INTRODUCTION TO ELECTROLYSIS (ELECTROLYTIC CELL)
|
|
|
- Crystal Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1
2 INTRODUCTION TO ELECTROLYSIS (ELECTROLYTIC CELL) 1.Electrolysis is defined simply as the decomposition of a compound by an electric current/electricity. A compound that is decomposed by an electric current is called an electrolyte. Some electrolytes are weak while others are strong. 2.Strong electrolytes are those that are fully ionized/dissociated into (many) ions. Common strong electrolytes include: (i)all mineral acids (ii)all strong alkalis/sodium hydroxide/potassium hydroxide. (iii)all soluble salts 3.Weak electrolytes are those that are partially/partly ionized/dissociated into (few) ions. Common weak electrolytes include: (i)all organic acids (ii)all bases except sodium hydroxide/potassium hydroxide. (iii)water 4. A compound that is not decomposed by an electric current is called nonelectrolyte. Non-electrolytes are those compounds /substances that exist as molecules and thus cannot ionize/dissociate into(any) ions. Common non-electrolytes include: (i) most organic solvents (e.g. petrol/paraffin/benzene/methylbenzene/ethanol) (ii)all hydrocarbons(alkanes /alkenes/alkynes) (iii)chemicals of life(e.g. proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, starch, sugar) 5. An electrolytes in solid state have fused /joined ions and therefore do not conduct electricity but the ions (cations and anions) are free and mobile in molten and aqueous (solution, dissolved in water) state. 6.During electrolysis, the free ions are attracted to the electrodes. An electrode is a rod through which current enter and leave the electrolyte during electrolysis. 2
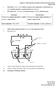
3 An electrode that does not influence/alter the products of electrolysis is called an inert electrode. Common inert electrodes include: (i)platinum (ii)carbon graphite Platinum is not usually used in a school laboratory because it is very expensive. Carbon graphite is easily/readily and cheaply available (from used dry cells). 7.The positive electrode is called Anode.The anode is the electrode through which current enter the electrolyte/electrons leave the electrolyte 8.The negative electrode is called Cathode. The cathode is the electrode through which current leave the electrolyte / electrons enter the electrolyte 9. During the electrolysis, free anions are attracted to the anode where they lose /donate electrons to form neutral atoms/molecules. i.e. M(l) -> M + (l) + e (for cations from molten electrolytes) M(s) -> M + (aq) + e (for cations from electrolytes in aqueous state / solution / dissolved in water) The neutral atoms /molecules form the products of electrolysis at the anode. This is called discharge at anode 10. During electrolysis, free cations are attracted to the cathode where they gain /accept/acquire electrons to form neutral atoms/molecules. X + (aq) + 2e -> X(s) (for cations from electrolytes in aqueous state / solution / dissolved in water) 2X + (l) + 2e -> X (l) (for cations from molten electrolytes) The neutral atoms /molecules form the products of electrolysis at the cathode. This is called discharge at cathode. 11. The below set up shows an electrolytic cell. 3
4 Simple set up of electrolytic cell Gaseous product at cathode Gaseous product at anode Electrolyte Cathode(-) Anode(+) Battery 12. For a compound /salt containing only two ion/binary salt the products of electrolysis in an electrolytic cell can be determined as in the below examples: a)to determine the products of electrolysis of molten Lead(II)chloride (i)decomposition of electrolyte into free ions; PbCl 2 (l) -> Pb 2+ (l) + 2Cl - (l) (ii)at the cathode/negative electrode(-); Pb 2+ (l) + 2e -> Pb (l) (Cation / Pb 2+ gains / accepts / acquires electrons to form free atom) 2Cl - (l) -> Cl 2 (g) + 2e (Anion / Cl - donate/lose electrons to form free atom then a gas molecule) I.At the cathode grey beads /solid lead metal. II.At the anode pale green chlorine gas. b)to determine the products of electrolysis of molten Zinc bromide 4
5 (i)decomposition of electrolyte into free ions; ZnBr 2 (l) -> Zn 2+ (l) + 2Br - (l) (ii)at the cathode/negative electrode(-); Zn 2+ (l) + 2e -> Zn(l) (Cation / Zn 2+ gains / accepts / acquires electrons to form free atom) 2Br - (l) -> Br 2 (g) + 2e (Anion / Br - donate/lose electrons to form free atom then a liquid molecule which change to gas on heating) I.At the cathode grey beads /solid Zinc metal. II.At the anode red bromine liquid / red/brown bromine gas. c)to determine the products of electrolysis of molten sodium chloride (i)decomposition of electrolyte into free ions; NaCl (l) -> Na + (l) + Cl - (l) (ii)at the cathode/negative electrode(-); 2Na + (l) + 2e -> Na (l) (Cation / Na + gains / accepts / acquires electrons to form free atom) 2Cl - (l) -> Cl 2 (g) + 2e (Anion / Cl - donate/lose electrons to form free atom then a gas molecule) I.At the cathode grey beads /solid sodium metal. II.At the anode pale green chlorine gas. d)to determine the products of electrolysis of molten Aluminium (III)oxide (i)decomposition of electrolyte into free ions; Al 2 O 3 (l) -> 2Al 3+ (l) + 3O 2- (l) 5
6 (ii)at the cathode/negative electrode(-); 4Al 3+ (l) + 12e -> 4Al (l) (Cation / Al 3+ gains / accepts / acquires electrons to form free atom) 6O 2- (l) -> 3O 2 (g) + 12e (Anion /6O 2- donate/lose 12 electrons to form free atom then three gas molecule) I.At the cathode grey beads /solid aluminium metal. II.At the anode colourless gas that relights/rekindles glowing splint. 13.In industries electrolysis has the following uses/applications: (a)extraction of reactive metals from their ores. Potassium, sodium,magnesium, and aluminium are extracted from their ores using electrolytic methods. (b)purifying copper after exraction from copper pyrites ores. Copper obtained from copper pyrites ores is not pure. After extraction, the copper is refined by electrolysing copper(ii)sulphate(vi) solution using the impure copper as anode and a thin strip of pure copper as cathode. Electrode ionization take place there: (i)at the cathode; Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e -> Cu(s) (Pure copper deposits on the strip (ii)at the anode; Cu(s) ->Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e (impure copper erodes/dissolves) (c)electroplating The label EPNS(Electro Plated Nickel Silver) on some steel/metallic utensils mean they are plated/coated with silver and/or Nickel to improve their appearance(add their aesthetic value)and prevent/slow corrosion(rusting of iron). Electroplating is the process of coating a metal with another metal using an electric current. During electroplating, the cathode is made of the metal to be coated/impure. Example: During the electroplating of a spoon with silver (i)the spoon/impure is placed as the cathode(negative terminal of battery) (ii)the pure silver is placed as the anode(positive terminal of battery) (iii)the pure silver erodes/ionizes/dissociates to release electrons: Ag(s) ->Ag + (aq) + e (impure silver erodes/dissolves) 6
7 (iv) silver (Ag + )ions from electrolyte gain electrons to form pure silver deposits / coat /cover the spoon/impure Ag + (aq) + e ->Ag(s) (pure silver deposits /coat/cover on spoon) 7
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science
 IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Chemistry 5 - Electricity and Chemistry Electrolysis You need to know that electrolysis is: - The breakdown of ionic substances into their constituent elements
3. Solids cannot conduct electricity because the ions cannot move freely 4. Electrolytic cell
 Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chapter 6 Electrochemistry (Credits to Thennarasu Pannirselvam) Page 1 of 10 1. Electrolysis : Process where molten or aqueous state compounds are broken down into their constitute elements by passing
Chemistry std10 ELECTROLYSIS Important terms in Electrolysis
 Chemistry std10 ELECTROLYSIS Important terms in Electrolysis 1) Electrolysis: it is the process of decomposition of a chemical compound in aqueous solution or fused state by the passage of a direct electric
Chemistry std10 ELECTROLYSIS Important terms in Electrolysis 1) Electrolysis: it is the process of decomposition of a chemical compound in aqueous solution or fused state by the passage of a direct electric
5.0 Electricity and Chemistry
 5.0 Electricity and hemistry Question Paper Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic Electricity and hemistry Sub-Topic 5.0 Electricity and hemistry ooklet
5.0 Electricity and hemistry Question Paper Level IGSE Subject hemistry (0620) Exam oard ambridge International Examinations (IE) Topic Electricity and hemistry Sub-Topic 5.0 Electricity and hemistry ooklet
Lesson on Electrolysis
 Lesson on Electrolysis This lesson package includes a lesson plan, a worksheet for students, and teachers notes on the worksheet. Activity Lesson 1 (50 min-2 Period lesson) Teacher explains (page 1 to
Lesson on Electrolysis This lesson package includes a lesson plan, a worksheet for students, and teachers notes on the worksheet. Activity Lesson 1 (50 min-2 Period lesson) Teacher explains (page 1 to
Unit 4: Chemical Changes (Higher Content)
 Metals react with oxygen to produce metal oxides. E.g. Copper + Oxygen > Copper Oxide The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metals gain oxygen. Reactivity of Metals Metal Extraction Metals
Metals react with oxygen to produce metal oxides. E.g. Copper + Oxygen > Copper Oxide The reactions are oxidation reactions because the metals gain oxygen. Reactivity of Metals Metal Extraction Metals
In the exam, you will be asked to tackle questions such as the one below. 6 volt d.c. power supply
 Get started AO1, AO2 3 Electrolysis Electrolysis is the decomposition (breakdown) of a compound using electricity. This unit will help you to explain what happens in electrolysis and to predict and explain
Get started AO1, AO2 3 Electrolysis Electrolysis is the decomposition (breakdown) of a compound using electricity. This unit will help you to explain what happens in electrolysis and to predict and explain
Electrochemistry. Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts
 Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Part One: Introduction to Electrolysis and the Electrolysis of Molten Salts What do I need to know about electrochemistry? Electrochemistry Learning Outcomes: Candidates should be able to: a) Describe
Electrolytic processes Notes
 Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Topic 3: Chemical changes Electrolytic processes Notes 3.22 Recall that electrolytes are ionic compounds in the molten state or dissolved in water When an ionic substance is melted
Edexcel GCSE Chemistry Topic 3: Chemical changes Electrolytic processes Notes 3.22 Recall that electrolytes are ionic compounds in the molten state or dissolved in water When an ionic substance is melted
Definition 1 An element or compound is oxidized when it gains oxygen atoms
 Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Oxidation and Reduction Part I Learning Outcomes 1. Introduction to oxidation and reduction: simple examples only, e.g. Na with Cl 2, Mg with O 2, Zn with Cu 2+. 2. Oxidation and reduction in terms of
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry. Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry. Notes.
 Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 5: Electricity and chemistry Notes Define electrolysis as The breakdown of an ionic compound, molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of electricity Describe the electrode
Electrolysis. Question Paper. Cambridge International Examinations. Score: /48. Percentage: /100
 Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
Electrolysis Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic ooklet O Level hemistry ambridge International Examinations Electrolysis Question Paper Time llowed: 58 minutes Score: /48 Percentage: /100 1 queous
11.3. Electrolytic Cells. Electrolysis of Molten Salts. 524 MHR Unit 5 Electrochemistry
 11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
Electrolysis. Introduction. Electrolysis APPENDIX. The key ideas required to understand this section are:
 Electrolysis APPENDIX 7 1 Introduction The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Redox reactions 100 Writings and balancing redox equations 104 Standard electrode potentials
Electrolysis APPENDIX 7 1 Introduction The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Redox reactions 100 Writings and balancing redox equations 104 Standard electrode potentials
Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Process. The Galvanic Cell or Voltaic Cell
 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Process The conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy are electrochemical process. Recall that an
Electrochemistry Electrochemical Process The conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy are electrochemical process. Recall that an
Aim: What are electrochemical cells?
 Aim: What are electrochemical cells? Electrochemistry Electrochemistry- involves a redox reaction and a flow of electrons TWO TYPES of ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 1.Voltaic (similar to a battery) 2.Electrolytic
Aim: What are electrochemical cells? Electrochemistry Electrochemistry- involves a redox reaction and a flow of electrons TWO TYPES of ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 1.Voltaic (similar to a battery) 2.Electrolytic
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC TEXT REFERENCE. Electrochemistry. Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18. Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1
 Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Electrodes are normally made out of inert (unreactive) materials. Graphite and platinum are common electrode materials.
 Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
Electrolysis Electrolysis is using an electric current to break up an ionic compound to form elements. Covalent compounds can t be split up by electrolysis. Terms used in electrolysis: Electrolyte - the
YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min
 YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Useful data: Q = It. Faraday Constant = 96,500 C mol -1. Use the Periodic table, given below, where necessary. Marks Grid [For Examiners use only] Question
YEAR 10 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min NAME: CLASS: Useful data: Q = It. Faraday Constant = 96,500 C mol -1. Use the Periodic table, given below, where necessary. Marks Grid [For Examiners use only] Question
Electrolysis 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016
 Electrolysis 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Electrolysis 2 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are ionic compounds? 3 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Ionic compounds are made up of positive ions and negative ions. What
Electrolysis 1 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Electrolysis 2 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What are ionic compounds? 3 of 21 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Ionic compounds are made up of positive ions and negative ions. What
Chapter 32. Electrolysis
 Chapter 32 Electrolysis 32.1 Electrolysis a type of redox reactions 32.2 Predicting preferential discharge of ions 32.3 Electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid 32.4 Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution
Chapter 32 Electrolysis 32.1 Electrolysis a type of redox reactions 32.2 Predicting preferential discharge of ions 32.3 Electrolysis of dilute sulphuric acid 32.4 Electrolysis of sodium chloride solution
MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet I. Term I. Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY
![MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet I. Term I. Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL. Work sheet I. Term I. Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY](/thumbs/90/103695152.jpg) MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Work sheet I Term I Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY 1. The diagram shows how aluminium is manufactured by electrolysis. What are the anode and
MARIYA INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL Work sheet I Term I Level 9 Chemistry [PAPER 1-MCQ] Name: ELECTRICITY AND CHEMISTRY 1. The diagram shows how aluminium is manufactured by electrolysis. What are the anode and
MC 17 C SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section.
 Question 1. (a) SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Choose from the following list of substances, as to what matches the description from to given below : [Bronze,
Question 1. (a) SECTION - I (40 marks) Compulsory : Attempt all questions from this section. Choose from the following list of substances, as to what matches the description from to given below : [Bronze,
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
C4 Quick Revision Questions
 C4 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 Write the equation which shows the formation of iron oxide Answer 1... of 50 4Fe + 3O 2 2Fe 2 O 3 Question
C4 Quick Revision Questions H = Higher tier only SS = Separate science only Question 1... of 50 Write the equation which shows the formation of iron oxide Answer 1... of 50 4Fe + 3O 2 2Fe 2 O 3 Question
(i) Voltameter consist of a vessel, two electrodes and electrolytic solution.
 Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes taking place in redox reactions i.e., how chemical energy produced
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical changes taking place in redox reactions i.e., how chemical energy produced
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice
 IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al
IB Topics 9 & 19 Multiple Choice Practice 1. What are the oxidation states of chromium in (NH 4) 2Cr 2O 7 (s) and Cr 2O 3 (s)? 2. Which of the following is a redox reaction? 3Mg (s) + 2AlCl 3 (aq) 2Al
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW. C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3. A. Fe B. CO
 CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW 1. The following represents the process used to produce iron from iron III oxide: Fe 2 O 3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO 2 What is the reducing agent in this process? A. Fe B. CO C. CO 2 D. Fe 2 O 3
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes
 4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
4.4. Revision Checklist: Chemical Changes Reactivity of metals When metals react with other substances the metal atoms form positive ions. The reactivity of a metal is related to its tendency to form positive
Today s Objectives: and an electrolytic cell. standard cell potentials. Section 14.3 (pp )
 Today s Objectives: 1. Identify the similarities and differences between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell 2. Predict the spontaneity of REDOX reactions based on standard cell potentials. 3. Recognize
Today s Objectives: 1. Identify the similarities and differences between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell 2. Predict the spontaneity of REDOX reactions based on standard cell potentials. 3. Recognize
Chemistry 102 Chapter 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS
 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful
 What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful work. This is accomplished by constructing a voltaic
What is the importance of redox reactions? Their importance lies in the fact that we can use the transfer of electrons between species to do useful work. This is accomplished by constructing a voltaic
Electrochemical Cells
 CH302 LaBrake and Vanden Bout Electrochemical Cells Experimental Observations of Electrochemical Cells 1. Consider the voltaic cell that contains standard Co 2+ /Co and Au 3+ /Au electrodes. The following
CH302 LaBrake and Vanden Bout Electrochemical Cells Experimental Observations of Electrochemical Cells 1. Consider the voltaic cell that contains standard Co 2+ /Co and Au 3+ /Au electrodes. The following
Electrolysis. Specification points. Year 11 Electrolysis
 Electrolysis Specification points Year Electrolysis The process of electrolysis When an ionic compound is melted or dissolved in water, the ions are free to move about within the liquid or solution (the
Electrolysis Specification points Year Electrolysis The process of electrolysis When an ionic compound is melted or dissolved in water, the ions are free to move about within the liquid or solution (the
(Q.) By which process, we can easily obtain gold ornaments at cheaper costs? (1 Mark)
 Science Class 8 (CBSE) Page: 1 (Q.) Define electrolysis. (1 Mark) (Ans) The chemical reaction (decomposition) of an electrolyte (conducting liquid) into its componentswhen electricity is passed through
Science Class 8 (CBSE) Page: 1 (Q.) Define electrolysis. (1 Mark) (Ans) The chemical reaction (decomposition) of an electrolyte (conducting liquid) into its componentswhen electricity is passed through
Topic IV. Electrolysis
 IV. Electrolysis Page 1 Topic IV. Electrolysis Reference Reading Integrated Chemistry Today, L.H.M. Chung, Book 1 pg. 316 335 Objectives 3.4 understand that electrical energy can cause redox reactions
IV. Electrolysis Page 1 Topic IV. Electrolysis Reference Reading Integrated Chemistry Today, L.H.M. Chung, Book 1 pg. 316 335 Objectives 3.4 understand that electrical energy can cause redox reactions
NABTEB Past Questions and Answers - Uploaded online
 NATIONAL BUSINESS AND TECHNICAL EXAMINATIONS BOARD (GENERAL EDUCATION EXAMINATION) CHEMISTRY 005-1 (100 Marks) MAY/JUNE 2006. QUESTION AND ANSWER. TIME: 1 HR 40 MINS (1a) An atom has 14 neutrons in the
NATIONAL BUSINESS AND TECHNICAL EXAMINATIONS BOARD (GENERAL EDUCATION EXAMINATION) CHEMISTRY 005-1 (100 Marks) MAY/JUNE 2006. QUESTION AND ANSWER. TIME: 1 HR 40 MINS (1a) An atom has 14 neutrons in the
Worked solutions. Chapter 9. Exercises O 3
 Worked solutions Chapter 9 Exercises 1 The numbers are assigned following the strategy on page 408. In most of these it is best to assign the values for [2] and H [+1] first, and then assign values to
Worked solutions Chapter 9 Exercises 1 The numbers are assigned following the strategy on page 408. In most of these it is best to assign the values for [2] and H [+1] first, and then assign values to
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction
 9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS NAME ROW PD
 4-26-12 NAME ROW PD (1) Which statement describes the redox reaction that occurs when an object is electroplated? The diagram below shows the electrolysis of fused KCl. A) It is spontaneous and requires
4-26-12 NAME ROW PD (1) Which statement describes the redox reaction that occurs when an object is electroplated? The diagram below shows the electrolysis of fused KCl. A) It is spontaneous and requires
 Today we are going to be introducing the basic ideals of electrolysis, just what you need to get a basic ideal. in the future topic will go further in that. Essential ideas Conduction of electricity through
Today we are going to be introducing the basic ideals of electrolysis, just what you need to get a basic ideal. in the future topic will go further in that. Essential ideas Conduction of electricity through
Sindh Text Book Board, Jamshoro. ELECTROCHEMISTRY
 Chapter # 8 ELECTROCHEMISTRY You will learn in this chapter about: Electrolytes and non-electrolytes. Electrolysis. Electrolysis of molten NaCl. Electrolysis of water. Faraday's laws of electrolysis. Electrochemical
Chapter # 8 ELECTROCHEMISTRY You will learn in this chapter about: Electrolytes and non-electrolytes. Electrolysis. Electrolysis of molten NaCl. Electrolysis of water. Faraday's laws of electrolysis. Electrochemical
Conductivity of Electrolytes in Solution
 Conductivity of Electrolytes in Solution Introduction: Electrical current can be thought of as the movement of electrons or ionic charges from an area of high potential to an area of low potential. Materials
Conductivity of Electrolytes in Solution Introduction: Electrical current can be thought of as the movement of electrons or ionic charges from an area of high potential to an area of low potential. Materials
Figure 1. Describe what happens when two atoms of potassium react with one atom of sulfur. Give your answer in terms of electron transfer
 Q1.Figure 1 shows the outer electrons in an atom of the Group 1 element potassium and in an atom of the Group 6 element sulfur. Figure 1 (a) Potassium forms an ionic compound with sulfur. Describe what
Q1.Figure 1 shows the outer electrons in an atom of the Group 1 element potassium and in an atom of the Group 6 element sulfur. Figure 1 (a) Potassium forms an ionic compound with sulfur. Describe what
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
GraspIT AQA GCSE Chemical and Energy Changes
 A. Reactivity of metals The reactivity series, metal oxides and extractions 1. Three metals, X, Y and Z were put into water. The reactions are shown below: a) Use the diagrams to put metals X, Y and Z
A. Reactivity of metals The reactivity series, metal oxides and extractions 1. Three metals, X, Y and Z were put into water. The reactions are shown below: a) Use the diagrams to put metals X, Y and Z
AP Questions: Electrochemistry
 AP Questions: Electrochemistry I 2 + 2 S 2O 2-3 2 I - + S 4O 2-6 How many moles of I 2 was produced during the electrolysis? The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected
AP Questions: Electrochemistry I 2 + 2 S 2O 2-3 2 I - + S 4O 2-6 How many moles of I 2 was produced during the electrolysis? The hydrogen gas produced at the cathode during the electrolysis was collected
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding Learning Objectives Describe the formation of ions by electron loss/gain to obtain the electronic configuration of a noble gas. Describe the formation of ionic bonds between
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding Learning Objectives Describe the formation of ions by electron loss/gain to obtain the electronic configuration of a noble gas. Describe the formation of ionic bonds between
4.4.1 Reactivity of metals Metal oxides The reactivity series. Key opportunities for skills development.
 4.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
4.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
Solved Examples On Electrochemistry
 Solved Examples On Electrochemistry Example 1. Find the charge in coulomb on 1 g-ion of Charge on one ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 coulomb Thus, charge on one g-ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 6.02 10 23 = 2.89
Solved Examples On Electrochemistry Example 1. Find the charge in coulomb on 1 g-ion of Charge on one ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 coulomb Thus, charge on one g-ion of N 3- = 3 1.6 10-19 6.02 10 23 = 2.89
ELECTROCHEMISTRY OXIDATION-REDUCTION
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. covalent ionic non-metallic
 1 The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. (a) (i) Choose a word from the box to complete the sentence. covalent ionic non-metallic Electrolysis takes place when electricity
1 The electrolysis of sodium chloride solution produces useful substances. (a) (i) Choose a word from the box to complete the sentence. covalent ionic non-metallic Electrolysis takes place when electricity
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015
 Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Grade 11B Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2015 Chemistry - I Duration: 1.00 Hour Part 1 1) A liquid boils at a temperature of 100 o C. Which other property of the liquid
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Answer all the questions. 1. During the electrolysis of molten potassium chloride, what is made at the cathode?
 Answer all the questions. 1. During the electrolysis of molten potassium chloride, what is made at the cathode? A chlorine B hydrogen C potassium D potassium hydroxide Your answer [1] OCR 2018. You may
Answer all the questions. 1. During the electrolysis of molten potassium chloride, what is made at the cathode? A chlorine B hydrogen C potassium D potassium hydroxide Your answer [1] OCR 2018. You may
GCSE Additional Science
 GCSE Additional Science Module C5 Chemicals of the Natural Environment: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this
GCSE Additional Science Module C5 Chemicals of the Natural Environment: What you should know Name: Science Group: Teacher: each of the statements to help focus your revision: R = Red: I don t know this
Extracting metals QuestionIT
 Extracting metals QuestionIT 1. What is an ore? Metal compound in a rock. 2. What is produced when metals react with oxygen? Metal oxide. 3. What is this process called and why? Oxidation, gain of oxygen.
Extracting metals QuestionIT 1. What is an ore? Metal compound in a rock. 2. What is produced when metals react with oxygen? Metal oxide. 3. What is this process called and why? Oxidation, gain of oxygen.
Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes
 Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes Chemical Activity (or Chemical Reactivity) is the measure of the reactivity of elements. If an element has high activity, then it means that the element is willing to
Oxidation & Reduction (Redox) Notes Chemical Activity (or Chemical Reactivity) is the measure of the reactivity of elements. If an element has high activity, then it means that the element is willing to
One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday Q=It One mole of any gas occupies 22.4dm 3 at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p.
 1 One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday Q=It One mole of any gas occupies 22.4dm 3 at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p.) Standard temperature is 0 0 C or 273K and standard
1 One mole of electrons carries a charge of 96500C or 1 Faraday Q=It One mole of any gas occupies 22.4dm 3 at standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p.) Standard temperature is 0 0 C or 273K and standard
5.4 Chemical changes Reactivity of metals Metal oxides The reactivity series. Key opportunities for skills development
 5.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
5.4 Chemical changes Understanding of chemical changes began when people began experimenting with chemical reactions in a systematic way and organising their results logically. Knowing about these different
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Cells
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
EFFECT OF AN ELECTRIC CURRENT ON SUBSTANCES
 CHEMISTRY TOPIC WORKSHEETS/TESTS NAME:.... SCHOOL: EFFECT OF AN ELECTRIC CURRENT ON SUBSTANCES 1. The set-up was used to electrolyse Lead (II) bromide. Study it and answer the questions that follow; Anode
CHEMISTRY TOPIC WORKSHEETS/TESTS NAME:.... SCHOOL: EFFECT OF AN ELECTRIC CURRENT ON SUBSTANCES 1. The set-up was used to electrolyse Lead (II) bromide. Study it and answer the questions that follow; Anode
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species.
 Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
Introduction Oxidation/reduction reactions involve the exchange of an electron between chemical species. The species that loses the electron is oxidized. The species that gains the electron is reduced.
(c) dilute solution of glucose (d) chloroform 12 Which one of the following represents the same net reaction as the electrolysis of aqueous H2SO4
 1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
V-25: You Light Up My Life Classifying Substances ChemCatalyst
 V-25: You Light Up My Life Classifying Substances ChemCatalyst 1. If you were to drop a spoonful of salt, NaCl, into a glass of water, what would happen? 2. If you were to drop a gold ring into a glass
V-25: You Light Up My Life Classifying Substances ChemCatalyst 1. If you were to drop a spoonful of salt, NaCl, into a glass of water, what would happen? 2. If you were to drop a gold ring into a glass
Section A: Summary Notes
 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 25 AUGUST 2015 Section A: Summary Notes Important definitions: Oxidation: the loss of electrons by a substance during a chemical reaction Reduction: the gain of electrons by a substance
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 25 AUGUST 2015 Section A: Summary Notes Important definitions: Oxidation: the loss of electrons by a substance during a chemical reaction Reduction: the gain of electrons by a substance
Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction
 Name Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction 1. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4? Hydrogen Sulfur Oxygen A. +1 +6 2 B. +1 +4 2 C. +2 +1 +4 D. +2 +6 8 2. Consider
Name Practice Exam Topic 9: Oxidation & Reduction 1. What are the oxidation numbers of the elements in sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4? Hydrogen Sulfur Oxygen A. +1 +6 2 B. +1 +4 2 C. +2 +1 +4 D. +2 +6 8 2. Consider
Chemical measurements QuestionIT
 Chemical measurements QuestionIT 1. What is the law of conservation of mass? Mass of reactants = mass products. 2. Why might some reactions appear to show a change in mass? A reactant or a product is a
Chemical measurements QuestionIT 1. What is the law of conservation of mass? Mass of reactants = mass products. 2. Why might some reactions appear to show a change in mass? A reactant or a product is a
Oxidation-Reduction Review. Electrochemistry. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Sample Problem.
 1 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction Review Topics Covered Oxidation-reduction reactions Balancing oxidationreduction equations Voltaic cells Cell EMF Spontaneity of redox reactions Batteries Electrolysis
1 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction Review Topics Covered Oxidation-reduction reactions Balancing oxidationreduction equations Voltaic cells Cell EMF Spontaneity of redox reactions Batteries Electrolysis
IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date...
 IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date... 1 Winston Churchill, a British Prime Minister, had his false teeth electroplated with gold. The teeth were coated with a thin layer of carbon and were then placed
IGCSE TEST_ (Ch. 2,3,4,5,6) Name... Date... 1 Winston Churchill, a British Prime Minister, had his false teeth electroplated with gold. The teeth were coated with a thin layer of carbon and were then placed
1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number
 General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
General Chemistry II Exam 4 Practice Problems 1 1.In which of the following is the oxidation number of the underlined element given incorrectly? oxidation number a. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 +6 b. NaAl(OH) 4 +3 c.
8.1 The Ionic Theory.
 Chemistry Form 4 Page 21 Ms. R. Buttigieg 8.1 The Ionic Theory. What you should Learn: Writing formulae for cations and anions Writing ionic formulae for ionic substances Representing the change from atoms/molecules
Chemistry Form 4 Page 21 Ms. R. Buttigieg 8.1 The Ionic Theory. What you should Learn: Writing formulae for cations and anions Writing ionic formulae for ionic substances Representing the change from atoms/molecules
Net Ionic Equations. Making Sense of Chemical Reactions
 Making Sense of Chemical Reactions Now that you have mastered writing balanced chemical equations it is time to take a deeper look at what is really taking place chemically in each reaction. There are
Making Sense of Chemical Reactions Now that you have mastered writing balanced chemical equations it is time to take a deeper look at what is really taking place chemically in each reaction. There are
GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL
 GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL Embracing Diversity Half Yearly Exams 2013-2014 FORM 4 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min Name: Class: Useful Data: One Faraday is equivalent to 96500 C. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 H 1
GOZO COLLEGE BOYS SECONDARY SCHOOL Embracing Diversity Half Yearly Exams 2013-2014 FORM 4 CHEMISTRY TIME: 1h 30min Name: Class: Useful Data: One Faraday is equivalent to 96500 C. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 H 1
Unit 8 Redox 8-1. At the end of this unit, you ll be able to
 8-1 Unit 8 Redox At the end of this unit, you ll be able to Define and identify oxidation reactions Define and identify reduction reactions Assign oxidation numbers to elements in a compound Write and
8-1 Unit 8 Redox At the end of this unit, you ll be able to Define and identify oxidation reactions Define and identify reduction reactions Assign oxidation numbers to elements in a compound Write and
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E.
 MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - II - SET -A 020 Periodic Table, Chemical bonding, Acid, Bases and Salts, Practical Work, Mole Concept, Electrolysis Chemistry
MAHESH TUTORIALS I.C.S.E. GRADE - X (2017-2018) Exam No. : MT/ICSE/SEMI PRELIM - II - SET -A 020 Periodic Table, Chemical bonding, Acid, Bases and Salts, Practical Work, Mole Concept, Electrolysis Chemistry
Practice Packet Unit 13: Electrochemistry (RedOx)
 Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 13: Electrochemistry (RedOx) Redox and Batteries? Ain t nobody got time for that!!! 1 Lesson 1: Oxidation States Oxidation numbers are very important
Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 13: Electrochemistry (RedOx) Redox and Batteries? Ain t nobody got time for that!!! 1 Lesson 1: Oxidation States Oxidation numbers are very important
Electrochemistry Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid
 Electrochemistry 18.1 Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid 18.3 Voltaic (or Galvanic) Cells: Generating Electricity from Spontaneous Chemical Reactions 18.4 Standard Electrode Potentials 18.7 Batteries:
Electrochemistry 18.1 Pulling the Plug on the Power Grid 18.3 Voltaic (or Galvanic) Cells: Generating Electricity from Spontaneous Chemical Reactions 18.4 Standard Electrode Potentials 18.7 Batteries:
Year 10 Track 3 CHEMISTRY Time: 1:30min
 Year 10 Track 3 CHEMISTRY Time: 1:30min Name: Class: Useful Data: A copy of the Periodic Table is printed below. Relative atomic mass may be taken as: Cu = 63.5 1 Faraday = 96, 500C Q = It Instructions
Year 10 Track 3 CHEMISTRY Time: 1:30min Name: Class: Useful Data: A copy of the Periodic Table is printed below. Relative atomic mass may be taken as: Cu = 63.5 1 Faraday = 96, 500C Q = It Instructions
2. Relative molecular mass, M r - The relative molecular mass of a molecule is the average mass of the one molecule when compared with
 Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations 1. Relative atomic mass, A r - The relative atomic mass of an element is the average mass of one atom of an element when compared with mass of an atom of carbon-12
Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations 1. Relative atomic mass, A r - The relative atomic mass of an element is the average mass of one atom of an element when compared with mass of an atom of carbon-12
CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems
 1. When the redox equation CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems MnO 4 (aq) + H + (aq) + H 3 AsO 3 (aq) Mn 2+ (aq) + H 3 AsO 4 (aq) + H 2 O(l) is properly balanced, the coefficients will
1. When the redox equation CHEMISTRY 13 Electrochemistry Supplementary Problems MnO 4 (aq) + H + (aq) + H 3 AsO 3 (aq) Mn 2+ (aq) + H 3 AsO 4 (aq) + H 2 O(l) is properly balanced, the coefficients will
Chapter 18. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-chemistry/ Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-chemistry/ Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes
(c) In marble, we assign calcium ion an oxidation number of +2, and oxygen a value of 2. We can determine the value of carbon in CaCO 3 as follows:
 Example Exercise 17.1 Calculating Oxidation Numbers for Carbon Calculate the oxidation number for carbon in each of the following compounds: (a) diamond, C (b) dry ice, CO 2 (c) marble, CaCO 3 (d) baking
Example Exercise 17.1 Calculating Oxidation Numbers for Carbon Calculate the oxidation number for carbon in each of the following compounds: (a) diamond, C (b) dry ice, CO 2 (c) marble, CaCO 3 (d) baking
CS C1 H Acid reactions and electrolysis
 Name: CS C1 H Acid reactions and electrolysis Date: Time: 47 minutes Total marks available: 47 Total marks achieved: Questions Q1. Acids (a) Magnesium carbonate reacts with dilute nitric acid. Give the
Name: CS C1 H Acid reactions and electrolysis Date: Time: 47 minutes Total marks available: 47 Total marks achieved: Questions Q1. Acids (a) Magnesium carbonate reacts with dilute nitric acid. Give the
Name: Regents Chemistry Date:
 Name: Date: 1. The reaction CuO + CO CO 2 + Cu is an example of (A) reduction, only (B) oxidation, only (C) both oxidation and reduction (D) neither oxidation nor reduction 6. In which compound does chlorine
Name: Date: 1. The reaction CuO + CO CO 2 + Cu is an example of (A) reduction, only (B) oxidation, only (C) both oxidation and reduction (D) neither oxidation nor reduction 6. In which compound does chlorine
Sample Exercise 20.2 Practice Exercise 1 with feedback
 Homework Chapter 20 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 16, 2016 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy Sample Exercise 20.2 Practice Exercise 1 with
Homework Chapter 20 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 16, 2016 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due. Grading Policy Sample Exercise 20.2 Practice Exercise 1 with
ICSE Chemistry Model Paper-9
 ICSE Chemistry Model Paper-9 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading the
ICSE Chemistry Model Paper-9 Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading the
Introduction to electrochemistry
 Introduction to electrochemistry Oxidation reduction reactions involve energy changes. Because these reactions involve electronic transfer, the net release or net absorption of energy can occur in the
Introduction to electrochemistry Oxidation reduction reactions involve energy changes. Because these reactions involve electronic transfer, the net release or net absorption of energy can occur in the
CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials. Compiled by. Dr. A.O. Oladebeye
 CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr. A.O. Oladebeye Department of Chemistry University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, Nigeria Electrochemical Cell Electrochemical
CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr. A.O. Oladebeye Department of Chemistry University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, Nigeria Electrochemical Cell Electrochemical
CHEMISTRY. SCIENCE Paper 2
 CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
CHEMISTRY SCIENCE Paper 2 (Two hours) Answers to this Paper must be written on the paper provided separately. You will not be allowed to write during the first 15 minutes. This time is to be spent in reading
i) An article X is to be plated with Nickel. Answer the following questions: c) Write the reactions that take place at cathode and anode.
 Work sheet Electrolysis i) An article X is to be plated with Nickel. Answer the following questions: a) Name the anode and cathode used. b) Name the electrolyte used. c) Write the reactions that take place
Work sheet Electrolysis i) An article X is to be plated with Nickel. Answer the following questions: a) Name the anode and cathode used. b) Name the electrolyte used. c) Write the reactions that take place
BATTERIES AND ELECTROLYTIC CELLS. Practical Electrochemistry
 BATTERIES AND ELECTROLYTIC CELLS Practical Electrochemistry How Batteries Work One of the most practical applications of spontaneous redox reactions is making batteries. In a battery, a spontaneous electron
BATTERIES AND ELECTROLYTIC CELLS Practical Electrochemistry How Batteries Work One of the most practical applications of spontaneous redox reactions is making batteries. In a battery, a spontaneous electron
Electrochemical Cells
 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Cells The Voltaic Cell Electrochemical Cell = device that generates electricity through redox rxns 1 Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell An electrochemical cell that produces an electrical
Electrochemistry Electrochemical Cells The Voltaic Cell Electrochemical Cell = device that generates electricity through redox rxns 1 Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell An electrochemical cell that produces an electrical
Electrochemistry Worksheets
 Electrochemistry Worksheets Donald Calbreath, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive
Electrochemistry Worksheets Donald Calbreath, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive
Partner: Judy 6 October An Activity Series
 Partner: Judy 6 October 2011 An Activity Series Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to verify the activity series of five metals and three halogens. This can be done by reacting the metal with various
Partner: Judy 6 October 2011 An Activity Series Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to verify the activity series of five metals and three halogens. This can be done by reacting the metal with various
Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions
 Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions 19-1 Oxidation and Reduction I. Oxidation States A. The oxidation rules (as summarized by Mr. Allan) 1. In compounds, hydrogen has an oxidation # of +1. In compounds,
Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions 19-1 Oxidation and Reduction I. Oxidation States A. The oxidation rules (as summarized by Mr. Allan) 1. In compounds, hydrogen has an oxidation # of +1. In compounds,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
Year 10 Chemistry. Practice questions. Topics
 Year 10 Chemistry Practice questions Topics 1 Group 1 2 Group 7 3 Reactivity series 4 Air and Water 5 Rates of reaction 6 Electrolysis 7 Acids, Alkali and Salts Objective: Evaluate group 1 & 7 reactivity
Year 10 Chemistry Practice questions Topics 1 Group 1 2 Group 7 3 Reactivity series 4 Air and Water 5 Rates of reaction 6 Electrolysis 7 Acids, Alkali and Salts Objective: Evaluate group 1 & 7 reactivity
