IUPAC Nomenclature of Alkyne. Chapter 13: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
|
|
|
- Curtis Small
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chemistry 121(01) Winter Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) Office: 311 Carson Taylor all ; Phone: ; Office ours: MWF 8:00 am - 10:00 am; TT 9:00 10:00 am & 1:00-2:00 pm. December 17, 2010 Test 1 (Chapters 12-13) January 19, 2011 Test 2 (Chapters 14,15 & 16) February 7, 2011 Test 3(Chapters 17, 18 & 19) February 23, 2011 Test 4 (Chapters 20, 21 & 22) February 24, 2011 Comprehensive Make Up Exam: Chapter 13: Unsaturated ydrocarbons Sections Chapter 13: Unsaturated ydrocarbons 13.2 Characteristics of Alkenes and Cycloalkenes 13.3 Names for Alkenes and Cycloalkenes 13.4 Line-Angle Formulas for Alkenes 13.5 Isomerism in Alkenes 13.6 Naturally Occurring Alkenes 13.7 Physical Properties of Alkenes 13.8 Chemical Reactions of Alkenes 13.9 Polymerization of Alkenes: Addition Polymers Alkynes Aromatic ydrocarbons Names for Aromatic ydrocarbons Aromatic ydrocarbons: Physical Properties and Sources Chemical Reactions of Aromatic ydrocarbons Fused-Ring Aromatic Compounds Chemical Connections: Ethene: A Plant ormone and igh-volume Industrial Chemical; Cis-Trans Isomerism and Vision; Carotenoids: A Source of Color; Fused-Ring Aromatic ydrocarbons and Cancer IUPAC Nomenclature of Alkyne CAG
2 Unsaturated ydrocarbons cont d Fig chlorotoluene molecule Unsaturated hydrocabons ydrocarbons with carbon-carbon double bonds and triple bonds double bonds: alkenes triple bonds: alkynes three alternating double bond in 6 carbon ring: aromatics Copyright oughton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved Unsaturated ydrocarbons in Use Beta-carotene is in carrots Acetylene: Welding Unsaturated ydrocarbons: Alkenes Alkynes Arenes C C C C C C Ethene is the hormone that causes tomatoes to ripen. sex pheromones in insect control involves luring insect into a trap. ethene ethyne benzene C 2 4 C 2 2 C 6 6 C n 2n C n 2n-2 C n n unsaturated unsaturated Aromatic alkene alkyne Arene Chapters 13 Chapters 13 Chapter
3 Units of Unsaturation Compounds that have have fewer hydrogens than saturated hydrocarbons (C n 2n+2 ). Two hydrogen are considered as unit of unstauration Cycloalkane ring C n 2n (one unit of unsat.) Structure of Alkenes Alkene: contains a carbon-carbon double bond and has the general formula C n 2n The two carbon atoms of a double bond and the four atoms bonded to them lie in a plane, with bond angles of approximately 120 Unsaturated hydrocarbons: bond C n 2n (one unit of unsat.) bond C n 2n-2 (two units of unsat.) C C Ethylene C 3 C C Propene Bonding in ethene (ethylene) Fig In ethene, the atoms are in a flat rather than a tetrahedral arrangement. Planar Structure of Alkenes According to the orbital overlap model, a double bond consists of a s bond formed by overlap of sp 2 hybrid orbitals a p bond formed by overlap of parallel 2p orbital Rotating by 90 breaks the pi bond
4 Structure of Alkynes The functional group of an alkyne is a carbon-carbon triple bond A triple bond consists of one s bond formed by the overlap of sp hybrid orbitals two p bonds formed by the overlap of sets of parallel 2p orbitals Alkenes Second members of the hydrocarbon family. contain only hydrogen and carbon have single bonds and at least one C=C double bond All members have the general formula of C n 2n Twice as many hydrogen as carbon Alkenes: Naming and Structures One simple class of compound is the alkene which has only C, and single bonds. ethene propene 2- butene C 2 4 C 3 6 C 4 8 C 2 C 2 C 3 C 2 C 2 C 3 C 2 CC IUPAC Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes name the longest continuous carbon chain containing the multiple bond(s) (parent chain). If cyclic, ring is the parent. use the infix -en- to show the presence of a carbon-carbon double bond use the infix -yn- to show the presence of a carbon-carbon triple bond number the parent chain to give the 1st carbon of the double/triple bond the lower number If both double and triple are present and cannot have the same #, then double bonds take priority. follow IUPAC general rules for numbering and naming substituents for a cycloalkene, the double bond must be numbered 1,
5 IUPAC Nomenclature of Alkynes use the infix -yn- to show the presence of a carboncarbon triple bond number the parent chain to give the 1st carbon of the triple bond the lower number follow IUPAC rules for numbering and naming substituents Methyl-1-butyne 6,6-Dimethyl-3-heptyne Example of IUPAC Nomenclature of Alkenes Cycloalkanes exene Methyl-1-hexene C Methylcyclopentene 1,6-Dimethylcyclohexene 2-Ethyl-3-methyl- 1-pentene C 3 C Nomenclature of Alkenes: Common Names Alkenes Some alkenes, particularly low-molecular-weight ones, are known almost exclusively by their common names C 3 First four members of the alkanes Name # of C Condensed formula IUPAC: Common: C 2 =C 2 C 3 C=C 2 C 3 C=C 2 Ethene Propene 2-Methylpropene Ethylene Propylene Isobutylene Ethene 2 C 2 =C 2 Propene 3 C 3 C=C 2 2-Butene 4 C 3 C=CC 3 Called a homologous series Members differ by number of C 2 groups
6 Physical State of Alkynes Physical state summary for unbranched 1 alkynes at room temperature and pressure. Cis and trans Geometrical isomers of alkenes two groups are said to be located cis to each other if they lie on the same side of a plane with respect to the double bond. If they are on opposite sides, their relative position is described as trans Isomerism in Alkanes & Alkenes Cis-trans isomerism in 2-butene Fig Cis-trans isomers: Different representatives of the cis and trans isomers of 2-butene. Fig A comparison of structural isomerism possibilities for four and five-carbon alkane and alkene systems
7 Unsaturated Aromatic ydrocarbons Geometrical Stereoisomerism Because of restricted rotation about a C-C double bond, groups on adjacent carbons are either cis or trans to each other CC C C C C 3 cis-2-butene mp -139 C, bp 4 C 3 C C C C 3 t rans-2-butene mp -106 C, bp 1 C Physical Properties Alkenes and alkynes are nonpolar compounds the only attractive forces between their molecules are dispersion forces Their physical properties are similar to those of alkanes of similar carbon skeletons those that are liquid at room temperature are less dense than water (1.0 g/m L) they dissolve in each other and in nonpolar organic solvents they are insoluble in water Cis-Trans Isomerism trans alkenes are more stable than cis alkenes because of nonbonded interaction strain between alkyl substituents of the same side of the double bond
8 Summary of Physical State of Unsaturated ydrocarbons Geometric isomers There are two possible arrangements. Example 2-butene 3C C3 3C C=C C=C C3 cis Largest groups are on the same side. trans Largest groups are on opposite sides Cis-Trans Isomerism in Cycloalkenes the configuration of the double bond in cyclopropene through cycloheptene must be cis; these rings are not large enough to accommodate a trans double bond C 3 C 3 cyclooctene is the smallest cycloalkene that can accommodate a trans double bond Cis-Trans Isomerism Dienes, trienes, and polyenes for an alkene with n carbon-carbon double bonds, each of which can show cis-trans isomerism, 2 n cis-trans isomers are possible consider 2,4-heptadiene; it has four cis-trans isomers, two of which are drawn here Double bond C 2 -C 3 C 4 -C 5 trans trans trans cis cis trans cis cis t rans,t rans-2,4- heptadiene trans,cis-2,4- heptadiene trans- Cyclooctene cis-cyclooctene
9 Naturally Occurring AlkenesCis-Trans Isomerism vitamin A has five double bonds four of the five can show cis-trans isomerism vitamin A is the all-trans isomer O enzymecatalyzed oxidation Naturally Occurring Alkenes: The Terpenes Terpene: a compound whose carbon skeleton can be divided into two or more units identical with the carbon skeleton of isoprene Vitamin A (retinol) O head tail Vitamin A aldehyde (retinal) 2-Methyl-1,3-butadiene (Isoprene) Terpenes with isoprene units Terpenes: Polymers of Isoprene myrcene, C 10 16, a component of bayberry wax and oils of bay and verbena menthol, from peppermint O
10 Terpenes Vitamin A (retinol) the four isoprene units in vitamin A are shown in red they are linked head to tail, and cross linked at one point (the blue bond) to give the six-membered ring Reactions of Unsaturated ydrocarbons CAG 13.1 O Reactions of alkenes Combustion C O 2 2 CO O + heat Addition Reactions The exposed electrons of double bonds make alkenes more reactive than alkanes and show addition reactions. Alkynes also under go combustion reactions similarly
11 Addition Reaction of Alkenes In an alkene addition, reaction, the atoms provided by an incoming molecule are attached to the carbon atoms originally joined by a double bond. In the process, the double bond becomes a single bond. Addition of Bromines Fig A bromine in water solution is reddish brown. When a small amount of such a solution is added to an unsaturated hydrocarbon, the added solution is decolorized Markovnikov s Rule Vladimir Markovnikov synthesized rings containing four carbon atoms and seven carbon atoms. Markovnikov Rule Non symmetric alkene In hydrohalogenation and hydration reations hydrogen adds to the double-bonded carbon with the most hydrogens
12 Addition Polymerizations Preparation of polystyrene. Polymers of Unsaturated ydrocarbons (a) polyethylene (b) polypropylene (c) poly (vinyl chloride) alogenation alogenation - Addition of halogen to the double bond. Textbook page xx
13 ydrogenation Addition of hydrogen to the double bond. Textbook page ydration Addition of water to the double bond. Textbook page
14 Polymerization Formula Name Monomer Polymer Polypropylene C 3 C=C 2 ( C-C 2 ) C 3 Polystyrene -C=C 2 ( C-C 2 ) Polychloroprene 2 C=CC=C 2 ( C 2 C=CC 2 ) Cl Cl
15 Naming alkenes and alkynes Find the longest carbon chain. Use as base name with an ene or yne ending. Number the chain to give lowest number for the carbons of the double or triple bond. Locate any branches on chain. Use base names with a yl ending. For multiple branch of the same type, modify name with di, tri,... Show the location of each branch with numbers. List multiple branches alphabetically - the di, tri,... don t count.. Alkyne Bonding Ethyne, is the simplest alkyne Reactions of alkynes Alkynes undergo hydration, halogenation, and hydrohalogenation just like alkenes. A special application is the carbide lamp (oxidation of alkyne). 2 C (coke) + CaO (lime) + heat ---> CaC 2 (calcium carbide) + CO CaC O ---> -C C- (acetylene) + Ca(O) 2 Acetylene serves as combustion fuel for the carbide lamp. Aromatic hydrocarbons Aromatic hydrocarbons - organic compounds that had aromas and had different chemical properties from alkane Benzene is the parent compound for the aromatic hydrocarbons. Textbook, page90. Consider benzene. C
16 Unsaturated ydrocarbons cont d Unsaturated ydrocarbons cont d Fig Space-filling and ball-and-stick models for the structure of benzene. CC Copyright oughton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved Resonance Structures of Benzene Resonance structures or contributing structures = when two or more structure can be drawn for a compound. In thiscase, the real structure is something between the proposed structures. Textbook, page Naming Aromatic ydroarbons. Monosubstituted benzenes: Ar-C 2 C 3 ethylbenzene Ar-C 2 -C 2 -C 2 -C 3 butylbenzene Ar-C 3 (methylbenzene) toluene Ar-X (halobenzene) bromobenzene, Ar-NO 2 nitrobenzene Ar-SO 3 benzenesulfonic acid Ar-N 2 a nitrile substituent X
17 Nomenclature Disubstituted benzenes locate substituents by numbering or use the locators ortho (1,2-), meta (1,3-), and para (1,4-) Where one group imparts a special name, name the compound as a derivative of that molecule C 3 Br 4-Bromotoluene (p-bromotoluene) N 2 Cl 3-Chloroaniline (m-chloroaniline) COO NO 2 2-Nitrobenzoic acid (o-nitrobenzoic acid) Nomenclature Polysubstituted benzenes with three or more substituents, number the atoms of the ring if one group imparts a special name, it becomes the parent name if no group imparts a special name, number to give the smallest set of numbers, and then list alphabetically C NO 2 O Br Br 5 NO Cl 4-Chloro-2-nitrotoluene Br 2,4,6-Tribromophenol Br C 2 C 3 2-Bromo-1-ethyl-4- nitrobenzene Disubstituted benzenes: Textbook, page ,6-dibromotoluene p-diethylbenzene 3,5-dinitrotoluene p-cholonitrobenzene o-nitrobenzenesulfonic acid 4-benzyl-1-octene m-cyanotoluene
18 Reactions of Benzene The most characteristic reaction of aromatic compounds is substitution at a ring carbon alogenation: FeCl + Cl 3 2 Cl + Cl Chlorobenzene Nitration: 2 SO 4 + NO 3 NO O Nitrobenzene
19 Benzylic Oxidation Benzene is unaffected by strong oxidizing agents such as 2 CrO 4 and KMnO 4 halogen and nitro substituents are unaffected by these reagents an alkyl group with at least one hydrogen on the benzylic carbon is oxidized to a carboxyl group C 3 2 CrO 4 COO O 2 N Cl O 2 N Cl 2-Chloro-4-nitrotoluene 2-Chloro-4-nitrobenzoic acid Benzylic Oxidation if there is more than one alkyl group, each is oxidized to a -COO group 3 C C 3 1,4-Dimethylbenzene (p-xylene) 2 CrO 4 O OC O CO 1,4-Benzenedicarboxylic acid (terephthalic acid) terephthalic acid is one of the two monomers required for the synthesis of poly(ethylene terephthalate), a polymer that can be fabricated into Dacron polyester fibers and into Mylar films Reactions of Benzene Sulfonation: Alkylation: + 2 SO 4 SO O Acylation: + RX + O R-C-X An acyl halide Benzenesulfonic acid AlCl 3 R + X An alkylbenzene AlCl 3 O CR An acylbenzene + X Nitration The electrophile is NO 2+, generated in this way O NO 2 + O SO 3 + O NO 2 + SO 4 Nitric acid Conjugate acid of nitric acid + O NO 2 O + + NO 2 The nitronium ion
20 Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Friedel-Crafts alkylation forms a new C-C bond between an aromatic ring and an alkyl group + Cl AlCl 3 Benzene 2-Chloropropane (Isopropyl chloride) Isopropylbenzene (Cumene) + Cl Friedel-Crafts Acylations Treating an aromatic ring with an acid chloride in the presence of AlCl 3 acid (acyl) chloride: a derivative of a carboxylic acid in which the -O is replaced by a chlorine + O C 3 CCl O CC 3 AlCl 3 + Cl Benzene Acetyl chloride (an acyl halide) Acetophenone (a ketone)
Chapter 13: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Chemistry 121(01) Winter 2009 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@chem.latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor all ; Phone:
Chemistry 121(01) Winter 2009 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@chem.latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor all ; Phone:
Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Chapter 13
 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Chapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes
 BR M 102 lass Notes hapter 12 Page 1 of 8 hapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes * alkenes = double bonds * alkynes triple bonds * aromatics or arenes alternating double and single bonds such as in benzene * saturated
BR M 102 lass Notes hapter 12 Page 1 of 8 hapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes * alkenes = double bonds * alkynes triple bonds * aromatics or arenes alternating double and single bonds such as in benzene * saturated
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette
 Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Organic Chemistry. February 18, 2014
 Organic Chemistry February 18, 2014 What does organic mean? Organic Describes products Grown through natural biological process Without synthetic materials In the 18 th century Produced by a living system
Organic Chemistry February 18, 2014 What does organic mean? Organic Describes products Grown through natural biological process Without synthetic materials In the 18 th century Produced by a living system
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
3. What number would be used to indicate the double bond position in the IUPAC name for CH 3 CH 2 CH=CH CH 3 a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d.
 Chapter 2 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Name a difference between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon. a. Saturated hydrocarbons are composed of only carbon and hydrogen, and unsaturated
Chapter 2 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Name a difference between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon. a. Saturated hydrocarbons are composed of only carbon and hydrogen, and unsaturated
Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC AND BIOCHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the IUPAC name
INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC AND BIOCHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the IUPAC name
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
Organic Chemistry. Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon.
 Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. In this chapter we will discuss the structural features of organic molecules, nomenclature, and a
Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. In this chapter we will discuss the structural features of organic molecules, nomenclature, and a
Introduction to Organic Chemistry. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 8 Dr Ali El-Agamey Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives To name a benzene ring with one substituent, name
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 8 Dr Ali El-Agamey Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives To name a benzene ring with one substituent, name
CHAPTER 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons IMPORTANT COMMON NAMES: 12.1 NOMENCLATURE GEOMETRY of ALKENES. Page 12-1
 APTER 12: Unsaturated ydrocarbons lassify unsaturated hydrocarbons as alkenes, alkynes, or aromatics Write the IUPA names of alkenes from structural formulas Predict and describe geometric (cis-trans)
APTER 12: Unsaturated ydrocarbons lassify unsaturated hydrocarbons as alkenes, alkynes, or aromatics Write the IUPA names of alkenes from structural formulas Predict and describe geometric (cis-trans)
AP Chemistry Chapter 22 - Organic and Biological Molecules
 AP Chemistry Chapter - Organic and Biological Molecules.1 Alkanes: Saturated Hydrocarbons A. Straight-chain Hydrocarbons 1. Straight-chain alkanes have the formula C n H n+. Carbons are sp hybridized The
AP Chemistry Chapter - Organic and Biological Molecules.1 Alkanes: Saturated Hydrocarbons A. Straight-chain Hydrocarbons 1. Straight-chain alkanes have the formula C n H n+. Carbons are sp hybridized The
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 3. AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS Aromatic
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 3. AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS Aromatic
240 Chem. Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 6
 240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
Chapter 22. Organic and Biological Molecules
 Chapter 22 Organic and Biological Molecules The Bonding of Carbon Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. Because carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds, the following
Chapter 22 Organic and Biological Molecules The Bonding of Carbon Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. Because carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds, the following
HISTORY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 hemistry 52 hapter 12 ISTORY OF ORGANI EMISTRY In the early days of chemistry, scientists classified chemical substances into 2 groups: 1. Inorganic: those that were composed of minerals, such as rocks
hemistry 52 hapter 12 ISTORY OF ORGANI EMISTRY In the early days of chemistry, scientists classified chemical substances into 2 groups: 1. Inorganic: those that were composed of minerals, such as rocks
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Unsaturated ydrocarbons hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n 2n n 2n+2 n 2n+2 hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n n n 2n n 2n hemical Formulas and Unsaturation ydrocarbons Saturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated
Unsaturated ydrocarbons hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n 2n n 2n+2 n 2n+2 hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n n n 2n n 2n hemical Formulas and Unsaturation ydrocarbons Saturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated
Chem101 General Chemistry. Lecture 11 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 hem101 General hemistry Lecture 11 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. University of Wisconsin-Eau laire hem101 - Lecture 11 2 Unsaturated
hem101 General hemistry Lecture 11 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. University of Wisconsin-Eau laire hem101 - Lecture 11 2 Unsaturated
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Excluded sections 3.15&3.16
 Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Chemistry B11 Chapters Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Benzene
 Chapters 10-11 Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Benzene Organic compounds: organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon and only a few other elements-chiefly, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, halogens,
Chapters 10-11 Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Benzene Organic compounds: organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon and only a few other elements-chiefly, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, halogens,
Chemistry 110. Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell. Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes.
 Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes
 Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
UNIT (7) ORGANIC COMPOUNDS: HYDROCARBONS
 UNIT (7) RGANI MPUNDS: YDRARBNS rganic chemistry is the study carbon containing compounds. 7.1 Bonding in rganic ompounds rganic compounds are made up of only a few elements and the bonding is almost entirely
UNIT (7) RGANI MPUNDS: YDRARBNS rganic chemistry is the study carbon containing compounds. 7.1 Bonding in rganic ompounds rganic compounds are made up of only a few elements and the bonding is almost entirely
CHEMISTRY CHAPTER- HYDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions
 CEMISTRY CAPTER- YDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions 1. What type of structural isomerism is shown by alkanes? 2. Which metal is used in Wurtz reaction? 3. What happens when isopropyl bromide is subjected
CEMISTRY CAPTER- YDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions 1. What type of structural isomerism is shown by alkanes? 2. Which metal is used in Wurtz reaction? 3. What happens when isopropyl bromide is subjected
Chemical Reactions of Unsaturated Compounds
 hemical Reactions of Unsaturated ompounds hemical Reactions of Alkenes hemical Reactions of Alkenes Structure of the Double Bond in Alkenes The two components of the double bond are pictured the same,
hemical Reactions of Unsaturated ompounds hemical Reactions of Alkenes hemical Reactions of Alkenes Structure of the Double Bond in Alkenes The two components of the double bond are pictured the same,
Alkenes, Alkynes and Aromatic
 BIO-ORGANI EMISTRY (Organic hemistry for Biology Students) (SQBS 1603) Alkenes, Alkynes and Aromatic Dr Nik Ahmad Nizam Bin Nik Malek, BSc (Ind. hem.)(utm), MSc (hem)(utm), PhD (hem)(utm), A.M.I. Senior
BIO-ORGANI EMISTRY (Organic hemistry for Biology Students) (SQBS 1603) Alkenes, Alkynes and Aromatic Dr Nik Ahmad Nizam Bin Nik Malek, BSc (Ind. hem.)(utm), MSc (hem)(utm), PhD (hem)(utm), A.M.I. Senior
Chapters 2 & 25: Covalent bonds & Organic Chemistry
 hapters 2 & 25: ovalent bonds & Organic hemistry Read: BLB 2.6, 2.9; 25.1-25.4 (only nomenclature in Table 25.1, NOT reactions) W: BLB 2:43, 45, 69, 76, 77 BLB 25:11, 12, 25, 40a, c-f Packet Organic:1
hapters 2 & 25: ovalent bonds & Organic hemistry Read: BLB 2.6, 2.9; 25.1-25.4 (only nomenclature in Table 25.1, NOT reactions) W: BLB 2:43, 45, 69, 76, 77 BLB 25:11, 12, 25, 40a, c-f Packet Organic:1
Ch09. Alkenes & Alkynes. Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Double and triple bonds in our carbon backbone. version 1.0
 Ch09 Alkenes & Alkynes Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Double and triple bonds in our carbon backbone. version 1.0 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2015 Ch09 Alkenes & Alkynes Alkenes & Alkynes Definition and bond angles.
Ch09 Alkenes & Alkynes Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Double and triple bonds in our carbon backbone. version 1.0 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2015 Ch09 Alkenes & Alkynes Alkenes & Alkynes Definition and bond angles.
Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing.
 Chapter 21 Lecture Notes Organic Chemistry Intro Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing. The Bonding of Carbon Because carbon has four valence electrons, it can form covalent bonds.
Chapter 21 Lecture Notes Organic Chemistry Intro Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing. The Bonding of Carbon Because carbon has four valence electrons, it can form covalent bonds.
Chapter 13 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 hapter 1 1 hapter 1 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Solutions to In-hapter Problems 1.1 To draw a complete structure for each condensed structure, first draw in the multiple bonds. Then draw in all the other s
hapter 1 1 hapter 1 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Solutions to In-hapter Problems 1.1 To draw a complete structure for each condensed structure, first draw in the multiple bonds. Then draw in all the other s
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Paul D. Adams University of Arkansas Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Paul D. Adams University of Arkansas Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives
Alkenes. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
 Alkenes Alkenes Each member contains one double covalent bond between two C atoms. Draw condensed structural formulas of first three members of alkenes family. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
Alkenes Alkenes Each member contains one double covalent bond between two C atoms. Draw condensed structural formulas of first three members of alkenes family. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- 1
 ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Interchapter G Unsaturated ydrocarbons The flame from an acetylene torch. Acetylene, which is used extensively in welding, is an example of an unsaturated hydrocarbon. University Science Books, 2011. All
Interchapter G Unsaturated ydrocarbons The flame from an acetylene torch. Acetylene, which is used extensively in welding, is an example of an unsaturated hydrocarbon. University Science Books, 2011. All
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
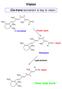 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Alkenes. Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents
 Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Name Date Class HYDROCARBONS
 22.1 HYDROCARBONS Section Review Objectives Describe the relationship between number of valence electrons and bonding in carbon Define and describe alkanes Relate the polarity of hydrocarbons to their
22.1 HYDROCARBONS Section Review Objectives Describe the relationship between number of valence electrons and bonding in carbon Define and describe alkanes Relate the polarity of hydrocarbons to their
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chemistry 11. Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons
 Chemistry 11 Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons 2 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbons So far, we have studied the hydrocarbons in which atoms are connected exclusively by
Chemistry 11 Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons 2 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbons So far, we have studied the hydrocarbons in which atoms are connected exclusively by
Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline
 Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Slide 2 Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of and its compounds. The major sources of carbon are the fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas,
Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Slide 2 Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of and its compounds. The major sources of carbon are the fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas,
Chemistry 121(01) Winter 2014
 Chemistry 121(01) Winter 2014 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121(01) Winter 2014 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS
 C20 09/16/2013 15:47:28 Page 295 CHAPTER 20 UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The sigma bond in the double bond of ethene is formed by the overlap of two sp 2 electron orbitals
C20 09/16/2013 15:47:28 Page 295 CHAPTER 20 UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The sigma bond in the double bond of ethene is formed by the overlap of two sp 2 electron orbitals
Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Why this Chapter? Continuation of coverage of aromatic compounds in preceding chapter focus shift to understanding reactions Examine relationship
Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Why this Chapter? Continuation of coverage of aromatic compounds in preceding chapter focus shift to understanding reactions Examine relationship
CHAPTER 3 ALKENES, ALKYNES & CONJUGATE DIENES
 CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
Chapter 20 (part 2) Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 20 (part 2) Organic Chemistry Section 20.7 Alkenes and Alkynes Alkenes: hydrocarbons that contain a carbon carbon double bond. [C n H 2n ] CH 3 CH=CH 2 propene Alkynes: hydrocarbons containing
Chapter 20 (part 2) Organic Chemistry Section 20.7 Alkenes and Alkynes Alkenes: hydrocarbons that contain a carbon carbon double bond. [C n H 2n ] CH 3 CH=CH 2 propene Alkynes: hydrocarbons containing
Alkanes 3/27/17. Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means fat ) - Open chain Aromatic - ring. Alkane Alkene Alkyne
 Alkanes EQ 1. How will I define Hydrocarbons? 2. Compare and contrast the 3 types of hydrocarbons (Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes). Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means
Alkanes EQ 1. How will I define Hydrocarbons? 2. Compare and contrast the 3 types of hydrocarbons (Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes). Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means
08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16
 08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16 Benzene is a nucleophile p electrons make benzene nucleophile, like alkenes.
08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16 Benzene is a nucleophile p electrons make benzene nucleophile, like alkenes.
MOLECULER MODELS/ISOMERS ORGANIC STRUCTURES AND NAMING
 REVISED 10/14 EMISTRY 1101L MOLEULER MODELS/ISOMERS ORGANI STRUTURES AND NAMING NOTE: This lab does not require safety glasses or lab coats. INTRODUTION Electron Dot Structures: Electron dot structures,
REVISED 10/14 EMISTRY 1101L MOLEULER MODELS/ISOMERS ORGANI STRUTURES AND NAMING NOTE: This lab does not require safety glasses or lab coats. INTRODUTION Electron Dot Structures: Electron dot structures,
Reading: Chapter 4 Practice Problems: in text problems and 19 22, 24, 26, 27, 29, 30, 33 35, 39, 40.
 Reading: Chapter Practice Problems: in text problems and 19 22, 24, 26, 27, 29, 30, 33 35, 39, 40. Alkenes: Structure, Nomenclature, Stability, and an Introduction to Reactivity Alkenes are unsaturated
Reading: Chapter Practice Problems: in text problems and 19 22, 24, 26, 27, 29, 30, 33 35, 39, 40. Alkenes: Structure, Nomenclature, Stability, and an Introduction to Reactivity Alkenes are unsaturated
Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic Compounds
 Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic Compounds Alkenes and Alkynes Unsaturated Contain carbon-carbon DOUBLE and TRIPLE bond to which more hydrogen atoms can be added Alkenes: carbon-carbon double bonds Alkynes:
Alkenes, Alkynes, and Aromatic Compounds Alkenes and Alkynes Unsaturated Contain carbon-carbon DOUBLE and TRIPLE bond to which more hydrogen atoms can be added Alkenes: carbon-carbon double bonds Alkynes:
Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chapter 10 Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide 10.1 Know that unstable nuclei can undergo radioactive decay. Identify alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays based on physical properties such
Chapter 10 Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide 10.1 Know that unstable nuclei can undergo radioactive decay. Identify alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays based on physical properties such
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry Organic Chemistry The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to form long chains. Without this property, large biomolecules such as proteins,
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry Organic Chemistry The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to form long chains. Without this property, large biomolecules such as proteins,
Chapter 2. Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism
 Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. There are three main classes of hydrocarbons, based on the
Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. There are three main classes of hydrocarbons, based on the
(1) Recall the classification system for substituted alkenes. (2) Look at the alkene indicated. Count the number of bonds to non-hydrogen groups.
 Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 10: Alkenes, Alkynes, and Dienes No. 1 of 10 1. What is the substitution pattern for alkene indicated below? (A) mono (B) di (C) tri (D) tetra (E) unsubstituted Mono is
Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 10: Alkenes, Alkynes, and Dienes No. 1 of 10 1. What is the substitution pattern for alkene indicated below? (A) mono (B) di (C) tri (D) tetra (E) unsubstituted Mono is
Chapter 17. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
A. They all have a benzene ring structure in the molecule. B. They all have the same molecular formula. C. They all have carbon and hydrogen only
 Ch 21 G12 CoreI- Choose the best answer, then transfer your answers to page (1) [32 marks; 2 each] 1. What characteristic do all aromatic hydrocarbons share? A. They all have a benzene ring structure in
Ch 21 G12 CoreI- Choose the best answer, then transfer your answers to page (1) [32 marks; 2 each] 1. What characteristic do all aromatic hydrocarbons share? A. They all have a benzene ring structure in
1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane?
 1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? The formation of ethane is due to the side reaction in termination step by the combination of two CH 3 free radicals. 2.
1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? The formation of ethane is due to the side reaction in termination step by the combination of two CH 3 free radicals. 2.
Straight. C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized. Butane, C 4 H 10 H 3 C
 Hydrocarbons Straight Chain Alkanes aren t Straight C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized Butane, C 4 H 10 Structural Shorthand Explicit hydrogens (those required to complete carbon s valence) are usually left
Hydrocarbons Straight Chain Alkanes aren t Straight C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized Butane, C 4 H 10 Structural Shorthand Explicit hydrogens (those required to complete carbon s valence) are usually left
Organic Chemistry. A. Introduction
 Organic Chemistry A. Introduction 1. Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of CARBON compounds. There are a huge number of organic compounds. This results from the fact that carbon forms chains
Organic Chemistry A. Introduction 1. Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of CARBON compounds. There are a huge number of organic compounds. This results from the fact that carbon forms chains
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds
 1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds. Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde
 Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde Sources of Benzene Benzene, C 6 H 6, is the parent hydrocarbon of the especially stable compounds known
Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde Sources of Benzene Benzene, C 6 H 6, is the parent hydrocarbon of the especially stable compounds known
William H. Brown & Christopher S. Foote
 William. Brown & Christopher S. Foote Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:permissions Department, arcourt Brace & Company, 6277 Sea arbor Drive, Orlando,
William. Brown & Christopher S. Foote Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:permissions Department, arcourt Brace & Company, 6277 Sea arbor Drive, Orlando,
CHEM 203 Exam 1. Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHEM 203 Exam 1 Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both the earth's
CHEM 203 Exam 1 Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both the earth's
Unit 12 Organic Chemistry
 Unit 12 Organic Chemistry Day 138 5/5/14 QOD: What is Organic Chemistry? Do Now: True or false? 1. Electrochemical cells generate electricity. 2. Electrons flow from left to right in a battery. 3. Redox
Unit 12 Organic Chemistry Day 138 5/5/14 QOD: What is Organic Chemistry? Do Now: True or false? 1. Electrochemical cells generate electricity. 2. Electrons flow from left to right in a battery. 3. Redox
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes
 Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons generally fall into 2 general groupings, aliphatic hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatic hydrocarbons contain chains and rings of hydrocarbons,
Alkanes, Alkenes and Alkynes Hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons generally fall into 2 general groupings, aliphatic hydrocarbons and aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatic hydrocarbons contain chains and rings of hydrocarbons,
HISTORY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 ISTORY OF ORGANI EMISTRY In the early days of chemistry, scientists classified chemical substances into 2 groups: 1. Inorganic: those that were composed of minerals, such as rocks and nonliving matter.
ISTORY OF ORGANI EMISTRY In the early days of chemistry, scientists classified chemical substances into 2 groups: 1. Inorganic: those that were composed of minerals, such as rocks and nonliving matter.
CHEMISTRY - TRO 4E CH.21 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com TOPI: ORGANI EMISTRY Organic hemistry is the study of carbon and the other common nonmetals it is connected to:,, &. Some organic molecules are made of just carbons and hydrogens
!! www.clutchprep.com TOPI: ORGANI EMISTRY Organic hemistry is the study of carbon and the other common nonmetals it is connected to:,, &. Some organic molecules are made of just carbons and hydrogens
BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS Dr. Zainab M Almarhoon 2 Learning Objectives By the end of chapter four the students will: Understand the resonance description of structure of benzene Understand the hybridization
BENZENE & AROMATIC COMPOUNDS Dr. Zainab M Almarhoon 2 Learning Objectives By the end of chapter four the students will: Understand the resonance description of structure of benzene Understand the hybridization
1.3 Reactions of Hydrocarbons
 1.3 Reactions of ydrocarbons All hydrocarbons readily burn in air to give carbon dioxide and water, with the release of large amounts of energy (Figure 1); this chemical reaction accounts for the extensive
1.3 Reactions of ydrocarbons All hydrocarbons readily burn in air to give carbon dioxide and water, with the release of large amounts of energy (Figure 1); this chemical reaction accounts for the extensive
Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes
 Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes Chapter 4 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 st semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition for Alkynes. Nomenclature of
Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes Chapter 4 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 st semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition for Alkynes. Nomenclature of
4. AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BOOKS 1) Organic Chemistry Structure and Function, K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil Schore, 6th Edition 2) Organic Chemistry, T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle 3) Organic Chemistry: A Short Course, H.
BOOKS 1) Organic Chemistry Structure and Function, K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil Schore, 6th Edition 2) Organic Chemistry, T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle 3) Organic Chemistry: A Short Course, H.
Alkenes and Alkynes 10/27/2010. Chapter 7. Alkenes and Alkynes. Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes CHP6 Problems: 6.1-13, 16-34, 36. CHP7 Problems: 7.1-23, 25-28, 31-34, 37-39, 41-47, 49-56. Alkenes and Alkynes Alkene (or olefin ) Hydrocarbon that contains a carbon-carbon
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes CHP6 Problems: 6.1-13, 16-34, 36. CHP7 Problems: 7.1-23, 25-28, 31-34, 37-39, 41-47, 49-56. Alkenes and Alkynes Alkene (or olefin ) Hydrocarbon that contains a carbon-carbon
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
Chemistry 20 Chapters 2 Alkanes
 Chemistry 20 Chapters 2 Alkanes ydrocarbons: a large family of organic compounds and they contain only carbon and hydrogen. ydrocarbons are divided into two groups: 1. Saturated hydrocarbon: a hydrocarbon
Chemistry 20 Chapters 2 Alkanes ydrocarbons: a large family of organic compounds and they contain only carbon and hydrogen. ydrocarbons are divided into two groups: 1. Saturated hydrocarbon: a hydrocarbon
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Organic Chemistry, 7 L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter , Prentice Hall
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula C 6 H 6
 Aromatic compounds 2814 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Aromatic compounds 2814 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Classifying Hydrocarbons
 Classifying Hydrocarbons alkanes- single C-C bonds, if all C s have H s attached, molecules are called saturated hydrocarbons alkenes- have one or more C=C double bonds alkynes- have one or more CΞC triple
Classifying Hydrocarbons alkanes- single C-C bonds, if all C s have H s attached, molecules are called saturated hydrocarbons alkenes- have one or more C=C double bonds alkynes- have one or more CΞC triple
Classes of Alkenes. Alkenes and Alkynes. Saturated compounds (alkanes): Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom.
 Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
Alkenes and Alkynes Saturated compounds (alkanes): ave the maximum number of hydrogen atoms attached to each carbon atom. Unsaturated compounds: ave fewer hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon chain than
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Organic molecules are everywhere! The Alkanes (See pages 25-4 and 25-5) Naming Alkanes (See pages 25-7 to 25-10)
 RGANI EMISTRY hemistry 11 rganic molecules are everywhere! Some common examples: Sucrose (sugar) Methane (natural gas) Butane (lighter fluid) Plastic Acetic Acid (vinegar) Ethanol (fuel additive) What
RGANI EMISTRY hemistry 11 rganic molecules are everywhere! Some common examples: Sucrose (sugar) Methane (natural gas) Butane (lighter fluid) Plastic Acetic Acid (vinegar) Ethanol (fuel additive) What
Chapter 22 Hydrocarbon Compounds
 Chapter 22 Hydrocarbon Compounds 1 ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Organic compounds are carbon compounds and there are over a million. The simplest organic compounds are hydrocarbons and they are composed of hydrogen
Chapter 22 Hydrocarbon Compounds 1 ORGANIC COMPOUNDS Organic compounds are carbon compounds and there are over a million. The simplest organic compounds are hydrocarbons and they are composed of hydrogen
Organic Chemistry - Introduction
 It s All About Carbon! Unit 15: Organic Chemistry Lesson 15.1: Hydrocarbons Organic Chemistry - Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon. Animals, plants, and other forms
It s All About Carbon! Unit 15: Organic Chemistry Lesson 15.1: Hydrocarbons Organic Chemistry - Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon. Animals, plants, and other forms
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Lecture 12 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution E E February 22, 2018 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic aromatic substitution: a reaction in which a hydrogen atom on an aromatic ring is
Lecture 12 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution E E February 22, 2018 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophilic aromatic substitution: a reaction in which a hydrogen atom on an aromatic ring is
5.1 Alkene Nomenclature
 5.1 Alkene Nomenclature Alkenes Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain a carbon-carbon double bond also called "olefins" characterized by molecular formula n 2n said to be "unsaturated" Alkene Nomenclature
5.1 Alkene Nomenclature Alkenes Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain a carbon-carbon double bond also called "olefins" characterized by molecular formula n 2n said to be "unsaturated" Alkene Nomenclature
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Anthracite alkanes arene alkenes aromatic compounds alkyl group asymmetric carbon Alkynes benzene 1a
 Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Anthracite alkanes arene alkenes aromatic compounds alkyl group asymmetric carbon Alkynes benzene 1a Hard coal, which is high in carbon content any straight-chain or branched-chain
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Anthracite alkanes arene alkenes aromatic compounds alkyl group asymmetric carbon Alkynes benzene 1a Hard coal, which is high in carbon content any straight-chain or branched-chain
CHAPTER 16 - CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION
 CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
IUPAC Nomenclature Chem12A, Organic Chemistry I
 IUPAC Nomenclature ChemA, rganic Chemistry I IUPAC PEFIXES Prefix Substituent Group Number of Carbons meth- methyl eth- ethyl prop- propyl but- butyl pent- pentyl hex- hexyl hept- heptyl 7 oct- octyl 8
IUPAC Nomenclature ChemA, rganic Chemistry I IUPAC PEFIXES Prefix Substituent Group Number of Carbons meth- methyl eth- ethyl prop- propyl but- butyl pent- pentyl hex- hexyl hept- heptyl 7 oct- octyl 8
Chapter 9 Alkynes. Introduction
 hapter 9 Alkynes Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is n 2n-2. Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. MST reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions
hapter 9 Alkynes Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is n 2n-2. Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. MST reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions
Seminar_3. 1. Substituded derivatives of benzene and their nomenclature
 1. Substituded derivatives of benzene and their nomenclature 2. Reactions of arenes. Electrophilic aromatic substitutions 3. Activating substituents. Orientation in the aromatic ring Seminar_3 TEST - Aromatic
1. Substituded derivatives of benzene and their nomenclature 2. Reactions of arenes. Electrophilic aromatic substitutions 3. Activating substituents. Orientation in the aromatic ring Seminar_3 TEST - Aromatic
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Classification of organic compounds
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic chemistry is very important branch of chemistry and it study the compounds which contain carbon (C) and hydrogen (H), in general, and may contains other atoms such as oxygen (O),
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic chemistry is very important branch of chemistry and it study the compounds which contain carbon (C) and hydrogen (H), in general, and may contains other atoms such as oxygen (O),
Explain how the structure and bonding of carbon lead to the diversity and number of organic compounds.
 Section 1 Organic ompounds Objectives Explain how the structure and bonding of carbon lead to the diversity and number of organic compounds. ompare the use of molecular and structural formulas to represent
Section 1 Organic ompounds Objectives Explain how the structure and bonding of carbon lead to the diversity and number of organic compounds. ompare the use of molecular and structural formulas to represent
