DEVELOPMENT OF A CARTOGRAPHIC STRATEGY AND GEOSPATIAL SERVICES FOR DISASTER EARLY WARNING AND MITIGATION IN THE ECOWAS SUBREGION
|
|
|
- Magdalen Haynes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DEVELOPMENT OF A CARTOGRAPHIC STRATEGY AND GEOSPATIAL SERVICES FOR DISASTER EARLY WARNING AND MITIGATION IN THE ECOWAS SUBREGION L. A. Gueye a, M. S. Keita b,, J. O. Akinyede c, O. Kufoniyi d, G. Erin a a ECOWAS Commission 101 Yakubu Gowon Crescent, Asokoro District, Abuja, Nigeria. (latgueye@yahoo.com, gbengaerin@yahoo.com); b Regional Centre for Training in Aerospace Surveys (RECTAS), OAU Campus, Ile Ife, Osun State, Nigeria (keita@rectas.org); c Department of Remote Sensing and Geosciences Information System, Federal University of Technology, Akure, Ondo State, Nigeria (jakinyede@yahoo.com); d Department of Geography, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Osun State, Nigeria (jidekufoniyi@yahoo.com). Commission IV, WG IV/7 KEY WORDS: Cartographic Strategy, Geospatial Services, Disaster, Early Warning, Mitigation ABSTRACT: The West Africa Sub-region has been crisis and disaster ridden in recent times with enormous challenges for disaster mitigation. The crisis/disasters range from conflicts fuelled by political upheaval to epidemics that take their tolls on the population of some countries in the sub-region. The crisis and disaster events have overwhelming magnitudes and are highly dynamic, requiring a well-articulated plan for immediate response in order to mitigate their effects. A study carried out by the Early Warning Directorate (EWD) of the Economic Commission of West African States (ECOWAS) highlighted the risks and vulnerabilities of the region despite the considerable progress made in development and peace consolidation in some parts of the region. The study identified apparent institutional and infrastructural deficiencies, such as the lack of up-to-date geospatial data and information, and inadequate platforms for data gathering and data sharing among the relevant national agencies, which have made much of the region particularly vulnerable to the emerging threats. It is against the foregoing that the development of a Cartographic Strategy and Geospatial Services for EWD and the ECOWAS is being proposed. In addition to the resolution of the crucial need of reliable geospatial data capacity of member states, this initiative will spearhead the realisation of a Geospatial Data Infrastructure for ECOWAS Commission, through the appropriate policy formulation and implementation. Through the proper implementation of the Cartographic Strategy and Geospatial Services, ECOWAS will have the capacity to provide geospatial analysis and mapping support focusing on areas related to conflict prevention and resolution, regional planning for food security, early warning of viral diseases and epidemics, disaster preparedness, mitigation and response, infrastructural development and refugee resettlement, and a host of other vital projects/programmes for promoting ECOWAS regional integration agenda. This paper discusses the outcome of the preliminary studies and activities carried out by an Expert Group commissioned by the EWD to develop a Cartographic Strategy and propose a framework for its implementation. These include the assessment of the status of mapping and Geographic Information System uptake in member states, the formulation of policy and the realisation of a work plan for its successful implementation in the region. 1. INTRODUCTION One of the sustainable development challenges of any nation is its capacity to manage its environment and disasters. Both natural and manmade disasters can have devastating effects on people, properties and economies (Akinyede, 2005). Today, the frequency and magnitude of natural hazards and disasters threatening large populations living in diverse environments have shown a dramatic rise. The impact of disasters on the global environment has become increasingly severe over the last decades. The reported number of disasters has risen dramatically, as well as the number of people affected and the cost to global economy. About 95% of the deaths due to disasters occur in developing countries (Kufoniyi, 2007). West African nations have experienced many serious disaster challenges including drought, flood, coastal erosion, wild fires, epidemics, conflicts, etc. The sahelian drought of the 1980s affected West African countries and led to the loss of thousands of people, livestock and livelihoods. The increasing desertification and loss of prime agricultural lands occasioned by climate change and increased desiccation of the sudano-sahelian region led to landuse conflicts, communal and ethnic clashes and loss of lives (Adeniyi, 2009). The occurrence and severity of droughts and floods in the sub-region are happening with increasing frequency, accompanied by various diseases. Communities are more and more vulnerable to the unfamiliar hazards and cannot cope with the shocks leading to a constant rise in the number of people needing humanitarian assistance. Moreover, the number of emergencies in Africa per year has almost tripled since the mid-1980s to about 25 million people in 2005 (IFRC, 2008). To face these challenges, efforts are being deployed in the countries through national entities which include Emergency Management Agencies, Civil Protection Agencies and Early Warning Departments. Nevertheless, despite the contributions of those agencies, tackling disaster challenges still remains a difficult task for decision makers as demonstrated by the recurrent calamities, crisis and diseases in many countries of the region in recent times. To overcome the inconsistencies, regional bodies like the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) have embarked on initiatives using geospatial technology to find solutions to the problems. The advances in geospatial technology, specifically earth observation satellite and Geographical Information System (GIS), have increased their potential to meet challenges in scientific and social fields of studies. In disaster management, Corresponding author 203
2 space-based technologies and more efficient GIS tools are used to monitor the environmental changes at certain intervals and to carry out risk analysis. Indeed, geospatial technologies have contributed to providing significant solutions in all phases of disaster management areas (early warning, mitigation, preparedness, emergency response, relief and rehabilitation) in both developed and developing countries (Stevens, 2004). However, access to relevant geospatial data needed for planning, development and management of resources has remained limited in Africa, particularly in West African countries. In addition, accurate and up-to-date base maps which provide accurate locational information as basic requirement for emergency response are not always readily available. Although national capabilities in the use of the technologies are increasing at a significant rate, yet there is a definite need to support the technology transfer, while proposing methodological approaches that are appropriate to the specific needs of the countries in the planning and decision-making on disaster management. The current initiative of the ECOWAS Early Warning Directorate aims at assisting the ECOWAS and its Member states to improve the capabilities to manage the disaster events (pre-disaster, response and post-disaster) by using geospatial technology. The proposed Cartographic Strategy and Geospatial Services will surely provide appropriate solutions for the prevention of disaster events and emergency responses. The main purpose of this paper is to do a systematic analysis of the geospatial capability of ECOWAS Member States in overcoming the disaster challenges affecting the region and present an overview of the Cartographic Strategy and Geospatial Services initiative of the Early Warning Directorate aimed at mainstreaming geospatial data and services. The expected results, in terms of contribution to the improvement of the ability to deal with emergencies and mitigation of major disasters, are also highlighted. 2. DISASTER CHALLENGES IN WEST AFRICA The West African sub-region is comprised of 15 countries: Benin, Burkina Faso, Cabo Verde, Cote d Ivoire, the Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone and Togo. Recurrent natural and human-induced disasters, such as drought, trans-boundary animal and human diseases, plant pests and diseases, as well as socio-economic and political crises have been more frequent in the sub-region of West Africa. The consequences include significantly increasing food security, child malnutrition and vulnerability of populations to shocks. The sub-region s vulnerability to disaster is already exacerbated by a number of factors, such as: poverty, low education levels and a lack of access to basic services, political instability, conflicts, poor governance, weak economic dependent on international markets, high population growth and a trend towards unplanned urbanisation and exodus from rural areas. Indeed, as of 2010, all the countries in the sub-region, with the exception of Cabo Verde, were among the countries with the lowest level of human development (FAO, 2010). These crises in West Africa are aggravated by the impact of climate change: over the last fifty (50) years. The sub-region has undergone changes in rainfall patterns that have translated not only into serious, extensive droughts, especially in 2005, but also irregular and violent storms causing destructive floods damaging public infrastructures, homes, crops and livestock. Such increasingly complex and diverse disasters and crises, the majority of which are transnational, require urgent commitment and intervention of regional bodies like the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) taking advantage of its regional integration agenda. 3. ECOWAS CONTRIBUTION THROUGH EARLY WARNING IN WEST AFRICA 3.1 Why Early Warning Systems? Early warning Systems are essential in order to assess, to monitor risks and to warn of a potential crisis. In West African countries, there were local and national initiatives which often tended to prioritise the analysis of food supplies (food security) rather than other disaster challenges. This has prevented them from being able to identify vulnerabilities and formulate adequate preparation and response plans. Since the preparedness and emergency intervention capacities and capabilities of local populations and national governments to deal with the extensive and frequent crises were weak, it became necessary to establish more efficient systems to strengthen the national capacities and coordinate the activities at regional level. Therefore, the limited capacity of the national systems to find solutions to the crises and disaster challenges has necessitated ECOWAS Commission to initiate the establishment of a subregional peace and security observation system, pursuant to the protocol relating to the mechanism for conflict prevention, management, resolution, peace-keeping and security. 3.2 ECOWAS Early Warning / Observation Monitoring Centre The ECOWAS Early Warning System (EWS) was established under Chapter IV of the 1999 Protocol Relating to the Mechanism for Conflict Prevention, Management, Resolution, Peacekeeping and Security. The Early Warning Directorate s activities include collecting open sourced information largely based on 66 pre-determined indicators of regional peace and security, analysing and submitting timely reports with recommendations to the Office of the President of ECOWAS Commission through the Office of the Commissioner, Political Affairs, Peace and Security. The EWD performs these activities through the ECOWARN Field Reporter, a web-based field monitoring, interactive analysis, and visualization tool customized for the ECOWAS region. It functions by a network of 77 field monitors, collecting early warning data and feeding it to the ECOWARN Situation Room in Abuja, the headquarters of the system. 204
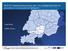
3 Recent developments in the system seeks to operationalise the National Early Warning and Response Mechanisms (NEWRMs) in Member States, a decentralized early warning and response system that involves all key stakeholders at the local, national and regional levels. Figure 1. - ECOWAS Early Warning Observation zones by country The Directorate works in partnership with representatives of ECOWAS Member States and Civil Society Organisations like West African Network for Peacebuilding (WANEP), West African Civil Society Forum (WACSOF) and research Institutes. It also collaborates with other Regional Economic Communities (RECs) and the African Union (AU) in the establishment of the Continental Early Warning System (CEWS). 3.3 Best practice in risk prevention and disaster mitigation Experience has shown that the difference in the level of vulnerability of hazards in the developed and developing countries is not really in the number and magnitude of occurrence of hazards, but in the level of disaster management - disaster preparedness (risk reduction), mitigation, and emergency responses. This is made possible through the use of geographic data i.e. geospatial data (Adeniyi, 2009). The actual questions to respond are how prepared are we for disaster management? How much do we know about our environment? and how much data and information do we have that can help us respond to crisis situation if it occurs? Today, geospatial technology finds responses to those questions and many other pertinent questions. It has been identified as the best applied technology for risk prevention and disaster mitigation. Geospatial technology comprises many other technologies which include Remote Sensing, Geographic Information System (GIS) and Global Positioning System (GPS). While Remote Sensing remains the most comprehensive and economically cost effective tool for obtaining synoptic geospatial data required for disaster monitoring, GIS plays a major role in the acquisition and management of related to the spatial characteristics and dimensions of disasters and hazards. For high precision information on disasters location on the Earth surface, the GPS technology provides accurate field point data required for a GIS. The adoption of Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI) as a veritable tool in mitigating the impact of disaster has also become very obvious and widely acknowledged (Kufoniyi et al, 2013). Many countries in West Africa sub-region are already familiar with these technologies and they have the expertise and technical know-how required for disaster management using geospatial technology. Nigeria, for example, is a member of the Disaster Monitoring Constellation (DMC), which, via collaboration, is able to provide data to and access data from other partners in the event of any disaster. (Akinyede, 2005). One of the best solutions to explore for efficient disaster management is therefore the development of a plan of action at the EWD that would coordinate the efforts being deployed by national agencies/institutions, and organise a co-operative network making use of geospatial technology. The adoption of such best practice will greatly encourage the governments of Member States, while servicing the vulnerable communities. 4. USE OF GEOSPATIAL TECHNOLOGY IN DISASTER MANAGEMENT IN WEST AFRICA 4.1 Status of mapping in West Africa Following the setting up of a GIS unit within the ECOWAS Early Warning Department, a meeting of the Directors General of the National Mapping Organisations of the 15 Member States was held in Dakar, Senegal in February, The goal of that meeting was to review the mapping status of the region and discuss a global cartographic strategy for ECOWAS. The meeting was attended by all the 15 directors, the representatives of development partners (French Cooperation) and other experts. The different presentations highlighted the status of mapping of each country, the availability of digital data, geodetic networks, equipment and National Mapping Strategy/Policy. As follow-up actions, the inventory of geospatial data and policies was undertaken, using a questionnaire in the first instance and a visit to each of the member states to validate the questionnaires collected. The criteria used in assessing the geospatial performance of Member States are presented in table1. 205
4 Table 1. : Scoring sheet of geospatial performance criteria S/N Criteria Code Score Very Good Fair Poor Good 1. Status of C National Mapping 2. Number of agencies C2 8 (>3) 6 (=3) 3 (=2) 2 (=1) visited 3. Availability C of Geosptial Data 4. Synergy C between partners 5. Evidence of C SDI initiative 6. Level of commitment C The resulting geospatial performance of each Member State is presented in tables 2a.and 2b Table 2a. : Geospatial performance of Member States (1) Criteria Country s code BN BF CV CI GA GH GU GB C C C C C C P* From the above findings of the investigation, the status of mapping of some of the countries has been found as very low. That demonstrated the urgent need to undertake the updating of existing maps produced in the 60s, still in analogue form in most cases. It was further noted that the deficiency observed in the mapping industry in the region has contributed to a large extent to the widening gap between the countries and the developed world. That has seriously influenced the successful implementation of many projects including disaster management programmes. 4.2 Approach of establishing a Cartographic Strategy and Geospatial Services for ECOWAS In order to achieve its intended effect of positively affecting sustainable development, geospatial information must be readily available and easily accessible to the users who need it for various decision-making processes in economic planning and development. This informed the decision to set up a standing committee of Experts to work with the Commission to spearhead the rapid development of a Cartographic Strategy and Geospatial Services for ECOWAS. Table 2b. : Geospatial performance of Member States (2) Criteria Country s code LB ML NIG NG SN SL TO C C C C C C P* Note: * P (Performance) = C1+C2+C3+C4+C5+C6 (confirmed by countries and validated by ECOWAS) Where BN = Benin, BF = Burkina Faso, CV = Cabo Verde, CI = Cote d Ivoire, GA = the Gambia, GH = Ghana, GU = Guinea, GB = Guinea-Bissau, LB = Liberia, ML = Mali, NIG = Niger, NG = Nigeria, SN = Senegal, SL = Sierra Leone and TO = Togo. Performance BN BF CV CI GA GH GU GB LB ML NIGNG SN SL TO Member States Figure 2. - Geospatial performance of ECOWAS Member States During the first stakeholders meeting held in Dakar in February, 2010, the main activities recommended by the participants include the following: - Identification and collection of geospatial data available in ECOWAS member states and the Multinational Geospatial Co-production Program (MGCP) project through the French Co-operation; - Definition and adoption of a Cartographic Strategy and Geospatial Policy for ECOWAS; - Building and strengthening capacity and capability of Mapping agencies and other stakeholders of member States; - Development of an ECOWAS Geospatial Data Infrastructure (EGDI). Sequel to the meeting held in Dakar, different workshops and seminars were held in Ouagadougou (2011), Banjul (2012), Abidjan (2013) and Cotonou (2014) to discuss the development and implementation of the ECOWAS Cartographic Strategy and Geospatial Data Infrastructure initiative. A plan of action was designed and adopted, based on activities to be executed in 206
5 collaboration with all the stakeholders, in synergy with experts and resource persons under the coordination of ECOWAS Early Warning Directorate Geospatial data and technology availability in ECOWAS Member States The mission undertaken to do the inventory of geospatial data and technology available in Member States permitted to identify the data available, the data gaps and the problems of accessibility. The available data include topographic and thematic maps, geodetic networks, databases and other statistical data. The inventory also identified the types of data and the difficulties of data sharing and dissemination between stakeholders. The inventory shows that the required geospatial technology platform including Remote Sensing technology (satellite and photography), Geographic Information Systems, Digital Cartography, ground surveying, is not fully present in all the Member States. Most countries are yet to set up a digital platform, thus the existing geospatial data are only in analogue form in many countries. The lack of internet connectivity makes in most cases the access to and dissemination of data very difficult. However, through the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) and the European Union funding, some mapping projects (large scale mapping and map revision) are currently going on in some countries (Burkina, Benin, Mali, Niger and Senegal). Furthermore, Nigeria has almost completed the analogue to digital conversion of the country s 1:50000 topographic map series and is currently undertaking the 1:25000 topographic mapping of the country Cartographic Strategy and Geospatial Data Infrastructure Policy The need to acquire reliable and up-to-date geospatial data arose when the GIS Unit was put in place at ECOWAS Early Warning Directorate in For the production of situation reports, there was need to integrate data acquired from different sources. That brought up the necessity to harmonise the geospatial data production system in all the countries. Thus, the development of a Cartographic Strategy for the sub-region. The Multinational Geospatial Co-production Program (MGCP) mapping project, working on the elaboration of topographic maps of West Africa at 1:50,000 scale, using satellite imageries was initiated by the French Cooperation at ECOWAS. However, the Head of National Mapping Agencies of ECOWAS Member States, during the meeting in Dakar in January 2010, strongly recommended that each country be responsible for the production of its own national maps, using at least regional standards to be developed as guidelines. It was finally decided that each country be encouraged to implement its National Spatial Data Infrastructure, while a Regional Geospatial Data Infrastructure should be developed under the coordination of EWD. The draft policy of the ECOWAS Mapping Strategy and Geospatial Data Infrastructure was then developed in Ouagadougou in 2011, amended by Working Group of Experts and resource persons in Banjul in 2012 and validated in Abidjan in An action plan was then finalised with concrete terms of reference for working groups comprising representatives of Member States and Experts resource persons at the Expert Group meetings in Cotonou and Banjul in 2014 and 2015 respectively Capacity building and Institutional strengthening The action plan will start will a full awareness building and buy-in of Ministers, Political Authorities and decision makers at ECOWAS Commission and in Member States. One of the important components of the strategy will be the increasing of the current available capacities of the region through training and capacity building programmes, institutional strengthening and funding. The capacity building exercises will target the available human resources, who are very important for the interventions during disasters, as well as experts and resource persons who will advise on relevant equipment and infrastructure to be acquired. Other selected expert will be in charge of all institutional arrangements for putting in place conducive working environment at both national and regional levels Development and Implementation of ECOWAS Geospatial Data Policy The development and maintenance of a Regional Geospatial Data Infrastructure at ECOWAS will consist of building of synergies among institutions and Member States and enabling the sharing of data and expertise for preparation of contingency plans and interventions in case of emergencies. The proposed ECOWAS Geospatial Data Infrastructure will: Ensure orderliness and common standard in the development and processes for executing mapping projects in the geographic space of ECOWAS. Facilitate the identification, production and sharing of fundamental datasets paramount to the regional development and integration. Facilitate and increase the rate of mapping activities within the member states. Provide a framework for standardizing the acquisition, processing, analysis, storage and dissemination of various geospatial datasets for socio-economic and environmental data needed to sustain and enhance regional integration and development. Eliminate duplication in the acquisition and maintenance of geospatial datasets in the region. Encourage regional use of EGDI-endorsed standards in order to create and maintain data at a high level of quality, consistency and harmony with the ISO standards. 207
6 Promote the awareness of Geographic Information and its applications. Ensure adequate funding to maintain the EGDI vision and sustain the spirit of cooperation and collaboration amongst the member states. Promote research, training, education and capacity building related to geospatial data production, management, dissemination and usage. 6. CONCLUSION An action plan for the establishment of a geospatial data infrastructure for ECOWAS sub-region has been presented in this paper. The infrastructure will provide effective tool for disaster mitigation, emergency response and relief. The infrastructure will provide timely and essential geospatial data and information to generate resources for preparing for and responding to various forms of disaster. The implementation of EGDI will be done under the coordination of EWD with the contribution of Experts and resource persons. It will be done in accordance with the Plan of Action and terms of reference defining the different activities to be undertaken by the following six (6) working groups: a. Geospatial dataset b. Nomenclature & Codification c. Standards d. Coordination, Communication & Partnership e. Clearinghouse & Metadata f. Capacity building & Sustainability 5. EXPECTED OUTCOMES AND BENEFITS For ECOWAS Geospatial Data Infrastructure to meet the stated objectives and purposes, it has to be well organised in such a way that it can provide reliable and up-to-date geospatial data and products for disaster mitigation, preparedness, emergency responses and reconstruction. It will be able to provide a Crisis Information Management System for the Early Warning Directorate, as well as relevant databases for the activities of ECOWAS Commission. The benefits of the geospatial data and products to be generated will cover many areas of endeavour. The EGDI will be in assistance of planning and implementation of projects and programmes, as well as decision making processes in ECOWAS Commission and Member States. In the area of disaster management, conflict prevention and resolution, peace keeping and security, the following will be fulfilled: a. Preparation of action plans for assignment of resources in response to potential crisis situations; b. Monitoring the execution of operations, projects and programmes through the correlation and integration of information from governments, military services and other civil sources; c. Evaluation of the potential and actual conflict situations, military force capabilities, planning for resources, use of map products, etc...; d. Generation and updating of maps and databases that are important for disaster management, conflict prevention and peace keeping activities; e. Preparation of reports and briefings for ECOWAS Early Warning Directorate and authorities of other departments and also for use in regional activities on disaster management. Geospatial data are often used for the preparation of contingency plans. The popular adage has it that prevention is better than cure. While we may not necessarily be able to prevent some natural hazards, we can act to prevent their disastrous effects on vulnerable people and places. (Adeniyi, 2009). Given the heavy and enduring costs of disaster management, there is no disputing the fact that making efforts to prevent them from breaking out in the first place is better than waiting until it is too late (Souare, 2006). The earlier a disaster, a disease, a dispute or a conflict can be identified, diagnosed and its causes properly addressed, the less likely it is that the situation will deteriorate into crisis, epidemic or violence. Normally, the calamities and conflicts do not occur suddenly without warning indicators. Thus, in order to guarantee the sustainability of the prevention measures, governments and regional and international organisations must ensure that there are proper mechanisms for conflict early warning in place, based on information gathering and informal and formal fact-finding. EWD is in a position to play that role in the sub-region. Therefore, the development of a Cartographic Strategy and Geospatial Services is not going to improve only the performance of EWD, but will be useful for the successful implementation of projects and programmes for ECOWAS Commission, as well as the execution of disaster management activities in Member States. REFERENCES D. Stevens (2004): Space Technology and Disaster Management- A Plan-of-action for Africa O. Akinyede (2005): Aspects of Space Science and Technology most relevant to Africa s development: Short term and Long Term., paper presented at the 1 st African Leadership Conference on Space Science and Technology for Sustainable Development, November, A.L. Gueye, A.O. Akingbade, O. Kufoniyi and P.B. Borisade (2004): The Use of GIS in Crisis Management: A Case Study of the Crisis Information Management System for the West African Sub-region. Kufoniyi O., O. A. Ogundele and D. O. Baloye (2013), Spatial Data Infrastructure (SDI): a plausible solution to improve disaster management processes in Nigeria, Journal of Sustainable Development in Africa, Vol. 15(3), 2013, Clarion University of Pennsylvania, Clarion, Pennsylvania, p
7 I.K. Souare (2006): Conflict Prevention and Early Warning Mechanisms in West Africa: A Critical Assessment of Progress. - African Security Review 16.3 / Institute for Security Studies. P.O. Adeniyi (2009): Geospatial Information and Disaster Management - Geoinformation Technology & Development: A compendium of Selected papers. 209
ACTION PLAN FOR WORLD HERITAGE IN LATIN AMERICA AND THE CARIBBEAN ( )
 Annex ACTION PLAN FOR WORLD HERITAGE IN LATIN AMERICA AND THE CARIBBEAN (2014-2024) The current Regional Action Plan for Latin America and the Caribbean for 2014-2024 has been elaborated by the State Parties
Annex ACTION PLAN FOR WORLD HERITAGE IN LATIN AMERICA AND THE CARIBBEAN (2014-2024) The current Regional Action Plan for Latin America and the Caribbean for 2014-2024 has been elaborated by the State Parties
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 2 July 2012 E/C.20/2012/10/Add.1 Original: English Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Second session New York, 13-15
United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 2 July 2012 E/C.20/2012/10/Add.1 Original: English Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Second session New York, 13-15
RCOF Review [Regional Climate Outlook Forum for the Gulf of Guinea region of Africa - PRESAGG] Status Report
![RCOF Review [Regional Climate Outlook Forum for the Gulf of Guinea region of Africa - PRESAGG] Status Report RCOF Review [Regional Climate Outlook Forum for the Gulf of Guinea region of Africa - PRESAGG] Status Report](/thumbs/78/77466191.jpg) RCOF Review 2017 [Regional Climate Outlook Forum for the Gulf of Guinea region of Africa - PRESAGG] Status Report Specific Climate features of concerned region This region typically covers the area below
RCOF Review 2017 [Regional Climate Outlook Forum for the Gulf of Guinea region of Africa - PRESAGG] Status Report Specific Climate features of concerned region This region typically covers the area below
Economic and Social Council
 United Nation E/C.20/2012/4/Add.1 Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 2 July 2012 Original: English Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Second session New York, 13-15
United Nation E/C.20/2012/4/Add.1 Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 2 July 2012 Original: English Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Second session New York, 13-15
African requirements for SDI standardization Antony Cooper Operating Unit Fellow Built Environment CSIR PO Box 395, Pretoria, 0001, South Africa
 ISO/TC 211 workshop on spatial data infrastructures (SDIs) African requirements for SDI standardization Antony Cooper Operating Unit Fellow Built Environment CSIR PO Box 395, Pretoria, 0001, South Africa
ISO/TC 211 workshop on spatial data infrastructures (SDIs) African requirements for SDI standardization Antony Cooper Operating Unit Fellow Built Environment CSIR PO Box 395, Pretoria, 0001, South Africa
13 th EUMETSAT User Forum in Africa
 13 th EUMETSAT User Forum in Africa GMES & Africa implementation in Western Africa Dogbeda M.Y. Azumah Regional Marine Centre University of Ghana Pictures zone UG GMES Presentation Layout UG G Project
13 th EUMETSAT User Forum in Africa GMES & Africa implementation in Western Africa Dogbeda M.Y. Azumah Regional Marine Centre University of Ghana Pictures zone UG GMES Presentation Layout UG G Project
Republic of Mozambique
 Republic of Mozambique Second Expert's Symposium on Multi-Hazard Early Warning Systems with focus on the Role of National Meteorological and Hydrological Services 5-7 May 2009, Toulouse France 1. Background
Republic of Mozambique Second Expert's Symposium on Multi-Hazard Early Warning Systems with focus on the Role of National Meteorological and Hydrological Services 5-7 May 2009, Toulouse France 1. Background
By Lillian Ntshwarisang Department of Meteorological Services Phone:
 By Lillian Ntshwarisang Department of Meteorological Services Phone: +267 3612200 Email: lntshwarisang@gov.bw/ lntshwarisang@gmail.com Introduction Mandate of DMS Function of the Department Services to
By Lillian Ntshwarisang Department of Meteorological Services Phone: +267 3612200 Email: lntshwarisang@gov.bw/ lntshwarisang@gmail.com Introduction Mandate of DMS Function of the Department Services to
A Presenta*on to the Interna*onal Workshop on Global Fundamental Geospa*al Data Themes for Africa By Sultan Mohammed Alya Chairman of UN-GGIM: Africa
 A Presenta*on to the Interna*onal Workshop on Global Fundamental Geospa*al Data Themes for Africa By Sultan Mohammed Alya Chairman of UN-GGIM: Africa Execu*ve Bureau and Director General of Ethiopian Geospa*al
A Presenta*on to the Interna*onal Workshop on Global Fundamental Geospa*al Data Themes for Africa By Sultan Mohammed Alya Chairman of UN-GGIM: Africa Execu*ve Bureau and Director General of Ethiopian Geospa*al
REGIONAL SDI DEVELOPMENT
 REGIONAL SDI DEVELOPMENT Abbas Rajabifard 1 and Ian P. Williamson 2 1 Deputy Director and Senior Research Fellow Email: abbas.r@unimelb.edu.au 2 Director, Professor of Surveying and Land Information, Email:
REGIONAL SDI DEVELOPMENT Abbas Rajabifard 1 and Ian P. Williamson 2 1 Deputy Director and Senior Research Fellow Email: abbas.r@unimelb.edu.au 2 Director, Professor of Surveying and Land Information, Email:
ACTION PLAN FOR WORLD HERITAGE IN LATIN AMERICA AND THE CARIBBEAN
 Final version-to send to the ACTION PLAN FOR WORLD HERITAGE IN LATIN AMERICA AND THE CARIBBEAN 2014-2024 The current Regional Action Plan for Latin America and the Caribbean has been elaborated by the
Final version-to send to the ACTION PLAN FOR WORLD HERITAGE IN LATIN AMERICA AND THE CARIBBEAN 2014-2024 The current Regional Action Plan for Latin America and the Caribbean has been elaborated by the
2018/1 The integration of statistical and geospatial information. The Regional Committee of UN-GGIM: Americas:
 The following are the conclusions and recommendations of the Regional Committee of the United Nations on Global Geospatial Information Management for the Americas, during its Fifth Session, Thursday 8
The following are the conclusions and recommendations of the Regional Committee of the United Nations on Global Geospatial Information Management for the Americas, during its Fifth Session, Thursday 8
The Global Statistical Geospatial Framework and the Global Fundamental Geospatial Themes
 The Global Statistical Geospatial Framework and the Global Fundamental Geospatial Themes Sub-regional workshop on integration of administrative data, big data and geospatial information for the compilation
The Global Statistical Geospatial Framework and the Global Fundamental Geospatial Themes Sub-regional workshop on integration of administrative data, big data and geospatial information for the compilation
GEOMATICS. Shaping our world. A company of
 GEOMATICS Shaping our world A company of OUR EXPERTISE Geomatics Geomatics plays a mayor role in hydropower, land and water resources, urban development, transport & mobility, renewable energy, and infrastructure
GEOMATICS Shaping our world A company of OUR EXPERTISE Geomatics Geomatics plays a mayor role in hydropower, land and water resources, urban development, transport & mobility, renewable energy, and infrastructure
Weather Climate Science to Service Partnership South Africa
 PROJECTS UNDERWAY Title of the Weather Climate Science to Service Partnership South Africa Together, building on an existing strong partnership, South African Weather Service and the Met Office will build
PROJECTS UNDERWAY Title of the Weather Climate Science to Service Partnership South Africa Together, building on an existing strong partnership, South African Weather Service and the Met Office will build
Geographical Names Activities in Africa The Gaborone Action Plan
 United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names Geographical Names Activities in Africa The Gaborone Action Plan 6 th Meeting of the Committee of Director -Generals of National Statistics Offices
United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names Geographical Names Activities in Africa The Gaborone Action Plan 6 th Meeting of the Committee of Director -Generals of National Statistics Offices
Briefing. H.E. Mr. Gyan Chandra Acharya
 Briefing by H.E. Mr. Gyan Chandra Acharya Under-Secretary-General and High Representative for the Least Developed Countries, Landlocked Developing Countries and Small Island Developing States Briefing
Briefing by H.E. Mr. Gyan Chandra Acharya Under-Secretary-General and High Representative for the Least Developed Countries, Landlocked Developing Countries and Small Island Developing States Briefing
Impact of Cyclone Nargis
 Lessons Learnt from Nargis Recovery for the Next Disaster International Recovery Forum (2011) 12, JAN 2011, Kobe, Japan Home for over 100 national races. Profile of Myanmar The 2 nd largest country in
Lessons Learnt from Nargis Recovery for the Next Disaster International Recovery Forum (2011) 12, JAN 2011, Kobe, Japan Home for over 100 national races. Profile of Myanmar The 2 nd largest country in
Launch of the Atlas and workshop on Land Use Land Cover
 The formal opening ceremony of the meeting took place on Tuesday 11 July 2017 and was chaired by Mrs. Fanta C. Kafando, Director of Environmental Preservation representing the Minister of the Environment
The formal opening ceremony of the meeting took place on Tuesday 11 July 2017 and was chaired by Mrs. Fanta C. Kafando, Director of Environmental Preservation representing the Minister of the Environment
Report of the Working Group 2 Data Sharing and Integration for Disaster Management *
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.104/6 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Twentieth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Jeju, 6-9 October 2015 Item 5 of the provisional agenda Report
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.104/6 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Twentieth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Jeju, 6-9 October 2015 Item 5 of the provisional agenda Report
RECTAS
 RECTAS www.rectas.org RECTAS: Capacity Building in Space Technology and Geospatial Data Applications Isi A. Ikhuoria Executive Director, RECTAS, Ile-Ife, Nigeria e-mail: edrectas@rectas.org +234 803 373
RECTAS www.rectas.org RECTAS: Capacity Building in Space Technology and Geospatial Data Applications Isi A. Ikhuoria Executive Director, RECTAS, Ile-Ife, Nigeria e-mail: edrectas@rectas.org +234 803 373
Georeferencing and Satellite Image Support: Lessons learned, Challenges and Opportunities
 Georeferencing and Satellite Image Support: Lessons learned, Challenges and Opportunities Shirish Ravan shirish.ravan@unoosa.org UN-SPIDER United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) UN-SPIDER
Georeferencing and Satellite Image Support: Lessons learned, Challenges and Opportunities Shirish Ravan shirish.ravan@unoosa.org UN-SPIDER United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) UN-SPIDER
Mahamadou S. KEITA Regional Centre for Training in Aerospace Surveys (RECTAS), Obafemi Awolowo University Campus, Ile-Ife - NIGERIA
 United Nations International Conference in Space-based Technologies for Disaster Management Disaster risk identification, assessment and monitoring Beijing CHINA, 23 25 October, 2013 Mahamadou S. KEITA
United Nations International Conference in Space-based Technologies for Disaster Management Disaster risk identification, assessment and monitoring Beijing CHINA, 23 25 October, 2013 Mahamadou S. KEITA
Statement of Mr. Sandagdorj Erdenebileg, Chief, Policy Development, Coordination, Monitoring and Reporting Service, UN-OHRLLS.
 Statement of Mr. Sandagdorj Erdenebileg, Chief, Policy Development, Coordination, Monitoring and Reporting Service, UN-OHRLLS at the Botswana National Workshop on the Vienna Programme of Action 27 th October
Statement of Mr. Sandagdorj Erdenebileg, Chief, Policy Development, Coordination, Monitoring and Reporting Service, UN-OHRLLS at the Botswana National Workshop on the Vienna Programme of Action 27 th October
A contribution to GEOSS from the SDI for Georesources in Africa
 A contribution to GEOSS from the SDI for Georesources in Africa A. TELLEZ-ARENAS BRGM, France in behalf of: Dr. Marc URVOIS Project Coordinator BRGM, France Mineral Resources Division INSPIRE Conference
A contribution to GEOSS from the SDI for Georesources in Africa A. TELLEZ-ARENAS BRGM, France in behalf of: Dr. Marc URVOIS Project Coordinator BRGM, France Mineral Resources Division INSPIRE Conference
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Session 8
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Session 8 Introduction Geography underpins all activities associated with a census Census geography is essential to plan and manage fieldwork as well as to report results
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS Session 8 Introduction Geography underpins all activities associated with a census Census geography is essential to plan and manage fieldwork as well as to report results
RETA 6422: Mainstreaming Environment for Poverty Reduction Category 2 Subproject
 RETA 6422: Mainstreaming Environment for Poverty Reduction Category 2 Subproject A. Basic Data 1. Subproject Title: Poverty-Environment Mapping to Support Decision Making 2. Country Director: Adrian Ruthenberg
RETA 6422: Mainstreaming Environment for Poverty Reduction Category 2 Subproject A. Basic Data 1. Subproject Title: Poverty-Environment Mapping to Support Decision Making 2. Country Director: Adrian Ruthenberg
KUNMING FORUM ON UNITED NATIONS GLOBAL GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION MANAGEMENT CITIES OF THE FUTURE: SMART, RESILIENT
 KUNMING FORUM ON UNITED NATIONS GLOBAL GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION MANAGEMENT CITIES OF THE FUTURE: SMART, RESILIENT and SUSTAINABLE Yunnan Zhenzhuang Guest House, Kunming, China 10 12 May 2017 BACKGROUND CONCEPT
KUNMING FORUM ON UNITED NATIONS GLOBAL GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION MANAGEMENT CITIES OF THE FUTURE: SMART, RESILIENT and SUSTAINABLE Yunnan Zhenzhuang Guest House, Kunming, China 10 12 May 2017 BACKGROUND CONCEPT
A/AC.105/C.1/2012/CRP.10
 A/AC.105/C.1/2012/CRP.10 1 February 2012 English only Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space Scientific and Technical Subcommittee Forty-ninth session Vienna, 6-17 February 2012 Item 6 of the provisional
A/AC.105/C.1/2012/CRP.10 1 February 2012 English only Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space Scientific and Technical Subcommittee Forty-ninth session Vienna, 6-17 February 2012 Item 6 of the provisional
Disaster Management in Mongolia
 The Third UN-GGIM-AP Plenary Meeting Disaster Management in Mongolia ~Coordination among NGIA & Other Related Organizations and Recommendations~ Bali Indonesia 10 November 2014 Khurelshagai Ayurzana, Director
The Third UN-GGIM-AP Plenary Meeting Disaster Management in Mongolia ~Coordination among NGIA & Other Related Organizations and Recommendations~ Bali Indonesia 10 November 2014 Khurelshagai Ayurzana, Director
Table ronde 5 : Cartographie d'urgence Emergency Mapping.
 Table ronde 5 : Cartographie d'urgence Emergency Mapping MapAction is an international NGO that provides maps and other information services to help humanitarian relief organisations in the field MapAction
Table ronde 5 : Cartographie d'urgence Emergency Mapping MapAction is an international NGO that provides maps and other information services to help humanitarian relief organisations in the field MapAction
Advancing Geoscientific Capability. Geological Survey of Finland
 Advancing Geoscientific Capability Geological Survey of Finland GTK in brief The Geological Survey of Finland (GTK) is one of the largest European centres of excellence in assessment, research and the
Advancing Geoscientific Capability Geological Survey of Finland GTK in brief The Geological Survey of Finland (GTK) is one of the largest European centres of excellence in assessment, research and the
Arctic Spatial Data Infrastructure Enabling Access to Arctic Location-Based Information
 Arctic Spatial Data Infrastructure Enabling Access to Arctic Location-Based Information Arctic SDI Side Event Co-Chairs: Arvo Kokkonen Arctic SDI Board Chair & Director General, National Land Survey of
Arctic Spatial Data Infrastructure Enabling Access to Arctic Location-Based Information Arctic SDI Side Event Co-Chairs: Arvo Kokkonen Arctic SDI Board Chair & Director General, National Land Survey of
Key Indicators for Territorial Cohesion & Spatial Planning Stakeholder Workshop - Project Update. 13 th December 2012 San Sebastián, Basque Country
 Key Indicators for Territorial Cohesion & Spatial Planning Stakeholder Workshop - Project Update 13 th December 2012 San Sebastián, Basque Country Key Aims Explore the use of territorial data in developing
Key Indicators for Territorial Cohesion & Spatial Planning Stakeholder Workshop - Project Update 13 th December 2012 San Sebastián, Basque Country Key Aims Explore the use of territorial data in developing
Inventory of United Nations Resolutions on Cartography Coordination, Geographic Information and SDI 1
 Inventory of United Nations Resolutions on Cartography Coordination, Geographic Information and SDI I. Resolutions on Cartography Coordination and Establishment of United Nations Regional Cartographic
Inventory of United Nations Resolutions on Cartography Coordination, Geographic Information and SDI I. Resolutions on Cartography Coordination and Establishment of United Nations Regional Cartographic
Economic and Social Council 2 July 2015
 ADVANCE UNEDITED VERSION UNITED NATIONS E/C.20/2015/11/Add.1 Economic and Social Council 2 July 2015 Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Fifth session New York, 5-7 August
ADVANCE UNEDITED VERSION UNITED NATIONS E/C.20/2015/11/Add.1 Economic and Social Council 2 July 2015 Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Fifth session New York, 5-7 August
ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.102/3 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Nineteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 29 October 1 November 2012 Item 4 of the provisional
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.102/3 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Nineteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 29 October 1 November 2012 Item 4 of the provisional
Foundation Geospatial Information to serve National and Global Priorities
 Foundation Geospatial Information to serve National and Global Priorities Greg Scott Inter-Regional Advisor Global Geospatial Information Management United Nations Statistics Division UN-GGIM: A global
Foundation Geospatial Information to serve National and Global Priorities Greg Scott Inter-Regional Advisor Global Geospatial Information Management United Nations Statistics Division UN-GGIM: A global
Compact guides GISCO. Geographic information system of the Commission
 Compact guides GISCO Geographic information system of the Commission What is GISCO? GISCO, the Geographic Information System of the COmmission, is a permanent service of Eurostat that fulfils the requirements
Compact guides GISCO Geographic information system of the Commission What is GISCO? GISCO, the Geographic Information System of the COmmission, is a permanent service of Eurostat that fulfils the requirements
FINDINGS OF THE ARCTIC METEOROLOGY SUMMIT
 FINDINGS OF THE ARCTIC METEOROLOGY SUMMIT 2018 WWW.FMI.FI CHAIR S SUMMARY: 1 2 3 We need to be curious to explore the known unknowns. Meteorology is an elemental part of international collaboration in
FINDINGS OF THE ARCTIC METEOROLOGY SUMMIT 2018 WWW.FMI.FI CHAIR S SUMMARY: 1 2 3 We need to be curious to explore the known unknowns. Meteorology is an elemental part of international collaboration in
Analysis of Regional Fundamental Datasets Questionnaire
 Permanent Committee on GIS Infrastructure for Asia and the Pacific Working Group 2 Regional Fundamental Data Summary Report on Analysis of Regional Fundamental Datasets Questionnaire ABBAS RAJABIFARD and
Permanent Committee on GIS Infrastructure for Asia and the Pacific Working Group 2 Regional Fundamental Data Summary Report on Analysis of Regional Fundamental Datasets Questionnaire ABBAS RAJABIFARD and
Overview of Early Warning Systems and the role of National Meteorological and Hydrological Services
 Overview of Early Warning Systems and the role of National Meteorological and Hydrological Services South Africa Second Experts Symposium on Multi-Hazard Early Warning Systems With focus on the Role of
Overview of Early Warning Systems and the role of National Meteorological and Hydrological Services South Africa Second Experts Symposium on Multi-Hazard Early Warning Systems With focus on the Role of
UN GGIM and National SDI Strategy
 MSDI Open Forum on 26 th January 2016 Contributing to the successful delivery of MSDI UN GGIM and National SDI Strategy Hiroshi Murakami Deputy Administrator Geospatial Information Authority of Japan Geospatial
MSDI Open Forum on 26 th January 2016 Contributing to the successful delivery of MSDI UN GGIM and National SDI Strategy Hiroshi Murakami Deputy Administrator Geospatial Information Authority of Japan Geospatial
The Role of the Louisiana Geographic Information Center in the Response to Hurricane Katrina
 The Role of the Louisiana Geographic Information Center in the Response to Hurricane Katrina By: Jared Chapiewsky & Laura Brown For: URPL 969- GIS Applications in Response to Hurricane Katrina Date: March
The Role of the Louisiana Geographic Information Center in the Response to Hurricane Katrina By: Jared Chapiewsky & Laura Brown For: URPL 969- GIS Applications in Response to Hurricane Katrina Date: March
Geospatial Technologies for Resources Planning & Management
 Geospatial Technologies for Resources Planning & Management Lal Samarakoon, PhD Director, Geoinformatics Center Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand Content Geoinformatics for SDG Information Integration
Geospatial Technologies for Resources Planning & Management Lal Samarakoon, PhD Director, Geoinformatics Center Asian Institute of Technology, Thailand Content Geoinformatics for SDG Information Integration
NSDI as a tool for Secure land tenure
 NSDI as a tool for Secure land tenure General Overview To look at the progress in SDI development and its application in policy formulation and impact on land tenure. INTEGRATION OF INFORMATION POLICIES
NSDI as a tool for Secure land tenure General Overview To look at the progress in SDI development and its application in policy formulation and impact on land tenure. INTEGRATION OF INFORMATION POLICIES
Fundamental Geospatial Datasets in Africa. Andre Nonguierma New York, 03 August 2015
 Fundamental Geospatial Datasets in Africa United Nations Economic Commission for Africa Geoinformation & Spatial Statistics Andre Nonguierma New York, 03 August 2015 Core Data : Lack of consistency Infrastructure
Fundamental Geospatial Datasets in Africa United Nations Economic Commission for Africa Geoinformation & Spatial Statistics Andre Nonguierma New York, 03 August 2015 Core Data : Lack of consistency Infrastructure
Disaster Management & Recovery Framework: The Surveyors Response
 Disaster Management & Recovery Framework: The Surveyors Response Greg Scott Inter-Regional Advisor Global Geospatial Information Management United Nations Statistics Division Department of Economic and
Disaster Management & Recovery Framework: The Surveyors Response Greg Scott Inter-Regional Advisor Global Geospatial Information Management United Nations Statistics Division Department of Economic and
Disaster RISK Management : Bhutanese Scenario
 Disaster RISK Management : Bhutanese Scenario Expert Group Meeting (EGM) on Geo-referenced Information Systems for Disaster Risk Management (Geo-DRM) and sustaining the Community of Practice (COP), Bangkok,
Disaster RISK Management : Bhutanese Scenario Expert Group Meeting (EGM) on Geo-referenced Information Systems for Disaster Risk Management (Geo-DRM) and sustaining the Community of Practice (COP), Bangkok,
Land Administration and Cadastre
 Geomatics play a major role in hydropower, land and water resources and other infrastructure projects. Lahmeyer International s (LI) worldwide projects require a wide range of approaches to the integration
Geomatics play a major role in hydropower, land and water resources and other infrastructure projects. Lahmeyer International s (LI) worldwide projects require a wide range of approaches to the integration
UNESCO World Heritage Centre - Arab States Unit
 UNESCO World Heritage Centre - Arab States Unit Post-Conflict Reconstruction in the Middle East Context and in the Old City of Aleppo in Particular UNESCO Headquarter, 18-19 June 2015 ACTION PLAN resulting
UNESCO World Heritage Centre - Arab States Unit Post-Conflict Reconstruction in the Middle East Context and in the Old City of Aleppo in Particular UNESCO Headquarter, 18-19 June 2015 ACTION PLAN resulting
THE SEVILLE STRATEGY ON BIOSPHERE RESERVES
 THE SEVILLE STRATEGY ON BIOSPHERE RESERVES 1 VISION FOR BIOSPHERE RESERVES IN THE 21 ST CENTURY The international Seville Conference on Biosphere Reserves, organised by UNESCO, adopted a two-pronged approach,
THE SEVILLE STRATEGY ON BIOSPHERE RESERVES 1 VISION FOR BIOSPHERE RESERVES IN THE 21 ST CENTURY The international Seville Conference on Biosphere Reserves, organised by UNESCO, adopted a two-pronged approach,
Space-based technology and applications and space science for humanitarian affairs, environment and security
 Space-based technology and applications and space science for humanitarian affairs, environment and security LUC ST-PIERRE United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs United Nations Office at Vienna
Space-based technology and applications and space science for humanitarian affairs, environment and security LUC ST-PIERRE United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs United Nations Office at Vienna
Geospatial Information and Services for Disasters (GIS4D)
 Geospatial Information and Services for Disasters (GIS4D) 31 July 2017 Tae Hyung KIM ICT and Disaster Risk Reduction Division (IDD) UNESCAP 1 About ESCAP Who is ESCAP? United Nations Economic and Social
Geospatial Information and Services for Disasters (GIS4D) 31 July 2017 Tae Hyung KIM ICT and Disaster Risk Reduction Division (IDD) UNESCAP 1 About ESCAP Who is ESCAP? United Nations Economic and Social
Realizing benefits of Spatial Data Infrastructure A user s perspective from Environment Agency - Abu Dhabi
 Realizing benefits of Spatial Data Infrastructure A user s perspective from Environment Agency - Abu Dhabi Anil Kumar Director, Environment Information Management 26 April 2012 Geospatial World Forum,
Realizing benefits of Spatial Data Infrastructure A user s perspective from Environment Agency - Abu Dhabi Anil Kumar Director, Environment Information Management 26 April 2012 Geospatial World Forum,
PAN AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF GEOGRAPHY AND HISTORY Specialized Organization of the OAS
 PAN AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF GEOGRAPHY AND HISTORY Specialized Organization of the OAS 10 th UNRCC Americas United Nations, New York, 20 August 2013 PAIGH, SIRGAS, PC-IDEA and GeoSUR 2013-2015 Joint Action
PAN AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF GEOGRAPHY AND HISTORY Specialized Organization of the OAS 10 th UNRCC Americas United Nations, New York, 20 August 2013 PAIGH, SIRGAS, PC-IDEA and GeoSUR 2013-2015 Joint Action
Background Document: Report of the Regional Committee of United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific
 Background Document: Report of the Regional Committee of United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific 1. Summary 1. This report highlights the activities carried out
Background Document: Report of the Regional Committee of United Nations Global Geospatial Information Management for Asia and the Pacific 1. Summary 1. This report highlights the activities carried out
Economic and Social Council
 United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 18 July 2016 Original: English Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Sixth session New York, 3-5 August 2016 Item 2
United Nations Economic and Social Council Distr.: General 18 July 2016 Original: English Committee of Experts on Global Geospatial Information Management Sixth session New York, 3-5 August 2016 Item 2
Jordan's Strategic Research Agenda in cultural heritage
 Jordan's Strategic Research Agenda in cultural heritage Analysis of main results Alessandra Gandini Amman, Jordan 3 rd November 2013 Main objectives The work performed had the main objective of giving
Jordan's Strategic Research Agenda in cultural heritage Analysis of main results Alessandra Gandini Amman, Jordan 3 rd November 2013 Main objectives The work performed had the main objective of giving
Systematic Observations, Data, Climate Methods and. Tools - Availability, Applicability, Accessibility. Prepared by.
 Systematic Observations, Data, Climate Methods and Tools - Availability, Applicability, Accessibility Prepared by Maletjane Motsomi Lesotho Meteorological Services P. O. Box 14515 Tell: (266) 22 327 659
Systematic Observations, Data, Climate Methods and Tools - Availability, Applicability, Accessibility Prepared by Maletjane Motsomi Lesotho Meteorological Services P. O. Box 14515 Tell: (266) 22 327 659
Better Topographic Map Production Using ArcGIS. A Comprehensive Solution for Mapping Organizations
 Better Topographic Map Production Using ArcGIS A Comprehensive Solution for Mapping Organizations The World Is Always Changing As a member of a national mapping organization, you know this is true. You
Better Topographic Map Production Using ArcGIS A Comprehensive Solution for Mapping Organizations The World Is Always Changing As a member of a national mapping organization, you know this is true. You
Bengt Kjellson Chair of the Executive Committee UN-GGIM: Europe. 2 nd Joint UN-GGIM: Europe ESS Meeting 11 th March 2016, Luxembourg
 Bengt Kjellson Chair of the Executive Committee UN-GGIM: Europe 2 nd Joint UN-GGIM: Europe ESS Meeting 11 th March 2016, Luxembourg A global geospatial mandate At its 47th plenary in July 2011, ECOSOC,
Bengt Kjellson Chair of the Executive Committee UN-GGIM: Europe 2 nd Joint UN-GGIM: Europe ESS Meeting 11 th March 2016, Luxembourg A global geospatial mandate At its 47th plenary in July 2011, ECOSOC,
EARLY WARNING IN SOUTHERN AFRICA:
 EARLY WARNING IN SOUTHERN AFRICA: Enhancing the Meteorological Early Warning System Eugene Poolman South African Weather Service OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION Impact of Climate Change Meteorological Early Warning
EARLY WARNING IN SOUTHERN AFRICA: Enhancing the Meteorological Early Warning System Eugene Poolman South African Weather Service OUTLINE OF PRESENTATION Impact of Climate Change Meteorological Early Warning
Integration for Informed Decision Making
 Geospatial and Statistics Policy Intervention: Integration for Informed Decision Making Greg Scott Global Geospatial Information Management United Nations Statistics Division Department of Economic and
Geospatial and Statistics Policy Intervention: Integration for Informed Decision Making Greg Scott Global Geospatial Information Management United Nations Statistics Division Department of Economic and
Cooperation is the key, FIG can facilitate
 Cooperation is the key, FIG can facilitate Mikael Lilje Vice President 2017-2020 Head, Geodetic infrastructure, Swedish mapping, cadastral and land registration authority Presented at the GIS/RS Conference
Cooperation is the key, FIG can facilitate Mikael Lilje Vice President 2017-2020 Head, Geodetic infrastructure, Swedish mapping, cadastral and land registration authority Presented at the GIS/RS Conference
STATUS OF HAZARD MAPS VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENTS AND DIGITAL MAPS
 JapanInternational Cooperation Agency STATUS OF HAZARD MAPS VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENTS AND DIGITAL MAPS ANGUILLA REPORT THE CARIBBEAN DISASTER EMERGENCY RESPONSE AGENCY () Table of Contents Page Preface
JapanInternational Cooperation Agency STATUS OF HAZARD MAPS VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENTS AND DIGITAL MAPS ANGUILLA REPORT THE CARIBBEAN DISASTER EMERGENCY RESPONSE AGENCY () Table of Contents Page Preface
Report of the Regional Committee of UN-GGIM for Asia and the Pacific (UN-GGIM-AP)
 Report of the Regional Committee of UN-GGIM for Asia and the Pacific (UN-GGIM-AP) At the Eighth Session of UN-GGIM UN Headquarters, New York, 1 3 August 2018 About UN-GGIM-AP One of the five regional committees
Report of the Regional Committee of UN-GGIM for Asia and the Pacific (UN-GGIM-AP) At the Eighth Session of UN-GGIM UN Headquarters, New York, 1 3 August 2018 About UN-GGIM-AP One of the five regional committees
2014 Russell County Hazard Mitigation Plan Update STAKEHOLDERS AND TECHNICAL ADVISORS MEETING 2/6/14
 2014 Russell County Hazard Mitigation Plan Update STAKEHOLDERS AND TECHNICAL ADVISORS MEETING 2/6/14 Welcome and Introductions We cannot direct the wind, but we can adjust our sails. 44 CFR 201.6; Local
2014 Russell County Hazard Mitigation Plan Update STAKEHOLDERS AND TECHNICAL ADVISORS MEETING 2/6/14 Welcome and Introductions We cannot direct the wind, but we can adjust our sails. 44 CFR 201.6; Local
Section 2. Indiana Geographic Information Council: Strategic Plan
 Section 2. Indiana Geographic Information Council: Strategic Plan Introduction A geographic information system (GIS) is an automated tool that allows the collection, modification, storage, analysis, and
Section 2. Indiana Geographic Information Council: Strategic Plan Introduction A geographic information system (GIS) is an automated tool that allows the collection, modification, storage, analysis, and
Summary of Global Mapping Forum 2003 in Okinawa and its Outcomes
 Summary of Global Mapping Forum 2003 in Okinawa and its Outcomes 1 Summary of Global Mapping Forum 2003 in Okinawa and its Outcomes Hidetoshi NAKAJIMA Abstract Global Mapping Forum 2003 in Okinawa was
Summary of Global Mapping Forum 2003 in Okinawa and its Outcomes 1 Summary of Global Mapping Forum 2003 in Okinawa and its Outcomes Hidetoshi NAKAJIMA Abstract Global Mapping Forum 2003 in Okinawa was
Pacific Geospatial and Surveying Council (PGSC) Geospatial and GNSS CORS Infrastructure Forum. Kuala Lumpur October
 Pacific Geospatial and Surveying Council (PGSC) Geospatial and GNSS CORS Infrastructure Forum. Kuala Lumpur 16-17 October Beginning and Progress Members PGSC Charter PGSC Strategy 2017-2027 Meetings Geodetic
Pacific Geospatial and Surveying Council (PGSC) Geospatial and GNSS CORS Infrastructure Forum. Kuala Lumpur 16-17 October Beginning and Progress Members PGSC Charter PGSC Strategy 2017-2027 Meetings Geodetic
8th FIG Regional Conference November 2012 Montevideo, Uruguay
 8th FIG Regional Conference 26 29 November 2012 Montevideo, Uruguay Platinum Sponsors: Member Associations; Affiliate Members; Academic Members; Corporate Members & Correspondents 120 Countries 1 FIG Foundation
8th FIG Regional Conference 26 29 November 2012 Montevideo, Uruguay Platinum Sponsors: Member Associations; Affiliate Members; Academic Members; Corporate Members & Correspondents 120 Countries 1 FIG Foundation
Natura 2000 and spatial planning. Executive summary
 Natura 2000 and spatial planning Executive summary DISCLAIMER The information and views set out in this study are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official opinion of the Commission.
Natura 2000 and spatial planning Executive summary DISCLAIMER The information and views set out in this study are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official opinion of the Commission.
INCA CE: Integrating Nowcasting with crisis management and risk prevention in a transnational framework
 INCA CE: Integrating Nowcasting with crisis management and risk prevention in a transnational framework Yong Wang ZAMG, Austria This project is implemented through the CENTRAL EUROPE Programme co-financed
INCA CE: Integrating Nowcasting with crisis management and risk prevention in a transnational framework Yong Wang ZAMG, Austria This project is implemented through the CENTRAL EUROPE Programme co-financed
Geospatial Information for Disaster Risk Management in Asia-Pacific Region
 Geospatial Information for Disaster Risk Management in Asia-Pacific Region Ram S. Tiwaree, Dr.Eng. Space Applications Section Information and Communications Technology and Disaster Risk Reduction Division
Geospatial Information for Disaster Risk Management in Asia-Pacific Region Ram S. Tiwaree, Dr.Eng. Space Applications Section Information and Communications Technology and Disaster Risk Reduction Division
NOAA S2S Planning. Dave DeWitt Fred Toepfer
 NOAA S2S Planning Dave DeWitt Fred Toepfer 1 Agenda 1. Brief synopsis of The Weather Research and Forecasting Act of 2017 2. Report to Congress a. Timeline b. Process c. Document Outline 3. Some Preliminary
NOAA S2S Planning Dave DeWitt Fred Toepfer 1 Agenda 1. Brief synopsis of The Weather Research and Forecasting Act of 2017 2. Report to Congress a. Timeline b. Process c. Document Outline 3. Some Preliminary
Land Use in the context of sustainable, smart and inclusive growth
 Land Use in the context of sustainable, smart and inclusive growth François Salgé Ministry of sustainable development France facilitator EUROGI vice president AFIGéO board member 1 Introduction e-content+
Land Use in the context of sustainable, smart and inclusive growth François Salgé Ministry of sustainable development France facilitator EUROGI vice president AFIGéO board member 1 Introduction e-content+
Regional EGM on Community of Practice of Georeferenced Information System. for Disaster Risk Management (Geo-DRM) April 2014, Bangkok, Thailand
 Regional EGM on Community of Practice of Georeferenced Information System for Disaster Risk Management (Geo-DRM) 23-25 April 2014, Bangkok, Thailand Presented By Mukesh Kumar Keshari Ministry of Home Affairs
Regional EGM on Community of Practice of Georeferenced Information System for Disaster Risk Management (Geo-DRM) 23-25 April 2014, Bangkok, Thailand Presented By Mukesh Kumar Keshari Ministry of Home Affairs
Climate Resilience Decision Making Framework in the Caribbean. A case of Spatial Data Management
 Climate Resilience Decision Making Framework in the Caribbean A case of Spatial Data Management Bishwa Pandey Sr. Data Management Specialist The World Bank Background The mission of The World Bank s Latin
Climate Resilience Decision Making Framework in the Caribbean A case of Spatial Data Management Bishwa Pandey Sr. Data Management Specialist The World Bank Background The mission of The World Bank s Latin
THE ROLE OF SEAMIC IN SUSTAINABLE MINERAL RESOURCES DEVELOPMENT IN AFRICA
 THE ROLE OF SEAMIC IN SUSTAINABLE MINERAL RESOURCES DEVELOPMENT IN AFRICA Ketema Tadesse Director General-SEAMIC Dar es Salaam, Tanzania August 11, 2009 SEAMIC BACKGROUND SEAMIC was established in 1977
THE ROLE OF SEAMIC IN SUSTAINABLE MINERAL RESOURCES DEVELOPMENT IN AFRICA Ketema Tadesse Director General-SEAMIC Dar es Salaam, Tanzania August 11, 2009 SEAMIC BACKGROUND SEAMIC was established in 1977
Implementing the Sustainable Development Goals: The Role of Geospatial Technology and Innovation
 Fifth High Level Forum on UN Global Geospatial Information Management Implementing the Sustainable Development Goals: The Role of Geospatial Technology and Innovation 28-30 November 2017 Sheraton Maria
Fifth High Level Forum on UN Global Geospatial Information Management Implementing the Sustainable Development Goals: The Role of Geospatial Technology and Innovation 28-30 November 2017 Sheraton Maria
UN-GGIM:Africa Caucus Meeting
 UN-GGIM:Africa Caucus Meeting United Nations Economic Commission for Africa UN-GGIM: Africa Andre Nonguierma UN-GGIM.7 New York, 01 August 2017 UN-GGIM:Africa Driving Africa to become more spatially enabled
UN-GGIM:Africa Caucus Meeting United Nations Economic Commission for Africa UN-GGIM: Africa Andre Nonguierma UN-GGIM.7 New York, 01 August 2017 UN-GGIM:Africa Driving Africa to become more spatially enabled
Presentation. Ms. Heidi Schroderus-Fox, Director, UN-OHRLLS
 Please Check Against Delivery United Nations Office of the High Representative for the Least Developed Countries, Landlocked Developing Countries and Small Island Developing States (UN-OHRLLS) Presentation
Please Check Against Delivery United Nations Office of the High Representative for the Least Developed Countries, Landlocked Developing Countries and Small Island Developing States (UN-OHRLLS) Presentation
Statewide Topographic Mapping Program
 Statewide Topographic Mapping Program February 28, 2018 www.dotd.la.gov Outline Purpose of the Statewide Topographic Mapping Program History Breakdown of R.S. 48:36 - Topographic Mapping Statewide Topographic
Statewide Topographic Mapping Program February 28, 2018 www.dotd.la.gov Outline Purpose of the Statewide Topographic Mapping Program History Breakdown of R.S. 48:36 - Topographic Mapping Statewide Topographic
GIS (GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS) AS A FACILITATION TOOL FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN AFRICA
 GIS (GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS) AS A FACILITATION TOOL FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN AFRICA a presentation by Elizabeth Hicken GDEST Conference on Geospatial Sciences for Sustainable Development
GIS (GEOGRAPHICAL INFORMATION SYSTEMS) AS A FACILITATION TOOL FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT IN AFRICA a presentation by Elizabeth Hicken GDEST Conference on Geospatial Sciences for Sustainable Development
TOWARDS CLIMATE-RESILIENT COASTAL MANAGEMENT: OPPORTUNITIES FOR IMPROVED ICZM IN BELIZE
 TOWARDS CLIMATE-RESILIENT COASTAL MANAGEMENT: OPPORTUNITIES FOR IMPROVED ICZM IN BELIZE CHANTALLE SAMUELS Coastal Zone Management Authority and Institute The Caribbean Community Climate Change Centre VULNERABILITY
TOWARDS CLIMATE-RESILIENT COASTAL MANAGEMENT: OPPORTUNITIES FOR IMPROVED ICZM IN BELIZE CHANTALLE SAMUELS Coastal Zone Management Authority and Institute The Caribbean Community Climate Change Centre VULNERABILITY
Country Report Nepal Geospatial Data Sharing Initiatives of Survey Department Supporting Disaster Management
 Third JPTM Step 2 for Sentinel Asia 6-8 July, 2010 Manila, The Philippines Country Report Nepal Geospatial Data Sharing Initiatives of Survey Department Supporting Disaster Management Durgendra M Kayastha
Third JPTM Step 2 for Sentinel Asia 6-8 July, 2010 Manila, The Philippines Country Report Nepal Geospatial Data Sharing Initiatives of Survey Department Supporting Disaster Management Durgendra M Kayastha
The future of SDIs. Ian Masser
 The future of SDIs Ian Masser Presentation Considers two questions relating to the future development of SDIs throughout the world Where have we got to now? Where should we go from here? Identifies four
The future of SDIs Ian Masser Presentation Considers two questions relating to the future development of SDIs throughout the world Where have we got to now? Where should we go from here? Identifies four
Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/67/440/Add.2)]
![Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/67/440/Add.2)] Resolution adopted by the General Assembly. [on the report of the Second Committee (A/67/440/Add.2)]](/thumbs/94/121301610.jpg) United Nations General Assembly Distr.: General 3 April 2013 Sixty-seventh session Agenda item 23 (b) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [on the report of the Second Committee (A/67/440/Add.2)]
United Nations General Assembly Distr.: General 3 April 2013 Sixty-seventh session Agenda item 23 (b) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly [on the report of the Second Committee (A/67/440/Add.2)]
The Third UN-GGIM-AP Plenary Meeting. Use of Geospatial Information in Disaster and Coordination among NDMA and Relevant Organizations/Stakeholders
 The Third UN-GGIM-AP Plenary Meeting Use of Geospatial Information in Disaster and Coordination among NDMA and Relevant Organizations/Stakeholders Bali Indonesia 10 November 2014 Bernardus Wisnu Widjaja
The Third UN-GGIM-AP Plenary Meeting Use of Geospatial Information in Disaster and Coordination among NDMA and Relevant Organizations/Stakeholders Bali Indonesia 10 November 2014 Bernardus Wisnu Widjaja
International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics. Resolutions
 International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics Resolutions ADOPTED BY THE COUNCIL AT THE XXVI GENERAL ASSEMBLY PRAGUE, CZECH REPUBLIC (22 JUNE 2 JULY 2015) 0 Page Resolution 1: Role of Ocean in Climate
International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics Resolutions ADOPTED BY THE COUNCIL AT THE XXVI GENERAL ASSEMBLY PRAGUE, CZECH REPUBLIC (22 JUNE 2 JULY 2015) 0 Page Resolution 1: Role of Ocean in Climate
Brazil Paper for the. Second Preparatory Meeting of the Proposed United Nations Committee of Experts on Global Geographic Information Management
 Brazil Paper for the Second Preparatory Meeting of the Proposed United Nations Committee of Experts on Global Geographic Information Management on Data Integration Introduction The quick development of
Brazil Paper for the Second Preparatory Meeting of the Proposed United Nations Committee of Experts on Global Geographic Information Management on Data Integration Introduction The quick development of
THE IMPACT OF EL NIÑO AND LA NIÑA ON SOUTHEAST ASIA
 THE IMPACT OF EL NIÑO AND LA NIÑA ON SOUTHEAST ASIA 21st-23rd February 2000 WORKSHOP SUMMARY Organized by the Indochina Global Change Network Funded by the Asia-Pacific Network for Global Change Research
THE IMPACT OF EL NIÑO AND LA NIÑA ON SOUTHEAST ASIA 21st-23rd February 2000 WORKSHOP SUMMARY Organized by the Indochina Global Change Network Funded by the Asia-Pacific Network for Global Change Research
Early Warning > Early Action: The Next Frontier. Dr. Arame Tall Climate Services- Global Coordinator, Champion
 Early Warning > Early Action: The Next Frontier Dr. Arame Tall Climate Services- Global Coordinator, Champion a.tall@cgiar.org 2 3/21/11 The Challenge: Bridging The Gap Seasonal Precipitation Forecast
Early Warning > Early Action: The Next Frontier Dr. Arame Tall Climate Services- Global Coordinator, Champion a.tall@cgiar.org 2 3/21/11 The Challenge: Bridging The Gap Seasonal Precipitation Forecast
Spatially Enabled Society
 International Seminar on Land Administration Trends and Issues in Asia and the Pacific Region Spatially Enabled Society Abbas Rajabifard Vice Chair PCGIAP-WG3 Vice-President (President Elect), GSDI Association
International Seminar on Land Administration Trends and Issues in Asia and the Pacific Region Spatially Enabled Society Abbas Rajabifard Vice Chair PCGIAP-WG3 Vice-President (President Elect), GSDI Association
Geographic Information Infrastructure and Policy Framework for Sustainable Mountain Development in the Hindu Kush-Himalayas
 Geo SMART ASIA 2017 22-24 August, Kualalampur Geographic Information Infrastructure and Policy Framework for Sustainable Mountain Development in the Hindu Kush-Himalayas Basanta Shrestha, Director Strategic
Geo SMART ASIA 2017 22-24 August, Kualalampur Geographic Information Infrastructure and Policy Framework for Sustainable Mountain Development in the Hindu Kush-Himalayas Basanta Shrestha, Director Strategic
REPORT ON ACTIVITIES UNDERTAKEN SINCE THE 25TH SESSION OF THE INTERNATIONAL COORDINATING COUNCIL OF THE MAN & THE BIOSPHERE PROGRAMME
 AFRICAN NETWORK OF BIOSPHERE RESERVES (AFRIMAB) REPORT ON ACTIVITIES UNDERTAKEN SINCE THE 25TH SESSION OF THE INTERNATIONAL COORDINATING COUNCIL OF THE MAN & THE BIOSPHERE PROGRAMME 26 TH MAB ICC SESSION
AFRICAN NETWORK OF BIOSPHERE RESERVES (AFRIMAB) REPORT ON ACTIVITIES UNDERTAKEN SINCE THE 25TH SESSION OF THE INTERNATIONAL COORDINATING COUNCIL OF THE MAN & THE BIOSPHERE PROGRAMME 26 TH MAB ICC SESSION
Concept note. High-Level Seminar: Accelerating Sustainable Energy for All in Landlocked Developing Countries through Innovative Partnerships
 Concept note High-Level Seminar: Accelerating Sustainable Energy for All in Landlocked Developing Countries through Innovative Partnerships Date: 24 and 25 October 2016 Venue: Conference Room C3, Vienna
Concept note High-Level Seminar: Accelerating Sustainable Energy for All in Landlocked Developing Countries through Innovative Partnerships Date: 24 and 25 October 2016 Venue: Conference Room C3, Vienna
Providers of Weather, Climate and Water Information
 Providers of Weather, Climate and Water Information Mnikeli Ndabambi World Meteorological Organization Task Force on Social and Economic Applications of Public Weather Services Geneva, 15-18 May 2006 Introductory
Providers of Weather, Climate and Water Information Mnikeli Ndabambi World Meteorological Organization Task Force on Social and Economic Applications of Public Weather Services Geneva, 15-18 May 2006 Introductory
UNITED NATIONS GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION WORKING GROUP
 UNGIWG UNITED NATIONS GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION WORKING GROUP New York, May 2014 UNSPACE & UNGIWG 14 INTRO. The United Nations Geographic Information Working Group (UNGIWG) is a voluntary network of UN professionals
UNGIWG UNITED NATIONS GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION WORKING GROUP New York, May 2014 UNSPACE & UNGIWG 14 INTRO. The United Nations Geographic Information Working Group (UNGIWG) is a voluntary network of UN professionals
