The EcoCyc Database. January 25, de Nitrógeno, UNAM,Cuernavaca, A.P. 565-A, Morelos, 62100, Mexico;
|
|
|
- Neal Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The EcoCyc Database Peter D. Karp, Monica Riley, Milton Saier,IanT.Paulsen +, Julio Collado-Vides + Suzanne M. Paley, Alida Pellegrini-Toole,César Bonavides ++, and Socorro Gama-Castro ++ January 25, 2002 Bioinformatics Research Group, SRI International, 333 Ravenswood Ave EK207, Menlo Park, CA 94025; pkarp@ai.sri.com. Marine Biological Laboratory, Woods Hole, MA 02543; mriley@mbl.edu. Department of Biology, University of California at San Diego, La Jolla, CA ; msaier@ucsd.edu. + The Institute for Genomic Research, 9712 Medical Center Drive Rockville, MD 20850; ipaulsen@tigr.org. ++ Programa de Biologia Molecular Computacional, Centro de Investigacion Sobre Fijación de Nitrógeno, UNAM,Cuernavaca, A.P. 565-A, Morelos, 62100, Mexico; collado@cifn.unam.mx Appears in Nucleic Acids Research (1):56 8 1
2 Abstract EcoCyc is an organism-specific Pathway/Genome Database that describes the metabolic and signal-transduction pathways of E. coli, its enzymes, its transport proteins, and its mechanisms of transcriptional control of gene expression. EcoCyc is queried using the Pathway Tools graphical user interface, which provides a wide variety of query operations and visualization tools. EcoCyc is available at URL 1 Introduction The EcoCyc database (DB) is a model-organism DB for E. coli K 12, and is a computational symbolic theory of the biochemical machinery of E. coli K 12 [1]. As well as describing the genes and proteins of E. coli, EcoCyc goes beyond most model-organism DBs because it provides structured symbolic descriptions of E. coli metabolic pathways, transport functions, and gene regulation. Intended uses of EcoCyc include the following. (1) EcoCyc is a resource for analysis of microbial genomes at the level of individual genes. Because the E. coli genome has a high fraction of genes whose functions were determined experimentally, it is an accurate reference for inferring gene function by sequence similarity. (2) EcoCyc describes the subunit structures of many enzymes, and therefore could be used as training or validation datasets for algorithms that detect protein protein interactions. (3) Because it contains a symbolic description of the genetic network of E. coli, EcoCyc can serve as a test set for algorithms that infer genetic networks from geneexpression data. (4) EcoCyc can be used for studies of pathway evolution. (5) EcoCyc is used as an aid in teaching biochemistry. This article describes recent enhancements to EcoCyc, and how to access it. We request that EcoCyc users cite this article in publications related to its use. Version 5.6 of EcoCyc was released in June, Pathway Tools Software and Database Environment The Pathway Tools software that underlies EcoCyc provides query, editing, and visualization operations for Pathway/Genome DBs [2, 3]. See URL The Pathway Tools is an environment for functional bioinformatics for managing, curating, and computing with a functional genome annotation. The Pathway Tools utilize a frame knowledge representation system (FRS) called Ocelot [2, 4]. FRSs use an object-oriented data model that organizes information within classes: collections of objects that share similar properties and attributes. 2
3 3 The EcoCyc Data Table 1 shows the current size of the principal EcoCyc classes. 3.1 Transcriptional Regulation of Gene Expression The current version 5.6 of EcoCyc includes information on regulation of transcription initiation, and organization of genes into transcription units (TUs). All data on gene regulation and TU organization were obtained from experimental characterizations of E. coli transcriptional regulatory mechanisms in the biomedical literature. A transcription unit (TU) is a region of DNA that includes a single promoter, the transcription factor binding sites that modulate the rate of transcription initiation at that promoter, the genes that are transcribed from the promoter, and the transcription terminator. A one-to-one relationship exists between TUs and promoters. A TU differs from an operon because by definition an operon must contain more than one gene, whereas a TU may contain one or more genes; an operon may also include several promoters and terminators, whereas a TU must contain a single promoter in this definition. Therefore, our approach defines a different TU for each promoter in an operon with multiple promoters. The descriptions of genetic networks in EcoCyc were derived from RegulonDB version 3.2 [5], which was loaded into EcoCyc in Many updates, additions, and corrections have been made since that time; curation of these data now occurs within EcoCyc. EcoCyc currently contains descriptions of 100 DNA-binding transcriptional regulators (of the 314 total estimated regulators of E. coli [6]), 740 experimentally mapped promoters, and 854 DNA-binding sites, as well as the clustering of 1185 genes into 629 transcription units. These data are incomplete in several respects. First, only 25% of all E. coli genes are clustered into TUs. Second, some of the defined TUs lack promoters because those promoters have not yet been physically mapped, although it is known that their genes are coregulated and produce a single transcript. Third, some defined TUs do not include regulatory interactions because they await experimental determination, or their promoters are constitutive. For instance, the glnalg operon is described in EcoCyc by three different TUs, corresponding to the glnap1, glnap2, and glnl promoters. The glnaap2 sigma 54 promoter and glnap1 sigma 70 promoter transcribe the three genes in this operon. The glnl internal promoter transcribes the last two genes. SRI has developed several visualization tools to facilitate exploration of transcriptional regulatory data. EcoCyc gene-display windows now display a schematic diagram of the TU containing a gene, when known. Clicking on the TU produces a new TU window that lists information about each TU binding site, and the regulatory interactions of each TU binding site. The display window for a transcription factor displays all TUs that the transcription factor controls (its regulon). The overview diagram of the full metabolic map of E. coli contains an operation to highlight those metabolic-reaction steps and transport reactions controlled by a specified transcription factor. 3
4 3.2 Transport The latest release of EcoCyc has considerably expanded coverage of membrane transport systems. Membrane transporters are responsible for uptake of metabolites and the export of metabolic end products, as well as being involved in other cellular processes. A total of 476 known and putative cytoplasmic membrane transport genes, corresponding to 304 probable transport systems, are currently represented in EcoCyc. A total of 177 distinct transport reactions are described in EcoCyc. In some cases single transporters mediate more than one transport reaction, and in other cases a single transport reaction may be mediated by more than one transporter. Approximately 85% of the E. coli transporters have been annotated with the same detailed, literature-based approach that EcoCyc uses for E. coli enzymes and pathways. It is anticipated that curation of the remaining transporters will be complete by the next release of EcoCyc. Future objectives include expanding annotation targets to include outer membrane channels, protein secretion, all other aspects of membrane biology, and membrane proteins of unknown function. Transporters are represented in the EcoCyc database by one or more DB objects that encode the transporter and its monomer subunits, if any. The transporter is linked to one or more (in the case of multifunctional transporters) objects that describe its function as a biochemical reaction. Our schema for reactions allows each substrate to be tagged with a cellular compartment, which if omitted defaults to the cytoplasm. These data are used to generate a cartoon diagram of each transporter that graphically represents the transport reactions. Transporters are now also displayed in the metabolic overview diagram with the directionality of transport indicated. By visual inspection, it becomes possible to probe the relationships between transported and metabolized compounds. 4 Additional Recent Enhancements The EcoCyc WWW site at has been expanded to also contain the Meta- Cyc DB, and to contain Pathway/Genome DBs for the following additional organisms, all created using the PathoLogic program [3]: B. subtilis, C. trachomatis, Hm. influenzae, Hb. pylori, Mb. tuberculosis, Mp. pneumoniae, S. cerevisiae, and T. pallidum. The majority of proteins in EcoCyc now have WWW links to the SWISS PROT and PIR DBs. 5 Distribution EcoCyc is available in four forms: It is accessible online through the WWW at URL (this version supports a subset of the GUI functionality of the X-windows and PC versions). 4
5 An X-windows version of EcoCyc for the Sun workstation bundles together the Pathway/Genome Navigator software with the EcoCyc DB. A new PC version of EcoCyc bundles together the Pathway/Genome Navigator software with the EcoCyc DB. A flatfile version of EcoCyc is available for global analyses. All four forms of access are free to academic institutions for research use; a fee applies to other forms of use. Contact ecocyc-info@ai.sri.com for information on obtaining the X-windows version, PC version, or flatfile version. The EcoCyc WWW site provides background information about the DBs and software, and access to the publications produced by the EcoCyc project. Acknowledgments This work was supported by grant 1-R01-RR from the Comparative Medicine Program at the NIH National Center for Research Resources. The contents of this article are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. References [1] Karp,P.D. (2001) Pathway databases: A case study in computational symbolic theories. Science, 293, [2] Karp,P. and Paley,S. (1996) Integrated access to metabolic and genomic data. Journal of Computational Biology, 3, [3] Karp,P.D., Krummenacker,M., Paley,S., and Wagg,J. (1999) Integrated pathway/genome databases and their role in drug discovery. Trends in Biotechnology, 17, [4] Karp,P.D., Chaudhri,V.C., and Paley,S.M. (1999) A collaborative environment for authoring large knowledge bases. Journal of Intelligent Information Systems, 13, [5] Salgado,H., Santos-Zavaleta,A., Gama-Castro,S., Millan-Zarate,D., Diaz-Peredo,E., Sanchez-Solano,F., Pérez-Rueda,E., Bonavides-Martinez,C., and Collado-Vides,J. (2001) RegulonDB (version 3.2): transcriptional regulation and operon organization in Escherichia coli K 12. Nucleic Acids Res., 29, [6] Pérez-Rueda,E., and Collado-Vides,J. (2000) The repertoire of DNA-binding transcriptional regulators in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 28,
6 Object Class Object Count Pathways 165 Reactions 2604 Enzymes 905 Transporters 162 Genes 4393 Transcription Units 629 Promoters 740 DNA-Binding Transcriptional Regulators 100 DNA Binding Sites 854 Citations 3508 Table 1: The number of objects in version 5.6 of EcoCyc. 6
AN EVIDENCE ONTOLOGY FOR USE IN PATHWAY/GENOME DATABASES
 AN EVIDENCE ONTOLOGY FOR USE IN PATHWAY/GENOME DATABASES Appears in Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 2004 Pages 190-201, World Scientific Publishers, Singapore P.D. KARP, S. PALEY, C.J. KRIEGER SRI International,
AN EVIDENCE ONTOLOGY FOR USE IN PATHWAY/GENOME DATABASES Appears in Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing 2004 Pages 190-201, World Scientific Publishers, Singapore P.D. KARP, S. PALEY, C.J. KRIEGER SRI International,
This document describes the process by which operons are predicted for genes within the BioHealthBase database.
 1. Purpose This document describes the process by which operons are predicted for genes within the BioHealthBase database. 2. Methods Description An operon is a coexpressed set of genes, transcribed onto
1. Purpose This document describes the process by which operons are predicted for genes within the BioHealthBase database. 2. Methods Description An operon is a coexpressed set of genes, transcribed onto
Transitioning BioCyc to a Subscription Model
 Transitioning BioCyc to a Subscription Model Peter D. Karp SRI International ecocyc.org biocyc.org metacyc.org BioCyc.org Collection of 9,300 Pathway/Genome Databases Pathway/Genome Database (PGDB) combines
Transitioning BioCyc to a Subscription Model Peter D. Karp SRI International ecocyc.org biocyc.org metacyc.org BioCyc.org Collection of 9,300 Pathway/Genome Databases Pathway/Genome Database (PGDB) combines
Microbial computational genomics of gene regulation*
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 74, No. 6, pp. 899 905, 2002. 2002 IUPAC Microbial computational genomics of gene regulation* Julio Collado-Vides, Gabriel Moreno-Hagelsieb, and Arturo Medrano-Soto Program of Computational
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 74, No. 6, pp. 899 905, 2002. 2002 IUPAC Microbial computational genomics of gene regulation* Julio Collado-Vides, Gabriel Moreno-Hagelsieb, and Arturo Medrano-Soto Program of Computational
Pathway Bioinformatics: Inference, Visualization, and Analysis. Peter D. Karp, Ph.D.
 Pathway Bioinformatics: Inference, Visualization, and Analysis Peter D. Karp, Ph.D. Bioinformatics Research Group SRI International pkarp@ai.sri.com BioCyc.org EcoCyc.org, MetaCyc.org, HumanCyc.org 1 SRI
Pathway Bioinformatics: Inference, Visualization, and Analysis Peter D. Karp, Ph.D. Bioinformatics Research Group SRI International pkarp@ai.sri.com BioCyc.org EcoCyc.org, MetaCyc.org, HumanCyc.org 1 SRI
V19 Metabolic Networks - Overview
 V19 Metabolic Networks - Overview There exist different levels of computational methods for describing metabolic networks: - stoichiometry/kinetics of classical biochemical pathways (glycolysis, TCA cycle,...
V19 Metabolic Networks - Overview There exist different levels of computational methods for describing metabolic networks: - stoichiometry/kinetics of classical biochemical pathways (glycolysis, TCA cycle,...
V14 extreme pathways
 V14 extreme pathways A torch is directed at an open door and shines into a dark room... What area is lighted? Instead of marking all lighted points individually, it would be sufficient to characterize
V14 extreme pathways A torch is directed at an open door and shines into a dark room... What area is lighted? Instead of marking all lighted points individually, it would be sufficient to characterize
Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Genomic Arrangement of Regulons in Bacterial Genomes
 l Genomes Han Zhang 1,2., Yanbin Yin 1,3., Victor Olman 1, Ying Xu 1,3,4 * 1 Computational Systems Biology Laboratory, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology and Institute of Bioinformatics,
l Genomes Han Zhang 1,2., Yanbin Yin 1,3., Victor Olman 1, Ying Xu 1,3,4 * 1 Computational Systems Biology Laboratory, Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology and Institute of Bioinformatics,
Computational methods for the analysis of bacterial gene regulation Brouwer, Rutger Wubbe Willem
 University of Groningen Computational methods for the analysis of bacterial gene regulation Brouwer, Rutger Wubbe Willem IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Computational methods for the analysis of bacterial gene regulation Brouwer, Rutger Wubbe Willem IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
Evaluation of the relative contribution of each STRING feature in the overall accuracy operon classification
 Evaluation of the relative contribution of each STRING feature in the overall accuracy operon classification B. Taboada *, E. Merino 2, C. Verde 3 blanca.taboada@ccadet.unam.mx Centro de Ciencias Aplicadas
Evaluation of the relative contribution of each STRING feature in the overall accuracy operon classification B. Taboada *, E. Merino 2, C. Verde 3 blanca.taboada@ccadet.unam.mx Centro de Ciencias Aplicadas
Pathway Databases: A Case Study in Computational Symbolic Theories
 sponsors development of the information technology infrastructure necessary for a National Virtual Observatory (NVO). There is a close cooperation with the particle physics community through the Grid Physics
sponsors development of the information technology infrastructure necessary for a National Virtual Observatory (NVO). There is a close cooperation with the particle physics community through the Grid Physics
Proteomics Systems Biology
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Proteomics Systems Biology IIT Bombay 2 1 DNA Genomics RNA Transcriptomics Global Cellular Protein Proteomics Global Cellular Metabolite Metabolomics Global Cellular
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Proteomics Systems Biology IIT Bombay 2 1 DNA Genomics RNA Transcriptomics Global Cellular Protein Proteomics Global Cellular Metabolite Metabolomics Global Cellular
Introduction. Gene expression is the combined process of :
 1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
1 To know and explain: Regulation of Bacterial Gene Expression Constitutive ( house keeping) vs. Controllable genes OPERON structure and its role in gene regulation Regulation of Eukaryotic Gene Expression
INTERACTIVE CLUSTERING FOR EXPLORATION OF GENOMIC DATA
 INTERACTIVE CLUSTERING FOR EXPLORATION OF GENOMIC DATA XIUFENG WAN xw6@cs.msstate.edu Department of Computer Science Box 9637 JOHN A. BOYLE jab@ra.msstate.edu Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
INTERACTIVE CLUSTERING FOR EXPLORATION OF GENOMIC DATA XIUFENG WAN xw6@cs.msstate.edu Department of Computer Science Box 9637 JOHN A. BOYLE jab@ra.msstate.edu Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Exploring molecular networks using MONET ontology
 J.P.M. da Silva et al. 182 Exploring molecular networks using MONET ontology João Paulo Müller da Silva, Ney Lemke, José Carlos Mombach, José Guilherme Camargo de Souza, Marialva Sinigaglia and Renata
J.P.M. da Silva et al. 182 Exploring molecular networks using MONET ontology João Paulo Müller da Silva, Ney Lemke, José Carlos Mombach, José Guilherme Camargo de Souza, Marialva Sinigaglia and Renata
Bioinformatics. Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics
 Bioinformatics Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 3 Bioinformatics - play with sequences & structures Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 4 ORGANIZATION OF LIFE ROLE OF BIOINFORMATICS
Bioinformatics Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 3 Bioinformatics - play with sequences & structures Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 4 ORGANIZATION OF LIFE ROLE OF BIOINFORMATICS
Written Exam 15 December Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no
 Technical University of Denmark Written Exam 15 December 2008 Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no. 27041 Aids allowed: Open book exam Provide your answers and calculations on separate
Technical University of Denmark Written Exam 15 December 2008 Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no. 27041 Aids allowed: Open book exam Provide your answers and calculations on separate
A genomic-scale search for regulatory binding sites in the integration host factor regulon of Escherichia coli K12
 The integration host factor regulon of E. coli K12 genome 783 A genomic-scale search for regulatory binding sites in the integration host factor regulon of Escherichia coli K12 M. Trindade dos Santos and
The integration host factor regulon of E. coli K12 genome 783 A genomic-scale search for regulatory binding sites in the integration host factor regulon of Escherichia coli K12 M. Trindade dos Santos and
L3.1: Circuits: Introduction to Transcription Networks. Cellular Design Principles Prof. Jenna Rickus
 L3.1: Circuits: Introduction to Transcription Networks Cellular Design Principles Prof. Jenna Rickus In this lecture Cognitive problem of the Cell Introduce transcription networks Key processing network
L3.1: Circuits: Introduction to Transcription Networks Cellular Design Principles Prof. Jenna Rickus In this lecture Cognitive problem of the Cell Introduce transcription networks Key processing network
Gene Ontology and overrepresentation analysis
 Gene Ontology and overrepresentation analysis Kjell Petersen J Express Microarray analysis course Oslo December 2009 Presentation adapted from Endre Anderssen and Vidar Beisvåg NMC Trondheim Overview How
Gene Ontology and overrepresentation analysis Kjell Petersen J Express Microarray analysis course Oslo December 2009 Presentation adapted from Endre Anderssen and Vidar Beisvåg NMC Trondheim Overview How
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05
 1 Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05 Morris Levy Biological Sciences Research: Evolutionary Ecology, Plant- Fungal Pathogen Interactions Coordinator: BIOL 495S/CS490B/STAT490B Introduction
1 Introduction to Bioinformatics Integrated Science, 11/9/05 Morris Levy Biological Sciences Research: Evolutionary Ecology, Plant- Fungal Pathogen Interactions Coordinator: BIOL 495S/CS490B/STAT490B Introduction
Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology. Genome sequencing Assembly. Gene prediction. Protein targeting.
 Genome Annotation Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Genome Annotation Frank Oliver Glöckner 1 Genome Analysis Roadmap Genome sequencing Assembly Gene prediction Protein targeting trna prediction
Genome Annotation Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Genome Annotation Frank Oliver Glöckner 1 Genome Analysis Roadmap Genome sequencing Assembly Gene prediction Protein targeting trna prediction
Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Learn how bacteria respond to changes of metabolites in their environment: short-term and longer-term. 2. Compare and contrast transcriptional control
Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Learn how bacteria respond to changes of metabolites in their environment: short-term and longer-term. 2. Compare and contrast transcriptional control
UNIVERSITY OF YORK. BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations Department : BIOLOGY. Title of Exam: Molecular microbiology
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular microbiology Time Allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Marking
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Molecular microbiology Time Allowed: 1 hour 30 minutes Marking
Integration of Omics Data to Investigate Common Intervals
 2011 International Conference on Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics IPCBEE vol.5 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Integration of Omics Data to Investigate Common Intervals Sébastien Angibaud,
2011 International Conference on Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics IPCBEE vol.5 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Integration of Omics Data to Investigate Common Intervals Sébastien Angibaud,
3.B.1 Gene Regulation. Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization.
 3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
3.B.1 Gene Regulation Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. We will focus on gene regulation in prokaryotes first. Gene regulation accounts for some of
Course plan Academic Year Qualification MSc on Bioinformatics for Health Sciences. Subject name: Computational Systems Biology Code: 30180
 Course plan 201-201 Academic Year Qualification MSc on Bioinformatics for Health Sciences 1. Description of the subject Subject name: Code: 30180 Total credits: 5 Workload: 125 hours Year: 1st Term: 3
Course plan 201-201 Academic Year Qualification MSc on Bioinformatics for Health Sciences 1. Description of the subject Subject name: Code: 30180 Total credits: 5 Workload: 125 hours Year: 1st Term: 3
AP Bio Module 16: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide
 Name: Period: Date: AP Bio Module 6: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide Getting started. Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get
Name: Period: Date: AP Bio Module 6: Bacterial Genetics and Operons, Student Learning Guide Getting started. Work in pairs (share a computer). Make sure that you log in for the first quiz so that you get
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS M1: ALGORITHM TO RECONSTRUCT TRANSCRIPTIONAL NETWORKS M-2 Figure 1: Procedure to reconstruct transcriptional regulatory networks M-2 M2: PROCEDURE TO IDENTIFY ORTHOLOGOUS PROTEINSM-3
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS M1: ALGORITHM TO RECONSTRUCT TRANSCRIPTIONAL NETWORKS M-2 Figure 1: Procedure to reconstruct transcriptional regulatory networks M-2 M2: PROCEDURE TO IDENTIFY ORTHOLOGOUS PROTEINSM-3
86 Part 4 SUMMARY INTRODUCTION
 86 Part 4 Chapter # AN INTEGRATION OF THE DESCRIPTIONS OF GENE NETWORKS AND THEIR MODELS PRESENTED IN SIGMOID (CELLERATOR) AND GENENET Podkolodny N.L. *1, 2, Podkolodnaya N.N. 1, Miginsky D.S. 1, Poplavsky
86 Part 4 Chapter # AN INTEGRATION OF THE DESCRIPTIONS OF GENE NETWORKS AND THEIR MODELS PRESENTED IN SIGMOID (CELLERATOR) AND GENENET Podkolodny N.L. *1, 2, Podkolodnaya N.N. 1, Miginsky D.S. 1, Poplavsky
ATLAS of Biochemistry
 ATLAS of Biochemistry USER GUIDE http://lcsb-databases.epfl.ch/atlas/ CONTENT 1 2 3 GET STARTED Create your user account NAVIGATE Curated KEGG reactions ATLAS reactions Pathways Maps USE IT! Fill a gap
ATLAS of Biochemistry USER GUIDE http://lcsb-databases.epfl.ch/atlas/ CONTENT 1 2 3 GET STARTED Create your user account NAVIGATE Curated KEGG reactions ATLAS reactions Pathways Maps USE IT! Fill a gap
Supplemental Materials
 JOURNAL OF MICROBIOLOGY & BIOLOGY EDUCATION, May 2013, p. 107-109 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v14i1.496 Supplemental Materials for Engaging Students in a Bioinformatics Activity to Introduce Gene
JOURNAL OF MICROBIOLOGY & BIOLOGY EDUCATION, May 2013, p. 107-109 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/jmbe.v14i1.496 Supplemental Materials for Engaging Students in a Bioinformatics Activity to Introduce Gene
Conservation of Gene Co-Regulation between Two Prokaryotes: Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli
 116 Genome Informatics 16(1): 116 124 (2005) Conservation of Gene Co-Regulation between Two Prokaryotes: Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli Shujiro Okuda 1 Shuichi Kawashima 2 okuda@kuicr.kyoto-u.ac.jp
116 Genome Informatics 16(1): 116 124 (2005) Conservation of Gene Co-Regulation between Two Prokaryotes: Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli Shujiro Okuda 1 Shuichi Kawashima 2 okuda@kuicr.kyoto-u.ac.jp
Name: SBI 4U. Gene Expression Quiz. Overall Expectation:
 Gene Expression Quiz Overall Expectation: - Demonstrate an understanding of concepts related to molecular genetics, and how genetic modification is applied in industry and agriculture Specific Expectation(s):
Gene Expression Quiz Overall Expectation: - Demonstrate an understanding of concepts related to molecular genetics, and how genetic modification is applied in industry and agriculture Specific Expectation(s):
COMPARATIVE PATHWAY ANNOTATION WITH PROTEIN-DNA INTERACTION AND OPERON INFORMATION VIA GRAPH TREE DECOMPOSITION
 COMPARATIVE PATHWAY ANNOTATION WITH PROTEIN-DNA INTERACTION AND OPERON INFORMATION VIA GRAPH TREE DECOMPOSITION JIZHEN ZHAO, DONGSHENG CHE AND LIMING CAI Department of Computer Science, University of Georgia,
COMPARATIVE PATHWAY ANNOTATION WITH PROTEIN-DNA INTERACTION AND OPERON INFORMATION VIA GRAPH TREE DECOMPOSITION JIZHEN ZHAO, DONGSHENG CHE AND LIMING CAI Department of Computer Science, University of Georgia,
Biological Pathways Representation by Petri Nets and extension
 Biological Pathways Representation by and extensions December 6, 2006 Biological Pathways Representation by and extension 1 The cell Pathways 2 Definitions 3 4 Biological Pathways Representation by and
Biological Pathways Representation by and extensions December 6, 2006 Biological Pathways Representation by and extension 1 The cell Pathways 2 Definitions 3 4 Biological Pathways Representation by and
Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
 Why? Control of Expression in Prokaryotes How do prokaryotes use operons to control gene expression? Houses usually have a light source in every room, but it would be a waste of energy to leave every light
Why? Control of Expression in Prokaryotes How do prokaryotes use operons to control gene expression? Houses usually have a light source in every room, but it would be a waste of energy to leave every light
Essentiality in B. subtilis
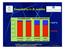 Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Regulation of gene expression. Premedical - Biology
 Regulation of gene expression Premedical - Biology Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cell Operon units system of negative feedback positive and negative regulation in eukaryotic cell - at any
Regulation of gene expression Premedical - Biology Regulation of gene expression in prokaryotic cell Operon units system of negative feedback positive and negative regulation in eukaryotic cell - at any
Gene Network Science Diagrammatic Cell Language and Visual Cell
 Gene Network Science Diagrammatic Cell Language and Visual Cell Mr. Tan Chee Meng Scientific Programmer, System Biology Group, Bioinformatics Institute Overview Introduction Why? Challenges Diagrammatic
Gene Network Science Diagrammatic Cell Language and Visual Cell Mr. Tan Chee Meng Scientific Programmer, System Biology Group, Bioinformatics Institute Overview Introduction Why? Challenges Diagrammatic
Welcome to Class 21!
 Welcome to Class 21! Introductory Biochemistry! Lecture 21: Outline and Objectives l Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes! l transcriptional regulation! l principles! l lac operon! l trp attenuation!
Welcome to Class 21! Introductory Biochemistry! Lecture 21: Outline and Objectives l Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes! l transcriptional regulation! l principles! l lac operon! l trp attenuation!
V14 Graph connectivity Metabolic networks
 V14 Graph connectivity Metabolic networks In the first half of this lecture section, we use the theory of network flows to give constructive proofs of Menger s theorem. These proofs lead directly to algorithms
V14 Graph connectivity Metabolic networks In the first half of this lecture section, we use the theory of network flows to give constructive proofs of Menger s theorem. These proofs lead directly to algorithms
Identification and annotation of promoter regions in microbial genome sequences on the basis of DNA stability
 Annotation of promoter regions in microbial genomes 851 Identification and annotation of promoter regions in microbial genome sequences on the basis of DNA stability VETRISELVI RANGANNAN and MANJU BANSAL*
Annotation of promoter regions in microbial genomes 851 Identification and annotation of promoter regions in microbial genome sequences on the basis of DNA stability VETRISELVI RANGANNAN and MANJU BANSAL*
Outline. Terminologies and Ontologies. Communication and Computation. Communication. Outline. Terminologies and Vocabularies.
 Page 1 Outline 1. Why do we need terminologies and ontologies? Terminologies and Ontologies Iwei Yeh yeh@smi.stanford.edu 04/16/2002 2. Controlled Terminologies Enzyme Classification Gene Ontology 3. Ontologies
Page 1 Outline 1. Why do we need terminologies and ontologies? Terminologies and Ontologies Iwei Yeh yeh@smi.stanford.edu 04/16/2002 2. Controlled Terminologies Enzyme Classification Gene Ontology 3. Ontologies
Bacterial Genetics & Operons
 Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Bacterial Genetics & Operons The Bacterial Genome Because bacteria have simple genomes, they are used most often in molecular genetics studies Most of what we know about bacterial genetics comes from the
Chapter 16 Lecture. Concepts Of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
 Chapter 16 Lecture Concepts Of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Chapter Contents 16.1 Prokaryotes Regulate Gene Expression in Response to Environmental Conditions 16.2
Chapter 16 Lecture Concepts Of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Chapter Contents 16.1 Prokaryotes Regulate Gene Expression in Response to Environmental Conditions 16.2
Computational Cell Biology Lecture 4
 Computational Cell Biology Lecture 4 Case Study: Basic Modeling in Gene Expression Yang Cao Department of Computer Science DNA Structure and Base Pair Gene Expression Gene is just a small part of DNA.
Computational Cell Biology Lecture 4 Case Study: Basic Modeling in Gene Expression Yang Cao Department of Computer Science DNA Structure and Base Pair Gene Expression Gene is just a small part of DNA.
BIOINFORMATICS: An Introduction
 BIOINFORMATICS: An Introduction What is Bioinformatics? The term was first coined in 1988 by Dr. Hwa Lim The original definition was : a collective term for data compilation, organisation, analysis and
BIOINFORMATICS: An Introduction What is Bioinformatics? The term was first coined in 1988 by Dr. Hwa Lim The original definition was : a collective term for data compilation, organisation, analysis and
networks in molecular biology Wolfgang Huber
 networks in molecular biology Wolfgang Huber networks in molecular biology Regulatory networks: components = gene products interactions = regulation of transcription, translation, phosphorylation... Metabolic
networks in molecular biology Wolfgang Huber networks in molecular biology Regulatory networks: components = gene products interactions = regulation of transcription, translation, phosphorylation... Metabolic
Introduction Biology before Systems Biology: Reductionism Reduce the study from the whole organism to inner most details like protein or the DNA.
 Systems Biology-Models and Approaches Introduction Biology before Systems Biology: Reductionism Reduce the study from the whole organism to inner most details like protein or the DNA. Taxonomy Study external
Systems Biology-Models and Approaches Introduction Biology before Systems Biology: Reductionism Reduce the study from the whole organism to inner most details like protein or the DNA. Taxonomy Study external
Regulation and signaling. Overview. Control of gene expression. Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on
 Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Regulation and signaling Overview Cells need to regulate the amounts of different proteins they express, depending on cell development (skin vs liver cell) cell stage environmental conditions (food, temperature,
Networks & pathways. Hedi Peterson MTAT Bioinformatics
 Networks & pathways Hedi Peterson (peterson@quretec.com) MTAT.03.239 Bioinformatics 03.11.2010 Networks are graphs Nodes Edges Edges Directed, undirected, weighted Nodes Genes Proteins Metabolites Enzymes
Networks & pathways Hedi Peterson (peterson@quretec.com) MTAT.03.239 Bioinformatics 03.11.2010 Networks are graphs Nodes Edges Edges Directed, undirected, weighted Nodes Genes Proteins Metabolites Enzymes
Types of biological networks. I. Intra-cellurar networks
 Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Types of biological networks I. Intra-cellurar networks 1 Some intra-cellular networks: 1. Metabolic networks 2. Transcriptional regulation networks 3. Cell signalling networks 4. Protein-protein interaction
Development of a Cell Signaling Networks Database. Division of Chem-Bio Informatics, National Institute of Health Sciences,
 Development of a Cell Signaling Networks Database TAKAKO IGARASHI and TSUGUCHIKA KAMINUMA Division of Chem-Bio Informatics, National Institute of Health Sciences, 1-18-1 Kami-Yoga, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo 158,
Development of a Cell Signaling Networks Database TAKAKO IGARASHI and TSUGUCHIKA KAMINUMA Division of Chem-Bio Informatics, National Institute of Health Sciences, 1-18-1 Kami-Yoga, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo 158,
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Systems biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Systems biology: modeling biological p Study of whole biological systems p Wholeness : Organization of dynamic interactions Different behaviour of the individual
Systems biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Systems biology: modeling biological p Study of whole biological systems p Wholeness : Organization of dynamic interactions Different behaviour of the individual
Analysis of Escherichia coli amino acid transporters
 Ph.D thesis Analysis of Escherichia coli amino acid transporters Presented by Attila Szvetnik Supervisor: Dr. Miklós Kálmán Biology Ph.D School University of Szeged Bay Zoltán Foundation for Applied Research
Ph.D thesis Analysis of Escherichia coli amino acid transporters Presented by Attila Szvetnik Supervisor: Dr. Miklós Kálmán Biology Ph.D School University of Szeged Bay Zoltán Foundation for Applied Research
GOSAP: Gene Ontology Based Semantic Alignment of Biological Pathways
 GOSAP: Gene Ontology Based Semantic Alignment of Biological Pathways Jonas Gamalielsson and Björn Olsson Systems Biology Group, Skövde University, Box 407, Skövde, 54128, Sweden, [jonas.gamalielsson][bjorn.olsson]@his.se,
GOSAP: Gene Ontology Based Semantic Alignment of Biological Pathways Jonas Gamalielsson and Björn Olsson Systems Biology Group, Skövde University, Box 407, Skövde, 54128, Sweden, [jonas.gamalielsson][bjorn.olsson]@his.se,
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm
 Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
Microbiome Metabolic Modeling with Pathway Tools
 Microbiome Metabolic Modeling with Pathway Tools Peter D. Karp SRI International Cost for High Quality Models of 300 Microbiome Organisms Mul/ple body sites of human, mouse, farm animals 500 species in
Microbiome Metabolic Modeling with Pathway Tools Peter D. Karp SRI International Cost for High Quality Models of 300 Microbiome Organisms Mul/ple body sites of human, mouse, farm animals 500 species in
BioControl - Week 6, Lecture 1
 BioControl - Week 6, Lecture 1 Goals of this lecture Large metabolic networks organization Design principles for small genetic modules - Rules based on gene demand - Rules based on error minimization Suggested
BioControl - Week 6, Lecture 1 Goals of this lecture Large metabolic networks organization Design principles for small genetic modules - Rules based on gene demand - Rules based on error minimization Suggested
EcoCyc: Encyclopedia of E. coli Genes and Metabolism
 EcoCyc: Encyclopedia of E. coli Genes and Metabolism Peter D. Karp, Monica Riley, Suzanne M. Paley, Alida Pellegrini-Toole, Markus Krummenacker November 8, 2001 Pangea Systems Inc, 4040 Campbell Ave.,
EcoCyc: Encyclopedia of E. coli Genes and Metabolism Peter D. Karp, Monica Riley, Suzanne M. Paley, Alida Pellegrini-Toole, Markus Krummenacker November 8, 2001 Pangea Systems Inc, 4040 Campbell Ave.,
2 Genome evolution: gene fusion versus gene fission
 2 Genome evolution: gene fusion versus gene fission Berend Snel, Peer Bork and Martijn A. Huynen Trends in Genetics 16 (2000) 9-11 13 Chapter 2 Introduction With the advent of complete genome sequencing,
2 Genome evolution: gene fusion versus gene fission Berend Snel, Peer Bork and Martijn A. Huynen Trends in Genetics 16 (2000) 9-11 13 Chapter 2 Introduction With the advent of complete genome sequencing,
Predicting Protein Functions and Domain Interactions from Protein Interactions
 Predicting Protein Functions and Domain Interactions from Protein Interactions Fengzhu Sun, PhD Center for Computational and Experimental Genomics University of Southern California Outline High-throughput
Predicting Protein Functions and Domain Interactions from Protein Interactions Fengzhu Sun, PhD Center for Computational and Experimental Genomics University of Southern California Outline High-throughput
GENE REGULATION AND PROBLEMS OF DEVELOPMENT
 GENE REGULATION AND PROBLEMS OF DEVELOPMENT By Surinder Kaur DIET Ropar Surinder_1998@ yahoo.in Mob No 9988530775 GENE REGULATION Gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a unit of function (polypeptide,
GENE REGULATION AND PROBLEMS OF DEVELOPMENT By Surinder Kaur DIET Ropar Surinder_1998@ yahoo.in Mob No 9988530775 GENE REGULATION Gene is a segment of DNA that codes for a unit of function (polypeptide,
Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p
 Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p.110-114 Arrangement of information in DNA----- requirements for RNA Common arrangement of protein-coding genes in prokaryotes=
Organization of Genes Differs in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Chapter 10 p.110-114 Arrangement of information in DNA----- requirements for RNA Common arrangement of protein-coding genes in prokaryotes=
Thiago M Venancio and L Aravind
 Minireview Reconstructing prokaryotic transcriptional regulatory networks: lessons from actinobacteria Thiago M Venancio and L Aravind Address: National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Library
Minireview Reconstructing prokaryotic transcriptional regulatory networks: lessons from actinobacteria Thiago M Venancio and L Aravind Address: National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Library
The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil PHY498BIO, HW 3
 The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil Rajaraman(rajaramn@uiuc.edu) PHY498BIO, HW 3 The number of genes in organisms varies from around 480 (for parasitic bacterium Mycoplasma genitalium) to the order of 100,000
The Minimal-Gene-Set -Kapil Rajaraman(rajaramn@uiuc.edu) PHY498BIO, HW 3 The number of genes in organisms varies from around 480 (for parasitic bacterium Mycoplasma genitalium) to the order of 100,000
CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016)
 CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016) Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions CISC636, F16, Lec22, Liao 1 Background Proteins do not function as isolated entities. Protein-Protein
CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016) Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions CISC636, F16, Lec22, Liao 1 Background Proteins do not function as isolated entities. Protein-Protein
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION. Bacterial Genetics Lac and Trp Operon
 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION Bacterial Genetics Lac and Trp Operon Levels of Metabolic Control The amount of cellular products can be controlled by regulating: Enzyme activity: alters protein function
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION Bacterial Genetics Lac and Trp Operon Levels of Metabolic Control The amount of cellular products can be controlled by regulating: Enzyme activity: alters protein function
CSCE555 Bioinformatics. Protein Function Annotation
 CSCE555 Bioinformatics Protein Function Annotation Why we need to do function annotation? Fig from: Network-based prediction of protein function. Molecular Systems Biology 3:88. 2007 What s function? The
CSCE555 Bioinformatics Protein Function Annotation Why we need to do function annotation? Fig from: Network-based prediction of protein function. Molecular Systems Biology 3:88. 2007 What s function? The
Computational Genomics. Reconstructing dynamic regulatory networks in multiple species
 02-710 Computational Genomics Reconstructing dynamic regulatory networks in multiple species Methods for reconstructing networks in cells CRH1 SLT2 SLR3 YPS3 YPS1 Amit et al Science 2009 Pe er et al Recomb
02-710 Computational Genomics Reconstructing dynamic regulatory networks in multiple species Methods for reconstructing networks in cells CRH1 SLT2 SLR3 YPS3 YPS1 Amit et al Science 2009 Pe er et al Recomb
BSc MATHEMATICAL SCIENCE
 Overview College of Science Modules Electives May 2018 (2) BSc MATHEMATICAL SCIENCE BSc Mathematical Science Degree 2018 1 College of Science, NUI Galway Fullscreen Next page Overview [60 Credits] [60
Overview College of Science Modules Electives May 2018 (2) BSc MATHEMATICAL SCIENCE BSc Mathematical Science Degree 2018 1 College of Science, NUI Galway Fullscreen Next page Overview [60 Credits] [60
Name Period The Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Notes
 Bacterial DNA contains genes that encode for many different proteins (enzymes) so that many processes have the ability to occur -not all processes are carried out at any one time -what allows expression
Bacterial DNA contains genes that encode for many different proteins (enzymes) so that many processes have the ability to occur -not all processes are carried out at any one time -what allows expression
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Advanced Higher Biology. Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins
 Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Advanced Higher Biology Unit 1- Cells and Proteins 2c) Membrane Proteins Membrane Structure Phospholipid bilayer Transmembrane protein Integral protein Movement of Molecules Across Membranes Phospholipid
Topic 4 - #14 The Lactose Operon
 Topic 4 - #14 The Lactose Operon The Lactose Operon The lactose operon is an operon which is responsible for the transport and metabolism of the sugar lactose in E. coli. - Lactose is one of many organic
Topic 4 - #14 The Lactose Operon The Lactose Operon The lactose operon is an operon which is responsible for the transport and metabolism of the sugar lactose in E. coli. - Lactose is one of many organic
METABOLIC PATHWAY PREDICTION/ALIGNMENT
 COMPUTATIONAL SYSTEMIC BIOLOGY METABOLIC PATHWAY PREDICTION/ALIGNMENT Hofestaedt R*, Chen M Bioinformatics / Medical Informatics, Technische Fakultaet, Universitaet Bielefeld Postfach 10 01 31, D-33501
COMPUTATIONAL SYSTEMIC BIOLOGY METABOLIC PATHWAY PREDICTION/ALIGNMENT Hofestaedt R*, Chen M Bioinformatics / Medical Informatics, Technische Fakultaet, Universitaet Bielefeld Postfach 10 01 31, D-33501
SCOTCAT Credits: 20 SCQF Level 7 Semester 1 Academic year: 2018/ am, Practical classes one per week pm Mon, Tue, or Wed
 Biology (BL) modules BL1101 Biology 1 SCOTCAT Credits: 20 SCQF Level 7 Semester 1 10.00 am; Practical classes one per week 2.00-5.00 pm Mon, Tue, or Wed This module is an introduction to molecular and
Biology (BL) modules BL1101 Biology 1 SCOTCAT Credits: 20 SCQF Level 7 Semester 1 10.00 am; Practical classes one per week 2.00-5.00 pm Mon, Tue, or Wed This module is an introduction to molecular and
BMC Systems Biology. Open Access. Abstract. BioMed Central
 BMC Systems Biology BioMed Central Research article Comparative analysis of the transcription-factor gene regulatory networks of and Lev Guzmán-Vargas* and Moisés Santillán 2,3 Open Access Address: Unidad
BMC Systems Biology BioMed Central Research article Comparative analysis of the transcription-factor gene regulatory networks of and Lev Guzmán-Vargas* and Moisés Santillán 2,3 Open Access Address: Unidad
Boolean models of gene regulatory networks. Matthew Macauley Math 4500: Mathematical Modeling Clemson University Spring 2016
 Boolean models of gene regulatory networks Matthew Macauley Math 4500: Mathematical Modeling Clemson University Spring 2016 Gene expression Gene expression is a process that takes gene info and creates
Boolean models of gene regulatory networks Matthew Macauley Math 4500: Mathematical Modeling Clemson University Spring 2016 Gene expression Gene expression is a process that takes gene info and creates
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Learn how bacteria respond to changes of metabolites in their environment: short-term and longer-term. 2. Compare and contrast transcriptional control
Prokaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Learn how bacteria respond to changes of metabolites in their environment: short-term and longer-term. 2. Compare and contrast transcriptional control
Elucidation of the sequential transcriptional activity in Escherichia coli using time-series RNA-seq data
 www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(1) Hypothesis Elucidation of the sequential transcriptional activity in Escherichia coli using time-series RNA-seq data Pui Shan Wong 1, Kosuke Tashiro 2, Satoru Kuhara
www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(1) Hypothesis Elucidation of the sequential transcriptional activity in Escherichia coli using time-series RNA-seq data Pui Shan Wong 1, Kosuke Tashiro 2, Satoru Kuhara
BEFORE TAKING THIS MODULE YOU MUST ( TAKE BIO-4013Y OR TAKE BIO-
 2018/9 - BIO-4001A BIODIVERSITY Autumn Semester, Level 4 module (Maximum 150 Students) Organiser: Dr Harriet Jones Timetable Slot:DD This module explores life on Earth. You will be introduced to the major
2018/9 - BIO-4001A BIODIVERSITY Autumn Semester, Level 4 module (Maximum 150 Students) Organiser: Dr Harriet Jones Timetable Slot:DD This module explores life on Earth. You will be introduced to the major
Introduction to Bioinformatics. Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr Lecture Outline: Technical Course Items Introduction to Bioinformatics Introduction to Databases This week and next week What is bioinformatics? A
Introduction to Bioinformatics Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr Lecture Outline: Technical Course Items Introduction to Bioinformatics Introduction to Databases This week and next week What is bioinformatics? A
Unit 3: Control and regulation Higher Biology
 Unit 3: Control and regulation Higher Biology To study the roles that genes play in the control of growth and development of organisms To be able to Give some examples of features which are controlled
Unit 3: Control and regulation Higher Biology To study the roles that genes play in the control of growth and development of organisms To be able to Give some examples of features which are controlled
Regulation of Transcription in Eukaryotes. Nelson Saibo
 Regulation of Transcription in Eukaryotes Nelson Saibo saibo@itqb.unl.pt In eukaryotes gene expression is regulated at different levels 1 - Transcription 2 Post-transcriptional modifications 3 RNA transport
Regulation of Transcription in Eukaryotes Nelson Saibo saibo@itqb.unl.pt In eukaryotes gene expression is regulated at different levels 1 - Transcription 2 Post-transcriptional modifications 3 RNA transport
STRING: Protein association networks. Lars Juhl Jensen
 STRING: Protein association networks Lars Juhl Jensen interaction networks association networks guilt by association protein networks STRING 9.6 million proteins common foundation Exercise 1 Go to http://string-db.org/
STRING: Protein association networks Lars Juhl Jensen interaction networks association networks guilt by association protein networks STRING 9.6 million proteins common foundation Exercise 1 Go to http://string-db.org/
# shared OGs (spa, spb) Size of the smallest genome. dist (spa, spb) = 1. Neighbor joining. OG1 OG2 OG3 OG4 sp sp sp
 Bioinformatics and Evolutionary Genomics: Genome Evolution in terms of Gene Content 3/10/2014 1 Gene Content Evolution What about HGT / genome sizes? Genome trees based on gene content: shared genes Haemophilus
Bioinformatics and Evolutionary Genomics: Genome Evolution in terms of Gene Content 3/10/2014 1 Gene Content Evolution What about HGT / genome sizes? Genome trees based on gene content: shared genes Haemophilus
Sequence Alignment Techniques and Their Uses
 Sequence Alignment Techniques and Their Uses Sarah Fiorentino Since rapid sequencing technology and whole genomes sequencing, the amount of sequence information has grown exponentially. With all of this
Sequence Alignment Techniques and Their Uses Sarah Fiorentino Since rapid sequencing technology and whole genomes sequencing, the amount of sequence information has grown exponentially. With all of this
CHAPTER : Prokaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
CHAPTER 13.3 13.5: Prokaryotic Genetics 1. Most bacteria are not pathogenic. Identify several important roles they play in the ecosystem and human culture. 2. How do variations arise in bacteria considering
Biological Networks. Gavin Conant 163B ASRC
 Biological Networks Gavin Conant 163B ASRC conantg@missouri.edu 882-2931 Types of Network Regulatory Protein-interaction Metabolic Signaling Co-expressing General principle Relationship between genes Gene/protein/enzyme
Biological Networks Gavin Conant 163B ASRC conantg@missouri.edu 882-2931 Types of Network Regulatory Protein-interaction Metabolic Signaling Co-expressing General principle Relationship between genes Gene/protein/enzyme
REVIEW SESSION. Wednesday, September 15 5:30 PM SHANTZ 242 E
 REVIEW SESSION Wednesday, September 15 5:30 PM SHANTZ 242 E Gene Regulation Gene Regulation Gene expression can be turned on, turned off, turned up or turned down! For example, as test time approaches,
REVIEW SESSION Wednesday, September 15 5:30 PM SHANTZ 242 E Gene Regulation Gene Regulation Gene expression can be turned on, turned off, turned up or turned down! For example, as test time approaches,
Bioinformatics Exercises
 Bioinformatics Exercises AP Biology Teachers Workshop Susan Cates, Ph.D. Evolution of Species Phylogenetic Trees show the relatedness of organisms Common Ancestor (Root of the tree) 1 Rooted vs. Unrooted
Bioinformatics Exercises AP Biology Teachers Workshop Susan Cates, Ph.D. Evolution of Species Phylogenetic Trees show the relatedness of organisms Common Ancestor (Root of the tree) 1 Rooted vs. Unrooted
Topic 4: Equilibrium binding and chemical kinetics
 Topic 4: Equilibrium binding and chemical kinetics Outline: Applications, applications, applications use Boltzmann to look at receptor-ligand binding use Boltzmann to look at PolII-DNA binding and gene
Topic 4: Equilibrium binding and chemical kinetics Outline: Applications, applications, applications use Boltzmann to look at receptor-ligand binding use Boltzmann to look at PolII-DNA binding and gene
Lecture 4: Transcription networks basic concepts
 Lecture 4: Transcription networks basic concepts - Activators and repressors - Input functions; Logic input functions; Multidimensional input functions - Dynamics and response time 2.1 Introduction The
Lecture 4: Transcription networks basic concepts - Activators and repressors - Input functions; Logic input functions; Multidimensional input functions - Dynamics and response time 2.1 Introduction The
CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS
 CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS PRBS 131 BIOSCI131 CELL BIOLOGY 3 units 3 hours lec Course Number Course Title Descriptive Title Credit Unit(s) Hour(s)/Week
CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS PRBS 131 BIOSCI131 CELL BIOLOGY 3 units 3 hours lec Course Number Course Title Descriptive Title Credit Unit(s) Hour(s)/Week
BMD645. Integration of Omics
 BMD645 Integration of Omics Shu-Jen Chen, Chang Gung University Dec. 11, 2009 1 Traditional Biology vs. Systems Biology Traditional biology : Single genes or proteins Systems biology: Simultaneously study
BMD645 Integration of Omics Shu-Jen Chen, Chang Gung University Dec. 11, 2009 1 Traditional Biology vs. Systems Biology Traditional biology : Single genes or proteins Systems biology: Simultaneously study
