Organo-transition Metal Chemistry
|
|
|
- Marshall Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 1 rgano-transition tal Chemistry 1. Some Basics Chemistry involves intermediates containing transition-metal carbon bonds tal-carbon sigma bond Coordination sp3 C sp2 C C sp C C C ligand sphere L 2 L 1 L 3 M C Ln M C L 5 L 4 Electron Counting: Formal neutral ligand (L): P 3, 3, C, alkyne, Alkene Formal anionic ligand ():, Ar,,, C, C 3 P 3 P Pd P 3 P 3 ML 4 Pd(0) d 10 = 10 e P3 2 e 4 = 8 e 18 e 3 P 3 P Pd ML 2 Pd(0) d 10 = 10 e P3 2 e 2 = 4 e 14 e 3 P 3 P Pd Ar Ar ML 2 2 Pd() d 8 = 8 e Ar, 2 e, 2 e = 4 e P3 2 e 2 = 4 e 16 e
2 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 2 Ligand Exchange: Ligand Association and Ligand Dissociation Ligand association L' ML n :L' Ligand dissociation 3 P P 3 Pd 3 P P 3 L-dissociation - P 3 3 P P 3 Pd P 3 L-dissociation - P 3 P 3 Pd P 3 xidative Addition/eductive Elimination Vacant site usually polar bond M(n)L n Y xidative Addition. eductive Elimination Y M(n2)L n P 0 Pd 0P 3 P 3 P 3 3 P Pd P 3 Pd 2 P 3 xidative Addition. eductive Elimination P Pd 2 3 P 3 Pd(P 3 ) 2 Ligand effect: Electron donating ligands facilitate oxidative addition (e.g. P 3,, ); electron withdrawing ligands facilitate reductive elimination (e.g., C, C, olefins). Migratory nsertion/de-insertion: Migration of one ligand to a neighboring unsaturated ligand (C, C, alkyne, alkene), generating a vacant site. Usually reversible. Vacant site is cis to the newly formed ligand. C nsertion De-insertion 2 C C L M n 2
3 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 3 Carbometallation/β-elimination Carbometallation β-elimination Dehydropalladation L n M vacant site Φ = 0 Pd L n Pd β-ydride Elimination L n Pd PdL n Carbometallation: nsertion into alkene/alkyne group Migrating aptitude of β-eliminaton : >> Alkyl, Ar > C> β-ydride Elimination : Very common pathway for the decomposition of alkylmetal complexes 2. eck eaction C 2 10 mol % Pd(Ac) 2 P 3, K 2 C 3 C 3 C 100 o C, 90 % C 2 cat. Pd Base, P 3 1: Aryl, Vinyl, Benzylic, Allylic, Acyl : 2 > > ~S2CF3 >> Cl (relative rate of oxidative addition) Pd: Pd(0) or Pd(). Active Pd(0) species can be instantaneously made from Pd() in reaction media Base : Scavenger of P 3 : Prevents Pd(0) from precipitation to make palladium mirror Solvent: ften coordinating solvents such as MP, DMA, DMF, acetonitrile but sometimes toluene can be used Temperature: room temp. to 140 o C
4 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 4 Catalytic cycle: Pd(P 3 ) 4 eductive Elim ination Base - Pd(0)(P 3 ) 2-2 P 3 1 xidative Addition 1 Pd()(P 3 ) Pd ()(P 3 ) 2 Pd ()(P 3 ) 2 Pd ()(P 3 ) Syn-β--Elimination 1 Syn- Carbopalldation Pd(P 3 ) 2 1 Pd(P 3 ) internal rotation ntramolecular eck Cascade Pd(0) PdL n' PdL n PdL n Si 3 Si 3 Si 3 Si 3 xidative addition ligand association Carbopalladation β--elimination PdL n PdL n Si 3 Si 3 Si 3 ligand association Carbopalladation PdL n Dehydropalladation Beta--elimination Tandem eck eaction ntermolecular eck reaction followed by intramolecular one Syn-Carbopalladation leads to only one geometric isomer
5 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 5 Stable rgano-pd intermediate without syn β- 3 mol % Pd(P 3 ) 4 C eq. Et o C, 12 h 80 % L n Pd L n Pd 2 C Syn-carbopalladation Sequential Tandem eck eaction tbu (: o-t ol) Syn- 10 % carbopalladation tbu P tbu Pd(Ac) 2, Pd Ac 22 % P 3, L n Pd 2.0 eq 60 o C, 60 h. 120 o C C 3 C, DMF nbu 4 (Ac) More eactive Syn- Elimination e tbu a e tbu L n Pd a L n Pd 63 % Stable rgano-pd ntermediates ntermediate organo-palladium species are thermally stable due to the absence of hydrogen β-syn to palladium 1 PdL n 1 PdL n PdL n - Pd L 2 1 PdL n 1 PdL n 1 PdL n 1 PdL n
6 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 6 3. Stille Coupling eaction 10 mol % Pd(P 3 ) 4 3 C Bu 3 Sn C3 100 o C 3 C 1 cat. Pd 2 SnBu SnBu 3 1, 2 : sp2-hybridized carbon : > S2CF3 > >> Cl Ability for transmetalation: alkynyl> alkenyl> benzyl, allyl> alkyl Exceptional functional group tolerance igh cost and toxicity of organotin reagent 4. Suzuki Coupling eaction 10 mol % Pd(Ac) 2 C () 2 B P 3, a 2 C 3 ipr, 2, reflux. 86 % C B C 3 mol % PdCl 2 (dppf) 2.0 eq. K 2 C 3 DMF, TF, 50 o C 81 % C Less expensive, less toxic alternative to Stille coupling Sp3 carbon can be involved in coupling partner elative rates of reductive elimination: aryl-aryl > alkyl -aryl> alkyl-alkyl Somewhat basic conditions needed
7 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 7 Catalytic Cycle of Stille/Suzuki Coupling 1 2 eductive Elimination Pd(0)L n 1 xidative Addition Pd()L n Pd()L n M M 1 Pd()L n 2 2 M Transmetallation Transmetallation step is supposed to be the slowest in the Stille coupling Depending on the leaving group, oxidative addition can be a rate determining step in Suzuki coupling Termination with Carbonylation Pd()L n C stable organo-pd species Pd()L n C ' eck Pd()L n u u Suzuki Stille u 2 Ar 2 3 igher affinity and fast insertion of C ligand to Pd elative migratory insertion rate: alkyne > carbon monoxide (ca. 1 atm) > alkene
8 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 8 1 SnBu C Pd catalyst 1 2 SnBu 3 2 = Aryl-, Alkyl-, Allylhalogenide und -triflate SnBu 3 (P 3 ) 2 PdCl 2 11 bar C 70% J. K. Stille J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, Sn TPS tbu 2.5 mol % Pd 2 (dba) 3 22% 3 As C (12 bar) LiCl, MP 70 o C 80% TPS tbu L. E. verman J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993,115,3966 Examples of the Stille reaction: SnBu Bu3 3 3 Sn 20 mol% Pd(C) 2 Cl 2 i-pr 2 Et 25 C DMF/TF 48 hours M e M e K. C. icolaou, Chem. Eur. J. 1995, 1, SnBu 3 2 Cl 2 Pd catalyst 2 1 Cl SnBu 3 1 =Alkyl,Alkenyl,Aryl,Alkynyl, 2 =Alkyl,Alkenyl,Aryl,Alkynyl The coupling of acid chlorides proceeds without Pd catalyst in many cases. Boc Sn 3 2 CCl Pd 2 dba 3 CCl 3 K 2 C 3 i-pr 2 Et Boc 2
9 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 9 Stille reactions with triflates Lii-Pr 2 2. Tf 2 Tf 1 2 Tf = CF 3 S 2 1. Lii-Pr 2 (< 1 equivalent) 2. Tf 2 Tf 3 Sn Si 3 Pd(P 3 ) 4 LiCl TF, Δ Si 3 W. D. Wulff Tetrahedron Lett. 1988, 29, Preparation of stannanes from triflates: Tf Sn 3 3 Sn Sn 3 Pd(P 3 ) 4 LiCl, Li 2 C 3 oder ( 3 Sn) 2 Cu(C)Li 2 W. D. Wulff J. rg. Chem. 1986, 51, 277. eterocycles: Bu 3 Sn Pd(P 3 ) 4 37% T.. Kelly J. rg. Chem. 1997, 62, 2774.
10 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 10 Palladium on charcoal can be used as a source of the catalyst: SnBu mol % Pd (10 mol % Pd/C) 10 mol % Cu 20 mol % As 3 12 hrs. (88%) 3 C 95 % trans SnBu mol % Pd (10 mol % Pd/C) 10 mol % Cu 20 mol % As 3 16 hrs. 3 C (82 %) 100 % trans Liebeskind, L.,Tetrahedron Letters, 1995, 36, Examples of the Suzuki reaction: 1 B() 2 Pd(Ac) 2 (2 mol%) K 2 C 3, 2, 25 C, 2h Bu % =, C S 1 B() 2 Pd(Ac) 2 (2 mol%) K 2 C 3, 2, 25 C, 2h Bu % =, C The addition of tetrabutylammonium bromide facilitates the reaction. Bu B 2 3 mol% Pd(P 3 ) 4 2MaEtinEt C 6 6, Δ Bu B 2 Yield E:Z B : 6 B(c-C 6 11 ) : 17 B(i-Pr) 2 98 >97 : 3
11 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 11 Yields with alkyl boron compounds are often low because of protodeboronation. Boronates are better reagents. ate of protodeboronation: 9-BB > B(c-C 6 11 ) 2 > B() 2 Coupling of primary alkylboron compounds: TBS B C 2 PdCl 2 (dppf) 3 As Cs 2 C 3 DMF/TF/ 2 25 C 70-80% TBS C 2 Johnson, C..; aun, M. P. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, Diazonium salts can be coupled in Suzuki reactions: 2 () 2 B Pd(Ac) 2 1,4-dioxane 22 C 79% J.-P. Genêt Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr. 1996, 133, Although not very reactive, chloroarenes can be used in the Suzuki reaction: Cl () 2 B 5 mol% PdCl 2 ( ) 2 CsF, MP 100 C 98% W. Shen Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38,5575.
12 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg Pd-catalyzed allylic alkylation (Tsuji Trost reaction) Ac 10 mol % Pd(P 3 ) 4, P 3 ac(c 2 Et) 2 TF, reflux C 2 Et C 2 Et General reactivty of substrates: alide, Carbonate > Acetate > epoxide (?) ucleophile: C-nucleophile- malonate, active methylene nucleophile; heteroatom (,, S, P, Si)-based nucleophile; hydride (B-, Sn-, Al- and formates); organometallics (Zn-, Zr-, Sn- etc.). Catalytic cycle: u Ligand dissociation Pd(0) Ligand association L n Pd u u L n Pd u-attack Second invesrion Pd L L - Pd L xidative Addition S 2'-like (invesrion) Active cationic form of η3- allyl Pd complex intermediate is favoured by the bidentate phosphine ligand. Stereoselectivity: etention of the carbon atom configuration by double inversion. u u PdL n PdL n PdL n
13 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 13 Allylic alkylation with ketone enolates Enolates can be used as the nucleophile in allylic alkylations, which broadens the scope of the reaction even further. n the example on the left, the enantioselectivity of the reaction (the direction of attack of the nucleophile to the prochiral allyl cation) is controlled by the chiral C2 symmetric ligand ()-BAP. The example on the right uses the same chemistry, but a different C2 symmetric chiral ligand to control the enantioselectivity of the reaction. Literatur: Angew. Chem. nt. Ed. 2006, 45, 6952.
14 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg Palladium-catalyzed Amination Cl 1 2 Pd(Ac) 2 (1-2 mol%) Ligand (2-4 mol%) atbu (1.4 equiv) Toluol, aumtemp h 1 1 P(tBu) 2 Ligand = Bn 98% 94% 90% 99% ucleophilic aromatic substitution. Pd-catalysis allows reaction of non-activated arenes. Catalytic cycle:
15 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 15 Examples: ickel-catalyzed aromatic amination Copper-catalyzed aromatic amination Diarylethers are accessible by a similar reaction using phenols as nucleophile.
16 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 16 A variation is the coupling of aryl boronic acids with amines or phenols. The reaction is called the Chan-Lam coupling. chanism: 7. Palladium-catalyzed Alkyne coupling reactions A. Castro-Stevens Kupplung 1 Cu B. The Sonogashira-agihara Kupplung 1 1 =,,Cl PdCl 2 (P 3 ) 2 (2 mol%) Cu oder CuAc(1 mol%) Amin = Et 2, Et 3 oder 25 C
17 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 17 The amine is necessary to deprotonate the alkyne. Best coupling results are obtained in TF. The mechanism is similar to the Suzuki or Stille coupling, but an organocopper species is transmetallated. Cu 1 1 Cu The halide, substituents in both coupling components, the catalyst and the amine influence the rate of the reaction. TF or amines are usually used as solvents. = > Ar > > Ar Cl 2 Pd(P 3 ) 2 Cl 2 (cat) 2 1 Cu (cat) 1 Et 3, TF 1 2 eaction conditions Yield [%] 4-C 4-C 2-C 2 3-C 2 4-C 2 4-C 4-C 4-C 3 Si 3 Si 3 Si 3 Si 3 Si n-bu 25 C / 1h 25 C / 1h 25 C / 16h 25 C / 16h 25 C / 16h 25 C / 16h 25 C / 16h 25 C / 16h C 5 11 C 5 11 C 5 11 Cl [Pd] (5%), Cu (10%), Amin, T C 5 11 [Pd] amine time [h] yield [%] PdCl 2 (C) 2 piperidine PdCl 2 (P 3 ) 2 piperidine Pd(P 3 ) 4 piperidine Pd(P 3 ) 4 n-pr
18 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 18 chanisms: Palladium-copper co-catalysis (left); copper-free (right) Examples: 3Si Si 3 Si i Pr 3 1) Pd(0) / Cu() 2) K 2 C 3, Pr i 3 Si Si i Pr 3 F. Diederich, Angew. Chem. 1993, 105,
19 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 19 Si 3 1) Pd(0) / Cu() 2) K, 28% K.P.C. Vollhart, Angew. Chem. 1986, 25, ndole synthesis: Ligand (10 mol%) All in one: Tandem eck-stille-sonogashira eaction Bn TBS Bu 3 Sn 3mol% Pd(P 3 ) eq. Et o C, 12 h 80 % Bn transmetallation SnBu 3 PdL ' n Bn Bu 3 Sn TBS PdL n ed. Elim. TBS TBS Pd(P 3 ) 4,Cu Bn Bn
20 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg Palladium--heterocyclic carbene (C) ligands for cross coupling reactions Synthetically useful C ligands derived from imidazolium () and 4,5 dihydroimidazolium (S) salts. Aldrichimica Acta, 2006, 39, 97. General description of C generation from various precursors and their complexation with palladium C Cl Precursors typically used in in situ cross-coupling protocols
21 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 21 Active Pd-precatalysts with C ligands Use of C ligands in the Suzuki cross coupling reaction Ligand 13 Use of C ligands in -aryl coupling reactions
22 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg lefin tathesis lefin tathesis: metal-catalyzed exchange of olefins 1 2 M Catalysts: tal-carbene Complex ucleophilic Electrophilic d 0 Schrock-carbene (metal-alkylidene) Fishcer-carbene (etero-atom stabilized) Pre-catalysts with a defined structure have been developed Cl W Cl i-pr F 3 C F Mo 3 C F 3 C CF 3 i-pr Cl u Cl Cl s s u Cl Aldehydes Ketones lefins Esters, amides Aldehydes lefins Ketones Esters, amides lefins Aldehydes Ketones Esters, amides xophilic reactive Cl u Cl Distorted Square planar Cl 2 u Cl 2 u s s Cl 2 u
23 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 23 verview: Modern olefin metathesis catalysts eaction mechanism: Sequence of reversible formal [22] cycloaddition/ cycloreversion processes. pre-catalyst 1 start ML n C ML n
24 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 24 Direction of metathesis reactions: CM (ing-closing metathesis) A B C D n M (ing-opening metathesis) C B A CM (Cross metathesis) A B D MP (ing-opening metathesis polymerization) C B E M A B C n n n n n ( a times) a n E n Ways to push the process in one direction: M n n n polymer Ethylene gas generally decreases CM rate Lower concentration can prevent polymerization and cross metathesis igher temperature usually promotes CM process ( ΔS gain)
25 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 25 Factors influencing the ring closing metathesis: Cl 2 u 31 eq. ' ' Cl 2 u PCy k rel Substrate specific reactivity of catalysts still difficult to predict! = C(C 2 Et) 2 1 A 1 B 2A > 99 % > 99 % > 99 % Cl 2 u 1 A 20 % > 99 % > 99 % 0 % 0 % > 31 % > 99 % 93 % 0 % s s Cl 2 u 1 B 39 % E/Z 1.6: 1 35 % E/Z 2:1 15 % E/Z 1.6: 1 Ar' Mo 2A Examples of CM in synthesis: rcinal A C Fluvirucin Dactylol EM Sugar
26 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 26 S 1 2 Yield (E/Z) 2 1 epothilone A TBS TBS 86 % (1: 2) 65 % (1: 2) Fluvirucin B synthesis Cyclophane synthesis Large scale pharmaceutical synthesis ote: Many functional groups are tolerated.
27 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 27 Double CM reactions: 25 mol % PMB Cl 2 u C 2 Cl 2 45 o C PMB 88 % 20 mol % Cl 2 u PMB C 2 Cl 2 45 o C PMB 77 % Synthesis of macrocycles: Presence of functional group that serves to assemble the reacting sites (not too basic) % Appropriate distance from functional group to olefin (not too close) Low steric congestion near the olefin : 52 % - : C 3 10 % 72 % Cl 2 u Yield of CM product using ing opening and cross metatheses reaction in synthesis:
28 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 28 Examples of cross metathesis reactions: 2.0 eq. cat. A C C 92 % (E/Z >20:1) =AcC 2 (C 2 ) 2 Bz 2.0 eq. cat. A Bz 81 % (E/Z >4:1) =AcC 2 (C 2 ) eq. Si(Et) 3 81 % (E/Z >11:1) cat. B Si(Et) 3 =AcC 2 (C 2 ) 2 s cat. A s Cl 2 u s cat. B s Cl 2 u C 3 C 3 Diyne tathesis Catalyst (Schrock alkylidyne complex) (t-bu) 3 W 1 3 ' chanism:
29 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 29 Examples 1 = ; 70 % Alkyne CM in combination with Lindlar partial hydrogenation is a selective way to generate macrocyclic (Z)-olefins ' 2 Z n n > 4 n Lindlar cat. n
30 Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, nstitut für rganische Chemie, Universität egensburg 30 Alkane metathesis
Additions to Metal-Alkene and -Alkyne Complexes
 Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
Additions to tal-alkene and -Alkyne Complexes ecal that alkenes, alkynes and other π-systems can be excellent ligands for transition metals. As a consequence of this binding, the nature of the π-system
Carbenes and Carbene Complexes I Introduction
 Carbenes and Carbene Complexes I Introduction A very interesting (honest) class of radical-like molecules Steadily becoming more important as they find far more synthetic applications We will primarily
Carbenes and Carbene Complexes I Introduction A very interesting (honest) class of radical-like molecules Steadily becoming more important as they find far more synthetic applications We will primarily
VI. Metal alkyls from oxidative addition / insertion
 V. Metal alkyls from oxidative addition / insertion A. Carbonylation - C insertion very facile, metal acyls easily cleaved, all substrates which undergo oxidative addition can in principle be carbonylated.
V. Metal alkyls from oxidative addition / insertion A. Carbonylation - C insertion very facile, metal acyls easily cleaved, all substrates which undergo oxidative addition can in principle be carbonylated.
Elementary Organometallic Reactions
 Elementary eactions CE 966 (Tunge) Elementary rganometallic eactions All mechanisms are simply a combination of elementary reactions. 1) Coordination -- issociation 2) xidative Addition -- eductive Elimination
Elementary eactions CE 966 (Tunge) Elementary rganometallic eactions All mechanisms are simply a combination of elementary reactions. 1) Coordination -- issociation 2) xidative Addition -- eductive Elimination
Suggested solutions for Chapter 40
 s for Chapter 40 40 PBLEM 1 Suggest mechanisms for these reactions, explaining the role of palladium in the first step. Ac Et Et BS () 4 2 1. 2. K 2 C 3 evision of enol ethers and bromination, the Wittig
s for Chapter 40 40 PBLEM 1 Suggest mechanisms for these reactions, explaining the role of palladium in the first step. Ac Et Et BS () 4 2 1. 2. K 2 C 3 evision of enol ethers and bromination, the Wittig
Lecture 6: Transition-Metal Catalysed C-C Bond Formation
 Lecture 6: Transition-Metal Catalysed C-C Bond Formation (a) Asymmetric allylic substitution 1 u - d u (b) Asymmetric eck reaction 2 3 Ar- d (0) Ar 2 3 (c) Asymmetric olefin metathesis alladium π-allyl
Lecture 6: Transition-Metal Catalysed C-C Bond Formation (a) Asymmetric allylic substitution 1 u - d u (b) Asymmetric eck reaction 2 3 Ar- d (0) Ar 2 3 (c) Asymmetric olefin metathesis alladium π-allyl
CH 3 TMG, DMF N H 3 CO 2 S. (PPh 3 ) 2 Pd 0
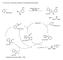 1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
1. (a) rovide a reasonable mechanism for the following transformation. I S 2 C 3 C 3 ( 3 ) 2 2, CuI C 3 TMG, DMF 3 C 2 S TMG = Me 2 Me 2 ICu ( 3 ) 2 0 I S 2 C 3 S 2 C 3 Cu I 3 3 3 C 2 S I 3 3 3 C 2 S 3
o-palladated cat. [Chem. Comm (1999)] [Org. Lett. 2, 1826 (2000)] [Org. Lett. 2, 2881 (2000)] [JACS 41, 9550 (1999)]
![o-palladated cat. [Chem. Comm (1999)] [Org. Lett. 2, 1826 (2000)] [Org. Lett. 2, 2881 (2000)] [JACS 41, 9550 (1999)] o-palladated cat. [Chem. Comm (1999)] [Org. Lett. 2, 1826 (2000)] [Org. Lett. 2, 2881 (2000)] [JACS 41, 9550 (1999)]](/thumbs/85/92754396.jpg) 3. Boron -- eview [Suzuki Chem. ev. 95, 2457 (1995)] U77b ydroboration also attractive but B Pd transmetallation difficult - must produce stable B product - solved (by Suzuki) by adding base to make Borates
3. Boron -- eview [Suzuki Chem. ev. 95, 2457 (1995)] U77b ydroboration also attractive but B Pd transmetallation difficult - must produce stable B product - solved (by Suzuki) by adding base to make Borates
Olefin Metathesis ROMP. L n Ru= ROMP n RCM. dilute
 lefin Metathesis MP: ing-opening metathesis polymerization Thermodynamically favored for 3,4, 8, larger ring systems Bridging groups (bicyclic olefins) make ΔG polymerization more favorable as a result
lefin Metathesis MP: ing-opening metathesis polymerization Thermodynamically favored for 3,4, 8, larger ring systems Bridging groups (bicyclic olefins) make ΔG polymerization more favorable as a result
Chapter 2 The Elementary Steps in TM Catalysis
 hapter 2 The Elementary Steps in TM atalysis + + ligand exchange A oxidative addition > n + A B n+2 reductive elimination < B n n+2 oxidative coupling + M' + M' transmetallation migratory insertion > (carbo-,
hapter 2 The Elementary Steps in TM atalysis + + ligand exchange A oxidative addition > n + A B n+2 reductive elimination < B n n+2 oxidative coupling + M' + M' transmetallation migratory insertion > (carbo-,
Electrophilic Carbenes
 Electrophilic Carbenes The reaction of so-called stabilized diazo compounds with late transition metals produces a metal carbene intermediate that is electrophilic. The most common catalysts are Cu(I)
Electrophilic Carbenes The reaction of so-called stabilized diazo compounds with late transition metals produces a metal carbene intermediate that is electrophilic. The most common catalysts are Cu(I)
Organic Tutorials 3 rd Year Michaelmas Transition Metals in Organic Synthesis: (General paper level) ! 1! Reading
 rganic Tutorials 3 rd Year Michaelmas 2010 Transition Metals in rganic Synthesis: (General paper level) Reading 1. Lecture Course, and suggested references from this. 2. Clayden, Greaves, Warren and Wothers.
rganic Tutorials 3 rd Year Michaelmas 2010 Transition Metals in rganic Synthesis: (General paper level) Reading 1. Lecture Course, and suggested references from this. 2. Clayden, Greaves, Warren and Wothers.
Three Type Of Carbene Complexes
 Three Type f arbene omplexes arbene complexes have formal metal-to-carbon double bonds. Several types are known. The reactivity of the carbene and how it contributes to the overall electron counting is
Three Type f arbene omplexes arbene complexes have formal metal-to-carbon double bonds. Several types are known. The reactivity of the carbene and how it contributes to the overall electron counting is
O CH 3. Mn CH 3 OC C. 16eelimination
 igratory Insertion igratory Insertion/Elimination 1 A migratory insertion reaction is when a cisoidal anionic and neutral ligand on a metal complex couple together to generate a new coordinated anionic
igratory Insertion igratory Insertion/Elimination 1 A migratory insertion reaction is when a cisoidal anionic and neutral ligand on a metal complex couple together to generate a new coordinated anionic
Oxidative Addition and Reductive Elimination
 xidative Addition and Reductive Elimination red elim coord 2 ox add ins Peter.. Budzelaar xidative Addition Basic reaction: n + X Y n X Y The new -X and -Y bonds are formed using: the electron pair of
xidative Addition and Reductive Elimination red elim coord 2 ox add ins Peter.. Budzelaar xidative Addition Basic reaction: n + X Y n X Y The new -X and -Y bonds are formed using: the electron pair of
Reaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. Reactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b.
 eaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. eactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b. Oxidative Addition c. eductive Elimination d. Nucleophillic
eaction chemistry of complexes Three general forms: 1. eactions involving the gain and loss of ligands a. Ligand Dissoc. and Assoc. (Bala) b. Oxidative Addition c. eductive Elimination d. Nucleophillic
Negishi Coupling of Secondary Alkylzinc Halides with Aryl Bromides and Chlorides
 Negishi Coupling of Secondary Alkylzinc alides with Aryl Bromides and Chlorides X X = Br, Cl 2 1 ZnBr 1, 2 = Alkyl Cat. Pd(OAc) 2 Ligand TF/Toluene rt or 60 o C 1 2 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, ASAP Article
Negishi Coupling of Secondary Alkylzinc alides with Aryl Bromides and Chlorides X X = Br, Cl 2 1 ZnBr 1, 2 = Alkyl Cat. Pd(OAc) 2 Ligand TF/Toluene rt or 60 o C 1 2 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, ASAP Article
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis
 rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
rganometallic hemistry and omogeneous atalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N8 Kashiwa ampus, December 11, 2009 Types of reactions in the coordination sphere of T 3. Reductive elimination X-L n -Y L n +
Direct Oxidative Heck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans
 Direct xidative eck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans by Zhang,.; Ferreira, E. M.; Stoltz, B. M. Angewandte
Direct xidative eck Cyclizations: Intramolecular Fujiwara-Moritani Arylations for the Synthesis of Functionalized Benzofurans and Dihydrobenzofurans by Zhang,.; Ferreira, E. M.; Stoltz, B. M. Angewandte
CuI CuI eage lic R tal ome rgan gbr ommon
 Common rganometallic eagents Li Et 2 Li Mg Et 2 Li alkyllithium rignard Mg Mg Li Zn TF ZnCl 2 TF dialkylzinc Zn 2 2 Zn Li CuI TF ganocuprate CuI 2 2 CuI common electrophile pairings ' Cl ' '' ' ' ' ' '
Common rganometallic eagents Li Et 2 Li Mg Et 2 Li alkyllithium rignard Mg Mg Li Zn TF ZnCl 2 TF dialkylzinc Zn 2 2 Zn Li CuI TF ganocuprate CuI 2 2 CuI common electrophile pairings ' Cl ' '' ' ' ' ' '
CHEM 153 PRACTICE TEST #1 ANSWER KEY
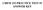 CEM 153 PACTICE TEST #1 ASWE KEY Provide a mechanism for the following transformation, indicating the electron count and oxidation state of each organometallic intermediate: u 3 (C) 12 (5 mol%) TF, 135
CEM 153 PACTICE TEST #1 ASWE KEY Provide a mechanism for the following transformation, indicating the electron count and oxidation state of each organometallic intermediate: u 3 (C) 12 (5 mol%) TF, 135
A Stille or Suzuki reaction is a good choice for this coupling O O because they are functional group tolerant, no radical chemistry F
 Chemistry 253 roblem et 3 Due: Friday, ctober 15th ame TF 1. For the following products of cross coupling reactions and indicated bond disconnections, please indicate a reasonable cross coupling protocol
Chemistry 253 roblem et 3 Due: Friday, ctober 15th ame TF 1. For the following products of cross coupling reactions and indicated bond disconnections, please indicate a reasonable cross coupling protocol
Direct, Catalytic Hydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated Olefins with N-Alkyl Arylamines
 Current Literature - May 12, 2007 Direct, Catalytic ydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated lefins with -Alkyl ylamines ' '' Ta[ 2 ] 5 (4-8 mol%), 160-165 o C 24-67h 66-95% ' '' S. B. erzon and J. F. artwig,
Current Literature - May 12, 2007 Direct, Catalytic ydroaminoalkylation of Unactivated lefins with -Alkyl ylamines ' '' Ta[ 2 ] 5 (4-8 mol%), 160-165 o C 24-67h 66-95% ' '' S. B. erzon and J. F. artwig,
Sonogashira: in situ, metal assisted deprotonation
 M.C. White, Chem 253 Cross-Coupling -120- Week of ctober 11, 2004 Sonogashira: in situ, metal assisted deprotonation catalytic cycle: ' (h 3 ) n d II The first report: h Sonogashira T 1975 (50) 4467. h
M.C. White, Chem 253 Cross-Coupling -120- Week of ctober 11, 2004 Sonogashira: in situ, metal assisted deprotonation catalytic cycle: ' (h 3 ) n d II The first report: h Sonogashira T 1975 (50) 4467. h
Total Syntheses of Minfiensine
 Total Syntheses of Minfiensine Douany, A. B.; umphreys, P. G.; verman, L. E.*; Wrobelski, A. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, ASAP. D: 10.1021/ja800163v Shen, L.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Qin, Y.*, Angew. Chem. nt.
Total Syntheses of Minfiensine Douany, A. B.; umphreys, P. G.; verman, L. E.*; Wrobelski, A. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, ASAP. D: 10.1021/ja800163v Shen, L.; Zhang, M.; Wu, Y.; Qin, Y.*, Angew. Chem. nt.
Course 201N 1 st Semester Inorganic Chemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. Bera
 andout-9 ourse 201N 1 st Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic hemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. Bera ontents 3. rganometallic hemistry xidative Addition, Reductive Elimination, Migratory Insertion, Elimination
andout-9 ourse 201N 1 st Semester 2006-2007 Inorganic hemistry Instructor: Jitendra K. Bera ontents 3. rganometallic hemistry xidative Addition, Reductive Elimination, Migratory Insertion, Elimination
Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) H Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group
 Literature eport Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group eporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Yue Ji Date: 2016-04-05 Yu, J.-Q. et al. Science 2016, 351, 252-256. Scripps esearch
Literature eport Functionalization of C(sp 3 ) Bonds Using a Transient Directing Group eporter: Mu-Wang Chen Checker: Yue Ji Date: 2016-04-05 Yu, J.-Q. et al. Science 2016, 351, 252-256. Scripps esearch
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July
 344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer 2013 Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July 30 2013 Summary of Grignard lecture Organometallic chemistry - the chemistry of compounds
344 Organic Chemistry Laboratory Summer 2013 Lecture 6 Transition metal organometallic chemistry and catalysis July 30 2013 Summary of Grignard lecture Organometallic chemistry - the chemistry of compounds
Zr-Catalyzed Carbometallation
 -Catalyzed Carbometallation C C C C ML n C C ML n ML n C C C C ML n ML n C C ML n Wipf Group esearch Topic Seminar Juan Arredondo November 13, 2004 Juan Arredondo @ Wipf Group 1 11/14/2004 Carbometallation
-Catalyzed Carbometallation C C C C ML n C C ML n ML n C C C C ML n ML n C C ML n Wipf Group esearch Topic Seminar Juan Arredondo November 13, 2004 Juan Arredondo @ Wipf Group 1 11/14/2004 Carbometallation
Chem 634. Metal Mediated Substitution Chemistry. Reading: Heg Ch 1 2 (handout), CS-B 7.1, , 11.3, Grossman Ch 6
 Chem 634 tal diated Substitution Chemistry eading: Heg Ch 1 2 (handout), CS-B 7.1, 8.2 8.3, 11.3, Grossman Ch 6 Announcements Problem Set 1 due NW. Mary Beth Kramer Lectureship 101 Brown Laboratory September
Chem 634 tal diated Substitution Chemistry eading: Heg Ch 1 2 (handout), CS-B 7.1, 8.2 8.3, 11.3, Grossman Ch 6 Announcements Problem Set 1 due NW. Mary Beth Kramer Lectureship 101 Brown Laboratory September
Highlights of Schmidt Reaction in the Last Ten Years
 ighlights of Schmidt eaction in the Last Ten Years Dendrobates histrionicus Jack Liu ov. 18, 2003 Introduction Classical Schmidt reaction of aldehydes and carboxylic acids Classical Schmidt reaction of
ighlights of Schmidt eaction in the Last Ten Years Dendrobates histrionicus Jack Liu ov. 18, 2003 Introduction Classical Schmidt reaction of aldehydes and carboxylic acids Classical Schmidt reaction of
Metal Catalyzed Outer Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated Olefins and Alkynes
 Metal Catalyzed uter Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated lefins and Alkynes Stephen Goble rganic Super-Group Meeting Literature Presentation ctober 6, 2004 1 utline I. Background Introduction to Carbometallation
Metal Catalyzed uter Sphere Alkylations of Unactivated lefins and Alkynes Stephen Goble rganic Super-Group Meeting Literature Presentation ctober 6, 2004 1 utline I. Background Introduction to Carbometallation
Chem 634. Introduction to Transition Metal Catalysis. Reading: Heg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, , 11.3 Grossman Ch 6
 Chem 634 Introduction to Transition etal Catalysis eading: eg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, 8.2 8.3, 11.3 Grossman Ch 6 Announcements Problem Set 1 due Thurs, 9/24 at beginning of class ffice our: Wed, 10:30-12, 220
Chem 634 Introduction to Transition etal Catalysis eading: eg Ch 1 2 CS-B 7.1, 8.2 8.3, 11.3 Grossman Ch 6 Announcements Problem Set 1 due Thurs, 9/24 at beginning of class ffice our: Wed, 10:30-12, 220
Journal Club Presentation by Remond Moningka 04/17/2006
 β-alkyl-α-allylation of Michael Acceptors through the Palladium-Catalyzed Three-Component Coupling between Allylic Substrate, Trialkylboranes, and Activated lefins Yoshinori Yamamoto, et al. J. rg. Chem.
β-alkyl-α-allylation of Michael Acceptors through the Palladium-Catalyzed Three-Component Coupling between Allylic Substrate, Trialkylboranes, and Activated lefins Yoshinori Yamamoto, et al. J. rg. Chem.
Chapter 4 Electrophilic Addition to Carbon Carbon Multiple Bonds 1. Addition of H X 2. Addition of H OH and addition of Y X 3. Addition to allene and
 Chapter 4 Electrophilic Addition to Carbon Carbon Multiple Bonds 1. Addition of X 2. Addition of and addition of Y X 3. Addition to allene and alkyne 4. Substitution at α-carbon 5. eactions via organoborane
Chapter 4 Electrophilic Addition to Carbon Carbon Multiple Bonds 1. Addition of X 2. Addition of and addition of Y X 3. Addition to allene and alkyne 4. Substitution at α-carbon 5. eactions via organoborane
Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Cross-Electrophile-Coupling Between Aryl and Alkyl Halides
 ickel-catalyzed Reductive Cross-Electrophile-Coupling Between Aryl and Alkyl Halides Eunjae Shim Zakarian Group Literature Talk / Dec 13 th, 2018 University of California, Santa Barbara Table of Contents
ickel-catalyzed Reductive Cross-Electrophile-Coupling Between Aryl and Alkyl Halides Eunjae Shim Zakarian Group Literature Talk / Dec 13 th, 2018 University of California, Santa Barbara Table of Contents
Organocopper Reagents
 rganocopper eagents General Information!!! why organocopper reagents? - Efficient method of C-C bond formation - Cu less electropositive than Li or Mg, so -Cu bond less polarized - consequences: 1. how
rganocopper eagents General Information!!! why organocopper reagents? - Efficient method of C-C bond formation - Cu less electropositive than Li or Mg, so -Cu bond less polarized - consequences: 1. how
deactivation or decomposition is therefore quantified using the turnover number.
 A catalyst may be defined by two important criteria related to its stability and efficiency. Name both of these criteria and describe how they are defined with respect to stability or efficiency. A catalyst
A catalyst may be defined by two important criteria related to its stability and efficiency. Name both of these criteria and describe how they are defined with respect to stability or efficiency. A catalyst
Organocopper Chemistry
 rganocopper Chemistry ave a great historical importance, but still remain highly useful reactions. If not the first organometallic reactions developed they are among the first. Most often used in conjugate
rganocopper Chemistry ave a great historical importance, but still remain highly useful reactions. If not the first organometallic reactions developed they are among the first. Most often used in conjugate
Chem 253 Problem Set 7 Due: Friday, December 3, 2004
 Chem 253 roblem Set 7 ue: Friday, ecember 3, 2004 Name TF. Starting with the provided starting material, provide a concise synthesis of. You may use any other reagents for your synthesis. It can be assumed
Chem 253 roblem Set 7 ue: Friday, ecember 3, 2004 Name TF. Starting with the provided starting material, provide a concise synthesis of. You may use any other reagents for your synthesis. It can be assumed
Organometallics Study Meeting Part 4. Reactions of Organometallic Complexes
 rganometallics Study eeting art 4. eactions of rganometallic Complexes 1. asics 2011/4/28 oshino(d1).10 1-1. igand Exchange Dissosiative echanism ' n n-1 ' n-1 Fe(C) 5 (18e):hoto-promoteddissociationofigand
rganometallics Study eeting art 4. eactions of rganometallic Complexes 1. asics 2011/4/28 oshino(d1).10 1-1. igand Exchange Dissosiative echanism ' n n-1 ' n-1 Fe(C) 5 (18e):hoto-promoteddissociationofigand
Advanced Organic Chemistry
 D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Question of the day: Chemistry 530A TBS Me 2 C Me toluene, 130 C 70% TBS C 2 Me H H Advanced rganic Chemistry Me Lecture 16 Cycloaddition Reactions Diels _ Alder Reaction Photochemical
D. A. Evans, G. Lalic Question of the day: Chemistry 530A TBS Me 2 C Me toluene, 130 C 70% TBS C 2 Me H H Advanced rganic Chemistry Me Lecture 16 Cycloaddition Reactions Diels _ Alder Reaction Photochemical
Carbon-heteroatom single bonds basic C N C X. X= F, Cl, Br, I Alkyl Halide C O. epoxide Chapter 14 H. alcohols acidic H C S C. thiols.
 hapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Structure and Properties of Alcohols Alkanes arbon - arbon Multiple Bonds arbon-heteroatom single bonds basic Alkenes X X= F, l,, I Alkyl alide amines hapter 23 nitro
hapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Structure and Properties of Alcohols Alkanes arbon - arbon Multiple Bonds arbon-heteroatom single bonds basic Alkenes X X= F, l,, I Alkyl alide amines hapter 23 nitro
Chiral Catalyst II. Palladium Catalysed Allylic Displacement ( -allyl complexes) 1. L n Pd(0) 2. Nuc
 Chiral Catalyst II ast lecture we looked at asymmetric catalysis for oxidation and reduction Many other organic transformations, this has led to much investigation Today we will look at some others...
Chiral Catalyst II ast lecture we looked at asymmetric catalysis for oxidation and reduction Many other organic transformations, this has led to much investigation Today we will look at some others...
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation
 Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Studies on Heck and Suzuki Reactions Catalyzed by Palladium(0) and Wacker- Type Oxidative Cyclization Catalyzed by Palladium(II)
 Studies on eck and Suzuki Reactions Catalyzed by Palladium(0) and Wacker- Type xidative Cyclization Catalyzed by Palladium() Zuhui Zhang enmark Group Meeting 10/21/2008 1 Part ne: Palladium(0)-Catalyzed
Studies on eck and Suzuki Reactions Catalyzed by Palladium(0) and Wacker- Type xidative Cyclization Catalyzed by Palladium() Zuhui Zhang enmark Group Meeting 10/21/2008 1 Part ne: Palladium(0)-Catalyzed
Loudon Chapter 18 Review: Vinyl/Aryl Reactivity Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 2/21/2016
 Chapter 18 covers leaving groups that are directly attached to double-bonded sp 2 carbons. These molecules don t do most of the regular alkyl halide chemistry from Ch. 9 (S N1/ S N2/E1), but they can do
Chapter 18 covers leaving groups that are directly attached to double-bonded sp 2 carbons. These molecules don t do most of the regular alkyl halide chemistry from Ch. 9 (S N1/ S N2/E1), but they can do
Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst
 Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst Cl 3 ; 2 h 3, reflux 3h h 3 Cl h 3 h Cl 3 Good catalyst especially for 2 1-alkenes 2, base toluene Cl h 3 h 3 h 3 Et 3 Cl h 3 Cl h 3 h 3 R h 3 h 3 Cl h 3 R RC 2 C
Wilkinson s other (ruthenium) catalyst Cl 3 ; 2 h 3, reflux 3h h 3 Cl h 3 h Cl 3 Good catalyst especially for 2 1-alkenes 2, base toluene Cl h 3 h 3 h 3 Et 3 Cl h 3 Cl h 3 h 3 R h 3 h 3 Cl h 3 R RC 2 C
14-1 Reactions Involving Gain or Loss of Ligands Reactions Involving Modification of Ligands
 Organometallic Reaction and Catalysis 14-1 Reactions Involving Gain or Loss of Ligands 14-2 Reactions Involving Modification of Ligands 14-3 Organometallic Catalysts 14-4 Heterogeneous Catalysts Inorganic
Organometallic Reaction and Catalysis 14-1 Reactions Involving Gain or Loss of Ligands 14-2 Reactions Involving Modification of Ligands 14-3 Organometallic Catalysts 14-4 Heterogeneous Catalysts Inorganic
sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito
 1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
1 sp 3 C-H insertion by α-oxo Gold Carbene B4 Kei Ito 2016. 1. 30 1. Introduction 2 About Carbene 3 Brief history of carbene (~2000) Carbene Neutral compounds featuring a divalent carbon atom with only
Functionalization of terminal olefins via H migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence Hydrogenation
 M.C. White, Chem 153 verview -282- Week of ovember 11, 2002 Functionalization of terminal olefins via migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence ydrogenation ML n E ydrosilylation Si 3 Si 3 ML
M.C. White, Chem 153 verview -282- Week of ovember 11, 2002 Functionalization of terminal olefins via migratory insertion /reductive elimination sequence ydrogenation ML n E ydrosilylation Si 3 Si 3 ML
Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing Oxazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129,
 Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing xazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3058-3059 - versus -Arylation of Aminoalcohols: rthogonal Selectivity in Copper-Based
Intramolecular Ene Reactions Utilizing xazolones and Enol Ethers Fisk, J.S. and Tepe, J..J J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3058-3059 - versus -Arylation of Aminoalcohols: rthogonal Selectivity in Copper-Based
Microwave-promoted synthesis in water
 Microwave-promoted synthesis in water icholas E. Leadbeater nicholas.leadbeater@uconn.edu Outline of what we do Synthesis / Methodology / ew techniques Pure organic synthesis eg. Baylis-Hillman eaction
Microwave-promoted synthesis in water icholas E. Leadbeater nicholas.leadbeater@uconn.edu Outline of what we do Synthesis / Methodology / ew techniques Pure organic synthesis eg. Baylis-Hillman eaction
Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium
 Literature report Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium Compounds Reporter: Zhang-Pei Chen Checker: Mu-Wang Chen Date: 02/07/2013 Feringa, B.L.et al. Feringa, B. L. et al. Nature Chem. 2013,
Literature report Direct Catalytic Cross-Coupling of Organolithium Compounds Reporter: Zhang-Pei Chen Checker: Mu-Wang Chen Date: 02/07/2013 Feringa, B.L.et al. Feringa, B. L. et al. Nature Chem. 2013,
ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY )
 CHAPTER IV ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY ) n the end of the 1960s the leading specialist in homogeneous catalysis Jack Halpern wrote [1]: to develop
CHAPTER IV ACTIVATION OF C H BONDS BY LOW-VALENT METAL COMPLEXES ( THE ORGANOMETALLIC CHEMISTRY ) n the end of the 1960s the leading specialist in homogeneous catalysis Jack Halpern wrote [1]: to develop
Asymmetric Nucleophilic Catalysis
 Asymmetric ucleophilic Catalysis Chiral catalyst X 2 Chiral catalyst X = alkyl, X 1 2 1 Vedejs, E.; Daugulis,. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4166-4173 Shaw, S. A.; Aleman,.; Vedejs, E. J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Asymmetric ucleophilic Catalysis Chiral catalyst X 2 Chiral catalyst X = alkyl, X 1 2 1 Vedejs, E.; Daugulis,. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 4166-4173 Shaw, S. A.; Aleman,.; Vedejs, E. J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Enantioselective Borylations. David Kornfilt Denmark Group Meeting Sept. 14 th 2010
 Enantioselective Borylations David Kornfilt Denmark Group Meeting Sept. 14 th 2010 30.000-foot View Enantioenriched Organoboranes What to do with them Crudden C. M. et. al., Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 46
Enantioselective Borylations David Kornfilt Denmark Group Meeting Sept. 14 th 2010 30.000-foot View Enantioenriched Organoboranes What to do with them Crudden C. M. et. al., Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 46
24.2 Organometallic Compounds and Catalysis
 24.2 rganometallic Compounds and Catalysis We introduced organometallic compounds in Chapter 5. n the next few sections, we discuss several reactions of transition metals that are particularly useful for
24.2 rganometallic Compounds and Catalysis We introduced organometallic compounds in Chapter 5. n the next few sections, we discuss several reactions of transition metals that are particularly useful for
Chiral Diol Promoted Boronates Addi3on Reac3ons. Lu Yan Morken Group Boston College
 Chiral Diol Promoted Boronates Addi3on Reac3ons Lu Yan Morken Group Boston College Main Idea R R B or R R B Ar * exchange B * * or B Ar R 1 R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2 Products not nucleophilic enough nucleophilic
Chiral Diol Promoted Boronates Addi3on Reac3ons Lu Yan Morken Group Boston College Main Idea R R B or R R B Ar * exchange B * * or B Ar R 1 R 1 R 2 R 1 R 2 Products not nucleophilic enough nucleophilic
When something goes wrong. Goya: Mother showing her derformed child to two women Louvre, Paris
 1 ew Catalytic Asymmestric eactions Karl Anker Jørgensen Danish ational eserach Foundation: Center for Catalysis Department of Chemistry, Aarhus University Denmark kaj@chem.au.dk When something goes wrong
1 ew Catalytic Asymmestric eactions Karl Anker Jørgensen Danish ational eserach Foundation: Center for Catalysis Department of Chemistry, Aarhus University Denmark kaj@chem.au.dk When something goes wrong
Answers To Chapter 7 Problems.
 Answers To Chapter Problems.. Most of the Chapter problems appear as end-of-chapter problems in later chapters.. The first reaction is an ene reaction. When light shines on in the presence of light and
Answers To Chapter Problems.. Most of the Chapter problems appear as end-of-chapter problems in later chapters.. The first reaction is an ene reaction. When light shines on in the presence of light and
TMSCl imidazole DMF. Ph Ph OTMS. Michael reaction. Michael reaction Ph R 3. epoxidation O R
 eaction using diarylprolinol silyl ether derivatives as catalyst 1) C Et K C 3, ) MgBr, TF TMS hexane, 0 o C TBS p- C 6 4, T C Et 85%, 99% ee Angew. Chem., nt. Ed., 44, 41 (005). rg. Synth., 017, 94, 5.
eaction using diarylprolinol silyl ether derivatives as catalyst 1) C Et K C 3, ) MgBr, TF TMS hexane, 0 o C TBS p- C 6 4, T C Et 85%, 99% ee Angew. Chem., nt. Ed., 44, 41 (005). rg. Synth., 017, 94, 5.
Insertion Reactions. 1) 1,1 insertion in which the metal and the X ligand end up bound to the same (1,1) atom
 Insertion Reactions xidative addition and substitution allow us to assemble 1e and 2e ligands on the metal, respectively. With insertion, and its reverse reaction, elimination, we can now combine and transform
Insertion Reactions xidative addition and substitution allow us to assemble 1e and 2e ligands on the metal, respectively. With insertion, and its reverse reaction, elimination, we can now combine and transform
Tips for taking exams in 852
 Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Copper-Catalyzed Reaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium Reagent
 Copper-Catalyzed eaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium eagent Mg 1) cat. Cu(Tf) 2 i Pr 2, 25 o C, 3 h 2) H 2, Pt 2 Masahiro Sai, Hidenori Someya, Hideki Yorimitsu, and Koichiro shima
Copper-Catalyzed eaction of Alkyl Halides with Cyclopentadienylmagnesium eagent Mg 1) cat. Cu(Tf) 2 i Pr 2, 25 o C, 3 h 2) H 2, Pt 2 Masahiro Sai, Hidenori Someya, Hideki Yorimitsu, and Koichiro shima
Catellani Reaction (Pd-Catalyzed Sequential Reaction) Todd Luo
 Catellani Reaction (Pd-Catalyzed Sequential Reaction) Todd Luo 2014.1.6 1 Content Introduction Progress of Catellani Reaction o-alkylation and Applications o-arylation and Applications Conclusion and Outlook
Catellani Reaction (Pd-Catalyzed Sequential Reaction) Todd Luo 2014.1.6 1 Content Introduction Progress of Catellani Reaction o-alkylation and Applications o-arylation and Applications Conclusion and Outlook
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions
 Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Metal Hydrides, Alkyls, Aryls, and their Reactions A Primer on MO Theory σ-bonding in Organotransition Metal Complexes M-C Bond Energies in Organotransition Metal Complexes Thermodynamic Predictions
Arylhalide-Tolerated Electrophilic Amination of Arylboronic Acids with N-Chloroamides Catalyzed by CuCl at Room Temperature
 Current Literature July 19, 08 Jitendra Mishra Arylhalide-Tolerated Electrophilic Amination of Arylboronic Acids with -Chloroamides Catalyzed by CuCl at Room Temperature Aiwen Lei et.al. College of the
Current Literature July 19, 08 Jitendra Mishra Arylhalide-Tolerated Electrophilic Amination of Arylboronic Acids with -Chloroamides Catalyzed by CuCl at Room Temperature Aiwen Lei et.al. College of the
Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group.
 Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group. akatani, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Yamasaki, R.; Saito, S. rg. Lett. 2008, 10, 2067-2070. An Annulation Reaction for the Synthesis
Copper-Catalyzed Synthesis of Esters from Ketones. Alkyl Group as a Leaving Group. akatani, Y.; Koizumi, Y.; Yamasaki, R.; Saito, S. rg. Lett. 2008, 10, 2067-2070. An Annulation Reaction for the Synthesis
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Description
 CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
Chem 251 Fall Learning Objectives
 Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Some Hartwig Chemistry Experimental Approaches and Detailed Mechanistic Analysis
 Some artwig Chemistry Experimental Approaches and Detailed chanistic Analysis b. 1964 1986 A.B. Princeton U, Maitland Jones 1990.D. UC Berkeley, obert Bergman and ichard Anderson 1990-92 Post-doc, MIT,
Some artwig Chemistry Experimental Approaches and Detailed chanistic Analysis b. 1964 1986 A.B. Princeton U, Maitland Jones 1990.D. UC Berkeley, obert Bergman and ichard Anderson 1990-92 Post-doc, MIT,
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation
 Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Boronic Acids. Preparation and Applications in. Organic Synthesis, Edited by Dennis G. Hall. Volume 1. Second Completely Revised Edition
 Edited by Dennis G. Hall Boronic Acids Volume 1 Preparation and Applications in Medicine and Materials Organic Synthesis, Second Completely Revised Edition With a Foreword by Akira Suzuki WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH
Edited by Dennis G. Hall Boronic Acids Volume 1 Preparation and Applications in Medicine and Materials Organic Synthesis, Second Completely Revised Edition With a Foreword by Akira Suzuki WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar. Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry
 A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
A. Loupy, B.Tchoubar Salt Effects in Organic and Organometallic Chemistry 1 Introduction - Classification of Specific Salt Effects 1 1.1 Specific Salt Effects Involving the Salt's Lewis Acid or Base Character
Ready; Catalysis Conjugate Addition
 eady; Catalysis Conjugate Addition Topics covered 1. 1,4 addition involving copper a. stoichiometric reactions b. catalytic reactions c. allylic substitution. Conjugate addition without copper a. Ni-based
eady; Catalysis Conjugate Addition Topics covered 1. 1,4 addition involving copper a. stoichiometric reactions b. catalytic reactions c. allylic substitution. Conjugate addition without copper a. Ni-based
Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon
 Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon bond Chung-Yeh Wu, Takahiro oribe, Christian Borch Jacobsen & F. Dean Toste ature, 517, 449-454 (2015) presented by Ian Crouch Literature
Stable gold(iii) catalysts by oxidative addition of a carboncarbon bond Chung-Yeh Wu, Takahiro oribe, Christian Borch Jacobsen & F. Dean Toste ature, 517, 449-454 (2015) presented by Ian Crouch Literature
Inorganic Chemistry Year 3
 Inorganic Chemistry Year 3 Transition Metal Catalysis Eighteen Electron Rule 1.Get the number of the group that the metal is in (this will be the number of d electrons) 2.Add to this the charge 1.Negative
Inorganic Chemistry Year 3 Transition Metal Catalysis Eighteen Electron Rule 1.Get the number of the group that the metal is in (this will be the number of d electrons) 2.Add to this the charge 1.Negative
Strained Molecules in Organic Synthesis
 Strained Molecules in rganic Synthesis 0. Introduction ~ featuring on three-membered rings ~ Tatsuya itabaru (M) Lit. Seminar 08068 for cyclobutadienes : see Mr. Yamatsugu's Lit. Sem. 069 eat of Formation
Strained Molecules in rganic Synthesis 0. Introduction ~ featuring on three-membered rings ~ Tatsuya itabaru (M) Lit. Seminar 08068 for cyclobutadienes : see Mr. Yamatsugu's Lit. Sem. 069 eat of Formation
Ac 2 O, py. Keywords: silyl hydrides silanes organosilanes chiral silanes hydrosilylation dehydrogenative
 VII Abstracts 2015 p1 4.4.4.8 Silyl ydrides R. W. Clark and S. L. Wiskur This chapter is an update to the earlier article in Science of Synthesis (Section 4.4.4) covering the synthesis and use of silyl
VII Abstracts 2015 p1 4.4.4.8 Silyl ydrides R. W. Clark and S. L. Wiskur This chapter is an update to the earlier article in Science of Synthesis (Section 4.4.4) covering the synthesis and use of silyl
Asymmetric Catalysis by Lewis Acids and Amines
 Asymmetric Catalysis by Lewis Acids and Amines Asymmetric Lewis acid catalysis - Chiral (bisooxazoline) copper (II) complexes - Monodentate Lewis acids: the formyl -bond Amine catalysed reactions Asymmetric
Asymmetric Catalysis by Lewis Acids and Amines Asymmetric Lewis acid catalysis - Chiral (bisooxazoline) copper (II) complexes - Monodentate Lewis acids: the formyl -bond Amine catalysed reactions Asymmetric
Nucleophilic attack on ligand
 Nucleophilic attack on ligand Nucleophile "substitutes" metal hapticity usually decreases xidation state mostly unchanged Competition: nucleophilic attack on metal usually leads to ligand substitution
Nucleophilic attack on ligand Nucleophile "substitutes" metal hapticity usually decreases xidation state mostly unchanged Competition: nucleophilic attack on metal usually leads to ligand substitution
Radical Reactions. Radical Stability!!! bond dissociation energies X Y X + Y. bond BDE (kcal/mol) bond BDE (kcal/mol) CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 95 O H R 2 C H
 adical eactions adical Stability!!! bond dissociation energies X Y X Y bond BDE (kcal/mol) bond BDE (kcal/mol) C 3 104 108 C 3 C 2 98 110 95 2 C 102 (-) 93 (C-) 92 C 3 C 3 36 89 85 C 3 C 3 80 adical eactions
adical eactions adical Stability!!! bond dissociation energies X Y X Y bond BDE (kcal/mol) bond BDE (kcal/mol) C 3 104 108 C 3 C 2 98 110 95 2 C 102 (-) 93 (C-) 92 C 3 C 3 36 89 85 C 3 C 3 80 adical eactions
Chiral Brønsted Acid Catalysis
 Chiral Brønsted Acid Catalysis Aryl Aryl Aryl Aryl S CF 3 2 P Fe CF 3 CF 3 2 Jack Liu ov. 16, 2004 CF 3 Introduction Chiral Brønsted acid catalysis in nature: enzymes and peptides Chiral Brønsted acid
Chiral Brønsted Acid Catalysis Aryl Aryl Aryl Aryl S CF 3 2 P Fe CF 3 CF 3 2 Jack Liu ov. 16, 2004 CF 3 Introduction Chiral Brønsted acid catalysis in nature: enzymes and peptides Chiral Brønsted acid
C H Activated Trifluoromethylation
 Literature report C H Activated Trifluoromethylation Reporter:Yan Fang Superior:Prof. Yong Huang Jun. 17 th 2013 Contents Background Trifluoromethylation of sp-hybridized C-H Bonds Trifluoromethylation
Literature report C H Activated Trifluoromethylation Reporter:Yan Fang Superior:Prof. Yong Huang Jun. 17 th 2013 Contents Background Trifluoromethylation of sp-hybridized C-H Bonds Trifluoromethylation
Reduction. Boron based reagents. NaBH 4 / NiCl 2. Uses: Zn(BH 4 ) 2. Preparation: Good for base sensitive groups Chelation control model.
 Uses: Ar N 2 Ar N 2 Ar N Ar N 2 eduction Boron based reagents NaB 4 / NiCl 2 2 Ar C N Ar C N 2 Preparation: Zn(B 4 ) 2 ZnCl 2 (Ether) NaB 4 Zn(B 4 ) 2 Good for base sensitive groups Chelation control model
Uses: Ar N 2 Ar N 2 Ar N Ar N 2 eduction Boron based reagents NaB 4 / NiCl 2 2 Ar C N Ar C N 2 Preparation: Zn(B 4 ) 2 ZnCl 2 (Ether) NaB 4 Zn(B 4 ) 2 Good for base sensitive groups Chelation control model
N-Heterocyclic Carbenes (NHCs)
 N-Heterocyclic Carbenes (NHCs) In contrast to Fischer and Schrock type carbenes NHCs are extremely stable, inert ligands when complexed to a metal centre. Similar to phosphine ligands they are electronically
N-Heterocyclic Carbenes (NHCs) In contrast to Fischer and Schrock type carbenes NHCs are extremely stable, inert ligands when complexed to a metal centre. Similar to phosphine ligands they are electronically
Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3. Nitrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic
 hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
Chemistry 335 Supplemental Slides: Interlude 1. Reduction: addition of hydrogen to the substrate. Oxidation: addition of oxygen to the substrate
 Interlude 1: Oxidations, Reductions & Other Functional Group Interconversions (FGI) 1. Definition of Oxidation and Reduction For practical purposes in organic chemistry, oxidation and reduction are defined
Interlude 1: Oxidations, Reductions & Other Functional Group Interconversions (FGI) 1. Definition of Oxidation and Reduction For practical purposes in organic chemistry, oxidation and reduction are defined
π-alkyne metal complex and vinylidene metal complex in organic synthesis
 Literature Seminar 080220 Kenzo YAMATSUGU (D1) π-alkyne metal complex and vinylidene metal complex in organic synthesis 0. Introduction ' ' = π-alkyne metal complex vinylidene metal complex ecently, electrophilic
Literature Seminar 080220 Kenzo YAMATSUGU (D1) π-alkyne metal complex and vinylidene metal complex in organic synthesis 0. Introduction ' ' = π-alkyne metal complex vinylidene metal complex ecently, electrophilic
Denmark Group Meeting. & Electrophilic rearrangement of amides
 Denmark Group Meeting Palladium catalyzed Dearomatizationeaction & Electrophilic rearrangement of amides 11 th Bo Peng th Feb. 2014 1 https://maps.google.com 2 Palladium catalyzed Dearomatization eaction
Denmark Group Meeting Palladium catalyzed Dearomatizationeaction & Electrophilic rearrangement of amides 11 th Bo Peng th Feb. 2014 1 https://maps.google.com 2 Palladium catalyzed Dearomatization eaction
CEM 852 Final Exam. May 6, 2010
 CEM 852 Final Exam May 6, 2010 This exam consists of 7 pages. Please make certain that your exam has all of the necessary pages. Total points possible for this exam are 150. n answering your questions,
CEM 852 Final Exam May 6, 2010 This exam consists of 7 pages. Please make certain that your exam has all of the necessary pages. Total points possible for this exam are 150. n answering your questions,
Keisuke Suzuki. Baran lab Group Meeting 6/11/16. Shigenobu Umemiya. Akira Suzuki. Takanori Suzuki (Hokkaido University)
 197.D., Teruaki Mukaiyama, University of Tokyo 193 Assistant Professor, Keio University 197 Lecturer, Keio University 199 Assocate Professor, Keio University 1990 Visiting Professor, ET 1994 ull Professor,
197.D., Teruaki Mukaiyama, University of Tokyo 193 Assistant Professor, Keio University 197 Lecturer, Keio University 199 Assocate Professor, Keio University 1990 Visiting Professor, ET 1994 ull Professor,
Stereoselective reactions of the carbonyl group
 1 Stereoselective reactions of the carbonyl group We have seen many examples of substrate control in nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group (Felkin-Ahn & chelation control) If molecule does not contain
1 Stereoselective reactions of the carbonyl group We have seen many examples of substrate control in nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl group (Felkin-Ahn & chelation control) If molecule does not contain
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis
 Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N6 Kashiwa Campus, November 27, 2009 Group VIB: Cr, Mo, W -Oxidation states from -2 to +6 -While +2 and +3 for Cr are quite
Organometallic Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis Dr. Alexey Zazybin Lecture N6 Kashiwa Campus, November 27, 2009 Group VIB: Cr, Mo, W -Oxidation states from -2 to +6 -While +2 and +3 for Cr are quite
Transition Metal Chemistry
 Transition Metal Chemistry 2 2011.12.2 Ⅰ Fundamental Organometallic Reactions Following four reactions are important formal reaction patterns in organotransition metal complexes, which would conveniently
Transition Metal Chemistry 2 2011.12.2 Ⅰ Fundamental Organometallic Reactions Following four reactions are important formal reaction patterns in organotransition metal complexes, which would conveniently
Palladium-Mediated Functionalization of Heteroaromatic Cations: Comparative Study on Quinolizinium Cations
 Palladium-Mediated Functionalization of Heteroaromatic Cations: Comparative Study on Quinolizinium Cations Domingo Garcia-Cuadrado, Ana M. Cuadro, Bernado M. Barchin, Ana unez, Tatiana Caneque, Julio Alvarez-
Palladium-Mediated Functionalization of Heteroaromatic Cations: Comparative Study on Quinolizinium Cations Domingo Garcia-Cuadrado, Ana M. Cuadro, Bernado M. Barchin, Ana unez, Tatiana Caneque, Julio Alvarez-
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
The aldol reaction with metal enolates proceeds by a chair-like, pericyclic process: favored. disfavored. favored. disfavored
 The aldol reaction with metal enolates proceeds by a chair-like, pericyclic process: Z-enolates: M 2 M 2 syn 2 C 2 favored 2 M 2 anti disfavored E-enolates: M 2 2 C 3 C 3 C 2 favored 2 M M disfavored In
The aldol reaction with metal enolates proceeds by a chair-like, pericyclic process: Z-enolates: M 2 M 2 syn 2 C 2 favored 2 M 2 anti disfavored E-enolates: M 2 2 C 3 C 3 C 2 favored 2 M M disfavored In
