It s really this simple.
|
|
|
- Gregory Stanley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Background Light harvesting complexes exist to facilitate and maximize the absorption capacity of the reaction centers (RC) as well as PSI and PSII Purple bacteria utilize these functions by having an LH1 complex serving as a primary complex and a peripheral LH2 and LH3 complex As such, LH1 and RC are in stoichiometric equivalence and LH2 and LH3 are expressed as needed for the circumstances LH1, LH2 and LH3 absorb photons shuttle excitons to the RC
2 It s really this simple.
3 Apoprotein Structure in the LH2 Complex from Rhodopseudomonas acidophila Strain 10050: Modular Assembly and Protein Pigment Interactions S.M. Prince, M.Z. Papiz, A.A. Freer, G. Mcdermott, A.M. Hawthorethwaite-Lawless, R.J. Cogdell and N.W. Isaacs
4 Apoprotein Structure LH2 is a nonomeric symmetrical assembly of alpha-beta apoproteins, with alpha helical secondary structure, noncovalently binding prosthetic groups Oligomerize into concentric circles: alpha on the inside, perpendicular to the membrane normal, and beta on the outside, tilted roughly 15 degrees to the alpha plane Alpha a-helices here inside Beta a-helices outside (~15 degree tilt) Alpha Helices here, perpendicular to Membrane plane
5 LH2 Molecule A-A-K-K- Alpha-C Beta-C The alpha-beta subunits of LH2 is composed of two TM alpha helices, noncovalently bound, each with unique characteristics Beta apoprotein has 41 residues, all shown, while apha has 53 residues, 49 of which are shown Remaining alpha residues shown are on C-terminus and are K-K-A-A TM Hydrophobic alpha residues From AA N terminus TM Hydrophobic beta residues from AA Cytoplasm N-Terminal Met of alpha Is coordinating bacterial Prosthetic group Bchl a, fifth position
6 LH2 s 2 structure reflected in amino acids One can look at the amino acid sequnces to deduce at least some level of structural detail What amino acids would you expect in the kinks of the beta helix? What kinds of amino acids should coordinate pigments? This is roughly where alpha-12 Starts. Note the proline, is this an essential residue?
7 Tertiary structure Interestingly, the N and C termini of the helices are exposed to the aqueous environment and must H- bond the hydrophilic side residues of the interior With regards to the alpha helix, it s turns coordinate oligomerization and pigment binding H-bonding interactions between hydrophilic side chains Bchl a Alpha N-formyl Met
8 Membrane Interaction The LH2 complex forms a ring, and as such gives way to a 12 A cylindrical enclosure Lipids are inside, but a single alpha helix could have fit Why not? Hydrophobic interactions between alpha helices and core The outside is made of largely hydrophobic beta apoproteins, which lack protruding side chain anchors Lots of cofactors are present, which dominate over lipid-protein interaction LH2 s Hole 12 Angstrom s
9 Protein-Protein Interactions Pigment distribution important for protein-protein as well as protein-pigments interactions H-bonding interactions observed at cytosolic and periplasmic faces between proteins and pigments Alpha-Y-Bchl a does double duty with oligomer contact and Bchl a coordination Beta transmembrane helices don t touch: pigments form lining bewteen them Alpha helices do form contacts of hydrophobic nature Here, interactions between two alpha chains may be discerned. They are mostly hydrophobic Spheres indicate Van der Waals Interactions while yellow and Green spheres are pigments
10 Pigment Coordination Bchl a molecules posses two main interactions with protein Coordination of Mg++ ion, and an H-bond to C-3 acytl group on ring a Protein donor residue for Mg++: B850 is His residue and for B800 is alpha Met-1 For C-3 acetyl: B850 is alpha- W45/Y44 and B800 is beta- R20 B850:Alpha-W45/Y44 B800: Beta-R20 B850: His B800: alpha-met-1
11 Pigment Contacts cntd.
12 Coordination Effects Because Bchl a has two transition dipoles, Qx and Qy, two absorption spectra result The conjugated pie system is susceptible to distortion, and ultimately changes in wavelength absorption which accompany this Thus, the local protein environment determines the absorptive properties of the pigments Generally arise from axial ligand and peripheral contact coordination Mg++ is penta-coordinated. Which side this coordination Is on depends on the protein environment. If on one side of the plane, then the B800 species results. The other side produces B850
13 Coordination The alpha-b800 species is slightly domed while the alpha-b850 species is roughly C-3 acetyl planar
14
15 The Crystallographic Structure of the B LH3 Light- Harvesting Complex from the Purple Bacteria Rhodopseudomonas Acidophila K. McLuskey, S.M. Prince, R.J. Cogdell, and N.W. Isaacs
16 Background LH3 is a lot like LH2 in structure, with a few minor differences (a few AA s) It is from a different gene than LH2 Why? It seems alternative splicing could do this job quite well, as well as other post transcriptional modifications It s expressed in stressful conditions (low illumination/temperature) when different wavelength light needs to be absorbed and maximized It follows these different wavelengths of light can be attributed to different structures. Thus, the crystal structure can help explain functional differences The differences arise in primary structure, while secondary structure is more or less the same Thought to be differences in H-bonding patterns on C-3 acetyl position of Bchl a
17 Physics To change the wavelength of light absorbed, the quanta of the atom(s), or electronic structure, must change in energy What is being changed in the structure ultimately results from intermolecular bonding, as pigment-protein interactions are noncovalent It follows that these differing noncovalent interactions result in the change of the atomic quanta, allowing different wavelength light to be absorbed Emmision Spectra
18 Absorptive properties Bchl a is asymmetric and has two transition dipoles on a pie conjugated plane Qy is lower energy (higher wavelength) and is influenced by the local environment Because Bchl a is used in multiple harvesting complexes, and in each one has a range of spectra, It follows that it s coordination determines its absorptive properties LH3 absorbs at 800 and 820 nm
19 Structural Differences in LH3 As mentioned, the differences in LH3 ( when compared to LH2) arise in primary structural differences The most notable differences are in Bchl a C-3 acetyl group binding proteins on alpha-w44/y45, which have been changed to F and L respectively Mutagenesis confirmed this, as an 850->820 shift was seen after F/L replacement LH2 Alpha W45/Y44 changed to Non-H-bonding F44/L45 in LH3
20 Structure determination of LH3 During crystallization, hard to separate LH2 and LH3 Beta-Glu-7 and Beta-K-7 are involved in crystal contacts and lack NCS contraint. This results in abnormally high B-factor Overall B factor less than we would prefer
21
22 Results: comparison of LH2 and LH3 LH3 also nonameric, but differs in pigment coordination LH2 and LH3 nearly identical at secondary structural level Pigments also close but deviate in phytyl chain Superimposition of LH2 and LH3 Changes in H-bonding patterns can be seen here With respect to C-3 acetyl group, among others
23 Pigment Comparison 2.46 for LH2 B800
24 Other Differences LH3 contains rhodopinal glucoside, a modified form of rhodopin glucoside which is present in LH2 The difference in both is the 3 rd of 4 th methyl group (chemically equivalent) on rhodopin which is replaced by a keto group in rhodopinal Rhodopin
25
the primary donor in the RC. Here, charge separation is promoted across the photosynthetic membrane.
 Research Article 449 Pigment pigment interactions and energy transfer in the antenna complex of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas acidophila Andy Freer 1 *, Steve Prince 1, Ken Sauer 2, Miroslav
Research Article 449 Pigment pigment interactions and energy transfer in the antenna complex of the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas acidophila Andy Freer 1 *, Steve Prince 1, Ken Sauer 2, Miroslav
The original publication is available at DOI: /S (97)
 The original publication is available at www.sciencedirect.com DOI:10.1016/S0079-6107(97)00010-2 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE LH2 (B800-850) COMPLEX FROM THE PURPLE PHOTOSYNTHETIC BACTERIUM RHODOPSEUDOMONAS
The original publication is available at www.sciencedirect.com DOI:10.1016/S0079-6107(97)00010-2 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE LH2 (B800-850) COMPLEX FROM THE PURPLE PHOTOSYNTHETIC BACTERIUM RHODOPSEUDOMONAS
Structures of photosynthetic pigment-protein
 Structures of photosynthetic pigment-protein protein complexes and probing electrostatic field inside them by Stark spectroscopy Hideki Hashimoto, 1 Ritsuko Fujii, 1 Satoru Suzuki, 1 Katsunori Nakagawa,
Structures of photosynthetic pigment-protein protein complexes and probing electrostatic field inside them by Stark spectroscopy Hideki Hashimoto, 1 Ritsuko Fujii, 1 Satoru Suzuki, 1 Katsunori Nakagawa,
Potassium channel gating and structure!
 Reading: Potassium channel gating and structure Hille (3rd ed.) chapts 10, 13, 17 Doyle et al. The Structure of the Potassium Channel: Molecular Basis of K1 Conduction and Selectivity. Science 280:70-77
Reading: Potassium channel gating and structure Hille (3rd ed.) chapts 10, 13, 17 Doyle et al. The Structure of the Potassium Channel: Molecular Basis of K1 Conduction and Selectivity. Science 280:70-77
The Crystallographic Structure of the B LH3 Light-Harvesting Complex from the Purple Bacteria Rhodopseudomonas Acidophila Strain 7050
 Biochemistry 2001, 40, 8783-8789 8783 The Crystallographic Structure of the B800-820 LH3 Light-Harvesting Complex from the Purple Bacteria Rhodopseudomonas Acidophila Strain 7050 K. McLuskey, S. M. Prince,
Biochemistry 2001, 40, 8783-8789 8783 The Crystallographic Structure of the B800-820 LH3 Light-Harvesting Complex from the Purple Bacteria Rhodopseudomonas Acidophila Strain 7050 K. McLuskey, S. M. Prince,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING Volume 11, 2017
 B850 Ring from Light Harvesting Complex LH2 - Fluctuations in Dipole Moment Orientations of Bacteriochlorophyll Molecules Pavel Heřman, David Zapletal Abstract Interactions with fluctuated environment
B850 Ring from Light Harvesting Complex LH2 - Fluctuations in Dipole Moment Orientations of Bacteriochlorophyll Molecules Pavel Heřman, David Zapletal Abstract Interactions with fluctuated environment
From Amino Acids to Proteins - in 4 Easy Steps
 From Amino Acids to Proteins - in 4 Easy Steps Although protein structure appears to be overwhelmingly complex, you can provide your students with a basic understanding of how proteins fold by focusing
From Amino Acids to Proteins - in 4 Easy Steps Although protein structure appears to be overwhelmingly complex, you can provide your students with a basic understanding of how proteins fold by focusing
Fluctuations of Pigment s Dipole Moment Orientations in B850 Ring from Photosynthetic Complex LH2
 Fluctuations of Pigment s Dipole Moment Orientations in B850 Ring from Photosynthetic Complex LH2 PAVEL HEŘMAN Univ. of Hradec Králové Faculty of Science Department of Physics Rokitanského 62 Hradec Králové
Fluctuations of Pigment s Dipole Moment Orientations in B850 Ring from Photosynthetic Complex LH2 PAVEL HEŘMAN Univ. of Hradec Králové Faculty of Science Department of Physics Rokitanského 62 Hradec Králové
Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters
 Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters Most ABC transporters contain heterodimeric TMDs (e.g. HisMQ, MalFG) TMDs show only limited sequence homology (high diversity) High degree of conservation
Transmembrane Domains (TMDs) of ABC transporters Most ABC transporters contain heterodimeric TMDs (e.g. HisMQ, MalFG) TMDs show only limited sequence homology (high diversity) High degree of conservation
Bi 8 Midterm Review. TAs: Sarah Cohen, Doo Young Lee, Erin Isaza, and Courtney Chen
 Bi 8 Midterm Review TAs: Sarah Cohen, Doo Young Lee, Erin Isaza, and Courtney Chen The Central Dogma Biology Fundamental! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Nucleic Acid Components Nucleic Acid Structure DNA Base
Bi 8 Midterm Review TAs: Sarah Cohen, Doo Young Lee, Erin Isaza, and Courtney Chen The Central Dogma Biology Fundamental! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Nucleic Acid Components Nucleic Acid Structure DNA Base
The Structure and Functions of Proteins
 Wright State University CORE Scholar Computer Science and Engineering Faculty Publications Computer Science and Engineering 2003 The Structure and Functions of Proteins Dan E. Krane Wright State University
Wright State University CORE Scholar Computer Science and Engineering Faculty Publications Computer Science and Engineering 2003 The Structure and Functions of Proteins Dan E. Krane Wright State University
Review. Membrane proteins. Membrane transport
 Quiz 1 For problem set 11 Q1, you need the equation for the average lateral distance transversed (s) of a molecule in the membrane with respect to the diffusion constant (D) and time (t). s = (4 D t) 1/2
Quiz 1 For problem set 11 Q1, you need the equation for the average lateral distance transversed (s) of a molecule in the membrane with respect to the diffusion constant (D) and time (t). s = (4 D t) 1/2
Protein Structure. Hierarchy of Protein Structure. Tertiary structure. independently stable structural unit. includes disulfide bonds
 Protein Structure Hierarchy of Protein Structure 2 3 Structural element Primary structure Secondary structure Super-secondary structure Domain Tertiary structure Quaternary structure Description amino
Protein Structure Hierarchy of Protein Structure 2 3 Structural element Primary structure Secondary structure Super-secondary structure Domain Tertiary structure Quaternary structure Description amino
1.9 Practice Problems
 1.9 Practice Problems 1. Solution: B It s not only chlorophyll a but a combination of pigments. 2. Solution: D See at what wavelength rate of photosynthesis is the highest. 3. Solution: D It s a fact.
1.9 Practice Problems 1. Solution: B It s not only chlorophyll a but a combination of pigments. 2. Solution: D See at what wavelength rate of photosynthesis is the highest. 3. Solution: D It s a fact.
Lecture 26: Polymers: DNA Packing and Protein folding 26.1 Problem Set 4 due today. Reading for Lectures 22 24: PKT Chapter 8 [ ].
![Lecture 26: Polymers: DNA Packing and Protein folding 26.1 Problem Set 4 due today. Reading for Lectures 22 24: PKT Chapter 8 [ ]. Lecture 26: Polymers: DNA Packing and Protein folding 26.1 Problem Set 4 due today. Reading for Lectures 22 24: PKT Chapter 8 [ ].](/thumbs/84/90810734.jpg) Lecture 26: Polymers: DA Packing and Protein folding 26.1 Problem Set 4 due today. eading for Lectures 22 24: PKT hapter 8 DA Packing for Eukaryotes: The packing problem for the larger eukaryotic genomes
Lecture 26: Polymers: DA Packing and Protein folding 26.1 Problem Set 4 due today. eading for Lectures 22 24: PKT hapter 8 DA Packing for Eukaryotes: The packing problem for the larger eukaryotic genomes
Protein Structure Basics
 Protein Structure Basics Presented by Alison Fraser, Christine Lee, Pradhuman Jhala, Corban Rivera Importance of Proteins Muscle structure depends on protein-protein interactions Transport across membranes
Protein Structure Basics Presented by Alison Fraser, Christine Lee, Pradhuman Jhala, Corban Rivera Importance of Proteins Muscle structure depends on protein-protein interactions Transport across membranes
Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure. You will be given a start time with your exam instructions
 BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology Date: Thursday, 1st September 2011 Time: 3 hours You will be given a start
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) Advanced Certificate in Principles in Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology Date: Thursday, 1st September 2011 Time: 3 hours You will be given a start
Biomolecules: lecture 9
 Biomolecules: lecture 9 - understanding further why amino acids are the building block for proteins - understanding the chemical properties amino acids bring to proteins - realizing that many proteins
Biomolecules: lecture 9 - understanding further why amino acids are the building block for proteins - understanding the chemical properties amino acids bring to proteins - realizing that many proteins
Patrick: An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e Chapter 04
 01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
01) Which of the following statements is not true about receptors? a. Most receptors are proteins situated inside the cell. b. Receptors contain a hollow or cleft on their surface which is known as a binding
Protein Structure. W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES
 Protein Structure W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the structure and characteristic properties of typical proteins. 2. List and describe the four levels of structure found in proteins. 3. Relate
Protein Structure W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the structure and characteristic properties of typical proteins. 2. List and describe the four levels of structure found in proteins. 3. Relate
Outline. Levels of Protein Structure. Primary (1 ) Structure. Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins
 Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2004 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2004 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Biophysics 490M Project
 Biophysics 490M Project Dan Han Department of Biochemistry Structure Exploration of aa 3 -type Cytochrome c Oxidase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides I. Introduction: All organisms need energy to live. They
Biophysics 490M Project Dan Han Department of Biochemistry Structure Exploration of aa 3 -type Cytochrome c Oxidase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides I. Introduction: All organisms need energy to live. They
Chem 204. Mid-Term Exam I. July 21, There are 3 sections to this exam: Answer ALL questions
 Chem 204 Mid-Term Exam I July 21, 2009 Name: Answer Key Student ID: There are 3 sections to this exam: Answer ALL questions Section I: Multiple-Choice 20 questions, 2 pts each Section II: Fill-in-the-Blank
Chem 204 Mid-Term Exam I July 21, 2009 Name: Answer Key Student ID: There are 3 sections to this exam: Answer ALL questions Section I: Multiple-Choice 20 questions, 2 pts each Section II: Fill-in-the-Blank
Biomolecules: lecture 10
 Biomolecules: lecture 10 - understanding in detail how protein 3D structures form - realize that protein molecules are not static wire models but instead dynamic, where in principle every atom moves (yet
Biomolecules: lecture 10 - understanding in detail how protein 3D structures form - realize that protein molecules are not static wire models but instead dynamic, where in principle every atom moves (yet
Denaturation and renaturation of proteins
 Denaturation and renaturation of proteins Higher levels of protein structure are formed without covalent bonds. Therefore, they are not as stable as peptide covalent bonds which make protein primary structure
Denaturation and renaturation of proteins Higher levels of protein structure are formed without covalent bonds. Therefore, they are not as stable as peptide covalent bonds which make protein primary structure
Outline. Levels of Protein Structure. Primary (1 ) Structure. Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins
 Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2003 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Lecture 6:Protein Architecture II: Secondary Structure or From peptides to proteins Margaret Daugherty Fall 2003 Outline Four levels of structure are used to describe proteins; Alpha helices and beta sheets
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information The structural basis of modularity in ECF-type ABC transporters Guus B. Erkens 1,2, Ronnie P-A. Berntsson 1,2, Faizah Fulyani 1,2, Maria Majsnerowska 1,2, Andreja Vujičić-Žagar
Supplementary information The structural basis of modularity in ECF-type ABC transporters Guus B. Erkens 1,2, Ronnie P-A. Berntsson 1,2, Faizah Fulyani 1,2, Maria Majsnerowska 1,2, Andreja Vujičić-Žagar
1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures?
 1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures? The ångstrom unit is a unit of distance suitable for measuring atomic scale objects. 1 ångstrom (Å) = 1 10-10 m. The diameter
1. What is an ångstrom unit, and why is it used to describe molecular structures? The ångstrom unit is a unit of distance suitable for measuring atomic scale objects. 1 ångstrom (Å) = 1 10-10 m. The diameter
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015,
 Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
From gene to protein. Premedical biology
 From gene to protein Premedical biology Central dogma of Biology, Molecular Biology, Genetics transcription replication reverse transcription translation DNA RNA Protein RNA chemically similar to DNA,
From gene to protein Premedical biology Central dogma of Biology, Molecular Biology, Genetics transcription replication reverse transcription translation DNA RNA Protein RNA chemically similar to DNA,
Key Terms (1 point each). Fill in the blank with the proper term. Each term may be used only once.
 CHM60 Takehome Test 3 Form Student Page 1 of 6 Key Terms (1 point each). Fill in the blank with the proper term. Each term may be used only once. Acid Active transport Alpha helix Beta pleated sheet Buffer
CHM60 Takehome Test 3 Form Student Page 1 of 6 Key Terms (1 point each). Fill in the blank with the proper term. Each term may be used only once. Acid Active transport Alpha helix Beta pleated sheet Buffer
Biophysics Lectures Three and Four
 Biophysics Lectures Three and Four Kevin Cahill cahill@unm.edu http://dna.phys.unm.edu/ 1 The Atoms and Molecules of Life Cells are mostly made from the most abundant chemical elements, H, C, O, N, Ca,
Biophysics Lectures Three and Four Kevin Cahill cahill@unm.edu http://dna.phys.unm.edu/ 1 The Atoms and Molecules of Life Cells are mostly made from the most abundant chemical elements, H, C, O, N, Ca,
Membrane Proteins: 1. Integral proteins: 2. Peripheral proteins: 3. Amphitropic proteins:
 Membrane Proteins: 1. Integral proteins: proteins that insert into/span the membrane bilayer; or covalently linked to membrane lipids. (Interact with the hydrophobic part of the membrane) 2. Peripheral
Membrane Proteins: 1. Integral proteins: proteins that insert into/span the membrane bilayer; or covalently linked to membrane lipids. (Interact with the hydrophobic part of the membrane) 2. Peripheral
 There are two types of polysaccharides in cell: glycogen and starch Starch and glycogen are polysaccharides that function to store energy Glycogen Glucose obtained from primary sources either remains soluble
There are two types of polysaccharides in cell: glycogen and starch Starch and glycogen are polysaccharides that function to store energy Glycogen Glucose obtained from primary sources either remains soluble
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London)
 BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes. From Alberts et al
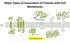 Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes From Alberts et al Proteins Are Polymers of Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Amino Acid central carbon atom to which are attached amino group
Major Types of Association of Proteins with Cell Membranes From Alberts et al Proteins Are Polymers of Amino Acids Peptide Bond Formation Amino Acid central carbon atom to which are attached amino group
Basics of protein structure
 Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
Today: 1. Projects a. Requirements: i. Critical review of one paper ii. At least one computational result b. Noon, Dec. 3 rd written report and oral presentation are due; submit via email to bphys101@fas.harvard.edu
Exam I Answer Key: Summer 2006, Semester C
 1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
1. Which of the following tripeptides would migrate most rapidly towards the negative electrode if electrophoresis is carried out at ph 3.0? a. gly-gly-gly b. glu-glu-asp c. lys-glu-lys d. val-asn-lys
Secondary Structure. Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2. Structure and Function of Proteins. Further Reading. Φ, Ψ angles alone determine protein structure
 Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Bioch/BIMS 503 Lecture 2 Structure and Function of Proteins August 28, 2008 Robert Nakamoto rkn3c@virginia.edu 2-0279 Secondary Structure Φ Ψ angles determine protein structure Φ Ψ angles are restricted
Conformational Geometry of Peptides and Proteins:
 Conformational Geometry of Peptides and Proteins: Before discussing secondary structure, it is important to appreciate the conformational plasticity of proteins. Each residue in a polypeptide has three
Conformational Geometry of Peptides and Proteins: Before discussing secondary structure, it is important to appreciate the conformational plasticity of proteins. Each residue in a polypeptide has three
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
Lucas M. P. Beekman, Martin Steffen, Ivo H. M. van Stokkum, John D. Olsen, C. Neil Hunter, Steven G. Boxer, and Rienk van Grondelle*,
 7284 J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 7284-7292 Characterization of the Light-Harvesting Antennas of Photosynthetic Purple Bacteria by Stark Spectroscopy. 1. LH1 Antenna Complex and the B820 Subunit from Rhodospirillum
7284 J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 7284-7292 Characterization of the Light-Harvesting Antennas of Photosynthetic Purple Bacteria by Stark Spectroscopy. 1. LH1 Antenna Complex and the B820 Subunit from Rhodospirillum
Examples of Protein Modeling. Protein Modeling. Primary Structure. Protein Structure Description. Protein Sequence Sources. Importing Sequences to MOE
 Examples of Protein Modeling Protein Modeling Visualization Examination of an experimental structure to gain insight about a research question Dynamics To examine the dynamics of protein structures To
Examples of Protein Modeling Protein Modeling Visualization Examination of an experimental structure to gain insight about a research question Dynamics To examine the dynamics of protein structures To
What is the central dogma of biology?
 Bellringer What is the central dogma of biology? A. RNA DNA Protein B. DNA Protein Gene C. DNA Gene RNA D. DNA RNA Protein Review of DNA processes Replication (7.1) Transcription(7.2) Translation(7.3)
Bellringer What is the central dogma of biology? A. RNA DNA Protein B. DNA Protein Gene C. DNA Gene RNA D. DNA RNA Protein Review of DNA processes Replication (7.1) Transcription(7.2) Translation(7.3)
Model Mélange. Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins
 Model Mélange Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins In the Model Mélange activity, you will visit four different stations each featuring a variety of different physical models of peptides or proteins.
Model Mélange Physical Models of Peptides and Proteins In the Model Mélange activity, you will visit four different stations each featuring a variety of different physical models of peptides or proteins.
Objective: Students will be able identify peptide bonds in proteins and describe the overall reaction between amino acids that create peptide bonds.
 Scott Seiple AP Biology Lesson Plan Lesson: Primary and Secondary Structure of Proteins Purpose:. To understand how amino acids can react to form peptides through peptide bonds.. Students will be able
Scott Seiple AP Biology Lesson Plan Lesson: Primary and Secondary Structure of Proteins Purpose:. To understand how amino acids can react to form peptides through peptide bonds.. Students will be able
Introduction to Protein Folding
 Introduction to Protein Folding Chapter 4 Proteins: Three Dimensional Structure and Function Conformation - three dimensional shape Native conformation - each protein folds into a single stable shape (physiological
Introduction to Protein Folding Chapter 4 Proteins: Three Dimensional Structure and Function Conformation - three dimensional shape Native conformation - each protein folds into a single stable shape (physiological
Photosynthesis provides the energy source for essentially all lifes on Earth. The molecular details of photosynthesis are not yet fully elucidated
 Photosynthesis provides the energy source for essentially all lifes on Earth The molecular details of photosynthesis are not yet fully elucidated Remarkable efficiency of photosynthesis processes is not
Photosynthesis provides the energy source for essentially all lifes on Earth The molecular details of photosynthesis are not yet fully elucidated Remarkable efficiency of photosynthesis processes is not
BCH 4053 Spring 2003 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes
 BCH 4053 Spring 2003 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes 1 CHAPTER 6 Proteins: Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary Structure 2 Levels of Protein Structure Primary (sequence) Secondary (ordered structure along peptide
BCH 4053 Spring 2003 Chapter 6 Lecture Notes 1 CHAPTER 6 Proteins: Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary Structure 2 Levels of Protein Structure Primary (sequence) Secondary (ordered structure along peptide
Dana Alsulaibi. Jaleel G.Sweis. Mamoon Ahram
 15 Dana Alsulaibi Jaleel G.Sweis Mamoon Ahram Revision of last lectures: Proteins have four levels of structures. Primary,secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Primary structure is the order of amino acids
15 Dana Alsulaibi Jaleel G.Sweis Mamoon Ahram Revision of last lectures: Proteins have four levels of structures. Primary,secondary, tertiary and quaternary. Primary structure is the order of amino acids
BME Engineering Molecular Cell Biology. Structure and Dynamics of Cellular Molecules. Basics of Cell Biology Literature Reading
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 05: Structure and Dynamics of Cellular Molecules Basics of Cell Biology Literature Reading BME42-620 Lecture 05, September 13, 2011 1 Outline Review:
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 05: Structure and Dynamics of Cellular Molecules Basics of Cell Biology Literature Reading BME42-620 Lecture 05, September 13, 2011 1 Outline Review:
1. (5) Draw a diagram of an isomeric molecule to demonstrate a structural, geometric, and an enantiomer organization.
 Organic Chemistry Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date. Working by yourself or in a group, answer the following questions about the Organic Chemistry material. This assignment is worth 35 points with the
Organic Chemistry Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date. Working by yourself or in a group, answer the following questions about the Organic Chemistry material. This assignment is worth 35 points with the
Lecture 2-3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability
 Lecture 2-3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions Van der Waals Interactions
Lecture 2-3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions Van der Waals Interactions
Gene Control Mechanisms at Transcription and Translation Levels
 Gene Control Mechanisms at Transcription and Translation Levels Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi School of Chemical and Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 9
Gene Control Mechanisms at Transcription and Translation Levels Dr. M. Vijayalakshmi School of Chemical and Biotechnology SASTRA University Joint Initiative of IITs and IISc Funded by MHRD Page 1 of 9
Patrick: An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e Chapter 01
 Questions Patrick: An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e 01) Which of the following molecules is a phospholipid? a. i b. ii c. iii d. iv 02) Which of the following statements is false regarding the
Questions Patrick: An Introduction to Medicinal Chemistry 5e 01) Which of the following molecules is a phospholipid? a. i b. ii c. iii d. iv 02) Which of the following statements is false regarding the
Membrane proteins Porins: FadL. Oriol Solà, Dimitri Ivancic, Daniel Folch, Marc Olivella
 Membrane proteins Porins: FadL Oriol Solà, Dimitri Ivancic, Daniel Folch, Marc Olivella INDEX 1. INTRODUCTION TO MEMBRANE PROTEINS 2. FADL: OUTER MEMBRANE TRANSPORT PROTEIN 3. MAIN FEATURES OF FADL STRUCTURE
Membrane proteins Porins: FadL Oriol Solà, Dimitri Ivancic, Daniel Folch, Marc Olivella INDEX 1. INTRODUCTION TO MEMBRANE PROTEINS 2. FADL: OUTER MEMBRANE TRANSPORT PROTEIN 3. MAIN FEATURES OF FADL STRUCTURE
Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently become
 Homology Modeling and Docking of Melatonin Receptors Andrew Kohlway, UMBC Jeffry D. Madura, Duquesne University 6/18/04 INTRODUCTION Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently
Homology Modeling and Docking of Melatonin Receptors Andrew Kohlway, UMBC Jeffry D. Madura, Duquesne University 6/18/04 INTRODUCTION Computational modeling of G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) has recently
1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties
 1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties Chemical nature of amino acids The!-amino acids in peptides and proteins (excluding proline) consist of a carboxylic acid ( COOH) and an amino ( NH
1. Amino Acids and Peptides Structures and Properties Chemical nature of amino acids The!-amino acids in peptides and proteins (excluding proline) consist of a carboxylic acid ( COOH) and an amino ( NH
Lecture 2 and 3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability
 Lecture 2 and 3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions: Van der Waals Interactions
Lecture 2 and 3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions: Van der Waals Interactions
HOMOLOGY MODELING. The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target.
 HOMOLOGY MODELING Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "target" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental
HOMOLOGY MODELING Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the "target" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental
Chem Homework = cm -1, HF; cm -1, H 35 Cl; cm -1, H 81 Br; cm -1, H 127 I
 1. Chem 344 - Homework 10 2. 3. 4. 0 = 4141.3 cm -1, HF; 2988.9 cm -1, H 35 Cl; 2649.7 cm -1, H 81 Br; 2309.5 cm -1, H 127 I 5. 6. 7. Q16.26,27,28,29) Identify the molecular orbitals for F 2 in the images
1. Chem 344 - Homework 10 2. 3. 4. 0 = 4141.3 cm -1, HF; 2988.9 cm -1, H 35 Cl; 2649.7 cm -1, H 81 Br; 2309.5 cm -1, H 127 I 5. 6. 7. Q16.26,27,28,29) Identify the molecular orbitals for F 2 in the images
Lec.1 Chemistry Of Water
 Lec.1 Chemistry Of Water Biochemistry & Medicine Biochemistry can be defined as the science concerned with the chemical basis of life. Biochemistry can be described as the science concerned with the chemical
Lec.1 Chemistry Of Water Biochemistry & Medicine Biochemistry can be defined as the science concerned with the chemical basis of life. Biochemistry can be described as the science concerned with the chemical
Reading Assignments. A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides. Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
Lecture Series 7 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments Read Chapter 7 From DNA to Protein A. Genes and the Synthesis of Polypeptides Genes are made up of DNA and are expressed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1: Data collection, phasing and refinement statistics ChbC/Ta 6 Br 12 Native ChbC Data collection Space group P4 3 2 1 2 P4 3 2 1 2 Cell dimensions a, c (Å) 132.75, 453.57 132.81, 452.95
Supplementary Table 1: Data collection, phasing and refinement statistics ChbC/Ta 6 Br 12 Native ChbC Data collection Space group P4 3 2 1 2 P4 3 2 1 2 Cell dimensions a, c (Å) 132.75, 453.57 132.81, 452.95
Chapter 1. Topic: Overview of basic principles
 Chapter 1 Topic: Overview of basic principles Four major themes of biochemistry I. What are living organism made from? II. How do organism acquire and use energy? III. How does an organism maintain its
Chapter 1 Topic: Overview of basic principles Four major themes of biochemistry I. What are living organism made from? II. How do organism acquire and use energy? III. How does an organism maintain its
Homology models of the tetramerization domain of six eukaryotic voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.1-Kv1.6
 Homology models of the tetramerization domain of six eukaryotic voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.1-Kv1.6 Hsuan-Liang Liu* and Chin-Wen Chen Department of Chemical Engineering and Graduate Institute
Homology models of the tetramerization domain of six eukaryotic voltage-gated potassium channels Kv1.1-Kv1.6 Hsuan-Liang Liu* and Chin-Wen Chen Department of Chemical Engineering and Graduate Institute
From DNA to protein, i.e. the central dogma
 From DNA to protein, i.e. the central dogma DNA RNA Protein Biochemistry, chapters1 5 and Chapters 29 31. Chapters 2 5 and 29 31 will be covered more in detail in other lectures. ph, chapter 1, will be
From DNA to protein, i.e. the central dogma DNA RNA Protein Biochemistry, chapters1 5 and Chapters 29 31. Chapters 2 5 and 29 31 will be covered more in detail in other lectures. ph, chapter 1, will be
Intro Secondary structure Transmembrane proteins Function End. Last time. Domains Hidden Markov Models
 Last time Domains Hidden Markov Models Today Secondary structure Transmembrane proteins Structure prediction NAD-specific glutamate dehydrogenase Hard Easy >P24295 DHE2_CLOSY MSKYVDRVIAEVEKKYADEPEFVQTVEEVL
Last time Domains Hidden Markov Models Today Secondary structure Transmembrane proteins Structure prediction NAD-specific glutamate dehydrogenase Hard Easy >P24295 DHE2_CLOSY MSKYVDRVIAEVEKKYADEPEFVQTVEEVL
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Today. Last time. Secondary structure Transmembrane proteins. Domains Hidden Markov Models. Structure prediction. Secondary structure
 Last time Today Domains Hidden Markov Models Structure prediction NAD-specific glutamate dehydrogenase Hard Easy >P24295 DHE2_CLOSY MSKYVDRVIAEVEKKYADEPEFVQTVEEVL SSLGPVVDAHPEYEEVALLERMVIPERVIE FRVPWEDDNGKVHVNTGYRVQFNGAIGPYK
Last time Today Domains Hidden Markov Models Structure prediction NAD-specific glutamate dehydrogenase Hard Easy >P24295 DHE2_CLOSY MSKYVDRVIAEVEKKYADEPEFVQTVEEVL SSLGPVVDAHPEYEEVALLERMVIPERVIE FRVPWEDDNGKVHVNTGYRVQFNGAIGPYK
Sunhats for plants. How plants detect dangerous ultraviolet rays
 Sunhats for plants How plants detect dangerous ultraviolet rays Anyone who has ever suffered sunburn will know about the effects of too much ultraviolet (UV) radiation, in particular UV-B (from 280-315
Sunhats for plants How plants detect dangerous ultraviolet rays Anyone who has ever suffered sunburn will know about the effects of too much ultraviolet (UV) radiation, in particular UV-B (from 280-315
The Structure of Enzymes!
 The Structure of Enzymes Levels of Protein Structure 0 order amino acid composition Primary Secondary Motifs Tertiary Domains Quaternary ther sequence repeating structural patterns defined by torsion angles
The Structure of Enzymes Levels of Protein Structure 0 order amino acid composition Primary Secondary Motifs Tertiary Domains Quaternary ther sequence repeating structural patterns defined by torsion angles
The Structure of Enzymes!
 The Structure of Enzymes Levels of Protein Structure 0 order amino acid composition Primary Secondary Motifs Tertiary Domains Quaternary ther sequence repeating structural patterns defined by torsion angles
The Structure of Enzymes Levels of Protein Structure 0 order amino acid composition Primary Secondary Motifs Tertiary Domains Quaternary ther sequence repeating structural patterns defined by torsion angles
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11744 Supplementary Table 1. Crystallographic data collection and refinement statistics. Wild-type Se-Met-BcsA-B SmCl 3 -soaked EMTS-soaked Data collection Space
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11744 Supplementary Table 1. Crystallographic data collection and refinement statistics. Wild-type Se-Met-BcsA-B SmCl 3 -soaked EMTS-soaked Data collection Space
Structural insights into energy regulation of light-harvesting complex from spinach CP29
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Structural insights into energy regulation of light-harvesting complex from spinach CP29 Xiaowei Pan 1, Mei Li 1, Tao Wan 1,2, Longfei Wang 1,2, Chenjun Jia 1,2, Zhiqiang Hou
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Structural insights into energy regulation of light-harvesting complex from spinach CP29 Xiaowei Pan 1, Mei Li 1, Tao Wan 1,2, Longfei Wang 1,2, Chenjun Jia 1,2, Zhiqiang Hou
Problem Set 1
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 1 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, September 15, 2006. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. For each of the following parts, pick
2006 7.012 Problem Set 1 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, September 15, 2006. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. For each of the following parts, pick
Exploratory Examination of Photosystem I in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Exploratory Examination of Photosystem I in Arabidopsis thaliana A. Role of Photosystem I Photosystem I (PSI) captures the sunlight and transfers the energy through a pigment network to the center of the
Exploratory Examination of Photosystem I in Arabidopsis thaliana A. Role of Photosystem I Photosystem I (PSI) captures the sunlight and transfers the energy through a pigment network to the center of the
GCD3033:Cell Biology. Transcription
 Transcription Transcription: DNA to RNA A) production of complementary strand of DNA B) RNA types C) transcription start/stop signals D) Initiation of eukaryotic gene expression E) transcription factors
Transcription Transcription: DNA to RNA A) production of complementary strand of DNA B) RNA types C) transcription start/stop signals D) Initiation of eukaryotic gene expression E) transcription factors
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Data collection Supplementary Table 1 Statistics of data collection, phasing and refinement Native Se-MAD Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell dimensions a, b, c (Å) 50.4, 94.2, 115.4 49.8, 94.2,
Data collection Supplementary Table 1 Statistics of data collection, phasing and refinement Native Se-MAD Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell dimensions a, b, c (Å) 50.4, 94.2, 115.4 49.8, 94.2,
Nanobiotechnology. Place: IOP 1 st Meeting Room Time: 9:30-12:00. Reference: Review Papers. Grade: 40% midterm, 60% final report (oral + written)
 Nanobiotechnology Place: IOP 1 st Meeting Room Time: 9:30-12:00 Reference: Review Papers Grade: 40% midterm, 60% final report (oral + written) Midterm: 5/18 Oral Presentation 1. 20 minutes each person
Nanobiotechnology Place: IOP 1 st Meeting Room Time: 9:30-12:00 Reference: Review Papers Grade: 40% midterm, 60% final report (oral + written) Midterm: 5/18 Oral Presentation 1. 20 minutes each person
Lecture 25: Protein Synthesis Key learning goals: Be able to explain the main stuctural features of ribosomes, and know (roughly) how many DNA and
 Lecture 25: Protein Synthesis Key learning goals: Be able to explain the main stuctural features of ribosomes, and know (roughly) how many DNA and protein subunits they contain. Understand the main functions
Lecture 25: Protein Synthesis Key learning goals: Be able to explain the main stuctural features of ribosomes, and know (roughly) how many DNA and protein subunits they contain. Understand the main functions
Human Biology. The Chemistry of Living Things. Concepts and Current Issues. All Matter Consists of Elements Made of Atoms
 2 The Chemistry of Living Things PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation Robert J. Sullivan, Marist College Michael D. Johnson Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues THIRD EDITION Copyright 2006 Pearson
2 The Chemistry of Living Things PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation Robert J. Sullivan, Marist College Michael D. Johnson Human Biology Concepts and Current Issues THIRD EDITION Copyright 2006 Pearson
Photosynthesis 1. Light Reactions and Photosynthetic Phosphorylation. Lecture 31. Key Concepts. Overview of photosynthesis and carbon fixation
 Photosynthesis 1 Light Reactions and Photosynthetic Phosphorylation Lecture 31 Key Concepts Overview of photosynthesis and carbon fixation Chlorophyll molecules convert light energy to redox energy The
Photosynthesis 1 Light Reactions and Photosynthetic Phosphorylation Lecture 31 Key Concepts Overview of photosynthesis and carbon fixation Chlorophyll molecules convert light energy to redox energy The
Kang, Lin-Woo, Ph.D. Professor Department of Biological Sciences Konkuk University Seoul, Korea nd Semester
 Kang, Lin-Woo, Ph.D. Professor Department of Biological Sciences Konkuk University Seoul, Korea 2018. 2 nd Semester Absorbance Assay (280 nm) Considerations for use Absorbance assays are fast and
Kang, Lin-Woo, Ph.D. Professor Department of Biological Sciences Konkuk University Seoul, Korea 2018. 2 nd Semester Absorbance Assay (280 nm) Considerations for use Absorbance assays are fast and
Introduction to Polymer Physics
 Introduction to Polymer Physics Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium February-May, 2016 Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium Introduction to Polymer Physics February-May, 2016 1 / 28 Polymers in Chemistry and
Introduction to Polymer Physics Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium February-May, 2016 Enrico Carlon, KU Leuven, Belgium Introduction to Polymer Physics February-May, 2016 1 / 28 Polymers in Chemistry and
Detailed description of overall and active site architecture of PPDC- 3dThDP, PPDC-2HE3dThDP, PPDC-3dThDP-PPA and PPDC- 3dThDP-POVA
 Online Supplemental Results Detailed description of overall and active site architecture of PPDC- 3dThDP, PPDC-2HE3dThDP, PPDC-3dThDP-PPA and PPDC- 3dThDP-POVA Structure solution and overall architecture
Online Supplemental Results Detailed description of overall and active site architecture of PPDC- 3dThDP, PPDC-2HE3dThDP, PPDC-3dThDP-PPA and PPDC- 3dThDP-POVA Structure solution and overall architecture
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
Charged amino acids (side-chains)
 Proteins are composed of monomers called amino acids There are 20 different amino acids Amine Group Central ydrocarbon N C C R Group Carboxyl Group ALL amino acids have the exact same structure except
Proteins are composed of monomers called amino acids There are 20 different amino acids Amine Group Central ydrocarbon N C C R Group Carboxyl Group ALL amino acids have the exact same structure except
Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase Cwc27
 Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Bahnson Biochemistry Cume, April 8, 2006 The Structural Biology of Signal Transduction
 Name page 1 of 6 Bahnson Biochemistry Cume, April 8, 2006 The Structural Biology of Signal Transduction Part I. The ion Ca 2+ can function as a 2 nd messenger. Pick a specific signal transduction pathway
Name page 1 of 6 Bahnson Biochemistry Cume, April 8, 2006 The Structural Biology of Signal Transduction Part I. The ion Ca 2+ can function as a 2 nd messenger. Pick a specific signal transduction pathway
Saba Al Fayoumi. Tamer Barakat. Dr. Mamoun Ahram + Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan
 1 Saba Al Fayoumi Tamer Barakat Dr. Mamoun Ahram + Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan What is BIOCHEMISTRY??? Biochemistry = understanding life Chemical reactions are what makes an organism (An organism is simply atoms
1 Saba Al Fayoumi Tamer Barakat Dr. Mamoun Ahram + Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan What is BIOCHEMISTRY??? Biochemistry = understanding life Chemical reactions are what makes an organism (An organism is simply atoms
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Chemical structure of LPS and LPS biogenesis in Gram-negative bacteria. a. Chemical structure of LPS. LPS molecule consists of Lipid A, core oligosaccharide and O-antigen. The polar
Supplementary Figure 1 Chemical structure of LPS and LPS biogenesis in Gram-negative bacteria. a. Chemical structure of LPS. LPS molecule consists of Lipid A, core oligosaccharide and O-antigen. The polar
Packing of Secondary Structures
 7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
7.88 Lecture Notes - 4 7.24/7.88J/5.48J The Protein Folding and Human Disease Professor Gossard Retrieving, Viewing Protein Structures from the Protein Data Base Helix helix packing Packing of Secondary
Absorption and CD Spectroscopy and Modeling of Various LH2 Complexes from Purple Bacteria
 2184 Biophysical Journal Volume 82 April 22 2184 2197 and CD Spectroscopy and Modeling of Various LH2 Complexes from Purple Bacteria Sofia Georgakopoulou,* Raoul N. Frese,* Evelyn Johnson, Corline Koolhaas,
2184 Biophysical Journal Volume 82 April 22 2184 2197 and CD Spectroscopy and Modeling of Various LH2 Complexes from Purple Bacteria Sofia Georgakopoulou,* Raoul N. Frese,* Evelyn Johnson, Corline Koolhaas,
Rama Abbady. Zina Smadi. Diala Abu-Hassan
 1 Rama Abbady Zina Smadi Diala Abu-Hassan (00:00) (10:00) Types of Molecules in the Cell 1. Water Molecules: a large portion of the cell mass is water (70% of total cell mass). 2. Organic molecules (carbon
1 Rama Abbady Zina Smadi Diala Abu-Hassan (00:00) (10:00) Types of Molecules in the Cell 1. Water Molecules: a large portion of the cell mass is water (70% of total cell mass). 2. Organic molecules (carbon
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
2. In regards to the fluid mosaic model, which of the following is TRUE?
 General Biology: Exam I Sample Questions 1. How many electrons are required to fill the valence shell of a neutral atom with an atomic number of 24? a. 0 the atom is inert b. 1 c. 2 d. 4 e. 6 2. In regards
General Biology: Exam I Sample Questions 1. How many electrons are required to fill the valence shell of a neutral atom with an atomic number of 24? a. 0 the atom is inert b. 1 c. 2 d. 4 e. 6 2. In regards
The ideal fiber pattern exhibits 4-quadrant symmetry. In the ideal pattern the fiber axis is called the meridian, the perpendicular direction is
 Fiber diffraction is a method used to determine the structural information of a molecule by using scattering data from X-rays. Rosalind Franklin used this technique in discovering structural information
Fiber diffraction is a method used to determine the structural information of a molecule by using scattering data from X-rays. Rosalind Franklin used this technique in discovering structural information
Principles of Physical Biochemistry
 Principles of Physical Biochemistry Kensal E. van Hold e W. Curtis Johnso n P. Shing Ho Preface x i PART 1 MACROMOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS 1 1 Biological Macromolecules 2 1.1 General Principles
Principles of Physical Biochemistry Kensal E. van Hold e W. Curtis Johnso n P. Shing Ho Preface x i PART 1 MACROMOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND DYNAMICS 1 1 Biological Macromolecules 2 1.1 General Principles
Biophysics II. Hydrophobic Bio-molecules. Key points to be covered. Molecular Interactions in Bio-molecular Structures - van der Waals Interaction
 Biophysics II Key points to be covered By A/Prof. Xiang Yang Liu Biophysics & Micro/nanostructures Lab Department of Physics, NUS 1. van der Waals Interaction 2. Hydrogen bond 3. Hydrophilic vs hydrophobic
Biophysics II Key points to be covered By A/Prof. Xiang Yang Liu Biophysics & Micro/nanostructures Lab Department of Physics, NUS 1. van der Waals Interaction 2. Hydrogen bond 3. Hydrophilic vs hydrophobic
