Química Orgânica I. Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química. Análise estrutural AFB QO I 2007/08 1 AFB QO I 2007/08 2
|
|
|
- Eustacia Golden
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Química Orgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1 Análise estrutural AFB QO I 2007/08 2 1
2 Adaptado de: Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition; L. G. Wade, Jr. Organic Chemistry, William H. Brown AFB QO I 2007/08 3 methods determine the molecular structure Crystallography Mass Spectrometry Elemental Analysis Infrared Spectroscopy UV/VIS Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Coupled methods: GC-MS; HPLC-NMR... (comparative methods for know structures) AFB QO I 2007/08 4 2
3 methods Crystallography: diffraction patterns relates to atomic positions Mass Spectrometry: molecular weight and fragmentation pattern Elemental Analysis: determination of elemental and isotopic composition. Infrared Spectroscopy: determine the presence or absence of functional groups. UV/VIS Spectroscopy: Spectrophotometry uses a spectrophotometer to measure how much light is absorbed by the sample (Gives information about conjugated π electron systems). Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR): NMR spectroscopy works by studying the magnetism of a nucleus by placing it in alignment with a magnetic field, and then using an electromagnetic field to disrupt this alignment. AFB QO I 2007/08 5 E = hν and spectroscopy AFB QO I 2007/08 6 3
4 AFB QO I 2007/08 7 Electromagnetic Radiation Common units used to express λ wavelength Relation Unit to Meter Meter (m) ---- Millimeter (mm) 1 mm = 10-3 m Micrometer (µm) N anometer (nm) Angstrom (Å) 1 µm = 10-6 m 1 nm = 10-9 m 1 Å = m AFB QO I 2007/08 8 4
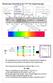
5 Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation: light and other forms of radiant energy Wavelength (λ):( the distance between consecutive peaks on a wave Frequency (ν):( the number of full cycles of a wave that pass a given point in a second Hertz (Hz): the unit in which radiation frequency is reported; s -1 (read per second ) AFB QO I 2007/08 9 electronic vibrational rotational nuclear spin UV-Vis Vis infrared microwave radiofrequency AFB QO I 2007/
6 UV-vis spectroscopy AFB QO I 2007/08 11 UV-vis E = hν ν = c / λ Electromagnetic radiation is absorbed when the energy of photon corresponds to difference in energy between two states. AFB QO I 2007/
7 Why UV-vis? Many organic molecules have chromophores that absorb UV UV absorbance is about 1000 x easier to detect per mole than NMR Still used in following reactions where the chromophore changes. Useful because timescale is so fast, and sensitivity so high. Kinetics, esp. in biochemistry, enzymology. Most quantitative Analytical chemistry in organic chemistry is conducted using HPLC with UV detectors AFB QO I 2007/08 13 One of the best ways for identifying the presence of acidic or basic groups, due to big shifts in λ for a chromophore containing a phenol, carboxylic acid, etc. hypsochromic shift bathochromic shift λ AFB QO I 2007/
8 UV-vis - range Conjugated compounds can absorb light in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum The region from 2 x 10-7 m to 4 x 10-7 m (200 to 400 nm) is most useful in organic chemistry AFB QO I 2007/08 15 UV-vis range in detail σ σ* and σ π* transitions: high-energy, accessible in vacuum UV (λ max <150 nm). n σ* and π σ* transitions: non-bonding electrons (lone pairs), wavelength (λ max ) in the nm region. n π* and π π* transitions: most common transitions observed in organic molecular UV-Vis, observed in compounds with lone pairs and multiple bonds with λ max = nm. AFB QO I 2007/
9 Electronic transitions σ π σ σ σ π alkanes carbonyls Energy n π n π σ unsaturated cmpds. O, N, S, halogens π n π carbonyls σ AFB QO I 2007/08 17 calculated π π* transitions Example: π π* transitions responsible for ethylene UV absorption at ~170 nm calculated with ZINDO semi-empirical excited-states methods (Gaussian 03W): hν 170nm photon HOMO π u bonding molecular orbital LUMO π g antibonding molecular orbital AFB QO I 2007/
10 1,3-butadiene The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) undergo a transition to the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) AFB QO I 2007/08 19 Other electronic transitions AFB QO I 2007/
11 AFB QO I 2007/08 21 AFB QO I 2007/
12 AFB QO I 2007/08 23 How Do UV spectrometers work? Rotates, to achieve scan Two photomultiplier inputs, differential voltage drives amplifier. Matched quartz cuvettes Sample in solution at ca M. System protects PM tube from stray light D2 lamp-uv Tungsten lamp-vis Double Beam makes it a difference technique AFB QO I 2007/
13 Transmittance vs Absorbance % Transmittance = (I / I 0 ) * 100% where: I = intensity of transmitted light I 0 = intensity of incident light Absorbance = -log(i / I 0 ) AFB QO I 2007/08 25 Diode Array Detectors Model from Agilent literature. Imagine replacing cell with a microflow cell for HPLC! Diode array alternative puts grating, array of photosens. Semiconductors after the light goes through the sample. Advantage, speed, sensitivity, The Multiplex advantage Disadvantage, resolution is 1 nm, vs 0.1 nm for normal UV AFB QO I 2007/
14 UV vis Spectrum 1.0 λ max with certain extinction ε UV Visible Make solution of concentration low enough that A 1 Even though a dual beam goes through a solvent blank, choose solvents that are UV transparent. Absorbance Wavelength, λ, generally in nanometers (nm) Can extract the ε value if conc. (M) and b (cm) are known UV bands are much broader than the photonic transition event. This is because vibration levels are superimposed on UV. AFB QO I 2007/08 27 Electronic Transitions and UVvisible Spectra in Molecules AFB QO I 2007/
15 Quantitative Use of UV Spectra Beers law: A = εcl A absorbance ε is molar absorptivity (extinction coefficient c is concentration in mol/l l is path of light through sample in cm AFB QO I 2007/08 29 meaning λ max : wavelength where UV absorbance for a compound is greatest Energy difference between HOMO and LUMO decreases as the extent of conjugation increases AFB QO I 2007/
16 Effect of Conjugation λ max increases as conjugation increases (lower energy) 1,3-butadiene: 217 nm 1,3,5-hexatriene: 258 nm Substituents on π system increase λ max AFB QO I 2007/08 31 Ψ 2 Ψ 4 Ψ 3 Ψ 1 π Ψ 2 Ψ 1 E for the HOMO LUMO transition is reduced AFB QO I 2007/
17 Energy Lower energy = Longer wavelengths ethylene butadiene hexatriene octatetraene AFB QO I 2007/08 33 AFB QO I 2007/
18 AFB QO I 2007/08 35 Conjugation, Color and the Chemistry of Vision Visible region is about 400 to 800 nm Extended systems of conjugation absorb in visible region β-carotene, 11 double bonds in conjugation λ max = 455 nm AFB QO I 2007/
19 AFB QO I 2007/08 37 Conjugation, Color and the Chemistry of Vision β-carotene is converted to Vitamin A, which is converted to 11-cis-retinal: AFB QO I 2007/
20 Conjugation, Color and the Chemistry of Vision 11-cis-retinal is converted to rhodopsin in the rod cells of the retina. Visual pigments are responsible for absorbing light in eye and triggering nerves to send signal to brain AFB QO I 2007/08 39 Transmission and Color The human eye sees the complementary color to that which is absorbed AFB QO I 2007/
21 Absorbance and Complementary Colors AFB QO I 2007/08 41 The colors of M&M s Bright Blue Common Food Uses Beverages, dairy products, powders, jellies, confections, condiments, icing. Royal Blue Common Food Uses Baked goods, cereals, snack foods, ice-cream, confections, cherries. Orange-red Common Food Uses Gelatins, puddings, dairy products, confections, beverages, condiments. Lemon-yellow Common Food Uses Custards, beverages, ice-cream, confections, preserves, cereals. Orange Common Food Uses Cereals, baked goods, snack foods, ice-cream, beverages, dessert powders, confections AFB QO I 2007/
22 Biological applications In the biological sciences these compounds are used as dyes to selectively stain different tissues or cell structures Biebrich Scarlet - Used with picric acid/aniline blue for staining collagen, recticulum, muscle, and plasma. Luna's method for erythrocytes & eosinophil granules. Guard's method for sex chromatin and nuclear chromatin. HO O 3 S N N N N SO 3 AFB QO I 2007/08 43 ph paper Methyl Orange In the chemical sciences these are the acid-base indicators used for the various ph ranges: Remember the effects of ph on aromatic substituents O 3 S N N CH 3 N CH 3 O 3 S H N N CH 3 N CH 3 Yellow, ph > 4.4 Red, ph < 3.2 AFB QO I 2007/
23 designing colours AFB QO I 2007/08 45 UV spectra and structure From Skoog and West et al. Ch 14 AFB QO I 2007/
24 Empirical understandind of structural effects R.B. Woodward, L.F. Fieser and others have predicted λ max for π π* in extended conjugation systems to within ca. 2-3 nm. Homoannular, base 253 nm Acyclic, base 217 nm heteroannular, base 214 nm Attached group increment, nm Extend conjugation +30 Addn exocyclic DB +5 Alkyl +5 O-Acyl 0 S-alkyl +30 O-alkyl +6 NR2 +60 Cl, Br +5 AFB QO I 2007/08 47 Expected UV (Woodward) Base value x alkyl subst. 10 exo DB 5 total 232 Obs. 237 Base value x alkyl subst. 30 exo DB 5 total 234 Obs. 235 O Base value ß alkyl subst. 24 total 239 Obs. 237 AFB QO I 2007/
25 Distinguish Isomers! HO 2 C Base value x alkyl subst. 20 exo DB 5 total 239 Obs. 238 Base value x alkyl subst. 20 total 273 Obs. 273 AFB HO 2 C QO I 2007/08 49 Substituent effects i. Bathochromic shift (red shift) a shift to longer λ; lower energy ii. Hypsochromic shift (blue shift) shift to shorter λ; higher energy iii. Hyperchromic effect an increase in intensity iv. Hypochromic effect a decrease in intensity ε Hypsochromic Hyperchromic Bathochromic Hypochromic 200 nm 700 nm AFB QO I 2007/
26 Quantitative analysis Isosbestic points Single clear point, can exclude intermediate state, exclude light scattering and Beer s law applies Great for nonaqueous titrations Example here gives detn of endpoint for bromcresol green Binding studies Form I to form II Binding of a lanthanide complex to an oligonucleotide AFB QO I 2007/08 51 Other Electronic Processes Fluorescence: absorption of radiation to an excited state, followed by emission of radiation to a lower state of the same multiplicity Phosphorescence: absorption of radiation to an excited state, followed by emission of radiation to a lower state of different multiplicity Singlet state: spins are paired, no net angular momentum (and no net magnetic field) Triplet state: spins are unpaired, net angular momentum (and net magnetic field) AFB QO I 2007/
27 rtualtext/spectrpy/uv- Vis/spectrum.htm#uv3b vich/teaching/316/index.html AFB QO I 2007/
ULTRAVIOLET SPECTROSCOPY or ELECTRONIC SPECTROSCOPY
 ULTRAVILET SPECTRSCPY or ELECTRNIC SPECTRSCPY S. SANKARARAMAN Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600036, INDIA Sanka@iitm.ac.in Absorption of electromagnetic radiation
ULTRAVILET SPECTRSCPY or ELECTRNIC SPECTRSCPY S. SANKARARAMAN Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology Madras Chennai 600036, INDIA Sanka@iitm.ac.in Absorption of electromagnetic radiation
Molecular Spectroscopy
 Molecular Spectroscopy Types of transitions: 1) Electronic (UV-Vis-Near IR) 2) Vibrational (IR) 3) Rotational (microwave) Electronic Absorption Spectra π π* Gary L. Miessler and Donald A. Tarr, Inorganic
Molecular Spectroscopy Types of transitions: 1) Electronic (UV-Vis-Near IR) 2) Vibrational (IR) 3) Rotational (microwave) Electronic Absorption Spectra π π* Gary L. Miessler and Donald A. Tarr, Inorganic
Spektroskopi Molekul Organik
 Spektroskopi Molekul rganik Chapter 7: UV & electronic transitions Usable ranges & observations Selection rules Band Structure Instrumentation & Spectra Beer-Lambert Law Application of UV-spec 1 Dosen:
Spektroskopi Molekul rganik Chapter 7: UV & electronic transitions Usable ranges & observations Selection rules Band Structure Instrumentation & Spectra Beer-Lambert Law Application of UV-spec 1 Dosen:
Spectroscopy. Page 1 of 8 L.Pillay (2012)
 Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
Spectroscopy Electromagnetic radiation is widely used in analytical chemistry. The identification and quantification of samples using electromagnetic radiation (light) is called spectroscopy. Light has
UV Spectroscopy: Empirical Approach to Molecular Structures. Dr. Mishu Singh Department of Chemistry M. P.Govt P. G.
 UV Spectroscopy: Empirical Approach to Molecular Structures Dr. Mishu Singh Department of Chemistry M. P.Govt P. G.College, Hardoi WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY? Atoms and molecules interact with electromagnetic
UV Spectroscopy: Empirical Approach to Molecular Structures Dr. Mishu Singh Department of Chemistry M. P.Govt P. G.College, Hardoi WHAT IS SPECTROSCOPY? Atoms and molecules interact with electromagnetic
Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy :
 Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy : X-ray: core electron excitation UV: valance electronic excitation IR: molecular vibrations Radio waves: Nuclear spin states (in a magnetic field) The wavelength
Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy : X-ray: core electron excitation UV: valance electronic excitation IR: molecular vibrations Radio waves: Nuclear spin states (in a magnetic field) The wavelength
Instrumental Chemical Analysis
 L6 page 1 Instrumental Chemical Analysis Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Dr. Ahmad Najjar Philadelphia University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2 nd semester, 2016/2017
L6 page 1 Instrumental Chemical Analysis Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Dr. Ahmad Najjar Philadelphia University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2 nd semester, 2016/2017
Instrumental Chemical Analysis
 L6 page 1 Instrumental Chemical Analysis Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Dr. Ahmad Najjar Philadelphia University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2 nd semester, 2016/2017
L6 page 1 Instrumental Chemical Analysis Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Dr. Ahmad Najjar Philadelphia University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2 nd semester, 2016/2017
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy. CH- 521 Course on Interpreta2ve Molecular Spectroscopy; Course Instructor: Krishna P. Kaliappan
 Ultraviolet Spectroscopy CH- 521 Course on Interpreta2ve Molecular Spectroscopy; Course Instructor: Krishna P. Kaliappan Ultraviolet Spectroscopy UV light can be absorbed by molecules to excite higher
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy CH- 521 Course on Interpreta2ve Molecular Spectroscopy; Course Instructor: Krishna P. Kaliappan Ultraviolet Spectroscopy UV light can be absorbed by molecules to excite higher
UV-Vis Spectroscopy. Chem 744 Spring Gregory R. Cook, NDSU Thursday, February 14, 13
 UV-Vis Spectroscopy Chem 744 Spring 2013 UV-Vis Spectroscopy Every organic molecule absorbs UV-visible light Energy of electronic transitions saturated functionality not in region that is easily accessible
UV-Vis Spectroscopy Chem 744 Spring 2013 UV-Vis Spectroscopy Every organic molecule absorbs UV-visible light Energy of electronic transitions saturated functionality not in region that is easily accessible
Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy
 Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy Chromophore The part of a molecule responsible for imparting color, are called as chromospheres. OR The functional groups containing multiple bonds capable of absorbing
Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy Chromophore The part of a molecule responsible for imparting color, are called as chromospheres. OR The functional groups containing multiple bonds capable of absorbing
Spectroscopy may be defined as the study of interaction between electromagnetic radiations and matter.
 Spectroscopy may be defined as the study of interaction between electromagnetic radiations and matter. Spectroscopy has a wide range of applications. It is heavily used in astronomy and remote sensing.
Spectroscopy may be defined as the study of interaction between electromagnetic radiations and matter. Spectroscopy has a wide range of applications. It is heavily used in astronomy and remote sensing.
Chemistry 304B, Spring 1999 Lecture 5 1. UV Spectroscopy:
 Chemistry 304B, Spring 1999 Lecture 5 1 Ultraviolet spectroscopy; UV Spectroscopy: Infrared spectroscopy; Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy General basis of spectroscopy: Shine light at a collection
Chemistry 304B, Spring 1999 Lecture 5 1 Ultraviolet spectroscopy; UV Spectroscopy: Infrared spectroscopy; Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy General basis of spectroscopy: Shine light at a collection
UV / Visible Spectroscopy. Click icon to add picture
 UV / Visible Spectroscopy Click icon to add picture Spectroscopy It is the branch of science that deals with the study of interaction of matter with light. OR It is the branch of science that deals with
UV / Visible Spectroscopy Click icon to add picture Spectroscopy It is the branch of science that deals with the study of interaction of matter with light. OR It is the branch of science that deals with
Chapter 4 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Molecular Spectrophotometry
 Chapter 4 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Molecular Spectrophotometry Properties of light Electromagnetic radiation and electromagnetic spectrum Absorption of light Beer s law Limitation of Beer s
Chapter 4 Ultraviolet and visible spectroscopy Molecular Spectrophotometry Properties of light Electromagnetic radiation and electromagnetic spectrum Absorption of light Beer s law Limitation of Beer s
09/05/40 MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS
 MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of wavelength ( absorption spectrum ), due to its interaction
MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of wavelength ( absorption spectrum ), due to its interaction
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy :
 Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy : X-ray: core electron excitation UV: valance electronic excitation IR: molecular vibrations Radio waves: Nuclear spin states (in a magnetic field) The wavelength
Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy : X-ray: core electron excitation UV: valance electronic excitation IR: molecular vibrations Radio waves: Nuclear spin states (in a magnetic field) The wavelength
9/28/10. Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Valence Electronic Structure. n σ* transitions
 Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Electromagnetic Spectrum - Molecular transitions Widely used in chemistry. Perhaps the most widely used in Biological Chemistry.
Visible and Ultraviolet Molecular Spectroscopy - (S-H-C Chapters 13-14) Electromagnetic Spectrum - Molecular transitions Widely used in chemistry. Perhaps the most widely used in Biological Chemistry.
two slits and 5 slits
 Electronic Spectroscopy 2015January19 1 1. UV-vis spectrometer 1.1. Grating spectrometer 1.2. Single slit: 1.2.1. I diffracted intensity at relative to un-diffracted beam 1.2.2. I - intensity of light
Electronic Spectroscopy 2015January19 1 1. UV-vis spectrometer 1.1. Grating spectrometer 1.2. Single slit: 1.2.1. I diffracted intensity at relative to un-diffracted beam 1.2.2. I - intensity of light
Chapter 12 Mass Spectrometry and Infrared Spectroscopy
 Organic Chemistry, 6 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 12 Mass Spectrometry and Infrared Spectroscopy Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District 2006, Prentice
Organic Chemistry, 6 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 12 Mass Spectrometry and Infrared Spectroscopy Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District 2006, Prentice
4.3A: Electronic transitions
 Ashley Robison My Preferences Site Tools Popular pages MindTouch User Guide FAQ Sign Out If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it
Ashley Robison My Preferences Site Tools Popular pages MindTouch User Guide FAQ Sign Out If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it
William H. Brown & Christopher S. Foote
 Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:permissions Department, Harcourt Brace & Company, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando, Florida 32887-6777 William H. Brown
Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:permissions Department, Harcourt Brace & Company, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando, Florida 32887-6777 William H. Brown
Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Key Words Conjugated Diene Resonance Structures Dienophiles Concerted Reaction Pericyclic Reaction Cycloaddition Reaction Bridged Bicyclic Compound Cyclic
Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Key Words Conjugated Diene Resonance Structures Dienophiles Concerted Reaction Pericyclic Reaction Cycloaddition Reaction Bridged Bicyclic Compound Cyclic
Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy :
 SPECTROSCOPY Light interacting with matter as an analytical tool III Pharm.D Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis SRM College Of Pharmacy,Katankulathur Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy : X-ray:
SPECTROSCOPY Light interacting with matter as an analytical tool III Pharm.D Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis SRM College Of Pharmacy,Katankulathur Electronic Excitation by UV/Vis Spectroscopy : X-ray:
Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy
 Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy Chromophore The part of a molecule responsible for imparting color, are called as chromospheres. OR The functional groups containing multiple bonds capable of absorbing
Terms used in UV / Visible Spectroscopy Chromophore The part of a molecule responsible for imparting color, are called as chromospheres. OR The functional groups containing multiple bonds capable of absorbing
Organic Chemistry: CHEM2322
 Conjugated Systems Organic Chemistry: We met in Chem 2321 unsaturated bonds as either a C=C bond or C C bond. If these unsaturated bonds are well separated then they react independently however if there
Conjugated Systems Organic Chemistry: We met in Chem 2321 unsaturated bonds as either a C=C bond or C C bond. If these unsaturated bonds are well separated then they react independently however if there
Lecture 09 MO theory. (Refer Slide Time: 00:33)
 (Refer Slide Time: 00:33) Atomic and Molecular Absorption Spectrometry for Pollution Monitoring Dr. J R Mudakavi Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture 09 MO
(Refer Slide Time: 00:33) Atomic and Molecular Absorption Spectrometry for Pollution Monitoring Dr. J R Mudakavi Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture 09 MO
Lecture 2 nmr Spectroscopy
 Lecture 2 nmr Spectroscopy Pages 427 430 and Chapter 13 Molecular Spectroscopy Molecular spectroscopy: the study of the frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that are absorbed or emitted by substances
Lecture 2 nmr Spectroscopy Pages 427 430 and Chapter 13 Molecular Spectroscopy Molecular spectroscopy: the study of the frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that are absorbed or emitted by substances
Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry
 Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451
Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451
Reference literature. (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters )
 September 17, 2018 Reference literature (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters 13-14 ) Reference.: https://slideplayer.com/slide/8354408/ Spectroscopy Usual Wavelength Type of Quantum
September 17, 2018 Reference literature (See: CHEM 2470 notes, Module 8 Textbook 6th ed., Chapters 13-14 ) Reference.: https://slideplayer.com/slide/8354408/ Spectroscopy Usual Wavelength Type of Quantum
Molecular Spectroscopy. H 2 O e -
 Molecular Spectroscopy ν (cm -1 ) λ (cm) 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10 14 10 16 10 18 10 20 10 22 ν (Hz) NMR ESR microwave IR UV/Vis VUV X-Ray Gamma Ray H 2 e - UV/Vis Spectroscopy absorption technique X hν
Molecular Spectroscopy ν (cm -1 ) λ (cm) 10 6 10 8 10 10 10 12 10 14 10 16 10 18 10 20 10 22 ν (Hz) NMR ESR microwave IR UV/Vis VUV X-Ray Gamma Ray H 2 e - UV/Vis Spectroscopy absorption technique X hν
17.1 Classes of Dienes
 W 2/1 Due: HW14, spec03 Due: n/a M 2/6 Lecture HW14 grading Lect17a Conjugated π systems Lecture quiz Lect17b Lab Lab02 Qual Analysis II (cont) 7-1 17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for
W 2/1 Due: HW14, spec03 Due: n/a M 2/6 Lecture HW14 grading Lect17a Conjugated π systems Lecture quiz Lect17b Lab Lab02 Qual Analysis II (cont) 7-1 17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for
Infrared Spectroscopy: Identification of Unknown Substances
 Infrared Spectroscopy: Identification of Unknown Substances Suppose a white powder is one of the four following molecules. How can they be differentiated? H N N H H H H Na H H H H H A technique that is
Infrared Spectroscopy: Identification of Unknown Substances Suppose a white powder is one of the four following molecules. How can they be differentiated? H N N H H H H Na H H H H H A technique that is
Chapter 13 An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption Spectrometry
 Chapter 13 An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption Spectrometry 13A Measurement Of Transmittance and Absorbance Absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet and visible radiation
Chapter 13 An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption Spectrometry 13A Measurement Of Transmittance and Absorbance Absorption measurements based upon ultraviolet and visible radiation
Lectures Spectroscopy. Fall 2012
 Lectures 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2012 1 spectroscopic principles (Chem 1M/1N exps. #6 and #11) 4 1 spectroscopic excitations ( E = h = hc/ ; = c ) (nm) (sec -1 ) radiation technique molecular excitation
Lectures 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2012 1 spectroscopic principles (Chem 1M/1N exps. #6 and #11) 4 1 spectroscopic excitations ( E = h = hc/ ; = c ) (nm) (sec -1 ) radiation technique molecular excitation
Lectures Spectroscopy. Fall 2012
 Lectures 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2012 1 spectroscopic principles (Chem 1M/1N exps. #6 and #11) 4 spectroscopic excitations ( E = h = hc/ ; = c ) (nm) (sec -1 ) radiation technique molecular excitation
Lectures 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2012 1 spectroscopic principles (Chem 1M/1N exps. #6 and #11) 4 spectroscopic excitations ( E = h = hc/ ; = c ) (nm) (sec -1 ) radiation technique molecular excitation
17.1 Classes of Dienes
 17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for dienes: Cumulated: pi bonds are adjacent. Conjugated: pi bonds are separated by exactly ONE single bond. Isolated: pi bonds are separated by any distance
17.1 Classes of Dienes There are three categories for dienes: Cumulated: pi bonds are adjacent. Conjugated: pi bonds are separated by exactly ONE single bond. Isolated: pi bonds are separated by any distance
Química Orgânica I. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (I) Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1 AFB QO I 2007/08 2
 Química Orgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (I) AFB QO I 2007/08 2 1 Adaptado de: Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition; L. G. Wade,
Química Orgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (I) AFB QO I 2007/08 2 1 Adaptado de: Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition; L. G. Wade,
Spectroscopy: Introduction. Required reading Chapter 18 (pages ) Chapter 20 (pages )
 Spectroscopy: Introduction Required reading Chapter 18 (pages 378-397) Chapter 20 (pages 424-449) Spectrophotometry is any procedure that uses light to measure chemical concentrations Properties of Light
Spectroscopy: Introduction Required reading Chapter 18 (pages 378-397) Chapter 20 (pages 424-449) Spectrophotometry is any procedure that uses light to measure chemical concentrations Properties of Light
Questions on Instrumental Methods of Analysis
 Questions on Instrumental Methods of Analysis 1. Which one of the following techniques can be used for the detection in a liquid chromatograph? a. Ultraviolet absorbance or refractive index measurement.
Questions on Instrumental Methods of Analysis 1. Which one of the following techniques can be used for the detection in a liquid chromatograph? a. Ultraviolet absorbance or refractive index measurement.
CHEM*3440. Photon Energy Units. Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation. Chemical Instrumentation. Spectroscopic Experimental Concept.
 Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation is light. Different energy light interacts with different motions in molecules. CHEM*344 Chemical Instrumentation Topic 7 Spectrometry Radiofrequency
Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic radiation is light. Different energy light interacts with different motions in molecules. CHEM*344 Chemical Instrumentation Topic 7 Spectrometry Radiofrequency
The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU
 The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU 1 Agilent is committed to the educational community and is willing to provide access to company-owned material. This slide
The Fundamentals of Spectroscopy: Theory BUILDING BETTER SCIENCE AGILENT AND YOU 1 Agilent is committed to the educational community and is willing to provide access to company-owned material. This slide
Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry
 Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451
Ultraviolet-Visible and Infrared Spectrophotometry Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451
Analytical Technologies in Biotechnology Prof. Dr. Ashwani K Sharma Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee
 Analytical Technologies in Biotechnology Prof. Dr. Ashwani K Sharma Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 6 Spectroscopic Techniques Lecture - 2 UV-Visible Spectroscopy
Analytical Technologies in Biotechnology Prof. Dr. Ashwani K Sharma Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Module - 6 Spectroscopic Techniques Lecture - 2 UV-Visible Spectroscopy
CHEM 261 Notes Nov 22, 2017 REVIEW:
 155 CEM 261 Notes Nov 22, 2017 REVIEW: Recall how we can show the energy levels of the atomic orbitals of C. If the C is sp 2 hybridized, two of the 2p orbitals combine with the 2s orbital to form two
155 CEM 261 Notes Nov 22, 2017 REVIEW: Recall how we can show the energy levels of the atomic orbitals of C. If the C is sp 2 hybridized, two of the 2p orbitals combine with the 2s orbital to form two
What is spectroscopy?
 Absorption Spectrum What is spectroscopy? Studying the properties of matter through its interaction with different frequency components of the electromagnetic spectrum. With light, you aren t looking directly
Absorption Spectrum What is spectroscopy? Studying the properties of matter through its interaction with different frequency components of the electromagnetic spectrum. With light, you aren t looking directly
Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods
 Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods General Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation (EM) Wave Properties of EM Quantum Mechanical Properties of EM Quantitative Aspects of Spectrochemical
Skoog Chapter 6 Introduction to Spectrometric Methods General Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation (EM) Wave Properties of EM Quantum Mechanical Properties of EM Quantitative Aspects of Spectrochemical
Chapter 13 Spectroscopy
 hapter 13 Spectroscopy Infrared spectroscopy Ultraviolet-Visible spectroscopy Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy Mass Spectrometry 13.1 Principles of Molecular Spectroscopy: Electromagnetic Radiation
hapter 13 Spectroscopy Infrared spectroscopy Ultraviolet-Visible spectroscopy Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy Mass Spectrometry 13.1 Principles of Molecular Spectroscopy: Electromagnetic Radiation
Increasing energy. ( 10 4 cm -1 ) ( 10 2 cm -1 )
 The branch of science which deals with the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter is called spectroscopy The energy absorbed or emitted in each transition corresponds to a definite frequency
The branch of science which deals with the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter is called spectroscopy The energy absorbed or emitted in each transition corresponds to a definite frequency
Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy
 Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy Introduction to UV-Visible Absorption spectroscopy from 160 nm to 780 nm Measurement of transmittance Conversion to absorbance * A=-logT=εbc Measurement of transmittance
Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy Introduction to UV-Visible Absorption spectroscopy from 160 nm to 780 nm Measurement of transmittance Conversion to absorbance * A=-logT=εbc Measurement of transmittance
Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy
 Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated Systems - Conjugated systems have alternating single and double bonds. For example: C=C C=C C=C and C=C C=O - This is not conjugated because the double
Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated Systems - Conjugated systems have alternating single and double bonds. For example: C=C C=C C=C and C=C C=O - This is not conjugated because the double
William H. Brown & Christopher S. Foote
 Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:permissions Department, Harcourt Brace & Company, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando, Florida 32887-6777 William H. Brown
Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:permissions Department, Harcourt Brace & Company, 6277 Sea Harbor Drive, Orlando, Florida 32887-6777 William H. Brown
Spectrophotometry. Introduction
 Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
Spectrophotometry Spectrophotometry is a method to measure how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through sample solution. The basic principle
Lecture 3: Light absorbance
 Lecture 3: Light absorbance Perturbation Response 1 Light in Chemistry Light Response 0-3 Absorbance spectrum of benzene 2 Absorption Visible Light in Chemistry S 2 S 1 Fluorescence http://www.microscopyu.com
Lecture 3: Light absorbance Perturbation Response 1 Light in Chemistry Light Response 0-3 Absorbance spectrum of benzene 2 Absorption Visible Light in Chemistry S 2 S 1 Fluorescence http://www.microscopyu.com
MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS
 MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of wavelength ( absorption spectrum ), due to its interaction
MOLECULAR ABSORPTION METHODS Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of wavelength ( absorption spectrum ), due to its interaction
Classification of spectroscopic methods
 Introduction Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between the electromagnetic radiation and the matter. Spectrophotometry is the measurement of these interactions i.e. the measurement of the intensity
Introduction Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between the electromagnetic radiation and the matter. Spectrophotometry is the measurement of these interactions i.e. the measurement of the intensity
R O Y G B V. Spin States. Outer Shell Electrons. Molecular Rotations. Inner Shell Electrons. Molecular Vibrations. Nuclear Transitions
 Spin States Molecular Rotations Molecular Vibrations Outer Shell Electrons Inner Shell Electrons Nuclear Transitions NMR EPR Microwave Absorption Spectroscopy Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy UV-vis Absorption,
Spin States Molecular Rotations Molecular Vibrations Outer Shell Electrons Inner Shell Electrons Nuclear Transitions NMR EPR Microwave Absorption Spectroscopy Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy UV-vis Absorption,
Topics Spectroscopy. Fall 2016
 Topics 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2016 1 SPECTROSCOPY: short wavelength regions ESCA (photoelectron) and UV handout 2 alert approach for spectroscopy material not straight from text chapter must FOLLOW videos,
Topics 19-20 Spectroscopy Fall 2016 1 SPECTROSCOPY: short wavelength regions ESCA (photoelectron) and UV handout 2 alert approach for spectroscopy material not straight from text chapter must FOLLOW videos,
Chapter 18. Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry. Properties of Light
 Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
Chapter 18 Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Properties of Light Electromagnetic Radiation energy radiated in the form of a WAVE caused by an electric field interacting with a magnetic field result of
7a. Structure Elucidation: IR and 13 C-NMR Spectroscopies (text , , 12.10)
 2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7a.1 7a. Structure Elucidation: IR and 13 C-NMR Spectroscopies (text 11.1 11.5, 12.1 12.5, 12.10) A. Electromagnetic Radiation Energy is
2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western Ontario 7a.1 7a. Structure Elucidation: IR and 13 C-NMR Spectroscopies (text 11.1 11.5, 12.1 12.5, 12.10) A. Electromagnetic Radiation Energy is
CHEM Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy
 CHEM 21112 Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy References: 1. Fundamentals of Molecular Spectroscopy by C.N. Banwell 2. Physical Chemistry by P.W. Atkins Dr. Sujeewa De Silva Sub topics Light and matter
CHEM 21112 Atomic and Molecular Spectroscopy References: 1. Fundamentals of Molecular Spectroscopy by C.N. Banwell 2. Physical Chemistry by P.W. Atkins Dr. Sujeewa De Silva Sub topics Light and matter
Infrared Spectroscopy
 Infrared Spectroscopy Introduction Spectroscopy is an analytical technique which helps determine structure. It destroys little or no sample. The amount of light absorbed by the sample is measured as wavelength
Infrared Spectroscopy Introduction Spectroscopy is an analytical technique which helps determine structure. It destroys little or no sample. The amount of light absorbed by the sample is measured as wavelength
Chapter 5 Materials Characterization Lecture III
 Chapter 5 Materials Characterization Lecture III Dr. Alagiriswamy A A (PhD., PDF) Dept. of Physics and Nanotechnology SRM University Main Campus, Ktr., SRM Nagar, Chennai, Tamilnadu 5.0 Characterization
Chapter 5 Materials Characterization Lecture III Dr. Alagiriswamy A A (PhD., PDF) Dept. of Physics and Nanotechnology SRM University Main Campus, Ktr., SRM Nagar, Chennai, Tamilnadu 5.0 Characterization
Lecture- 08 Emission and absorption spectra
 Atomic and Molecular Absorption Spectrometry for Pollution Monitoring Dr. J R Mudakavi Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture- 08 Emission and absorption spectra
Atomic and Molecular Absorption Spectrometry for Pollution Monitoring Dr. J R Mudakavi Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture- 08 Emission and absorption spectra
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 3. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 3 Quantum Transitions The energy of a photon can also be transferred to an elementary particle by adsorption if the energy of the photon exactly matches the
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 3 Quantum Transitions The energy of a photon can also be transferred to an elementary particle by adsorption if the energy of the photon exactly matches the
24 Introduction to Spectrochemical Methods
 24 Introduction to Spectrochemical Methods Spectroscopic method: based on measurement of the electromagnetic radiation produced or absorbed by analytes. electromagnetic radiation: include γ-ray, X-ray,
24 Introduction to Spectrochemical Methods Spectroscopic method: based on measurement of the electromagnetic radiation produced or absorbed by analytes. electromagnetic radiation: include γ-ray, X-ray,
Lecture 0. NC State University
 Chemistry 736 Lecture 0 Overview NC State University Overview of Spectroscopy Electronic states and energies Transitions between states Absorption and emission Electronic spectroscopy Instrumentation Concepts
Chemistry 736 Lecture 0 Overview NC State University Overview of Spectroscopy Electronic states and energies Transitions between states Absorption and emission Electronic spectroscopy Instrumentation Concepts
UV Visible Spectroscopy
 UV Visible Spectroscopy It involves the measurement of absorption of light in the UV region(10-200(far UV)-200-400nm(near UV) and visible region(400-800nm)by the compound under investigation. It is also
UV Visible Spectroscopy It involves the measurement of absorption of light in the UV region(10-200(far UV)-200-400nm(near UV) and visible region(400-800nm)by the compound under investigation. It is also
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry
 Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back
 Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Reflection = EM strikes a boundary between two media differing in η and bounces back Incident ray θ 1 θ 2 Reflected ray Medium 1 (air) η = 1.00 Medium 2 (glass) η = 1.50 Specular reflection = situation
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry
 Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
Chapter 17: Fundamentals of Spectrophotometry Spectroscopy: the science that deals with interactions of matter with electromagnetic radiation or other forms energy acoustic waves, beams of particles such
1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory.
 Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. Objectives: 1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory: atom, subatomic particles, atomic number, mass number, atomic mass, isotopes, simplified atomic diagrams,
Lecture 5. Radiation and energy. Objectives: 1. The most important aspects of the quantum theory: atom, subatomic particles, atomic number, mass number, atomic mass, isotopes, simplified atomic diagrams,
Conjugated Systems. With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn
 Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
Conjugated Systems Double bonds in conjugation behave differently than isolated double bonds With conjugated double bonds resonance structures can be drawn With isolated double bonds cannot draw resonance
NPTEL/IITM. Molecular Spectroscopy Lectures 1 & 2. Prof.K. Mangala Sunder Page 1 of 15. Topics. Part I : Introductory concepts Topics
 Molecular Spectroscopy Lectures 1 & 2 Part I : Introductory concepts Topics Why spectroscopy? Introduction to electromagnetic radiation Interaction of radiation with matter What are spectra? Beer-Lambert
Molecular Spectroscopy Lectures 1 & 2 Part I : Introductory concepts Topics Why spectroscopy? Introduction to electromagnetic radiation Interaction of radiation with matter What are spectra? Beer-Lambert
February 8, 2018 Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 7 UV-Vis spectroscopy February 8, 2018 First Midterm Exam When: Wednesday, 2/14 When: 7-9 PM (please do not be late) Where: WEL 2.122 This room!!! What: Covers material through today s lecture
Lecture 7 UV-Vis spectroscopy February 8, 2018 First Midterm Exam When: Wednesday, 2/14 When: 7-9 PM (please do not be late) Where: WEL 2.122 This room!!! What: Covers material through today s lecture
Absorption spectrometry summary
 Absorption spectrometry summary Rehearsal: Properties of light (electromagnetic radiation), dual nature light matter interactions (reflection, transmission, absorption, scattering) Absorption phenomena,
Absorption spectrometry summary Rehearsal: Properties of light (electromagnetic radiation), dual nature light matter interactions (reflection, transmission, absorption, scattering) Absorption phenomena,
Spectroscopy Chapter 13
 Spectroscopy Chapter 13 Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic spectrum in terms of wavelength, frequency and Energy c=λν c= speed of light in a vacuum 3x108 m/s v= frequency in Hertz (Hz s-1 ) λ= wavelength
Spectroscopy Chapter 13 Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic spectrum in terms of wavelength, frequency and Energy c=λν c= speed of light in a vacuum 3x108 m/s v= frequency in Hertz (Hz s-1 ) λ= wavelength
13.24: Mass Spectrometry: molecular weight of the sample
 hapter 13: Spectroscopy Methods of structure determination Nuclear Magnetic Resonances (NMR) Spectroscopy (Sections 13.3-13.19) Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy (Sections 13.20-13.22) Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis)
hapter 13: Spectroscopy Methods of structure determination Nuclear Magnetic Resonances (NMR) Spectroscopy (Sections 13.3-13.19) Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy (Sections 13.20-13.22) Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis)
Course: M.Sc (Chemistry) Analytical Chemistry Unit: III
 Course: M.Sc (Chemistry) Analytical Chemistry Unit: III Syllabus: Principle of spectrophotometry Types of spectrophotometer Applications - Dissociation constants of an indicator simultaneous spectrophotometric
Course: M.Sc (Chemistry) Analytical Chemistry Unit: III Syllabus: Principle of spectrophotometry Types of spectrophotometer Applications - Dissociation constants of an indicator simultaneous spectrophotometric
Lecture 6: Physical Methods II. UV Vis (electronic spectroscopy) Electron Spin Resonance Mossbauer Spectroscopy
 Lecture 6: Physical Methods II UV Vis (electronic spectroscopy) Electron Spin Resonance Mossbauer Spectroscopy Physical Methods used in bioinorganic chemistry X ray crystallography X ray absorption (XAS)
Lecture 6: Physical Methods II UV Vis (electronic spectroscopy) Electron Spin Resonance Mossbauer Spectroscopy Physical Methods used in bioinorganic chemistry X ray crystallography X ray absorption (XAS)
10/2/2008. hc λ. νλ =c. proportional to frequency. Energy is inversely proportional to wavelength And is directly proportional to wavenumber
 CH217 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Module Leader: Dr. Alison Willows Electromagnetic spectrum Properties of electromagnetic radiation Many properties of electromagnetic radiation can be described
CH217 Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Module Leader: Dr. Alison Willows Electromagnetic spectrum Properties of electromagnetic radiation Many properties of electromagnetic radiation can be described
on-line spectroscopy 1!!! Chemistry 1B Fall 2013 Chemistry 1B, Fall 2013 Lecture Spectroscopy Lectures Spectroscopy Fall 2013
 Lecture 190 Spectroscopy Flipping the lecture discussion Flip teaching (or flipped classroom) is a form of blended learning in which students learn new content online by watching video lectures, usually
Lecture 190 Spectroscopy Flipping the lecture discussion Flip teaching (or flipped classroom) is a form of blended learning in which students learn new content online by watching video lectures, usually
levels. The signal is either absorbance vibrational and rotational energy levels or percent transmittance of the analyte
 1 In this chapter, absorption by molecules, rather than atoms, is considered. Absorption in the ultraviolet and visible regions occurs due to electronic transitions from the ground state to excited state.
1 In this chapter, absorption by molecules, rather than atoms, is considered. Absorption in the ultraviolet and visible regions occurs due to electronic transitions from the ground state to excited state.
Assumed knowledge. Chemistry 2. Learning outcomes. Electronic spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules. Franck-Condon Principle (reprise)
 Chemistry 2 Lecture 11 Electronic spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules Assumed knowledge For bound excited states, transitions to the individual vibrational levels of the excited state are observed with
Chemistry 2 Lecture 11 Electronic spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules Assumed knowledge For bound excited states, transitions to the individual vibrational levels of the excited state are observed with
and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Chemistry 311: Instrumentation Analysis Topic 2: Atomic Spectroscopy. Chemistry 311: Instrumentation Analysis Topic 2: Atomic Spectroscopy
 Topic 1: Atomic Spectroscopy Text: Chapter 12,13 & 14 Rouessac (~2 weeks) 1.0 Review basic concepts in Spectroscopy 2.0 Atomic Absorption and Graphite Furnace Instruments 3.0 Inductively Coupled Plasmas
Topic 1: Atomic Spectroscopy Text: Chapter 12,13 & 14 Rouessac (~2 weeks) 1.0 Review basic concepts in Spectroscopy 2.0 Atomic Absorption and Graphite Furnace Instruments 3.0 Inductively Coupled Plasmas
Spectroscopy. a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation.
 Spectroscopy a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation. Mass Spectrometry Determines the relative abundance of the different isotopes of an element Used to determine the average
Spectroscopy a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation. Mass Spectrometry Determines the relative abundance of the different isotopes of an element Used to determine the average
Spectroscopy. a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation
 Spectroscopy a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation The electromagnetic spectrum Radiation Scale of Absorption involves: Example of spectroscopy Gamma rays pm Nuclear reactions
Spectroscopy a laboratory method of analyzing matter using electromagnetic radiation The electromagnetic spectrum Radiation Scale of Absorption involves: Example of spectroscopy Gamma rays pm Nuclear reactions
E35 SPECTROSCOPIC TECHNIQUES IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 E35 SPECTRSCPIC TECNIQUES IN RGANIC CEMISTRY Introductory Comments. These notes are designed to introduce you to the basic spectroscopic techniques which are used for the determination of the structure
E35 SPECTRSCPIC TECNIQUES IN RGANIC CEMISTRY Introductory Comments. These notes are designed to introduce you to the basic spectroscopic techniques which are used for the determination of the structure
Calculate a rate given a species concentration change.
 Kinetics Define a rate for a given process. Change in concentration of a reagent with time. A rate is always positive, and is usually referred to with only magnitude (i.e. no sign) Reaction rates can be
Kinetics Define a rate for a given process. Change in concentration of a reagent with time. A rate is always positive, and is usually referred to with only magnitude (i.e. no sign) Reaction rates can be
Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Diene: molecule with two double bonds Conjugated diene: alternating double and single bonds
 Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Diene: molecule with two double bonds Conjugated diene: alternating double and single bonds C-C single bond lkene Diene C=C double bonds Conjugate
Chapter 14: Conjugated Dienes and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Diene: molecule with two double bonds Conjugated diene: alternating double and single bonds C-C single bond lkene Diene C=C double bonds Conjugate
Paper: 12, Organic Spectroscopy Module: 5, Applications of UV spectroscopy
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 12: Organic Spectroscopy Applications of UV-visible Spectroscopy CHE_P12_M5 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag Paper 12: Organic Spectroscopy Applications of UV-visible Spectroscopy CHE_P12_M5 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Química Orgânica I. Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química. IR spectroscopy AFB QO I 2007/08 1 AFB QO I 2007/08 2
 Química Orgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1 IR spectroscopy AFB QO I 2007/08 2 1 Adaptado de: Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition; L. G. Wade, Jr. Organic Chemistry, William
Química Orgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1 IR spectroscopy AFB QO I 2007/08 2 1 Adaptado de: Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition; L. G. Wade, Jr. Organic Chemistry, William
A very brief history of the study of light
 1. Sir Isaac Newton 1672: A very brief history of the study of light Showed that the component colors of the visible portion of white light can be separated through a prism, which acts to bend the light
1. Sir Isaac Newton 1672: A very brief history of the study of light Showed that the component colors of the visible portion of white light can be separated through a prism, which acts to bend the light
Chapter 13. Conjugated Unsaturated Systems. +,., - Allyl. What is a conjugated system? AllylicChlorination (High Temperature)
 What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
What is a conjugated system? Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital may be empty (a carbocation The
Quantum Chemistry. NC State University. Lecture 5. The electronic structure of molecules Absorption spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy
 Quantum Chemistry Lecture 5 The electronic structure of molecules Absorption spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy NC State University 3.5 Selective absorption and emission by atmospheric gases (source:
Quantum Chemistry Lecture 5 The electronic structure of molecules Absorption spectroscopy Fluorescence spectroscopy NC State University 3.5 Selective absorption and emission by atmospheric gases (source:
Topic 6: Light Absorption and Color in Biomolecules
 1 6.1 INTRODUCTION Topic 6: Light Absorption and Color in Biomolecules Why are trees green? Blood red? Carrots orange? Most colors in biological tissues arise from natural pigments. A pigment is a molecule
1 6.1 INTRODUCTION Topic 6: Light Absorption and Color in Biomolecules Why are trees green? Blood red? Carrots orange? Most colors in biological tissues arise from natural pigments. A pigment is a molecule
高等食品分析 (Advanced Food Analysis) I. SPECTROSCOPIC METHODS *Instrumental methods: 1. Spectroscopic methods (spectroscopy): a) Electromagnetic radiation
 *Instrumental methods: 1. Spectroscopic methods (spectroscopy): a) Electromagnetic radiation (EMR): γ-ray emission X-Ray absorption, emission, fluorescence and diffraction Vacuum ultraviolet (UV) absorption
*Instrumental methods: 1. Spectroscopic methods (spectroscopy): a) Electromagnetic radiation (EMR): γ-ray emission X-Ray absorption, emission, fluorescence and diffraction Vacuum ultraviolet (UV) absorption
