Cell Structure. Cell Structure. Investigating Cells. Investigating Cells. Cell Division. Cell Division. Transport In and Out of Cells
|
|
|
- Amelia Phebe Barrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cell Structure What are the two main types of cell? Cell Structure The two main types of cell are prokaryotic and eukaryotic. 1 1 Investigating Cells How is magnification calculated? 2 Investigating Cells Magnification is the size of the image divided by the size of the real object. 2 Cell Division What are chromosomes made of? Cell Division Chromosomes are made of DNA. 3 3 Transport In and Out of Cells Name the process by which water molecules move across a semipermeable membrane from a dilute solution to a more concentrated one. 4 Transport In and Out of Cells Osmosis is the movement of water molecules to a more concentrated solution across a semi-permeable membrane. 4 Levels of Organisation What is an organ? 5 Levels of Organisation An organ is a group of different tissues working together to perform a specific job. 5
2 Digestion What are the three main types of digestive enzymes? Digestion The three types of digestive enzymes are protease, lipase and carbohydrase. 6 6 Blood and the Circulation What are the three different types of blood vessel? Blood and the Circulation The three types of blood vessel are arteries, veins and capillaries. 7 7 Non-Communicable Diseases What two treatments can be used for coronary heart disease? 8 Non-Communicable Diseases Coronary heart disease can be treated with stents to keep coronary arteries open or statins to reduce cholesterol. 8 Transport in Plants Name the process by which water evaporates through stomata in the leaves. 9 Transport in Plants The loss of water through stomata in the leaves is called transpiration. 9 Pathogens and Disease What is the vector of malaria? 10 Pathogens and Disease A type of mosquito is the vector of malaria. 10
3 Human Defences Against Disease How can a person be made immune to a specific disease? 11 Human Defences Against Disease A vaccination will make a person immune to the disease. 11 Treating Diseases What is MRSA? 12 Treating Diseases MRSA is a strain of bacteria that is resistant to antibiotics. 12 Photosynthesis What two products are produced when carbon dioxide and water combine in photosynthesis? Photosynthesis Glucose and oxygen are produced by photosynthesis Respiration and Exercise What is anaerobic respiration in yeast cells called? Respiration and Exercise Anaerobic respiration in yeast cells is called fermentation Homeostasis and the Nervous System What is the difference between receptors and effectors? 15 Homeostasis and the Nervous System Receptors are cells which detect stimuli, whereas effectors are parts of the body (e.g. muscles or glands) which produce responses to stimuli. 15
4 Hormones and Homeostasis What are the chemical messengers produced by glands of the endocrine system? Hormones and Homeostasis Hormones are the chemical messengers produced by glands of the endocrine system Hormones and Reproduction What four hormones are involved in the menstrual cycle? Hormones and Reproduction The four hormones that control the menstrual cycle are follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), oestrogen, luteinising hormone (LH) and progesterone Sexual and Asexual Reproduction What type of cell division forms gametes? 18 Sexual and Asexual Reproduction Gametes are formed by meiosis. 18 Patterns of Inheritance What word describes having two different alleles for a gene? 19 Patterns of Inheritance Heterozygous means having two different alleles for a gene. 19 Variation and Evolution What process is the gradual change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time? 20 Variation and Evolution Evolution is the gradual change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time. 20
5 Manipulating Genes How is selective breeding different from genetic engineering? 21 Manipulating Genes Selective breeding is the traditional, natural process of breeding plants and animals with certain, desirable genetic features. Genetic engineering is a modern, faster way of bringing about changes in organisms. It is the artificial process of transplanting genes for a desired characteristic into an organism. 21 Classification What is the classification system called in which organisms are given a two-part name made up of their genus + species? Classification The binomial system names organisms by their genus + species Ecosystems What is a population? Ecosystems A population is a group of individuals of one species living in a habitat Cycles and Feeding Relationships What are the top consumers in a food chain called? 24 Cycles and Feeding Relationships The top consumers in a food chain are apex predators. 24 Disrupting Ecosystems Name two gases that contribute to global warming. 25 Disrupting Ecosystems Carbon dioxide and methane both contribute to global warming. 25
6 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 26 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components with different boiling points from a mixture. The mixture is heated gradually and each component is collected when it boils. 26 Atoms and the Periodic Table If an element has different isotopes, what does this mean? Atoms and the Periodic Table Each isotope of an element has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in each atom The Periodic Table What are the elements in these groups of the Periodic Table known as? a) Group 0 b) Group 1 c) Group 7 28 The Periodic Table a) Group 0 the noble gases b) Group 1 the alkali metals c) Group 7 the halogens 28 States of Matter Complete the table. State of substance State symbol solid ( ) (l) (g) ( ) dissolved ( ) in water 29 States of Matter State of substance solid liquid gas (aqueous) dissolved in water State symbol (s) (l) (g) (aq) 29 Ionic Compounds Describe what happens to a metal atom and a non-metal atom when an ionic bond forms between them. 30 Ionic Compounds The metal atoms lose electrons to become positively charged ions. The electrons are transferred to the non-metal atoms, which gain electrons to become negatively charged ions. 30
7 Covalent Compounds Describe what happens when one chlorine atom forms a bond with another chlorine atom. 31 Covalent Compounds An electron from each atom is shared so that each atom has a complete outer shell of electrons. 31 Metals and Special Materials Explain why most polymers are solid at room temperature. 32 Metals and Special Materials The atoms within polymer molecules are held together by strong covalent bonds. The intermolecular forces between the large polymer molecules are also quite strong. 32 Conservation of Mass Why do chemical symbol equations always need to be balanced? 33 Conservation of Mass Mass is conserved. In a chemical reaction, no atoms are made or lost. 33 Reactivity of Metals Use these words to complete the sentences that follow. (Use each word once only.) together loses gains In oxidation reactions, a substance often oxygen. In reduction reactions, a substance often oxygen. Oxidation and reduction always occur. Reactivity of Metals In oxidation reactions, a substance often gains oxygen. In reduction reactions, a substance often loses oxygen. Oxidation and reduction always occur together The ph Scale and Salts Why is the following reaction called a neutralisation reaction? HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) KCl(aq) + H 2 O(l) 35 The ph Scale and Salts Hydrochloric acid (HCl) neutralises the alkali potassium hydroxide (KOH). The solution that remains has a ph of 7, meaning that it is neutral. 35
8 Electrolysis Explain why electrolysis is an expensive way of extracting metals from their ores. Electrolysis Electrolysis requires a lot of heat and electrical energy Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions What is the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions? 37 Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions Endothermic reactions take in energy from the surroundings and cause a temperature drop. Exothermic reactions give out energy to the surroundings and cause a temperature rise. 37 Rate of Reaction A sample of solid calcium carbonate is divided precisely into two equal masses. One half is a single solid piece, which is then reacted with an acid. The other half is broken into small pieces and reacted with a fresh sample of the same acid. Which half will react faster, and why? 38 Rate of Reaction The half that is broken into small pieces will react faster. This is because small pieces have a large surface area in relation to their volume. More solid particles are exposed to contact with acid particles, so there are more collisions and a faster reaction. 38 Reversible Reactions Choose the correct phrase from this list to complete the sentence that follows. much less than exactly the same as much more than When a reversible reaction takes place in a closed system, an equilibrium is achieved when the rate of the backward reaction is the rate of the forward reaction. Reversible Reactions When a reversible reaction takes place in a closed system, an equilibrium is achieved when the rate of the backward reaction is exactly the same as the rate of the forward reaction Alkanes Choose the correct general formula for alkanes from the following list. C n H 2n 2 C 2n H n Alkanes C n H 2n+2 C n H 2n C n H 2n
9 Cracking Hydrocarbons What are the two main methods of cracking hydrocarbons? 41 Cracking Hydrocarbons The two main methods of cracking hydrocarbons are steam cracking and catalytic cracking. 41 Chemical Analysis Complete the following table that describes tests for different gases. Gas Hydrogen Oxygen Test for gas Turns limewater cloudy Turns damp indicator paper 42 white Chemical Analysis Gas Carbon dioxide Hydrogen Oxygen Chlorine Test for gas Turns limewater cloudy Burns with a squeaky pop Relights a glowing splint Turns damp indicator paper white 42 The Earth s Atmosphere Describe the effects that the evolution of plants had on the Earth s atmosphere. 43 The Earth s Atmosphere Plants use carbon dioxide and water to produce oxygen in the reaction called photosynthesis. As more plants evolved, the amount of oxygen in the atmosphere increased. Eventually the levels of oxygen were enough for land-based animals that breathed oxygen from the air to evolve. 43 Greenhouse Gases What is the carbon footprint? 44 Greenhouse Gases The carbon footprint of a product, service or event is the total amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that are emitted over its full life cycle. 44 Earth s Resources Why can t we release our waste water directly into the environment? 45 Earth s Resources Waste water can contain toxic chemicals, harmful microorganisms and other organic matter. All these things can cause pollution and affect plants and animals, including humans. 45
10 Using Resources What is the purpose of a life cycle assessment? 46 Using Resources A life cycle assessment provides a way of comparing different products to see which cause least damage to the environment, over their whole lifetime. 46 Forces An Introduction A force is a vector quantity. What does this mean? Forces An Introduction A vector quantity, such as force, has a direction as well as a magnitude Forces in Action Define the spring constant and write an equation for calculating it. Forces in Action The spring constant is a measure of how easy it is to stretch or compress a spring. force spring constant = extension Forces and Motion What is a typical speed for a person walking? Choose from: 2.5 m/s 1.5 m/s 0.5 m/s 49 Forces and Motion A typical speed for a person walking is 1.5 m/s. 2.5 m/s would be running. 0.5 m/s would be very slow walking. 49 Forces and Acceleration Which equation is used to summarise Newton s Second Law? 50 Forces and Acceleration We can use this equation to summarise Newton s Second Law: force = mass acceleration 50
11 Terminal Velocity, Stopping and Braking What can you say about the forces on an object that is falling at its terminal velocity? 51 Terminal Velocity, Stopping and Braking The resistive force acting upwards equals the weight acting downwards. The forces are balanced and there is no resultant force on the object. 51 Energy Stores and Transfers In the equation E e = 1 2 ke2 for calculating the elastic potential energy stored in a stretched spring, what does k represent and what is its unit? 52 Energy Stores and Transfers k is the spring constant of the spring, which is a measure of its stiffness: force applied to spring = k extension The unit of k is N/m. 52 Energy Transfers and Resources Complete this sentence correctly. On a very cold day, a hut with thin metal walls will cool down very quickly because of the metal s low thermal conductivity high thermal conductivity 53 Energy Transfers and Resources On a very cold day, a hut with thin metal walls will cool down very quickly because of the metal s high thermal conductivity. The higher the thermal conductivity of a material, the higher the rate of energy transfer by conduction through the material. 53 Waves and Wave Properties What is the relationship between wave speed, wave frequency and wavelength? 54 Waves and Wave Properties wave speed = frequency wavelength 54 Electromagnetic Waves Light travels across a boundary from a material of high refractive index into air. Describe its change of direction. 55 Electromagnetic Waves The light changes direction (is refracted) away from the normal (the perpendicular to the boundary) unless the light is travelling perpendicular to the boundary, in which case it will continue straight. 55
12 The Electromagnetic Spectrum Which type of electromagnetic radiation correctly fills the gap in these sentences? In an energy efficient lamp, waves are produced by the gas inside when an electric current passes. These waves are absorbed by the coating on the lamp, which 56 then gives off visible light. The Electromagnetic Spectrum Ultraviolet (UV) 56 An Introduction to Electricity What is the equation relating the potential difference across, the current through and the resistance of a component in a circuit? 57 An Introduction to Electricity Potential difference = current resistance 57 Circuits and Resistance State the behaviour of an LDR in a circuit when the light intensity falling on it decreases. 58 Circuits and Resistance An LDR is a light-dependent resistor. Its electrical resistance increases when the light intensity decreases. 58 Circuits and Power State the equation for calculating the electrical power P of a device of resistance R, when the current through it is I, and state the unit of power. 59 Circuits and Power Power P = I 2 R The unit of power is the watt, W (equivalent to J/s). 59 Domestic Uses of Electricity State the colours of the wires in the cable of a domestic appliance: the live wire, the neutral wire and the earth wire. 60 Domestic Uses of Electricity Live wire: brown Neutral wire: blue Earth wire: green and yellow (stripes) 60
13 Electrical Energy in Devices True or false? If all of the electrical energy supplied to an efficient kettle is used to heat the water, this equation determines the change in temperature of the water, θ. I V t = m c θ 61 Electrical Energy in Devices True. The electrical energy supplied to the kettle is power time = I V t. The rise in temperature of the water θ depends on the mass m and the specific heat capacity c of the water. Energy change of water = m c θ. 61 Magnetism and Electromagnetism Which of these sentence endings makes the statement correct? A magnetic material brought close to a magnet is always attracted to the N pole of the magnet. is attracted to the nearest pole of the magnet. 62 Magnetism and Electromagnetism A magnetic material brought close to a magnet is attracted to the nearest pole of the magnet. The strong magnetic field near either magnet pole makes the nearby magnetic material an induced magnet and this always causes attraction. 62 Specific heat capacity is the energy Particle Model of Matter What is the difference between the specific heat capacity and the specific latent heat of a material? 63 Particle Model of Matter needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the material by 1 C, with no change of state. Specific latent heat is the energy needed to change the state of 1 kg of the material, with no change in temperature. 63 Atoms and Isotopes Choose the correct word to complete this sentence. Isotopes of an element contain the same number of neutrons protons 64 Atoms and Isotopes Isotopes of an element contain the same number of protons. They have different numbers of neutrons. 64 Nuclear Radiation Complete the gaps in the sentences. Choose from: greater smaller more less Beta radiation has a ionising power than alpha radiation and so is penetrating and has a range in air. A beta source a few metres away from you is therefore likely to be dangerous than an alpha source at that distance. 65 Nuclear Radiation Beta radiation has a smaller ionising power than alpha radiation and so is more penetrating and has a greater range in air. A beta source a few metres away from you is therefore likely to be more dangerous than an alpha source at that distance. 65
14 Half-Life State two definitions of radioactive half-life. Half-Life 1. The half-life is the (average) time taken for half of the radioactive nuclei in a sample to decay. 2. The half-life is the time taken for the activity (or count rate) of a radioactive sample to fall to half its 66 original value. 66
Atoms, Elements, Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures. Compounds and Mixtures. Atoms and the Periodic Table. Atoms and the.
 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Explain how fractional distillation can be used to separate a mixture. 1 Atoms, Elements, Compounds and Mixtures Fractional distillation is used to separate components
Introduction. Introduction. Forces An. Forces An. Forces in Action. Forces in Action. Pressure and Pressure. Pressure and Pressure.
 Forces An Introduction A force is a vector quantity. What does this mean? Forces An Introduction A vector quantity, such as force, has a direction as well as a magnitude. 1 1 Forces in Action The moment
Forces An Introduction A force is a vector quantity. What does this mean? Forces An Introduction A vector quantity, such as force, has a direction as well as a magnitude. 1 1 Forces in Action The moment
Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks
 Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks Cell Biology (Yr9) Cell Organisation (Yr9) Infection and Response (Yr10) Bioenergetics (Yr10) Cells Cell Organisation Competition Photosynthesis Microscopy Enzymes Abiotic
Biology Paper 1 1hr 15mins 70 marks Cell Biology (Yr9) Cell Organisation (Yr9) Infection and Response (Yr10) Bioenergetics (Yr10) Cells Cell Organisation Competition Photosynthesis Microscopy Enzymes Abiotic
Combined GCSE OCR Revision Science magnification tur tur magnification ell Struc ell Struc ells ells Combined GCSE OCR Revision Science
 Cell Structures How is the magnification of a light microscope calculated? Cell Structures Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of
Cell Structures How is the magnification of a light microscope calculated? Cell Structures Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of
Combined GCSE OCR Revision Science magnification tur tur magnification ell Struc ell Struc ells ells Combined GCSE OCR Revision Science
 Cell Structures How is the magnification of a light microscope calculated? Cell Structures Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of
Cell Structures How is the magnification of a light microscope calculated? Cell Structures Total magnification is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the eyepiece lens by the magnification of
GCSE OCR Revision Chemistry. GCSE OCR Revision Chemistry. GCSE OCR Revision Chemistry. Bonding. GCSE OCR Revision Chemistry
 Particle Model and Atomic Structure The following symbols describe two different substances. Deduce all the information you can from these symbols. 13 C 12 6 6 C 1 Particle Model and Atomic Structure The
Particle Model and Atomic Structure The following symbols describe two different substances. Deduce all the information you can from these symbols. 13 C 12 6 6 C 1 Particle Model and Atomic Structure The
Science Years 9 to 10
 Boardworks Contents Guide Boardworks Presentations: Acids and metal oxides 10 slides Reactions of metal oxides with acids. Adapting to changes 9 slides Ways that animals adapt to their habitats. Air pollution
Boardworks Contents Guide Boardworks Presentations: Acids and metal oxides 10 slides Reactions of metal oxides with acids. Adapting to changes 9 slides Ways that animals adapt to their habitats. Air pollution
Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined. Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours
 Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours Half Term.7.. Communities Competition Ecosystems Interdependence ASSESSED HOMEWORK (Communities).7.. Abiotic
Biology Combined Chemistry Combined Physics Combined Content Hours Content Hours Content Hours Half Term.7.. Communities Competition Ecosystems Interdependence ASSESSED HOMEWORK (Communities).7.. Abiotic
Science 9-1 Grades Guidance
 U1 U2 U3 Science 9-1 Grades Guidance This guide is designed to help explain the level that a student is working at using examples of the curriculum that a student should be able to access. This is not
U1 U2 U3 Science 9-1 Grades Guidance This guide is designed to help explain the level that a student is working at using examples of the curriculum that a student should be able to access. This is not
Subject: GCSE Physics
 Subject: GCSE Physics Density States of matter SHC Atoms and radiation Discovery of the nucleus Changes in the nucleus Alpha, beta and gamma Activity and half life Nuclear radiation and medicine Nuclear
Subject: GCSE Physics Density States of matter SHC Atoms and radiation Discovery of the nucleus Changes in the nucleus Alpha, beta and gamma Activity and half life Nuclear radiation and medicine Nuclear
This unit will help you define health, learn about some pathogens and the diseases they cause, medicines and about the immune system.
 YEAR 10 Biology Units 1-5 Biology Unit CB1 Key biological concepts [Paper 1 & CB2 Cells and Control CB3 Genetics CB4 Natural Selection and Genetic Modification CB5 Health, Disease and the Development of
YEAR 10 Biology Units 1-5 Biology Unit CB1 Key biological concepts [Paper 1 & CB2 Cells and Control CB3 Genetics CB4 Natural Selection and Genetic Modification CB5 Health, Disease and the Development of
0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/22 Paper 2 (Core Theory), maximum
Edexcel Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Topic 1. Key concepts in chemistry Video: Developing the atomic model Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time. Describe the difference between the plum-pudding model of the atom and
Time (s) Velocity (m/s)
 29.01.18 22.01.18 15.01.18 w/c Weekly Combined Science revision countdown plan (revision guide / workbook page numbers) *content across both paper 1 and paper 2 15 14 13 Revise *Key concepts in biology
29.01.18 22.01.18 15.01.18 w/c Weekly Combined Science revision countdown plan (revision guide / workbook page numbers) *content across both paper 1 and paper 2 15 14 13 Revise *Key concepts in biology
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
LONGMAN STUDY GUIDES. Science. Di Barton. SUB Q6ttlngen B1842 LONGMAN
 LONGMAN STUDY GUIDES Science Di Barton SUB Q6ttlngen 206 451 652 97B1842 LONGMAN CONTENTS Editors' Preface vii Acknowledgements vii Information about this book viii 1 Revision, examinations and coursework
LONGMAN STUDY GUIDES Science Di Barton SUB Q6ttlngen 206 451 652 97B1842 LONGMAN CONTENTS Editors' Preface vii Acknowledgements vii Information about this book viii 1 Revision, examinations and coursework
Science. synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis Using physics to make things work 3 Magnetic fields to keep things moving Energy calculations 4 Energy
 Year 11 (Triple science) 2016-17 Half-term Topic Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 1 Exchange of materials Keeping internal conditions constant Analysis and synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis
Year 11 (Triple science) 2016-17 Half-term Topic Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Week 7 1 Exchange of materials Keeping internal conditions constant Analysis and synthesis 2 Analysis and synthesis
Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE)
 Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE) This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our legacy Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology (8401) to
Summary of changes (certificate to new GCSE) This resource outlines the main changes that have been made to the assessment and subject content from our legacy Level 1/2 Certificate in Biology (8401) to
AQA Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell biology Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Distinguish between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Compare animal and plant cells. Relate cell structures to their functions. Video: Specialised
Topic 1. Cell biology Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Distinguish between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Compare animal and plant cells. Relate cell structures to their functions. Video: Specialised
Curriculum overview Key Stage 2 Living things and their habitats: Animals: Properties and changes of materials: Earth and Space: Forces: Evolution:
 Curriculum overview: Science (Foundation) Key Stage 2 Living things and their habitats: Life cycles of a mammal, an amphibian, an insect and a bird Reproduction in some plants and animals. Classification
Curriculum overview: Science (Foundation) Key Stage 2 Living things and their habitats: Life cycles of a mammal, an amphibian, an insect and a bird Reproduction in some plants and animals. Classification
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
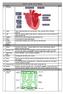 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
YEAR 7. St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map New AQA Course Started November 2016
 YEAR 7 St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map 201-2017 New AQA Course Started November 2016 05/09/2016 12/09/2016 19/09/2016 26/09/2016 03/10/2016 10/10/2016 17/10/2016 24/10/2016
YEAR 7 St Edmund Arrowsmith CCFL Science Department Curriculum Map 201-2017 New AQA Course Started November 2016 05/09/2016 12/09/2016 19/09/2016 26/09/2016 03/10/2016 10/10/2016 17/10/2016 24/10/2016
Level 789 Pathway: Combined Science Double Award
 Level 789 Pathway: Combined Science Double Award Yr Combined Science Targets: Pathway 8 11 Biology a) Explain in detail the role of the hormone ADH on the nephron b) Explain in detail the process by which
Level 789 Pathway: Combined Science Double Award Yr Combined Science Targets: Pathway 8 11 Biology a) Explain in detail the role of the hormone ADH on the nephron b) Explain in detail the process by which
KS3 Science Levelness Posters
 KS Science Levelness Posters Contents Year Year 8 Year 9 A. Cells 8A. Food and digestion 9A. Inheritance and selection B. Reproduction 8B. Respiration 9B. Fit and healthy C. Environment and feeding 8C.
KS Science Levelness Posters Contents Year Year 8 Year 9 A. Cells 8A. Food and digestion 9A. Inheritance and selection B. Reproduction 8B. Respiration 9B. Fit and healthy C. Environment and feeding 8C.
GCSE OCR Revision Physics. GCSE OCR Revision Physics. GCSE OCR Revision Physics. GCSE OCR Revision Physics. Journeys. GCSE OCR Revision Physics
 Matter, Models and Density What is a typical size of an atom? Choose from the following. 10 15 m 10 12 m 10 10 m Matter, Models and Density The size of an atom is of the order of 10 10 m. 1 1 Temperature
Matter, Models and Density What is a typical size of an atom? Choose from the following. 10 15 m 10 12 m 10 10 m Matter, Models and Density The size of an atom is of the order of 10 10 m. 1 1 Temperature
Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Keywords
 Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Respiration. Know that respiration in living organisms can be aerobic or anaerobic The word equation for aerobic respiration The process of anaerobic respiration
Y8 Science Controlled Assessment Topics & Biology Respiration. Know that respiration in living organisms can be aerobic or anaerobic The word equation for aerobic respiration The process of anaerobic respiration
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
OCR Biology Checklist
 Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Topic 1. Cell level systems Video: Eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Compare the structure of animal and plant cells. Label typical and atypical prokaryotic cells. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and recall names used for these inter-conversions
 Understand the arrangements, movements and energy of the particle in each of the 3 states of matter : solid, liquid and gas Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and
Understand the arrangements, movements and energy of the particle in each of the 3 states of matter : solid, liquid and gas Describe how the inter-conversion of solids, liquids and gases are achieved and
UNIT 9A Inheritance and Selection
 UNIT 9A Inheritance and Selection Know what inheritance means Know what characteristics are Know that sexual reproduction needs two parents Know that animals and plants can be bred for their characteristics
UNIT 9A Inheritance and Selection Know what inheritance means Know what characteristics are Know that sexual reproduction needs two parents Know that animals and plants can be bred for their characteristics
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 017 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 10
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/4 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) May/June 017 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 10
Topic Student Checklist R A G
 Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Physics (8464) from 2016 Topics T6.1. Energy Topic Student Checklist R A G 6.1.1 Energy changes in a system, and the ways energy is stored before and after such
Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Physics (8464) from 2016 Topics T6.1. Energy Topic Student Checklist R A G 6.1.1 Energy changes in a system, and the ways energy is stored before and after such
AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists. Name: Teacher:
 AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists Name: Teacher: Paper 1-4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic
AQA Chemistry (Combined Science) Specification Checklists Name: Teacher: Paper 1-4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic
Curriculum Mapping Subject: Science Year Group Autumn Term 1a Autumn Term 1b Spring Term 2a Spring Term 2b Summer Term 3a Summer Term 3b
 Curriculum Mapping Subject: Science Year Group Autumn Term 1a Autumn Term 1b Spring Term 2a Spring Term 2b Summer Term 3a Summer Term 3b Year 11 Topic(s) Forces and Energy Atomic Structure Electromagnetism
Curriculum Mapping Subject: Science Year Group Autumn Term 1a Autumn Term 1b Spring Term 2a Spring Term 2b Summer Term 3a Summer Term 3b Year 11 Topic(s) Forces and Energy Atomic Structure Electromagnetism
Switching to AQA from OCR Gateway Science B and Additional Science B
 Switching to AQA from OCR Gateway Science B and Additional Science B If you re thinking of switching to AQA from OCR Science B (Gateway) and Additional Science B (J261 and J262) for teaching from September
Switching to AQA from OCR Gateway Science B and Additional Science B If you re thinking of switching to AQA from OCR Science B (Gateway) and Additional Science B (J261 and J262) for teaching from September
Lymm High School- KS3 Life after levels - Science Y9
 Biology BRONZE SILVER GOLD PLATINUM D and below= GCSE 1,2,3 C= GCSE 4 C/B= GCSE 5,6 A/A*= GCSE 7,8,9 Explain that cells are very Demonstrate an small and a microscope is understanding of the scale needed
Biology BRONZE SILVER GOLD PLATINUM D and below= GCSE 1,2,3 C= GCSE 4 C/B= GCSE 5,6 A/A*= GCSE 7,8,9 Explain that cells are very Demonstrate an small and a microscope is understanding of the scale needed
Year 8 Tracking Document. Year 8 Science National Curriculum. Health and Lifestyle
 Health and Lifestyle Describe the components of a healthy diet Explain the role of each food group in the body Describe the test for starch, lipids, sugar and proteins Describe the positive test for each
Health and Lifestyle Describe the components of a healthy diet Explain the role of each food group in the body Describe the test for starch, lipids, sugar and proteins Describe the positive test for each
Cecil Jones Academy Science Fundamentals Map
 Fundamentals: Year 9 Biology Knowledge Unit 1 Skills B1 Cell Structure and Transport Unit 2 Use the terms 'eukaryotic' and 'prokaryotic' to describe types of cells Describe the features of bacterial (prokaryotic)
Fundamentals: Year 9 Biology Knowledge Unit 1 Skills B1 Cell Structure and Transport Unit 2 Use the terms 'eukaryotic' and 'prokaryotic' to describe types of cells Describe the features of bacterial (prokaryotic)
Science. Biology Year 7. Chemistry Year 7. Physics Year 7
 Science Biology Year 7 Chemistry Year 7 Physics Year 7 Using a microscope Slide Preparation o Prepare specimens of plant cells and animal cells o Describe the role of stain in specimen preparation o Draw
Science Biology Year 7 Chemistry Year 7 Physics Year 7 Using a microscope Slide Preparation o Prepare specimens of plant cells and animal cells o Describe the role of stain in specimen preparation o Draw
Y9 3Y Combined BIOLOGY POS
 Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 4... 4... 4... 4... Animal and Plant Cells - Eukaryotes Structure Organelle function Bacterial cells - Prokaryotes Structure Organelle function Term (7w) 4... Cell
Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 4... 4... 4... 4... Animal and Plant Cells - Eukaryotes Structure Organelle function Bacterial cells - Prokaryotes Structure Organelle function Term (7w) 4... Cell
AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) To pic. Student Checklist
 Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 s T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are 5.1.1 A simple
Personalised Learning Checklist AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 s T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table (Paper 1) State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are 5.1.1 A simple
Curriculum overview Key Stage 2 Living things and their habitats: Animals: Properties and changes of materials: Earth and Space: Forces: Evolution:
 Curriculum overview: Science (Separate award) Key Stage 2 Living things and their habitats: Life cycles of a mammal, an amphibian, an insect and a bird Reproduction in some plants and animals. Classification
Curriculum overview: Science (Separate award) Key Stage 2 Living things and their habitats: Life cycles of a mammal, an amphibian, an insect and a bird Reproduction in some plants and animals. Classification
Reproduction Chemical Reactions. 8J Light 8G Metals & Their Uses 8C Breathing & Respiration 8D Unicellular Organisms
 Science: Key Stage 3 Based on the Exploring Science Scheme of Learning Term 1 & 2 Term 3 & 4 Term 5 & 6 Year 7 Cells, Tissues & Organs Particles Forces & Motion Reproduction Chemical Reactions Chemical
Science: Key Stage 3 Based on the Exploring Science Scheme of Learning Term 1 & 2 Term 3 & 4 Term 5 & 6 Year 7 Cells, Tissues & Organs Particles Forces & Motion Reproduction Chemical Reactions Chemical
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 2009. M 37 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 2009 PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY ORDINARY LEVEL MONDAY, 15 JUNE MORNING 9:30 TO 12:30 Six questions to be
2009. M 37 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION 2009 PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY ORDINARY LEVEL MONDAY, 15 JUNE MORNING 9:30 TO 12:30 Six questions to be
Same theme covered in Combined but extra content Extra parts atomic symbols (first 20, Group 1 and Group 7)
 Co-teaching document new ELC Science 5960 and Foundation Level GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy (8464) Chemistry: Component 3 Elements, mixtures and compounds ELC Outcomes Summary of content covered in ELC
Co-teaching document new ELC Science 5960 and Foundation Level GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy (8464) Chemistry: Component 3 Elements, mixtures and compounds ELC Outcomes Summary of content covered in ELC
GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST
 GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Physics (J249) from 2016 Topic P1: Matter P1.1 Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time Describe the structure of the atom and discuss the charges
GCSE PHYSICS REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Physics (J249) from 2016 Topic P1: Matter P1.1 Describe how and why the atomic model has changed over time Describe the structure of the atom and discuss the charges
Trilogy - Science Revision
 Trilogy - Science Revision Sept 2015- June 2018 Year 11 Subject Unit Date AM/PM Name: Biology Paper 1 Biology Paper 2 Chemistry Paper 1 Chemistry Paper 2 Physics Paper 1 Physics Paper 2 Target: Tuesday
Trilogy - Science Revision Sept 2015- June 2018 Year 11 Subject Unit Date AM/PM Name: Biology Paper 1 Biology Paper 2 Chemistry Paper 1 Chemistry Paper 2 Physics Paper 1 Physics Paper 2 Target: Tuesday
HASTINGS HIGH SCHOOL
 Subject HASTINGS HIGH SCHOOL YEAR 11 EXAMINATION GUIDE 20167-19 COMBINED SCIENCE TRILOGY Physics Course code AQA GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE TRILOGY 8464 Website address Provisional examination dates http://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/science/gcse/combined-science-trilogy-
Subject HASTINGS HIGH SCHOOL YEAR 11 EXAMINATION GUIDE 20167-19 COMBINED SCIENCE TRILOGY Physics Course code AQA GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE TRILOGY 8464 Website address Provisional examination dates http://www.aqa.org.uk/subjects/science/gcse/combined-science-trilogy-
Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8. atom.
 Student checklist C1 Atomic structure Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8 C1.1 Atoms I can define the word element. I can classify familiar substances as elements or compounds. I can use the periodic table
Student checklist C1 Atomic structure Lesson Target 4 Target 6 Target 8 C1.1 Atoms I can define the word element. I can classify familiar substances as elements or compounds. I can use the periodic table
Additional Science Chemistry
 Additional Science Chemistry C2 Core Questions and Keywords and Definitions Question How did Mendeleev arrange the elements known at the time into a periodic table? How did Mendeleev use his table? Where
Additional Science Chemistry C2 Core Questions and Keywords and Definitions Question How did Mendeleev arrange the elements known at the time into a periodic table? How did Mendeleev use his table? Where
Physics GCSE (9-1) Energy
 Topic Student Checklist R A G Define a system as an object or group of objects and State examples of changes in the way energy is stored in a system Describe how all the energy changes involved in an energy
Topic Student Checklist R A G Define a system as an object or group of objects and State examples of changes in the way energy is stored in a system Describe how all the energy changes involved in an energy
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview
 Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Year 11 Science Learning Cycle 3 Overview Learning Cycle Overview: Biology Hypothesis 1 Hypothesis 2 Hypothesis 3 Hypothesis 4 Hypothesis 5 Hypothesis 6 Hypothesis 7 Hypothesis 8 Hypothesis 9 How does
Cells the Building Blocks of Life. Cells the Building Blocks of Life. Cells the Building Blocks of Life. Cells the Building Blocks of Life
 1 What is gestation? 2 Give three ways in which alveoli are adapted for gas exchange. 3 Describe what happens to someone when they suffer from an asthma attack. 4 What is meant by the term antagonistic
1 What is gestation? 2 Give three ways in which alveoli are adapted for gas exchange. 3 Describe what happens to someone when they suffer from an asthma attack. 4 What is meant by the term antagonistic
AQA Physics Checklist
 Topic 1. Energy Video: Energy changes in a system To understand the ways in which energy can be stored in a system and can be transferred from one energy store to another within a system To understand
Topic 1. Energy Video: Energy changes in a system To understand the ways in which energy can be stored in a system and can be transferred from one energy store to another within a system To understand
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST
 GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
GCSE CHEMISTRY REVISION LIST OCR Gateway Chemistry (J248) from 2016 Topic C1: Particles C1.1 Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter and change of state Explain, in
PROGRAMME OF STUDY FOR SCIENCE BECKET KEYS CHURCH OF ENGLAND SECONDARY SCHOOL. Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Term 4 Term 5 Term 6 Matter. Genes.
 Year 7 Matter Genes Earth Ecosystems Revision of year 7 Particle model Variation Earth Structure Interdependence Separating materials Human Reproduction Universe Plant reproduction (GFE Plan) (PTU-Review)
Year 7 Matter Genes Earth Ecosystems Revision of year 7 Particle model Variation Earth Structure Interdependence Separating materials Human Reproduction Universe Plant reproduction (GFE Plan) (PTU-Review)
8/24/2018. Bio 1101 Lecture 2 (guided) Chapters 2: Essential Chemistry. Chapter 2: Essential Chemistry for Biology
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lecture 2 (guided) Chapters 2: Essential Chemistry Chapter 2: Essential Chemistry for Biology Levels of biological organization Ecosystem (e.g. savanna) Community (e.g. the organisms
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1101 Lecture 2 (guided) Chapters 2: Essential Chemistry Chapter 2: Essential Chemistry for Biology Levels of biological organization Ecosystem (e.g. savanna) Community (e.g. the organisms
Chemical reactions. C2- Topic 5
 Chemical reactions C2- Topic 5 What is a chemical reaction? A chemical reaction is a change that takes place when one or more substances (called reactants) form one or more new substances (called products)
Chemical reactions C2- Topic 5 What is a chemical reaction? A chemical reaction is a change that takes place when one or more substances (called reactants) form one or more new substances (called products)
Department Curriculum and Assessment Outline
 Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of the cell wall. membrane?
 Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
Page 1 What is the role of the nucleus? What is the role of the cytoplasm? What is the role of the cell membrane? What is the role of the mitochondria? What is the role of ribosomes? What is the role of
Chemistry (separate) for November PPE
 1.1 Elements and 1.2 Atoms, formulae and Chapter 1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table Recognise the properties of elements and. Identify the elements
1.1 Elements and 1.2 Atoms, formulae and Chapter 1 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Identify symbols of elements from the periodic table Recognise the properties of elements and. Identify the elements
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE
 THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE ATOMS All living things are made up of matter Atoms are the smallest unit of matter Made up of 3 subatomic particles: 1. Protons- positively charged, found in the nucleus, has mass
THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE ATOMS All living things are made up of matter Atoms are the smallest unit of matter Made up of 3 subatomic particles: 1. Protons- positively charged, found in the nucleus, has mass
Paper Reference. Sample Assessment Material Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4CH0/1C Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Chemistry Paper 1 Sample Assessment Material Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Items included with question
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4CH0/1C Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry Chemistry Paper 1 Sample Assessment Material Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Items included with question
Proficiency Review #1
 Proficiency Review #1 What is the best way to determine how two people are most closely DNA related? What best measures a liquid? Graduated Cylinder A hydro-electric generator converts mechanical energy
Proficiency Review #1 What is the best way to determine how two people are most closely DNA related? What best measures a liquid? Graduated Cylinder A hydro-electric generator converts mechanical energy
Paper Atomic structure and the periodic table
 Paper 1 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in
Paper 1 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table 4.1.1 A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in
KS4 CURRICULUM. Science - BTEC
 KS4 CURRICULUM Science - BTEC Students have four lessons per fortnight completing a BTEC in the Principles of Applied Science. This is the equivalent to one GCSE. Unit One Principles of Science; externally
KS4 CURRICULUM Science - BTEC Students have four lessons per fortnight completing a BTEC in the Principles of Applied Science. This is the equivalent to one GCSE. Unit One Principles of Science; externally
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment
 Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
5 Energy from chemicals
 5 Energy from chemicals Content 5.1 Enthalpy 5.2 Hydrogen fuel cell Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) describe the meaning of enthalpy change in terms of exothermic (H
5 Energy from chemicals Content 5.1 Enthalpy 5.2 Hydrogen fuel cell Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) describe the meaning of enthalpy change in terms of exothermic (H
Paget High School. Preparing for A level Biology
 Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
Paget High School Preparing for A level Biology You will need a copy of the Head Start guide above and use it to make notes on the learning outcomes below. Topic areas Learning outcome Describe with the
PLC Booklet for. Paper 1
 PLC Booklet for Combined Science Paper 1 This personalised learning checklist (PLC) booklet has been put together to support your preparation for Biology Paper 1, Chemistry Paper 1 and Physics Paper1.
PLC Booklet for Combined Science Paper 1 This personalised learning checklist (PLC) booklet has been put together to support your preparation for Biology Paper 1, Chemistry Paper 1 and Physics Paper1.
7. Chlorine has an atomic number of 17, how many electrons does it have in its outermost (third) shell? a. 7 c. 2 e. 8 b. 4 d. 10
 Multiple Choice: 1-32 (1.5 points each). Circle the best answer here and fill in your bubble sheet. This portion of the exam will be graded using the bubble sheets only. 1. According to modern science,
Multiple Choice: 1-32 (1.5 points each). Circle the best answer here and fill in your bubble sheet. This portion of the exam will be graded using the bubble sheets only. 1. According to modern science,
0653 COMBINED SCIENCE
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0653 COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/31 Paper 3 (Extended
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 0653 COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/31 Paper 3 (Extended
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)
 PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Trilogy Chemistry Paper 1
 AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State
AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State
B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY
 B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY What are the 7 components of a healthy diet? 1.. 2.. 3.. 4.. 5.. 6.. 7.. What are the different methods of infection? Describe the issues with being overweight Describe
B1 REVISION CHAPTER 1 KEEPING HEALTHY What are the 7 components of a healthy diet? 1.. 2.. 3.. 4.. 5.. 6.. 7.. What are the different methods of infection? Describe the issues with being overweight Describe
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/41 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) 017 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 10
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/41 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) 017 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 10
AQA C1 Atomic Structure
 AQA C1 Atomic Structure What s in an atom? Elements in the periodic have different sizes of atoms. The size of the atoms depends on the number of protons, electrons and neutrons they have. Each element
AQA C1 Atomic Structure What s in an atom? Elements in the periodic have different sizes of atoms. The size of the atoms depends on the number of protons, electrons and neutrons they have. Each element
Chapter: Cell Processes
 Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Table of Contents Chapter: Cell Processes Section 1: Chemistry of Life Section 2: Moving Cellular Materials Section 3: Energy for Life 1 Chemistry of Life The Nature of Matter Matter is anything that has
Use estimations and explain when they should be used to judge the relative size or area of sub-cellular structures
 Trilogy Biology Paper 1 Topic Student Checklist R A G Use the terms 'eukaryotic' and 'prokaryotic' to describe types of cells Describe the features of bacterial (prokaryotic) cells Demonstrate an understanding
Trilogy Biology Paper 1 Topic Student Checklist R A G Use the terms 'eukaryotic' and 'prokaryotic' to describe types of cells Describe the features of bacterial (prokaryotic) cells Demonstrate an understanding
UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY
 UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 1: Biochemistry Chapter 6.1: Chemistry of Life I. Atoms, Ions, and Molecules A. Living things consist of atoms of different elements 1. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter
UNIT 1: BIOCHEMISTRY UNIT 1: Biochemistry Chapter 6.1: Chemistry of Life I. Atoms, Ions, and Molecules A. Living things consist of atoms of different elements 1. An atom is the smallest basic unit of matter
Review Chemistry Paper 1
 Atomic Structure Topic Define an atom and element. Use scientific conventions to identify chemical symbols Identify elements by chemical symbols Define compound Use chemical formulae to show different
Atomic Structure Topic Define an atom and element. Use scientific conventions to identify chemical symbols Identify elements by chemical symbols Define compound Use chemical formulae to show different
2.1. KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. 34 Reinforcement Unit 1 Resource Book
 2.1 ATOMS, IONS, AND MOLECULES KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. All matter, whether living or nonliving, is made of the same tiny building blocks, called atoms.
2.1 ATOMS, IONS, AND MOLECULES KEY CONCEPT All living things are based on atoms and their interactions. All matter, whether living or nonliving, is made of the same tiny building blocks, called atoms.
4 Energy and Rates of Chemical Reactions
 CHAPTER 14 4 and Rates of Chemical Reactions SECTION Chemical Reactions BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How is energy involved in a chemical reaction?
CHAPTER 14 4 and Rates of Chemical Reactions SECTION Chemical Reactions BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How is energy involved in a chemical reaction?
0654 CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-DINATED SCIENCES 0654/32 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 0654 CO-DINATED SCIENCES 0654/32 Paper 3 (Extended Theory), maximum
5. What is the name of the compound PbO? 6. What is the name of HCl(aq)?
 1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? (A) Atoms are extremely small. (B) Atoms of the same element have identical masses. (C) Atoms combine in simple whole
1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? (A) Atoms are extremely small. (B) Atoms of the same element have identical masses. (C) Atoms combine in simple whole
Exampro GCSE Chemistry
 Exampro GCSE Chemistry C Chapter 4 Higher Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 59 Marks: 59 Comments: Page of 0 Q. The picture shows a lump of phosphate rock. Rob Lavinsky, irocks.com CC-BY-SA-3.0 [CC-BY-SA-3.0],
Exampro GCSE Chemistry C Chapter 4 Higher Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 59 Marks: 59 Comments: Page of 0 Q. The picture shows a lump of phosphate rock. Rob Lavinsky, irocks.com CC-BY-SA-3.0 [CC-BY-SA-3.0],
0653 COMBINED SCIENCE
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2008 question paper 0653 COMBINED SCIENCE
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2008 question paper 0653 COMBINED SCIENCE
Orchard School. New Document 1 Name: Class: Date: 129 minutes. Time: 126 marks. Marks: Comments: Page 1
 New Document Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: 29 minutes 26 marks Comments: Page Q. The ph scale is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. (a) Solution Draw one line from each solution to
New Document Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: 29 minutes 26 marks Comments: Page Q. The ph scale is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. (a) Solution Draw one line from each solution to
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Physics Paper 1
 6.1.1 Energy changes in a system, and the ways energy is stored before and after such changes AQA TRILOGY Physics (8464) from 2016 Topics T6.1. Energy Topic Student Checklist R A G Define a system as an
6.1.1 Energy changes in a system, and the ways energy is stored before and after such changes AQA TRILOGY Physics (8464) from 2016 Topics T6.1. Energy Topic Student Checklist R A G Define a system as an
The response made by part of a plant, by which it grow towards
 Word/phrase Biology Nutrition Excretion Sensitivity Growth Reproduction Movement Digestion Enzyme Partially permeable Membrane Egestion Ingestion Photosynthesis Absorbtion Transpiration Translocation Respiration
Word/phrase Biology Nutrition Excretion Sensitivity Growth Reproduction Movement Digestion Enzyme Partially permeable Membrane Egestion Ingestion Photosynthesis Absorbtion Transpiration Translocation Respiration
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/41 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 10 Published
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education CO-ORDINATED SCIENCES 0654/41 Paper 4 Theory (Extended) MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 10 Published
New Specification 2018 Recurring Exam Questions. How Science Works. C1 - Particles. Atom with the same atomic number and different mass number
 How Science Works Why is it important that scientist publish their results? Results can be checked Further evidence can be collected How do scientists publish their work? Scientific conference Scientific
How Science Works Why is it important that scientist publish their results? Results can be checked Further evidence can be collected How do scientists publish their work? Scientific conference Scientific
C2.1 Structure and bonding
 C2.1 Structure and bonding C2 1.1 Chemical bonding Key words: A compound contains two or more elements which are chemically combined Covalent bonding sharing electrons Ionic bonding transferring electrons
C2.1 Structure and bonding C2 1.1 Chemical bonding Key words: A compound contains two or more elements which are chemically combined Covalent bonding sharing electrons Ionic bonding transferring electrons
for sodium ion (Na + )
 3.4 Unit 2 Chemistry 2 Throughout this unit candidates will be expected to write word equations for reactions specified. Higher tier candidates will also be expected to write and balance symbol equations
3.4 Unit 2 Chemistry 2 Throughout this unit candidates will be expected to write word equations for reactions specified. Higher tier candidates will also be expected to write and balance symbol equations
What do each of the hazard warning symbols below mean?
 Question 1 What do each of the hazard warning symbols below mean? Question 2 Draw a line to match the name of the separation technique to the type of mixture it is used to separate. filtration Used to
Question 1 What do each of the hazard warning symbols below mean? Question 2 Draw a line to match the name of the separation technique to the type of mixture it is used to separate. filtration Used to
In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium salt to produce potassium
 Q1. This question is about potassium. (a) Humphrey Davy was a professor of chemistry. In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium
Q1. This question is about potassium. (a) Humphrey Davy was a professor of chemistry. In 1807 Davy did an electrolysis experiment to produce potassium. Davy first tried to electrolyse a solid potassium
CHAPTER 2. Life s Chemical Basis
 CHAPTER 2 Life s Chemical Basis The Chemistry of Life We are made up of elements. Atoms of one kind make up an element. Atoms are the smallest unit of an element still maintaing the element s properties.
CHAPTER 2 Life s Chemical Basis The Chemistry of Life We are made up of elements. Atoms of one kind make up an element. Atoms are the smallest unit of an element still maintaing the element s properties.
OCR Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
Topic 1. Particles Video: The Particle Model Describe the main features of the particle model in terms of states of matter. Explain in terms of the particle model the distinction between physical changes
