This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS
|
|
|
- Josephine Caitlin Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp:// ETS Comprehensive Study Material For NEET & AIIMS
2 GENERAL RGANIC EMISTRY APTER 14 We define chemistry as the chemistry of carbon compounds. AUGUST KEKULE INTRDUCTIN General organic chemistry is the base of organic chemistry If we want to under stand GC well, then definitely we are going to be a pro in organic chemistry overall. Topics which mention in GC 1. Inductive effect. Mesomeric effect. Resonance effect 4. yperconjugation. We have to remember the condition for every effect and when they are applicable for e.g. If resonance and inductive effect both are operating, then resonance is dominating effect there. In GC we also know about the reaction intermediate which is a molecular entity that is promed from the reactants and reacts further to give the directly observed products of a chemcial reaction most chemical reaction are stepwise, that is take more than one chemistry step to complete.
3 PYSICS FR NEET & AIIMS Reaction : Breaking of old bond and formation of new bond is known as chemical reaction A sequential account of each step, describing details of electron movement, energetics during bond cleavage and bond formation, and the rates of transformation of reactants into products (kinetics) is referred to as reaction mechanism. Species on which reagent is attacking is known as substrate or reactant. Species which attack on substrate, is known as reagent. Type of cleavage of bond (I) eterolytical cleavage/fission : Cleavage in which unequal distribution of electrons takes place during the bond cleavage is known as heterolytical cleavage. Due to unequal distribution of electrons, ions are formed. That s why it is also known as ionic cleavage or heterolytical cleavage. (II) omolytical cleavage/fission : Cleavage in which equal distribution of e s takes place during the chemical reaction is known as homolytical cleavage. Due to equally distribution of electrons, without charge unpaired electrons species is formed, which is known as free radical and cleavage is known as unionic cleavage/homolytical fission. By both cleavage [ionic/non ionic] three type of species are formed [ne carrying positive charge, other carrying negative charge and third one is neutral with unpaired electrons] is known as reaction intermidiate. Attacking reagents The species which attack on a substrate molecule or intermediate and form a product is called as attacking reagent. These are of two types : (I) Electrophilic reagent or electrophiles Electrophilic (electro philic) (electron loving) The reagent which attacks on the negative of the molecule or loves electrons are called electrophiles. Electrophiles may be positively charged or electron deficient molecule (molecule with sextet or septet). (i) Positively charged electrophiles, S, N, N, X, R, C6 N, C, C, C (ii) Neutral electrophiles :- Which possess a electron dificiency. (a) All Lewis acids as : BF, AlCl, S, ZnCl, BeCl, FeCl, SnCl, C, SnCl etoosindia.com India s No. 1 nline Coaching Institute IIT-JEE PRE-MEDICAL CBSE FUNDATIN
4 GENERAL RGANIC EMISTRY Ex. Sol. Which of the following has minimum heat of hydrogenation. (i) ethene (ii) Propene (iii) cis--butene (iv) trans--butene (iv) maximum stable alkene means minimum reactive. Ex. If eat of hydrogenation of 1-butene is 0 Kcal then heat of hydrogenation of 1,-butadiene is? (i) 0 (ii) 60 (iii) 7 (iv) Sol. (iii) 1,-butadiene requires two moles of hydrogen so heat of hydrogenation should be 60 Kcal but 1,-butadiene is stabilized by resonance than propane so heat of hydrogenation of 1,-butadiene will not be twice of 0. Actual - 60 > > 0 Kcal. Ex. Which of the following is maximum stable. (i) Conjugated alkadiene ( ) (ii) Isolated alkadiene ( ) (iii) Cumulated alkadiene ( C ) (iv) All are equal. Sol. (i) Due to resonance conjugated alkadiene is maximum stable. Isolated is more stable than cumulated alkadiene due to -effect. E T INT S KEY P S Reactivity of Benzene : -effect of R groups increases electron density in benzene ring. C due to group there is more e density at ortho and para position so is ortho/para directing and activating group. If -effect is more than e density will be more. Ex. Give electrophilic sustitution reaction order : Maximum -. So maximum -effect So maximum e density So maximum reactive ESR order I > II > III > IV 160 etoosindia.com Study with Best Etoos Faculties of Kota IIT-JEE PRE-MEDICAL CBSE FUNDATIN
5 PYSICS FR NEET & AIIMS 1. All the ve charge species are electrophile except and N 4.. Relative electron withdrawing order ( 1 order). I order N > CN > C > F > R > > C 6 > = N > > C > alkyl > alkyl < 1 alkyl 4. Greater the number of -ydrogen, more stable is carbocation and free radical due to hyperconjugation. (A) Carbocation > (Ph) C > (Ph) > Ph > = () C > ( ) > > > = > C (B) Free radical (Ph) C > (Ph) > Ph > = > ( ) C > ( ) > (C) Carbanion (Ph) C > (Ph) > Ph > = > > Acidic Strength > ( ) (i) > > N > ( ) C (ii) > = > (iii) R S > R C > > R (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) C > C > C CCl C > Cl C > ClC C > C > C F F F C 6 4 Phenol > m > p > 0 (viii) C 6 4 N p > o > m > Phenol etoosindia.com 167 India s No. 1 nline Coaching Institute IIT-JEE PRE-MEDICAL CBSE FUNDATIN
6 SLVED EXAMPLE GENERAL RGANIC EMISTRY Ex.1 Which one of the following species is most stable p N C C (A) 6 4 p C (B) 6 4 p Cl C (C) 6 4 Ex. Which of the following gives most stable carbocation by dehydration (A) ( ) (B) ( ) C (C) C C (D) 6 Sol. (D) (B) alcohols carbocation Me Me C Me is most stable Sol. (B) N Nitro-group is electron withdrawing therefore decreases stability. Ex. Sol. Which of the following orders regarding relative stability of free radicals is correct (A) < < 1 (B) > > 1 (C) 1 < > (D) > < 1 (B) Due to the increasing no. of hyperconjugative structures free radical stabilise following as 1. Ex.4 The I effect of alkyl groups is in the order (A) > > 1 (B) 1 > > (C) > > 1 (D) None of these Sol. (C) 1 C C C Methoxy group is electron releasing. Therefore increases stability by donating electron. Ex. Which of the following compounds will show metamerism (A) CC (B) C S C (C) (D) C Cl Chlorine is also electron withdrawing but its effect is less than N group. ence, correct order of stability. Most stable Cl N Most stable Sol. (B) C S C Ex.6 Sol. Diethyl thioether are metamers. S C and 7 Methyl propyl thioether ow many carbon atoms in the molecule C () C are asymmetric (A) 1 (B) (C) (D) None of these (B) C C * * (1) () Two carbon atoms in the molecule are asymmetric. etoosindia.com Study with Best Etoos Faculties of Kota IIT-JEE PRE-MEDICAL CBSE FUNDATIN 169
7 PYSICS FR NEET & AIIMS Exercise # 1 SINGLE BJECTIVE NEET LEVEL 1. The molecular formula of diphenyl methane,, is C 1 1 ow many structural isomers are possible when one of the hydrogens is replaced by a chlorine atom (A) 8 (B) 7 (C) 6 (D) 4. SN 1 reaction is faster in (A) Cl (B) - Cl (C) C Cl (D) Cl. ow many enantiomer pairs are obtained by monochlorination of, -dimethylbutane (A) Nil (B) Four (C) Two (D) Three (E) ne 4. Among the following compounds which can be dehydrated very easily is (A) C (B) (C) (D). Which of the following statements is not characteristic of free radical chain reaction (A) It gives major product derived from most stable free radical (B) It is usually sensitive to change in solvent polarity (C) It proceeds in three main steps like initiation, propagation and termination (D) It may be initiated by U.V. light 6. Most stable carbanion is (A) (B) (C) N - (D) 7. Which one is electrophilic addition (A) Cl CCl Cl (B) CN ( ) C()CN (C) ( ) C CN ()CN (D) Br BrBr 8. A compound has chiral carbon atoms. The number of possible optical isomers it can have (A) (B) (C)8 (D) 4 9. ow many chiral isomers can be drawn from - bromo, -chloro butane (A) (B) (C) 4 (D) 10. Number of isomers of C 4 10 is (A) (B) (C) 4 (D) Isomerism not exist 11. The number of possible isomers for compound CClBr is (A) (B) (C) 4 (D) 1. The optically active tartaric acid is named as D-()- tartaric acid because it has a positive (A) ptical rotation and is derived from D-glucose (B) p in organic solvent (C) ptical rotation and is derived from D() glyceraldehyde (D) ptical rotation only when substituted by deuterium 1. Among the following compounds (I-III) the correct order of reaction with electrophilic reagent is N I II III (A) II > III > I (B) III < I < II (C) I > II > III (D) I = II > III - etoosindia.com 171 India s No. 1 nline Coaching Institute IIT-JEE PRE-MEDICAL CBSE FUNDATIN
8 Exercise # SINGLE BJECTIVE GENERAL RGANIC EMISTRY AIIMS LEVEL 1. bserve the following statements and choose the correct option. S1 : Inductive effect is more powerful than mesomeric effect. S : The bond polarity order of bonds a, b, and c in the given molecule (I) is c > a > b b = Ph a c C ( I) S : The hybrid structure has always have equal contribution from all the resonating structures. S4 : shows inductive effect, resonance, hyperconjugation & intramolecular hydrogen bonding. (A) TFTF (B) FTFTC (C) FTTF (D) TTFF. Which of the following is correct about the following compound (Naphthalene) (A) All the C-C bond length are same (B) C 1 C bond length is shorter than C C bond length (C) C 1 C bond length is greater than C C bond length (D) All the C-C bond length are equal to C-C bond length of benzene. The stability order of alkene in following compounds is : (I) (II) (III) (IV) (A) I < II < III < IV (B) II < I < III < IV (C) II < III < I < IV (D) II < IV < I < III 4. Number of electrons in conjugation for these compounds,, & will be respectively : (A) 8, 6, 6, 6 (B) 6, 4, 6, 6 (C) 6, 6, 6, 6 (D) 6, 6, 8, 6. The hybridisation of nitrogen in (pyrrole) is : (A) sp (B) sp (C) sp (D) Cann't be predicted 178 etoosindia.com Study with Best Etoos Faculties of Kota IIT-JEE PRE-MEDICAL CBSE FUNDATIN
9 PYSICS FR NEET & AIIMS Exercise # PART - 1 MATRIX MAT CLUMN 1. Column-I Column-II (Stability order) (Responsible effect) (A) (p) Inductive effect (B) > (q) Resonance (C) > (r) yperconjugation (D) > (s) Mesomeric effect. Match the following Coulmn - I (Compounds) Coulmn - II (Characteristics) (A) (p) Mesomeric effect / resonance (B) Ph = (q) Inductive effect. (C) (r) yperconjugative effect (D) (s) Nonpolar (t) Polar 188 etoosindia.com India s No. 1 nline Coaching Institute IIT-JEE PRE-MEDICAL CBSE FUNDATIN
10 GENERAL RGANIC EMISTRY Exercise # 4 PART - 1 PREVIUS YEAR (NEET/AIPMT) 1. Among the following compounds the decreasing order of reactivity towards electrophilic substitution is [CBSE AIPMT 000] CF I II III IV (A) II > I > III > IV (B) III > I > II > IV (C) IV > I > II > IV (D) I > II > III > IV. In S, I, RN, N order of proton accepting tendency will be [CBSE AIPMT 001] (A) I > N > RN > S (B) N > RN > S > I (C) RN > N > S > I (D) S > RN > N > I. The correct order of reactivity towards the electrophilic substitution of the compounds aniline (I). benzene (II) and nitrobenzene (III) is [CBSE AIPMT 00] (A) II < III > I (B) I > II > III (C) III > II > I (D) II > III > I 4. Which of the following is least reactive in a nucleophilic substitution reaction? [CBSE AIPMT 004] (A) ( ) C Cl (B) = Cl (C) Cl (D) = Cl. The molecular formula of diphenyl methane is C 1 1 ow many structural isomers are possible when one of the hydrogen is replaced by a chlorine atom? [CBSE AIPMT 004] (A) 6 (B) 4 (C) 8 (D) 7 6. Which amongst the following is the most stable carbocation? [CBSE AIPMT 00] (A) C (C) (B) (D) C 7. The correct order regarding the electronegativity of hybrid orbitals of carbon is [CBSE AIPMT 00] (A) sp > sp < sp (B) sp > sp > sp (C) sp < sp > sp (D) sp < sp < sp 8. The order of decreasing reactivity towards an electrophilic reagent, for the following (i) Benzene (ii) Toluene (iii) Chlorobenzene (iv) Phenol would be [CBSE AIPMT 007] (A) (i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv) (B) (ii) > (iv) > (i) > (iii) (C) (iv) > (iii) > (ii) > (i) (D) (iv) > (ii) > (i) > (iii) 9. Which one of the following is most reactive towards electrophilic attack? [CBSE AIPMT 008] (A) (C) N 10. Base strength of (i) CC (B) (D) Cl (ii) C (iii) C C is in the order of [CBSE AIPMT 008] (A) (ii) > (i) (iii) (B) (iii) > (ii) > (i) (C) (i) > (iii) > (ii) (D) (i) > (ii) > (iii) 11. The stability of carbanions in the following (i) RC C C (B) C (ii) R C (D) R C is in the order of [CBSE AIPMT 008] (A) (i) > (ii) > (iii) > (iv) (C) (iv) > (ii) > (iii) > (i) 1. In the hydrocarbon 6 (B) (ii) > (iii) > (iv) > (i) (D) (i) > (iii) > (ii) > (iv) C 4 the state of hybridisation of carbons 1, and are in the following sequence [CBSE AIPMT 008] (A) sp, sp, sp (B) sp, sp, sp (C) sp, sp, sp (D) sp, sp, sp 1 etoosindia.com Study with Best Etoos Faculties of Kota IIT-JEE PRE-MEDICAL CBSE FUNDATIN 191
11 PYSICS FR NEET & AIIMS MCK TEST 1. Molecule can be enolised by which hydrogen. (A) x (B) y (C) z (D) None of these. ow many enolisable are present in the above compound? (A) (B) (C) 4 (D). ow many total enolic forms (including stereoisomers) are possible for. (A) (B) 7 (C) 4 (D) 4. Which statement about tautomerism is incorrect? (A) Tautomers always exist in equilibrium. (B) Tautomers can be separated by physical / chemical process. (C) Tautomerism is a chemical phenomenon which takes place in liquid and gaseous state and catalysed by acid as well as base. (D) All tautomers are always functional group isomers.. The enolic form of acetone contains : (A) 9 bonds, 1 bond and lone pairs (C) 10 bond, 1 bond and 1 lone pair 6. Keto-enol tautomerism does not observe in : (B) 8 bond, bond and lone pairs (D) 9 bond, bond and 1 lone pair (A) (B) (C) 7. Which among the following compound will give maximum enol content in solution : (A) C C C 6 (C) C (D) (B) C C (D) C CC 8. Arrange the followings in decreasing order of percentage enol content. (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (A) I > II > III > IV (B) II > I > III > IV (C) II > III > I > IV (D) III > II > IV > I etoosindia.com 19 India s No. 1 nline Coaching Institute IIT-JEE PRE-MEDICAL CBSE FUNDATIN
12 11 th Class Modules Chapter Details Physics Modules Chemistry Modules Mathematics Modules Module-1 PYSICS 1. Physical World & Measurements. Basic Maths & Vector. Kinematics Module- 1. Law of Motion & Friction. Work, Energy & Power Module- 1. Motion of system of particles & Rigid Body. Gravitation Module-4 1. Mechanical Properties of Matter. Thermal Properties of Matter Module- 1. scillations. Waves Module-1(PC) EMISTRY 1. Some Basic Conceps of Chemistry. Atomic Structure. Chemical Equilibrium 4. Ionic Equilibrium Module-(PC) 1. Thermodynamics & Thermochemistry. Redox Reaction. States f Matter (Gaseous & Liquid) Module-(IC) 1. Periodic Table. Chemical Bonding. ydrogen & Its Compounds 4. S-Block Module-4(C) 1. Nomenclature of rganic Compounds. Isomerism. General rganic Chemistry Module-(C) 1. Reaction Mechanism. ydrocarbon. Aromatic ydrocarbon 4. Environmental Chemistry & Analysis f rganic Compounds Module-1 BILGY 1. Diversity in the Living World. Plant Kingdom. Animal Kingdom Module- 1. Morphology in Flowering Plants. Anatomy of Flowering Plants. Structural rganization in Animals Module- 1. Cell: The Unit of Life. Biomolecules. Cell Cycle & Cell Division 4. Transport in Plants. Mineral Nutrition Module-4 1. Photosynthesis in igher Plants. Respiration in Plants. Plant Growth and Development 4. Digestion & Absorption. Breathing & Exchange of Gases Module- 1. Body Fluids & Its Circulation. Excretory Products & Their Elimination. Locomotion & Its Movement 4. Neural Control & Coordination. Chemical Coordination and Integration To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://
13 1 th Class Modules Chapter Details Physics Modules Chemistry Modules Mathematics Modules Module-1 PYSICS 1. Electrostatics. Capacitance Module- 1. Current Electricity. Magnetic Effect of Current and Magnetism Module- 1. Electromagnetic Induction. Alternating Current Module-4 1. Geometrical ptics. Wave ptics Module- 1. Modern Physics. Nuclear Physics. Solids & Semiconductor Devices 4. Electromagnetic Waves Module-1(PC) EMISTRY 1. Solid State. Chemical Kinetics. Solutions and Colligative Properties Module-(PC) 1. Electrochemistry. Surface Chemistry Module-(IC) 1. P-Block Elements. Transition Elements (d & f block). Co-ordination Compound 4. Metallurgy Module-4(C) 1. aloalkanes & aloarenes. Alcohol, Phenol & Ether. Aldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic Acid Module-(C) 1. Nitrogen & Its Derivatives. Biomolecules & Polymers. Chemistry in Everyday Life Module-1 BILGY 1. Reproduction in rganisms. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants. uman Reproduction 4. Reproductive ealth Module- 1. Principles of Inheritance and Variation. Molecular Basis of Inheritance. Evolution Module- 1. uman ealth and Disease. Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production. Microbes in uman Welfare Module-4 1. Biotechnology: Principles and Processes. Biotechnology and Its Applications. rganisms and Populations Module- 1. Ecosystem. Biodiversity and Conservation. Environmental Issues To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://
Re AIPMT 2015 Paper Analysis
 Re AIPMT 2015 Paper Analysis Biology The Biology section of the paper was slightly easier than the previous paper and the distribution pattern of the paper shows that there are 49 questions from 11 th
Re AIPMT 2015 Paper Analysis Biology The Biology section of the paper was slightly easier than the previous paper and the distribution pattern of the paper shows that there are 49 questions from 11 th
Class Biology
 Class - 10+1 Biology April & May Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 The Living World Biological Classification Plant Kingdom July Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Animal kingdom Morphology of flowering plants August Chapter
Class - 10+1 Biology April & May Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3 The Living World Biological Classification Plant Kingdom July Chapter 4 Chapter 5 Animal kingdom Morphology of flowering plants August Chapter
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS
 This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our omprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETS omprehensive Study
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our omprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETS omprehensive Study
JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS
 7TH - STANDARD SCIENCE 1. Measurement 2. Motion 3. Force and Friction 4. Fluids 5. Heat 6. Light 7. Sound 8. Electricity 9. Universe 10. Symbol & Chemical Formulae 11. Air and Water 12. Physical & Chemical
7TH - STANDARD SCIENCE 1. Measurement 2. Motion 3. Force and Friction 4. Fluids 5. Heat 6. Light 7. Sound 8. Electricity 9. Universe 10. Symbol & Chemical Formulae 11. Air and Water 12. Physical & Chemical
7 th May Only few Days are remaining
 in 30 Days 7 th May 2017 - Only few Days are remaining Confusion: How to start revision? What should I study first? What should be my target of study to secure good rank? Board Exam is also approaching
in 30 Days 7 th May 2017 - Only few Days are remaining Confusion: How to start revision? What should I study first? What should be my target of study to secure good rank? Board Exam is also approaching
JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS
 7TH - STANDARD SCIENCE MATHS 1. Measurement 2. Motion 3. Force and Friction 4. Fluids 5. Heat 6. Light 7. Sound 8. Electricity 9. Universe 10. Symbol & Chemical Formulae 11. Air and Water 12. Physical
7TH - STANDARD SCIENCE MATHS 1. Measurement 2. Motion 3. Force and Friction 4. Fluids 5. Heat 6. Light 7. Sound 8. Electricity 9. Universe 10. Symbol & Chemical Formulae 11. Air and Water 12. Physical
AIPMT (NEET) A Detailed Analysis by Resonance
 AIPMT (NEET) - 2016 AIPMT (NEET) 2016 A Detailed by Resonance As per the directions of honorable Supreme Court, NEET 2016 was conducted as per the schedule (01 st May 2016) decided for AIPMT 2016. This
AIPMT (NEET) - 2016 AIPMT (NEET) 2016 A Detailed by Resonance As per the directions of honorable Supreme Court, NEET 2016 was conducted as per the schedule (01 st May 2016) decided for AIPMT 2016. This
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS
 This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our omprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETS omprehensive Study
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our omprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETS omprehensive Study
For more info visit
 Bond Fission: a) Homolytic fission: Each atom separates with one electron, leading to the formation of highly reactive entities called radicals, owing their reactivity to their unpaired electron. b) Heterolytic
Bond Fission: a) Homolytic fission: Each atom separates with one electron, leading to the formation of highly reactive entities called radicals, owing their reactivity to their unpaired electron. b) Heterolytic
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS
 This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETOOS Comprehensive
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETOOS Comprehensive
Dr. Sangeeta Khanna Ph.D 1 CHEMISTRY COACHING CIRCLE D:\Important Data\2016\+1\Org\Test\GT-5\Grand Test -V (organic Chemistry) Level - 1.
 1 EMISTRY ING IRLE :\Important ata\016\+1\rg\test\gt-5\grand Test -V (organic hemistry) Level - 1.docx LEVEL 1 (1.1.016) TPI: IUP NMING, GENERL RGNI EMISTRY & ISMERISM RE INSTRUTINS REFULLY 1. The test
1 EMISTRY ING IRLE :\Important ata\016\+1\rg\test\gt-5\grand Test -V (organic hemistry) Level - 1.docx LEVEL 1 (1.1.016) TPI: IUP NMING, GENERL RGNI EMISTRY & ISMERISM RE INSTRUTINS REFULLY 1. The test
Study of Chemical Reactions
 Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Unit Title Marks HOURS Starting Date I Basic Concepts of Chemistry April-2019 II Structure of Atom
 Class 11+12, Classes Schedule & Syllabus [ CBSE ] Chemistry Class 11 Unit Title Marks HOURS Starting Date I Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11 18 1-April- II Structure of Atom III Classification of Elements
Class 11+12, Classes Schedule & Syllabus [ CBSE ] Chemistry Class 11 Unit Title Marks HOURS Starting Date I Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11 18 1-April- II Structure of Atom III Classification of Elements
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI - 87
 HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
NEET A Detailed Analysis by Resonance
 NEET 2017 A Detailed by Resonance As per the directions of honorable Supreme Court, NEET 2017 was conducted as per the schedule (7 th May 2017). This exam is conducted for entrance into state and national
NEET 2017 A Detailed by Resonance As per the directions of honorable Supreme Court, NEET 2017 was conducted as per the schedule (7 th May 2017). This exam is conducted for entrance into state and national
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry
 Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
CHEM120 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WORKSHEET 1
 EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRKSEET 1 Some of the objectives To understand and know the hybridization concept Be able to distinguish different geometries, including basic bond lengths and angles within organic
EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRKSEET 1 Some of the objectives To understand and know the hybridization concept Be able to distinguish different geometries, including basic bond lengths and angles within organic
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
4.15 Halogenation of Alkanes RH + X 2 RX + HX
 4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Aromatic compounds do not react like other alkenes. With an appropriate catalyst, however, benzene will react
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Aromatic compounds do not react like other alkenes 2 Fe 3 2 Does not form A major part of the problem for this reaction is the product has lost all aromatic stabilization,
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Aromatic compounds do not react like other alkenes 2 Fe 3 2 Does not form A major part of the problem for this reaction is the product has lost all aromatic stabilization,
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
JEE MEDICAL-UG BOARDS KVPY NTSE OLYMPIADS
 5TH - STANDARD SCIENCE 1. Simple machine 2. State of matter 3. Rock and minerals 4. Air & water 5. Our environment 6. Living and non-living things 7. Plants animal life 8. The human body 9. Food 10. Health
5TH - STANDARD SCIENCE 1. Simple machine 2. State of matter 3. Rock and minerals 4. Air & water 5. Our environment 6. Living and non-living things 7. Plants animal life 8. The human body 9. Food 10. Health
Chapter 17: Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 1 Chapter 17: Reactions of Aromatic Compounds I. Introduction to Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) A. General Mechanism II. Reactions of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution A. Halogenation (E =
1 Chapter 17: Reactions of Aromatic Compounds I. Introduction to Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) A. General Mechanism II. Reactions of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution A. Halogenation (E =
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
Overview of Types of Organic Reactions and Basic Concepts of Organic Reaction Mechanisms Dr. Solomon Derese 1 A chemical reaction is the transformation of one chemical or collection of chemicals into another
CHEM 242 REACTIONS OF ARENES: CHAP 12 ASSIGN ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION A B C D E
 CHEM 242 REACTIONS OF ARENES: CHAP 12 ASSIGN ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION 1. Consider carefully the mechanism of the following electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and indicate which of
CHEM 242 REACTIONS OF ARENES: CHAP 12 ASSIGN ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION 1. Consider carefully the mechanism of the following electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction and indicate which of
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE (AUTONOMOUS) ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE ROAD, CUDDALORE CH101T ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (SEMESTER-I)
 UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
Lecture Topics: I. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
AND TECHNIQUES. Unit. I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 12 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SOME BASIC B PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name? 3-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane 4,4-Dimethyl-3-ethylheptane
Unit 12 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SOME BASIC B PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Which of the following is the correct IUPAC name? 3-Ethyl-4, 4-dimethylheptane 4,4-Dimethyl-3-ethylheptane
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 203/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry
 E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases SAMPLE. Chapter Outline
 Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Chapter utline I. Polar covalent bonds (Sections 2.1 2.3). A. Electronegativity (Section 2.1). 1. Although some bonds are totally ionic and some are totally
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases Chapter utline I. Polar covalent bonds (Sections 2.1 2.3). A. Electronegativity (Section 2.1). 1. Although some bonds are totally ionic and some are totally
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King I. Conjugation
 Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Chapter 2 Polar Covalent Bonds; Acids and Bases. Chapter Outline
 rganic Chemistry 9th Edition McMurry SLUTINS MANUAL Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/organic-chemistry-9th-edition-mcmurrysolutions-manual/ rganic Chemistry 9th Edition McMurry
rganic Chemistry 9th Edition McMurry SLUTINS MANUAL Full clear download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/organic-chemistry-9th-edition-mcmurrysolutions-manual/ rganic Chemistry 9th Edition McMurry
Worksheet Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary
 Worksheet 10.1 Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary Addition elimination reaction A reaction in which two molecules combine with the release of a small molecule, often water. This type of reaction is
Worksheet 10.1 Chapter 10: Organic chemistry glossary Addition elimination reaction A reaction in which two molecules combine with the release of a small molecule, often water. This type of reaction is
Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes
 alo Alkanes and alo Arenes Short Answer Questions: **1. Write the isomers of the compound having formula C 4 9 Br? Sol. There are five isomers of C 4 9 Br. These are: 2-bromobutane is expected to exhibit
alo Alkanes and alo Arenes Short Answer Questions: **1. Write the isomers of the compound having formula C 4 9 Br? Sol. There are five isomers of C 4 9 Br. These are: 2-bromobutane is expected to exhibit
There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert:
 Substituent Effects There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert: RESONANCE effects are those that occur through the π system and can be represented by resonance structures. These
Substituent Effects There are two main electronic effects that substituents can exert: RESONANCE effects are those that occur through the π system and can be represented by resonance structures. These
CHEMISTRY CHAPTER- HYDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions
 CEMISTRY CAPTER- YDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions 1. What type of structural isomerism is shown by alkanes? 2. Which metal is used in Wurtz reaction? 3. What happens when isopropyl bromide is subjected
CEMISTRY CAPTER- YDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions 1. What type of structural isomerism is shown by alkanes? 2. Which metal is used in Wurtz reaction? 3. What happens when isopropyl bromide is subjected
CH 3 Cl + Cl 2 CH 2 Cl 2 + HCl
 Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Chapter Organic Chemistry Basics
 29 Chapter Organic Chemistry Basics 2. A similarity between optical and geometrical isomerism is that [2002] (a) each forms equal number of isomers for a given compound (b) if in a compound one is present
29 Chapter Organic Chemistry Basics 2. A similarity between optical and geometrical isomerism is that [2002] (a) each forms equal number of isomers for a given compound (b) if in a compound one is present
Kota Academy Karad Chemistry - Isomerism
 Kota cademy Karad 1. Which of the following compounds exhibit optical isomerism : () C C C () C CC (C) C C C (D) C CC. C 7 9 N has how many isomeric forms that contain a benzene ring : () 4 () (C) 6 (D)
Kota cademy Karad 1. Which of the following compounds exhibit optical isomerism : () C C C () C CC (C) C C C (D) C CC. C 7 9 N has how many isomeric forms that contain a benzene ring : () 4 () (C) 6 (D)
Chapter 17. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
PAPER No. 5: REACTION MECHANISM MODULE No. 2: Types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper No. 5:Organic Chemistry-II Module No. 2: Overview of different types of Organic Reaction Mechanisms CHE_P5_M2 TABLE OF CONTENTS
NEET A Detailed Analysis by Resonance
 NEET 2018 A Detailed Analysis by Resonance NEET 2018 was conducted as per the schedule (6 th May 2018). This exam is conducted for entrance into state and national level medical colleges for MBBS, BDS
NEET 2018 A Detailed Analysis by Resonance NEET 2018 was conducted as per the schedule (6 th May 2018). This exam is conducted for entrance into state and national level medical colleges for MBBS, BDS
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 rganic Chemistry, 6 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District 2006, Prentice all Electrophilic
rganic Chemistry, 6 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District 2006, Prentice all Electrophilic
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS
 This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETOOS Comprehensive
This PDF is the Sample PDF taken from our Comprehensive Study Material for NEET & AIIMS To purchase the books, go through the link belowhttp://www.etoosindia.com/smartmall/booklist.do ETOOS Comprehensive
1. Which compound would you expect to have the lowest boiling point? A) NH 2 B) NH 2
 MULTIPLE CICE QUESTINS Topic: Intermolecular forces 1. Which compound would you expect to have the lowest boiling point? A) N 2 B) N 2 C) N D) E) N Ans: : N 2 D Topic: Molecular geometry, dipole moment
MULTIPLE CICE QUESTINS Topic: Intermolecular forces 1. Which compound would you expect to have the lowest boiling point? A) N 2 B) N 2 C) N D) E) N Ans: : N 2 D Topic: Molecular geometry, dipole moment
1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
3.1 Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 3.1 Introduction to Organic hemistry Organic hemistry is the study of carbon chemistry as carbon has the ability to join together in chains, rings, balls etc. arbon also joins with other elements easily
3.1 Introduction to Organic hemistry Organic hemistry is the study of carbon chemistry as carbon has the ability to join together in chains, rings, balls etc. arbon also joins with other elements easily
A.M Wake up, Have Breakfast & Get ready for School. In free time during school- revise formulae/reactions in chemistry
 NEET Study Plan 2018 PDF Below we have provided the NEET Study Plan 2018 with the proper time table for 3 Months. Get the 3 Months-Week Wise Study Plan with time slot details. The below study plan for
NEET Study Plan 2018 PDF Below we have provided the NEET Study Plan 2018 with the proper time table for 3 Months. Get the 3 Months-Week Wise Study Plan with time slot details. The below study plan for
CHEMISTRY. Module No and Title Module-, Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: The ortho/para ipso attack, orientation in other ring systems.
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Paper-5, Organic Chemistry-II Module No and Title Module-, Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: The ortho/para Module Tag CHE_P5_M29 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Paper-5, Organic Chemistry-II Module No and Title Module-, Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: The ortho/para Module Tag CHE_P5_M29 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes
CHEM Chapter 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (homework) W
 CHEM 2425. Chapter 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (homework) W Short Answer Exhibit 16-1 MATCH a structure or term from the following list with each description below. Place
CHEM 2425. Chapter 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (homework) W Short Answer Exhibit 16-1 MATCH a structure or term from the following list with each description below. Place
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1. The credit for synthesizing first organic compound in the laboratory went to a) Berzelius b) Wohler c) Kolbe d) Berthelot Ans : b) Wohler [Note : (i) N H 4 Cl+KCNO NH 4 CNO
SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1. The credit for synthesizing first organic compound in the laboratory went to a) Berzelius b) Wohler c) Kolbe d) Berthelot Ans : b) Wohler [Note : (i) N H 4 Cl+KCNO NH 4 CNO
Theory 70 Marks + Practical 30 marks= maximum Marks 100 for both ISC and CBSE
 Theory 70 Marks + Practical 30 marks= maximum Marks 100 for both ISC and CBSE ISC CHEMISTRY XI CBSE CHEMISTRY XI Units Mark Units Mark 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 2 Structure of Atom 3 Classification
Theory 70 Marks + Practical 30 marks= maximum Marks 100 for both ISC and CBSE ISC CHEMISTRY XI CBSE CHEMISTRY XI Units Mark Units Mark 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 2 Structure of Atom 3 Classification
UNIT.10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
 UNIT.10 ALOALKANES AND ALOARENES ONE MARKS QUESTIONS 1. What are haloalkanes? aloalkane is a derivative obtained by replacing hydrogen atom of alkane by halogen atom. 2. What is the hybridization of the
UNIT.10 ALOALKANES AND ALOARENES ONE MARKS QUESTIONS 1. What are haloalkanes? aloalkane is a derivative obtained by replacing hydrogen atom of alkane by halogen atom. 2. What is the hybridization of the
The Study of Chemical Reactions. Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order.
 The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES.
 COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Text Sections (N0 1.9, 9-11) Homework: Chapter 1:
 CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
2015 (No. of Questions)
 TREND ANALYSIS OF JEE Advanced PHYSICS The complexity of the JEE arises from the fact that the questions are always unique in their context, and solving them often requires a combination of concepts from
TREND ANALYSIS OF JEE Advanced PHYSICS The complexity of the JEE arises from the fact that the questions are always unique in their context, and solving them often requires a combination of concepts from
REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2)
 REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2) 1.) Why do haloalkenes under go nucleophillic substitution whereas haloarenes under go electophillic substitution. Ans. Due to more electro negative
REASONING QUESTIONS FROM ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (CH. 1 & 2) 1.) Why do haloalkenes under go nucleophillic substitution whereas haloarenes under go electophillic substitution. Ans. Due to more electro negative
Organic Chemistry Practice Problems: Solutions
 rganic Chemistry Practice Problems: Solutions 1. 2. a. B, A b. D, B c. A, D d. D, A a. Resonance b. Electronegativity of fluorine atoms F F c. Neither is very acidic, but the oxygen will help stabilise
rganic Chemistry Practice Problems: Solutions 1. 2. a. B, A b. D, B c. A, D d. D, A a. Resonance b. Electronegativity of fluorine atoms F F c. Neither is very acidic, but the oxygen will help stabilise
Organic Chemistry. Why are these compounds called Organic. What is a Hydrocarbon? Questions: P167 Read
 Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Introduction to Organic Chemistry. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: Acids and Bases
 There are 4 types of Organic Reactions Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: SUBSTITUTION: ADDITION: X Y + A X A + Y Example Example A B + X Y A B X Y ELIMINATION There are 4 Types of Organic
There are 4 types of Organic Reactions Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Reactions: SUBSTITUTION: ADDITION: X Y + A X A + Y Example Example A B + X Y A B X Y ELIMINATION There are 4 Types of Organic
Organic Mechanisms 1
 Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
Organic Chemistry. Second Edition. Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions. David Klein. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e
 Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 19.1 Introduction to Electrophilic
Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 19.1 Introduction to Electrophilic
CHAPTER 16 - CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION
 CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
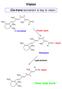 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Chapter 24 From Petroleum to Pharmaceuticals
 hapter 24 From Petroleum to Pharmaceuticals 24.1 Petroleum Refining and the ydrocarbons 24.2 Functional Groups and Organic Synthesis 24.3 Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals IR Tutor and Infrared Spectroscopy
hapter 24 From Petroleum to Pharmaceuticals 24.1 Petroleum Refining and the ydrocarbons 24.2 Functional Groups and Organic Synthesis 24.3 Pesticides and Pharmaceuticals IR Tutor and Infrared Spectroscopy
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Chemistry 102 Organic Chemistry: Introduction to Isomers Workshop
 Chemistry 102 Organic Chemistry: Introduction to Isomers Workshop What are isomers? Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula, but different arrangements of atoms. There are different types
Chemistry 102 Organic Chemistry: Introduction to Isomers Workshop What are isomers? Isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula, but different arrangements of atoms. There are different types
Physical Organic Chemistry (15 h)
 Course code : CEM 43244 Course title : Advanced rganic Chemistry I Physical rganic Chemistry (15 h) Dr. Dinesh Pandithavidana E-mail: dinesh@kln.ac.lk Mobile: 0777-745-720 ffice: B1 222/3 Stereochemical
Course code : CEM 43244 Course title : Advanced rganic Chemistry I Physical rganic Chemistry (15 h) Dr. Dinesh Pandithavidana E-mail: dinesh@kln.ac.lk Mobile: 0777-745-720 ffice: B1 222/3 Stereochemical
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
and Stereochemistry) PAPER 1: ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- I (Nature of Bonding and Stereochemistry) MODULE 4: Applications of Electronic Effects
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 1: ORGANIC - I (Nature of Bonding Module 4: Applications of Electronic Effects CHE_P1_M4 PAPER 1: ORGANIC - I (Nature of Bonding
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 1: ORGANIC - I (Nature of Bonding Module 4: Applications of Electronic Effects CHE_P1_M4 PAPER 1: ORGANIC - I (Nature of Bonding
Class -XII Topic : GOC DPP - 1 to 3. DPP No - 01
 UCLE CEMISTRY CLASSES FR IIT-JEE DPP RGAIC CEMISTRY Target IIT-JEE 2016 Class -XII Topic : GC DPP - 1 to 3 DPP o - 01 1. The inductive effect : implies the atom's and group s ability to cause bond polarization
UCLE CEMISTRY CLASSES FR IIT-JEE DPP RGAIC CEMISTRY Target IIT-JEE 2016 Class -XII Topic : GC DPP - 1 to 3 DPP o - 01 1. The inductive effect : implies the atom's and group s ability to cause bond polarization
CHEM 2312 practice final. Version - II
 EM 2312 practice final Version - II The following standardized final examination covers the entire introductory year of organic chemistry (EM 2311 and 2312 at Georgia Tech). The exam consists of 70 multiple
EM 2312 practice final Version - II The following standardized final examination covers the entire introductory year of organic chemistry (EM 2311 and 2312 at Georgia Tech). The exam consists of 70 multiple
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
CHEMISTRY - TRO 4E CH.21 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com TOPI: ORGANI EMISTRY Organic hemistry is the study of carbon and the other common nonmetals it is connected to:,, &. Some organic molecules are made of just carbons and hydrogens
!! www.clutchprep.com TOPI: ORGANI EMISTRY Organic hemistry is the study of carbon and the other common nonmetals it is connected to:,, &. Some organic molecules are made of just carbons and hydrogens
Organic Chemistry, 7 L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter , Prentice Hall
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms]
![Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms] Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms]](/thumbs/89/100347388.jpg) Program Name B.Sc. (Chemistry) B.Sc. - Part I Paper Code CH- 02 (Organic chemistry) Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Each Question Carries 2 Marks Part -1 1. Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital
Program Name B.Sc. (Chemistry) B.Sc. - Part I Paper Code CH- 02 (Organic chemistry) Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Each Question Carries 2 Marks Part -1 1. Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital
Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry
 Lesmahagow High School AHChemistry Organic Chemistry& Instrumental Analysis Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Organic Chemistry and Instrumental Analysis Alkanes, Alkenes and
Lesmahagow High School AHChemistry Organic Chemistry& Instrumental Analysis Lesmahagow High School CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Organic Chemistry and Instrumental Analysis Alkanes, Alkenes and
CPT-26 ANSWERS 73. (1) 145. (4) 2. (1) 74. (3) 146. (4) 3. (3) 75. (2) 147. (3) 4. (2) 5. (4) 76. (4) 77. (2) 148. (2) 149. (3) 6. (3) 78.
 1 08/01/2018 COMMON PRACTICE TEST [PMT] : 2017-19 CPT-26 ANSWERS CODE GOL 1. (1) 37. (3) 73. (1) 109. (3) 145. (4) 2. (1) 38. (1) 74. (3) 110. (3) 146. (4) 3. (3) 39. (1) 75. (2) 111. (2) 147. (3) 4. (2)
1 08/01/2018 COMMON PRACTICE TEST [PMT] : 2017-19 CPT-26 ANSWERS CODE GOL 1. (1) 37. (3) 73. (1) 109. (3) 145. (4) 2. (1) 38. (1) 74. (3) 110. (3) 146. (4) 3. (3) 39. (1) 75. (2) 111. (2) 147. (3) 4. (2)
2/28/2011. Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions. Organic Chemical Reactions. 6.1 Kinds of Organic Reactions
 John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions CHP 6 Problems: 6.1-13, 17-36. Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions
John E. McMurry http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 6 An Overview of Organic Reactions CHP 6 Problems: 6.1-13, 17-36. Richard Morrison University of Georgia, Athens Organic Chemical Reactions
Treatment of cyclooctatetrene with potassium gives you a dianion. Classify the starting material and product as aromatic, antiaromatic or
 Treatment of cyclooctatetrene with potassium gives you a dianion. Classify the starting material and product as aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic? 1 2 Classify cyclononatetrene and it s various ions
Treatment of cyclooctatetrene with potassium gives you a dianion. Classify the starting material and product as aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic? 1 2 Classify cyclononatetrene and it s various ions
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number CHM 235 (SUN# CHM 2235) Title General Organic Chemistry I Credits 4 Developed
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Organic Chemistry I Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number CHM 235 (SUN# CHM 2235) Title General Organic Chemistry I Credits 4 Developed
Chemistry 2030 Survey of Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2015 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 Chemistry 2030 Survey of Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2015 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #2 Reactions of Alkenes & Alkynes, Chemistry of Aromatic Compounds, and Stereochemistry Thursday, October 8,
Chemistry 2030 Survey of Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2015 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #2 Reactions of Alkenes & Alkynes, Chemistry of Aromatic Compounds, and Stereochemistry Thursday, October 8,
Chapter 8: Chemistry of Alkynes (C n H 2n-2 )
 hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
Reaction mechanisms offer us insights into how reactions work / how molecules react with one another.
 Introduction 1) Lewis Structures 2) Representing Organic Structures 3) Geometry and Hybridization 4) Electronegativities and Dipoles 5) Resonance Structures (a) Drawing Them (b) Rules for Resonance 6)
Introduction 1) Lewis Structures 2) Representing Organic Structures 3) Geometry and Hybridization 4) Electronegativities and Dipoles 5) Resonance Structures (a) Drawing Them (b) Rules for Resonance 6)
The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature of alkenes.
 Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Chemistry 2030 Survey of Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2015 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 Chemistry 2030 Survey of Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2015 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #2 Reactions of Alkenes & Alkynes, Chemistry of Aromatic Compounds, and Stereochemistry Thursday, October 8,
Chemistry 2030 Survey of Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2015 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #2 Reactions of Alkenes & Alkynes, Chemistry of Aromatic Compounds, and Stereochemistry Thursday, October 8,
Arrange the following alkene in increasing order of their enthalpy of hydrogenation ( )
 Q.1. Which of the statements is correct? (I) Melting point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms and with increase in branching. (II) Boiling point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms but
Q.1. Which of the statements is correct? (I) Melting point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms and with increase in branching. (II) Boiling point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms but
Exam. Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? 1) A) All of the carbon
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? 1) A) All of the carbon
SCIENCEBEAM SYLLABUS CLASS VI MATHEMATICS CLASS VI - SCIENCE
 SCIENCEBEAM SYLLABUS CLASS VI MATHEMATICS Number system HCF, LCM, Prime factorisation Whole numbers Negative numbers and Integers Fractions Algebra Ratio and Proportion Geometry Mensuration- area and perimeter
SCIENCEBEAM SYLLABUS CLASS VI MATHEMATICS Number system HCF, LCM, Prime factorisation Whole numbers Negative numbers and Integers Fractions Algebra Ratio and Proportion Geometry Mensuration- area and perimeter
