Prof. M. G. Thakkar & Gaurav Chauhan Department of Earth and Environmental Science KSKV Kachchh University Bhuj-Kachchh
|
|
|
- Adam Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prof. M. G. Thakkar & Gaurav Chauhan Department of Earth and Environmental Science KSKV Kachchh University Bhuj-Kachchh
2 CONTINENTAL DRIFTING: PRE-JURASSIC POSITION OF THE CONTINENTS Kachchh rift model INTERSECTING RIFTS Rifting generated the normal tectonics and open embayment half graben system in the western margin of Indian plate On this basement the Jurassic rocks laid down
3 Location of Kachchh Rift basin in Indian plate context. Location map of Kachchh rift basin See the Kachchh Rift is situated to the south of Indian foreland basin, north of Kathiyawar horst and west of the Cambay Rift. It is a marginal cratonic basin bounded by NPF Nagar Parkar Fault and NKF North Kathiyawar Fault (Top) DEM of Kachchh basin
4 Basin Evolution 1. Gondwana Fracturing 2. Rifting 3. Rift basin formation 4. Rift sedimentation (continental to shallow marine and carbonates) 5. Drifting and continental deposition 6. Sagging 7. Sag basin formation 8. Half graben open embayment basin 9. Marine transgressive and regressive sediments 10. Rift inversion 11. Half graben formation 12. Formation of Banni, Rann and various uplifts TRIASSIC to EARLY JURASSIC QUATERNARY MID LATE JURASSIC CRETACEOUS CRETACEOUS TO EARLY TERTIARY EARLY TO LATE TERTIARY QUATERNARY Reactivation of Old faults Generation of new faults blind faults Collision of India and Asia produced the Himalaya and uplifted the Kachchh basin Landscape evolution : Generation of geomorphic features like Gorges, Gullies, Straight mountain fronts, Young Fault Scarps, Triangular facets etc.
5 X NKF KHF KMF BF GDF IBF NPF : North Kathiyawar Fault : Katrol Hill Fault : Kachchh Mainland Fault : Banni Fault : Goradungar Fault : Island Belt Fault : Nagar Parkar Fault Y After Biswas, S. K. (1971) IBF Geological Cross section across Kachchh basin, (cross section line is marked by red colour)
6 Great Rann of Kachchh Island belt Wagad Kachchh mainland
7 Geological map of Kachchh (After Biswas, 1987)
8 TECTONIC MAP OF KACHCHH
9 North facing view: straight mountain fronts and escarpments Khadir Island PAKISTAN Nagar Parker (Pak) IBF Sir Creek Luckp Kori Creek at Kachchh Mainland Linear Trench Zone Bet Zone Banni Plains Kuar Bet Patchham Is. Great Barren Zone Khadir Is. Bela Is. Wagad uplift Chorar Is. BELA ISLAND South facing view: a gentle slope to south Fault (IBF) expression on landscape Kaladungar range Rann of Kachchh N IBF Goradungar range Style of Reverse faulting in Kachchh basin IBF Kaladungar scarp Receding scarp of IBF at Kaladongar range Kuar bet
10 TRANSVERSE strike slip faults that displace the domes Topography of Structural Domes in Kachchh Domes developed along the E-W master faults while uplift GUNERI DOME (small dome along KMF) Mainland of Kachchh (Upthrown hanging block) Transverse fault KMF Plain of Banni
11 Transverse Faults
12 Segmentation of Katrol Hill Fault by many transverse faults (C) Distribution of Quaternary deposits in the hinterland are mostly on the hinge zone of median high (A) (B) (D)
13 Clustering of the transverse faults (N-S, NW-SE, NE- SW, NNE-SSW) in the central part of the Kachchh mainland indicates fracturing along the Median High bulging axes (See the above tectonic map for median high region in the basin)
14 NEOTECTONIC STUDY OF RATIYA AND KODKI FAULTS Khari River Regional Slope Dn Stream direction BHUJ Locations of Ratiya and Kodki transverse faults in the middle part of the Median High. Red arrows indicate Parallel faults in the central mainland Kachchh; while close field observation unfolds the facts that the downthrow of these hinge faults are very small and Normal in nature. Regional slope of terrain is SW, SE or East, but downstream direction is to the North.
15 N-S and NNE-SSW trending Transverse faults are very distinct features in Central Kachchh Mainland. Several transverse faults do have dykes along the faults, which indicates that the TF are not young, but initiated during the basin inversion in early Tertiary Reactivation of median high axes also triggers less throw, extensive faults
16 Kodki Fault FIELD OBSERVATION Dolaritic dyke Black shale Black shale Deltaic sandstone of Cretaceous age is traversed by the N-S trending faults and igneous dykes. The dykes are post-cretaceous trappean age Faults are reactivated in Quaternary modifying the landscape These transverse faults with normal nature are high angle, small throw hinge fractures
17 Katrol Hill Range a fault controlled ridge Early Quaternary erosional surface Late Tertiary erosional remnants Fault controlled morphology (Transverse fault controlled ridge is perpendicular to the Katrol Hill Fault) Transverse fault controlled ridge II to N-S dykes Kodki Transverse fault Sliken slides on this fault indicates Normal Fault with dip slip motion
18 Ratiya Fault FIELD OBSERVATION Fault controlled young valley N 53 0 S Fault plane
19 Fault controlled young bedrock river and responsible Ratiya Fault S2 E Downstream Upthrown block S S1 Fault plane 53 0 Downthrown block N S2
20 Fault controlled young bedrock river Ratiya Nala S2 Upthrown block Downstream Footwall S1 Downthrown block Hanging wall The downthrown block in the foreground is standing at higher position while the upthrown block is more incised to the base level Wider bedrock channel of Ratiya Nala indicates prolonged erosion The Ratiya channel is fed by two younger streams S1 and S2 that post dates the fault
21 R1= ka Angular to sub-angular platy lthoclasts (Debris deposits) Ratiya fault and arrested debris deposits Sand dominated clast supported gravels Clast supported gravels with fine yellow sand and clay Clayey and silty sand Fluvial coarse sand Bedrock sandstone R1= ka
22 1. Youthful incision developed on the downthron block 2. N- S flowing fault controlled valley (S1) 3. A new stream S2 developed during lateral erosion
23 Incision along the newly generated S 1 stream (post 38k) with bedrock terraces and gorges SUBSIDIARY STREAM OF RATIYA NALA
24 Ratiya Fault has arrested significant fluvial deposits for ~ 38 ka (OSL dates confirm it). Based on the present study we could construct the
25 Paleochannel Paleochannel Paleochannel Satellite picture of Ratiya Nala (flowing to the east) Note plough fields on the paleochannel deposits owing its fertility. Note River offset due to the Ratiya Fault, and Two young streams formed due to lateral incision They all meet at the fault sags and finally occupies the old bedrock channel
26 N Fault plane is here Extended N-S S2 E Upthrown block N-S trending Ratiya Fault S1 S Downthrown block HANGING WALL Paleo waterfall / knick point Quaternary channel debris flow and fluvial sand bar deposits Chronology of Landscape Evolution along N-S Ratiya Nala (Conclusion) 1. Formation of East flowing master bedrock channel (Ratiya) earlier then 38 k 2. Formation of Ratiya fault (N-S) with > 2.0 m down throw towards west 3. East flowing master channel (from the foreground to background) blockage due to hanging wall subsidence 4. Deposition of Quaternary channel debris, fluvial sand bar deposits (6.5m deposits) until ~ 33k 5. Lateral incision formation of two subsidiary channels flowing towards the fault sag 6. Footwall incision intensifies with lateral incision 7. Two lateral streams S1 and S2 with youthful valleys confluence at the middle and occupied the older/ East flowing bedrock channel
27 Block model of Ratiya fault Median high hinge fault and subequent landscape evolution from 38.8 k to present day (based on OSL dates)
28 University Fault Kachchh University UNIVERSITY FAULT Another NE-SW trending hinge fault passes through the Kachchh University campus having 2 m throw categorized as extensional fracture faults on bulging axes. Such faults are not much deep seated; however the deeper parts are showing compressional shear zones evidenced from large shear zone exposed within the city of Bhuj
29 A C Closer look of University Fault: Note the ground to the east is uplifted and rocks are exposed as bright and brown colors. The DEM (below) prepared by the detail mapping using Total Station A typical fracture fault where one block overrides other as epigenetic brittle faulting D B
30 Neotectonic features developed along the median high region of Kachchh mainland Significant incision along the bedrock rivers Incision in the Quaternary fluvial deposits N-S trending Fault scarps preserved in hard rocks Incised valleys and intermittent gorges in the valley fill miliolites Other Transverse valley incision along the Median High axis (Loc. Khari River Bharasar village) Exposing the Jurassic Rocks
31 (A) (B) (C) Landscape features developed along the transverse faults and lineaments (E) (F) (D) A - KHF Scarp at Katrod B - Close view of the colluvial deposits incised by a small stream at the base of Khatrod scarp C - Cliff section of Gunawari stream showing incision in the fluvial deposits. Note the incision in the Jurassic rocks exposed in the river bed D - Upstream view of Khari gorge north of KHF E - Close up of Khari gorge F - Narrow gorge developed in Cretaceous sandstone near Bharapar village south of KHF
32 KACHCHH MAINLAND Youthful Neotectonic feature along the transverse faults / median high hinge fractures Bedrock terraces with deep gorges developed in Bhuj sandstone. The paleo-channel passes NW of present day gorge indicates shifting of the bedrock river forming epigenetic gorge LANDSCAPE EVOLUTION : HILLY UPLANDS QUATERNARY LANDSCAPE
33 Summery Kachchh Mainland Fault and Katrol Hill Fault are dissected by transverse faults of varying trends Most transverse faults are caused by the structural bending of Median high University fault, Ratiya Fault and Kodki faults are low amplitude faults developed as bending fractures on the crest of the Median High. These show geometry of normal, reserve and strike slip movement in the field N-S trending Kodki fault shows normal nature forming graben and half-graben structures, while NNE-SSW trending University fault is reverse forming a small scarp. Ratiya fault is oblique slip in nature evidenced by drainage offsetting and alluvial fan and debris deposits on the hanging wall, above the fault plane Presently studied varied (normal, reverse and oblique slip) transverse faults are restricted to the Median High region between two major E-W trending reverse faults (KMF & KHF) suggesting N-S and E-W compressive stresses. The studies suggest that in neotectonic movement in median high of Kachchh mainland has generated varied transverse faults due to multiple stress regimes during inversion phase. It needs detailed geodetic and structural analysis to know the sources of these tectonic forces.
34 TYPICAL SAND BLOW OF 2001 AT CHOBARI MANFARA FAULT (4 Km EAST OF KHAROI) Photographs taken in March 2003 Transverse faults developed in 2001 Bhuj earthquake LIQUEFACTION GROUND
35 Dr. M. G. Thakkar Department of Earth and Environmental Science, KSKV Kachchh University, Bhuj, Kachchh
36 Salt encrustation in the Great Rann of Kachchh
37 Banjaras Nomads in Kachchh
38 The youngest topography in Kachchh, western India: It is the axial region of 90 km long 16 km wide and 2.5m high co-seismic hump developed in the Great Rann-salt playa of Kachchh during AD 1819 Allahbund earthquake in western India
39 The invertebrates like Sepia Belemnites in the narrow Jurassic sea of Kachchh flourished ~ 160 million years from today: The rock of Kachchh say it
Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting
 Crustal Deformation AKA Structural geology (adapted from Brunkel, 2012) Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting How Rocks Deform: 4 Controls
Crustal Deformation AKA Structural geology (adapted from Brunkel, 2012) Study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. Folding and Faulting How Rocks Deform: 4 Controls
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building
 Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
Earth Science, (Tarbuck/Lutgens) Chapter 10: Mountain Building 1) A(n) fault has little or no vertical movements of the two blocks. A) stick slip B) oblique slip C) strike slip D) dip slip 2) In a(n) fault,
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Geologic Structures. Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress
 Geologic Structures Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress Figure 15.19 Can be as big as a breadbox Or much bigger than a breadbox Three basic types Fractures >>>
Geologic Structures Changes in the shape and/or orientation of rocks in response to applied stress Figure 15.19 Can be as big as a breadbox Or much bigger than a breadbox Three basic types Fractures >>>
Active fault traces along Bhuj Fault and Katrol Hill Fault, and trenching survey at Wandhay, Kachchh, Gujarat, India
 Active fault traces along Bhuj Fault and Katrol Hill Fault, and trenching survey at Wandhay, Kachchh, Gujarat, India Michio Morino 1,, Javed N Malik 2,, Prashant Mishra 2,, Chandrashekhar Bhuiyan 2, and
Active fault traces along Bhuj Fault and Katrol Hill Fault, and trenching survey at Wandhay, Kachchh, Gujarat, India Michio Morino 1,, Javed N Malik 2,, Prashant Mishra 2,, Chandrashekhar Bhuiyan 2, and
Deformation of Rocks. Orientation of Deformed Rocks
 Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Deformation of Rocks Folds and faults are geologic structures caused by deformation. Structural geology is the study of the deformation of rocks and its effects. Fig. 7.1 Orientation of Deformed Rocks
Chapter 15 Structures
 Chapter 15 Structures Plummer/McGeary/Carlson (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. TECTONIC FORCES AT WORK Stress & Strain Stress Strain Compressive stress Shortening strain Tensional stress stretching
Chapter 15 Structures Plummer/McGeary/Carlson (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. TECTONIC FORCES AT WORK Stress & Strain Stress Strain Compressive stress Shortening strain Tensional stress stretching
Evidence of neotectonic reactivation of the Katrol Hill Fault during late Quaternary and its GPR characterization
 Evidence of neotectonic reactivation of the Katrol Hill Fault during late Quaternary and its GPR characterization A. K. Patidar 1, D. M. Maurya 1, *, M. G. Thakkar 2 and L. S. Chamyal 1 1 Department of
Evidence of neotectonic reactivation of the Katrol Hill Fault during late Quaternary and its GPR characterization A. K. Patidar 1, D. M. Maurya 1, *, M. G. Thakkar 2 and L. S. Chamyal 1 1 Department of
Active Low-Angle Reverse Fault and Wide Quaternary Deformation Identified in Jhura Trench across the Kachchh Mainland Fault, Kachchh, Gujarat, India
 活断層研究 29 号 71 77 2008 71 Active Low-Angle Reverse Fault and Wide Quaternary Deformation Identified in Jhura Trench across the Kachchh Mainland Fault, Kachchh, Gujarat, India Michio Morino a, Javed N. Malik
活断層研究 29 号 71 77 2008 71 Active Low-Angle Reverse Fault and Wide Quaternary Deformation Identified in Jhura Trench across the Kachchh Mainland Fault, Kachchh, Gujarat, India Michio Morino a, Javed N. Malik
Tectonics is a study of the major structural features of the Earth s crust or a broad structure of a region. Tecto- means building
 TECTONICS AND TECTONIC STRUCTURES Tectonics is a study of the major structural features of the Earth s crust or a broad structure of a region. Tecto- means building The plate theory Different stages are
TECTONICS AND TECTONIC STRUCTURES Tectonics is a study of the major structural features of the Earth s crust or a broad structure of a region. Tecto- means building The plate theory Different stages are
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures. But first a short review
 How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first a short review Where do we see deep earthquakes? What is happening there? What can happen at a plate boundary? 1. Plates can move apart
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first a short review Where do we see deep earthquakes? What is happening there? What can happen at a plate boundary? 1. Plates can move apart
Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building. Fig. 10.1
 Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building Fig. 10.1 OBJECTIVES Describe the processes of rock deformation and compare and contrast ductile and brittle behavior in rocks. Explain how strike and dip
Chapter 10: Deformation and Mountain Building Fig. 10.1 OBJECTIVES Describe the processes of rock deformation and compare and contrast ductile and brittle behavior in rocks. Explain how strike and dip
Plate Tectonics - Demonstration
 Name: Reference: Prof. Larry Braile - Educational Resources Copyright 2000. L. Braile. Permission granted for reproduction for non-commercial uses. http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~braile/indexlinks/educ.htm
Name: Reference: Prof. Larry Braile - Educational Resources Copyright 2000. L. Braile. Permission granted for reproduction for non-commercial uses. http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~braile/indexlinks/educ.htm
Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11
 Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11 Objectives: 1)Explain how some of Earth s major mountain belts formed 2) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins 3) Explain how compression,
Mountains and Mountain Building: Chapter 11 Objectives: 1)Explain how some of Earth s major mountain belts formed 2) Compare and contrast active and passive continental margins 3) Explain how compression,
GEOLOGIC MAPS PART II
 EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT THROUGH TIME LABORATORY - EES 1005 LABORATORY FIVE GEOLOGIC MAPS PART II Introduction Geologic maps of orogenic belts are much more complex than maps of the stable interior. Just
EARTH AND ENVIRONMENT THROUGH TIME LABORATORY - EES 1005 LABORATORY FIVE GEOLOGIC MAPS PART II Introduction Geologic maps of orogenic belts are much more complex than maps of the stable interior. Just
Stress and Strain. Stress is a force per unit area. Strain is a change in size or shape in response to stress
 Geologic Structures Geologic structures are dynamically-produced patterns or arrangements of rock or sediment that result from, and give information about, forces within the Earth Produced as rocks change
Geologic Structures Geologic structures are dynamically-produced patterns or arrangements of rock or sediment that result from, and give information about, forces within the Earth Produced as rocks change
STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI
 STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI LAURA K.O. SMITH AND SARAHTSETSEG PUREDORG Princeton University, Mongolian University of Science and Technology Sponsors: Ramon Gonzalez-Mieres
STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI LAURA K.O. SMITH AND SARAHTSETSEG PUREDORG Princeton University, Mongolian University of Science and Technology Sponsors: Ramon Gonzalez-Mieres
How mountains are made. We will talk about valleys (erosion and weathering later)
 How mountains are made We will talk about valleys (erosion and weathering later) http://www.ilike2learn.com/ilike2learn/mountainmaps/mountainranges.html Continent-continent plate convergence Less dense,
How mountains are made We will talk about valleys (erosion and weathering later) http://www.ilike2learn.com/ilike2learn/mountainmaps/mountainranges.html Continent-continent plate convergence Less dense,
Cenozoic Extensional Basin Development and Sedimentation in SW Montana
 Cenozoic Extensional Basin Development and Sedimentation in SW Montana Robert C. Thomas Department of Environmental Sciences, The University of Montana Western, Dillon, MT 59725, (406) 683-7615, r_thomas@umwestern.edu
Cenozoic Extensional Basin Development and Sedimentation in SW Montana Robert C. Thomas Department of Environmental Sciences, The University of Montana Western, Dillon, MT 59725, (406) 683-7615, r_thomas@umwestern.edu
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Press & Siever, compressive forces. Compressive forces cause folding and faulting.
 Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures. But first, questions
 How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first, questions Questions your students might ask How were Montana s mountains formed? How old are the mountains? What are the different ways
How to Build a Mountain and other Geologic Structures But first, questions Questions your students might ask How were Montana s mountains formed? How old are the mountains? What are the different ways
Vail et al., 1977b. AAPG 1977 reprinted with permission of the AAPG whose permission is required for further use.
 Well 5 Well 4 Well 3 Well 2 Well 1 Vail et al., 1977b AAPG 1977 reprinted with permission of the AAPG whose permission is required for further use. Well 5 Well 4 Well 3 Well 2 Well 1 Vail et al., 1977b
Well 5 Well 4 Well 3 Well 2 Well 1 Vail et al., 1977b AAPG 1977 reprinted with permission of the AAPG whose permission is required for further use. Well 5 Well 4 Well 3 Well 2 Well 1 Vail et al., 1977b
Geology (Mellow) Hike, Santa Lucia Memorial Park February 16, I. Overview of Santa Lucia Range geology and tectonic history
 Geology (Mellow) Hike, Santa Lucia Memorial Park February 16, 2015 I. Overview of Santa Lucia Range geology and tectonic history A. Basement Rocks 1. Salinian Block Rocks Sierra Nevada Type, continental
Geology (Mellow) Hike, Santa Lucia Memorial Park February 16, 2015 I. Overview of Santa Lucia Range geology and tectonic history A. Basement Rocks 1. Salinian Block Rocks Sierra Nevada Type, continental
KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B
 GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
GEOLOGY 12 KEY CHAPTER 12 TAKE-HOME QUIZ INTERNAL STRUCTURES AND PROCESSES Score Part B = / 55 PART B CHAPTER 12 Isostacy and Structural Geology 1. Using the terms below, label the following diagrams and
UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS
 UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS ROCK DEFORMATION Tectonic forces exert different types of stress on rocks in different geologic environments. STRESS The first, called confining stress
UNIT 10 MOUNTAIN BUILDING AND EVOLUTION OF CONTINENTS ROCK DEFORMATION Tectonic forces exert different types of stress on rocks in different geologic environments. STRESS The first, called confining stress
Structural Modelling of Inversion Structures: A case study on South Cambay Basin
 10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 065 Structural Modelling of Inversion Structures: A case study on South Cambay Basin Dr. Mayadhar Sahoo & S.K Chakrabarti Summary The inversion in
10 th Biennial International Conference & Exposition P 065 Structural Modelling of Inversion Structures: A case study on South Cambay Basin Dr. Mayadhar Sahoo & S.K Chakrabarti Summary The inversion in
Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building
 Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared
Crags, Cracks, and Crumples: Crustal Deformation and Mountain Building Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared
Lab 7: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY FOLDS AND FAULTS
 Lab 7: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY FOLDS AND FAULTS This set of labs will focus on the structures that result from deformation in earth s crust, namely folds and faults. By the end of these labs you should be able
Lab 7: STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY FOLDS AND FAULTS This set of labs will focus on the structures that result from deformation in earth s crust, namely folds and faults. By the end of these labs you should be able
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education
 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
depression above scarp scarp
 1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
1 LAB 1: FIELD TRIP TO McKINLEYVILLE AND MOUTH OF THE MAD RIVER OBJECTIVES: a. to look at geomorphic and geologic evidence for large scale thrust-faulting of young sediments in the Humboldt Bay region
Name: Date: Use the following to answer question 2.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following statements regarding the scientific method is false? A) A hypothesis must be agreed upon by more than one scientist. B) A theory is a hypothesis that has withstood
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following statements regarding the scientific method is false? A) A hypothesis must be agreed upon by more than one scientist. B) A theory is a hypothesis that has withstood
December 21, Chapter 11 mountain building E.notebook. Feb 19 8:19 AM. Feb 19 9:28 AM
 Mountains form along convergent plate boundaries. Typically (usually) if you look at a mountain range, you know that it is at a plate boundary (active continental margin) or has been some time in the past
Mountains form along convergent plate boundaries. Typically (usually) if you look at a mountain range, you know that it is at a plate boundary (active continental margin) or has been some time in the past
The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System. The Structure of the Earth. Temperature 3000º ºC. Mantle
 The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System Objectives: Understand the structure of the planet Earth Review the geologic timescale as a point of reference for the history of the Earth Examine the major relief
The Lithosphere and the Tectonic System Objectives: Understand the structure of the planet Earth Review the geologic timescale as a point of reference for the history of the Earth Examine the major relief
Name. GEOL.5220 Structural Geology Faults, Folds, Outcrop Patterns and Geologic Maps. I. Properties of Earth Materials
 I. Properties of Earth Materials GEOL.5220 Structural Geology Faults, Folds, Outcrop Patterns and Geologic Maps Name When rocks are subjected to differential stress the resulting build-up in strain can
I. Properties of Earth Materials GEOL.5220 Structural Geology Faults, Folds, Outcrop Patterns and Geologic Maps Name When rocks are subjected to differential stress the resulting build-up in strain can
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone
 General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone David Hoffman University of Missouri Rolla Natural Hazards Mitigation Institute Civil, Architectural & Environmental
General Geologic Setting and Seismicity of the FHWA Project Site in the New Madrid Seismic Zone David Hoffman University of Missouri Rolla Natural Hazards Mitigation Institute Civil, Architectural & Environmental
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Crustal Deformation. Earth Systems 3209
 Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Crustal Deformation Earth Systems 3209 Crustal Deformation pg. 415 Refers to all changes in the original form and/or size of a rock body. May also produce changes in the location and orientation of rocks.
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name
 Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The portion of a fracture
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The portion of a fracture
A comparison of structural styles and prospectivity along the Atlantic margin from Senegal to Benin. Peter Conn*, Ian Deighton* & Dario Chisari*
 A comparison of structural styles and prospectivity along the Atlantic margin from Senegal to Benin Overview Peter Conn*, Ian Deighton* & Dario Chisari* * TGS, Millbank House, Surbiton, UK, KT6 6AP The
A comparison of structural styles and prospectivity along the Atlantic margin from Senegal to Benin Overview Peter Conn*, Ian Deighton* & Dario Chisari* * TGS, Millbank House, Surbiton, UK, KT6 6AP The
What Causes Rock to Deform?
 Crustal Deformation Earth, Chapter 10 Chapter 10 Crustal Deformation What Causes Rock to Deform? Deformation is a general term that refers to all changes in the shape or position of a rock body in response
Crustal Deformation Earth, Chapter 10 Chapter 10 Crustal Deformation What Causes Rock to Deform? Deformation is a general term that refers to all changes in the shape or position of a rock body in response
Geology 15 West Valley College. Exam IV: Sierra Nevada
 Geology 15 West Valley College Name Exam IV: Sierra Nevada 1) On the diagram above, where is the Arc- Trench Gap? a. 1 and 3 c. 7 and 8 d. 6 e. 5 and 10 2) On the diagram above, where is the subduction
Geology 15 West Valley College Name Exam IV: Sierra Nevada 1) On the diagram above, where is the Arc- Trench Gap? a. 1 and 3 c. 7 and 8 d. 6 e. 5 and 10 2) On the diagram above, where is the subduction
Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands
 Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Chapter. Mountain Building
 Chapter Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock type, and
Chapter Mountain Building 11.1 Rock Deformation Factors Affecting Deformation Factors that influence the strength of a rock and how it will deform include temperature, confining pressure, rock type, and
Learning Objectives (LO) What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 13: Mountain Building Read: Chapter 10 Homework #11 due Tuesday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Define the types of stress that are present in the crust! 2. Define the
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 13: Mountain Building Read: Chapter 10 Homework #11 due Tuesday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Define the types of stress that are present in the crust! 2. Define the
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems
 Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 5, 2017 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems Leszek Starkel Department of Geoenvironmental
Journal of Indian Geomorphology Volume 5, 2017 ISSN 2320-0731 Indian Institute of Geomorphologists (IGI) Paradoxes of Fluvial Evolution in Young Orogenic Systems Leszek Starkel Department of Geoenvironmental
Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice
 Name: Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice 1. Earth s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm 3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11
Name: Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice 1. Earth s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm 3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11
Meandering Miocene Deep Sea Channel Systems Offshore Congo, West Africa
 Meandering Miocene Deep Sea Channel Systems Offshore Congo, West Africa S. Baer* (PGS), J. E. Comstock (PGS), K. Vrålstad (PGS), R. Borsato (PGS), M. Martin (PGS), J.P. Saba (SNPC), B. Débi-Obambé (SNPC)
Meandering Miocene Deep Sea Channel Systems Offshore Congo, West Africa S. Baer* (PGS), J. E. Comstock (PGS), K. Vrålstad (PGS), R. Borsato (PGS), M. Martin (PGS), J.P. Saba (SNPC), B. Débi-Obambé (SNPC)
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
EDIMENTARY BASINS. What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour
 EDIMENTARY BASINS What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour WHAT IS A SEDIMENTARY BASIN? A low area on the Earth s surface relative to surroundings e.g. deep ocean basin (5-10 km deep) e.g.
EDIMENTARY BASINS What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour WHAT IS A SEDIMENTARY BASIN? A low area on the Earth s surface relative to surroundings e.g. deep ocean basin (5-10 km deep) e.g.
(1) Identify 5 major principles of relative dating? For each principle, describe how you tell what is younger and what is older.
 Things to Know - Third GLG101Exam Page 1 Important Note: This is not everything you need to know or study. However, it provides you with a relatively comprehensive list of questions to help you study.
Things to Know - Third GLG101Exam Page 1 Important Note: This is not everything you need to know or study. However, it provides you with a relatively comprehensive list of questions to help you study.
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
 Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory What is Plate Tectonics? - 7 large tectonic plates and many smaller ones that break up the lithosphere - Plates are brittle and float on asthenosphere and glide past
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory What is Plate Tectonics? - 7 large tectonic plates and many smaller ones that break up the lithosphere - Plates are brittle and float on asthenosphere and glide past
Not For Web Reproduction. New Topic: TECTONIC GEOMORPHOLOGY. Tectonic Geomorphology vs. Structural Geomorphology
 New Topic: TECTONIC GEOMORPHOLOGY Tectonic Geomorphology vs. Structural Geomorphology Late Cenozoic Tectonic Movement vs. Late Cenozoic Erosion of Older Structures Geologic Time Scale Not For Web Reproduction
New Topic: TECTONIC GEOMORPHOLOGY Tectonic Geomorphology vs. Structural Geomorphology Late Cenozoic Tectonic Movement vs. Late Cenozoic Erosion of Older Structures Geologic Time Scale Not For Web Reproduction
Correlation of gravel deposits from trenching project on Alder Creek fluvial terrace near Point Arena, California
 Correlation of gravel deposits from trenching project on Alder Creek fluvial terrace near Point Arena, California Aletha Lee Department of Geology and Geography, West Virginia University, White Hall, Morgantown,
Correlation of gravel deposits from trenching project on Alder Creek fluvial terrace near Point Arena, California Aletha Lee Department of Geology and Geography, West Virginia University, White Hall, Morgantown,
Depositional History and Petroleum Potential of Ombilin Basin, West Sumatra - Indonesia, Based on Surface Geological Data*
 Depositional History and Petroleum Potential of Ombilin Basin, West Sumatra - Indonesia, Based on Surface Geological Data* Yahdi Zaim 1, Litto Habrianta 2, Chalid I. Abdullah 1, Aswan 1, Yan Rizal 1, Nurcahyo
Depositional History and Petroleum Potential of Ombilin Basin, West Sumatra - Indonesia, Based on Surface Geological Data* Yahdi Zaim 1, Litto Habrianta 2, Chalid I. Abdullah 1, Aswan 1, Yan Rizal 1, Nurcahyo
Monday 16 May 2016 Morning
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Monday 16 May 2016 Morning AS GCE GEOLOGY F791/01 Global Tectonics *6007922565* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Monday 16 May 2016 Morning AS GCE GEOLOGY F791/01 Global Tectonics *6007922565* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
The Building of the NYC Region
 The Building of the NYC Region Definitions Fall Line marks the area where an upland region (continental bedrock) and a coastal plain meet Piedmont the plateau region of the eastern United States which
The Building of the NYC Region Definitions Fall Line marks the area where an upland region (continental bedrock) and a coastal plain meet Piedmont the plateau region of the eastern United States which
Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009
 Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves.
 Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Forces That Shape Earth. How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle?
 Forces That Shape Earth How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle? Plate Motion Mountain ranges are produced by plate tectonics. The theory of plate
Forces That Shape Earth How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle? Plate Motion Mountain ranges are produced by plate tectonics. The theory of plate
Lecture 9 faults, folds and mountain building
 Lecture 9 faults, folds and mountain building Rock deformation Deformation = all changes in size, shape, orientation, or position of a rock mass Structural geology is the study of rock deformation Deformation
Lecture 9 faults, folds and mountain building Rock deformation Deformation = all changes in size, shape, orientation, or position of a rock mass Structural geology is the study of rock deformation Deformation
What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley
 1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
Rilles Lunar Rilles are long, narrow, depressions formed by lava flows, resembling channels.
 Rilles Lunar Rilles are long, narrow, depressions formed by lava flows, resembling channels. Rugged Terra Rugged terra are mountainous regions of the moon. Wrinkle Ridges Wrinkle Ridges are created through
Rilles Lunar Rilles are long, narrow, depressions formed by lava flows, resembling channels. Rugged Terra Rugged terra are mountainous regions of the moon. Wrinkle Ridges Wrinkle Ridges are created through
Controls on clastic systems in the Angoche basin, Mozambique: tectonics, contourites and petroleum systems
 P2-2-13 Controls on clastic systems in the Angoche basin, Mozambique: tectonics, contourites and petroleum systems Eva Hollebeek, Olivia Osicki, Duplo Kornpihl Schlumberger, London, UK Introduction Offshore
P2-2-13 Controls on clastic systems in the Angoche basin, Mozambique: tectonics, contourites and petroleum systems Eva Hollebeek, Olivia Osicki, Duplo Kornpihl Schlumberger, London, UK Introduction Offshore
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor
 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
Figure 2.1: Constituent Area
 2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
2 The Region 2.1 CONSTITUENT AREA The National Capital Region includes NCT-Delhi, nine districts of Haryana, six districts of Uttar Pradesh and one district of Rajasthan. Total area of the region is 34,144
Cretaceous Tertiary Contraction, Shear and Inversion in the Western Barents Sea
 Cretaceous Tertiary Contraction, Shear and Inversion in the Western Barents Sea Roy H. Gabrielsen,* Jan Inge Faleide*, Karen A. Leever*,** * Department of Geosciences, University of Oslo GeoForschungZentrum
Cretaceous Tertiary Contraction, Shear and Inversion in the Western Barents Sea Roy H. Gabrielsen,* Jan Inge Faleide*, Karen A. Leever*,** * Department of Geosciences, University of Oslo GeoForschungZentrum
Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
 CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Words Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Words Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 06, 2016 ISSN (online):
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 06, 2016 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Geomorphological Study of the Coast between Lakhpat to Koteshwar (Kori Creek), Kachchh,
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 4, Issue 06, 2016 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Geomorphological Study of the Coast between Lakhpat to Koteshwar (Kori Creek), Kachchh,
Strike-Slip Faults. ! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.
 Strike-Slip Faults! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.! Usually vertical, no hanging-wall/footwall blocks.! Classified by the relative sense of motion. " Right lateral opposite block
Strike-Slip Faults! Fault motion is parallel to the strike of the fault.! Usually vertical, no hanging-wall/footwall blocks.! Classified by the relative sense of motion. " Right lateral opposite block
Landforms and Rock Structure
 Landforms and Rock Structure Rock Structure as a Landform Control Landforms of Horizontal Strata and Coastal Plains Landforms of Warped Rock Layers Landforms Developed on Other Land-Mass Types Landforms
Landforms and Rock Structure Rock Structure as a Landform Control Landforms of Horizontal Strata and Coastal Plains Landforms of Warped Rock Layers Landforms Developed on Other Land-Mass Types Landforms
Chapter 16. Mountain Building. Mountain Building. Mountains and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection?
 Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Structural Style and Tectonic Evolution of the Nakhon Basin, Gulf of Thailand
 Structural Style and Tectonic Evolution of the Nakhon Basin, Gulf of Thailand Piyaphong Chenrai Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok
Structural Style and Tectonic Evolution of the Nakhon Basin, Gulf of Thailand Piyaphong Chenrai Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok
Directed Reading. Section: How Mountains Form MOUNTAIN RANGES AND SYSTEMS. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Movement of the Earth s Crust: Formation of: Mountain s Plateau's and Dome s
 Movement of the Earth s Crust: Formation of: Mountain s Plateau's and Dome s References Information taken from several places including Prentice Hall Earth Science: @ http://www.eram.k12.ny.us/education/components/docmgr/default.php?sectiondetaili
Movement of the Earth s Crust: Formation of: Mountain s Plateau's and Dome s References Information taken from several places including Prentice Hall Earth Science: @ http://www.eram.k12.ny.us/education/components/docmgr/default.php?sectiondetaili
Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter Pearson Education, Inc.
 Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter 10 Structural Geology Structural geologists study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. A working knowledge of rock structures
Crustal Deformation Earth - Chapter 10 Structural Geology Structural geologists study the architecture and processes responsible for deformation of Earth s crust. A working knowledge of rock structures
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
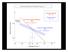 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Cattaraugus Creek: A Story of Flowing Water and the Geology of the Channel It Flows Through Presentation to West Valley Citizen Task Force 4/27/16
 Cattaraugus Creek: A Story of Flowing Water and the Geology of the Channel It Flows Through Presentation to West Valley Citizen Task Force 4/27/16 Raymond C. Vaughan, Ph.D. What happens if you drop a
Cattaraugus Creek: A Story of Flowing Water and the Geology of the Channel It Flows Through Presentation to West Valley Citizen Task Force 4/27/16 Raymond C. Vaughan, Ph.D. What happens if you drop a
Description of faults
 GLG310 Structural Geology Description of faults Horizontal stretch Crustal thickness Regional elevation Regional character Issues Normal Thrust/reverse Strike-slip >1 1 in one direction and < 1 in
GLG310 Structural Geology Description of faults Horizontal stretch Crustal thickness Regional elevation Regional character Issues Normal Thrust/reverse Strike-slip >1 1 in one direction and < 1 in
Lecture # 6. Geological Structures
 1 Lecture # 6 Geological Structures ( Folds, Faults and Joints) Instructor: Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 The wavy undulations
1 Lecture # 6 Geological Structures ( Folds, Faults and Joints) Instructor: Dr. Attaullah Shah Department of Civil Engineering Swedish College of Engineering and Technology-Wah Cantt. 2 The wavy undulations
Faults, folds and mountain building
 Faults, folds and mountain building Mountain belts Deformation Orogens (Oro = Greek all changes for mountain, in size, shape, genesis orientation, = Greek for or formation) position of a rock mass Structural
Faults, folds and mountain building Mountain belts Deformation Orogens (Oro = Greek all changes for mountain, in size, shape, genesis orientation, = Greek for or formation) position of a rock mass Structural
Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition
 Chapter Chapter 1 2 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
Chapter Chapter 1 2 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
24. Ocean Basins p
 24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on the planet s surface. In
 Chapter 4 Landforms, Water, and Natural Resources Earth is home to many different types of landforms. These landforms are shaped by forces deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on
Chapter 4 Landforms, Water, and Natural Resources Earth is home to many different types of landforms. These landforms are shaped by forces deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on
Active Tectonics. Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape. Edward A. Keller University of California, Santa Barbara
 Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Sequence Stratigraphy. Historical Perspective
 Sequence Stratigraphy Historical Perspective Sequence Stratigraphy Sequence Stratigraphy is the subdivision of sedimentary basin fills into genetic packages bounded by unconformities and their correlative
Sequence Stratigraphy Historical Perspective Sequence Stratigraphy Sequence Stratigraphy is the subdivision of sedimentary basin fills into genetic packages bounded by unconformities and their correlative
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution. (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins)
 Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
GCE. Geology. Mark Scheme for June Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F791: Global Tectonics. Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Geology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F79: Global Tectonics Mark Scheme for June 202 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing a wide
GCE Geology Advanced Subsidiary GCE Unit F79: Global Tectonics Mark Scheme for June 202 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing a wide
Structural Geology Lab. The Objectives are to gain experience
 Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
Geology 2 Structural Geology Lab The Objectives are to gain experience 1. Drawing cross sections from information given on geologic maps. 2. Recognizing folds and naming their parts on stereoscopic air
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor
 Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
Structural Geology of the Mountains
 Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES
 USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
Lab 6: Plate tectonics, structural geology and geologic maps
 Geology 103 Name(s): Lab 6: Plate tectonics, structural geology and geologic maps Objective: To show the effects of plate tectonics on a large-scale set of rocks and to reconstruct the geological history
Geology 103 Name(s): Lab 6: Plate tectonics, structural geology and geologic maps Objective: To show the effects of plate tectonics on a large-scale set of rocks and to reconstruct the geological history
Crustal Deformation. (Building Earth s Surface, Part 1) Science 330 Summer Mapping geologic structures
 Crustal Deformation (Building Earth s Surface, Part 1) Science 330 Summer 2005 Mapping geologic structures When conducting a study of a region, a geologist identifies and describes the dominant rock structures
Crustal Deformation (Building Earth s Surface, Part 1) Science 330 Summer 2005 Mapping geologic structures When conducting a study of a region, a geologist identifies and describes the dominant rock structures
Shape Earth. Plate Boundaries. Building. Building
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Chapter Wrap-Up Forces That Shape Earth Landforms at Plate Boundaries Mountain Building Continent Building How is Earth s surface shaped by plate
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Chapter Wrap-Up Forces That Shape Earth Landforms at Plate Boundaries Mountain Building Continent Building How is Earth s surface shaped by plate
Terrain Units PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION. Present Geology of NYS. Detailed Geologic Map of NYS
 NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
NYS TOPOGRAPHY Why so? PALEOGEOGRAPHY: LANDFORM CREATION Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 014 Present Geology of NYS Detailed Geologic Map of NYS Generalized Geology Detailed Geology Hot links to the fold out
4 Deforming the Earth s Crust
 CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID: GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom
 TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID:1542715 GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows
TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID:1542715 GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows
