grades 4-8
 Fascinating Fossils Grades 4-8 This activity introduces students to a variety of fossils: large animal bones, small fragment pieces, and microfossils. Students will analyze fossils like that of a field
Fascinating Fossils Grades 4-8 This activity introduces students to a variety of fossils: large animal bones, small fragment pieces, and microfossils. Students will analyze fossils like that of a field
8. GEOLOGIC TIME LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions 8. GEOLOGIC TIME Refer to Exercise 6 in your Lab Manual on pages 151-168 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will be graded on the basis
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions 8. GEOLOGIC TIME Refer to Exercise 6 in your Lab Manual on pages 151-168 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will be graded on the basis
Earth s History. The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
 Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
A fossil is the preserved remains of a once-living organism.
 What is a fossil? A fossil is the preserved remains of a once-living organism. What do fossils tell us? Fossils give clues about organisms that lived long ago. They help to show that evolution has occurred.
What is a fossil? A fossil is the preserved remains of a once-living organism. What do fossils tell us? Fossils give clues about organisms that lived long ago. They help to show that evolution has occurred.
Remains or traces of prehistoric life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Homework. Directed Reading Chapter 5 Section 1 #1-17
 Homework Directed Reading Chapter 5 Section 1 #1-17 Create a Species Project Learning Targets I can explain how comparing organisms can provide evidence that they have common ancestors. What is the evidence
Homework Directed Reading Chapter 5 Section 1 #1-17 Create a Species Project Learning Targets I can explain how comparing organisms can provide evidence that they have common ancestors. What is the evidence
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale
 Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
How can fossils tell us about organisms that lived millions of years ago?
 Seashells seem to be everywhere. Most of the time, you will find them on beaches, but every now and then, you may find them far from the sea. For example, you may find a shell stuck in a rock, high on
Seashells seem to be everywhere. Most of the time, you will find them on beaches, but every now and then, you may find them far from the sea. For example, you may find a shell stuck in a rock, high on
THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH EARTH SCIENCE
 THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH EARTH SCIENCE FOSSILS Paleontology is the study of life that existed in prehistoric times A fossil is any evidence of earlier life preserved in rock. Shells Bones Petrified trees
THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH EARTH SCIENCE FOSSILS Paleontology is the study of life that existed in prehistoric times A fossil is any evidence of earlier life preserved in rock. Shells Bones Petrified trees
Station 8 Station Station 9 Station Station 10 Station Sample 9 Station
 Fossil Lab Answer sheet It s time to learn Station 1 about Fossils! 1. 2. Station 2 3. 4. Station 8 Station 3 19. 20. 5. 6. 7. Station 9 Station 4 21. 22. 8. 9. 10. Station 10 Station 5 11. 12. Station
Fossil Lab Answer sheet It s time to learn Station 1 about Fossils! 1. 2. Station 2 3. 4. Station 8 Station 3 19. 20. 5. 6. 7. Station 9 Station 4 21. 22. 8. 9. 10. Station 10 Station 5 11. 12. Station
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 10 1 Change Over Time SECTION The Evolution of Living Things 7.3.c, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 10 1 Change Over Time SECTION The Evolution of Living Things 7.3.c, 7.3.d California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
Dino Detectives 60 Minute Life Science Lesson Science- To- Go Program Grades: 2-4. Dino Detectives
 TEACHER GUIDE Dino Detectives 60 Minute Life Science Lesson Science- To- Go Program Grades: 2-4 Dino Detectives Description Calling all Jr. paleontologists: we need your help to identify the latest fossilized
TEACHER GUIDE Dino Detectives 60 Minute Life Science Lesson Science- To- Go Program Grades: 2-4 Dino Detectives Description Calling all Jr. paleontologists: we need your help to identify the latest fossilized
.Biology Chapter 14 Test: The History of Life
 Class: Date:.Biology Chapter 14 Test: The History of Life True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. On the geologic time scale, an eon is longer than an era. 2. The oblong shape of
Class: Date:.Biology Chapter 14 Test: The History of Life True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. On the geologic time scale, an eon is longer than an era. 2. The oblong shape of
3rd Grade. Slide 1 / 134. Slide 2 / 134. Slide 3 / 134. Biological Evolution. Table of Contents
 Slide 1 / 134 Slide 2 / 134 3rd Grade Biological Evolution 2015-12-03 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 134 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section Habitats Adaptations Fossils How Fossils Are
Slide 1 / 134 Slide 2 / 134 3rd Grade Biological Evolution 2015-12-03 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 134 Table of Contents Click on the topic to go to that section Habitats Adaptations Fossils How Fossils Are
3rd Grade. Habitats. Slide 1 / 134 Slide 2 / 134. Slide 4 / 134. Slide 3 / 134. Slide 6 / 134. Slide 5 / 134. Biological Evolution
 Slide 1 / 134 Slide 2 / 134 3rd Grade Biological Evolution 2015-12-03 www.njctl.org Habitats Adaptations Fossils How Fossils Are Used Disturbances Slide 3 / 134 Table of Contents Click on the topic to
Slide 1 / 134 Slide 2 / 134 3rd Grade Biological Evolution 2015-12-03 www.njctl.org Habitats Adaptations Fossils How Fossils Are Used Disturbances Slide 3 / 134 Table of Contents Click on the topic to
Who s on First?
 Who s on First? http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/fosrec/barbar.html Focus on Inquiry The students will focus on inquiry by identifying patterns in fossils and explaining their understanding of how rock layers
Who s on First? http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/fosrec/barbar.html Focus on Inquiry The students will focus on inquiry by identifying patterns in fossils and explaining their understanding of how rock layers
Fossils. Ch. 29 and 30 Overview
 Ch. 29 and 30 Overview What you need to know: Chapter 29: Fossils, Relative Time, Absolute Time Chapter 30: Geologic Time Fossils Study of fossils called paleontology Original remains rare usually dead
Ch. 29 and 30 Overview What you need to know: Chapter 29: Fossils, Relative Time, Absolute Time Chapter 30: Geologic Time Fossils Study of fossils called paleontology Original remains rare usually dead
Paleontology. 5 th Grade
 Paleontology 5 th Grade Introduction 5-10 minutes Geologic Time Scale 15-20 minutes Measuring tape at least 50ft long tabs Trace Fossils Casting materials Molds Water Drying paper Tooth picks cups Strata
Paleontology 5 th Grade Introduction 5-10 minutes Geologic Time Scale 15-20 minutes Measuring tape at least 50ft long tabs Trace Fossils Casting materials Molds Water Drying paper Tooth picks cups Strata
