Supporting Document HUMBER HOLOCENE CHRONOLOGY
|
|
|
- Gwendoline Osborne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HUMBER HOLOCENE CHRONOLOGY Solid Geology The solid geology of the area has been extensively described in a number of previous publications (BGS, 1982; Gaunt, 1994; Gaunt et al. 1992; Berridge & Pattison, 1994; Jones, 1988). It is summarised pictorially in Figure 1. Holocene Geology This section focuses on the changes that have taken place within the basin defined by the solid geology and how this may continue to evolve in the future. The chronology of the Holocene development in the Humber basin is summarised in Table 1. Table 1. Holocene chronology Time BP Chronology of Events pre Ice cover Outer channel scoured out by ice melt waters out to -25mODN contour post Outer channel continues to be scoured by fluvial waters End of last glacial period Sea levels below -45mODN Lake Humber infills with fresh water sediments from land runoff Sill at Hull creates either a complete barrier or more likely a waterfall to a lower level river which flows on to the North Sea (see Figure 4) Sea level somewhere between -16m and -30mODN Possible that fluvial incision is formed in sill at Hull Lake remains fresh water 8500 Garthorpe suite begins to develop in outer estuary (see Figure 6 for details of how suites relate to take up of accommodation space) 8000 Sea level somewhere between -12 and -14mODN Lower crest of sill overtopped by tidal waters (sill now at -12mODN but it may have been subject to further erosion since initial tidal breakthrough see Figure 4) Lake begins to exhibit brackish influence 7400 Deposition of Newland and Butterwick suites within the lake upstream of the sill. This is overlain by the Garthorpe suite from about 6600, reflecting the progressive marine influence Extensive saltmarsh 6500 Sea level about -8mODN Peats at the end of Spurn (at -7mODN ) suggest a period of marine regression and narrowing of the estuary; possibly linked with the marked slowing in the rate of sea level rise Full channel flow established Lake becomes part of the tidal headwaters and marine influence begins to dominate flora, fauna and sediments Plenty of accommodation space for sediment infilling, which probably meant that the channel maintained a stable alignment. Upstream of Trent Falls the channel may not have followed its present day alignment but there are insufficient data to properly map any change (?) Sea level rises from -4 to -2mODN (a rate of 1mm/year) Extensive sandflats and mudflats as the Saltend suite is laid down in an environment with pronounced channel switching 1600(?)-600 Return to a more stable channel alignment and saltmarsh habitat. The Sunk Island suite begins to be laid down in this period (from at least 800BP see Figure 6) Climatic optimum occurs from BP ( AD) Deposits are once again largely channel sediments (sand and mudflats) with channel incision and migration Anthropogenic reclamation and sea walls may have removed some of the available accommodation space. Little Ice Age occurs from BP ( AD) Sediment continues to infill the channel but sea walls limit take up of accommodation space 50-present Sea level in estuary rising at between 1 and 2mm/year Erosion of channel in outer and middle Humber 1
2 The pre-holocene basin initially comprised an ice melt/fluvial channel from the North Sea to Hull, where a sill held back much of the fresh water in the Humber Lake. This is shown as a perspective view in Figure 4. As sea level rose so the sea began to occupy the river channel and the estuary started to migrate landwards. During this phase the channel is likely to have been wide and shallow, allowing sediments to deposit at the margins, so beginning to infill the pre-holocene basin; see Figure 5. The channel is likely to have followed a fairly stable alignment and given the rate of infilling, was almost certainly flood dominant, importing marine sediments as well as receiving fluvial run-off sediments. The process of sediment deposition takes up space within the basin, referred to as accommodation space. Changes in this space are instructive in helping to understand how the estuary has evolved. The general pattern for the Humber as a whole is illustrated in Figure 6. The rapid take-up of sediment in the early period is clearly evident. It is also worth noting that an analysis based on subdividing the basin in to a number of smaller areas indicates a similar pattern of infilling. Whilst other factors such as climate change and deforestation have been examined, these changes do not correlate with borehole data, such that it would appear that accommodation space may be the controlling influence on channel migration. River flows progressively scoured the sill and at the same time, sea levels were rising. In the end the overflow of freshwater at the Hull sill (a sort of waterfall) became a tidal channel, with fully marine conditions being established in the inner part of the basin by about 6000 years BP. Based on evidence from other estuaries, the reduced rate of sea level rise at about this time enabled the system to adjust to something close to a steady state (i.e. to catch-up with itself). One might therefore have expected a slow down and switch to ebb dominant conditions some time after about 6000 years BP. This does not appear to have happened, possibly because the break through to the inner basin at roughly the same time would have created an additional demand for sediment (possibly indicated by the flattening of accommodation space curve over the period from years BP, Figure 6). Such a change does however appear to have happened after about 4000 years BP, as accommodation space reduces. Over the interval -8 to -4mODN, the sides of the Holocene basin become steeper, particularly in the reach from Paull to Ferriby. This would have constrained the channel, possibly keeping more material in suspension and increasing the potential for channel migration. This is reflected in: i) The sediments of the Saltend suite, which comprise of laminated muds and fine grained sands, characteristic of sand and mudflats; and ii) The erosional contact with the Garthorpe suite, which suggests channel migration away from the present day alignment. As accommodation space increases (from about 1600 years BP) due to high level widening of the Holocene basin (from about -4mODN), so the channel stabilised and the saltmarsh habitat was re-established 1. Some time, possibly in the interval 800 to 200 years BP, the channel migrated again and the most recent suite of sediments (Sunk Island suite) are once again dominated by sands and muds characteristic of sand and mudflats. 1 The relationship between accommodation space and channel sinuosity has long been recognised within fluvial environments (Allen, 1985; Selley, 1988) and studies (Dalrymple et al. 1992) have shown that channel migration is most common in transitional parts of the estuary where river currents become dominated by tidal currents. 2
3 The accommodation space has been calculated for this study by (a) lowering a horizontal surface based on the relative sea level curve and (b) lowering the existing channel bathymetry in the same way. This approach has been adopted because one of the outstanding difficulties is to define the size and position of the channel through the Holocene. The sediments reveal that the channel has moved about and in part define a boundary to that movement (based on the erosional contact between suites of sediment). Defining the changes in volume of the channel is, however, going to require more detailed modelling of the palaeo-tidal changes in the estuary. One other important contribution from the Holocene studies is the improved definition of the thickness of the Holocene sediments, which have now been mapped for the entire Humber basin and out along the palaeo-channel to New Sand Hole. This is shown as a contoured map of sediment thickness in Figure 7. The plot illustrates where the sediments are thin or non-existent, so that erosion is likely to be constrained by the underlying Pleistocene deposits of till material, and where there is a substantial thickness of Holocene sediment, presenting the possibility for future channel migration. Overall the estuary has undergone landward transgression under influence of a, largely, monotonically increasing sea level. Within this period there will have been oscillations and stands in the rate of sea level rise and the importance of these within human time scales should not be underestimated. Indeed the forecast increase in rate as a consequence of global warming could be just such a fluctuation. Such an increase might be expected to increase the take-up of accommodation space, providing an environment for a stable channel alignment and saltmarsh development. The presence of sea walls will, however, limit the available accommodation space, so that the system may retain its present form of incised migrating channels with extensive sand and mudflats. In the longer term (centuries) one might expect the estuary to encroach into some of the accommodation space currently behind the sea walls. Estuary Features Mouth Recent work by Balson (1999) develops the possible Holocene evolution from that presented by (Berridge & Pattison, 1994). This suggests that the north bank of the estuary followed the line of the palaeo-channel out to New Sand Hole. Under the influence of rising sea levels the seaward point has retreated in line with the retreat of the Holderness coast, Figure 8. This is not to say that the spit necessarily existed in its present form in this seaward position. A borehole taken on the southern end of Spurn shows the presence of a peat (dated as 6500 years BP at 7m ODN), overlaying shelly gravel, which extends down to the till surface at about 17mODN. Seismic records of the palaeo-channel indicate that rounded beach gravels have overspilled from the north into the channel along much of its length. It is possible that at some point prior to 6500 years BP, a recurve spit formed to seaward with its distal end terminating at the current most southerly point of the spit. Alternatively, recognising the lower sea level at this time, wave exposures would have been very different. The Dogger Bank would still be limiting fetches from the north, so that the longest fetches would have been from the east and south-east. Consequently alongshore drift on a northeast to south-west oriented coast would have been into the estuary and may have formed a gravel beach along the northern side of the channel. 3
4 The peat horizon at about 6500 years BP suggests that extensive mudflats formed in the sheltered area behind the spit or barrier beach. Subsequently the system has rolled back over the mudflats, exposing mudflat and peats to seaward, from where they have been eroded. This reflects the current structure of sediments along Spurn, which form two distinct lengths, Figure 9. Over the more northerly length, mudflat overlies the till surface and is exposed on the seaward beach face. The surficial spit is formed from a small volume of blown sand. In contrast to the south, there is a substantial volume of sand and gravel forming the beach face and extending out to the Binks. This mass of sediments protects the mudflat sediments to the rear and is overlain by the blown sand, which again forms surficial spit as seen on OS maps. The crucial difference between these two lengths is that whilst the one to the north can erode and realign, the length to the south is protected. This pattern of evolution is broadly consistent with the one proposed by Pethick (IECS, 1992), although he suggests that the protection is in part provided by a glacial moraine along the edge of the channel. It also accommodates the movements noted by (de Boer, 1964), recognising that he focused on maps of the surficial spit rather than the underlying structure as discussed above. Meanders The meandering form of the channel from Hull out to the North Sea was probably cut into the tills by ice melt and subsequently fluvial flows at the end of the last glaciation. Why it took this form is not clear but one suggestion is that the ice front may have halted or re-advanced to a line roughly following the north bank. Thereafter tidal waters progressively occupied the channel and began the process of infilling the basin, as described above. Whether the alignment has been maintained because of the resistance of the underlying tills (where exposed), or the presence of glacial moraines, deposited along the line of the ice front, is not clear. Rivers The major change within what is now the river section of the Humber, is clearly the transition from a fresh water lake to a brackish lake before it finally became the head waters for the estuary itself. Comparing the present day channel alignment with the depths of the pre- Holocene basin it would appear that the channel for the Ouse may have migrated southwards between Trent Falls and Goole. There are however only a few boreholes in this area and the true extent of the pre-holocene basin may not have been reproduced in the model of this surface. Delta As a mobile feature resulting from contemporary processes, the development of the estuary delta would have to be inferred from the nature of underlying sediments. Information in the vicinity of the mouth is however scarce and whilst the locations of some sub and intertidal sandbanks have been suggested (Berridge & Pattison, 1994) nothing has been reported on the ebb/flood delta. Some recent work using seismic data along the palaeo-channel from Spurn to the New Sand Hole (Balson, 1999), shows some evidence of scour holes. This may reflect the landward migration of the mouth and it is to be expected that any delta would have followed this migration. 4
5 References Allen JRL, 1985, Principles of physical sedimentology, George Allen and Unwin, London Balson P, 1999, BGS, Keyworth, pers comm. Berridge NG, Pattison J, 1994, Geology of the country around Grimsby and Patrington, HMSO, London BGS, 1982, Eastern England from the Tees to the Wash, HMSO, London Dalrymple RW, Zaitlin BA, Boyd R, 1992, Estuarine facies models: Conceptual basis and stratigraphic implications, Journal of Sediment Petrology, 62, de Boer G, 1964, Spurn Head: its history and evolution, Transactions Institute of British Geographers, 34(71) Gaunt GD, 1994, Geology of the country around Goole, Doncaster and the Isle of Axholme, HMSO, London Gaunt GD, Fletcher TP, Wood CJ, 1992, Geology of the country around Kingston upon Hull and Brigg, HMSO, London IECS, 1992, Spurn Heritage Coast Study, Final Report, Institute of Estuarine and Coastal Studies, figures Jones NV, 1988, A Dynamic Estuary: Man, Nature and the Humber, Hull University Press Rees JG, Ridgway J, Ellis S, Knox RWO, Newsham R, Parkes A, 2000, Holocene sediment storage in the Humber Estuary, In: Shennan I, Andrews JE (eds.), Land-ocean evolution perspective study, Special Publications 166, Geological Society, London, pp Selley RC, 1988, Applied Sedimentology, Academic Press, London Acknowledgements This summary was prepared for the Environment Agency Humber Estuary Geomorphology Study - Stage 2, Final Report, 2000, drawing heavily on two more detailed study reports prepared by John Rees and Peter Balson from British Geological Survey 2. These can be found in the Annexes to the Interim Report, June Their assistance in drafting this summary is gratefully acknowledged. 2 See also (Rees et al. 2000). 5
6 Figure 1. Solid geology (BGS) 6
7 m msl Humber - summary cal ka BP Inner - basal Inner - intercalated Outer - basal Outer - intercalated RSL model limiting dates Figure 2. Regional sea level curve for the Humber 120 MHWST above MTL as proportion of present 100 t % of presen cal ka BP Figure 3. Changes in high water over the Holocene 7
8 Figure 4. Perspective view of pre-holocene basin 8
9 Figure 5. Sketch of Humber basin pre 6000 years BP 9
10 Figure 6. Holocene infilling of the Humber basin 10
11 m Figure 7. Thickness of Holocene sediments 11
12 Figure 8. Conjectural evolution of the outer Humber estuary during the Holocene (Berridge and Pattison, 1994) 12
13 Figure 9. Sedimentary structures of Spurn Head 13
Understanding and Managing Morphological Change in Estuaries
 PRESENTATION OF FINDINGS This chapter: Explores ways in which the findings from coastal studies can be communicated to others and provides a number of worked examples of the techniques outlined; Reviews
PRESENTATION OF FINDINGS This chapter: Explores ways in which the findings from coastal studies can be communicated to others and provides a number of worked examples of the techniques outlined; Reviews
DATA REPOSITORY MATERIAL: PALEOCHANNEL GROUP MAPPING DESCRIPTIONS
 Data Repository item 2695 DATA REPOSITORY MATERIAL: PALEOCHANNEL GROUP MAPPING DESCRIPTIONS Groups 1 (North Myrtle Beach) and 2 (Atlantic Beach) Channel Groups 1 (North Myrtle Beach) and 2 (Atlantic Beach)
Data Repository item 2695 DATA REPOSITORY MATERIAL: PALEOCHANNEL GROUP MAPPING DESCRIPTIONS Groups 1 (North Myrtle Beach) and 2 (Atlantic Beach) Channel Groups 1 (North Myrtle Beach) and 2 (Atlantic Beach)
Active Coastal Processes in the Lubec Embayment
 The Lubec Embayment Maine Geologic Facts and Localities August, 1998 Active Coastal Processes in the Lubec Embayment 44 49 50.51 N, 66 59 34.16 W Text by Joseph T. Kelley, Department of Agriculture, Conservation
The Lubec Embayment Maine Geologic Facts and Localities August, 1998 Active Coastal Processes in the Lubec Embayment 44 49 50.51 N, 66 59 34.16 W Text by Joseph T. Kelley, Department of Agriculture, Conservation
Michael Walsworth, Ryan Sullivan, Simi Odueyungbo, William Budd
 Michael Walsworth, Ryan Sullivan, Simi Odueyungbo, William Budd Estuarine Environment At first (Pritchard, 1967), an estuary was defined by the salinity of the water. Then by Clifton (1982) as an inlet
Michael Walsworth, Ryan Sullivan, Simi Odueyungbo, William Budd Estuarine Environment At first (Pritchard, 1967), an estuary was defined by the salinity of the water. Then by Clifton (1982) as an inlet
The Geology of Sebago Lake State Park
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions.
The Coast: Beaches and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10
 The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
The Coast: es and Shoreline Processes Trujillo & Thurman, Chapter 10 Oceanography 101 Chapter Objectives Recognize the various landforms characteristic of beaches and coastal regions. Identify seasonal
Moosehead Lake and the Tale of Two Rivers
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2005 45 o 53 5.09 N, 69 o 42 14.54 W Text by Kelley, A.R.; Kelley, J.T.; Belknap, D.F.; and Gontz, A.M. Department of Earth Sciences, University of Maine, Orono,
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2005 45 o 53 5.09 N, 69 o 42 14.54 W Text by Kelley, A.R.; Kelley, J.T.; Belknap, D.F.; and Gontz, A.M. Department of Earth Sciences, University of Maine, Orono,
Holderness Erosion and Evolution of the Spurn Peninsula
 Holderness Erosion and Evolution of the Spurn Peninsula Prof. Ken Pye and Dr. Simon Blott Kenneth Pye Associates Ltd. Outline of the Presentation Overview of historical erosion trends Effects of coast
Holderness Erosion and Evolution of the Spurn Peninsula Prof. Ken Pye and Dr. Simon Blott Kenneth Pye Associates Ltd. Outline of the Presentation Overview of historical erosion trends Effects of coast
Australian Coastal Councils Conference
 Australian Coastal Councils Conference 11 March 2015 Estimating Future Coastal Inundation and Erosion Hazards Dr Andrew McCowan Dr Christine Lauchlan-Arrowsmith Warwick Bishop Background Victorian Future
Australian Coastal Councils Conference 11 March 2015 Estimating Future Coastal Inundation and Erosion Hazards Dr Andrew McCowan Dr Christine Lauchlan-Arrowsmith Warwick Bishop Background Victorian Future
4. The map below shows a meandering stream. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations along the stream bottom.
 1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
What are the different ways rocks can be weathered?
 Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
The Systems Approach. Alun Williams, ABPmer
 The Systems Approach Alun Williams, ABPmer Overview What is A Systems Approach? Behavioural / Qualitative Modelling? System Definition / Mapping (Behavioural Statements Objective) What is a Systems Approach?
The Systems Approach Alun Williams, ABPmer Overview What is A Systems Approach? Behavioural / Qualitative Modelling? System Definition / Mapping (Behavioural Statements Objective) What is a Systems Approach?
Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities December, 2000 Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture,
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities December, 2000 Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture,
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which event is the best example of erosion? dissolving of rock particles on a limestone gravestone by acid rain breaking apart of shale as a result of water freezing in a crack rolling of a pebble
Name: 1) Which event is the best example of erosion? dissolving of rock particles on a limestone gravestone by acid rain breaking apart of shale as a result of water freezing in a crack rolling of a pebble
Addendum to the Essex and South Suffolk Second Generation Shoreline Management Plan
 Addendum to the Essex and South Suffolk Second Generation Shoreline Management Plan September 2012 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1 2. Changes in saltmarsh habitat 1 3. Preferred managed realignment policy options
Addendum to the Essex and South Suffolk Second Generation Shoreline Management Plan September 2012 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1 2. Changes in saltmarsh habitat 1 3. Preferred managed realignment policy options
Geol 117 Lecture 18 Beaches & Coastlines. I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition:
 I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition. The Big Question:
 Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
 Page 1 of 9 Name: Base your answer to the question on the diagram below. The arrows show the direction in which sediment is being transported along the shoreline. A barrier beach has formed, creating a
Page 1 of 9 Name: Base your answer to the question on the diagram below. The arrows show the direction in which sediment is being transported along the shoreline. A barrier beach has formed, creating a
1. The map below shows a meandering river. A A' is the location of a cross section. The arrows show the direction of the river flow.
 1. The map below shows a meandering river. A A' is the location of a cross section. The arrows show the direction of the river flow. Which cross section best represents the shape of the river bottom at
1. The map below shows a meandering river. A A' is the location of a cross section. The arrows show the direction of the river flow. Which cross section best represents the shape of the river bottom at
Annual transport rates at two locations on the fore-slope.
 Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
Sediment Transport by Currents Fore-slope Sediment transport rates and sediment concentrations were computed from the hydrodynamic model runs as well as from direct measurements of current velocities at
Name. 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different soil horizons, A, B, C, and D, are shown.
 Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
Winfried Siefert ; Volker Barthel**' and
 CHAPTER 176 THE GERMAN "MORAN" PROJECT by Winfried Siefert ; Volker Barthel**' and Abstract The project "MORAN" (Morphological Analyses of the North- Sea-Coast) is an extensive program in order to try
CHAPTER 176 THE GERMAN "MORAN" PROJECT by Winfried Siefert ; Volker Barthel**' and Abstract The project "MORAN" (Morphological Analyses of the North- Sea-Coast) is an extensive program in order to try
Lab 12 Coastal Geology
 Lab 12 Coastal Geology I. Fluvial Systems Hydrologic Cycle Runoff that flows into rivers = precipitation (rain and snowmelt) [infiltration (loss to groundwater) + evaporation (loss to atmosphere) + transpiration
Lab 12 Coastal Geology I. Fluvial Systems Hydrologic Cycle Runoff that flows into rivers = precipitation (rain and snowmelt) [infiltration (loss to groundwater) + evaporation (loss to atmosphere) + transpiration
Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms
 Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms Costa Concordia Shipwreck, Isola del Giglio, Italy Depositional Coastal Landforms Can interpret landforms in light of geomorphic processes, both terrestrial
Importance of Understanding Coastal Landforms Costa Concordia Shipwreck, Isola del Giglio, Italy Depositional Coastal Landforms Can interpret landforms in light of geomorphic processes, both terrestrial
Pre-Lab Reading Questions ES202
 ES202 The are designed to encourage students to read lab material prior to attending class during any given week. Reading the weekly lab prior to attending class will result in better grade performance
ES202 The are designed to encourage students to read lab material prior to attending class during any given week. Reading the weekly lab prior to attending class will result in better grade performance
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 GENERAL Washover sandsheets are often found in low-lying coastal embayment s (Sedgwick and Davis 2003). Washover deposition of marine sand is usually attributed to storm activity
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 GENERAL Washover sandsheets are often found in low-lying coastal embayment s (Sedgwick and Davis 2003). Washover deposition of marine sand is usually attributed to storm activity
2.2.7 Backbarrier flats
 FIGURE 24. VERTICAL PHOTOGRAPH SHOWING THE DEVELOPMENT OF SMALL PARABOLIC DUNES FROM BLOWOUTS IN A LARGE RELICT FOREDUNE NORTHWEST OF HUNTER'S CREEK. PHOTOGRAPH COURTESY OF CAR'T'ER HOLT HARVEY FORESTS
FIGURE 24. VERTICAL PHOTOGRAPH SHOWING THE DEVELOPMENT OF SMALL PARABOLIC DUNES FROM BLOWOUTS IN A LARGE RELICT FOREDUNE NORTHWEST OF HUNTER'S CREEK. PHOTOGRAPH COURTESY OF CAR'T'ER HOLT HARVEY FORESTS
COASTAL QUATERNARY GEOLOGY MAPPING FOR NSW: EXAMPLES AND APPLICATIONS
 COASTAL QUATERNARY GEOLOGY MAPPING FOR NSW: EXAMPLES AND APPLICATIONS A Troedson Geological Survey of New South Wales Abstract Detailed geological mapping of the coastal plains of regional NSW was undertaken
COASTAL QUATERNARY GEOLOGY MAPPING FOR NSW: EXAMPLES AND APPLICATIONS A Troedson Geological Survey of New South Wales Abstract Detailed geological mapping of the coastal plains of regional NSW was undertaken
The Impact of Changing Winds on Estuarine Evolution, Copano Bay, TX
 The Impact of Changing Winds on Estuarine Evolution, Copano Bay, TX Purpose: The fulfillment of partial requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Geology Oklahoma State University, Stillwater
The Impact of Changing Winds on Estuarine Evolution, Copano Bay, TX Purpose: The fulfillment of partial requirements for the Degree of Master of Science in Geology Oklahoma State University, Stillwater
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators
 Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
Which landscape best represents the shape of the valleys occupied by glaciers? A) B) C) D)
 1. Glaciers often form parallel scratches and grooves in bedrock because glaciers A) deposit sediment in unsorted piles B) deposit rounded sand in V-shaped valleys C) continually melt and refreeze D) drag
1. Glaciers often form parallel scratches and grooves in bedrock because glaciers A) deposit sediment in unsorted piles B) deposit rounded sand in V-shaped valleys C) continually melt and refreeze D) drag
THE QUATERNARY GEOLOGY OF NEWARK BAY AND KILL VAN KULL CHANNEL, NEW YORK AND NEW JERSEY. and
 THE QUATERNARY GEOLOGY OF NEWARK BAY AND KILL VAN KULL CHANNEL, NEW YORK AND NEW JERSEY Stephanie Beda, W. Bruce Ward, William Murphy, Robert Fleming, Gary Fleming, Beckett Boyd Earthworks LLC 27 Glen
THE QUATERNARY GEOLOGY OF NEWARK BAY AND KILL VAN KULL CHANNEL, NEW YORK AND NEW JERSEY Stephanie Beda, W. Bruce Ward, William Murphy, Robert Fleming, Gary Fleming, Beckett Boyd Earthworks LLC 27 Glen
Chapter 5. The Sedimentary Archives
 Chapter 5 The Sedimentary Archives Factors affecting Sedimentary Characteristics 1. Tectonic setting 2. Physical, chemical, and biological processes in the depositional environment 3. Method of sediment
Chapter 5 The Sedimentary Archives Factors affecting Sedimentary Characteristics 1. Tectonic setting 2. Physical, chemical, and biological processes in the depositional environment 3. Method of sediment
Geology and coastal change
 Geology and coastal change Chichester Harbour lies within the Solent River system that is dominated by Cretaceous Chalk and overlying muds, sands and gravels of the early Tertiary deposits. A natural basin
Geology and coastal change Chichester Harbour lies within the Solent River system that is dominated by Cretaceous Chalk and overlying muds, sands and gravels of the early Tertiary deposits. A natural basin
Reading Material. See class website. Sediments, from Oceanography M.G. Gross, Prentice-Hall
 Reading Material See class website Sediments, from Oceanography M.G. Gross, Prentice-Hall Materials filling ocean basins Dissolved chemicals especially from rivers and mid-ocean ridges (volcanic eruptions)
Reading Material See class website Sediments, from Oceanography M.G. Gross, Prentice-Hall Materials filling ocean basins Dissolved chemicals especially from rivers and mid-ocean ridges (volcanic eruptions)
FLUVIAL LANDFORMS. Floodplains
 FLUVIAL LANDFORMS Floodplains fairly flat & continuous surface occupying much of a valley bottom normally underlain by unconsolidated sediments subject to periodic flooding (usually once every year or
FLUVIAL LANDFORMS Floodplains fairly flat & continuous surface occupying much of a valley bottom normally underlain by unconsolidated sediments subject to periodic flooding (usually once every year or
1. Any process that causes rock to crack or break into pieces is called physical weathering. Initial product = final product
 Weathering 1. Any process that causes rock to crack or break into pieces is called physical weathering. Initial product = final product End Result of physical weathering is increased surface area. 2. Physical
Weathering 1. Any process that causes rock to crack or break into pieces is called physical weathering. Initial product = final product End Result of physical weathering is increased surface area. 2. Physical
Natural Susceptibility to Coastal Erosion: Methodology and Mapping Summary
 Natural Susceptibility to Coastal Erosion: Methodology and Mapping Summary. Introduction The Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act 2009 (FRM Act) introduced a coordinated and partnership approach to how
Natural Susceptibility to Coastal Erosion: Methodology and Mapping Summary. Introduction The Flood Risk Management (Scotland) Act 2009 (FRM Act) introduced a coordinated and partnership approach to how
Accommodation. Tectonics (local to regional) Subsidence Uplift
 Accommodation Accommodation varies over time; it is the distance between a reference horizon and the sea surface (i.e. relative sea level). The space to be filled in with sediments or water What are the
Accommodation Accommodation varies over time; it is the distance between a reference horizon and the sea surface (i.e. relative sea level). The space to be filled in with sediments or water What are the
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
Seaton to Seaton Hole SUMMARY OF PREFERRED PLAN RECOMMENDATIONS AND JUSTIFICATION
 Location reference: Policy Unit reference: Plan: Seaton to Seaton Hole 6a29 and 6a30 SUMMARY OF PREFERRED PLAN RECOMMENDATIONS AND JUSTIFICATION The large number of properties and assets at risk in the
Location reference: Policy Unit reference: Plan: Seaton to Seaton Hole 6a29 and 6a30 SUMMARY OF PREFERRED PLAN RECOMMENDATIONS AND JUSTIFICATION The large number of properties and assets at risk in the
The Building of the NYC Region
 The Building of the NYC Region Definitions Fall Line marks the area where an upland region (continental bedrock) and a coastal plain meet Piedmont the plateau region of the eastern United States which
The Building of the NYC Region Definitions Fall Line marks the area where an upland region (continental bedrock) and a coastal plain meet Piedmont the plateau region of the eastern United States which
FUTURE MEANDER BEND MIGRATION AND FLOODPLAIN DEVELOPMENT PATTERNS NEAR RIVER MILES 241 TO 235, SACRAMENTO RIVER
 FUTURE MEANDER BEND MIGRATION AND FLOODPLAIN DEVELOPMENT PATTERNS NEAR RIVER MILES 241 TO 235, SACRAMENTO RIVER Eric W. Larsen University of California, Davis With the assistance of Evan Girvetz REPORT
FUTURE MEANDER BEND MIGRATION AND FLOODPLAIN DEVELOPMENT PATTERNS NEAR RIVER MILES 241 TO 235, SACRAMENTO RIVER Eric W. Larsen University of California, Davis With the assistance of Evan Girvetz REPORT
Map 4: Cowal Peninsula: Cluniter to Ardyne Point Map Content Descriptions
 Map 4: Cowal Peninsula: Cluniter to Ardyne Point Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of twenty four sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 4. Of these six were previously
Map 4: Cowal Peninsula: Cluniter to Ardyne Point Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of twenty four sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 4. Of these six were previously
Map 9: Ayrshire Coast: Stevenston Pier to Barassie Map Content Descriptions
 Map 9: Ayrshire Coast: Stevenston Pier to Barassie Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of thirteen sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 9. Of these five were previously
Map 9: Ayrshire Coast: Stevenston Pier to Barassie Map Content Descriptions 1. Built Heritage and Archaeology A total of thirteen sites were recorded in the area covered by Map 9. Of these five were previously
Depositional Environment
 Depositional Environment Sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment. Types
Depositional Environment Sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment. Types
Long-term estuary processes and morphological change
 Long-term estuary processes and morphological change Professor Ken Pye with contributions from Dr. Simon Blott and Dr. Daphne van der Wal Department of Geology Available top-down methods relying on data
Long-term estuary processes and morphological change Professor Ken Pye with contributions from Dr. Simon Blott and Dr. Daphne van der Wal Department of Geology Available top-down methods relying on data
Jasper Beach, Machiasport, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2000 Jasper Beach, Machiasport, Maine 44 o 38 30.28 N, 67 o 22 31.96 W Text by Joesph T. Kelley, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by USGS
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2000 Jasper Beach, Machiasport, Maine 44 o 38 30.28 N, 67 o 22 31.96 W Text by Joesph T. Kelley, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by USGS
ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution % in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b.
 ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution 1. +97% in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b. >1/3% liquid, fresh water in streams and lakes~1/10,000 of water
ES 105 Surface Processes I. Hydrologic cycle A. Distribution 1. +97% in oceans 2. >3% surface water a. +99% surface water in glaciers b. >1/3% liquid, fresh water in streams and lakes~1/10,000 of water
Science EOG Review: Landforms
 Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
Permafrost-influenced Geomorphic Processes
 Section 4 Permafrost-influenced Geomorphic Processes Geomorphic processes vary greatly among ecoregions in northern Alaska, extending from the Beaufort Sea coast to the Brooks Range (Figure 4.1). Regional
Section 4 Permafrost-influenced Geomorphic Processes Geomorphic processes vary greatly among ecoregions in northern Alaska, extending from the Beaufort Sea coast to the Brooks Range (Figure 4.1). Regional
EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES WEATHERING 1 1998 Q 7 (a) (i) What is the difference between weathering and mass wasting (ii) List five processes involved in chemical weathering
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE EXTERNAL LAND FORMING PROCESSES WEATHERING 1 1998 Q 7 (a) (i) What is the difference between weathering and mass wasting (ii) List five processes involved in chemical weathering
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition
 Weathering, Erosion, Deposition The breakdown of rocks at or near the Earth s Surface. Physical Chemical - The breakdown of rock into smaller pieces without chemical change. - Dominant in moist /cold conditions
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition The breakdown of rocks at or near the Earth s Surface. Physical Chemical - The breakdown of rock into smaller pieces without chemical change. - Dominant in moist /cold conditions
For the multiple-choice questions, completely fill in the circle alongside the appropriate answer.
 DRAFT SPECIMEN MATERIAL A-level GEOGRAPHY Paper 1 Physical geography Specimen Question Paper Time allowed: 2 hours 30 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a pencil a rubber a ruler. You may
DRAFT SPECIMEN MATERIAL A-level GEOGRAPHY Paper 1 Physical geography Specimen Question Paper Time allowed: 2 hours 30 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a pencil a rubber a ruler. You may
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2. Implications for Coastal Engineering
 SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
Weathering of Rocks. Weathering - Breakdown of rocks into pieces (sediment) 2 main types of weathering to rocks
 Weathering of Rocks Weathering - Breakdown of rocks into pieces (sediment) 2 main types of weathering to rocks Mechanical weathering requires physical forces to break rocks into smaller pieces. Chemical
Weathering of Rocks Weathering - Breakdown of rocks into pieces (sediment) 2 main types of weathering to rocks Mechanical weathering requires physical forces to break rocks into smaller pieces. Chemical
Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR
 Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on on the diagram below, which shows laboratory materials used for an investigation of the effects of sediment size on permeability,
Name: Mid-Year Review #2 SAR Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on on the diagram below, which shows laboratory materials used for an investigation of the effects of sediment size on permeability,
Physical landscapes River landscapes in the UK
 Physical landscapes River landscapes in the UK The shape of river valleys change s as rivers flow downstream - PROCESSES Erosion Abrasion or corrasion Attrition Hydraulic Action Solution or corrosion Deposition
Physical landscapes River landscapes in the UK The shape of river valleys change s as rivers flow downstream - PROCESSES Erosion Abrasion or corrasion Attrition Hydraulic Action Solution or corrosion Deposition
Shallow marine facies. Outline 13: The Paleozoic World. Shallow marine and terrestrial facies
 Outline 13: The Paleozoic World Shallow marine and terrestrial facies Shallow marine facies Sea level was much higher than today during much of the Paleozoic. Shallow epicontinental seas flooded continental
Outline 13: The Paleozoic World Shallow marine and terrestrial facies Shallow marine facies Sea level was much higher than today during much of the Paleozoic. Shallow epicontinental seas flooded continental
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100. Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event
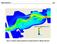 ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 100 Figure 7-3 Maximum velocity magnitudes for existing conditions for 100-year flood event ERDC/LAB TR-0X-X 101 Figure 7-4 Model schematization of Option 1 Figure 7-5 Bed displacement
The Montauk Peninsula: Data and Preliminary Interpretations of the Ditch Plains Area Introduction
 The Montauk Peninsula: Data and Preliminary Interpretations of the Ditch Plains Area John A. Black GSI Patchogue, New York R.S. Welch Suffolk Community College Selden, New York Introduction Sirkin, (1982)
The Montauk Peninsula: Data and Preliminary Interpretations of the Ditch Plains Area John A. Black GSI Patchogue, New York R.S. Welch Suffolk Community College Selden, New York Introduction Sirkin, (1982)
Elwha River response to dam removals through four years and a big flood:
 Elwha River response to dam removals through four years and a big flood: Lessons learned, channel response, and sediment effects from the world s largest engineered dam removal Andy Ritchie NPS Elwha Restoration
Elwha River response to dam removals through four years and a big flood: Lessons learned, channel response, and sediment effects from the world s largest engineered dam removal Andy Ritchie NPS Elwha Restoration
Glacial Deposition and Groundwater in Dutchess County
 Glacial Deposition and Groundwater in Dutchess County Name: Period: Thousands of years ago an enormous ice sheet blanketed the Hudson Valley in what was called the Wisconsinan Glaciation. The ice reshaped
Glacial Deposition and Groundwater in Dutchess County Name: Period: Thousands of years ago an enormous ice sheet blanketed the Hudson Valley in what was called the Wisconsinan Glaciation. The ice reshaped
EARTH SURFACE PROCESSES AND SEDIMENTATION!
 Sed and Strat EARTH SURFACE PROCESSES AND SEDIMENTATION! 2/27 Lecture 7- Exposure: Weathering and the Sediment Factory 3/04 Lecture 8 - Rivers and Landscapes 3/06 Lecture 9 - Waves (not Tides) 3/11 Lecture
Sed and Strat EARTH SURFACE PROCESSES AND SEDIMENTATION! 2/27 Lecture 7- Exposure: Weathering and the Sediment Factory 3/04 Lecture 8 - Rivers and Landscapes 3/06 Lecture 9 - Waves (not Tides) 3/11 Lecture
ON THE EVOLUTION OF A HOLOCENE BARRIER COAST
 ON THE EVOLUTION OF A HOLOCENE BARRIER COAST Response to sea-level change and sediment supply DANCORE Seminar 2014 COADAPT - Danish Coasts and Climate Adaptation Flooding Risk and Coastal Protection Mikkel
ON THE EVOLUTION OF A HOLOCENE BARRIER COAST Response to sea-level change and sediment supply DANCORE Seminar 2014 COADAPT - Danish Coasts and Climate Adaptation Flooding Risk and Coastal Protection Mikkel
Appendix C Baseline processes
 Appendix C Baseline processes North Norfolk SMP2 Appendix C Baseline processes Appendix C Contents C1 Introduction... 1 C2 Review of information... 1 C3 General overview... 2 C3.1 General description...
Appendix C Baseline processes North Norfolk SMP2 Appendix C Baseline processes Appendix C Contents C1 Introduction... 1 C2 Review of information... 1 C3 General overview... 2 C3.1 General description...
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
Ch 10 Deposition Practice Questions
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
Buried-valley Aquifers: Delineation and Characterization from Reflection Seismic and Core Data at Caledon East, Ontario
 Buried-valley Aquifers: Delineation and Characterization from Reflection Seismic and Core Data at Caledon East, Ontario Russell, H.A.J. 1, S.E. Pullan 1, J.A. Hunter 1, D.R. Sharpe 1, and S. Holysh 2 1
Buried-valley Aquifers: Delineation and Characterization from Reflection Seismic and Core Data at Caledon East, Ontario Russell, H.A.J. 1, S.E. Pullan 1, J.A. Hunter 1, D.R. Sharpe 1, and S. Holysh 2 1
How do glaciers form?
 Glaciers What is a Glacier? A large mass of moving ice that exists year round is called a glacier. Glaciers are formed when snowfall exceeds snow melt year after year Snow and ice remain on the ground
Glaciers What is a Glacier? A large mass of moving ice that exists year round is called a glacier. Glaciers are formed when snowfall exceeds snow melt year after year Snow and ice remain on the ground
Supplemental Slides. Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Junction of Land & Water. Sea Level Variations. Shore vs. Coast. Sea Level Variations
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
The Palmer Hill Glacial-Marine Delta, Whitefield, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities December, 2010, Maine 44 o 10 12.16 N, 69 o 37 18.93 W Text by Woodrow Thompson, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Introduction The most recent continental
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities December, 2010, Maine 44 o 10 12.16 N, 69 o 37 18.93 W Text by Woodrow Thompson, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Introduction The most recent continental
Bulletin of Earth Sciences of Thailand
 Depositional Environments and Stratigraphic Development of the Grand Taman Sari Circuit Outcrop: an Analogue for Transgressive Mahakam Delta Successions Ridha Santika Riadi Petroleum Geoscience Program,
Depositional Environments and Stratigraphic Development of the Grand Taman Sari Circuit Outcrop: an Analogue for Transgressive Mahakam Delta Successions Ridha Santika Riadi Petroleum Geoscience Program,
Erosion Surface Water. moving, transporting, and depositing sediment.
 + Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
+ Erosion Surface Water moving, transporting, and depositing sediment. + Surface Water 2 Water from rainfall can hit Earth s surface and do a number of things: Slowly soak into the ground: Infiltration
Journal of Earth Sciences and Geotechnical Engineering, vol. 4, no. 1, 2014, ISSN: (print), (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2014
 Journal of Earth Sciences and Geotechnical Engineering, vol. 4, no. 1, 2014, 17-24 ISSN: 1792-9040 (print), 1792-9660 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2014 Reconstruction of Relative Tectonic Movements Using Transgressive
Journal of Earth Sciences and Geotechnical Engineering, vol. 4, no. 1, 2014, 17-24 ISSN: 1792-9040 (print), 1792-9660 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2014 Reconstruction of Relative Tectonic Movements Using Transgressive
Search and Discovery Article #40536 (2010) Posted June 21, 2010
 Modern Examples of Mass Transport Complexes, Debrite and Turbidite Associations: Geometry, Stratigraphic Relationships and Implications for Hydrocarbon Trap Development* Fabiano Gamberi 1, Marzia Rovere
Modern Examples of Mass Transport Complexes, Debrite and Turbidite Associations: Geometry, Stratigraphic Relationships and Implications for Hydrocarbon Trap Development* Fabiano Gamberi 1, Marzia Rovere
Scenarios for the NI coast in the 21 st Century
 Scenarios for the NI coast in the 21 st Century Prof Julian Orford Geography, Archaeology & Palaeoecology Queen s University, Belfast Challenging perspective Living by the coast is good for your health!
Scenarios for the NI coast in the 21 st Century Prof Julian Orford Geography, Archaeology & Palaeoecology Queen s University, Belfast Challenging perspective Living by the coast is good for your health!
What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using
 7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
Chapter 2. Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice. Physical Weathering
 Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Shoreline and Climate Change Adaptation Alternatives for The Letter Parcel, Bolinas Lagoon
 Shoreline and Climate Change Adaptation Alternatives for The Letter Parcel, Bolinas Lagoon Scenic shoreline vista of Bolinas Lagoon and ridges, from Letter Parcel, March 2016 Peter Baye, Coastal Ecologist
Shoreline and Climate Change Adaptation Alternatives for The Letter Parcel, Bolinas Lagoon Scenic shoreline vista of Bolinas Lagoon and ridges, from Letter Parcel, March 2016 Peter Baye, Coastal Ecologist
Landscape evolution. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities and life
 Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Introduction to sequence stratigraphy and its application to reservoir geology
 Introduction to sequence stratigraphy and its application to reservoir geology Massimo Zecchin Istituto Nazionale di Oceanografia e di Geofisica Sperimentale - OGS Historical development Definitions Systems
Introduction to sequence stratigraphy and its application to reservoir geology Massimo Zecchin Istituto Nazionale di Oceanografia e di Geofisica Sperimentale - OGS Historical development Definitions Systems
QU: Where does sand do jail time? AIM: To explain the sediment cell concept as a system and what human and natural factors create/upset a dynamic
 QU: Where does sand do jail time? AIM: To explain the sediment cell concept as a system and what human and natural factors create/upset a dynamic equilibrium. ST: On your copy draw and label future depositional
QU: Where does sand do jail time? AIM: To explain the sediment cell concept as a system and what human and natural factors create/upset a dynamic equilibrium. ST: On your copy draw and label future depositional
Year 6. Geography. Revision
 Year 6 Geography Revision November 2017 Rivers and World knowledge How the water cycle works and the meaning of the terms evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, surface run-off, groundwater
Year 6 Geography Revision November 2017 Rivers and World knowledge How the water cycle works and the meaning of the terms evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration, surface run-off, groundwater
Topic 6: Weathering, Erosion and Erosional-Deposition Systems (workbook p ) Workbook Chapter 4, 5 WEATHERING
 Topic 6: Weathering, Erosion and Erosional-Deposition Systems (workbook p. 95-125) Workbook Chapter 4, 5 THE BIG PICTURE: Weathering, erosion and deposition are processes that cause changes to rock material
Topic 6: Weathering, Erosion and Erosional-Deposition Systems (workbook p. 95-125) Workbook Chapter 4, 5 THE BIG PICTURE: Weathering, erosion and deposition are processes that cause changes to rock material
10/27/2014. Surface Processes. Surface Processes. Surface Processes. Surface Processes. Surface Processes
 Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 25 Surface or surficial processes originate at Earth's surface and reshape its contours. Surface processes include: Weathering Erosion Deposition
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 25 Surface or surficial processes originate at Earth's surface and reshape its contours. Surface processes include: Weathering Erosion Deposition
Facies Analysis Of The Reservoir Rocks In The. Sylhet Trough, Bangladesh. Abstract
 Facies Analysis Of The Reservoir Rocks In The Sylhet Trough, Bangladesh Joyanta Dutta Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok 10330, Thailand
Facies Analysis Of The Reservoir Rocks In The Sylhet Trough, Bangladesh Joyanta Dutta Petroleum Geoscience Program, Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok 10330, Thailand
Holocene Lower Mississippi River Avulsions: Autogenic Versus Allogenic Forcing*
 Holocene Lower Mississippi River Avulsions: Autogenic Versus Allogenic Forcing* Eric Prokocki 1,2 Search and Discovery Article #50330 (2010) Posted October 14, 2010 *Adapted from oral presentation at AAPG
Holocene Lower Mississippi River Avulsions: Autogenic Versus Allogenic Forcing* Eric Prokocki 1,2 Search and Discovery Article #50330 (2010) Posted October 14, 2010 *Adapted from oral presentation at AAPG
CARD #1 The Shape of the Land: Effects of Crustal Tilting
 CARD #1 The Shape of the Land: Effects of Crustal Tilting When we look at a birds-eye view of the Great Lakes, it is easy to assume the lakes are all at a similar elevation, but viewed in this way, we
CARD #1 The Shape of the Land: Effects of Crustal Tilting When we look at a birds-eye view of the Great Lakes, it is easy to assume the lakes are all at a similar elevation, but viewed in this way, we
June 9, R. D. Cook, P.Eng. Soils Engineer Special Services Western Region PUBLIC WORKS CANADA WESTERN REGION REPORT ON
 PUBLIC WORKS CANADA WESTERN REGION REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION PROPOSED MARTIN RIVER BRIDGE MILE 306.7 MACKENZIE HIGHWAY Submitted by : R. D. Cook, P.Eng. Soils Engineer Special Services Western
PUBLIC WORKS CANADA WESTERN REGION REPORT ON GEOTECHNICAL INVESTIGATION PROPOSED MARTIN RIVER BRIDGE MILE 306.7 MACKENZIE HIGHWAY Submitted by : R. D. Cook, P.Eng. Soils Engineer Special Services Western
Pat Dryer Half Moon Lake: A True Oxbow Lake? Geography 364 April 1 st, 2007
 Pat Dryer Half Moon Lake: A True Oxbow Lake? Geography 364 April 1 st, 2007 Appendix Abstract 2 Introduction 3 Methods 3 Results 3 Discussion 5 Conclusion 11 1 Abstract Half Moon Lake appears to be an
Pat Dryer Half Moon Lake: A True Oxbow Lake? Geography 364 April 1 st, 2007 Appendix Abstract 2 Introduction 3 Methods 3 Results 3 Discussion 5 Conclusion 11 1 Abstract Half Moon Lake appears to be an
Dunes Growth Estimation for Coastal Protection
 Dunes Growth Estimation for Coastal Protection Muhammad Zikra Department of Ocean Engineering, Faculty of Marine Technology, ITS, Kampus ITS Keputih Sukolilo, Surabaya 60111 Abstract: This paper describes
Dunes Growth Estimation for Coastal Protection Muhammad Zikra Department of Ocean Engineering, Faculty of Marine Technology, ITS, Kampus ITS Keputih Sukolilo, Surabaya 60111 Abstract: This paper describes
Summary. Streams and Drainage Systems
 Streams and Drainage Systems Summary Streams are part of the hydrologic cycle and the chief means by which water returns from the land to the sea. They help shape the Earth s surface and transport sediment
Streams and Drainage Systems Summary Streams are part of the hydrologic cycle and the chief means by which water returns from the land to the sea. They help shape the Earth s surface and transport sediment
PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS. Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES. Faulting. Folding 9/6/2012. TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS GRADATIONAL TECTONIC
 TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the scientific study
TOPOGRAPHIC RELIEF MAP of NYS PALEOGEOGRAPHY of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 2012 Definitions GEOLOGIC PROCESSES Geography: study of people living on the surface of the earth. Geology: the scientific study
L7/ Historical Perspec=ve, Deltas
 Colin Woodroffe (2002) Coasts: Form, Process and Evolu=on, Outline of Chapter 7: L7/1 L7/2 7.1. Historical Perspec=ve, 7.1.1. Deltas Herodotus (450, B.C.) delta = Shape of Nile River Delta = Δ Gilbert
Colin Woodroffe (2002) Coasts: Form, Process and Evolu=on, Outline of Chapter 7: L7/1 L7/2 7.1. Historical Perspec=ve, 7.1.1. Deltas Herodotus (450, B.C.) delta = Shape of Nile River Delta = Δ Gilbert
Rivers T. Perron
 1 Rivers T. Perron 12.001 After our discussions of large-scale topography, how we represent topography in maps, and how topography interacts with geologic structures, you should be frothing at the mouth
1 Rivers T. Perron 12.001 After our discussions of large-scale topography, how we represent topography in maps, and how topography interacts with geologic structures, you should be frothing at the mouth
Caspian Rapid Sea Level Changing Impact on Estuaries Morphodynamic Deformation
 2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Caspian Rapid Sea Level Changing Impact on Estuaries Morphodynamic Deformation Naser Ebadati
2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Caspian Rapid Sea Level Changing Impact on Estuaries Morphodynamic Deformation Naser Ebadati
