Body Fossils are preserved remains where an organism's body tissue, or parts thereof, become fossilized in an altered or actual state.
|
|
|
- Horatio Maxwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TYPES OF FOSSILS By: Scott Marlowe Paleontology science essentially studies two principle fossil types: Body Fossils are preserved remains where an organism's body tissue, or parts thereof, become fossilized in an altered or actual state. Trace Fossils constitute any evidence of left behind by an organism that is not tissue remains. Examples of trace fossils are animal tracks, trails, burrows borings, impressions, molds, casts, and steinkerns. Body Fossils include remains like this peccary mandible which includes teeth and bone. Trace Fossils are evidence of the presence of an organism in its environment like this therapod track METHOD OF PRESERVATION An vital observation about any fossil find is the way in which the remains are preserved. The method of preservation indicates what happened to the organism's remains subsequent to death, and the conditions under which the fossil was originally created. Most remains do not become fossilized after death. All life begins to decay after it dies and will decompose over time. Animal remains are often subjected to predation. To become fossilized, tissue has to be subjected to particular environmental conditions that are conducive to preservation. The more important circumstances are rapid burial and the existence of hard part in the remains. If an organism is not quickly buried, microbes and other animals will devour the remains and the material will be lost to the fossil record. Even if remains become fossilized, erosional processes can destroy them. Unless an organism happens to die in anaerobic environment, its soft parts will not be preserved. For this reason, fossilization of soft tissue is highly unusual.
2 BODY FOSSILS Unaltered Preservation refers to fossils that have undergone little or no change in structure and composition. A fossil of an organism that lived recently is more likely to be unaltered than a more aged one. Original Skeletal Material refers to the hard tissues that are preserved as the original material. This includes many invertebrate molluska that have shells composed of calcium carbonate, silica, or chitin and vertebrate species with bones of calcium phosphate. Encrustations occur in caves where ground water with a high concentration of dissolved minerals seeps or drips constantly. As the water evaporates, the minerals are remain. These chemicals then form a thin coating on the interior surface of the cave and remains that lie in it thereby preserving organisms that die there. Tar Impregnation is excellent for fossilization. The La Brea tar pits of California yield particularly fine collections of vertebrate bones, wood, and so forth. Smaller tar pits frequently yield perfectly preserved insects their larvae. In Amber Entombment coniferous trees, like spruce, pine and fir, that have a sticky resinous pitch that seeps from damage to the tree's bark. Many small insects and other small organisms occasionally become trapped in the resin. After burial the sap hardens into amber. Particular areas of the Baltic Sea coastline and a few islands in the West Indies are well known for insects preserved in amber. Refrigeration occurred primarily during the Pleistocene, when ice sheets covered much of the Northern Hemisphere. Some animals fell into crevasses or became trapped in permanently frozen soil. Although infrequent, some have been discovered perfectly preserved in this manner. Mummification occurs in very arid environments. The animal's remains dehydrate or desiccate quickly and become preserved -- usually including its soft tissues. Unaltered preservation (like insects or plant parts trapped in amber, a hardened form of tree sap)
3 Altered Remains As sediment layers become compressed by the weight of overlying material, they slowly undergo the process of lithification. It is common for cementing materials in the groundwater like carbonate, silica, and iron oxides, to bond the sediment together and harden. Often the groundwater, and the minerals contained in it, impacts the fossilization process. In Permineralization, bones, teeth, shells, and plant stems have porous internal structures. These pores can become filled with mineral deposits in the soil and groundwater. In the process of permineralization, the actual chemical composition of the original hard parts of the organism may not change but it generally will be altered in some way. Permineralization or petrification in which rock-like minerals seep in slowly and replace the original organic tissues with silica, calcite or pyrite, forming a rock-like fossil - can preserve hard and soft parts - most bone and wood fossils are permineralized. Carbonization occurs when an organism becomes pressed into sediment and its volatile, liquid or gaseous contents are forced out leaving a thin film of carbon. When other organic material remains, as when plants are entombed, coal is formed. Thus, coal mines are typically a good source for carbonized fossils. In Recrystallization the hard tissues are converted, usually in a solid state, into a new mineral or to coarser crystals of than those of the original mineral. Carbonization or coalification in which only the carbon remains in the specimen - other elements, like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen are removed.
4 Dissolution or Replacement refers to fossils formed when groundwater, particularly if it is acidic, acts upon the remains to dissolve the hard and soft tissue structures of an organism trapped in sediments. The hard tissues are often simultaneously replaced by minerals contained in the water -- molecule by molecule. Petrified wood is a classic example of this type of fossilization where even the internal microscopic cellular structure of the plant is replaced by silica in the process of fossilization. Replacement where an organism s hard tissues dissolve and are replaced by other more stable minerals, like calcite, silica, pyrite, or iron. Authingenic Preservation occurs when a mold or form of an organism is made after it decomposes in sediment and is replaced by material that hardens into casting of the original animal's likeness. Animals with exoskeletons or shells are often fossilized in this way. Fossils of animals with shells, particularly molluska, are sometimes called Steinkerns. Authigenic preservation molds and casts of organism itself occur where the animal becomes destroyed or dissolved leaving a replica of the creature incased in matrix. TRACE FOSSILS As in Authingenic Preservation, a Mold refers to any reproduction of an organism's past presence in the environment that has been preserved by leaving an impression, but not necessarily filled with hardened material such as an animal's track or footprint. Generally speaking, a Cast is any copy of the original form when the "positive" item is removed or dissolved away and the remaining "negative" impression becomes filled with sediment or mineral material that subsequently hardens into a replica of the original.
5 Compression refers to fossils that form as a result of pressure from sediments that cover an organism or its trace fossils of it. Compression usually is used to describe the casts and/or molds of plant leaves. Borings and Burrows from when worms, clams and other burrowing invertebrates "drill" into rocks, wood, shells, and all types of sediment. These cavities are frequently preserved, especially in fine-grained rocks and may also appear in the bones of vertebrate animals. Coprolite is the fossilized excrement from a animal and is sometimes very useful in providing knowledge about specific diet of the animal concerned. Gastroliths are smooth, polished stones that are typically found in the abdominal cavities of skeletal fossils of dinosaurs and large mammals. These "grinding stones" are thought to have been essential for the animal's digestion of plant material by grinding up vegetable matter in their stomach. Gnawings are the result of rodent, marsupial and other animals that chewed on bones or trees. These Gastroliths were found in the abdonimal area of a dinosaur fossil and may have helped the animal digest plant material. Similar small gastroliths are often found associated with certain fish and mammal species. Coprolite, like this preserved dung from an alligator, can be useful in determining the type of foods that the animal ingested for nurishment or may reveal digestive disorders and allomentary parasites.
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs. LAB 3: Fossils and Fossilization
 Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 3: Fossils and Fossilization The odds of an organism making it into the fossil record are not very good. Flesh rots away, hair falls out, bones are weathered and crumble,
Geo 302D: Age of Dinosaurs LAB 3: Fossils and Fossilization The odds of an organism making it into the fossil record are not very good. Flesh rots away, hair falls out, bones are weathered and crumble,
Hard Parts of Organisms: Bones Shells Hard Parts of Insects Woody Material (trunks) Fossils provide evidence of how life has changed over time.
 PLEASE, PICK UP OUTLINE FROM THE FRONT TABLE! *recommend adding the extra stuff to the notes Fossus - means to dig up Fossils are preserved remains or traces of living things. Most fossils form when living
PLEASE, PICK UP OUTLINE FROM THE FRONT TABLE! *recommend adding the extra stuff to the notes Fossus - means to dig up Fossils are preserved remains or traces of living things. Most fossils form when living
Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification
 Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification page - INTRODUCTION The objectives of this exercise are to understand what fossils are, to recognize the different styles of fossil preservation,
Paleo Lab #5 - Fossilization and Fossil Identification page - INTRODUCTION The objectives of this exercise are to understand what fossils are, to recognize the different styles of fossil preservation,
Module 9: Earth s History Topic 4 Content: Formation of Fossils Notes
 Introduction There are a variety of ways in which fossils can form. In this interactivity, click on each of the thumbnail images in the panel to explore the types of fossils and their formation. 1 Tar
Introduction There are a variety of ways in which fossils can form. In this interactivity, click on each of the thumbnail images in the panel to explore the types of fossils and their formation. 1 Tar
Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past
 Table of Contents Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past Section : Section 2: Relative Ages of Rocks Section 3: Absolute Ages of Rocks Traces of the Distant Past Paleontologists, scientists who study fossils,
Table of Contents Chapter: Clues to Earth s Past Section : Section 2: Relative Ages of Rocks Section 3: Absolute Ages of Rocks Traces of the Distant Past Paleontologists, scientists who study fossils,
Fossils. Presented by Kesler Science
 Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are fossils? 2. What are some different types of fossilization? 3. What is the difference between relative and absolute age? 4. What does the fossil
Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are fossils? 2. What are some different types of fossilization? 3. What is the difference between relative and absolute age? 4. What does the fossil
Fossils. Who studies fossils? How do fossils form? Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of living things.
 Fossils Essential Questions: What are fossils and how are they formed? What are the different kinds of fossils? What do fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time? Who studies fossils? Scientists
Fossils Essential Questions: What are fossils and how are they formed? What are the different kinds of fossils? What do fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time? Who studies fossils? Scientists
THE PRESERVATION OF FOSSILS
 WHAT ARE FOSSILS? THE PRESERVATION OF FOSSILS Fossils are the remains of living organisms. Most fossils are the hard parts of whole or fragmented organisms, such as shells of a bivalve or the skeleton
WHAT ARE FOSSILS? THE PRESERVATION OF FOSSILS Fossils are the remains of living organisms. Most fossils are the hard parts of whole or fragmented organisms, such as shells of a bivalve or the skeleton
Name Class Date. What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils tell us about the history of life on earth?
 CHAPTER 5 2 Looking at Fossils SECTION The Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils
CHAPTER 5 2 Looking at Fossils SECTION The Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils
Program Objectives. Fossil Casting 1. Science: Building with a Variety of Materials
 Fossil Casting 1 Program OVERVIEW Topic: Casting Theme: By using simple chemical reactions, we can create a cast of an original fossil for display. Program Description: In this popular program, each student
Fossil Casting 1 Program OVERVIEW Topic: Casting Theme: By using simple chemical reactions, we can create a cast of an original fossil for display. Program Description: In this popular program, each student
1 Looking at Fossils. What are fossils? How are fossils formed? What can fossils tell us about the history of life on earth?
 CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 1 Looking at Fossils California Science Standards 7.3.c, 7.4.c, 7.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 9 SECTION The History of Life on Earth 1 Looking at Fossils California Science Standards 7.3.c, 7.4.c, 7.4.e BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
Studying The Past. II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks?
 Studying The Past I. What is a Fossil? A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? A. To provide evidence of the past existence of
Studying The Past I. What is a Fossil? A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? A. To provide evidence of the past existence of
Studying The Past. II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks?
 Studying The Past I. What is a Fossil? A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? A. To provide evidence of the past existence of
Studying The Past I. What is a Fossil? A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals II. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? A. To provide evidence of the past existence of
Studying The Past. Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks?
 I. What is a Fossil? Studying The Past A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? QQ#1 what is a fossil? Why are they important? A.
I. What is a Fossil? Studying The Past A. Definition: The evidence or remains of once-living plants or animals Why Do We Study Fossils Found in Rocks? QQ#1 what is a fossil? Why are they important? A.
NOTES: The Fossil Record and Geologic Time
 NOTES: The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Vocabulary: Paleontologist Fossil record extinct Relative dating Absolute dating Geologic time scale Objectives: What are fossils? How are they made? How do scientists
NOTES: The Fossil Record and Geologic Time Vocabulary: Paleontologist Fossil record extinct Relative dating Absolute dating Geologic time scale Objectives: What are fossils? How are they made? How do scientists
Ecology and Paleoecology. A brief review
 Ecology and Paleoecology A brief review Definitions Fossil assemblages Collection of fossils of organisms Lived in the same environment At the same time In the same rock record Diversity The measure of
Ecology and Paleoecology A brief review Definitions Fossil assemblages Collection of fossils of organisms Lived in the same environment At the same time In the same rock record Diversity The measure of
PALEONTOLOGY - the study of the history of life as reflected in the fossil record
 Paleontology PALEONTOLOGY - the study of the history of life as reflected in the fossil record FOSSIL - remains or traces of organisms that lived in the geologic past and are preserved in the crust of
Paleontology PALEONTOLOGY - the study of the history of life as reflected in the fossil record FOSSIL - remains or traces of organisms that lived in the geologic past and are preserved in the crust of
Section 1 Darwin s theory
 Evolution Section 1 Darwin s theory EVOLUTION The gradual change in a species over time. 2 types EVOLUTION Microevolution: change within a species. Macroevolution: change of a species into a new species.
Evolution Section 1 Darwin s theory EVOLUTION The gradual change in a species over time. 2 types EVOLUTION Microevolution: change within a species. Macroevolution: change of a species into a new species.
Hot Sync. Materials Needed Today
 Materials Needed Today Please take these materials out of your backpack. Pencil Age of the Earth Research Assignment Hot Sync Tuesday 12/10/13 Answer the following questions in complete sentences on a
Materials Needed Today Please take these materials out of your backpack. Pencil Age of the Earth Research Assignment Hot Sync Tuesday 12/10/13 Answer the following questions in complete sentences on a
Chapter 6. Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal?
 Chapter 6 Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal? Fossils Fossils are the remains or traces of ancient life which have been preserved by natural causes in the Earth's crust. Fossils include both the remains
Chapter 6 Life on Earth: What do Fossils Reveal? Fossils Fossils are the remains or traces of ancient life which have been preserved by natural causes in the Earth's crust. Fossils include both the remains
Looking at Fossils. Fossilized Organisms. Fossils in Rocks. Fossils in Amber
 1 Looking at Fossils Key Concept Fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. What You Will Learn Evidence of past life is preserved as fossils in sedimentary rock and
1 Looking at Fossils Key Concept Fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. What You Will Learn Evidence of past life is preserved as fossils in sedimentary rock and
FOSSILS. Book G Chapter 4 Section 1
 FOSSILS Book G Chapter 4 Section 1 OVERVIEW Explain what fossils are and how most fossils form. Describe what fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time. Identify and describe different types
FOSSILS Book G Chapter 4 Section 1 OVERVIEW Explain what fossils are and how most fossils form. Describe what fossils tell about how organisms have changed over time. Identify and describe different types
Lecture Title ( Fossils ) & Date. Main Ideas/Lecture Topics/Questions. Big Ideas or Chunking the Lecture
 Lecture Title ( Fossils ) & Date Main Ideas/Lecture Topics/Questions Big Ideas or Chunking the Lecture Fossil Trilobites Point of View #1 Natural selection provides a scientific explanation for the fossil
Lecture Title ( Fossils ) & Date Main Ideas/Lecture Topics/Questions Big Ideas or Chunking the Lecture Fossil Trilobites Point of View #1 Natural selection provides a scientific explanation for the fossil
Tales of the Past. Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education
 Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
What we will learn about Fossils?
 The fossil Record What we will learn about Fossils? We will learn how fossils form? What types of fossils exist? How do scientists determine the age of fossils? What do fossils reveal to scientists? What
The fossil Record What we will learn about Fossils? We will learn how fossils form? What types of fossils exist? How do scientists determine the age of fossils? What do fossils reveal to scientists? What
Directed Reading. Section: The Fossil Record. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Fossil Record 1. For what geological information are fossils an important source? a. learning whether rock is sedimentary, igneous, or metamorphic b. finding
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Fossil Record 1. For what geological information are fossils an important source? a. learning whether rock is sedimentary, igneous, or metamorphic b. finding
A Trip Through Geologic Time
 A Trip Through Geologic Time A Trip Through Geologic Time Review In: Have the same animals that live today always been on Earth? Illustrate and JUSTIFY. When finished with this In Question, show Ms. Johnson
A Trip Through Geologic Time A Trip Through Geologic Time Review In: Have the same animals that live today always been on Earth? Illustrate and JUSTIFY. When finished with this In Question, show Ms. Johnson
NOTES 1. Fossils. The BIG Idea Rocks, fossils, and other types of natural evidence tell Earth s story.
 Name Period Date UNIT 6 NOTES 1 Fossils Objectives Identify and describe the types of fossils. Define fossils Explain fossil formation Explain how different kinds of fossils show traces of life from Earth
Name Period Date UNIT 6 NOTES 1 Fossils Objectives Identify and describe the types of fossils. Define fossils Explain fossil formation Explain how different kinds of fossils show traces of life from Earth
7.1 Life in the past. Fossil formation
 7 The drawing shows an artist s impression of a number of dinosaurs ancient reptiles that lived in eastern Australia about 100 million years ago. From your knowledge of modern-day animals, what evidence
7 The drawing shows an artist s impression of a number of dinosaurs ancient reptiles that lived in eastern Australia about 100 million years ago. From your knowledge of modern-day animals, what evidence
Unit 2 Lesson 1 Geologic Change over Time. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of uniformitarianism states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of uniformitarianism states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
11/5/2015. Creating a Time Scale - Relative Dating Principles. Creating a Time Scale - Relative Dating Principles. The Geologic Time Scale
 GEOL 110: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is the Geologic Time Scale important? Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth s history Without a time perspective, events have little meaning Chapter
GEOL 110: PHYSICAL GEOLOGY Why is the Geologic Time Scale important? Rocks record geologic and evolutionary changes throughout Earth s history Without a time perspective, events have little meaning Chapter
The History of Life. Section 3-2. The Fossil Record
 The History of Life Section 3-2 The Fossil Record The History of Life Draw a line that has as many inches as you have years. Mark the years at every inch. For each year, record at least one major event
The History of Life Section 3-2 The Fossil Record The History of Life Draw a line that has as many inches as you have years. Mark the years at every inch. For each year, record at least one major event
There are actually 5 processes
 There are actually 5 processes )WEATHERING hen rocks are roken down nto sediment y Physical and hemical orces 2) ERODE - when sediment is CARRIED to a new location 3) DEPOSIT - when sediment is DROPPED
There are actually 5 processes )WEATHERING hen rocks are roken down nto sediment y Physical and hemical orces 2) ERODE - when sediment is CARRIED to a new location 3) DEPOSIT - when sediment is DROPPED
Evolution Evidence of Change
 6 Evolution Evidence of Change lesson 1 Fossils and Evolution Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.e. Students know fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. Also
6 Evolution Evidence of Change lesson 1 Fossils and Evolution Grade Seven Science Content Standard. 4.e. Students know fossils provide evidence of how life and environmental conditions have changed. Also
Fossils and EH LT 1 and 2
 Fossils and EH LT 1 and 2 Grade:«grade» Subject:Science Date:«date» Apr 9 11:39 AM 1 1 Which of the following does NOT explain why soft tissues are less likely to fossilize than hard parts? A Soft tissues
Fossils and EH LT 1 and 2 Grade:«grade» Subject:Science Date:«date» Apr 9 11:39 AM 1 1 Which of the following does NOT explain why soft tissues are less likely to fossilize than hard parts? A Soft tissues
Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11
 Correlation of rock layers Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Correlation of rock layers Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Earth Science 105. Geologic Time Chapter 11. Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens
 Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Correlation of rock layers Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Earth Science 105 Geologic Time Chapter 11 Earth Science 11 th ed. Tarbuck & Lutgens Correlation of rock layers Matching same age rocks In local area Across wide area In different regions Grand Canyon
Marquette County in the ICE AGE and before
 Marquette County in the ICE AGE and before Millions and millions of years ago, what we know as Marquette County was a giant sea that shifted and changed and left evidence of the animals and plants that
Marquette County in the ICE AGE and before Millions and millions of years ago, what we know as Marquette County was a giant sea that shifted and changed and left evidence of the animals and plants that
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck)
 The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
The Significance of the Fossil Record ( Susan Matthews and Graeme Lindbeck) The fossil record indicates the evolutionary history of life. Many events together, including: continental drift, changes in
Earth s Changing Surface Chapter 4
 Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Name Hour Due Date Earth s Changing Surface Chapter (You do not need your book) Page 1 Fossils Summary Page 2 Traces of Tracks Page 3 Finding the Relative Age of Rocks Summary. Page - Finding the Relative
Fossils: evidence of past life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed and
Clues to Earth s Past. Fossils and Geologic Time
 Clues to Earth s Past Fossils and Geologic Time Fossils A. Paleontologists study fossils and reconstruct the appearance of animals. Fossils B. Fossils remains, imprints, or traces of prehistoric organisms
Clues to Earth s Past Fossils and Geologic Time Fossils A. Paleontologists study fossils and reconstruct the appearance of animals. Fossils B. Fossils remains, imprints, or traces of prehistoric organisms
Rock cycle diagram. Relative dating. Placing rocks and events in proper sequence of formation Deciphering Earth s history from clues in the rocks
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Modern geology Uniformitarianism Fundamental principle of geology "The present is the key to the past Relative dating Placing rocks and events
Evidence for Evolution Notes:
 Evidence for Evolution Notes: Evidence that supports the theory of evolution is usually grouped into four main areas, such as 1. Biochemical DNA analysis 2. Comparative anatomy morphology, homologous structures,
Evidence for Evolution Notes: Evidence that supports the theory of evolution is usually grouped into four main areas, such as 1. Biochemical DNA analysis 2. Comparative anatomy morphology, homologous structures,
A fossil is the preserved remains of a once-living organism.
 What is a fossil? A fossil is the preserved remains of a once-living organism. What do fossils tell us? Fossils give clues about organisms that lived long ago. They help to show that evolution has occurred.
What is a fossil? A fossil is the preserved remains of a once-living organism. What do fossils tell us? Fossils give clues about organisms that lived long ago. They help to show that evolution has occurred.
Remains or traces of prehistoric life
 Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Fossils: evidence of past life Remains or traces of prehistoric life Petrified Cavities and pores are filled with precipitated p mineral matter Petrified Formed by replacement Cell material is removed
Objectives: Define Relative Age, Absolute Age
 S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
5 total items = 10 points
 Learning Activity Task Focus: Narrative Descriptive Task Title/Topic Fossils Guiding Question What can we learn about the past from fossils? Task Type Narrative Grade 4 Curriculum Connections Text Type
Learning Activity Task Focus: Narrative Descriptive Task Title/Topic Fossils Guiding Question What can we learn about the past from fossils? Task Type Narrative Grade 4 Curriculum Connections Text Type
Geologic Time. What is Age? Absolute Age The number of years since the rock formed. (150 million years old, 10 thousand years old.
 Geologic Time There are 2 kinds: What is Age? Absolute Age The number of years since the rock formed. (150 million years old, 10 thousand years old.) Relative Age The age compared to the ages of other
Geologic Time There are 2 kinds: What is Age? Absolute Age The number of years since the rock formed. (150 million years old, 10 thousand years old.) Relative Age The age compared to the ages of other
Rock cycle diagram. Principle of Original Horizontality. Sediment is deposited horizontally
 Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Geologic Time Rock cycle diagram Leaves of History Chapter 21 Lateral Continuity Principle of Original Horizontality Sediment is deposited horizontally Principle of Superposition Oldest rock A Younger
Fossils. 1. Introduction. 2. What are fossils? PO IN TS OF IN TE RES T : Introduction. What are fossils? Factors which affect the fossilization
 TECHNICAL SHEET OF POPULAR SCIENCE Fossils PO IN TS OF IN TE RES T : Introduction What are fossils? Factors which affect the fossilization Fossilization Process. Kinds of fossilizations Importance of fossils.
TECHNICAL SHEET OF POPULAR SCIENCE Fossils PO IN TS OF IN TE RES T : Introduction What are fossils? Factors which affect the fossilization Fossilization Process. Kinds of fossilizations Importance of fossils.
Integrated Science. Geologic Time Notes. Section 1: Geologic Time
 Integrated Science Geologic Time Notes Section 1: Geologic Time To help in the analysis of Earth s rocks, geologists have divided the history of Earth into time units based upon the fossils contained in
Integrated Science Geologic Time Notes Section 1: Geologic Time To help in the analysis of Earth s rocks, geologists have divided the history of Earth into time units based upon the fossils contained in
Do Now HW due Friday 9/30
 Do Now HW due Friday 9/30 1. Describe the process of formation of a sedimentary rock. 2. Draw out the rock cycle clearly state how each rock type becomes another rock type. 3. Make a chart and compare
Do Now HW due Friday 9/30 1. Describe the process of formation of a sedimentary rock. 2. Draw out the rock cycle clearly state how each rock type becomes another rock type. 3. Make a chart and compare
GEO 302D: Age of Dinosaurs Laboratory 1: Introduction to Paleontology
 GEO 302D: Age of Dinosaurs Laboratory 1: Introduction to Paleontology Welcome to Age of Dinosaurs! In this course, dinosaurs will be used as a means of introducing you to the methods and practice of natural
GEO 302D: Age of Dinosaurs Laboratory 1: Introduction to Paleontology Welcome to Age of Dinosaurs! In this course, dinosaurs will be used as a means of introducing you to the methods and practice of natural
LEARN * DREAM * AWAKEN* DISCOVER * ENLIGHTEN * INVESTIGATE * QUESTION * EXPLORE
 S C I N C P L A N T S PLANTS Ancient Plants in Focus This nrichment4you e-guide provides a brief overview of ancient leaves. In this e-guide you will: *Learn basic Information About Fossilized Leaves *Learn
S C I N C P L A N T S PLANTS Ancient Plants in Focus This nrichment4you e-guide provides a brief overview of ancient leaves. In this e-guide you will: *Learn basic Information About Fossilized Leaves *Learn
Relative aging, fossils, natural disasters
 Relative aging, fossils, natural disasters Rocks breaking down into smaller pieces Water that moves over Earth s surface Causes sheet erosion Moves downhill Forms rills and gullies Erosion creates valleys,
Relative aging, fossils, natural disasters Rocks breaking down into smaller pieces Water that moves over Earth s surface Causes sheet erosion Moves downhill Forms rills and gullies Erosion creates valleys,
Spilsbu Engag e Literacy Fo ssil Hunters
 Advance Fossil Hunters GRL S Nonfiction Word count: 3,304 Curriculum links: social science/archaeology; biography and autobiography; science and nature/fossils Text type: biography, informational text
Advance Fossil Hunters GRL S Nonfiction Word count: 3,304 Curriculum links: social science/archaeology; biography and autobiography; science and nature/fossils Text type: biography, informational text
Directed Reading. Section: Determining Relative Age. conclusions? UNIFORMITARIANISM. geology? of Earth? Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Determining Relative Age 1. How old is Earth estimated to be? 2. Who originated the idea that Earth is billions of years old? 3. On what did the 18th-century
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Determining Relative Age 1. How old is Earth estimated to be? 2. Who originated the idea that Earth is billions of years old? 3. On what did the 18th-century
Lesson Checkpoint: Name one animal that you know is extinct.
 FOSSILS AND EXTINCT ANIMALS Extinct Animals Many animals have become extinct over millions of years. Extinct means that no longer living on Earth. When a species is extinct, it means there aren t any animals
FOSSILS AND EXTINCT ANIMALS Extinct Animals Many animals have become extinct over millions of years. Extinct means that no longer living on Earth. When a species is extinct, it means there aren t any animals
Geology 1023 Lab #6, Winter Introduction to fossils and fossilisation
 Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #6, Winter 2014 Introduction to fossils and fossilisation What is a fossil? A fossil is any evidence of ancient life preserved in sediments or rocks. Why are fossils important?
Name: Answers Geology 1023 Lab #6, Winter 2014 Introduction to fossils and fossilisation What is a fossil? A fossil is any evidence of ancient life preserved in sediments or rocks. Why are fossils important?
Final Revision G8 Biology ( ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Final Revision G8 Biology ( 2017-2018 ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A species is a group of similar organisms that A can mate with each
Final Revision G8 Biology ( 2017-2018 ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1 A species is a group of similar organisms that A can mate with each
LECTURE 2: Taphonomy and Time
 1 LECTURE 2: Taphonomy and Time OUTLINE Fossils: Definition, Types Taphonomy Preservation: Modes and Biases Depositional environments Preservation potential of dinosaurs Geologic Time Scale: Relative and
1 LECTURE 2: Taphonomy and Time OUTLINE Fossils: Definition, Types Taphonomy Preservation: Modes and Biases Depositional environments Preservation potential of dinosaurs Geologic Time Scale: Relative and
FOSSIL "FUN"DAMENTALS
 NAME DATE PARTNER(S) FOSSIL "FUN"DAMENTALS You are taking a stroll on a beach in Calvert or southern Charles County when you come across a shark s tooth laying in the sand at the water s edge. You pick
NAME DATE PARTNER(S) FOSSIL "FUN"DAMENTALS You are taking a stroll on a beach in Calvert or southern Charles County when you come across a shark s tooth laying in the sand at the water s edge. You pick
Name Date EARTH S HISTORY VOCABULARY
 Name Date EARTH S HISTORY VOCABULARY Use Figure 2 to answer the following two questions. 10. Interpreting Graphics Which is older the sandstone layer or Dike A? Explain your answer. Conglomerate Sandstone
Name Date EARTH S HISTORY VOCABULARY Use Figure 2 to answer the following two questions. 10. Interpreting Graphics Which is older the sandstone layer or Dike A? Explain your answer. Conglomerate Sandstone
Fossils. Definitions. Fossil: any evidence of ancient life that is preserved in an unconsolidated sediment or sedimentary rock.
 Fossils defined Types of fossils Fossilization Mass extinctions Fossils and Time Fossils Definitions Fossil: any evidence of ancient life that is preserved in an unconsolidated sediment or sedimentary
Fossils defined Types of fossils Fossilization Mass extinctions Fossils and Time Fossils Definitions Fossil: any evidence of ancient life that is preserved in an unconsolidated sediment or sedimentary
Fossils, Fossils Everywhere
 Fossils, Fossils Everywhere Level: Grades 4 6 Standards: Explain how fossils provide evidence of the history of the Earth. (Michigan E.ST.04.31) Objectives: Materials: Time Consideration: Background: Learners
Fossils, Fossils Everywhere Level: Grades 4 6 Standards: Explain how fossils provide evidence of the history of the Earth. (Michigan E.ST.04.31) Objectives: Materials: Time Consideration: Background: Learners
Topic 7: Historical Geology
 Topic 7: Historical Geology (ES. 8 b, 9 a-e, 10 a-d, 12 a, b, e) ES.8 The student will investigate and understand geologic processes including plate tectonics. Key concepts include: b) processes (faulting,
Topic 7: Historical Geology (ES. 8 b, 9 a-e, 10 a-d, 12 a, b, e) ES.8 The student will investigate and understand geologic processes including plate tectonics. Key concepts include: b) processes (faulting,
FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past
 FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past Fossils form when water replaces the cells of dead animals or plants with minerals. These minerals then petrify into rock to form the fossils we see in museums.
FOSSILS Uncovering Clues to the Earth s Past Fossils form when water replaces the cells of dead animals or plants with minerals. These minerals then petrify into rock to form the fossils we see in museums.
Fossils and Evolution 870:125
 Fossils and Evolution 870:125 Review syllabus Text Supplemental resources Objectives Tests and grading Trip to Ashfall (NE) Fossils & Evolution Chapter 1 1 Ch. 1 Key concepts to know The fossil record
Fossils and Evolution 870:125 Review syllabus Text Supplemental resources Objectives Tests and grading Trip to Ashfall (NE) Fossils & Evolution Chapter 1 1 Ch. 1 Key concepts to know The fossil record
1 The origin of life (pp )
 ST chapter only Checkup Chapter 10 1 The origin of life (pp. 300 305) 1. Earth took millions of years to form. a) Where did the matter that formed our planet come from? From a cloud of gas and dust that
ST chapter only Checkup Chapter 10 1 The origin of life (pp. 300 305) 1. Earth took millions of years to form. a) Where did the matter that formed our planet come from? From a cloud of gas and dust that
Earth s History. The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
 Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Study Guide. Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change CHAPTER 14
 Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 14 Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change In your textbook, read about Earth s early history. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. Solid Earth formed about
Name Date Class Study Guide CHAPTER 14 Section 1: Fossil Evidence of Change In your textbook, read about Earth s early history. For each statement below, write true or false. 1. Solid Earth formed about
THE CHANGING SURFACE OF THE EARTH
 THE CHANGING SURFACE OF THE EARTH Key words Drain geological agent weathering erosion Sediment deposition transport The landscape is a consequence of the action of two types of geological processes; internal
THE CHANGING SURFACE OF THE EARTH Key words Drain geological agent weathering erosion Sediment deposition transport The landscape is a consequence of the action of two types of geological processes; internal
THIRD GRADE PAST LIFE
 THIRD GRADE PAST LIFE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES ROCK CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE CHEMISTRY WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing elements of the periodic table. LAB: Discovering properties of compounds. POST:
THIRD GRADE PAST LIFE 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES ROCK CYCLE OVERVIEW OF THIRD GRADE CHEMISTRY WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing elements of the periodic table. LAB: Discovering properties of compounds. POST:
Presented to grade 5-7; appropriate for grades 1-9 with age appropriate modifications Duration of lesson: 1 hour Notes:
 Science Unit: Lesson # 8: Fossils Making Fossils School Year: 2015/2016 Developed for: George T. Cunningham, Vancouver School District Developed by: Kate Gregory (scientist); Jodi Carson and Craig McNeil
Science Unit: Lesson # 8: Fossils Making Fossils School Year: 2015/2016 Developed for: George T. Cunningham, Vancouver School District Developed by: Kate Gregory (scientist); Jodi Carson and Craig McNeil
3rd-4th Grade. The Fossilization Process Flip Chart
 3rd-4th Grade The Fossilization Process Flip Chart Step 1 Page 2 Step 1 Apologetics What are fossils? A fossil is any trace left by something that lived in the past. Animals, plants, and humans have all
3rd-4th Grade The Fossilization Process Flip Chart Step 1 Page 2 Step 1 Apologetics What are fossils? A fossil is any trace left by something that lived in the past. Animals, plants, and humans have all
test date Name date Review: Geologic Time & Geologic Procesess-: You will record 1-38 answers on the scan sheet! These are worth 1.
 Review: Geologic Time & Geologic Procesess-: You will record 1-38 answers on the scan sheet! These are worth 1.5 points each Use your EARTH HISTORY CHART Part I. Matching All of the statements match to
Review: Geologic Time & Geologic Procesess-: You will record 1-38 answers on the scan sheet! These are worth 1.5 points each Use your EARTH HISTORY CHART Part I. Matching All of the statements match to
FoSSil Puzzler (1 Hour)
 FoSSil Puzzler (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 2 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW Students will examine and sketch various trace fossils from an unknown creature and then construct an image of the
FoSSil Puzzler (1 Hour) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 2 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW Students will examine and sketch various trace fossils from an unknown creature and then construct an image of the
A Trip Through Geologic Time
 Date Class _ A Trip Through Geologic Time Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Late in the Paleozoic Era, the supercontinent Pangaea formed.
Date Class _ A Trip Through Geologic Time Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Late in the Paleozoic Era, the supercontinent Pangaea formed.
6/30/2018. Geologic Time. Earth, Chapter 9 Chapter 9 Geologic Time
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Geologic Time Earth, Chapter 9 Chapter 9 Geologic Time The Importance of a Time Scale Interpreting Earth s history is an important goal of the science of
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Geologic Time Earth, Chapter 9 Chapter 9 Geologic Time The Importance of a Time Scale Interpreting Earth s history is an important goal of the science of
Clues to Earth s Past
 Chapter Review Clues to Earth s Past Part A. Vocabulary Review Directions: Use the clues below to complete the crossword puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Across 2. Element found in tissues of most organisms 4.
Chapter Review Clues to Earth s Past Part A. Vocabulary Review Directions: Use the clues below to complete the crossword puzzle. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Across 2. Element found in tissues of most organisms 4.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 1, pages 56 to 66 2.4: Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rock Formation All sedimentary rocks form through compaction and cementation
Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 1, pages 56 to 66 2.4: Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rock Formation All sedimentary rocks form through compaction and cementation
Online Fossil Lab Fossil Formation How Fossils Form 1. Describe the process in which fossils form.
 Name: Online Fossil Lab Fossil Formation How Fossils Form 1. Describe the process in which fossils form. Period: 2. What is a Mold? 3. What is a cast? Getting into the Fossil Record 4. What is the fossil
Name: Online Fossil Lab Fossil Formation How Fossils Form 1. Describe the process in which fossils form. Period: 2. What is a Mold? 3. What is a cast? Getting into the Fossil Record 4. What is the fossil
Common Fossils in Pennsylvania
 Common Fossils in Pennsylvania Dinosaurs? Not common in Pennsylvania Only found in Southeastern Part of the state Dinosaurs wondered near the lakes and swamps and are preserved there dating from the Triassic
Common Fossils in Pennsylvania Dinosaurs? Not common in Pennsylvania Only found in Southeastern Part of the state Dinosaurs wondered near the lakes and swamps and are preserved there dating from the Triassic
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks
 Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
 UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
NUTRIENT CYCLES. Water Carbon Nitrogen
 NUTRIENT CYCLES Water Carbon Nitrogen NUTRIENT CYCLES Energy transfer through an ecosystem is ONE WAY Most energy is lost as heat Nutrients such as nitrogen, water and carbon are able to cycle through
NUTRIENT CYCLES Water Carbon Nitrogen NUTRIENT CYCLES Energy transfer through an ecosystem is ONE WAY Most energy is lost as heat Nutrients such as nitrogen, water and carbon are able to cycle through
Fossils. Name Date Class. A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary
 Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
Name Date Class A Trip Through Geologic Time Section Summary Fossils Guide for Reading How do fossils form? What are the different kinds of fossils? What does the fossil record tell about organisms and
3 Absolute Dating: A Measure of Time
 CHAPTER 3 3 Absolute Dating: A Measure of Time SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can geologists learn the
CHAPTER 3 3 Absolute Dating: A Measure of Time SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How can geologists learn the
Objectives. Vocabulary. Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch.
 The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch. Vocabulary geologic time scale eon era period
The Geologic Time Scale Objectives Describe the geologic time scale. Distinguish among the following geologic time scale divisions: eon, era, period, and epoch. Vocabulary geologic time scale eon era period
8. GEOLOGIC TIME LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions 8. GEOLOGIC TIME Refer to Exercise 6 in your Lab Manual on pages 151-168 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will be graded on the basis
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: Instructions 8. GEOLOGIC TIME Refer to Exercise 6 in your Lab Manual on pages 151-168 to answer the questions in this work sheet. Your work will be graded on the basis
and Fuels OSSIIS Vocabulary Process Skill
 \ Vocabulary fossil, C22 amber, C22 fuel, C26 OSSIIS and Fuels Process Skill The objects captured in this piece of amber were once alive. Now they are fossils. Fossils tell us the story of life on Earth
\ Vocabulary fossil, C22 amber, C22 fuel, C26 OSSIIS and Fuels Process Skill The objects captured in this piece of amber were once alive. Now they are fossils. Fossils tell us the story of life on Earth
Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale
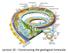 Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale Geologic Time Discovering the magnitude of the Earth s past was a momentous development in the history of humanity This discovery forever altered our perception
Lecture 10 Constructing the geological timescale Geologic Time Discovering the magnitude of the Earth s past was a momentous development in the history of humanity This discovery forever altered our perception
Geologic Time. Earth s History
 Geologic Time Chapter 12 Earth s History Earth s history is recorded in rocks Rocks record geological events and changing life forms of the past. We have learned that Earth is much older than anyone had
Geologic Time Chapter 12 Earth s History Earth s history is recorded in rocks Rocks record geological events and changing life forms of the past. We have learned that Earth is much older than anyone had
Name: Period: Date: ID: A. Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank.
 Name: Period: _ Date: _ ID: A Unit 7 Practice Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank. 1. What term describes the movement of rock
Name: Period: _ Date: _ ID: A Unit 7 Practice Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank. 1. What term describes the movement of rock
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (6) : Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Origin and nature of sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (6) : Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6: Sedimentary Rocks Origin and nature of sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale
 Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
Fossils & The Geologic Time Scale Fossils Preserved remains or traces of an organism that lived in the past. Fossils are formed when organisms die and are buried in sediment. Eventually the sediment builds
THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH EARTH SCIENCE
 THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH EARTH SCIENCE FOSSILS Paleontology is the study of life that existed in prehistoric times A fossil is any evidence of earlier life preserved in rock. Shells Bones Petrified trees
THE HISTORY OF THE EARTH EARTH SCIENCE FOSSILS Paleontology is the study of life that existed in prehistoric times A fossil is any evidence of earlier life preserved in rock. Shells Bones Petrified trees
Earth Materials Unit: Sedimen ntary Rocks and Processes Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Five and Six Lab: Laboratorry Six Name
 Earth Materi ials Unit: Sedimentary Rocks and Proces sses Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Fivee and Six Lab: Laboratory Six Name Page 1 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Purpose: To classify sedimentary rocks
Earth Materi ials Unit: Sedimentary Rocks and Proces sses Maybe One Day Text: Chapters Fivee and Six Lab: Laboratory Six Name Page 1 Sedimentary Rocks and Processes Purpose: To classify sedimentary rocks
