LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work):
|
|
|
- Julius Russell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Assignment #6 Review States LO: To identify areas of weakness. EQ: Describe the three states of matter in depth. Write the main force responsible in bold color. 4/27-4/28 AGENDA 1. CST Review 2. Phases Review HOMEWORK 1. Review packet LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work): 1. What are the elements of life? 2. The density of air is 1000 kg/m3. The density of lead is 6000 kg/m3. Which is lighter: a. 2 m3 of lead b. 10 m3 of air
2 Monday/Tuesday Minimum Day Thursday/Friday CST practice test None Worksheet CST review packet Practice Physics Test CST!!! Science fair project Develop question for sci fair Practice chem test Final Exam Develop project Project and Exploratorium Sci Fair Prep none Practice for Sci Fair Sci fair Last day
3 1. On your test, draw lines between each of the sections (use the key below) 2. Label each section (example: experiment/experimentation ) 3. Identify the three sections that you did the worst on, highlight or circle the label with a marker 4. Write in your notes the three topics you need help on I did well in. I need to improve on these sections. I can (do this to improve) CST Questions Review 1-5: experiment/investigation 6-11: motion 12-16: forces 17-19: density 20-31: periodic table/chemistry Space 37-41: Chemical Reactions 42-44: Chemistry of life
4 What is the definition of: Solid Liquid Gas
5 SOLID: atoms locked in position and can only vibrate LIQUID: atoms are loosely connected and can collide or move past each other GAS: atoms free to move independently and collide frequently
6 Which one has most ENERGY?? SOLID: atoms locked in position and can only vibrate LIQUID: atoms are loosely connected and can collide or move past each other GAS: atoms free to move independently and collide frequently
7 When liquid becomes gas. Does it absorb or release energy? SOLID: atoms locked in position and can only vibrate LIQUID: atoms are loosely connected and can collide or move past each other GAS: atoms free to move independently and collide frequently
8 When liquid becomes solid. Does it absorb or release energy? SOLID: atoms locked in position and can only vibrate LIQUID: atoms are loosely connected and can collide or move past each other GAS: atoms free to move independently and collide frequently
9 CST Question: Within a substance, atoms that collide frequently and move independently of one another are most likely in a: a. Liquid b. Solid c. Gas d. crystal
10 What is this???? DON T SAY IT!! GIVE PEOPLE TIME TO THINK!
11 What is the arrow pointing at???? DON T SAY IT!! GIVE PEOPLE TIME TO THINK!
12 What is the arrow pointing at???? DON T SAY IT!! GIVE PEOPLE TIME TO THINK!
13 What is the arrow pointing at???? DON T SAY IT!! GIVE PEOPLE TIME TO THINK!
14 What is the arrow pointing at???? DON T SAY IT!! GIVE PEOPLE TIME TO THINK!
15 What is the arrow pointing at???? DON T SAY IT!! GIVE PEOPLE TIME TO THINK!
16 Practice CST problems on the board These are some problem areas that some students have had
17 Agenda: 1. Correct practice CST Write correct answer and WHY it is correct 2. CST Practice Packet 3. Check what section you struggled with in CST Practice that section on ZINGY HOMEWORK: 1. FM worksheet 2. CST practice packet 3. Chemistry of Life reading (by request) CST BREADOWN 1-5: experiment/investigation 6-11: motion 12-16: forces 17-19: density 20-31: periodic table/chemistry Space 37-41: Chemical Reactions 42-44: Chemistry of life
18 Assignment #6 Review States LO: To identify areas of weakness. EQ: Describe the three states of matter in depth. 4/27-4/28 AGENDA 1. CST Review 2. Phases Review HOMEWORK 1. Chemistry of life 2. Worksheet LEVEL ZERO VOICE PROCESSING TASK (10 minutes, individual work): Draw a picture of the molecules in a solid, liquid, and gas. Next to the pictures write the definition of the state of matter. USE AT LEAST 3 COLORS
LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work):
 Assignment #5 Laws of Motion LO: To apply Newton s laws to real life situations. EQ: Describe each of Newton s laws. 3/5-3/6 AGENDA 1. Video 2. sticky note lecture 3. Process notes 4. Processing task HOMEWORK
Assignment #5 Laws of Motion LO: To apply Newton s laws to real life situations. EQ: Describe each of Newton s laws. 3/5-3/6 AGENDA 1. Video 2. sticky note lecture 3. Process notes 4. Processing task HOMEWORK
2. Is this balanced or not? 2 LiCl + Br 2 2 LiBr + Cl 2 3. Summarize notes from last assignment.
 Assignment #3 Temperature in Reactions LO: To recognize how to tell if a chemical reaction has occurred. EQ: Compare and contrast endothermic and exothermic reactions. Give examples of each. AGENDA 1.
Assignment #3 Temperature in Reactions LO: To recognize how to tell if a chemical reaction has occurred. EQ: Compare and contrast endothermic and exothermic reactions. Give examples of each. AGENDA 1.
LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (4 minutes, individual work): How do plants grow? What do plants eat?
 Assignment #5 Photosynthesis LO: To understand the process of photosynthesis. EQ: Explain the light dependent and light independent reactions. Include where they take place. (4-5 sentences) AGENDA 2/6-2/7
Assignment #5 Photosynthesis LO: To understand the process of photosynthesis. EQ: Explain the light dependent and light independent reactions. Include where they take place. (4-5 sentences) AGENDA 2/6-2/7
LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work):
 LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work): 1. Predict the properties of a metal. 2. Predict the properties of a nonmetal. 3. Which is more reactive? Ca or Cs? 4. How many electrons does N
LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work): 1. Predict the properties of a metal. 2. Predict the properties of a nonmetal. 3. Which is more reactive? Ca or Cs? 4. How many electrons does N
S8P1C. STATES OF MATTER E.Q. WHAT ARE THE STATES OF MATTER? WHAT ARE THE CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH STATE OF MATTER?
 S8P1C. STATES OF MATTER E.Q. WHAT ARE THE STATES OF MATTER? WHAT ARE THE CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH STATE OF MATTER? ATOMIC MODEL PROJECT BE CREATIVE!!! MIXTURES VS. SUBSTANCES TASK DUE BY FRIDAY, NOVEMBER
S8P1C. STATES OF MATTER E.Q. WHAT ARE THE STATES OF MATTER? WHAT ARE THE CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH STATE OF MATTER? ATOMIC MODEL PROJECT BE CREATIVE!!! MIXTURES VS. SUBSTANCES TASK DUE BY FRIDAY, NOVEMBER
LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work): 1. Counting atoms
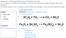 Assignment 4 Chemical Detectives at the Molecular Level LO: To explain the differences between chemical and physical changes through observable evidence. EQ: What evidence can be used to tell the difference
Assignment 4 Chemical Detectives at the Molecular Level LO: To explain the differences between chemical and physical changes through observable evidence. EQ: What evidence can be used to tell the difference
Why do cold packs get cold?
 Assignment #5 Temperature in Reactions LO: To determine which solute dissolves most endothermically and exothermically in water. EQ: What makes an endothermic reaction feel cold? (explain using bonds and
Assignment #5 Temperature in Reactions LO: To determine which solute dissolves most endothermically and exothermically in water. EQ: What makes an endothermic reaction feel cold? (explain using bonds and
States of Matter. What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another?
 Name States of Matter Date What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about states of
Name States of Matter Date What physical changes and energy changes occur as matter goes from one state to another? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about states of
Friday, November 2, 2018 GLE/Standard: The fact that atoms are conserved, together
 Mrs. Chausse s Physical Science Gifted Lesson Plan: Unit 7 Chemical Reactions November 1 16, 2018 Thursday, November 1, 2018 Objective: SWBAT balance a chemical equation that satisfies the Law of Conservation
Mrs. Chausse s Physical Science Gifted Lesson Plan: Unit 7 Chemical Reactions November 1 16, 2018 Thursday, November 1, 2018 Objective: SWBAT balance a chemical equation that satisfies the Law of Conservation
Inquiry 2.1 (Investigating Lunar Phases) Purpose: What causes you to see the moon going through eight different moon phases?
 Inquiry 2.1 (Investigating Lunar Phases) Purpose: What causes you to see the moon going through eight different moon phases? Background Information: What is an orbital plane? Does the moon make or reflect
Inquiry 2.1 (Investigating Lunar Phases) Purpose: What causes you to see the moon going through eight different moon phases? Background Information: What is an orbital plane? Does the moon make or reflect
Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page!1. Chemistry A States of Matter Packet
 Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page!1 Chemistry A States of Matter Packet Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page!2 Worksheet #1: States of Matter In this packet we will
Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page!1 Chemistry A States of Matter Packet Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page!2 Worksheet #1: States of Matter In this packet we will
Structure of Cells and Organisms (Week 1)
 Structure of Cells and Organisms (Week 1) 1/30 1/31 2/1 2/2 2/3 Topic: Introduction to Structure of Cells and Organisms 1. Sum up what you know about Earth 2. Introduce New Unit Get your Chromebook Logged
Structure of Cells and Organisms (Week 1) 1/30 1/31 2/1 2/2 2/3 Topic: Introduction to Structure of Cells and Organisms 1. Sum up what you know about Earth 2. Introduce New Unit Get your Chromebook Logged
SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Learning Objectives Possible Student Pre/Misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Students review the atomic arrangements for each state of matter, following trajectories of individual atoms to observe their motion and observing and manipulating
SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Students review the atomic arrangements for each state of matter, following trajectories of individual atoms to observe their motion and observing and manipulating
Phases of the Moon. Phenomenon: The appearance of the moon changes every night. 1. What questions do you have about this phenomenon?
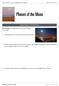 THE EARTH-SUN-MOON SYSTEM Phases of the Moon OBSERVING PHENOMENA Phenomenon: The appearance of the moon changes every night. 1. What questions do you have about this phenomenon? 2. Sketch a simple model
THE EARTH-SUN-MOON SYSTEM Phases of the Moon OBSERVING PHENOMENA Phenomenon: The appearance of the moon changes every night. 1. What questions do you have about this phenomenon? 2. Sketch a simple model
EGN 3310 Practice Final Spring 2017
 EGN 3310 Practice Final Spring 2017 *Try finishing each problem in 15 minutes or less to practice test-like time contraints. The topics on the practice exam are what I feel have been stressed in class,
EGN 3310 Practice Final Spring 2017 *Try finishing each problem in 15 minutes or less to practice test-like time contraints. The topics on the practice exam are what I feel have been stressed in class,
Density and Differentiation. Science Starter and Vocabulary
 Density and Differentiation Science Starter and Vocabulary Science Starter Answer the following and turn in. You have 5 minutes to complete. Use complete sentences to answer the following question. Be
Density and Differentiation Science Starter and Vocabulary Science Starter Answer the following and turn in. You have 5 minutes to complete. Use complete sentences to answer the following question. Be
7.4 Potential Energy Diagrams
 Name: Date: Chemistry ~ Ms. Hart Class: Anions or Cations Remember: 7.4 Potential Energy Diagrams Chemical reactions can react in both the and directions All chemical reactions need Reactions can either
Name: Date: Chemistry ~ Ms. Hart Class: Anions or Cations Remember: 7.4 Potential Energy Diagrams Chemical reactions can react in both the and directions All chemical reactions need Reactions can either
Quantum Theory and Electron Configurations
 Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Quantum Theory and Electron Configurations It s all about color In terms of atomic models, so far: Dalton (1803) = Tiny, solid particle Thomson (1897) = Plum Pudding model Electrons
Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Quantum Theory and Electron Configurations It s all about color In terms of atomic models, so far: Dalton (1803) = Tiny, solid particle Thomson (1897) = Plum Pudding model Electrons
ENERGY IN CHEMISTRY. R. Ashby Duplication by permission only.
 CH 11 TOPIC 28 CHANGING STATES OF MATTER 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) define or describe: ENERGY, POTENTIAL ENERGY, KINETIC ENERGY & KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY 2) define or describe HEAT
CH 11 TOPIC 28 CHANGING STATES OF MATTER 1 You have mastered this topic when you can: 1) define or describe: ENERGY, POTENTIAL ENERGY, KINETIC ENERGY & KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY 2) define or describe HEAT
SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Learning Objectives Possible Student Pre/Misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Students review the atomic arrangements for each state of matter, following trajectories of individual atoms to observe their motion. Students observe and manipulate
SAM Teachers Guide Phase Change Overview Students review the atomic arrangements for each state of matter, following trajectories of individual atoms to observe their motion. Students observe and manipulate
In a forward reaction, the reactants collide to produce products and it goes from left to
 Worksheet #1 Approaching Equilibrium Read unit II your textbook. Answer all of the questions. Do not start the questions until you have completed the reading. Be prepared to discuss your answers next period.
Worksheet #1 Approaching Equilibrium Read unit II your textbook. Answer all of the questions. Do not start the questions until you have completed the reading. Be prepared to discuss your answers next period.
Simulation: Density FOR THE TEACHER
 Simulation: Density FOR THE TEACHER Summary In this simulation, students will investigate the effect of changing variables on both the volume and the density of a solid, a liquid and a gas sample. Students
Simulation: Density FOR THE TEACHER Summary In this simulation, students will investigate the effect of changing variables on both the volume and the density of a solid, a liquid and a gas sample. Students
WEEK 1: 9 JAN THRU 15 JAN; LECTURES 1-4
 Learning objectives Basics: No recitation problems. Handled in ALEKs and week one homework problems but will be part of quiz. Measurement o Metric units, Unit Conversion within metric o Significant figures,
Learning objectives Basics: No recitation problems. Handled in ALEKs and week one homework problems but will be part of quiz. Measurement o Metric units, Unit Conversion within metric o Significant figures,
DO NOW. Choose one of the following and explain how that type of isolation leads to a new species: Geographic isolation. Behavioral isolation
 DO NOW Choose one of the following and explain how that type of isolation leads to a new species: Geographic isolation Behavioral isolation Temporal isolation Agenda Do Now Review Patterns for macroevolution
DO NOW Choose one of the following and explain how that type of isolation leads to a new species: Geographic isolation Behavioral isolation Temporal isolation Agenda Do Now Review Patterns for macroevolution
Carnation Experiment Day 1
 Carnation Experiment Day 1 Foss CA Science Standards: Life Sciences 2 Different types of plants and animals inhabit the earth. As a basis for understanding this concept: o C Students know how to identify
Carnation Experiment Day 1 Foss CA Science Standards: Life Sciences 2 Different types of plants and animals inhabit the earth. As a basis for understanding this concept: o C Students know how to identify
Pre-test Periodic Table of Elements (Socrative)
 Teacher(s): Littles Grade/Subject: 8 th /Physical Science Week of: Dec 7 - Dec 11, 2015 Unit : Atoms and the Periodic Table Dates: Nov 30 Dec 18, 2016 Florida Standard(s): Benchmarks, descriptions, DOK
Teacher(s): Littles Grade/Subject: 8 th /Physical Science Week of: Dec 7 - Dec 11, 2015 Unit : Atoms and the Periodic Table Dates: Nov 30 Dec 18, 2016 Florida Standard(s): Benchmarks, descriptions, DOK
Molecules and Matter. Grade Level: 4 6
 Molecules and Matter Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 4 Partner Project page 5 Crossword Puzzle page 6 Answer Key page 7 Classroom Procedure 1. Without introduction,
Molecules and Matter Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 4 Partner Project page 5 Crossword Puzzle page 6 Answer Key page 7 Classroom Procedure 1. Without introduction,
6 th Grade Earth-Space Science (Lesson Plans Subject to Change Based on Rate of Learning) Week of October 6-10, 2014
 6 th Grade Earth-Space Science (Lesson Plans Subject to Change Based on Rate of Learning) Week of October 6-10, 2014 6 th Grade Science Topic, Assignments, Agenda, Board Configurations Homeroom: Skill
6 th Grade Earth-Space Science (Lesson Plans Subject to Change Based on Rate of Learning) Week of October 6-10, 2014 6 th Grade Science Topic, Assignments, Agenda, Board Configurations Homeroom: Skill
Chemistry #3 Notebook States of Matter
 Name Hour Test Date Group # Chemistry #3 Notebook States of Matter LEARNING TARGETS I CAN model the motion and arrangement of particles in typical solids, liquids and gasses. I CAN describe how the motion
Name Hour Test Date Group # Chemistry #3 Notebook States of Matter LEARNING TARGETS I CAN model the motion and arrangement of particles in typical solids, liquids and gasses. I CAN describe how the motion
Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 1. Chemistry A States of Matter Packet
 Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 1 Chemistry A States of Matter Packet Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 2 Worksheet #1: States of Matter In this packet we will
Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 1 Chemistry A States of Matter Packet Chemistry A: States of Matter Packet Name: Hour: Page 2 Worksheet #1: States of Matter In this packet we will
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Day 19. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Spectroscopy
 Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Day 19. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Spectroscopy Topics: 1. The visible spectrum and the d-orbitals 3. Octahedral fields 2. Term symbols and the method of microstates
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Day 19. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Spectroscopy Topics: 1. The visible spectrum and the d-orbitals 3. Octahedral fields 2. Term symbols and the method of microstates
Content Standard 1: Motion: The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position. National Science Standard
 1: Motion: The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position. s 1.a) Position is defined relative to some choice of standard reference point and a set of reference directions. Identifying
1: Motion: The velocity of an object is the rate of change of its position. s 1.a) Position is defined relative to some choice of standard reference point and a set of reference directions. Identifying
Thermal Energy and Temperature Lab. Experiment Question: How can the difference between thermal energy and temperature be experimentally observed?
 Thermal Energy and Temperature Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Grade / 20 Experiment Question: How can the difference between thermal energy and temperature be experimentally observed? Hypothesis Starters: 1.
Thermal Energy and Temperature Lab Name 7 th Grade PSI Grade / 20 Experiment Question: How can the difference between thermal energy and temperature be experimentally observed? Hypothesis Starters: 1.
Assessment Plan Pre-Assessment: Survey to gage what information students already know, what skills we need to build on, and which concepts when need
 Assessment Plan Pre-Assessment: Survey to gage what information students already know, what skills we need to build on, and which concepts when need to spend the most time on. (One the following page)
Assessment Plan Pre-Assessment: Survey to gage what information students already know, what skills we need to build on, and which concepts when need to spend the most time on. (One the following page)
Name: Unit 3 Guide-Electrons In Atoms
 Name: Unit 3 Guide-Electrons In Atoms Importance of Electrons Draw a complete Bohr model of the atom. Write an element s electron configuration. Know how the symbols used in ECs relate to electron properties
Name: Unit 3 Guide-Electrons In Atoms Importance of Electrons Draw a complete Bohr model of the atom. Write an element s electron configuration. Know how the symbols used in ECs relate to electron properties
Grade 8: Physical Sciences, Life Sciences Earth Sciences, Investigation and Experimentation. California State Science Content Standards
 Grade 8: Physical Sciences, Life Sciences Earth Sciences, Investigation and Experimentation California State Science Content Standards Covered in: Hands-on science labs, demonstrations, & activities. Investigation
Grade 8: Physical Sciences, Life Sciences Earth Sciences, Investigation and Experimentation California State Science Content Standards Covered in: Hands-on science labs, demonstrations, & activities. Investigation
Electrical Circuits Question Paper 1
 Electrical Circuits Question Paper 1 Level IGCSE Subject Physics Exam Board CIE Topic Electricity and Magnetism Sub-Topic Electrical Circuits Paper Type Alternative to Practical Booklet Question Paper
Electrical Circuits Question Paper 1 Level IGCSE Subject Physics Exam Board CIE Topic Electricity and Magnetism Sub-Topic Electrical Circuits Paper Type Alternative to Practical Booklet Question Paper
Saturday Science Lesson Plan Fall 2008
 Saturday Science Lesson Plan Fall 2008 LEARNING OBJECTIVES STANDARDS 1.1.1 Observe, describe, draw, and sort objects carefully to learn about them. 1.2.6 Describe and compare objects in terms of number,
Saturday Science Lesson Plan Fall 2008 LEARNING OBJECTIVES STANDARDS 1.1.1 Observe, describe, draw, and sort objects carefully to learn about them. 1.2.6 Describe and compare objects in terms of number,
CHEM 116 EXAM #2 PRACTICE
 Circle the correct answers (2 points each) CHEM 116 EXAM #2 PRACTICE 1. If the half-life of a reaction depends on the concentration of the reactant, then the reaction cannot be order. a. second b. zero
Circle the correct answers (2 points each) CHEM 116 EXAM #2 PRACTICE 1. If the half-life of a reaction depends on the concentration of the reactant, then the reaction cannot be order. a. second b. zero
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Learning Objectives Possible Student Pre/Misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
Math 1132 Practice Exam 1 Spring 2016
 University of Connecticut Department of Mathematics Math 32 Practice Exam Spring 206 Name: Instructor Name: TA Name: Section: Discussion Section: Read This First! Please read each question carefully. Show
University of Connecticut Department of Mathematics Math 32 Practice Exam Spring 206 Name: Instructor Name: TA Name: Section: Discussion Section: Read This First! Please read each question carefully. Show
2.1 The Nature of Matter
 2.1 The Nature of Matter Lesson Objectives Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. Explain how compounds
2.1 The Nature of Matter Lesson Objectives Identify the three subatomic particles found in atoms. Explain how all of the isotopes of an element are similar and how they are different. Explain how compounds
Unit 2 review for finals
 Unit 2 review for finals These are the topics you should know and be able to answer questions about: 1. Heating/cooling curve (phase change diagram) a. Draw a heating curve showing a solid melting to a
Unit 2 review for finals These are the topics you should know and be able to answer questions about: 1. Heating/cooling curve (phase change diagram) a. Draw a heating curve showing a solid melting to a
Mass, Volume, & Density
 Mass, Volume, & Density Short Informational Videos Mass Volume & Density Buoyancy Mass Measurement of the amount of matter (or stuff) in an object Measured in grams (g) There are 3 states of matter: Solid
Mass, Volume, & Density Short Informational Videos Mass Volume & Density Buoyancy Mass Measurement of the amount of matter (or stuff) in an object Measured in grams (g) There are 3 states of matter: Solid
Atoms. Grade Level: 4 6. Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Activity Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9
 Atoms Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Activity Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Display the different items collected
Atoms Grade Level: 4 6 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Activity Pages pages 6 7 Homework Page page 8 Answer Key page 9 Classroom Procedure: 1. Display the different items collected
CHEMISTRY 112A FALL 2016 EXAM 2 OCTOBER 20, 2016 NAME- WRITE BIG STUDENT ID: SECTION AND/OR GSI IF YOU ARE IN THE LABORATORY COURSE: Points (Maximum)
 CEMISTRY 112A FALL 2016 EXAM 2 CTBER 20, 2016 NAME- WRITE BIG STUDENT ID: SECTIN AND/R GSI IF YU ARE IN TE LABRATRY CURSE: You will have 75 minutes in which to work. BE NEAT! Non-legible structure drawings
CEMISTRY 112A FALL 2016 EXAM 2 CTBER 20, 2016 NAME- WRITE BIG STUDENT ID: SECTIN AND/R GSI IF YU ARE IN TE LABRATRY CURSE: You will have 75 minutes in which to work. BE NEAT! Non-legible structure drawings
LO: What are the Inferred Properties of the Earth s Interior? Do Now: Based on what you remember, record the layers of the earth in your notes.
 LO: What are the Inferred Properties of the Earth s Interior? Do Now: Based on what you remember, record the layers of the earth in your notes. Brain Pop p Watch the Brain Pop video at copy down 5 facts
LO: What are the Inferred Properties of the Earth s Interior? Do Now: Based on what you remember, record the layers of the earth in your notes. Brain Pop p Watch the Brain Pop video at copy down 5 facts
Wheels Radius / Distance Traveled
 Mechanics Teacher Note to the teacher On these pages, students will learn about the relationships between wheel radius, diameter, circumference, revolutions and distance. Students will use formulas relating
Mechanics Teacher Note to the teacher On these pages, students will learn about the relationships between wheel radius, diameter, circumference, revolutions and distance. Students will use formulas relating
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS)
 The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) CHAPTER 3, LESSON 1: WHAT IS DENSITY? MS-PS1-1. Develop models to describe the atomic composition of simple molecules and extended structures. DISCIPLINARY
The Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) CHAPTER 3, LESSON 1: WHAT IS DENSITY? MS-PS1-1. Develop models to describe the atomic composition of simple molecules and extended structures. DISCIPLINARY
Science Is A Verb! Part 7. Let s do it! ISBN
 Let s do it! Science Is A Verb! Part 7 ISBN 978-1-847003-60-7 Contents INTRODUCTION Lab Title Where are we positioned? Students know position is defined in relation to some choice of a standard reference
Let s do it! Science Is A Verb! Part 7 ISBN 978-1-847003-60-7 Contents INTRODUCTION Lab Title Where are we positioned? Students know position is defined in relation to some choice of a standard reference
Modeling Probability: Building Spinners
 .SP. Objective Common Core State Standards Modeling : Building Spinners A spinner is a convenient way to model probabilitythe likelihood that a specified event will occur. can be expressed as a fraction,
.SP. Objective Common Core State Standards Modeling : Building Spinners A spinner is a convenient way to model probabilitythe likelihood that a specified event will occur. can be expressed as a fraction,
TEACHER NOTES: ICE CUBE POSTER
 TEACHER NOTES: NATIONAL CURRICULUM LINKS THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF MATTER the properties of the different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) in terms of the particle model, including gas pressure
TEACHER NOTES: NATIONAL CURRICULUM LINKS THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF MATTER the properties of the different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) in terms of the particle model, including gas pressure
Chemical Reactions and Equations
 Name Date Chemical Reactions and Equations What happens to atoms and energy during a chemical reaction? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about chemical reactions Record
Name Date Chemical Reactions and Equations What happens to atoms and energy during a chemical reaction? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about chemical reactions Record
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Learning Objectives Possible Student Pre/Misconceptions
 SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
SAM Teachers Guide Newton s Laws at the Atomic Scale Overview Students explore how Newton s three laws apply to the world of atoms and molecules. Observations start with the originally contradictory observation
Pre and Post-Visit Activities. Water, Water Everywhere
 Pre and Post-Visit Activities Water, Water Everywhere Table of Contents: Important Information: 2 Vocabulary: 3 Pre-Visit Activities: 4 Post-Visit Activities: 5 Vocabulary Word Search: 6 Journey of Water
Pre and Post-Visit Activities Water, Water Everywhere Table of Contents: Important Information: 2 Vocabulary: 3 Pre-Visit Activities: 4 Post-Visit Activities: 5 Vocabulary Word Search: 6 Journey of Water
3) x -7 4) 3 < x. When multiplying or dividing by a NEGATIVE number, we SWITCH the inequality sign!
 Name: Date: / / WARM UP 1) What is the difference between an inequality and an equation.? QUIZ DAY! 2) One must be at least 35 years old in order to be president of the United States. If x represents age,
Name: Date: / / WARM UP 1) What is the difference between an inequality and an equation.? QUIZ DAY! 2) One must be at least 35 years old in order to be president of the United States. If x represents age,
Why Don t We See Stars in the Daytime?
 Why Don t We See Stars in the Daytime? Photo Credit: ESA Hubble NASA At night, we see many stars in the sky. Those stars are made of burning gases. They are hot, and they shine. But stars are in the sky
Why Don t We See Stars in the Daytime? Photo Credit: ESA Hubble NASA At night, we see many stars in the sky. Those stars are made of burning gases. They are hot, and they shine. But stars are in the sky
Lesson Plan Chapter 21 Atomic
 Atomic Physics Chapter Opener Tapping Prior Knowledge, TE Review previously learned concepts and check for preconceptions about the chapter content. Visual Concepts CD-ROM This CD-ROM consists of multimedia
Atomic Physics Chapter Opener Tapping Prior Knowledge, TE Review previously learned concepts and check for preconceptions about the chapter content. Visual Concepts CD-ROM This CD-ROM consists of multimedia
Applying Understanding Hinge Point Question Exemplars What A Good One Looks Like Example 1 Secondary Science
 This is a good hinge point question as there are multiple correct answers. Applying Understanding Hinge Point Question Exemplars What A Good One Looks Like Example 1 Secondary Science Which of these is/are
This is a good hinge point question as there are multiple correct answers. Applying Understanding Hinge Point Question Exemplars What A Good One Looks Like Example 1 Secondary Science Which of these is/are
Chemical Reactions Chapter 2 L book pages L44 - L73. examples?
 Name: Period: Chemical Reactions Chapter 2 L book pages L44 - L73 Vocabulary Word What is this? (definition) What are some examples? What does it look like? (draw a picture or diagram) Physical property
Name: Period: Chemical Reactions Chapter 2 L book pages L44 - L73 Vocabulary Word What is this? (definition) What are some examples? What does it look like? (draw a picture or diagram) Physical property
SILENTLY 1.Begin your Do Now 2.Write down tonight s homework: Unit 9 Quiz Corrections. AIM: How do we answer OR questions?
 Welcome to Chemistry Regents Prep! SILENTLY 1.Begin your Do Now 2.Write down tonight s homework: Unit 9 Quiz Corrections Binder Chemistry Reference Table HW for checking: Thanksgiving Break Quiz Corrections
Welcome to Chemistry Regents Prep! SILENTLY 1.Begin your Do Now 2.Write down tonight s homework: Unit 9 Quiz Corrections Binder Chemistry Reference Table HW for checking: Thanksgiving Break Quiz Corrections
Applications in Forensic Science. T. Trimpe
 Applications in Forensic Science T. Trimpe 2006 http://sciencespot.net/ What is chromatography? From Wikipedia... Chromatography (from Greek word for chromos for colour) is the collective term for a family
Applications in Forensic Science T. Trimpe 2006 http://sciencespot.net/ What is chromatography? From Wikipedia... Chromatography (from Greek word for chromos for colour) is the collective term for a family
Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes
 Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes As a piece of ice is exposed to a warmer environment, it begins to absorb heat. The heat causes the solid molecules to vibrate faster. Eventually, the ice
Name Chemistry / / Understanding Phase Changes As a piece of ice is exposed to a warmer environment, it begins to absorb heat. The heat causes the solid molecules to vibrate faster. Eventually, the ice
Objective: Recognize halves within a circular clock face and tell time to the half hour.
 Lesson 13 1 5 Lesson 13 Objective: Recognize halves within a circular clock face and tell time to the half Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief
Lesson 13 1 5 Lesson 13 Objective: Recognize halves within a circular clock face and tell time to the half Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief
Objective: Construct a paper clock by partitioning a circle and tell time to the hour. (10 minutes)
 Lesson 10 1 Lesson 10 Objective: Construct a paper clock by partitioning a circle and tell time to the Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief
Lesson 10 1 Lesson 10 Objective: Construct a paper clock by partitioning a circle and tell time to the Suggested Lesson Structure Fluency Practice Application Problem Concept Development Student Debrief
University of Houston-Downtown
 University of Houston-Downtown Course Prefix, Number, and Title: CHEM 1307: General Chemistry * Credits/Lecture/Lab Hours: 3/0/0 Foundational Component Area: Life and Physical Sciences Prerequisites: Credit
University of Houston-Downtown Course Prefix, Number, and Title: CHEM 1307: General Chemistry * Credits/Lecture/Lab Hours: 3/0/0 Foundational Component Area: Life and Physical Sciences Prerequisites: Credit
Students identify the International Space Station (ISS) and different types of rockets as objects in the sky built by humans.
 Activity 2 Destination: Station Objective Students identify the International Space Station (ISS) and different types of rockets as objects in the sky built by humans. Standards Science, Mathematics, Technology,
Activity 2 Destination: Station Objective Students identify the International Space Station (ISS) and different types of rockets as objects in the sky built by humans. Standards Science, Mathematics, Technology,
Chem I - Wed, 9/16/15
 Chem I - Wed, 9/16/15 Do Now Complete the back of worksheet 4.5 Homework Pennium Lab if not Finished E- Config POGIL Agenda Return Papers Wks 4.5 Pennium Lab Electron Config Chapter 5 Quantum Theory and
Chem I - Wed, 9/16/15 Do Now Complete the back of worksheet 4.5 Homework Pennium Lab if not Finished E- Config POGIL Agenda Return Papers Wks 4.5 Pennium Lab Electron Config Chapter 5 Quantum Theory and
CHEM 341: Organic Chemistry I at North Dakota State University Midterm Exam 02 - Fri, Mar 9, 2012!! Name:!
 CHEM 341: rganic Chemistry I at Nth Dakota State University Midterm Exam 02 - Fri, Mar 9, 2012!! Name:! You may use the blank pages of your test f scratch paper. Please read through each question carefully
CHEM 341: rganic Chemistry I at Nth Dakota State University Midterm Exam 02 - Fri, Mar 9, 2012!! Name:! You may use the blank pages of your test f scratch paper. Please read through each question carefully
1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2
 1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2 2.) A chemist has discovered what she thinks is a new molecule. In order for it to be a molecule,
1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2 2.) A chemist has discovered what she thinks is a new molecule. In order for it to be a molecule,
8 th Grade Science. Directed Reading Packet. Chemistry. Name: Teacher: Period:
 8 th Grade Science Directed Reading Packet Chemistry Name: Teacher: Period: Chapter 1, Section 1: Inside the Atom Introduction 1. Atoms are the particles of an element that still have the element s. 2.
8 th Grade Science Directed Reading Packet Chemistry Name: Teacher: Period: Chapter 1, Section 1: Inside the Atom Introduction 1. Atoms are the particles of an element that still have the element s. 2.
Separating Mixtures - lab diagrams Slip Quiz 1 (New) Classification of Matter (Pogil=notes) Homework Slip Quiz 2
 20 Sept 2017 Agenda Separating Mixtures - lab diagrams Slip Quiz 1 (New) Classification of Matter (Pogil=notes) Homework Slip Quiz 2 Separating Mixtures: What could we do to separate the mixture of materials
20 Sept 2017 Agenda Separating Mixtures - lab diagrams Slip Quiz 1 (New) Classification of Matter (Pogil=notes) Homework Slip Quiz 2 Separating Mixtures: What could we do to separate the mixture of materials
HOMEWORK IS WHERE THE REAL LEARNING HAPPENS!
 HOMEWORK IS WHERE THE REAL LEARNING HAPPENS! ALEKS does not do it all! All homework problems are in the Chem 110 Student Packet GOAL: learn HOW to solve problems Finish these before recitation each week???
HOMEWORK IS WHERE THE REAL LEARNING HAPPENS! ALEKS does not do it all! All homework problems are in the Chem 110 Student Packet GOAL: learn HOW to solve problems Finish these before recitation each week???
Every positive two digit number is greater than the product of it s digits. Asks class is it true? can you find a counter-example etc.
 Aim Activity Reasoning and Proof Introducing Proof Proof by Deduction Understand and use the structure of mathematical proof, proceeding from given assumptions through a series of logical steps to a conclusion;
Aim Activity Reasoning and Proof Introducing Proof Proof by Deduction Understand and use the structure of mathematical proof, proceeding from given assumptions through a series of logical steps to a conclusion;
2 4 Chemical Reactions
 SECTION 2 4 Chemical Reactions ^^^^^ ^^^ ^^ tff'\f f**^*.tffn*f i***i i i «i f.' KEY CONCEPT Life depends on chemical reactions. Student text pages 50-53 Bonds break and form during chemical reactions.
SECTION 2 4 Chemical Reactions ^^^^^ ^^^ ^^ tff'\f f**^*.tffn*f i***i i i «i f.' KEY CONCEPT Life depends on chemical reactions. Student text pages 50-53 Bonds break and form during chemical reactions.
11. Moving Plates 11/28/2016
 11. Moving Plates 11/28/2016 EQOD : What causes the surface of the Earth to Change? Initial Thoughts: In a Level 0 Silence Voice, take 5 minutes to answer the question. If you still have time, update your
11. Moving Plates 11/28/2016 EQOD : What causes the surface of the Earth to Change? Initial Thoughts: In a Level 0 Silence Voice, take 5 minutes to answer the question. If you still have time, update your
As you enter... (Write down the learning objective, the question and your answer.) What do you think it means for a reaction to occur spontaneously?
 Monday, March 23rd Learning objective 5.13: The student is able to predict whether or not a physical or chemical process is thermodynamically favored by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively)
Monday, March 23rd Learning objective 5.13: The student is able to predict whether or not a physical or chemical process is thermodynamically favored by determination of (either quantitatively or qualitatively)
FM: WARM-UP. Students gather evidence about the velocity change of objects in a collision. (10 min)
 CH.3 COLLISIONS FM: 3.3.1 WARM-UP Students gather evidence about the velocity change of objects in a collision. (10 min) Both Objects will Change Velocity Only 1 Object will Change Velocity Neither Object
CH.3 COLLISIONS FM: 3.3.1 WARM-UP Students gather evidence about the velocity change of objects in a collision. (10 min) Both Objects will Change Velocity Only 1 Object will Change Velocity Neither Object
Goals: Essential Questions: Properties. Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday. District Pre- Test. What is matter?
 Unit 1 Matter: Physical and Chemical Properties Agenda: What is matter? Wrap up Chemical and Physical Properties Notes White Board Practice Extensive/ Intensive Notes Extensive/Intensive Experiment Planning
Unit 1 Matter: Physical and Chemical Properties Agenda: What is matter? Wrap up Chemical and Physical Properties Notes White Board Practice Extensive/ Intensive Notes Extensive/Intensive Experiment Planning
Name: Block: Date: Student Notes. OBJECTIVE Students will investigate the relationship between temperature and the change of the state of matter.
 Name: Block: Date: LCPS Core Experience Heat Transfer Student Notes OBJECTIVE Students will investigate the relationship between temperature and the change of the state of matter. LINK 1. Particles in
Name: Block: Date: LCPS Core Experience Heat Transfer Student Notes OBJECTIVE Students will investigate the relationship between temperature and the change of the state of matter. LINK 1. Particles in
DJO AP Biology Summer Assignment
 DJO AP Biology Summer Assignment Welcome to AP Biology! Complete the summer assignment and use the key to check your answers. Also read the graphing appendix and complete the graphing assignment. Finally,
DJO AP Biology Summer Assignment Welcome to AP Biology! Complete the summer assignment and use the key to check your answers. Also read the graphing appendix and complete the graphing assignment. Finally,
Student Exploration: Collision Theory
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Collision Theory Vocabulary: activated complex, catalyst, chemical reaction, concentration, enzyme, half-life, molecule, product, reactant, surface area Prior Knowledge
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Collision Theory Vocabulary: activated complex, catalyst, chemical reaction, concentration, enzyme, half-life, molecule, product, reactant, surface area Prior Knowledge
UNIT 12: Forces in Fluids (8 days)
 UNIT 12: Forces in Fluids (8 days) Lesson Plans (Advanced and Regular Physical Science) Date Range: 12/1/14 12/9/14 Topic, Assignments, Agenda, Board Configurations Standard/ Homeroom: Announcements UNIT:
UNIT 12: Forces in Fluids (8 days) Lesson Plans (Advanced and Regular Physical Science) Date Range: 12/1/14 12/9/14 Topic, Assignments, Agenda, Board Configurations Standard/ Homeroom: Announcements UNIT:
Red Cabbage Lab Acids And Bases Answers
 Red Cabbage Lab Acids Answers Free PDF ebook Download: Red Cabbage Lab Answers Download or Read Online ebook red cabbage lab acids and bases answers in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Red
Red Cabbage Lab Acids Answers Free PDF ebook Download: Red Cabbage Lab Answers Download or Read Online ebook red cabbage lab acids and bases answers in PDF Format From The Best User Guide Database Red
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 2011 Day 19. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Spectroscopy
 Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 011 Day 19. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Spectroscopy Name(s): lement: Topics: 1. The visible spectrum and the d-orbitals 3. Octahedral fields. Term symbols
Inorganic Chemistry with Doc M. Fall Semester, 011 Day 19. Transition Metals Complexes IV: Spectroscopy Name(s): lement: Topics: 1. The visible spectrum and the d-orbitals 3. Octahedral fields. Term symbols
6E Lesson Plan Template
 6E Lesson Plan Template Author: Tiffany Chen Date: Day 2 October 17 th 2013 Topic: Earths Structure Title: Earth Model Grade Level: 6 th grade Lesson Summary: Students will learn about the earth s layers
6E Lesson Plan Template Author: Tiffany Chen Date: Day 2 October 17 th 2013 Topic: Earths Structure Title: Earth Model Grade Level: 6 th grade Lesson Summary: Students will learn about the earth s layers
Q1. (a) Define the term activation energy for a chemical reaction. (2)
 Q1. (a) Define the term activation energy for a chemical reaction. (b) Draw, with labelled axes, a curve to represent the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies in a gas. Label this curve
Q1. (a) Define the term activation energy for a chemical reaction. (b) Draw, with labelled axes, a curve to represent the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution of molecular energies in a gas. Label this curve
Practice Packet Unit 7: Heat
 Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 7: Heat Review (Things you need to know in order to understand the new stuff ) Particle Diagrams Draw a particle diagram of a compound of CaCl2, using
Regents Chemistry: Mr. Palermo Practice Packet Unit 7: Heat Review (Things you need to know in order to understand the new stuff ) Particle Diagrams Draw a particle diagram of a compound of CaCl2, using
Lesson Plan: Star Gazing By: Darby Feldwinn
 Lesson Plan: Star Gazing By: Darby Feldwinn Target Grade: 5 th Teacher Prep Time: 10 (1 hour if you need to print and laminate star cards.) Lesson Time: 3 hours (we recommend doing this lesson over three
Lesson Plan: Star Gazing By: Darby Feldwinn Target Grade: 5 th Teacher Prep Time: 10 (1 hour if you need to print and laminate star cards.) Lesson Time: 3 hours (we recommend doing this lesson over three
Life on other planets Life in space
 Life on other planets Life in space V 59 time 80 minutes learning outcomes To: discover that different celestial bodies have different conditions regarding temperature, gravity, atmosphere, and oxygen
Life on other planets Life in space V 59 time 80 minutes learning outcomes To: discover that different celestial bodies have different conditions regarding temperature, gravity, atmosphere, and oxygen
Crystal Clear Observations
 Crystal Clear Observations You may think of crystals as pretty rocks used in jewelry or found among other rocks on an outdoor exploration, but crystals are around us all the time and in lots of things
Crystal Clear Observations You may think of crystals as pretty rocks used in jewelry or found among other rocks on an outdoor exploration, but crystals are around us all the time and in lots of things
Name Energy Test period Date
 Name Energy Test period Date 1. The temperature 30. K expressed in degrees Celsius is 1) 243ºC 2) 243ºC 3) 303ºC 4) 303ºC 2. The potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction is shown below. 4. A sample
Name Energy Test period Date 1. The temperature 30. K expressed in degrees Celsius is 1) 243ºC 2) 243ºC 3) 303ºC 4) 303ºC 2. The potential energy diagram for a chemical reaction is shown below. 4. A sample
Solids, liquids and gases
 Solids, liquids and gases Duration 60 minutes Lesson overview Students share what they know about the three states of matter solid, liquid and gas and consider some of their scientific properties. They
Solids, liquids and gases Duration 60 minutes Lesson overview Students share what they know about the three states of matter solid, liquid and gas and consider some of their scientific properties. They
Gravity and Orbits Activity Page 1. Name: Grade: Gravity and Orbits. Pre-lab. 1. In the picture below, draw how you think Earth moves.
 Name: Grade: Gravity and Orbits Pre-lab 1. In the picture below, draw how you think Earth moves. 2. Draw a picture using arrows to show what you think the forces might be on the Earth and the Sun. You
Name: Grade: Gravity and Orbits Pre-lab 1. In the picture below, draw how you think Earth moves. 2. Draw a picture using arrows to show what you think the forces might be on the Earth and the Sun. You
What Is Air Temperature?
 2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
2.2 Read What Is Air Temperature? In Learning Set 1, you used a thermometer to measure air temperature. But what exactly was the thermometer measuring? What is different about cold air and warm air that
Gravity and Orbits. 1. Choose the picture you think shows the gravity forces on the Earth and the Sun.
 Name: Grade: Gravity and Orbits Pre-lab 1. Choose the picture you think shows the gravity forces on the Earth and the Sun. (a longer arrow to represents a big force, and a shorter arrow represent a smaller
Name: Grade: Gravity and Orbits Pre-lab 1. Choose the picture you think shows the gravity forces on the Earth and the Sun. (a longer arrow to represents a big force, and a shorter arrow represent a smaller
! Name: STUDENT JOURNAL Week 13 Radioactivity & Physical Changes
 ! Name: Period: STUDENT JOURNAL Week 13 Radioactivity & Physical Changes Overarching Goal for the Week: Distinguish between the types of physical changes and the change in particle motion Learning Objectives:
! Name: Period: STUDENT JOURNAL Week 13 Radioactivity & Physical Changes Overarching Goal for the Week: Distinguish between the types of physical changes and the change in particle motion Learning Objectives:
The relationship between these aspects is described by the following equation: E = hν =
 1 Learning Outcomes EXPERIMENT A10: LINE SPECTRUM Upon completion of this lab, the student will be able to: 1) Examine the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom. 2) Calculate the frequency and energy of the
1 Learning Outcomes EXPERIMENT A10: LINE SPECTRUM Upon completion of this lab, the student will be able to: 1) Examine the line spectrum of the hydrogen atom. 2) Calculate the frequency and energy of the
COLLISION THEORY AND REACTION RATES
 COLLISION THEORY AND REACTION RATES WHAT IS COLLISION THEORY All matter is made of atoms and these atoms are in constant motion. (some particles move faster than others) Collision theory applies to gas
COLLISION THEORY AND REACTION RATES WHAT IS COLLISION THEORY All matter is made of atoms and these atoms are in constant motion. (some particles move faster than others) Collision theory applies to gas
Partnerships Implementing Engineering Education Worcester Polytechnic Institute Worcester Public Schools Supported by: National Science Foundation
 Atoms and Molecules: 6.E.1 Modeling Molecules: Atoms & Molecules Grade Level 6 Sessions Seasonality Instructional Mode(s) Team Size WPS Benchmarks MA Frameworks Key Words 1 approximately 70 minutes N/A
Atoms and Molecules: 6.E.1 Modeling Molecules: Atoms & Molecules Grade Level 6 Sessions Seasonality Instructional Mode(s) Team Size WPS Benchmarks MA Frameworks Key Words 1 approximately 70 minutes N/A
