CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials. Compiled by. Dr. A.O. Oladebeye
|
|
|
- Marilyn McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHM 213 (INORGANIC CHEMISTRY): Applications of Standard Reduction Potentials Compiled by Dr. A.O. Oladebeye Department of Chemistry University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, Nigeria Electrochemical Cell Electrochemical cell is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy in an indirect redox reaction. An electrochemical cell can either drive an external electrical device (load) or be driven by it (power supply), depending upon the relative electromotive forces applied by the cell and the device. Oxidation and reduction half-reactions are kept separate in half-cells. Electron flow through a wire along with ion flow through a solution constitutes an electric circuit. It requires a conductive solid electrode to allow the transfer of electrons. Through external circuit Metal or graphite Requires ion exchange between the two half-cells of the system. Electrochemical Reactions The general form of the reaction can be written as: Spontaneity of Electrochemical Reactions A chemical reaction may or may not have a natural tendency to occur. If it has this tendency i.e., if it takes place spontaneously, it means, the net Gibbs Free Energy ( G) of the reaction (at that temperature and pressure) is negative. The spontaneity of any chemical reaction is well explained by thermodynamics. 1
2 At any given temperature and pressure, a negative Gibbs Energy change implies that the reaction will be spontaneous. Gibbs Free Energy, G is a state function (depends only on the thermodynamic state of the system, defined by quantities like P, T and composition). G= Η-Τ S For any spontaneous reaction, at any temperature and pressure, G is negative. This means, the driving force is the tendency to move towards lower Gibbs energy. This is favoured naturally by lower enthalpy (lowering of H i.e., negative Η favours negative value of G. Similarly, higher entropy (+ve S) is helpful in achieving lower G at a particular temperature and pressure. G is also related to the equilibrium constant of the reaction, K: G=-RT lnk G is related to electrode potential, E G= -nfe where, n is the number of electrons being transferred in the electrode reaction (reduction or oxidation) and F is faraday. Redox Reaction A redox reaction is an electrochemical reaction in which both reduction and oxidation take place together. The redox potential data are extensively used for prediction of the direction of a redox reaction under a given set of conditions. For the same, one needs to understand some basic terms. Redox Half Reaction Redox half reaction or the half-cell reaction is the chemical reaction taking place around one electrode of a cell. Consider the two parts of a complete redox system. In one part, oxidation is taking place and in the other, reduction is taking place. The electron is transferred from one part to the other. Oxidation half reaction Reduction half reaction Zn (s) Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e - Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e - Cu (s) The Overall Reaction Cu 2+ (aq) + Zn (s) Cu (s) + Zn 2+ (aq) Cu (s) : from +2 to 0 reduced (oxidizing agent) Zn (s) : from 0 to +2 oxidized (reducing agent) Oxidation (electron loss) is always accompanied by reduction (electron gain) Oxidizing agent is reduced the reducing agent is oxidized The total number of e- gained by the oxidizing agent is always equal to the total number lost by the reducing agent In order to bring out such a complete redox system, 2
3 a) the two parts (and the two species, the one undergoing oxidation and the other undergoing reduction) may form the bulk together (and electron transfer will be random) or, b) the two parts may be kept separated and connected by a conducting wire such that the electron released in one process, to the wire is collected by the other species and utilized in the reduction process there. Electrodes An electrode is solid electric conductor through which an electric current enters or leaves an electrolytic cell or other medium. In electrochemical reactions, oxidation or reduction reaction takes place at the electrodes. These are called electrode reactions, or half-reactions. A half-reaction can be either a reaction in which electrons appear as products (oxidation) or a reaction in which electrons appear as reactants (reduction). A combination of two half reaction forms the complete reaction. Anode Electrode where oxidation occurs Anions attracted to it Connected to positive end of battery in an electrolytic cell Loses weight in electrolytic cell Cathode Electrode where reduction occurs Cations attracted to it Connected to negative end of battery in an electrolytic cell Gains weight in electrolytic cell Electrode where plating takes place in electroplating TYPES of Electrochemical Cells The cell could be of two types viz.: Galvanic Cell: The overall reaction corresponds to a decrease in G (-ve G) and spontaneous reduction and oxidation are taking place in the two respective half cells. The cell reaction is unaided and spontaneous. It could be used as a source of electrical energy. 3
4 Electrolytic Cell: The G for the overall redox reaction is +ve and energy from outside is essential for the reaction to occur (E is ve). Electrode Potential When an electrode is in contact with the solution of its ions in a half-cell, it has a tendency to lose or gain electrons which is known as electrode potential. It is expressed in volts. It is an intensive property, i.e. independent of the amount of species in the reaction. It is denoted as E. If the flow of current is negligible between the two electrodes, the potentials difference is equal to the electromotive force (e.m.f.) of the cell, which is referred to as the absolute value of the difference of two individual electrode potentials, E 1 and E 2. e.m.f. = These electrode potentials are potential differences themselves, which are formed between the electrode (solid phase) and the electrolyte (liquid phase). Their occurrence can be most easily interpreted by the formation of double layers on the phase boundaries. If a piece of metal is immersed in a solution, which contains its own ions, say, Zn in a solution of ZnSO 4, two processes will immediately start. First, the atoms of the outside layer of the metal will 4
5 dissolve, leaving electrons on the metal itself, and slowly diffuse into the solution as metal ions. Secondly, metal ions from the solution will take up electrons from the metal and get deposited in the form of metal atoms. These two processes have different initial rates. If the rate of dissolution is higher than the rate of deposition, the net result of this process will be that an excess of positively charged ions will get into the solution, leaving behind and excess of electrons on the metal. Thus, the electrostatic attraction between the opposite charged particles, that is, the electrons in the metal phase and the ions in the solution, will accumulate at the phase boundary, forming an electric double layer. Once this layer is formed, the rate of dissolution becomes slower, because of the repulsion of the ionic layer at the phase boundary while the rate of deposition increases, because of the electrostatic attraction forces between the negatively charged metal and the positively charged ions. Soon the rate of the two processes will become equal and an equilibrium state will come into being, when, in a given time, the number of ions discharged equals the number of ions produced. The potential difference established between a metal and a solution of its salt will depend on: 1. The nature of the metal; and 2. The concentration of the ions in the solution Generally, for a half reaction, the half-cell potential (at 25 o C), E, is given by Or where, E = half-cell potential, E o = standard electrode potential, R = gas constant = JK - 1 mol -1, F = Faraday constant = Cmol -1, T = absolute temperature (K), [A] = concentration of chemical species, A, [B] = concentration of chemical species, B, a and b are the stoichiometric coefficients of A and B respectively and n = number of moles of electrons. For the overall reaction, The potential at 25 o C is given by Or This is called Nernst Equation. [ ] [ ] [ ] [ ] Standard Reduction Potentials The driving force for a spontaneous reaction is measured by the cell voltage. This is an intensive property, independent of the number of electrons passing through the cell. It is dependent on the: 1. nature of the redox reaction and 2. the concentrations of the species involved. The standard cell potential, E o cell, is measured at a: 5
6 i temperature of 25 o C, ii with the concentrations of all species in solution at 1M and iii all gases at 1 atm pressure. However, is not possible to determine the absolute value of electrode potential. For this a reference electrode is required. The electrode potential is only the difference of potentials between two electrodes that we can measure by combining them to give a complete cell. Reference Electrodes The electrode of known potential is called reference electrode. It may be primary reference electrode like hydrogen electrode or secondary reference electrode like calomel electrode. Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) also known as normal hydrogen electrode (NHE), consists of platinum wire, carrying platinum foil coated with finely divided platinum black. The wire is sealed into a glass tube placed in beaker containing 1 M HCl. The hydrogen gas at 1 atm pressure is bubbled through the solution at 298K. The electrode potential of SHE has been fixed as zero at all temperatures. Its main drawbacks are: 1. It is difficult to maintain 1 atm pressure of H 2 gas. 2. It is difficult to maintain H + ion concentration 1 M. 3. The platinum electrode is easily poisoned by traces of impurities. Hence, calomel electrodes are conveniently used as reference electrodes. Calomel electrode consists of mercury in contact with Hg 2 Cl 2 (calomel) paste in a solution of KCl. 6
7 Electrochemical Series The standard electrode potential values of common systems when arranged in descending order make a series. Thus, the one with the highest E o value is on the top (high positive value means the element has strong tendency to undergo reduction and so it is a strong oxidizing agent). Similarly, the low E o value (more on the negative side) signifies tendency to get converted to its oxidized form and hence it is a strong reducing agent. This series is called electrochemical series. Some of the general features of this series are: 1. The oxidized form of the couple is stronger oxidizing agent than the one below it in the series. 2. The reduced form of the couple is stronger reducing agent than the one above it in the series. 3. The reduced form of the couple that is below the H + / H 2 couple in the series, will have a natural tendency to liberate H 2 from acidic solutions. 4. The reduced form of the couple below in the list will reduce the oxidized form of a couple above it in the series. 5. The oxidized form of the couple above in the list will oxidize the reduced form of a couple below it in the series 6. The half-reaction with the greater reduction potential will drive the other half-reaction in the direction of oxidation 7. The difference between the two reduction potentials provides a quantitative description of the electromotive force of the cell. In simple terms, the electrochemical series is an arrangement of metals in their increasing reducing power such that the one in lower position in the series will reduce ions (aq) of metal in higher position. 7
8 Applications of Electrochemical Series (ECS) 1. The lower the value of E, the greater the tendency to form cation. M M n+ + ne - 2. Metals placed below hydrogen in ECS replace hydrogen from dil. acids but metals placed above hydrogen cannot replace hydrogen from dil. acids. 3. Oxides of metals placed below hydrogen are not reduced by H 2, but oxides of iron and metals placed above iron are reduced by H 2. SnO, PbO, CuO are reduced by H 2 CaO, K 2 O are not reduced by H 2 4. Reducing character increases down the series. 5. Reactivity increases down the series. 6. Determination of emf; emf is the difference of reduction potentials of two half-cells. E emf = E RHS E LHS If the value of emf is positive, then reaction take place spontaneously, otherwise not. 7. Greater the reduction potential of a substance, oxidising power. (e.g. F 2 > Cl 2 > Br 2 > I 2 ) 8. A negative value of standard reduction potential shows that it is the site of oxidation. 9. Oxides of metals having E red 0.79 will be decomposed by heating to form O 2 and metal. HgO (s) Hg (l) + ½O 2(g) Use of Redox Potentials 8
9 Although oxidation-reduction potentials can be treated in a general way, there are four broad classes of treating reduction potentials of redox systems. These are: 1. Metal electrodes 2. Simple redox system 3. Combined redox and acid-base systems, and 4. Gas electrodes Metal Electrodes The half-cell reaction on which their operation is based can be written as and the electrode potential can be calculated from the expression: [ ] Simple Redox System The half-cell reaction can be symbolized in general terms as Ox represents the oxidized form and Red the reduced form of the redox couple. Both the oxidized and reduced forms are in the dissolved phase. Combined Redox and Acid-Base Systems The half-cell reaction of such system can be written as Such half-cells are The Nernst Equation for such half-cells can be expressed as [ ] [ ] ) From this expression, it can be seen clearly that the oxidation-reduction potential of such systems depends as well on the hydrogen-ion concentration (ph) of the solution. 9
10 However, in cases of heterogeneous redox systems, where is change in the number of molecules (or ions) when a substance is reduced or oxidized, the general equations would be too complex to quote, but the potential can be easily expressed, if the half-cell reaction is known. Such systems are The oxidation-reduction potentials of these systems can be expressed as and [ ] ( [ ] Gas Electrodes Gaseous substances, when donating or accepting electrons, may act as electrons. As the gases themselves do not conduct electricity, a suitable inert electrode e.g. platinum or graphite must be used as a link to the electrical circuit. There are three gas electrodes of practical importance: 1. Hydrogen electrode 2. Oxygen electrode 3. Chlorine electrode Hydrogen Electrode It operates on the basis of the half-cell reaction: This can be regarded as a simple redox system and its potential expressed as However, the concentration of hydrogen gas cannot be easily measured. Thus, its pressure value is used. Hence, ) 10
11 Oxygen Electrode It operates based on the half-cell reaction The system is considered as a combined redox and acid-base reaction, and its potential can be expressed as [ ] Likewise, the concentration of oxygen, being a gas, cannot be easily measure. Thus, its pressure value is used. The concentration of water is taken as constant in dilute aqueous solutions. Hence, we have ) Chlorine Electrode The operation of chlorine electrode is based on the half-reaction, The electrode potential is expressed as ) Other Applications Determination of Solubility Products of Sparingly Soluble Salts The solubility product K sp (AB n An + + nb - ; Ksp is defined as K sp = [A n+ ][B - ] n ) is an equilibrium constant and its value can be predicted from a knowledge of the standard electrode potentials. The electrodes are chosen in such a way, that the overall cell reaction is the solubility product equilibrium. We will now illustrate the calculation of K sp for Hg 2 Cl 2(s) at 298 K from data on electrode potentials. [ ][ ] The half-cell reactions in which Hg 2 Cl 2 takes part and another reaction and take part are ; E o = V. (1) Eqn. (1) Eqn. (2): ; E o = V.(2) 11
12 E o = V = V But, where, Since[ ], then, [ ][ ] [ ] [ ][ ] Hence, where, n = 2, F = C, = V, R = JK -1 and T = 298 K Determination of ph of Solution The electrode reaction in the case of hydrogen electode is The electrode potential is expressed as ) Since atm,, then we have ) [ ] Potentiometric Titrations One of the widely used applications of e.m.f. measurements is to detect the endpoint of a titration by measuring the e.m.f. of a cell consisting of an indicator electrode (electrode, whose potential depends on the concentration of the reactant ions) and a reference electrode (e.g., SCE) as the titration progresses. This is called a potentiometric titration (varying e.m.f. 12
13 measured during the progress of titration). Since the electrode potential of the reference electrode is constant, the observed change in e.m.f. as the reaction progresses, is due to the change in the electrode potential of the indicator electrode. During acid-base titrations, the ph of the solution changes. By monitoring the change in ph as the titration progresses, it is possible to detect the end point in acid-base titrations using a ph meter. Near the equivalence point, the change in ph is quite large, and at the end point the variation is the largest. 13
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Cells
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 1 Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells are of two basic types: Galvanic Cells a spontaneous chemical reaction generates an electric current Electrolytic Cells
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 20: Electrochemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 20: Electrochemistry Redox reaction power batteries Electrochemistry is the study of the relationships between electricity and chemical reactions o It includes the
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 20: Electrochemistry Redox reaction power batteries Electrochemistry is the study of the relationships between electricity and chemical reactions o It includes the
17.1 Redox Chemistry Revisited
 Chapter Outline 17.1 Redox Chemistry Revisited 17.2 Electrochemical Cells 17.3 Standard Potentials 17.4 Chemical Energy and Electrical Work 17.5 A Reference Point: The Standard Hydrogen Electrode 17.6
Chapter Outline 17.1 Redox Chemistry Revisited 17.2 Electrochemical Cells 17.3 Standard Potentials 17.4 Chemical Energy and Electrical Work 17.5 A Reference Point: The Standard Hydrogen Electrode 17.6
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Electrochemistry 1. Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one reactant to another 2. Electric current is a flow of electrons in a circuit Many reduction-oxidation
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Electrochemistry 1. Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one reactant to another 2. Electric current is a flow of electrons in a circuit Many reduction-oxidation
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 20. Electrochemistry 20.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation-reduction reactions = chemical reactions in which the oxidation state of one or more substance changes (redox reactions). Recall:
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry 20.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation-reduction reactions = chemical reactions in which the oxidation state of one or more substance changes (redox reactions). Recall:
Chapter 17. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 17 Electrochemistry Contents Galvanic cells Standard reduction potentials Cell potential, electrical work, and free energy Dependence of cell potential on concentration Batteries Corrosion Electrolysis
Chapter 17 Electrochemistry Contents Galvanic cells Standard reduction potentials Cell potential, electrical work, and free energy Dependence of cell potential on concentration Batteries Corrosion Electrolysis
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry. Chapter 20 Problems. Electrochemistry 7/3/2012. Problems 15, 17, 19, 23, 27, 29, 33, 39, 59
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 20 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Chapter 20 Problems
Chemistry, The Central Science, 11th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 20 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Chapter 20 Problems
Chemistry 102 Chapter 19 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS
 OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS Some of the most important reaction in chemistry are oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions. In these reactions, electrons transfer from one reactant to the other. The rusting
Electrochemistry Pearson Education, Inc. Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School AP Chemistry
 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School AP Chemistry Electricity from Chemistry Many chemical reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions electron transfer
2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Mr. Matthew Totaro Legacy High School AP Chemistry Electricity from Chemistry Many chemical reactions involve the transfer of electrons between atoms or ions electron transfer
Electrochemical System
 Electrochemical System Topic Outcomes Week Topic Topic Outcomes 8-10 Electrochemical systems It is expected that students are able to: Electrochemical system and its thermodynamics Chemical reactions in
Electrochemical System Topic Outcomes Week Topic Topic Outcomes 8-10 Electrochemical systems It is expected that students are able to: Electrochemical system and its thermodynamics Chemical reactions in
Dr. Anand Gupta
 By Dr Anand Gupta Mr. Mahesh Kapil Dr. Anand Gupta 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Electrochemistry Electrolysis Electric energy Chemical energy Galvanic cell 2 Electrochemistry
By Dr Anand Gupta Mr. Mahesh Kapil Dr. Anand Gupta 09356511518 09888711209 anandu71@yahoo.com mkapil_foru@yahoo.com Electrochemistry Electrolysis Electric energy Chemical energy Galvanic cell 2 Electrochemistry
Introduction to electrochemistry
 Introduction to electrochemistry Oxidation reduction reactions involve energy changes. Because these reactions involve electronic transfer, the net release or net absorption of energy can occur in the
Introduction to electrochemistry Oxidation reduction reactions involve energy changes. Because these reactions involve electronic transfer, the net release or net absorption of energy can occur in the
Electrochemistry. Review oxidation reactions and how to assign oxidation numbers (Ch 4 Chemical Reactions).
 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction: Review oxidation reactions and how to assign oxidation numbers (Ch 4 Chemical Reactions). Half Reactions Method for Balancing Redox Equations: Acidic solutions: 1.
Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction: Review oxidation reactions and how to assign oxidation numbers (Ch 4 Chemical Reactions). Half Reactions Method for Balancing Redox Equations: Acidic solutions: 1.
Ch 20 Electrochemistry: the study of the relationships between electricity and chemical reactions.
 Ch 20 Electrochemistry: the study of the relationships between electricity and chemical reactions. In electrochemical reactions, electrons are transferred from one species to another. Learning goals and
Ch 20 Electrochemistry: the study of the relationships between electricity and chemical reactions. In electrochemical reactions, electrons are transferred from one species to another. Learning goals and
ELECTROCHEMISTRY OXIDATION-REDUCTION
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Can extract electrical energy from these.
Zn+2 (aq) + Cu (s) Oxidation: An atom, ion, or molecule releases electrons and is oxidized. The oxidation number of the atom oxidized increases.
 Oxidation-Reduction Page 1 The transfer of an electron from one compound to another results in the oxidation of the electron donor and the reduction of the electron acceptor. Loss of electrons (oxidation)
Oxidation-Reduction Page 1 The transfer of an electron from one compound to another results in the oxidation of the electron donor and the reduction of the electron acceptor. Loss of electrons (oxidation)
We can use chemistry to generate electricity... this is termed a Voltaic (or sometimes) Galvanic Cell
 Unit 6 Electrochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin Electrochemistry Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy. We can use chemistry to generate electricity...
Unit 6 Electrochemistry Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin Electrochemistry Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy. We can use chemistry to generate electricity...
Lecture 14. Thermodynamics of Galvanic (Voltaic) Cells.
 Lecture 14 Thermodynamics of Galvanic (Voltaic) Cells. 51 52 Ballard PEM Fuel Cell. 53 Electrochemistry Alessandro Volta, 1745-1827, Italian scientist and inventor. Luigi Galvani, 1737-1798, Italian scientist
Lecture 14 Thermodynamics of Galvanic (Voltaic) Cells. 51 52 Ballard PEM Fuel Cell. 53 Electrochemistry Alessandro Volta, 1745-1827, Italian scientist and inventor. Luigi Galvani, 1737-1798, Italian scientist
Chapter 20 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 20 Electrochemistry Learning goals and key skills: Identify oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agent, and reducing agent in a chemical equation Complete and balance redox equations using the method
Chapter 20 Electrochemistry Learning goals and key skills: Identify oxidation, reduction, oxidizing agent, and reducing agent in a chemical equation Complete and balance redox equations using the method
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry Recommendation: Review Sec. 4.4 (oxidation-reduction reactions) in your textbook
 Chapter 20. Electrochemistry Recommendation: Review Sec. 4.4 (oxidation-reduction reactions) in your textbook 20.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation-reduction reactions = chemical reactions in which
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry Recommendation: Review Sec. 4.4 (oxidation-reduction reactions) in your textbook 20.1 Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Oxidation-reduction reactions = chemical reactions in which
Q1. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
 Q1. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution? A1. Conductivity of a solution is the conductance of ions present in a unit volume of the solution. On dilution the number of ions per
Q1. Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution? A1. Conductivity of a solution is the conductance of ions present in a unit volume of the solution. On dilution the number of ions per
Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions
 Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions 19-1 Oxidation and Reduction I. Oxidation States A. The oxidation rules (as summarized by Mr. Allan) 1. In compounds, hydrogen has an oxidation # of +1. In compounds,
Chapter 19: Oxidation - Reduction Reactions 19-1 Oxidation and Reduction I. Oxidation States A. The oxidation rules (as summarized by Mr. Allan) 1. In compounds, hydrogen has an oxidation # of +1. In compounds,
Oxidation-Reduction Review. Electrochemistry. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions. Sample Problem.
 1 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction Review Topics Covered Oxidation-reduction reactions Balancing oxidationreduction equations Voltaic cells Cell EMF Spontaneity of redox reactions Batteries Electrolysis
1 Electrochemistry Oxidation-Reduction Review Topics Covered Oxidation-reduction reactions Balancing oxidationreduction equations Voltaic cells Cell EMF Spontaneity of redox reactions Batteries Electrolysis
Chapter Objectives. Chapter 13 Electrochemistry. Corrosion. Chapter Objectives. Corrosion. Corrosion
 Chapter Objectives Larry Brown Tom Holme Describe at least three types of corrosion and identify chemical reactions responsible for corrosion. www.cengage.com/chemistry/brown Chapter 13 Electrochemistry
Chapter Objectives Larry Brown Tom Holme Describe at least three types of corrosion and identify chemical reactions responsible for corrosion. www.cengage.com/chemistry/brown Chapter 13 Electrochemistry
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 20. Electrochemistry 20.1 OxidationReduction Reactions Oxidationreduction reactions = chemical reactions in which the oxidation state of one or more substance changes (redox reactions). Recall:
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry 20.1 OxidationReduction Reactions Oxidationreduction reactions = chemical reactions in which the oxidation state of one or more substance changes (redox reactions). Recall:
CHEM J-14 June 2014
 CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
AP CHEMISTRY NOTES 12-1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY: ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS
 AP CHEMISTRY NOTES 12-1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY: ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Review: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS the changes that occur when electrons are transferred between reactants (also known as a redox reaction)
AP CHEMISTRY NOTES 12-1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY: ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS Review: OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS the changes that occur when electrons are transferred between reactants (also known as a redox reaction)
CHEM J-14 June 2014
 CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
CHEM1101 2014-J-14 June 2014 An electrochemical cell consists of an Fe 2+ /Fe half cell with unknown [Fe 2+ ] and a Sn 2+ /Sn half-cell with [Sn 2+ ] = 1.10 M. The electromotive force (electrical potential)
Electrochemistry objectives
 Electrochemistry objectives 1) Understand how a voltaic and electrolytic cell work 2) Be able to tell which substance is being oxidized and reduced and where it is occuring the anode or cathode 3) Students
Electrochemistry objectives 1) Understand how a voltaic and electrolytic cell work 2) Be able to tell which substance is being oxidized and reduced and where it is occuring the anode or cathode 3) Students
Section Electrochemistry represents the interconversion of chemical energy and electrical energy.
 Chapter 21 Electrochemistry Section 21.1. Electrochemistry represents the interconversion of chemical energy and electrical energy. Electrochemistry involves redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions because
Chapter 21 Electrochemistry Section 21.1. Electrochemistry represents the interconversion of chemical energy and electrical energy. Electrochemistry involves redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions because
Chapter 19: Electrochemistry
 Chapter 19: Electrochemistry Overview of the Chapter review oxidation-reduction chemistry basics galvanic cells spontaneous chemical reaction generates a voltage set-up of galvanic cell & identification
Chapter 19: Electrochemistry Overview of the Chapter review oxidation-reduction chemistry basics galvanic cells spontaneous chemical reaction generates a voltage set-up of galvanic cell & identification
Electrochemical Reactions
 1 of 20 4/11/2016 1:00 PM Electrochemical Reactions Electrochemical Reactions Electrical Work From Spontaneous Oxidation- Reduction Reactions Predicting Spontaneous Redox Reactions from the Sign of E Line
1 of 20 4/11/2016 1:00 PM Electrochemical Reactions Electrochemical Reactions Electrical Work From Spontaneous Oxidation- Reduction Reactions Predicting Spontaneous Redox Reactions from the Sign of E Line
Electrochemistry. (Hebden Unit 5 ) Electrochemistry Hebden Unit 5
 (Hebden Unit 5 ) is the study of the interchange of chemical energy and electrical energy. 2 1 We will cover the following topics: Review oxidation states and assigning oxidation numbers Redox Half-reactions
(Hebden Unit 5 ) is the study of the interchange of chemical energy and electrical energy. 2 1 We will cover the following topics: Review oxidation states and assigning oxidation numbers Redox Half-reactions
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17
 Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Name AP CHEM / / Collected Essays Chapter 17 1980 - #2 M(s) + Cu 2+ (aq) M 2+ (aq) + Cu(s) For the reaction above, E = 0.740 volt at 25 C. (a) Determine the standard electrode potential for the reaction
Chapter Nineteen. Electrochemistry
 Chapter Nineteen Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemistry The study of chemical reactions through electrical circuits. Monitor redox reactions by controlling electron transfer REDOX: Shorthand for REDuction-OXidation
Chapter Nineteen Electrochemistry 1 Electrochemistry The study of chemical reactions through electrical circuits. Monitor redox reactions by controlling electron transfer REDOX: Shorthand for REDuction-OXidation
possesses negative potential & undergoes oxidation preferably act as ANODE
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Introduction: Electrochemistry is the area of Chemistry dealing with the interconversion of electrical energy and chemical energy. There are many applications of this in every day life.
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Introduction: Electrochemistry is the area of Chemistry dealing with the interconversion of electrical energy and chemical energy. There are many applications of this in every day life.
Oxidation number. The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred.
 Oxidation number The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred. 1. Free elements (uncombined state) have an oxidation number of zero. Na,
Oxidation number The charge the atom would have in a molecule (or an ionic compound) if electrons were completely transferred. 1. Free elements (uncombined state) have an oxidation number of zero. Na,
Unit 12 Redox and Electrochemistry
 Unit 12 Redox and Electrochemistry Review of Terminology for Redox Reactions OXIDATION loss of electron(s) by a species; increase in oxidation number. REDUCTION gain of electron(s); decrease in oxidation
Unit 12 Redox and Electrochemistry Review of Terminology for Redox Reactions OXIDATION loss of electron(s) by a species; increase in oxidation number. REDUCTION gain of electron(s); decrease in oxidation
Section A: Summary Notes
 ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 25 AUGUST 2015 Section A: Summary Notes Important definitions: Oxidation: the loss of electrons by a substance during a chemical reaction Reduction: the gain of electrons by a substance
ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS 25 AUGUST 2015 Section A: Summary Notes Important definitions: Oxidation: the loss of electrons by a substance during a chemical reaction Reduction: the gain of electrons by a substance
4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Redox Reaction. Rules for calculating oxidation Number
 4.1 Introduction Electrochemistry is that branch of chemistry which deals with the study of production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electrical
4.1 Introduction Electrochemistry is that branch of chemistry which deals with the study of production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electrical
CHEM Pharmacy Week 9: Nernst Equation. Dr. Siegbert Schmid School of Chemistry, Rm 223 Phone:
 CHEM1612 - Pharmacy Week 9: Nernst Equation Dr. Siegbert Schmid School of Chemistry, Rm 223 Phone: 9351 4196 E-mail: siegbert.schmid@sydney.edu.au Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have
CHEM1612 - Pharmacy Week 9: Nernst Equation Dr. Siegbert Schmid School of Chemistry, Rm 223 Phone: 9351 4196 E-mail: siegbert.schmid@sydney.edu.au Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have
Electron Transfer Reactions
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 Electron Transfer Reactions 2 Electron transfer reactions are oxidation- reduction or redox reactions. Results in the generation of an electric current (electricity) or be caused by
ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1 Electron Transfer Reactions 2 Electron transfer reactions are oxidation- reduction or redox reactions. Results in the generation of an electric current (electricity) or be caused by
Electrochemistry. The study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy.
 Electrochemistry The study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy. Oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction: involves a transfer of electrons from the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent. oxidation:
Electrochemistry The study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy. Oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction: involves a transfer of electrons from the reducing agent to the oxidizing agent. oxidation:
If a piece of magnesium is placed in an aqueous solution of copper (II) sulfate, the magnesium displaces the copper in a single displacement reaction.
 5.3 REDOX Reactions Half-reactions from Full Redox Equations If a piece of magnesium is placed in an aqueous solution of copper (II) sulfate, the magnesium displaces the copper in a single displacement
5.3 REDOX Reactions Half-reactions from Full Redox Equations If a piece of magnesium is placed in an aqueous solution of copper (II) sulfate, the magnesium displaces the copper in a single displacement
Electrochemistry. Galvanic Cell. Page 1. Applications of Redox
 Electrochemistry Applications of Redox Review Oxidation reduction reactions involve a transfer of electrons. OIL- RIG Oxidation Involves Loss Reduction Involves Gain LEO-GER Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain
Electrochemistry Applications of Redox Review Oxidation reduction reactions involve a transfer of electrons. OIL- RIG Oxidation Involves Loss Reduction Involves Gain LEO-GER Lose Electrons Oxidation Gain
General Chemistry I. Dr. PHAN TẠI HUÂN Faculty of Food Science and Technology Nong Lam University
 General Chemistry I Dr. PHAN TẠI HUÂN Faculty of Food Science and Technology Nong Lam University Module 7: Oxidation-reduction reactions and transformation of chemical energy Oxidation-reduction reactions
General Chemistry I Dr. PHAN TẠI HUÂN Faculty of Food Science and Technology Nong Lam University Module 7: Oxidation-reduction reactions and transformation of chemical energy Oxidation-reduction reactions
lect 26:Electrolytic Cells
 lect 26:Electrolytic Cells Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis
lect 26:Electrolytic Cells Voltaic cells are driven by a spontaneous chemical reaction that produces an electric current through an outside circuit. These cells are important because they are the basis
Electrochemical Cells
 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Cells The Voltaic Cell Electrochemical Cell = device that generates electricity through redox rxns 1 Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell An electrochemical cell that produces an electrical
Electrochemistry Electrochemical Cells The Voltaic Cell Electrochemical Cell = device that generates electricity through redox rxns 1 Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell An electrochemical cell that produces an electrical
Part One: Introduction. a. Chemical reactions produced by electric current. (electrolysis)
 CHAPTER 19: ELECTROCHEMISTRY Part One: Introduction A. Terminology. 1. Electrochemistry deals with: a. Chemical reactions produced by electric current. (electrolysis) b. Production of electric current
CHAPTER 19: ELECTROCHEMISTRY Part One: Introduction A. Terminology. 1. Electrochemistry deals with: a. Chemical reactions produced by electric current. (electrolysis) b. Production of electric current
Electrochemistry. Chapter 18. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Electrochemistry Chapter 18 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Electrochemical processes are oxidation-reduction reactions in which: the energy
Electrochemistry Chapter 18 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Electrochemical processes are oxidation-reduction reactions in which: the energy
Electrochemical Cells
 Electrochemical Cells There are two types: Galvanic and Electrolytic Galvanic Cell: a cell in which a is used to produce electrical energy, i.e., Chemical energy is transformed into Electrical energy.
Electrochemical Cells There are two types: Galvanic and Electrolytic Galvanic Cell: a cell in which a is used to produce electrical energy, i.e., Chemical energy is transformed into Electrical energy.
Electrochemistry : Electrochemistry is a branch of science which deals with the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous
 Electrochemistry : Electrochemistry is a branch of science which deals with the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electric energy to bring
Electrochemistry : Electrochemistry is a branch of science which deals with the production of electricity from energy released during spontaneous chemical reactions and the use of electric energy to bring
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox)
 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Electrochemistry involves the study of the conversions between chemical and electrical energy. Voltaic (galvanic) cells use chemical reactions to produce an electric current.
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Electrochemistry involves the study of the conversions between chemical and electrical energy. Voltaic (galvanic) cells use chemical reactions to produce an electric current.
Galvanic Cells Spontaneous Electrochemistry. Electrolytic Cells Backwards Electrochemistry
 Today Galvanic Cells Spontaneous Electrochemistry Electrolytic Cells Backwards Electrochemistry Balancing Redox Reactions There is a method (actually several) Learn one (4.10-4.12) Practice (worksheet)
Today Galvanic Cells Spontaneous Electrochemistry Electrolytic Cells Backwards Electrochemistry Balancing Redox Reactions There is a method (actually several) Learn one (4.10-4.12) Practice (worksheet)
Topic 5.3 REDOX EQUILIBRIA. Oxidation and Reduction Electrochemical Cells and Fuel Cells The Electrochemical Series Spontaneous Reactions
 Topic 5.3 REDOX EQUILIBRIA Oxidation and Reduction Electrochemical Cells and Fuel Cells The Electrochemical Series Spontaneous Reactions OXIDATION AND REDUCTION Redox reactions were studied extensively
Topic 5.3 REDOX EQUILIBRIA Oxidation and Reduction Electrochemical Cells and Fuel Cells The Electrochemical Series Spontaneous Reactions OXIDATION AND REDUCTION Redox reactions were studied extensively
Chapter 20 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 20 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Cell Consists of electrodes which dip into an electrolyte & in which a chem. rxn. uses or generates an electric current Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell Spont. rxn. -
Chapter 20 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Cell Consists of electrodes which dip into an electrolyte & in which a chem. rxn. uses or generates an electric current Voltaic (Galvanic) Cell Spont. rxn. -
Electrochemistry C020. Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy
 Electrochemistry C020 Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy Using chemistry to generate electricity involves using a Voltaic Cell or Galvanic Cell (battery)
Electrochemistry C020 Electrochemistry is the study of the interconversion of electrical and chemical energy Using chemistry to generate electricity involves using a Voltaic Cell or Galvanic Cell (battery)
REDOX EQUILIBRIA AND FEASIBILITY OF A REACTION
 REDOX EQUILIBRIA AND FEASIBILITY OF A REACTION Oxidizing agent Reducing agent Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Electron transfer reactions Electrons transferred from one substance to another Change in oxidation
REDOX EQUILIBRIA AND FEASIBILITY OF A REACTION Oxidizing agent Reducing agent Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Electron transfer reactions Electrons transferred from one substance to another Change in oxidation
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 18. Electrochemistry. Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Harnessing the Power in Nature The goal of scientific research is to understand nature. Once we understand the
Lecture Presentation Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Harnessing the Power in Nature The goal of scientific research is to understand nature. Once we understand the
(c) Na is deposited at the cathode (d) Na appears at the anode
 year chemiry n0tes new CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY MCQS Q.1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy
year chemiry n0tes new CHAPTER 10 ELECTROCHEMISTRY MCQS Q.1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 18. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 18 Oxidation/Reduction Reactions Transfer of electrons in solution from one reactant to another. Ce +4 + Fe +2 Ce +3 + Fe +3 Ce +4 and Fe 3+ Fe 2+ and Ce 3+
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 18 Oxidation/Reduction Reactions Transfer of electrons in solution from one reactant to another. Ce +4 + Fe +2 Ce +3 + Fe +3 Ce +4 and Fe 3+ Fe 2+ and Ce 3+
11.3. Electrolytic Cells. Electrolysis of Molten Salts. 524 MHR Unit 5 Electrochemistry
 11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
11.3 Electrolytic Cells Section Preview/ Specific Expectations In this section, you will identify the components of an electrolytic cell, and describe how they work describe electrolytic cells using oxidation
 Electrochem 1 Electrochemistry Some Key Topics Conduction metallic electrolytic Electrolysis effect and stoichiometry Galvanic cell Electrolytic cell Electromotive Force (potential in volts) Electrode
Electrochem 1 Electrochemistry Some Key Topics Conduction metallic electrolytic Electrolysis effect and stoichiometry Galvanic cell Electrolytic cell Electromotive Force (potential in volts) Electrode
University of Technology Corrosion Engineering Lecturer: Basheer Ahmed Chemical Engineering Dept. 4 th Class
 Example 1 Determine the corrosion rate of carbon steel in salt solution from the following laboratory data. Consider the corrosion rate by a)mpy, b)mdd. C) Calculate the current density in μa/cm 2 Δ W
Example 1 Determine the corrosion rate of carbon steel in salt solution from the following laboratory data. Consider the corrosion rate by a)mpy, b)mdd. C) Calculate the current density in μa/cm 2 Δ W
Topic 19 Redox 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials. IB Chemistry T09D04
 Topic 19 Redox 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials IB Chemistry T09D04 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials 19.1.1 Describe the standard hydrogen electrode. (2) 19.1.2 Define the term standard electrode potential,
Topic 19 Redox 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials IB Chemistry T09D04 19.1 Standard Electrode Potentials 19.1.1 Describe the standard hydrogen electrode. (2) 19.1.2 Define the term standard electrode potential,
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Definition The study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy in oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions This interchange can occur in both directions: 1. Conversion
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Definition The study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy in oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions This interchange can occur in both directions: 1. Conversion
Chapter 20. Electrochemistry
 Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 20 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice Hall,
Chemistry, The Central Science, 10th edition Theodore L. Brown; H. Eugene LeMay, Jr.; and Bruce E. Bursten Chapter 20 John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College St. Peters, MO 2006, Prentice Hall,
ELECTROCHEMISTRY I. The science concerned with the study of electron transfer across phase boundary
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY I The science concerned with the study of electron transfer across phase boundary Electrode: Is a conducting material immersed in a media. Electrode potential: Is the potential difference
ELECTROCHEMISTRY I The science concerned with the study of electron transfer across phase boundary Electrode: Is a conducting material immersed in a media. Electrode potential: Is the potential difference
Chapter 18. Electrochemistry
 Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-chemistry/ Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes
Chapter 18 Electrochemistry Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 http://www.bozemanscience.com/ap-chemistry/ Spontaneous Processes and Entropy Section 17.1 Spontaneous Processes
Ch 18 Electrochemistry OIL-RIG Reactions
 Ch 18 Electrochemistry OIL-RIG Reactions Alessandro Volta s Invention Modified by Dr. Cheng-Yu Lai Daily Electrochemistry Appliactions Electrochemistry: The area of chemistry that examines the transformations
Ch 18 Electrochemistry OIL-RIG Reactions Alessandro Volta s Invention Modified by Dr. Cheng-Yu Lai Daily Electrochemistry Appliactions Electrochemistry: The area of chemistry that examines the transformations
Galvanic cells. Galvanic cells (2) Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Baron Volta. John Frederic Daniell
 A quote of the week (or camel of the week): I have no special talents. I am only passionately curious Albert Einstein Physical Chemistry EPM/7 1 Galvanic cells Galvanic cells are devices permitting direct
A quote of the week (or camel of the week): I have no special talents. I am only passionately curious Albert Einstein Physical Chemistry EPM/7 1 Galvanic cells Galvanic cells are devices permitting direct
Chapter 19: Redox & Electrochemistry
 Chapter 19: Redox & Electrochemistry 1. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Definitions Oxidation - refers to the of electrons by a molecule, atom or ion Reduction - refers to the of electrons by an molecule,
Chapter 19: Redox & Electrochemistry 1. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Definitions Oxidation - refers to the of electrons by a molecule, atom or ion Reduction - refers to the of electrons by an molecule,
Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry
 Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 9th Edition George W.J. Kenney, Jr, Professor of Chemistry Last Update: 11July2009 Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Chem 1046 General Chemistry by Ebbing and Gammon, 9th Edition George W.J. Kenney, Jr, Professor of Chemistry Last Update: 11July2009 Chapter 19 ElectroChemistry These Notes are to SUPPLIMENT the Text,
Introduction to Electrochemical reactions. Schweitzer
 Introduction to Electrochemical reactions Schweitzer Electrochemistry Create and or store electricity chemically. Use electricity to drive a reaction that normally would not run. Plating metal onto a metal
Introduction to Electrochemical reactions Schweitzer Electrochemistry Create and or store electricity chemically. Use electricity to drive a reaction that normally would not run. Plating metal onto a metal
Chapter 7 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 7 Electrochemistry Outside class reading Levine: pp. 417 14.4 Galvanic cells: pp. 423 14.5 types of reversible electrodes 7.6.1 Basic concepts of electrochemical apparatus (1) Electrochemical apparatus
Chapter 7 Electrochemistry Outside class reading Levine: pp. 417 14.4 Galvanic cells: pp. 423 14.5 types of reversible electrodes 7.6.1 Basic concepts of electrochemical apparatus (1) Electrochemical apparatus
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC TEXT REFERENCE. Electrochemistry. Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18. Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1
 Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
Chemistry 1011 TOPIC Electrochemistry TEXT REFERENCE Masterton and Hurley Chapter 18 Chemistry 1011 Slot 5 1 18.5 Electrolytic Cells YOU ARE EXPECTED TO BE ABLE TO: Construct a labelled diagram to show
General Chemistry 1412 Spring 2008 Instructor: Dr. Shawn Amorde Website:
 General Chemistry 1412 Spring 2008 Instructor: Dr. Shawn Amorde Website: www.austincc.edu/samorde Email: samorde@austincc.edu Lecture Notes Chapter 21 (21.1-21.25) Suggested Problems () Outline 1. Introduction
General Chemistry 1412 Spring 2008 Instructor: Dr. Shawn Amorde Website: www.austincc.edu/samorde Email: samorde@austincc.edu Lecture Notes Chapter 21 (21.1-21.25) Suggested Problems () Outline 1. Introduction
Review: Balancing Redox Reactions. Review: Balancing Redox Reactions
 Review: Balancing Redox Reactions Determine which species is oxidized and which species is reduced Oxidation corresponds to an increase in the oxidation number of an element Reduction corresponds to a
Review: Balancing Redox Reactions Determine which species is oxidized and which species is reduced Oxidation corresponds to an increase in the oxidation number of an element Reduction corresponds to a
ELECTROCHEMISTRY. these are systems involving oxidation or reduction there are several types METALS IN CONTACT WITH SOLUTIONS OF THEIR IONS
 Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
Electrochemistry 1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY REDOX Reduction gain of electrons Cu 2+ (aq) + 2e > Cu(s) Oxidation removal of electrons Zn(s) > Zn 2+ (aq) + 2e HALF CELLS these are systems involving oxidation or
A + B C +D ΔG = ΔG + RTlnKp. Me n+ + ne - Me. Me n n
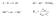 A + B C +D ΔG = ΔG + RTlnKp Me n+ + ne - Me K p a a Me Me n a n e 1 mol madde 6.2 x 1 23 atom elektron yükü 1.62 x 1-19 C FARADAY SABİTİ: 6.2 x 1 23 x 1.62 x 1-19 = 96485 A.sn (= coulomb) 1 Faraday 965
A + B C +D ΔG = ΔG + RTlnKp Me n+ + ne - Me K p a a Me Me n a n e 1 mol madde 6.2 x 1 23 atom elektron yükü 1.62 x 1-19 C FARADAY SABİTİ: 6.2 x 1 23 x 1.62 x 1-19 = 96485 A.sn (= coulomb) 1 Faraday 965
ELECTROCHEMISTRY. Oxidation/Reduction
 ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Examples: voltaic cells, batteries. NON-SPONTANEOUS
ELECTROCHEMISTRY Electrochemistry involves the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy. OXIDATION-REDUCTION REACTIONS SPONTANEOUS REACTIONS Examples: voltaic cells, batteries. NON-SPONTANEOUS
#13 Electrochemical Cells
 #13 Electrochemical Cells If a copper strip is placed in a solution of copper ions, one of the following reactions may occur: Cu 2+ + 2e - Cu Cu Cu 2+ + 2e - The electrical potential that would be developed
#13 Electrochemical Cells If a copper strip is placed in a solution of copper ions, one of the following reactions may occur: Cu 2+ + 2e - Cu Cu Cu 2+ + 2e - The electrical potential that would be developed
Chem 321 Lecture 16 - Potentiometry 10/22/13
 Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 16 - Potentiometry 10/22/13 In lab you will use an ion-selective electrode to determine the amount of fluoride in an unknown solution. In this approach, as
Student Learning Objectives Chem 321 Lecture 16 - Potentiometry 10/22/13 In lab you will use an ion-selective electrode to determine the amount of fluoride in an unknown solution. In this approach, as
Oxidation (oxidized): the loss of one or more electrons. Reduction (reduced): the gain of one or more electrons
 1 of 13 interesting links: Battery Chemistry Tutorial at http://www.powerstream.com/batteryfaq.html Duracell Procell: Battery Chemistry at http://www.duracell.com/procell/chemistries /default.asp I. Oxidation
1 of 13 interesting links: Battery Chemistry Tutorial at http://www.powerstream.com/batteryfaq.html Duracell Procell: Battery Chemistry at http://www.duracell.com/procell/chemistries /default.asp I. Oxidation
Electrochemistry. Redox reactions. Half Reactions. Nernst Equation Ion selective electrodes
 Electrochemistry Nernst Equation Ion selective electrodes Redox reactions oxidation - loss of electrons M n+ M n+1 + e - M is oxidized - reducing agent reduction - gain of electrons N n+ + e - N n-1 N
Electrochemistry Nernst Equation Ion selective electrodes Redox reactions oxidation - loss of electrons M n+ M n+1 + e - M is oxidized - reducing agent reduction - gain of electrons N n+ + e - N n-1 N
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 20. Electrochemistry. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 20 James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT is the study of the relationships between electricity and chemical reactions. It includes the study of both spontaneous and
Lecture Presentation Chapter 20 James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT is the study of the relationships between electricity and chemical reactions. It includes the study of both spontaneous and
Electrochemistry (Galvanic and Electrolytic Cells) Exchange of energy in chemical cells
 Electrochemistry (Galvanic and Electrolytic Cells) Exchange of energy in chemical cells Oxidation loss of electrons (oxidation number increases) OIL RIG Reduction gain of electrons (oxidation number decreases)
Electrochemistry (Galvanic and Electrolytic Cells) Exchange of energy in chemical cells Oxidation loss of electrons (oxidation number increases) OIL RIG Reduction gain of electrons (oxidation number decreases)
Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation
 Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation LEARNING OBJECTIVES The objectives of this experiment are to... construct galvanic cells and develop an electrochemical series based on potential differences between
Electrochemistry and the Nernst Equation LEARNING OBJECTIVES The objectives of this experiment are to... construct galvanic cells and develop an electrochemical series based on potential differences between
Review. Chapter 17 Electrochemistry. Outline. Voltaic Cells. Electrochemistry. Mnemonic
 Review William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley Edward J. Neth cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 17 Electrochemistry Oxidation Loss of electrons Occurs at electrode called the anode Reduction Gain of
Review William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley Edward J. Neth cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 17 Electrochemistry Oxidation Loss of electrons Occurs at electrode called the anode Reduction Gain of
(c) dilute solution of glucose (d) chloroform 12 Which one of the following represents the same net reaction as the electrolysis of aqueous H2SO4
 1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
1 Electrolysis is the process in which a chemical reaction takes place at the expense of (a) chemical energy (b) electrical energy (c) heat energy (d) none of these 2 Standard hydrogen electrode has an
How to Assign Oxidation Numbers. Chapter 18. Principles of Reactivity: Electron Transfer Reactions. What is oxidation? What is reduction?
 Chapter 18 Principles of Reactivity: Electron Transfer Reactions What is oxidation? When a molecule/ion loses electrons (becomes more positive) Whatever is oxidized is the reducing agent What is reduction?
Chapter 18 Principles of Reactivity: Electron Transfer Reactions What is oxidation? When a molecule/ion loses electrons (becomes more positive) Whatever is oxidized is the reducing agent What is reduction?
20.1 Consider the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction and the redox reaction below. + A
 20 Electrochemistry Visualizing Concepts 20.1 Consider the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction and the redox reaction below. HA + B BH + + A HA H + + A B + H + BH + X(red) + Y + (ox) X + (ox) + Y(red) X(red)
20 Electrochemistry Visualizing Concepts 20.1 Consider the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reaction and the redox reaction below. HA + B BH + + A HA H + + A B + H + BH + X(red) + Y + (ox) X + (ox) + Y(red) X(red)
Chapter 18: Electrochemistry
 Chapter 18: Electrochemistry Oxidation States An oxidation-reduction reaction, or redox reaction, is one in which electrons are transferred. 2Na + Cl 2 2NaCl Each sodium atom is losing one electron to
Chapter 18: Electrochemistry Oxidation States An oxidation-reduction reaction, or redox reaction, is one in which electrons are transferred. 2Na + Cl 2 2NaCl Each sodium atom is losing one electron to
Electrochemistry. Electrochemical Process. The Galvanic Cell or Voltaic Cell
 Electrochemistry Electrochemical Process The conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy are electrochemical process. Recall that an
Electrochemistry Electrochemical Process The conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy and the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy are electrochemical process. Recall that an
ELEMENTS OF ELEC TROCHEMIS TRY. A. A number of analytical techniques are based upon oxidation-reduction reactions.
 Page 1 of 8 Chem 201 Winter 2006 I. Introduction ELEMENTS OF ELEC TROCHEMIS TRY A. A number of analytical techniques are based upon oxidationreduction reactions. B. Examples of these techniques would include:
Page 1 of 8 Chem 201 Winter 2006 I. Introduction ELEMENTS OF ELEC TROCHEMIS TRY A. A number of analytical techniques are based upon oxidationreduction reactions. B. Examples of these techniques would include:
Chemistry 132 NT. Electrochemistry. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
 Chemistry 132 NT If you ever catch on fire, try to avoid seeing yourself in the mirror, because I bet that s what really throws you into a panic. Jack Handey 1 Chem 132 NT Electrochemistry Module 1 HalfReactions
Chemistry 132 NT If you ever catch on fire, try to avoid seeing yourself in the mirror, because I bet that s what really throws you into a panic. Jack Handey 1 Chem 132 NT Electrochemistry Module 1 HalfReactions
Electrochemical methods : Fundamentals and Applications Introduction
 Electrochemical methods : Fundamentals and Applications Introduction March 05, 2014 Kwang Kim Yonsei University kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 8 7 34 53 Y O N Se I 88.91 16.00 14.01 78.96 126.9 Electrochemical
Electrochemical methods : Fundamentals and Applications Introduction March 05, 2014 Kwang Kim Yonsei University kbkim@yonsei.ac.kr 39 8 7 34 53 Y O N Se I 88.91 16.00 14.01 78.96 126.9 Electrochemical
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells of a galvanic cell?
 Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
Unit - 3 ELECTROCHEMISTRY 1. What is a galvanic cell? VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 2. Give the cell representation for Daniell Cell. 3. Mention the purpose of salt-bridge placed between two half-cells
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction
 9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
9.1 Introduction to Oxidation and Reduction 9.1.1 - Define oxidation and reduction in terms of electron loss and gain Oxidation The loss of electrons from a substance. This may happen through the gain
Chapter 17 Electrochemistry
 Chapter 17 Electrochemistry 17.1 Galvanic Cells A. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Redox Rxns) 1. Oxidation = loss of electrons a. the substance oxidized is the reducing agent 2. Reduction = gain of electrons
Chapter 17 Electrochemistry 17.1 Galvanic Cells A. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Redox Rxns) 1. Oxidation = loss of electrons a. the substance oxidized is the reducing agent 2. Reduction = gain of electrons
