Ore Deposits and Mantle Plumes
|
|
|
- Oswald Marsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ore Deposits and Mantle Plumes by Franco Pirajno Geological Survey of Western Australia, Perth, Australia KLUWER ACADEMIC PUBLISHERS DORDRECHT / BOSTON / LONDON
2 CONTENTS PREFACE ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS INTRODUCTION XI XIII XVII PART ONE CHAPTER 1 The Earth's Internal Structure and Convection in the Mantle 1. 1 Introduction 1.2 Early planetary evolution 2.3 The Earth's internal structure The crust The mantle The core-mantle boundary (CMB) and D" layer The core 25.4 Convection in the mantle; theories and models Theories and dynamics of convection Physical parameters of mantle convection Whole mantle and two-layers mantle convection models 32.5 Mantle geochemistry 41.6 Mantle evolution through time and implications for Earth's history 46.7 Concluding remarks 53.8 References CHAPTER 2 Mantle Plumes and Superplumes; Continental Breakups, Supercontinent Cycles and Ore Deposits Introduction Hotspots: distribution and relationship to rifting Laboratory modelling, structure and dynamics of mantle plumes Doming of the crust (hotspot swells) and associated topographic and drainage features 71
3 VIII Contents 2.5 Mantle plume-lithosphere interactions and plume-generated melts Crustal stress regimes in response to mantle plumes Superplumes and continental breakup Gondwana and Rodinia breakups, mantle plumes or plate forces? Supercontinent cycles and ore deposits The "other side" of the mantle plume theory Concluding remarks References 105 CHAPTER 3 Oceanic Islands, Large Igneous Provinces, Mafic Dyke Swarms, and Intracontinental Alkaline Magmatism Introduction Oceanic volcanic islands The Hawaiian-Emperor seamounts chain Marquesas Islands Walvis Ridge and Tristan da Cunha Iceland Reunion Island Geochemical and isotopic characteristics of oceanic volcanic island basalts Large igneous provinces (LIP): oceanic plateaux and continental flood basalts (CFB) " Introduction Isotope systematics Oceanic plateaux \ Volcanic-rifted continental margins Continental flood basalts (CFB) Mafic dyke swarms Mafic dyke swarms in the Kaapvaal Craton, South Africa The Mackenzie dyke swarm, Canada Parana-Etendeka dykes Intracontinental alkaline magmatism Tectonic settings, ages and controls of intracontinental alkaline magmatism in Africa The Damaraland alkaline province, Namibia Carbonatites Kimberlites and lamproites Concluding remarks References 202
4 Contents IX CHAPTER 4 Rifting Processes, Volcano-Sedimentary Basins and the Role of Mantle Plumes Introduction Rifting dynamics: passive and active Passive rifting Active rifting Rifting and basic formation related to compression in thickened crust Geophysical signatures of rifts Stratigraphic successions as records of basin evolution The stratigraphic record of intracontinental basins and aulacogens The East African Rift System and the Afar Triangle: examples of modern continental rifting where mantle plume activity is recognised Introduction The East African Rift System (EARS) Examples of ancient continental rifts where mantle plume activity is assumed: Thuli-Sabi-Lebombo hotspot junction; Damara and Irumide hotspot junctions Tuli-Sabi-Lebombo hotspot junction Damara and Irumide hotspot junctions, southwestern Africa Sequence stratigraphy, eustasy and mantle plumes Concluding remarks References 256 CHAPTER 5 The Planetary and Meteorite Impact Context of Mantle Plumes Introduction Moon Mercury Venus Mars Large meteorite impacts and possible correlations with mantle plumes Ore deposits and impact structures Can meteorite mega-impacts trigger continental breakup and the ascent of mantle plumes? Concluding remarks References. 286
5 X Contents PART TWO CHAPTER 6 Intracontinental Magmatism, Anorogenic Metamorphism, Ore Systems and Mantle Plumes Introduction Intracontinental layered igneous intrusions Anorogenic prograde metamorphism and hydrothermal convention in hotspot-related rift systems Anorogenic metamorphism in the Central Zone of the Damara Orogen, Namibia Anorogenic metamorphism in the eastern Pyrenees Anorogenic metamorphism and intraplate magmatism around the Vredefort Dome, South Africa Metamorphism and fluid generation; metamorphogenic hydrothermal systems Concluding remarks References 317 CHAPTER 7 Direct Links; Magmatic Ore Deposits Fundamental Features and Concepts Introduction Definitions and terminology, Geometry of layered intrusions and magmatic processes Magmatic oxide ores Crystallisation of spinels from mafic-ultramafic magmas Magmatic sulphides and platinum group elements (PGE) ores The formation of Ni sulphide ores Platinum group elements (PGE) Concluding remarks References 380 CHAPTER 8 Magmatic Ore Deposits Introduction Large layered igneous complexes The Great Dyke, Zimbabwe The Bushveld Igneous Complex, South Africa Molopo Farms Complex, South Africa and Botswana Magmatic ore deposits in igneous complexes associated with continental flood basalts Duluth Complex, Mid-continent Rift System, USA Noril'sk-Talnakh, Siberian Traps, Russia 428
6 Contents XI The Insizwa Complex, Karoo Igneous Province Skaergaard and Kap Edvard Holm, East Greenland magmatic ores in Proterozoic troctolite-anorthosite complexes Voisey's Bay Ni-Cu-Co Komatiite-related magmatic ore deposits Komatiite volcanology Komatiite mineralogy and whole rock geochemistry Komatiite-hosted Fe-Ni-Cu sulphide ores Hydrothermal Ni-cu and PGE mineralisation in ultraultramafic rocks Concluding remarks References 459 CHAPTER 9 Indirect Links: Hydrothermal Mineral Deposits Introduction Ring complexes and carbonatites Proterozoic Cu-Au-U-REE-Fe deposits Mesothermal ore deposits Carlin-type epithermal ore deposits Ore deposits associated with intracontinental anorogenic magmatism Metallogeny of the Damara and Irumide orogens, Southwestern Africa, and the Mid Continent Rift System, USA Metallogeny of the Damara and Irumide orogens Metallogeny of the Mid-continent Rift System, North America Archaean lode Au deposits Concluding remarks References 504 CHAPTER 10 Indirect Links: Sedimentary Rock-Hosted Ore Deposits. Epilogue Introduction Metallogeny in modern rift settings The East African Rift System The Red Sea brine pools Sedimentary-hydrothermal ore deposits Mississippi Valley-type sulphide deposits Sedimentary exhalative (SEDEX) massive sulphide deposits Stratabound Cu-Ag and Cu-Co ore deposits Metalliferous black shales 531
7 XII Contents Mo-Ni-V-PGE-Au in black shales, southern China Iron-formations and manganese deposits Concluding remarks and epilogue References 540 APPENDIX 547 INDEX 549
The Lead 206/207 Dating Method
 The Lead 206/207 Dating Method 1 U Pb Zircon Ages, Chemical Geology, Volume 211 (2004) Pages 87 109 2 Lead Isotope Planetary Profiling, Chemical Geology, Volume 233 (2006) Pages 1 45 3 U Pb Step-Leaching
The Lead 206/207 Dating Method 1 U Pb Zircon Ages, Chemical Geology, Volume 211 (2004) Pages 87 109 2 Lead Isotope Planetary Profiling, Chemical Geology, Volume 233 (2006) Pages 1 45 3 U Pb Step-Leaching
Global Tectonics. Kearey, Philip. Table of Contents ISBN-13: Historical perspective. 2. The interior of the Earth.
 Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Global Tectonics Kearey, Philip ISBN-13: 9781405107778 Table of Contents Preface. Acknowledgments. 1. Historical perspective. 1.1 Continental drift. 1.2 Sea floor spreading and the birth of plate tectonics.
Tristan volcano complex: oceanic end-point of a major African lineament.
 Tristan volcano complex: oceanic end-point of a major African lineament. Ken Bailey and Gill Foulger No direct evidence for plumes is yet available: seismic tomography, currently the best hope, so far
Tristan volcano complex: oceanic end-point of a major African lineament. Ken Bailey and Gill Foulger No direct evidence for plumes is yet available: seismic tomography, currently the best hope, so far
Wilson cycle. 1. Intracontinental rift 2. From rifting to drifting
 Wilson cycle 1. Intracontinental rift 2. From rifting to drifting Stages of the Wilson Cycle Intracontinental Rifts 1. Contemporary examples (EAR, RGR, Baikal, Rhine graben) 2. Mechanical aspects. Characteristics
Wilson cycle 1. Intracontinental rift 2. From rifting to drifting Stages of the Wilson Cycle Intracontinental Rifts 1. Contemporary examples (EAR, RGR, Baikal, Rhine graben) 2. Mechanical aspects. Characteristics
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name Spring 2009 Sc ore / 40 QUIZ 3 1) Name two geologic features that provide physical evidence for the mineralogy of the earth s mantle (2 pts) Ophiolites,
Mantle plumes, associated intraplate tectonomagmatic processes and ore systems
 6 Articles by Franco Pirajno Mantle plumes, associated intraplate tectonomagmatic processes and ore systems Geological Survey of Western Australia, 100 Plain Street, East Perth, WA 6004, Australia. E-mail:
6 Articles by Franco Pirajno Mantle plumes, associated intraplate tectonomagmatic processes and ore systems Geological Survey of Western Australia, 100 Plain Street, East Perth, WA 6004, Australia. E-mail:
Questions and Topics
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
OCN 201 Mantle plumes and hot spots
 OCN 201 Mantle plumes and hot spots Question Long-term (>50 million years) changes in sea level are caused by: A. Changes in the volume of water in the ocean B. Changes in the volume of the ocean basins
OCN 201 Mantle plumes and hot spots Question Long-term (>50 million years) changes in sea level are caused by: A. Changes in the volume of water in the ocean B. Changes in the volume of the ocean basins
0.5 tcf gas. 1 mg contours. 10 tcf gas 70 k boe/day US$33.5 billion
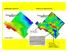 AIRBORNE GRAVITY VERTICAL DERIVATIVE 0.5 tcf gas 1 mg contours 10 tcf gas 70 k boe/day US$33.5 billion MAPPING IGNEOUS ACTIVITY ASSOCIATED WITH MANTLE PLUMES AND RIFTS TO TARGET MINERAL DEPOSITS SOME,
AIRBORNE GRAVITY VERTICAL DERIVATIVE 0.5 tcf gas 1 mg contours 10 tcf gas 70 k boe/day US$33.5 billion MAPPING IGNEOUS ACTIVITY ASSOCIATED WITH MANTLE PLUMES AND RIFTS TO TARGET MINERAL DEPOSITS SOME,
Plate Tectonics. 1)The plate tectonic system 2)A theory is born 3) Early evidence for continental drift 4) Continental drift and paleomagnetism
 Plate Tectonics Plate boundaries 1)The plate tectonic system 2)A theory is born 3) Early evidence for continental drift 4) Continental drift and paleomagnetism 6)History and future of plate motions system
Plate Tectonics Plate boundaries 1)The plate tectonic system 2)A theory is born 3) Early evidence for continental drift 4) Continental drift and paleomagnetism 6)History and future of plate motions system
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology. Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments
 GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
GY303 Igneous & Metamorphic Petrology Lecture 7: Magma Sources and Tectonic Environments Factors controlling Magma production Source rock composition Amount of fluids, especially H 2 O Pressure (Depth)
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education
 Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya -southern Asia 11.00.a VE 10X
Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice
 Name: Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice 1. Earth s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm 3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11
Name: Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice 1. Earth s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm 3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11
LATE ARCHAEAN FELSIC ALKALINE MAGMATISM: GEOLOGY, GEOCHEMISTRY, AND TECTONIC SETTING
 LATE ARCHAEAN FELSIC ALKALINE MAGMATISM: GEOLOGY, GEOCHEMISTRY, AND TECTONIC SETTING ZOZULYA DMITRY 1, EBY NELSON 2 1 - Geological Institute Kola Science Centre RAS, Apatity, Russia 2 - Department of Environmental,
LATE ARCHAEAN FELSIC ALKALINE MAGMATISM: GEOLOGY, GEOCHEMISTRY, AND TECTONIC SETTING ZOZULYA DMITRY 1, EBY NELSON 2 1 - Geological Institute Kola Science Centre RAS, Apatity, Russia 2 - Department of Environmental,
Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas
 Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY AND THE ENVIRONMENT (2 ND CANADIAN EDITION)
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES
 USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
Lecture 4.1 Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 4 California Science Content Standards Covered: Big Ideas 3A: Students know the features of the ocean floor that provide evidence of plate tectonics Mid Ocean Ridges (ex. Mid Atlantic
Plate Tectonics Chapter 4 California Science Content Standards Covered: Big Ideas 3A: Students know the features of the ocean floor that provide evidence of plate tectonics Mid Ocean Ridges (ex. Mid Atlantic
Introduction to Planetary Volcanism
 Introduction to Planetary Volcanism SUB G&ttlngen 204459 028 Gregory Mursky University of Wisconsin Milwaukee 96 A11088 Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 ' Preface Introduction 1 Historical
Introduction to Planetary Volcanism SUB G&ttlngen 204459 028 Gregory Mursky University of Wisconsin Milwaukee 96 A11088 Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 ' Preface Introduction 1 Historical
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
Geologic Evolution of Latin America. Plate Tectonics: General Concepts & Applications to Latin America
 Geologic Evolution of Latin America Plate Tectonics: General Concepts & Applications to Latin America Structure of Earth: 3 major divisions of Core, Mantle, and Crust Upper mantle differs in the way that
Geologic Evolution of Latin America Plate Tectonics: General Concepts & Applications to Latin America Structure of Earth: 3 major divisions of Core, Mantle, and Crust Upper mantle differs in the way that
Captain s Tryouts 2017
 Captain s Tryouts 2017 Dynamic Planet Test Written by: Araneesh Pratap (Chattahoochee High School) Name: Date: Answer all questions on the answer sheet. Point values are given next to each question or
Captain s Tryouts 2017 Dynamic Planet Test Written by: Araneesh Pratap (Chattahoochee High School) Name: Date: Answer all questions on the answer sheet. Point values are given next to each question or
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
Mineral Systems and Exploration Targeting. T. Campbell McCuaig - Centre for Exploration Targeting
 Mineral Systems and Exploration Targeting T. Campbell McCuaig - Centre for Exploration Targeting Mineral Geoscience Masters October 2013 We will cover Mineral Systems as an organising framework to understand
Mineral Systems and Exploration Targeting T. Campbell McCuaig - Centre for Exploration Targeting Mineral Geoscience Masters October 2013 We will cover Mineral Systems as an organising framework to understand
GY 112 Lecture Notes Archean Geology
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Archean Geology Lecture Goals: A) Time frame (the Archean and earlier) B) Rocks and tectonic elements (shield/platform/craton) C) Tectonics
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Archean Geology Lecture Goals: A) Time frame (the Archean and earlier) B) Rocks and tectonic elements (shield/platform/craton) C) Tectonics
12. The diagram below shows the collision of an oceanic plate and a continental plate.
 Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Chapter. Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc.
 Earth Chapter Plate Science 9 Tectonics Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc. 1 I. Earth s surface is made up of lithospheric plates. A. Lithospheric plates are composed of the crust and part of the upper
Earth Chapter Plate Science 9 Tectonics Graphics by Tasa Graphic Arts. Inc. 1 I. Earth s surface is made up of lithospheric plates. A. Lithospheric plates are composed of the crust and part of the upper
10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves.
 Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
At the beginning. Matter + antimatter. Matter has the advantage. baryons quarks, leptons, electrons, photons (no protons or neutrons)
 At the beginning Matter + antimatter Matter has the advantage baryons quarks, leptons, electrons, photons (no protons or neutrons) Hadrons protons, neutrons Hydrogen, helium (:0 H:He) Origin of the Universe
At the beginning Matter + antimatter Matter has the advantage baryons quarks, leptons, electrons, photons (no protons or neutrons) Hadrons protons, neutrons Hydrogen, helium (:0 H:He) Origin of the Universe
Remote Sensing of the Earth s Interior
 Remote Sensing of the Earth s Interior Earth s interior is largely inaccessible Origin and Layering of the Earth: Geochemical Perspectives Composition of Earth cannot be understood in isolation Sun and
Remote Sensing of the Earth s Interior Earth s interior is largely inaccessible Origin and Layering of the Earth: Geochemical Perspectives Composition of Earth cannot be understood in isolation Sun and
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway
 Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Why does the Earth have volcanoes? Why is there Earthquakes?
 Why does the Earth have volcanoes? Why is there Earthquakes? Turn to your neighbor and review: How and when did the Earth form? How old are the first traces of life on Earth? Logical? * 1.5Ga (1 st multicellular
Why does the Earth have volcanoes? Why is there Earthquakes? Turn to your neighbor and review: How and when did the Earth form? How old are the first traces of life on Earth? Logical? * 1.5Ga (1 st multicellular
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Seafloor Spreading and Paleomagnetism Activity
 Name: PART A: Ocean Bottom Profile Background: Seafloor spreading is the hypothesis that the sea floor moves sideways away from the crest of the mid- ocean ridge. It is estimated that 20 volcanic eruptions
Name: PART A: Ocean Bottom Profile Background: Seafloor spreading is the hypothesis that the sea floor moves sideways away from the crest of the mid- ocean ridge. It is estimated that 20 volcanic eruptions
Welcome to GEO 101 Introduction to Geology
 Welcome to GEO 101 Introduction to Geology so what is Geology? not just rocks! Geology is... study of Earth and planetary bodies processes responsible for formation processes that modify all areas of geology
Welcome to GEO 101 Introduction to Geology so what is Geology? not just rocks! Geology is... study of Earth and planetary bodies processes responsible for formation processes that modify all areas of geology
Structure of the Earth
 Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
3. PLATE TECTONICS LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES 3. PLATE TECTONICS The outer layers of the Earth are divided into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. The division is based on differences in mechanical properties
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES 3. PLATE TECTONICS The outer layers of the Earth are divided into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. The division is based on differences in mechanical properties
Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
 CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Words Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later... Words Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
 Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory What is Plate Tectonics? - 7 large tectonic plates and many smaller ones that break up the lithosphere - Plates are brittle and float on asthenosphere and glide past
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory What is Plate Tectonics? - 7 large tectonic plates and many smaller ones that break up the lithosphere - Plates are brittle and float on asthenosphere and glide past
Stop the Presses! New discovery about the origin of tetrapods!
 Mantle Plumes and Intraplate Volcanism Origin of Oceanic Island Volcanoes Lecture 20 Stop the Presses! New discovery about the origin of tetrapods! Tiktaalik rosaea Volcanism on the Earth Mid-ocean ridges
Mantle Plumes and Intraplate Volcanism Origin of Oceanic Island Volcanoes Lecture 20 Stop the Presses! New discovery about the origin of tetrapods! Tiktaalik rosaea Volcanism on the Earth Mid-ocean ridges
Introduction to Oceanography. Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Overview
 Introduction to Oceanography Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
Introduction to Oceanography Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition
 Chapter Chapter 1 2 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
Chapter Chapter 1 2 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Ore Formation as Primarily a Physical Process: A New Perspective on the Mineral Systems Method. Jon Hronsky July AESC 2010 Conference
 Ore Formation as Primarily a Physical Process: A New Perspective on the Mineral Systems Method Jon Hronsky July 5 2010 AESC 2010 Conference 1 Background Concepts Ore formation requires concentrating metal,
Ore Formation as Primarily a Physical Process: A New Perspective on the Mineral Systems Method Jon Hronsky July 5 2010 AESC 2010 Conference 1 Background Concepts Ore formation requires concentrating metal,
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA
 UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
Earthquakes. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy
 Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Plate Tectonics. Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15
 1 Plate Tectonics Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
1 Plate Tectonics Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
Crustal Activity. Plate Tectonics - Plates - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones
 Name: Date: Period: Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonics - s - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones The plates are
Name: Date: Period: Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonics - s - Lithosphere - Asthenosphere - Earth s surface consists of a major plates and some minor ones The plates are
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution. (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins)
 Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Introduction To Plate Tectonics Evolution (Continents, Ocean Basins, Mountains and Continental Margins) Geo 386 (Arabian Shield Course) Dr. Bassam A. A. Abuamarah Mohanna G E O 3 8 6 A R A B I A N G E
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Origin of the Oceans II. Earth A Living Planet. Earthquakes and Volcanoes. Plate Tectonics II
 Origin of the Oceans II Plate Tectonics II Earth A Living Planet Heat of formation of the planet is trapped at center, gradually escaping Center is nickel and iron Earthquakes and Volcanoes 1 Tracing the
Origin of the Oceans II Plate Tectonics II Earth A Living Planet Heat of formation of the planet is trapped at center, gradually escaping Center is nickel and iron Earthquakes and Volcanoes 1 Tracing the
Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009
 Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
Tectonics. Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust
 Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information
 Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Theory of Continental Drift
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener suggested that continents had once been part of a supercontinent named Pangaea, that later broke up. The pieces moved apart over millions of years
Plate Tectonics Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener suggested that continents had once been part of a supercontinent named Pangaea, that later broke up. The pieces moved apart over millions of years
Ch 9.1 Notes. Objective: Be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to explain evidence that supports it.
 Ch 9.1 Notes Objective: Be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to explain evidence that supports it. Pangaea Alfred Wegener proposed that land on Earth formed a single, huge landmass.
Ch 9.1 Notes Objective: Be able to explain the theory of plate tectonics and be able to explain evidence that supports it. Pangaea Alfred Wegener proposed that land on Earth formed a single, huge landmass.
Chapter Overview. Evidence for Continental Drift. Plate Tectonics. Evidence for Continental Drift. Evidence for Continental Drift 9/28/2010
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. Different plate boundaries have different features. Tectonic plates continue to move today.
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. Different plate boundaries have different features. Tectonic plates continue to move today.
Plate Tectonics Practice Test
 Plate Tectonics Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the Theory of Continental Drift that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to
Plate Tectonics Practice Test 1. What is the main idea Alfred Wegner proposed in the Theory of Continental Drift that he published in 1915? a. The continents float on a liquid layer that allows them to
The Building of a Continent. Delving into Deep Time
 The Building of a Continent Delving into Deep Time Methods for Studying the Past Identifying orogenies Mountain building events Mountains erode Can t study topography Study the evidence they leave behind
The Building of a Continent Delving into Deep Time Methods for Studying the Past Identifying orogenies Mountain building events Mountains erode Can t study topography Study the evidence they leave behind
A Systematic Approach To Geothermal Power Classification
 Geothermal Energy Utilization Associated With Oil & Gas Development June 17-18, 2008 SMU Dallas, Texas A Systematic Approach To Geothermal Power Classification Richard J. Erdlac, Jr. Peter Gross Edward
Geothermal Energy Utilization Associated With Oil & Gas Development June 17-18, 2008 SMU Dallas, Texas A Systematic Approach To Geothermal Power Classification Richard J. Erdlac, Jr. Peter Gross Edward
6. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
Occurrence of mafic-ultramafic rocks
 Occurrence of mafic-ultramafic rocks Mantle-derived magmas Oceanic Lithospheric mantle Continental lithospheric mantle Ultramafic xenoliths Oman ophiolite harzburgite upper mantle both from: http://www.bris.ac.uk/depts/geol/vft/oman.html
Occurrence of mafic-ultramafic rocks Mantle-derived magmas Oceanic Lithospheric mantle Continental lithospheric mantle Ultramafic xenoliths Oman ophiolite harzburgite upper mantle both from: http://www.bris.ac.uk/depts/geol/vft/oman.html
Discrimination between Archean A-type granitoids and sanukitoid suites using tectonic setting, geochemistry, and fertility type
 Discrimination between Archean A-type granitoids and sanukitoid suites using tectonic setting, geochemistry, and fertility type ZOZULYA DMITRY 1, EBY NELSON 2 1 - Geological Institute Kola Science Centre
Discrimination between Archean A-type granitoids and sanukitoid suites using tectonic setting, geochemistry, and fertility type ZOZULYA DMITRY 1, EBY NELSON 2 1 - Geological Institute Kola Science Centre
What Forces Drive Plate Tectonics?
 What Forces Drive Plate Tectonics? The tectonic plates are moving, but with varying rates and directions. What hypotheses have been proposed to explain the plate motion? Convection Cells in the Mantle
What Forces Drive Plate Tectonics? The tectonic plates are moving, but with varying rates and directions. What hypotheses have been proposed to explain the plate motion? Convection Cells in the Mantle
Earth overall average density = 5.5 g/cm 3 Temp increases with depth, the thermal gradient 30 0 C/km Pressure and the density also increase with
 Plate Tectonics Earth Earth overall average density = 5.5 g/cm 3 Temp increases with depth, the thermal gradient 30 0 C/km Pressure and the density also increase with depth Spheroid: with a longer major
Plate Tectonics Earth Earth overall average density = 5.5 g/cm 3 Temp increases with depth, the thermal gradient 30 0 C/km Pressure and the density also increase with depth Spheroid: with a longer major
The Sea Floor. Chapter 2
 The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
1. I can describe evidence for continental drift theory (e.g., fossil evidence, mountain belts, paleoglaciation)
 Science 10 Review Earth Science Vocabulary asthenosphere continental drift theory converging plates diverging plates earthquakes epicentre fault hot spot inner core lithosphere mantle mantle convection
Science 10 Review Earth Science Vocabulary asthenosphere continental drift theory converging plates diverging plates earthquakes epicentre fault hot spot inner core lithosphere mantle mantle convection
Basic Plate Kinematics
 Prof. Dr. Ibrahim Saad Aljumaily Geotectonics 4th year Geology Basic Plate Kinematics Plate kinematics refers to a description of the rates and directions of plate motion on the surface of the Earth. Description
Prof. Dr. Ibrahim Saad Aljumaily Geotectonics 4th year Geology Basic Plate Kinematics Plate kinematics refers to a description of the rates and directions of plate motion on the surface of the Earth. Description
5. Convergent boundaries produce a relatively low number of earthquakes compared to other boundaries. a. True
 1. Earth s crust is thinner than its mantle. ANSWER: True 2. The concept of isostacy states that high-density rock will stand higher than low-density rock, which explains the formation of subduction zones.
1. Earth s crust is thinner than its mantle. ANSWER: True 2. The concept of isostacy states that high-density rock will stand higher than low-density rock, which explains the formation of subduction zones.
In the space provided, write the letter of the definition that best matches the term or phrase.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Changing Continents 1. What is the result of slow movements of tectonic plates? RESHAPING EARTH S CRUST In the space provided, write the letter of the definition
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Changing Continents 1. What is the result of slow movements of tectonic plates? RESHAPING EARTH S CRUST In the space provided, write the letter of the definition
The High Lava Plains Project: Understanding the Causes of Continental Intraplate Tectonomagmatism
 The High Lava Plains Project: Understanding the Causes of Continental Intraplate Tectonomagmatism The High Lava Plains (HLP) of the northwestern USA is one of the most accessible yet least understood examples
The High Lava Plains Project: Understanding the Causes of Continental Intraplate Tectonomagmatism The High Lava Plains (HLP) of the northwestern USA is one of the most accessible yet least understood examples
Ore deposits related to mafic igneous rocks PGE s - GLY 361 Lecture 2
 Ore deposits related to mafic igneous rocks PGE s - GLY 361 Lecture 2 Ore deposits related to mafic igneous rocks Ores commonly associated with mafic rocks include: Platinum Group Elements (PGE s) Chromite
Ore deposits related to mafic igneous rocks PGE s - GLY 361 Lecture 2 Ore deposits related to mafic igneous rocks Ores commonly associated with mafic rocks include: Platinum Group Elements (PGE s) Chromite
Chapter 8: The Dynamic Planet
 Chapter 8: The Dynamic Planet I. The Pace of Change A. The Geologic Time Scale II. Earth s Structure and Internal Energy A. The Earth s Core B. The Earth s Mantle C. The Earth s Crust III. The Geologic
Chapter 8: The Dynamic Planet I. The Pace of Change A. The Geologic Time Scale II. Earth s Structure and Internal Energy A. The Earth s Core B. The Earth s Mantle C. The Earth s Crust III. The Geologic
Evidence from the Surface. Chapter 02. Continental Drift. Fossil Evidence for Pangaea. Seafloor Spreading. Seafloor Spreading 1/31/2012
 Evidence from the Surface Surface landforms Continental shelf and slope Abyssal Plane Mid-oceanic ridge Oceanic Trenches Chapter 02 Continental Drift Continental Drift - a hypothesis that the continents
Evidence from the Surface Surface landforms Continental shelf and slope Abyssal Plane Mid-oceanic ridge Oceanic Trenches Chapter 02 Continental Drift Continental Drift - a hypothesis that the continents
Divergent Boundaries: Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Divergent Boundaries: Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor Earth, 12 th Edition, Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Divergent Boundaries From 1872 to 1876, the HMS Challenger expedition
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Divergent Boundaries: Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor Earth, 12 th Edition, Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Divergent Boundaries From 1872 to 1876, the HMS Challenger expedition
INTRODUCTION. Basalt, the widespread igneous rock on the earth sur-face. today appear to have been equally important
 INTRODUCTION Basalt, the widespread igneous rock on the earth sur-face today appear to have been equally important in the geologic past. Basaltic rocks are mostly partial melting products of the upper
INTRODUCTION Basalt, the widespread igneous rock on the earth sur-face today appear to have been equally important in the geologic past. Basaltic rocks are mostly partial melting products of the upper
Full file at
 Essentials of Oceanography, 10e (Trujillo/Keller) Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. A)
Essentials of Oceanography, 10e (Trujillo/Keller) Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. A)
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor
 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Chapter Overview Much evidence supports plate tectonics theory. The plate tectonics model describes features and processes on Earth. Plate tectonic science
GENERAL GEOLOGY Fall Chapter 18: The Sea Floor. Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli
 GENERAL GEOLOGY 1113-005 Fall 2008 Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli Note that these are NOT questions, but rather are a list of topics that we have covered either in class or are
GENERAL GEOLOGY 1113-005 Fall 2008 Partial Examination IV Study Guide Dr. Glen S. Mattioli Note that these are NOT questions, but rather are a list of topics that we have covered either in class or are
Introduction to Prospecting. Session Four Ore Deposits
 Introduction to Prospecting Session Four Ore Deposits Ore Deposits What is ore? Common elements such as gold, copper, zinc and lead occur naturally in all rocks, however in very low quantities. Ore is
Introduction to Prospecting Session Four Ore Deposits Ore Deposits What is ore? Common elements such as gold, copper, zinc and lead occur naturally in all rocks, however in very low quantities. Ore is
Continental Drift. & Plate Tectonics
 Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics Alfred Wegener, a German scientist, proposed the hypothesis of CONTINENTAL DRIFT, in 1912. Hypothesis stated: All Earth s continents were once a single landmass (Pangaea)
Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics Alfred Wegener, a German scientist, proposed the hypothesis of CONTINENTAL DRIFT, in 1912. Hypothesis stated: All Earth s continents were once a single landmass (Pangaea)
Mineral Systems and Exploration Targeting. T. Campbell McCuaig - Centre for Exploration Targeting
 Mineral Systems and Exploration Targeting T. Campbell McCuaig - Centre for Exploration Targeting Mineral Geoscience Masters October 2013 Premise Exploration is an exercise in sequential volume reduction,
Mineral Systems and Exploration Targeting T. Campbell McCuaig - Centre for Exploration Targeting Mineral Geoscience Masters October 2013 Premise Exploration is an exercise in sequential volume reduction,
Earth. Temp. increases with depth, the thermal gradient is 25 o C/km. Pressure and density also increase with depth.
 Plate Tectonics Earth Earth overall average density = 5.5 g/cm 3. Temp. increases with depth, the thermal gradient is 25 o C/km. Pressure and density also increase with depth. Spheroid: with a longer major
Plate Tectonics Earth Earth overall average density = 5.5 g/cm 3. Temp. increases with depth, the thermal gradient is 25 o C/km. Pressure and density also increase with depth. Spheroid: with a longer major
5: ABSOLUTE PLATE MOTIONS & HOTSPOTS
 5-1 5: ABSOLUTE PLATE MOTIONS & HOTSPOTS 1 Relative motions between plates are most important In some applications important to consider absolute plate motions, those with respect to the deep mantle ABSOLUTE
5-1 5: ABSOLUTE PLATE MOTIONS & HOTSPOTS 1 Relative motions between plates are most important In some applications important to consider absolute plate motions, those with respect to the deep mantle ABSOLUTE
In 1912 Alfred Wegener proposed Continental Drift the continents have moved over time the continents were part of one giant landmass named Pangaea.
 Plate Tectonics In 1912 Alfred Wegener proposed Continental Drift the continents have moved over time the continents were part of one giant landmass named Pangaea. Pangaea Landmass movements over millions
Plate Tectonics In 1912 Alfred Wegener proposed Continental Drift the continents have moved over time the continents were part of one giant landmass named Pangaea. Pangaea Landmass movements over millions
Full file at CHAPTER 2 The Way the Earth Works: Plate Tectonics
 CHAPTER 2 The Way the Earth Works: Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Wegener proposed continental drift after he observed evidence from fossils, glacial deposits, and the fit of the continents that suggested
CHAPTER 2 The Way the Earth Works: Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Wegener proposed continental drift after he observed evidence from fossils, glacial deposits, and the fit of the continents that suggested
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
 The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Agree or Disagree? 1. The Earth if made up of 4 different layers. 2. The crust (where we live) can be made of either less dense continental crust or the more
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Agree or Disagree? 1. The Earth if made up of 4 different layers. 2. The crust (where we live) can be made of either less dense continental crust or the more
In order to study Plate Tectonics, we must first
 TB Chapter 13 In order to study Plate Tectonics, we must first reorganize our layering system for the Earth: Old System 4 layers Crust (rigid) id) (rigid) Mantle (putty like) (semi rigid) Outer core (liquid)
TB Chapter 13 In order to study Plate Tectonics, we must first reorganize our layering system for the Earth: Old System 4 layers Crust (rigid) id) (rigid) Mantle (putty like) (semi rigid) Outer core (liquid)
Do deep mantle plumes explain the Mesozoic igneous features of New England?
 Do deep mantle plumes explain the Mesozoic igneous features of New England? J. Gregory McHone 9 Dexters Lane, Grand Manan, New Brunswick, Canada E5G3A6 greg@earth2geologists.net Hotspots are regions of
Do deep mantle plumes explain the Mesozoic igneous features of New England? J. Gregory McHone 9 Dexters Lane, Grand Manan, New Brunswick, Canada E5G3A6 greg@earth2geologists.net Hotspots are regions of
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
 The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth is made up of 4 main layers: Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust Crust Mantle Outer core Inner core The Crust This is where
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics Structure of the Earth The Earth is made up of 4 main layers: Inner Core Outer Core Mantle Crust Crust Mantle Outer core Inner core The Crust This is where
RAYMOND SIEVER Harvard University
 E A R T H FOURTH EDITION FRANK PRESS National Academy of Sciences RAYMOND SIEVER Harvard University W. H. Freeman and Company New York Preface xiii Acknowledgments xviii PART I PROLOGUE CHAPTER 1 HISTORY
E A R T H FOURTH EDITION FRANK PRESS National Academy of Sciences RAYMOND SIEVER Harvard University W. H. Freeman and Company New York Preface xiii Acknowledgments xviii PART I PROLOGUE CHAPTER 1 HISTORY
Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor
 Chapter 13 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 13 Divergent Boundaries An Emerging Picture of the Ocean
Chapter 13 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Twelfth Edition Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 13 Divergent Boundaries An Emerging Picture of the Ocean
Plate Tectonics Notes
 Plate Tectonics Notes Last 30 Days Earthquakes Physical Features Last 30 Days Earthquakes with Plate Boundaries Earth s Structure Earth s Layers Core: Inner Core: Center of the earth, solid ball of metal
Plate Tectonics Notes Last 30 Days Earthquakes Physical Features Last 30 Days Earthquakes with Plate Boundaries Earth s Structure Earth s Layers Core: Inner Core: Center of the earth, solid ball of metal
The Rock Cycle A B C. Earth s Changing Face: The basics of plate tectonics
 The Rock Cycle IGNEOUS ROCKS Earth s Changing Face: The basics of plate tectonics A B C A SEDIMENTARY ROCKS B C B METAMORPHIC ROCKS MELTING OF PROTOLITH AND COOLING OF MAGMA UPLIFT AND EROSION OF PROTOLITH,
The Rock Cycle IGNEOUS ROCKS Earth s Changing Face: The basics of plate tectonics A B C A SEDIMENTARY ROCKS B C B METAMORPHIC ROCKS MELTING OF PROTOLITH AND COOLING OF MAGMA UPLIFT AND EROSION OF PROTOLITH,
5/24/2018. Plate Tectonics. A Scientific Revolution Unfolds
 1 Plate Tectonics A Scientific Revolution Unfolds 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics Prior to the late 1960s, most geologists believed that the
1 Plate Tectonics A Scientific Revolution Unfolds 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics Prior to the late 1960s, most geologists believed that the
The Geology of ORE DEPOSITS. John M. Guilbert. University of Arizona. Charles F. Park, Jr. W. H. Freeman and Company / New York
 The Geology of ORE DEPOSITS John M. Guilbert University of Arizona Charles F. Park, Jr. W. H. Freeman and Company / New York Contents Preface xii Introduction 1 Mineral Resource Problems 4 The Role of
The Geology of ORE DEPOSITS John M. Guilbert University of Arizona Charles F. Park, Jr. W. H. Freeman and Company / New York Contents Preface xii Introduction 1 Mineral Resource Problems 4 The Role of
PLATE TECTONICS. SECTION 17.1 Drifting Continents
 Date Period Name PLATE TECTONICS SECTION.1 Drifting Continents In your textbook, read about continental drift. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes each statement. 1. Early mapmakers thought
Date Period Name PLATE TECTONICS SECTION.1 Drifting Continents In your textbook, read about continental drift. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes each statement. 1. Early mapmakers thought
OS 1 The Oceans Fall 2007
 Name: Plate Tectonics (you must turn Activities 1-2 in during Section) Activity 1: Plate Boundaries A plate boundary simply describes where two plates (either oceanic or continental material) meet. There
Name: Plate Tectonics (you must turn Activities 1-2 in during Section) Activity 1: Plate Boundaries A plate boundary simply describes where two plates (either oceanic or continental material) meet. There
