Organic Synthesis and Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions. 1. To introduce basic concepts of organic synthesis:
|
|
|
- Prudence French
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 rganic Synthesis and Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming eactions 1. To introduce basic concepts of organic synthesis: etrosynthesis thinking backwards from relatively complex molecules to simpler ones the disconnection approach. Target Molecule Precursors Solomons p n.b. 2. To classify and extend the main carbon-carbon bond forming reactions (CCBF) introduced in CE1C1Y. 3. To illustrate the importance of organic synthesis with real examples. rganic Synthesis Introduction Why bother?! Ca. 7 million organic compounds known most have been made by synthesis rather than isolated from nature. easons for Synthesising rganic Compounds: a) Proof of structure of a natural compound by putting it together from simpler molecules. b) To prepare compounds that are useful to mankind e.g. pharmaceuticals, polymers, dyes etc. c) To prepare specific compounds to study reaction mechanisms or biological metabolism (e.g. labelled compounds). d) For the intellectual challenge new problems demand new solutions and can lead to the development of NEW CEMISTY, reagents etc. When faced with the challenge of preparing a specific organic compound ho do we go about it? This is the art of synthesis! e.g. ow might we attempt to make Z jasmone an important constituent of many perfumes?? α,β unsaturated ketone, alkene, 5-membered ring 1
2 In fact one synthesis uses the following as carbon sources C 2 C 2 It is not clear from this however, how the chemistry might be done! Therefore just being given the starting materials is not sufficient to help plan a synthesis. Note the importance of CCBF. We need a logical planning method. etrosynthetic Analysis (The Disconnection Approach) riginated by E.J. Corey (Nobel Prize 1990) p p p Definition of Terms Target Molecule (TM) the compound we wish to prepare e.g. methylphenyl ketone (acetophenone) etrosynthetic Analysis the process of WKING BACKWADS from the TM in order to devise a suitable synthetic route (or routes) on paper. Note: denotes disconnection of TM to its most immediate precursor. Multiple steps are required so this needs to be repeated. TM 1st Precursor 2nd Precursor Starting compounds - readily available After writing possible routes we would need to evaluate each one before deciding which to follow. 2
3 eadily Available Starting Materials (ASM) cheap, commercially available compounds. Disconnection a paper operation involving an imagined cleavage of a bond (yielding synthons ) to suggest a method and possible SM s for making the bond, ultimately leading to possible SM s for the overall synthesis. X Y X + + Y - X - + Y + X + Y Note: There must be a good chemical reaction corresponding to the reverse of the disconnections. Synthon an idealised fragment, usually a cation or anion, resulting from a disconnection. X + Y - X - Y + X Y Usually synthons don t exist as such, but help in the correct choice of reagent. In our example: Looks possible because it implies electrophilic attack on benzene ring Does not look so good (nucleophilic attack less usual) Synthetic Equivalent the actual compounds used to function as synthons. Cl AlCl 3 Friedel Crafts reagent Functional Group Interconversion (FGI) the process of writing one functional group for another to help synthetic planning and to help disconnection. Note, there must be a good reaction in the reverse (forward!) direction. 3
4 e.g. N 2? easy reduction (Sn/Cl) FGI N 2 N Easy! Nitration of benzene (N 3 / 2 S 4 ) Alternative synthesis of FGI C 3 C 3 Mg Many ways to make alcohols (e.g. via Grignard reagents) - suggests alternative synthesis to Friedel Crafts. In planning a synthetic strategy, apart from devising a means of constructing the carbon skeleton with the required functionality as above, there are other subtle factors, which we must address. X X X Control of egiochemistry Y AND NT Y Control of Stereochemistry AND NT enantiomers (Good summary p , , ) 4
5 We will illustrate this approach with examples, starting with synthesis of benzene derivatives. Starting point is usually fairly obvious simple benzene derivatives or perhaps benzene itself. The Synthesis of Substituted Benzene Derivatives (Solomons p ) eactions are usually straightforward (S E Ar) and you will have met most of them before. Synthesis is simplified because the nature of the starting materials is usually clear. Thus, most reactions correspond to the following disconnection: X X S E Ar Example 1 1 st decision which bond to disconnect first! N 2 S E Ar 1 N 2 Problem! No good synthetic equivalent for N 2 + (but o/p directing effect of sub is K) N can use 2 /Fe 3 o/p directing effect of N 2 is K BUT, problem is overbromination N 2 owever, we can carry out monobromination on the N-acyl derivative of the amine: NCC 3 NCC 3 2 N 2 (some o-isomer - separate) then we can remove the protecting group ( - / 2 ) to give the required product. 5
6 So formally: N 2 FGI NCC 3 NCC 3 FGI N 2 N 2 FGI 2 C 3 CCl Sn/Cl N 3 / 2 S 4 Is there an alternative route? Try a different FGI! N 2 FGI N 2 YES N 2 o/p directing effect of is K N N 2 N 2 group is m-directing therefore not a good disconnection Example 2 FGI N synthons are K but directing effect of acyl is meta, therefore no good good synthons directing effect of K Synthesis 2 /Fe 3 C 3 CCl NaB 4 AlCl 3 (some o-isomer, separate) racemate! 6
7 Example 3 C 3 CN (C 3 C) 2 FGI N 2 Sn/Cl FGI N 2 + N 2 S 3 N 2 N N S 4, S 3 K, heat 2, boil N Guidelines for designing a synthesis 1 Use retrosynthetic analysis to work backwards from TM to the precursors and eventually to ASM. 2 Locate the functional groups in the TM for most functional groups there are good DISCNNECTINS (the reverse of real chemical reactions). 3 Examine all possible disconnections check which are chemically sound (correspond to known reactions, reagents, directing effects etc.) 4 If you can make no progress try FGI: (N 2 /N 2 ; C 3 /C; C-/C- ; C/C 2 etc.) 5 aving obtained precursors to TM, repeat the process on these intermediates. Clearly you will need a good knowledge of your basic chemistry and an appreciation of reaction mechanisms, directing effects etc. With Aromatic systems the SM s are usually fairly obvious. Usually benzene or a benzene derivative such as toluene, phenol etc. bond to be disconnected is almost always the bond joining the aromatic ring to the rest of the molecule. Also FGI s often correspond to some simple types of reaction e.g. reduction (N 2 to N 2 ), oxidation (C 3 to C), diazonium chemistry (N 2 N 2 + Ar-X). 7
8 In aromatic chemistry CCBF revolve around: 1) Friedel Crafts type reactions Cl Ar Ar C 2) Displacements on aromatic diazonium salts Ar N 2 CN CuCN Ar C N (3) Not forgetting Grignard reagents + carbonyls) With aliphatic acyclic and cyclic systems the process is not always as straightforward need to consider a greater array of CCBF s and FGI s. etrosynthesis In An Aliphatic Molecule A Guide To Alternative Disconnections. etrosynthetic analysis 1 Path A B synthetic equiv.? (can't think of one) K Mg (+ + ) Synthesis Mg Mg 2 8
9 etrosynthetic analysis 2 Path A B synthetic equiv.? (can't think of one) Mg Synthesis Mg Mg 2 9
10 etrosynthetic analysis 3 Path A B synthetic equiv.? (can't think of one) (+ + ) Mg Synthesis Mg Mg 2 10
11 etrosynthetic analysis 4 FGI Path A B C 3 C 2 Et not great, but see later Synthesis C 3 base NaB 4 11
12 etrosynthetic analysis 5 FGI LiCu(C 2 C 2 ) 2 Synthesis LiCu C 2 C 2 C 2 C 2 CuI LiC 2 C 2 NaB 4 Li + C 2 C 2 We shall discuss possible synthesis later, but we will concentrate on CCBF in aliphatic systems. eview and extend CCBF from 1C1Y, in particular: Aldol and Claisen condensations Alkylation of β-keto esters (CC 2 C 2 ) Grignard reactions And illustrate their use in synthesis. 12
13 Classification of CCBF in aliphatic chemistry There are several ways of doing this. We shall consider the following: a) Carbanion Alkylation C X C i) Alkylation of enolate ions + X p ii) Alkylation of acetylide or cyanide C C + ' X ' p N C ' X + CN p 804 iii) rganometallic alkylation Mg X + p 483 Note iv) Direct alkylation of carbanions is possible in some cases 2 CuLi + ' X ' p Where ' = methyl or 1 o alkyl halide (Not a typical substitution mechanism!) b) Carbonyl Addition And Carbonyl Substitution eactions i) Aldol and related reactions (Add n ) 2 p ii) Claisen condensation and related reactions (Sub n ) 2 p
14 iii) rganometallic reactions (Add n ) + Mg p iv) Acetylide/cyanide addition + p N CN p v) Wittig reaction (Add n ) + CP 3 P 3 p P 3 c) Conjugate Addition eactions - Michael (1,4 Addition) + C(C 2 Et) 2 C 2 Et C 2 Et p Mg 2 CuLi better d) eaction f Alkenes, Alkynes And Aromatics p 777 i) Pericyclic reactions: Cycloadditions Diels Alder 14
15 Electrocyclic reactions (MJC) Sigmatropic reactions Cope earrangement ii) Friedel Crafts and related reactions C iii) Addition of carbenes to alkenes 2C: Simmons Smith (carbenoid) In the main we will be looking at ionic reactions. C C C C In CCBF the carbonyl group is very important δ- δ+ as an electrophile as a nucleophile Also in CCBF, organometallic compounds are important. e.g. δ - δ + Mg - Grignard eagents, Lithium alkyls Li etc 2 CuLi - rganocuprates 15
16 Carbonyl Chemistry for Forming C-C Bonds Carbonyl compounds having an α-hydrogen act as weak (protic) acids and react with a base to yield enolate anions. enolate anion base + base- Compare pka acetone = 19.3 ethane = 60 (approx) Ka = [ + ][C 3 CC 2 - ] [C 3 CC 3 ] pka = logka Presence of neighbouring carbonyl group increases the acidity of a ketone over an alkane by a factor of 10 40! The use of such enolate anions from carbonyl compounds is fundamental to organic synthesis and you will already have met them as intermediates in the aldol reaction and claisen condensation. When we have two carbonyl groups adjacent to a methylene group, the acidity of the α- is greatly increased. Because of the acidity of their methylene (C 2 ) hydrogens, malonic esters, ethylacetoacetate and β-dicarbonyl compounds etc are often called active hydrogen compounds. 16
17 Active Methylene Compounds 3 C C C 2 C Et ethylacetoacetate (ethyl 3-oxobutanoate) Et C C 2 C Et diethyl malonate (diethyl propandioate) 3 C C C 2 C C 3 acetyl acetone (2,4-pentandione) C 2 Me 2-methoxycarbonylcyclohexanone 1,3-cyclohexanedione pka 3 C C C 2 3 C C C 2 Et C C 2 C C 3 C Et C Et 9 (2 x ketones) 11 (1 x ketone, 1 x ester) 13 (2 x ester) 3 C C C 3 19 C 3 C Et 25 Compare: C 5 C 3 C C C 25 C 3 C
18 Such compounds are often used in synthesis because: 1) They are readily made and cheap 2) The anion can be generated quantitatively 3) Self condensation does not occur with 1 mole of base is deprotonated 4) The site of deprotonation is unambiguous 5) The enolate ions formed on deprotonation can be alkylated and acylated offering useful products. Example: Et NaEt (pka Et = 16) Et pka 20 pka 11 Et Et eactions of Active Methylene Compounds Et 1) Carbanion Alkylation Most important use is for preparation of ketones (from β-keto esters CC 2 C 2 Et) and of acids from malonic esters (C 2 (C 2 ) 2 ). Et 1) NaEt 2) Et Et heat decarboxylation Et 18
19 Note: is the synthetic equivalent to Et C 2 Et group is used to activate α-carbon atom So etrosynthesis Et synthetic equivs Why not just use? Seems K but problems 1 1) In unsymmetrical case, which α-position reacts? 2) Product may alkylate 3) may prefer to react with starting ketone or product 2 The use of activating group stabilises the required enolate so that conversion is complete with Et Et reaction with SM cannot therefore occur The alkyl halide is added in a separate step-no base remains to form anion of product Note. The activating group is easily removed 19
20 Acids C 2 Et C 2 Et 1) NaEt 2) C 2 Et C 2 Et 1) K 2) + / C +C 2 1) NaEt 2) ' ' C 2 Et C 2 Et 1) K 2) + / ' C +C 2 Note: with 2 equivalents of NaEt and a dihalide (e.g. (C 2 ) 4 ) - can get cycloalkane carboxylic acids. e.g. C So etrosynthesis: C 2 C 2 + C 2 C 2 C 2 Et C 2 Et - Practice with C C 2 Note: FGI s can be carried out on intermediates/products. Note especially: C 2 5 (LiAl 4 ) 2 1 C 2 Et C 2 Et FGI 2 1 C 2 C 2 1,3 diol elps in the synthesis of 1,3 diols. 20
21 Enolate Anions as Ambident Nucleophiles e.g. reacts as alkoxide 3 C C C 2 3 C C 2 reacts as carbanion Site of alkylation depends, in part, on substrate Alkyl halides C-alkylation (C 3 ) 3 SiCl -alkylation Si 3 C C (C 3 ) 3 SiCl 3 C C 3 CC 2 C 2 C 2 silyl enol ether (strong Si- bond formed 2. eaction of Active Methylene Compounds with Carbonyl Compounds (Knoevenagel Condensation) C 2 Et C 2 Et C 2 Et C 2 Et C C(C 2 Et) 2 (i) (ii) (iii) heat - 2 C 2 Et C 2 Et C CC 2 Usually uses weak base/weak acid as catalyst, ( 2 N/Ac). Any combination of stabilising groups can be used (CN, C 2 Et etc). 21
22 3. Michael eaction with Active Methylene Compounds (Conjugate Addition eaction) Carbanions derived from active methylene compounds react with α,β-unsaturated compounds by 1,4-(conjugate) addition known as Michael addition. 3 C C 2 Et C 2 Et 3 C C 2 Et C 2 Et 3 C C 2 (i) (ii) (iii) heat 3 C C 2 Et C 2 Et In retrosynthesis terms 3 C C 2 3 C 3 C C 2 Et C 2 Et Question ow would you prepare C 2? C 2 C 2 Et C 2 Et 22
23 4. Dianions in Synthesis We have discussed the regioselective reactions of this active methylene carbon (C- 2) in ethylacetoacetate. Can regiospecifically trap C-4 via the dianion. Et Et pka 20 pka 11 pka 30 least acidic forms most reactive anion Need two equivalents of base and second one needs to be strong (pka>20) Me 1)Na, 2) BuLi or 2 x LiN i Pr 2 (LDA) lithium diisoprpylamide Me LiN 1) X (1 equiv) 2) Me 23
24 Carbonyl Addition and Carbonyl Substitution Aldol and Claisen eactions. Usually self-condensations, these reactions combine nucleophilic attack and α- substitution as the first step. The Aldol Condensation of Aldehydes and Ketones 3 C C 2 C C 3 C C 3 C C C 2 C 2 C C 2 General for aldehydes and ketones with α- NB eversible Product favoured with C 2 C SM favoured with 2 CC 3 C 3-hydroxybutanal aldol C C 2 C - 2 more vigorous conditions (heat) eason for dehydration 1) Acidity of α- 2) Stability of conjugated product 3 C C C C C 3 C CC 2-butenal Note the Aldol condensation can also be performed with acid catalysis in which dehydration usually follows (enol form is involved mechanism p 773). NB dehydration drives the reaction when the equilibrium is unfavourable. 3 C C C 3 98% 3 C C C 2 C 3 2% C C 3 C good yield C 3 In retrosynthesis terms FGI ecognise aldol or aldol product 24
25 Unsymmetrical ketone? egioselectivity is a problem! strong base kinetic enolate proton removed from least hindered site - 2 thermodynamically preferred enol ence different products from acid and basic conditions Claisen Condensation of Esters 3 C Et 2 C Et not complete deprotonation Et pka = 16 C 3 C 2 Et pka = 25 2 C Et 3 C Et 3 C C 2 Et C 2 Et 2 C Et 2 C C 2 C 2 Et Et 3 C C C 2 Et pka 11, drives reaction Note: the only difference between the Aldol and Claisen reaction is the fate of the tetrahedral intermediate Claisen expels alkoxide, Aldol alkoxide is protonated. 25
26 Mixed Aldol and Mixed Claisen Condensations These are not very useful generally as there are four potential products. owever, they can be useful if one component has no α-. Mixed Aldol C Et Claisen Schmidt condensation Mixed Claisen Condensations nly successful when one of the ester components has no α- e.g. C 2 Et CEt. 1) Et Et Et 2) Et Can also carry out mixed Claisen between ester and ketone 1) Et Et 2) favoured because removal of proton from here drives equilibrium Synthesis of dimedone C 2 Et 2 x aldol C 2 Et Michael C 2 Et C 2 Et (i) (ii) C 2 Et (iii) heat 26
27 C-C Bond Formation to Make ings Intramolecular Aldol eactions and Claisen Condensations When certain dicarbonyl compounds are treated with base intramolecular Aldol reactions can occur. Similarly diesters can undergo intramolecular Claisen Condensations (this reactions is known as the Dieckmann cyclisation). Aldol Na - 2 Et 5 and 6 membered rings preferred The intramolecular Aldol condensation forms the basis of a very useful method for making rings The obinson Annulation eaction: Et Michael Et intramolecular C 2 Et aldol 27
28 Intramolecular Claisen Condensations The Dieckmann Cyclisation eaction works best with 1,6 or 1,7 diesters to give 5 or 6 membered rings. 1 Me 6 Me NaMe Me Me Me Me 1 Me C 2 Me cyclic β-ketoesters 7 can be functionalised and decarboxylated egioselective Formation of Enolate Ions (p786) W eak base LiN i Pr 2 Li Protic solvent DME (MeC 2 C 2 ME aprotic) Thermodynamically favoured (More stable due to more substituted double bond) Kinetically Favoured Sterically hindered base rapidly removes proton from less substituted α position (where there are more of them also) Alkylation is regiospecific: Li C 3 I but ClSiMe 3 SiMe 3 This kinetic enolate, trapped as the TMS ether can be regenerated with F (Si-F very strong) SiMe 3 F C ther Useful CCBF s 28
29 The Wittig eaction (p 734) ' + '' X P 3 ''' Base ' ''' '' + P 3 Very useful method for alkene synthesis as the position of the double bond is known. The first step is formation of a osphorus Ylide (a neutral compound with C - and P + ). 3 P: C 2 C 2 Et 3 P CC 2 Et. Base 3 P CC 2 Et Does not contribute much 3 P CC 2 Et C 3 C CC 2 Et P 3 C 2 Et Acetylene anion as a synthon for C 3 C= C' + ' gs ' Dithiane Anions Acyl anion equivalents which exhibit Umpolung (reversed polarity p 907). Two S atoms attached to the same carbon atom of a 1,3-dithiane cause the atoms to be more acidic (pka 32) than normal alkyl C-. 29
30 1,3-dithianes are easily prepared from aldehydes, they are thioacetals. C + S S + BuLi S S S S 1) 'C 'X ' 2) g 2+ / 2 0 1,2 -di g 2+ / 2 0 S S ' ' adical Dimerisation eactions Leading To 1,2-di Pattern 1. Pinacol Formation etrosynthesis C C C C Synthesis Mg/ether electron transfer C Mg C C Mg C 2 e- C C 30
31 2. Acyloin Condensation Similar to ester dimerisation, used traditionally to make large rings. (C 2 ) n C 2 Et 2 x Na (C 2 ) n Et (C 2 ) n Et C 2 Et Et Et 2 x Na (C 2 ) n (C 2 ) n (C 2 ) n 2 (C 2 ) n 2-hydroxy ketone (acyloin) Now improved by addition of Me 3 SiCl which traps the intermediate dianion. C 2 Et Na Me 3 SiCl SiMe 3 SiMe
32 So to finish -cis jasmone (Can J. Chem. 1978, Vol 56, p2301) C 2 Me K/TF C 2 C Et Pd/BaS 4 (Lindlar cat) C 2 Me 2 z-alkene C 2 Me 1) Na 2) BuLi C 2 Me (SiMe 3 ) gs 4, 2 C 2 Me 1) C 2 C SiMe 3 2) 2 C 2 Me then heat SiMe 3 intamolecular aldol
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
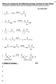 What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
Reactions at α-position
 Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~ 20
 Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Chapter 19. Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions. ß-dicarbonyl compounds. Why are ß-dicarbonyls useful?
 Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
CuI CuI eage lic R tal ome rgan gbr ommon
 Common rganometallic eagents Li Et 2 Li Mg Et 2 Li alkyllithium rignard Mg Mg Li Zn TF ZnCl 2 TF dialkylzinc Zn 2 2 Zn Li CuI TF ganocuprate CuI 2 2 CuI common electrophile pairings ' Cl ' '' ' ' ' ' '
Common rganometallic eagents Li Et 2 Li Mg Et 2 Li alkyllithium rignard Mg Mg Li Zn TF ZnCl 2 TF dialkylzinc Zn 2 2 Zn Li CuI TF ganocuprate CuI 2 2 CuI common electrophile pairings ' Cl ' '' ' ' ' ' '
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King. Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; Organometallic Reagents; Oxidation & Reduction
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 20 Introduction to Carbonyl Chemistry; rganometallic Reagents; xidation & Reduction I. The Reactivity of Carbonyl Compounds The carbonyl group is an extremely important
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon
 Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Enols and Enolates. A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl)
 Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Advanced Organic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis
 123.312 Advanced rganic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis Tutorial Question 1. Propose a retrosynthetic analysis of the following two compounds. Your answer should include both the synthons, showing your thinking,
123.312 Advanced rganic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis Tutorial Question 1. Propose a retrosynthetic analysis of the following two compounds. Your answer should include both the synthons, showing your thinking,
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
Chapter 22 Enols and Enolates
 Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
New bond. ph 4.0. Fischer esterification. New bond 2 O * New bond. New bond H 2N. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. O Cl.
 Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds.
 1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
20.10 Conjugate Additions
 894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction
 Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction G. S. Zweifel M. H. Nantz W.H. Freeman and Company Chapter 1 Synthetic Design 1 What is an ideal or viable synthesis, and how does one approach a synthetic project?
Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction G. S. Zweifel M. H. Nantz W.H. Freeman and Company Chapter 1 Synthetic Design 1 What is an ideal or viable synthesis, and how does one approach a synthetic project?
Practice Synthetic Problems: CHEM 235 Page 2
 Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
Michael and Aldol CH391 December 4, 2002
 Michael and Aldol H391 December 4, 2002 RH 2 H pk a = 16-20 + H RHH + Enolate anions... So.a basic solution contains comparable amounts of the aldehyde and its enolate. Which gives rise to..the Aldol ondensation
Michael and Aldol H391 December 4, 2002 RH 2 H pk a = 16-20 + H RHH + Enolate anions... So.a basic solution contains comparable amounts of the aldehyde and its enolate. Which gives rise to..the Aldol ondensation
Chem 263 Nov 14, e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents)
 hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
CHEM Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25
 CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
Tips for taking exams in 852
 Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman
 Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
b.p.=100 C b.p.=65 C b.p.=-25 C µ=1.69 D µ=2.0 D µ=1.3 D
 Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Lecture 23. The Aldol Condensation. an Aldol! April 12, 2018 O H O H - Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 23 The Aldol Condensation - b a an Aldol! April 12, 2018 Exam III - Wed April 18 WEL 2.122 7-9 PM Covers thru today omework ydrolysis Reactions Synthesis Get an A!!! Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA)
Lecture 23 The Aldol Condensation - b a an Aldol! April 12, 2018 Exam III - Wed April 18 WEL 2.122 7-9 PM Covers thru today omework ydrolysis Reactions Synthesis Get an A!!! Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA)
Chapter 11 Reaction of Alcohols
 Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
ORGANIC - BRUICE 8E CH CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III: REACTIONS AT THE ALPHA-CARBON
 !! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity
!! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity
Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
When we deprotonate we generate enolates or enols. Mechanism for deprotonation: Resonance form of the anion:
 Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Advanced Organic Synthesis
 به نام خدا 3 Advanced Organic Synthesis Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran SYNTHETIC DESIGN 1. Retrosynthetic Analysis 2. Reversal of the Carbonyl Group Polarity (Umpolung)
به نام خدا 3 Advanced Organic Synthesis Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran SYNTHETIC DESIGN 1. Retrosynthetic Analysis 2. Reversal of the Carbonyl Group Polarity (Umpolung)
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
ENOLATES IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS 1 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS Recall Enolate alkylation, Aldol addition and condensation can provide access to a wide variety of multi-functional compounds, which can lend themselves
ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS 1 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS Recall Enolate alkylation, Aldol addition and condensation can provide access to a wide variety of multi-functional compounds, which can lend themselves
Answers To Chapter 7 Problems.
 Answers To Chapter Problems.. Most of the Chapter problems appear as end-of-chapter problems in later chapters.. The first reaction is an ene reaction. When light shines on in the presence of light and
Answers To Chapter Problems.. Most of the Chapter problems appear as end-of-chapter problems in later chapters.. The first reaction is an ene reaction. When light shines on in the presence of light and
Chapter 19. Organic Chemistry. Carbonyl Compounds III. Reactions at the a-carbon. 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice
 Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry
 Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Aldehydes and Ketones
 Aldehydes and Ketones Preparation of Aldehydes xidation of Primary Alcohols --- 2 P 1o alcohol ydroboration of a Terminal Alkyne, followed by Tautomerization --- 1. B 3, TF 2. 2 2, K 2 terminal alkyne
Aldehydes and Ketones Preparation of Aldehydes xidation of Primary Alcohols --- 2 P 1o alcohol ydroboration of a Terminal Alkyne, followed by Tautomerization --- 1. B 3, TF 2. 2 2, K 2 terminal alkyne
Chem 263 Nov 3, 2016
 hem 263 Nov 3, 2016 Preparation of Aldehydes from Acid alides? + l l acid chloride aka acyl chloride aldehyde Needed: 2 Actual eagents: 2 /Pd Al This is lithium tri-t-butoxy aluminum hydride, a very sterically
hem 263 Nov 3, 2016 Preparation of Aldehydes from Acid alides? + l l acid chloride aka acyl chloride aldehyde Needed: 2 Actual eagents: 2 /Pd Al This is lithium tri-t-butoxy aluminum hydride, a very sterically
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH CONDENSATION CHEMISTRY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: CNDENSATIN REACTINS A condensation reaction spontaneously combines two or more molecules with the loss of a smaller molecule. Instead of just reacting with electophiles, enolates
!! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: CNDENSATIN REACTINS A condensation reaction spontaneously combines two or more molecules with the loss of a smaller molecule. Instead of just reacting with electophiles, enolates
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
Organic Chemistry, Third Edition. Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations
 rganic Chemistry, Third Edition Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations 1 Review: enolates LDA, -78 C TF kinetic RX R = Me, 1 alkyl R Na TF, RT RX R = Me, 1 alkyl thermodynamic R enolates = nucleophiles React
rganic Chemistry, Third Edition Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations 1 Review: enolates LDA, -78 C TF kinetic RX R = Me, 1 alkyl R Na TF, RT RX R = Me, 1 alkyl thermodynamic R enolates = nucleophiles React
Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar. Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry
 A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II
 KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
Organic Chemistry CHM 224
 rganic Chemistry CM 224 Final Exam Review Questions This is a compilation example final exam questions. Provide IUPAC names for each of the structures below. 2 ! Propose a structure for the compound that
rganic Chemistry CM 224 Final Exam Review Questions This is a compilation example final exam questions. Provide IUPAC names for each of the structures below. 2 ! Propose a structure for the compound that
Cape Cod Community College
 Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
acetaldehyde (ethanal)
 hem 263 Nov 2, 2010 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alkenes zonolysis 1. 3 2. Zn acetone 1. 3 2. Zn acetone acetaldehyde (ethanal) Mechanism: 3 3 3 + - oncerted reaction 3 3 3 + ozonide (explosive)
hem 263 Nov 2, 2010 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alkenes zonolysis 1. 3 2. Zn acetone 1. 3 2. Zn acetone acetaldehyde (ethanal) Mechanism: 3 3 3 + - oncerted reaction 3 3 3 + ozonide (explosive)
Conjugate Addition Reactions 2:02 PM
 1 Conjugate Addition vs Direct Addition What is Conjugate Addition? Conjugate addition refers to nucleophilic addition directed to the electrophilic carbon of the C=C (double bond) in a,bunsaturated systems.
1 Conjugate Addition vs Direct Addition What is Conjugate Addition? Conjugate addition refers to nucleophilic addition directed to the electrophilic carbon of the C=C (double bond) in a,bunsaturated systems.
Suggested solutions for Chapter 27
 uggested solutions for Chapter 27 27 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this reaction, commenting on the selectivity and the stereochemistry. Me 2 1. t-buk 2. Raney Ni Et The opportunity to explore the consequences
uggested solutions for Chapter 27 27 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this reaction, commenting on the selectivity and the stereochemistry. Me 2 1. t-buk 2. Raney Ni Et The opportunity to explore the consequences
CHEM 234: Organic Chemistry II Reaction Sheets
 EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
Chapter 16. Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group. Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones. Synthesis of Aldehydes
 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
ANSWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMINATIONS CHEMISTRY 249H
 AWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMIATI CEMITRY 249 1. (a) PDC / C 2 2 (b) t-bume 2 i (1 equiv) / imidazole (1 equiv) i TBDM protection of the less sterically hindered alcohol (c) BuLi (1 equiv) then (d) 2
AWER GUIDE APRIL/MAY 2006 EXAMIATI CEMITRY 249 1. (a) PDC / C 2 2 (b) t-bume 2 i (1 equiv) / imidazole (1 equiv) i TBDM protection of the less sterically hindered alcohol (c) BuLi (1 equiv) then (d) 2
Product obtained by reaction with resorcinol
 33 rd International hemistry lympiad Preparatory Problems 3 ( Z ) 3-( 4-methoxyphenyl )-2-pentenedioic acid d. Two products are possible when compound A reacts with bromine. 2 2 3 3 [1] [2] Structures
33 rd International hemistry lympiad Preparatory Problems 3 ( Z ) 3-( 4-methoxyphenyl )-2-pentenedioic acid d. Two products are possible when compound A reacts with bromine. 2 2 3 3 [1] [2] Structures
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction
 P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation:
 1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
CHAPTER 24 HW: CARBONYL CONDENSATIONS
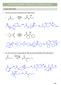 CAPTER 24 W: CARBNYL CNDENSATINS ALDL REACTIN 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism for each aldol reaction. Na 2 product Na Et prod. 2. Give the curved arrow mechanism for this aldol reaction (and dehydration
CAPTER 24 W: CARBNYL CNDENSATINS ALDL REACTIN 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism for each aldol reaction. Na 2 product Na Et prod. 2. Give the curved arrow mechanism for this aldol reaction (and dehydration
Lecture 23. Amines. Chemistry 328N. April 12, 2016
 Lecture 23 Amines April 12, 2016 Michael Reaction Michael reaction: conjugate addition of an enolate Arthur Michael anion to an, -unsaturated carbonyl compound!! Following are two examples in the first,
Lecture 23 Amines April 12, 2016 Michael Reaction Michael reaction: conjugate addition of an enolate Arthur Michael anion to an, -unsaturated carbonyl compound!! Following are two examples in the first,
The Final Learning Experience
 Chemistry 212 and 300 rganic Chemistry II Winter Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #5 Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions, Sugars & Nucleic Acids The Final Learning Experience Friday, May 5,
Chemistry 212 and 300 rganic Chemistry II Winter Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #5 Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions, Sugars & Nucleic Acids The Final Learning Experience Friday, May 5,
Background Information
 ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
EWG EWG EWG EDG EDG EDG
 Functional Group Interconversions Lecture 4 2.1 rganic Synthesis A. Armstrong 20032004 3.4 eduction of aromatic systems We can reduce aromatic systems to cyclohexanes under very forcing hydrogenolytic
Functional Group Interconversions Lecture 4 2.1 rganic Synthesis A. Armstrong 20032004 3.4 eduction of aromatic systems We can reduce aromatic systems to cyclohexanes under very forcing hydrogenolytic
c. Oxidizing agent shown here oxidizes 2º alcohols to ketones and 1º alcohols to carboxylic acids. 3º alcohols DO NOT REACT.
 Exam 1 (Ch 17 and Review of CEM 331) Answer Key: 1. ne-step Questions: You need to know reagents for reagent arrows and to be able to draw products. I know a lot of them seem to look alike its your job
Exam 1 (Ch 17 and Review of CEM 331) Answer Key: 1. ne-step Questions: You need to know reagents for reagent arrows and to be able to draw products. I know a lot of them seem to look alike its your job
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chapter 12. Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds Oxidation-Reduction & Organometallic Compounds. Structure
 Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds xidation-eduction & rganometallic Compounds Created by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis Chang Structure ~ 120 o ~ 120 o C ~ 120 o Carbonyl carbon: sp 2 hybridized
Chapter 12 Alcohols from Carbonyl Compounds xidation-eduction & rganometallic Compounds Created by Professor William Tam & Dr. Phillis Chang Structure ~ 120 o ~ 120 o C ~ 120 o Carbonyl carbon: sp 2 hybridized
Additions to the Carbonyl Groups
 Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Chem 263 Nov 7, elimination reaction. There are many reagents that can be used for this reaction. Only three are given in this course:
 hem 263 Nov 7, 2013 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alcohols xidation of Alcohols [] must have at least 1 E elimination reaction [] = oxidation; removal of electrons [] = reduction; addition
hem 263 Nov 7, 2013 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alcohols xidation of Alcohols [] must have at least 1 E elimination reaction [] = oxidation; removal of electrons [] = reduction; addition
Aldehydes & Ketones LEVEL I. Phenol (enol form) Phenol is aromatic, so equiulibrium is shifted to the right hand side. b) O
 Subjective Problems Aldehydes & Ketones LEVEL I 1. a) 2,4cyclohexadiene-1-one (keto form) Phenol (enol form) Phenol is aromatic, so equiulibrium is shifted to the right hand side. b) Base This ketone is
Subjective Problems Aldehydes & Ketones LEVEL I 1. a) 2,4cyclohexadiene-1-one (keto form) Phenol (enol form) Phenol is aromatic, so equiulibrium is shifted to the right hand side. b) Base This ketone is
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
THE CHEMISTRY OF THE CARBONYL GROUP
 TE CEMISTY F TE CABYL GUP Professor Tim Donohoe 8 lectures, T, weeks 1-4, 2007 andout A C C You will be able to download copies of the handouts from this course at http://users.ox.ac.uk/~magd1571/teaching/teaching.htm
TE CEMISTY F TE CABYL GUP Professor Tim Donohoe 8 lectures, T, weeks 1-4, 2007 andout A C C You will be able to download copies of the handouts from this course at http://users.ox.ac.uk/~magd1571/teaching/teaching.htm
Synthesis of Nitriles a. dehydration of 1 amides using POCl 3 : b. SN2 reaction of cyanide ion on halides:
 I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
CHAPTER 23 HW: ENOLS + ENOLATES
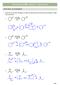 CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CHEM 330. Topics Discussed on Oct 5. Irreversible nature of the reaction of carbonyl enolates with the electrophiles discussed on Oct 2
 CEM 330 Topics Discussed on ct 5 Irreversible nature of the reaction of carbonyl enolates with the electrophiles discussed on ct 2 Kinetic control in an irreversible reaction: the product that is obtained
CEM 330 Topics Discussed on ct 5 Irreversible nature of the reaction of carbonyl enolates with the electrophiles discussed on ct 2 Kinetic control in an irreversible reaction: the product that is obtained
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones
 MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
September [KV 804] Sub. Code: 3804
![September [KV 804] Sub. Code: 3804 September [KV 804] Sub. Code: 3804](/thumbs/89/97855699.jpg) September 2009 [KV 804] Sub. Code: 3804 (Regulations 2008-2009) (Candidates admitted from 2008-2009 onwards) Paper IV PHARMACEUTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Time : Three hours Maximum : 70 marks Answer All questions
September 2009 [KV 804] Sub. Code: 3804 (Regulations 2008-2009) (Candidates admitted from 2008-2009 onwards) Paper IV PHARMACEUTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Time : Three hours Maximum : 70 marks Answer All questions
Loudon Chapter 19 Review: Aldehydes and Ketones CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 19 eview: Aldehydes and Ketones CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 Beginning with this chapter, we re looking at a very important functional group: the carbonyl. We ve seen
Loudon Chapter 19 eview: Aldehydes and Ketones CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 Beginning with this chapter, we re looking at a very important functional group: the carbonyl. We ve seen
AROMATIC & HETEROCYCLIC CHEMISTRY
 - 1 - AROMATIC & HETEROCYCLIC CHEMISTRY Aromatic Chemistry Aromaticity This confers an energetic stability over the equivalent double bond system. This can be explained from an MO point of view. The Huckel
- 1 - AROMATIC & HETEROCYCLIC CHEMISTRY Aromatic Chemistry Aromaticity This confers an energetic stability over the equivalent double bond system. This can be explained from an MO point of view. The Huckel
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones
 Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes (RCHO), with the exception of formaldehyde (H 2 CO), are compounds with both an H and an organic group attached to a carbonyl. Ketones (R 2 CO) are compounds with
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes (RCHO), with the exception of formaldehyde (H 2 CO), are compounds with both an H and an organic group attached to a carbonyl. Ketones (R 2 CO) are compounds with
Conjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions
 onjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions 1 onjugated Dienes from heats of hydrogenation-relative stabilities of conjugated vs unconjugated dienes can be studied: Name 1-Butene 1-Pentene Structural Formula
onjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions 1 onjugated Dienes from heats of hydrogenation-relative stabilities of conjugated vs unconjugated dienes can be studied: Name 1-Butene 1-Pentene Structural Formula
Luckily this intermediate has three saturated carbons between the carbonyls, which again points to a Michael reaction:
 Retrosynthesis Practice Problems Answer Key October 1, 2013 1. Draw a retrosynthesis for how to make the compound shown below from starting materials with eight or fewer carbon atoms. The first step is
Retrosynthesis Practice Problems Answer Key October 1, 2013 1. Draw a retrosynthesis for how to make the compound shown below from starting materials with eight or fewer carbon atoms. The first step is
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
Molecular Rearrangements
 Ø Migration of one the molecule group from one atom to another within Ø Generally the migrating group never leaves the molecule Ø There are five types of skeletal rearrangements- 1. Electron deficient
Ø Migration of one the molecule group from one atom to another within Ø Generally the migrating group never leaves the molecule Ø There are five types of skeletal rearrangements- 1. Electron deficient
Score: Homework Problem Set 9 Iverson CH320N Due Monday, April 17. NAME (Print): Chemistry 320N Dr. Brent Iverson 9th Homework April 10, 2017
 omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
235 Organic II. Final Exam Review REACTIONS OF CONJUGATED DIENES 1,2 VS 1,4 ADDITION REACTIONS OF CONJUGATED DIENES
 b. the ompound 7 i 1 Spectral Data: singlet, 196.5 ppm singlet, 14.1 ppm singlet, 14.4 ppm doublet, 19.1 ppm doublet, 18.5 ppm 1 MR Mass Spectrum Absorbance Intensity Infrared Spectrum 65 91 9. Structure:
b. the ompound 7 i 1 Spectral Data: singlet, 196.5 ppm singlet, 14.1 ppm singlet, 14.4 ppm doublet, 19.1 ppm doublet, 18.5 ppm 1 MR Mass Spectrum Absorbance Intensity Infrared Spectrum 65 91 9. Structure:
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
Synthetic possibilities Chem 315 Beauchamp 1
 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
Suggested solutions for Chapter 34
 s for Chapter 34 34 PRBLEM 1 Predict the structure of the product of this Diels- Alder reaction. C 2 +? 3 Si Can you deal with a moderately complicated Diels- Alder? The diene is electron- rich and will
s for Chapter 34 34 PRBLEM 1 Predict the structure of the product of this Diels- Alder reaction. C 2 +? 3 Si Can you deal with a moderately complicated Diels- Alder? The diene is electron- rich and will
First Year Organic Chemistry THE CHEMISTRY OF THE CARBONYL GROUP: CORE CARBONYL CHEMISTRY
 First Year rganic Chemistry TE CEMISTY F TE CABNYL GUP: CE CABNYL CEMISTY Professor Tim Donohoe 8 lectures, T, weeks 1-4, 2015 Wednesdays at 9am; Fridays at 10am (Dyson Perrins) andout A You will be able
First Year rganic Chemistry TE CEMISTY F TE CABNYL GUP: CE CABNYL CEMISTY Professor Tim Donohoe 8 lectures, T, weeks 1-4, 2015 Wednesdays at 9am; Fridays at 10am (Dyson Perrins) andout A You will be able
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis.
 Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
