Chapter 01: Microbes Shape Our History
|
|
|
- Anthony Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 01: Microbes Shape Our History MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following is NOT considered a benefit of microorganisms? a. nitrogen fixation c. synthesis of vitamins b. production of fermented foods d. causative agents of disease D DIF: Easy REF: 1.1 OBJ: 1.1a Describe how we define a microbe, and explain why the definition is a challenge. 2. A microbe that is 50 nm in size would most likely be a. fungi. c. virus. b. E. coli. d. algae. C DIF: Moderate REF: 1.1 what the three domains have in common and how they differ. 3. Based on the figure shown, the type of organism indicated with an arrow could be a a. virus. c. macroscopic fungi. b. bacteria. d. large ameba. B DIF: Easy REF: 1.1 what the three domains have in common and how they differ. 4. Based on the figure, the type of organism shown is a(n)
2 a. virus. c. archaea. b. bacteria. d. eukaryote. D DIF: Moderate REF: 1.1 what the three domains have in common and how they differ. 5. Which of the following demonstrates correct scientific notation of a bacterial organism? a. Staphylococcus Epidermidis c. Staphylococcus epidermidis b. Staphylococcus epidermidis d. Staphylococcus Epidermidis C DIF: Easy REF: 1.1 what the three domains have in common and how they differ. 6. Which key characteristic differentiates a prokaryote from a eukaryote? a. the absence of proteins b. the presence of DNA c. the absence of membrane-bound organelles d. the presence of a cell wall C DIF: Easy REF: 1.1 what the three domains have in common and how they differ. 7. Which of the following methods for classifying life forms can best be used to distinguish between two closely related rod-shaped bacterial organisms, Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli? a. physical characteristics c. DNA sequence comparison b. method of reproduction d. environmental habitat C DIF: Moderate REF: 1.1 what the three domains have in common and how they differ. 8. Which of the following is always classified as a eukaryote? a. papillomavirus c. Escherichia coli b. methanogen d. yeast D DIF: Moderate REF: 1.1 what the three domains have in common and how they differ.
3 9. Which of the following has been used as a tool for gene therapy? a. viruses c. protozoa b. archaea d. fungi A DIF: Easy REF: 1.1 what the three domains have in common and how they differ. 10. Which of the following would you not expect to find in the human digestive tract? a. archaea c. bacteria b. algae d. intestinal viruses B DIF: Moderate REF: 1.1 what the three domains have in common and how they differ. 11. Antibiotics are chemotherapeutic drugs that function by inhibiting an important cellular structure or process of an organism that is causing an infection. Which of the following would not be affected by an antibiotic that targets cellular metabolic enzymes? a. Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria c. ameba b. Herpes virus d. bread mold B DIF: Moderate REF: 1.1 OBJ: 1.1c Define viruses, and explain how they relate to living cells. MSC: Analyzing 12. Which scientist is credited with constructing the first microscope? a. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek c. Robert Hooke b. Catherine of Siena d. Louis Pasteur C DIF: Easy REF: 1.2 OBJ: 1.2a Explain how microbial diseases have changed human history. 13. Which of the following was an unexpected benefit of the bubonic plague? a. There was no benefit to the bubonic plague. b. The population of Europe experienced a baby boom. c. It resulted in a better understanding of aseptic practices and how to prevent the spread of infection. d. The population decline enabled the cultural advancement of the Renaissance. D DIF: Easy REF: 1.2 OBJ: 1.2a Explain how microbial diseases have changed human history. 14. Which of the following organisms would you NOT be able to see using Robert Hooke s microscope? a. vinegar eels c. mold filaments b. dust mites d. Mycobacterium tuberculosis D DIF: Moderate REF: 1.2 OBJ: 1.2a Explain how microbial diseases have changed human history.
4 15. Which of the following is NOT an explanation for the centuries it took between Leeuwenhoek observing microorganisms with his microscope and the discovery that microbes are capable of causing disease? a. Microbes are found everywhere. b. Bacteria appeared similar to sperm and blood cells under the microscope. c. Microorganisms are capable of existing through spontaneous generation. d. Diseases were not a problem in the world until long after the discovery of microorganisms. D DIF: Moderate REF: 1.2 OBJ: 1.2a Explain how microbial diseases have changed human history. 16. If Spallanzani had unknowingly poked a hole in the top of his flask of meat broth, what would this have implied about the theory of spontaneous generation? a. No growth would have occurred in the flask, refuting the theory of spontaneous generation. b. No growth would have occurred in the flask, supporting the theory of spontaneous generation. c. Growth would have occurred in the flask, refuting the theory of spontaneous generation. d. Growth would have occurred in the flask, supporting the theory of spontaneous generation. D DIF: Difficult REF: 1.2 OBJ: 1.2b Describe how microbes participate in human cultural practices such as production of food and drink. 17. What would John Tyndall have needed to use to disprove the theory of spontaneous generation with his experiments? a. a swan-neck flask c. an autoclave b. a microscope d. organic media C DIF: Moderate REF: 1.2 OBJ: 1.2b Describe how microbes participate in human cultural practices such as production of food and drink. 18. Which of the following theories was the Miller experiment designed to test? a. the endosymbiotic origin of life b. the idea that all the chemicals found in early Earth could have come together to form the basic components of cellular life c. spontaneous generation d. the RNA world hypothesis B DIF: Moderate REF: 1.2 OBJ: 1.2a Explain how microbial diseases have changed human history. 19. Why did fewer soldiers die from infectious disease during the Crimean War in the winter months? a. Pathogens do not multiply as quickly in colder temperatures. b. Pathogens do not multiply as quickly in wet environments. c. Soldiers have fewer close interactions with other individuals during the winter months. d. Chemical agents used to treat and prevent infections do not function effectively in warmer temperatures. A DIF: Moderate REF: 1.3 OBJ: 1.3b Explain how Florence Nightingale first drew a statistical correlation between
5 infectious disease and human mortality. 20. Based on the figure below, approximately what percentage of the hospitalizations in week 43 resulted in deaths? a. 80% c. 20% b. 40% d. 4% D DIF: Moderate REF: 1.3 OBJ: 1.3b Explain how Florence Nightingale first drew a statistical correlation between infectious disease and human mortality. MSC: Analyzing 21. What is the causative agent of the infectious disease used to establish Koch s postulates? a. Streptococcus pyogenes c. Helicobacter pylori b. Bacillus anthracis d. Chlamydia trachomatis B DIF: Easy REF: Why was the selection of anthrax by Robert Koch a fortunate one? a. The microbe that causes it multiplies slowly. b. The microbe that causes it multiplies to a high concentration in the kidneys. c. The microbe that causes it is not dangerous to humans. d. The microbe that causes it can remain infective outside the body for long periods. D DIF: Moderate REF: The arrow in the figure shows a(n)
6 a. gelatin suspension. c. colony. b. endospore. d. cell. C DIF: Easy REF: The first vaccination was done to prevent a. AIDS. c. tuberculosis. b. smallpox. d. anthrax. B DIF: Easy REF: Which of the following techniques is effective in creating an attenuated version of a pathogen useful for vaccinations? a. putting a liquid culture of the pathogen in the freezer b. heating an aged culture of the pathogen c. homogenizing a culture of the pathogen d. exposing a culture of the pathogen to nuclear radiation B DIF: Easy REF: Regarding the natural source for the production of antibiotics, the best weapon we have against pathogenic microorganisms is a. medical doctors. b. acclaimed scientific researchers. c. other microorganisms that can exist with the pathogenic microorganisms. d. the CDC. C DIF: Moderate REF: 1.3
7 27. What is happening in the figure shown? a. The mold on the left is producing a compound that inhibits the growth of the bacterial colonies on the right. b. The mold on the left is outcompeting the bacterial cells for nutrients and therefore is growing faster. c. The bacterial cells on the right are inhibiting the growth of the mold on the left. d. The mold and bacterial cells are growing in a symbiotic relationship. A DIF: Moderate REF: Warts are a common skin condition caused by an organism that cannot be grown in pure culture on an agar petri dish and is small enough to pass through a tiny-pored filter. What is the causative agent of warts? a. a bacterium c. an archaea b. a virus d. a fungus B DIF: Moderate REF: Thiobacillus ferrooxidans is a microorganism that gains its energy from the oxidation of ferrous iron (Fe 2 ) to ferric iron (Fe 3 ) and hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S) to sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4 ). Based on this information, T. ferrooxidans is an example of a a. nitrogen fixer. c. endosymbiont. b. lithotroph. d. biofilm participant. B DIF: Moderate REF: 1.4 OBJ: 1.4a Describe examples of how microbes contribute to natural ecosystems. 30. A microbial growth medium for Staphylococcus aureus is prepared with a high salt concentration to minimize the growth of many organisms that are not capable of growth in these conditions. This is an example of a. animal culture. c. pure culture. b. endosymbiosis. d. enrichment culture. D DIF: Moderate REF: 1.4
8 OBJ: 1.4a Describe examples of how microbes contribute to natural ecosystems. 31. Which of the following is NOT an example of an endosymbiont? a. Bacillus anthracis spores present in the soil of cattle farms b. rhizobial bacteria growing in the root nodules of certain plants c. microorganisms in the digestive system of the cow degrading cellulose d. bacteria in termite intestines digesting plant polymers A DIF: Moderate REF: 1.4 OBJ: 1.4a Describe examples of how microbes contribute to natural ecosystems. 32. Consider the figure below. What does the arrow pointing from cyanobacteria to plants and algae indicate according to the endosymbiotic origin of eukaryotic cells? a. Cyanobacteria are the early evolutionary ancestors of plants and algae. b. Cyanobacteria merged together to form plants and algae. c. Cyanobacteria serve as a common source of energy for plants and algae. d. Cyanobacteria were internalized by early cells to form the chloroplast present in plants and algae. D DIF: Difficult REF: 1.4 OBJ: 1.4b Explain how mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved by endosymbiosis. MSC: Analyzing 33. According to the endosymbiotic origin of eukaryotic cells, respiring bacteria similar to E. coli were engulfed by cells and evolved into the a. nucleotides. c. energy-generating organelles.
9 b. protein-producing organelles. d. waste-degrading organelles. C DIF: Easy REF: 1.4 OBJ: 1.4b Explain how mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved by endosymbiosis. 34. The endosymbiotic origin of eukaryotic cells explains how a. prokaryotic cells transformed into eukaryotic cells. b. eukaryotic cells evolved from viruses. c. prokaryotic cells were incorporated by pre-eukaryotes as eukaryotic organelles. d. eukaryotic cells eliminated prokaryotic cells. C DIF: Easy REF: 1.4 OBJ: 1.4b Explain how mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved by endosymbiosis. 35. Which of the following statements does NOT provide evidence in support of the endosymbiotic origin of eukaryotic cells? a. The DNA sequence of mitochondria is similar to the DNA sequence of respiring bacteria. b. The DNA of chloroplasts is circular like the DNA of phototrophic bacteria. c. Mitochondria are capable of free-living outside of a eukaryotic cell. d. There is a lot of sequence homology between the DNA sequences of chloroplasts and phototrophic bacteria. C DIF: Easy REF: 1.4 OBJ: 1.4b Explain how mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved by endosymbiosis. 36. Which of the following negative situations could be caused by the similarity between mitochondria and bacteria? a. Vincent s Staphylococcus skin infection cannot be treated because the only effective antibiotic has too many toxic side effects. b. Alexander suffers from myoclonic epilepsy with ragged red fibers, a mitochondrial c. Lauren inherited complex I deficiency, a mitochondrial disease that inhibits her mitochondria from producing enough energy in certain organs of her body. d. Sally was born with a pyruvate decarboxylase deficiency that prevents her mitochondria from functioning properly, resulting in severe mental retardation. A DIF: Difficult REF: 1.4 OBJ: 1.4b Explain how mitochondria and chloroplasts evolved by endosymbiosis. MSC: Evaluating 37. The X-ray diffraction pattern in the image seen here helped determine the structure of
10 a. alanine. c. vitamin B 12. b. penicillin. d. deoxyribonucleic acid. D DIF: Moderate REF: 1.5 OBJ: 1.5a Describe how the structure of DNA was discovered, and explain the significance of DNA for determining the traits of life. 38. Which of the following is NOT one of Rosalind Franklin s accomplishments? a. generating the X-ray diffraction pattern of the structure of DNA b. researching the structure of RNA c. determining the form of tobacco mosaic virus s RNA chromosome d. receiving a Nobel Prize D DIF: Easy REF: 1.5 OBJ: 1.5a Describe how the structure of DNA was discovered, and explain the significance of DNA for determining the traits of life. 39. The first cellular genome sequenced was a(n) a. animal. c. archaea. b. virus. d. bacteria. D DIF: Easy REF: 1.5 OBJ: 1.5b Describe how the manipulation of DNA information has transformed the practice of medicine. 40. The discovery of first stimulated the funding of millions of dollars into medical research. a. penicillin c. DNA sequencing b. the structure of DNA d. vaccines A DIF: Easy REF: 1.5 OBJ: 1.5b Describe how the manipulation of DNA information has transformed the practice of medicine. 41. CASE HISTORY
11 In 2000, on a farm in North Dakota, 67-year-old Caleb helped bury five cows that had died of anthrax. Wearing heavy leather gloves, Caleb placed chains around the heads and hooves of the carcasses and moved them to the burial site. Four days later, he noticed a small lump on his left cheek. Over two days, the lump enlarged and a lesion opened. Caleb then sought medical attention. The physician reported a firm, superficial nodule surrounded by a purple ring, with an overlying black eschar (piece of dead tissue sloughed from the skin). The physician prescribed ciprofloxacin, the standard antibiotic for cutaneous (affecting skin) anthrax. Testing the patient s serum with a bacterial antigen revealed the presence of antibodies, confirming the diagnosis of anthrax. The ciprofloxacin was continued, and the patient slowly improved over several weeks. If this scenario were an application of Koch s postulates rather than a natural infection, which of these case notes would NOT be relevant? a. Bacillus anthracis can be isolated from lesions on all dead cows. b. Antibiotics successfully treated the lesion. c. Caleb developed a lesion similar to those affecting the dead cows. d. Bacillus anthracis can be isolated from Caleb s lesion. B DIF: Easy REF: Case History 1.1 COMPLETION 1. Bacteria and archaea are classified as. prokaryotes DIF: Easy REF: 1.1 what the three domains have in common and how they differ. 2. In 1884, the Gram stain was devised to distinguish bacteria from cells. human DIF: Easy REF: 1.2 OBJ: 1.2a Explain how microbial diseases have changed human history. 3. Florence Nightingale used a polar area chart to track the of soldiers during the Crimean War. cause of death mortality DIF: Moderate REF: 1.3 OBJ: 1.3b Explain how Florence Nightingale first drew a statistical correlation between infectious disease and human mortality.
12 4. The involvement of bacteria in explains why their presence is essential to the continued existence of plants and animals. geochemical cycling DIF: Moderate REF: 1.4 OBJ: 1.4a Describe examples of how microbes contribute to natural ecosystems. 5. Observe the DNA sequence shown. This sequence terminates at the base. G DIF: Easy REF: 1.5 OBJ: 1.5b Describe how the manipulation of DNA information has transformed the practice of medicine. MSC: Analyzing SHORT ANSWER 1. Consider the statement below. Evaluate whether you agree or disagree with this statement and provide evidence supporting your position. Microorganisms are dangerous to human existence. A variety of answers are acceptable so long as they mention the positive and negative effects of microorganisms and provide appropriate evidence to support their claim. DIF: Difficult REF: 1.1 OBJ: 1.1a Describe how we define a microbe, and explain why the definition is a challenge. MSC: Evaluating 2. Explain how the piece of equipment shown in the image below was used to disprove the theory of spontaneous generation.
13 The curved shape of the neck prevented microbes in dust particles in the air from reaching the media while still allowing air to flow, demonstrating that even with oxygen, no spontaneous growth of microorganisms occurred without direct contact with dust particles from the environment. DIF: Difficult REF: 1.2 OBJ: 1.2b Describe how microbes participate in human cultural practices such as production of food and drink. MSC: Analyzing 3. Explain how it would have taken much longer to disprove the theory of spontaneous generation if John Tyndall was the only scientist investigating it. John Tyndall found the opposite result of Pasteur in his experiments because material he was boiling contained endospores that were resistant to boiling. His experiments would have appeared to support the theory of spontaneous generation as microbes from the spores germinated in a sealed flask. DIF: Difficult REF: 1.2 OBJ: 1.2b Describe how microbes participate in human cultural practices such as production of food and drink. MSC: Evaluating 4. Why did agar offer an improvement over gelatin for the growth of microorganisms? Agar remains more solid at higher temperatures than does gelatin. DIF: Easy REF: Give an example of a situation where Koch s postulates may not work properly. A variety of answers are acceptable so long as they deal with one of the following: a disease-causing agent present in a host that does not cause symptoms, a disease-causing agent in which the levels of the agent are very low or difficult to detect in the host, a disease-causing agent that cannot be grown in pure culture, or a disease-causing agent for which there is no known nonhuman model. DIF: Difficult REF: 1.3 OBJ: 1.3b Explain how Florence Nightingale first drew a statistical correlation between infectious disease and human mortality. MSC: Evaluating 6. Why does traditional microbial growth media only allow for the growth of 0.1% of all microorganisms in pure culture in the laboratory? Traditional microbial growth media contains nutrients that are used to feed humans. While some microorganisms can flourish in these conditions, many are much more diverse and cannot grow on these nutrients or will be outcompeted by those organisms that can. DIF: Easy REF: 1.4
14 OBJ: 1.4a Describe examples of how microbes contribute to natural ecosystems. 7. Explain how comparing the sequences of antibiotic-resistant and -sensitive Mycobacterium tuberculosis could be useful to treating tuberculosis. The answer should discuss how this can lead to identification of the difference(s) that lead(s) to resistance and from there how to possibly target the antibiotic-resistant organism. For example: comparing the sequences of antibiotic-resistant and -sensitive Mycobacterium tuberculosis can allow one to note the differences between the two. Knowing what is missing or present in the antibiotic-resistant variety can allow researchers to understand how the resistant organisms are developing resistance. This is the first step toward developing a method to combat these resistant organisms. DIF: Difficult REF: 1.5 OBJ: 1.5b Describe how the manipulation of DNA information has transformed the practice of medicine. MSC: Evaluating 8. CASE HISTORY Debi was an ordinary teenager attending an affluent American public high school when she contracted tuberculosis (TB). She did not know the person who infected her. Infection requires inhalation of the causative bacteria. Debi coughed all the time, felt tired, and was losing weight. Her coughing brought up blood. An X-ray revealed the signs of infection in her lung, including a large hole eaten away by the bacteria. From Debi s sputum sample, a DNA sequence was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The DNA sequence revealed Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the cause of TB. Doctors prescribed isoniazid and rifampin, antibiotics that kill most strains of M. tuberculosis. But Debi s TB strain proved resistant to nearly all known drugs (MDR-TB). Because drugs failed to eliminate the MDR strain, surgeons removed nearly half of her right lung to help the antibiotics overcome the infection. Debi recovered and returned to high school. She would have to continue taking antibiotics for years afterward. All the teachers and students in Debi s school were screened, and over 200 were found to have been infected by a student with tuberculosis misdiagnosed for two years. All required treatment to prevent When Debi contracted tuberculosis, she did not know who had infected her or how she had been infected. How could this be? The bacteria was airborne. DIF: Moderate REF: Chapter 1 Introduction what the three domains have in common and how they differ. 9. CASE HISTORY Debi was an ordinary teenager attending an affluent American public high school when she contracted tuberculosis (TB). She did not know the person who infected her. Infection requires inhalation of the causative bacteria. Debi coughed all the time, felt tired, and was losing weight. Her coughing brought up blood. An X-ray revealed the signs of infection in her lung, including a large hole eaten away by the bacteria.
15 From Debi s sputum sample, a DNA sequence was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The DNA sequence revealed Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the cause of TB. Doctors prescribed isoniazid and rifampin, antibiotics that kill most strains of M. tuberculosis. But Debi s TB strain proved resistant to nearly all known drugs (MDR-TB). Because drugs failed to eliminate the MDR strain, surgeons removed nearly half of her right lung to help the antibiotics overcome the infection. Debi recovered and returned to high school. She would have to continue taking antibiotics for years afterward. All the teachers and students in Debi s school were screened, and over 200 were found to have been infected by a student with tuberculosis misdiagnosed for two years. All required treatment to prevent Which organism in this case history is the pathogen? To what domain does this organism belong and what are the defining features of that domain? Pathogen should be identified as M. tuberculosis, a bacterium. Defining features that separate this group from Archaea and Eukarya should be included. DIF: Easy REF: Chapter 1 Introduction what the three domains have in common and how they differ.
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules
 Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules. Early History of Microbiology: Fig. 1.4
 Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Leeuwenhoek s Animacules Early History of Microbiology: 1668 Francesco Redi disproves spontaneous generation 1676 Antony van Leeuwenhoek first observes microbes 1861 Louis Pasteur disproves spontaneous
Introduction to Microbiology. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
Introduction To Microbiology CLS 311
 Introduction To Microbiology CLS 311 What is microbiology? It is a branch of biology that studies microorganisms and their effects on humans Microorganisms a collection of organisms that share the characteristic
Introduction To Microbiology CLS 311 What is microbiology? It is a branch of biology that studies microorganisms and their effects on humans Microorganisms a collection of organisms that share the characteristic
KNOW the MICROBES. What are microbes? What are the different types? Who saw them first? How small are they? How do they look?
 KNOW the MICROBES What are microbes? What are the different types? Who saw them first? How small are they? How do they look? - PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North
KNOW the MICROBES What are microbes? What are the different types? Who saw them first? How small are they? How do they look? - PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-formicrobiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-edition-by-cowan Chapter
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-formicrobiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-edition-by-cowan Chapter
Classification. Old 5 Kingdom system. New 3 Domain system. reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence
 Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Classification Old 5 Kingdom system Monera, Protists, Plants, Fungi, Animals New 3 Domain system reflects a greater understanding of evolution & molecular evidence Prokaryote: Bacteria Prokaryote: Archaebacteria
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Microbiology. Microbiology derived by Greek mikros (small) bios (life) logos (science)
 MBIO140 Lecture-1 Microbiology derived by Greek mikros (small) bios (life) logos (science) Microbiology The study of organisms too small to be seen individually with the naked eye during part or all of
MBIO140 Lecture-1 Microbiology derived by Greek mikros (small) bios (life) logos (science) Microbiology The study of organisms too small to be seen individually with the naked eye during part or all of
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS
 MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
MICROBIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS 1:1 What is Microbiology? MICROBIOLOGY: the study of living organisms that are individually too small to be seen with the unaided eye e.g. bacteria,
Kingdom Monera Bacteria
 Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Kingdom Monera Bacteria Common bacteria Prokaryotes Strep throat Anthrax Chlamydia E. coli Meningitis Salmonella Micrococcus(intestinal) Streptococcus mutans Haemophilusinfluenzae Cellphonious bacterious
Obligate anaerobes - cannot grow in the presence of oxygen Facultative anaerobes - can grow with or without oxygen Aerobic - require oxygen
 PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
PROKARYOTES *include bacteria and archaea *singular: bacterium / plural: bacteria PROPERTIES 1. Bacteria are classified into two kingdoms: Eubacteria (true bacteria) and Archaebacteria (Ancient Bacteria).
Microbe Mission C Test
 Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
Microbe Mission C Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Page 2 Part 1: Microscopes Names the following
PROPERTY OF: BIOLOGY UNIT 3 CHAPTER 19 NOTES THE HISTORY OF LIFE
 PROPERTY OF: BIOLOGY UNIT 3 CHAPTER 19 NOTES THE HISTORY OF LIFE Spontaneous Generation - theory that life arises from non-life (early-mid 1700 s) EX: rotting meat became covered with flies and maggots
PROPERTY OF: BIOLOGY UNIT 3 CHAPTER 19 NOTES THE HISTORY OF LIFE Spontaneous Generation - theory that life arises from non-life (early-mid 1700 s) EX: rotting meat became covered with flies and maggots
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei (Eukaryotic cells) This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
What are Cells? How is this bacterium similar to a human? organism: a living thing. The cell is the basic unit of life.
 Have you ever wondered how people are similar to bacteria? It may seem like a silly question. After all, humans and bacteria are very different in size and complexity. Yet scientists have learned that
Have you ever wondered how people are similar to bacteria? It may seem like a silly question. After all, humans and bacteria are very different in size and complexity. Yet scientists have learned that
Name Unit 1 Study Guide: Nature of Biology Test Date: Collect/Analyze Your Data: During the experiment, you collect your data/measurements so that
 1. I can analyze an experiment and identify the major parts. This means that I know the difference between an independent variable, dependent variable, constant, experimental group, and control group.
1. I can analyze an experiment and identify the major parts. This means that I know the difference between an independent variable, dependent variable, constant, experimental group, and control group.
Full file at
 Chapter # and Question type Short answer #1. Question How did Louis Pasteur help disprove spontaneous generation? Answer Pasteur demonstrated that swan necked flasks containing sterile growth medium would
Chapter # and Question type Short answer #1. Question How did Louis Pasteur help disprove spontaneous generation? Answer Pasteur demonstrated that swan necked flasks containing sterile growth medium would
Scientific names allow scientists to talk about particular species without confusion
 Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Bacteria are very small
 BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
BACTERIA BACTERIA Bacteria are very small Bacteria are very small compared to cells with nuclei This is a pore in human skin and the yellow spheres are bacteria BACTERIA LIVE ALMOST EVERYWHERE Hot springs
Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1
 Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th edition by Nester Anderson and Roberts Solution Manual. plants could use. microorganisms.
 Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th edition by Nester Anderson and Roberts Solution Manual Chapter # and Question Answer Question type Chapter 1 How did Louis Pasteur help Pasteur demonstrated that swan
Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th edition by Nester Anderson and Roberts Solution Manual Chapter # and Question Answer Question type Chapter 1 How did Louis Pasteur help Pasteur demonstrated that swan
Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
 Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY What are microbes? Germs, microbe s s microorganisms are minute living things that individually
Principles of Biotechnology Lectures of week 4 MICROBIOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY What are microbes? Germs, microbe s s microorganisms are minute living things that individually
Bacteria and Viruses. 1 Bacteria CHAPTER 18. MAINIDEA Bacteria are prokaryotic cells.
 CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
CHAPTER 18 Bacteria and Viruses 1 Bacteria 7(F), 8(B), 8(C), 11(C), 12(A) Before You Read When you hear the word bacteria, what comes to mind? On the lines below, describe places you think bacteria might
no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan
 no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan Introduction to microbiology Let's start! As you might have concluded, microbiology is the study of all organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, Ex:
no.1 Raya Ayman Anas Abu-Humaidan Introduction to microbiology Let's start! As you might have concluded, microbiology is the study of all organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye, Ex:
Solution Manual for Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition by Eugene Nester, Denise Anderson and C. Evans Roberts
 Solution Manual for Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition by Eugene Nester, Denise Anderson and C. Evans Roberts Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/solution-manualfor-microbiology-a-human-perspective-7th-edition-by-nester-andersonroberts/
Solution Manual for Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition by Eugene Nester, Denise Anderson and C. Evans Roberts Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/solution-manualfor-microbiology-a-human-perspective-7th-edition-by-nester-andersonroberts/
Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya
 Taxonomy Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya, mostly heterotrophic, live in all sorts of environments Largest group of organisms on Earth Only a small amount cause disease Most have very important roles:, such
Taxonomy Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya, mostly heterotrophic, live in all sorts of environments Largest group of organisms on Earth Only a small amount cause disease Most have very important roles:, such
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & Eubacteria)
 Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Plant and animal cells (eukaryotic cells) have a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material enclosed in a nucleus.
 4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
4.1 Cell biology Cells are the basic unit of all forms of life. In this section we explore how structural differences between types of cells enables them to perform specific functions within the organism.
The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms
 Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Biology Chapter 19 Notes - Bacteria and Viruses The invention of the microscope has opened to us a world of extraordinary numbers. A singular drop of pond water reveals countless life forms I. Classifying
Microbiology 2320 Spring 2017 Dr. Milind Suraokar CRN# 18168
 Microbiology 2320 Spring 2017 Dr. Milind Suraokar CRN# 18168 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 1 A Brief History of Microbiology
Microbiology 2320 Spring 2017 Dr. Milind Suraokar CRN# 18168 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 1 A Brief History of Microbiology
Classifying Prokaryotes: Eubacteria Plasma Membrane. Ribosomes. Plasmid (DNA) Capsule. Cytoplasm. Outer Membrane DNA. Flagellum.
 Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
SPECIES OF ARCHAEA ARE MORE CLOSELY RELATED TO EUKARYOTES THAN ARE SPECIES OF PROKARYOTES.
 THE TERMS RUN AND TUMBLE ARE GENERALLY ASSOCIATED WITH A) cell wall fluidity. B) cell membrane structures. C) taxic movements of the cell. D) clustering properties of certain rod-shaped bacteria. A MAJOR
THE TERMS RUN AND TUMBLE ARE GENERALLY ASSOCIATED WITH A) cell wall fluidity. B) cell membrane structures. C) taxic movements of the cell. D) clustering properties of certain rod-shaped bacteria. A MAJOR
4/17/2014. Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years
 Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years Fossil evidence shows that prokaryotes were abundant 3.5 bya, and they evolved alone for the following 2 billion years. Prokaryotes are ubiquitous,
Prokaryotes have inhabited the Earth for billions of years Fossil evidence shows that prokaryotes were abundant 3.5 bya, and they evolved alone for the following 2 billion years. Prokaryotes are ubiquitous,
Introduction to microbiology
 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Introduction to microbiology Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Molecular Medical Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Definition Microbiology: is the
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Introduction to microbiology Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Molecular Medical Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Definition Microbiology: is the
Unit 13.1: Prokaryotes
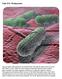 Unit 13.1: Prokaryotes Can you guess what organisms are pictured here? Are they fat green worms on a red leaf? Here s a clue: There are more organisms like these than any other on Earth. Here s another
Unit 13.1: Prokaryotes Can you guess what organisms are pictured here? Are they fat green worms on a red leaf? Here s a clue: There are more organisms like these than any other on Earth. Here s another
By signing below, you acknowledge that you have ensured that you are complying with the above statement.
 Instructions: This exam consists of 31 multiple choice questions on 8 pages, including this one. Please submit your answers on the scantron sheet provided and on this copy of the exam. This exam is closed
Instructions: This exam consists of 31 multiple choice questions on 8 pages, including this one. Please submit your answers on the scantron sheet provided and on this copy of the exam. This exam is closed
INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY
 INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY Spring 2015 Peering through the microscope into a drop of seawater is like looking at stars with a telescope on a clear night. Dr. Gallardo, ocean researcher What will you be studying
INTRO TO MICROBIOLOGY Spring 2015 Peering through the microscope into a drop of seawater is like looking at stars with a telescope on a clear night. Dr. Gallardo, ocean researcher What will you be studying
Dr. Raj Ramakrishnan, Ph.D.
 Page 1 of 5 Concept Questions Read the chapter materials. Take some time to write answers to these questions. If you can answer them, you have a good grasp of the material! Good luck! Chapter 1 1. Identify
Page 1 of 5 Concept Questions Read the chapter materials. Take some time to write answers to these questions. If you can answer them, you have a good grasp of the material! Good luck! Chapter 1 1. Identify
KINGDOM MONERA. Bacterial Cell Shape 8/22/2010. The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
KINGDOM MONERA The Prokaryotes: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are the most organisms living on the Earth. (i.e. 10mL of soil contains 1 x 10 10 bacteria. They are found in nearly every habitat
Microbe Mission B Test
 Microbe Mission B Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Part 1: Microscopes Names the following structures
Microbe Mission B Test Science Olympiad North Regional Tournament at the University of Florida Rank: Points: Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Part 1: Microscopes Names the following structures
Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you
 45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
45 The World of Microbes r e a d i n g Have you had a cold, flu, or other infectious disease recently? Do you know what caused your illness? Microbes cause most infectious diseases. Microbes include the
9/8/2017. Bacteria and Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life. Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success
 5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
Syllabus 1/20/2018. CSLOs. 1. BIOL 1406 PreRequisite Form Signup 2. Discuss Main Points in Syllabus 3. Why so many RULES?
 CSLOs Course Student Learning Outcomes (CSLOs) for BIOL 2320 LECTURE: 1. Describe distinctive characteristics and diverse growth requirements of prokaryotic organisms compared to eukaryotic organisms.
CSLOs Course Student Learning Outcomes (CSLOs) for BIOL 2320 LECTURE: 1. Describe distinctive characteristics and diverse growth requirements of prokaryotic organisms compared to eukaryotic organisms.
Course Student Learning Outcomes (CSLOs) for BIOL 2320 LECTURE: 1.
 CSLOs Course Student Learning Outcomes (CSLOs) for BIOL 2320 LECTURE: 1. Describe distinctive characteristics and diverse growth requirements of prokaryotic organisms compared to eukaryotic organisms.
CSLOs Course Student Learning Outcomes (CSLOs) for BIOL 2320 LECTURE: 1. Describe distinctive characteristics and diverse growth requirements of prokaryotic organisms compared to eukaryotic organisms.
The Prokaryotic World
 The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
BIOL 260-General Microbiology. Instructor: Seana Davidson
 BIOL 260-General Microbiology Instructor: Seana Davidson Welcome to BIOL 260: Microbiology! First day: Review of Syllabus Sign-in Introduce the course, review course expectations Begin with first lab Exercise
BIOL 260-General Microbiology Instructor: Seana Davidson Welcome to BIOL 260: Microbiology! First day: Review of Syllabus Sign-in Introduce the course, review course expectations Begin with first lab Exercise
BIOLOGY 345 Midterm I - 20 October 2008 PART I. Multiple choice questions (4 points each, 36 points total).
 BIOLOGY 345 Name Midterm I - 20 October 2008 PART I. Multiple choice questions (4 points each, 36 points total). 1. When considering the human body (made up of about 10 trillion Eucarya cells), which of
BIOLOGY 345 Name Midterm I - 20 October 2008 PART I. Multiple choice questions (4 points each, 36 points total). 1. When considering the human body (made up of about 10 trillion Eucarya cells), which of
Outline. Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea. Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea
 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea Chapter 21 Viruses Structure Classification Reproduction Prokaryotes Structure Reproduction Nutrition Bacteria Archaea Outline The Viruses The Viruses Viruses are noncellular
Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words)
 Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Chapter 01 Humans and the Microbial World
 Chapter 01 Humans and the Microbial World Multiple Choice Questions 1. The scientist usually considered the first to see microorganisms, which he called "animalcules", was A. Redi. B. van Leeuwenhoek.
Chapter 01 Humans and the Microbial World Multiple Choice Questions 1. The scientist usually considered the first to see microorganisms, which he called "animalcules", was A. Redi. B. van Leeuwenhoek.
Chapter 01 Humans and the Microbial World
 Chapter 01 Humans and the Microbial World Multiple Choice Questions 1. The scientist usually considered the first to see microorganisms, which he called "animalcules", was A. Redi. B. van Leeuwenhoek.
Chapter 01 Humans and the Microbial World Multiple Choice Questions 1. The scientist usually considered the first to see microorganisms, which he called "animalcules", was A. Redi. B. van Leeuwenhoek.
Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea
 Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Characteristics. Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome
 Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
Prokaryotes Characteristics Nucleoid Region single circular chromosome plasmids mesosome No membranebound organelles Ribosomes (70S) Plasma membrane Cell wall peptidoglycan Capsule glycocalyx Flagella
PDF // IS BACTERIA A PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE
 19 January, 2018 PDF // IS BACTERIA A PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE Document Filetype: PDF 222.61 KB 0 PDF // IS BACTERIA A PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE How to Tell the Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.
19 January, 2018 PDF // IS BACTERIA A PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE Document Filetype: PDF 222.61 KB 0 PDF // IS BACTERIA A PROKARYOTE OR EUKARYOTE How to Tell the Difference Between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes.
Test Bank for Burton s Microbiology for the Health Sciences 9th edition by Engelkrirk
 Test Bank for Burton s Microbiology for the Health Sciences 9th edition by Engelkrirk Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-forburtons-microbiology-for-the-health-sciences-9th-edition-by-engelkrirk
Test Bank for Burton s Microbiology for the Health Sciences 9th edition by Engelkrirk Link download full: https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-forburtons-microbiology-for-the-health-sciences-9th-edition-by-engelkrirk
Name Date Class. PAP Unit 10: Bacteria, Viruses, Protist, and Fungi TEST REVIEW. d. Do viruses contain nucleic acids/genetic material (Yes or No)?
 Name Date Class PAP Unit 10: Bacteria, Viruses, Protist, and Fungi TEST REVIEW Part A: Viruses 1. a. Are viruses biotic or abiotic? b. Are viruses made of cells (Yes or No)? c. Do viruses contain proteins
Name Date Class PAP Unit 10: Bacteria, Viruses, Protist, and Fungi TEST REVIEW Part A: Viruses 1. a. Are viruses biotic or abiotic? b. Are viruses made of cells (Yes or No)? c. Do viruses contain proteins
Download full Test Bank for Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition
 Download full Test Bank for Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-for-microbiology-a-human-perspective- 7th-edition Ch01: Humans and the Microbial
Download full Test Bank for Microbiology A Human Perspective 7th Edition https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-for-microbiology-a-human-perspective- 7th-edition Ch01: Humans and the Microbial
B. Correct! Bacillus anthraces produces spores that can cause anthrax. D. Incorrect! Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Microbiology - Problem Drill 09 - The Prokaryotes No. 1 of 10 1. Bacillus anthraces is most closely associated with which of the following? (A) Botulism poisoning (B) Anthrax (C) Gangrene (D) Diphtheria
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
Bacteria. Prepared by. Doua a Hamadi Gellan Ibrahim Rahma Younis Doua a Abdul-Hadi Doua a Amjad Hanin Laith Khamael Dawood
 Bacteria Prepared by Doua a Hamadi Gellan Ibrahim Rahma Younis Doua a Abdul-Hadi Doua a Amjad Hanin Laith Khamael Dawood History of Bacteriology Doua a Hamadi Bacteria were first observed by Antonie van
Bacteria Prepared by Doua a Hamadi Gellan Ibrahim Rahma Younis Doua a Abdul-Hadi Doua a Amjad Hanin Laith Khamael Dawood History of Bacteriology Doua a Hamadi Bacteria were first observed by Antonie van
Bio-CP Chapter 7 Cell Notes
 Bio-CP Chapter 7 Cell Notes I. Cell = Building block of all living organisms A. Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork under a crude microscope 1. He called the boxes cells because they looked like little rooms
Bio-CP Chapter 7 Cell Notes I. Cell = Building block of all living organisms A. Robert Hooke (1665) observed cork under a crude microscope 1. He called the boxes cells because they looked like little rooms
Eukaryotic Cells. Figure 1: A mitochondrion
 Eukaryotic Cells Figure 1: A mitochondrion How do cells accomplish all their functions in such a tiny, crowded package? Eukaryotic cells those that make up cattails and apple trees, mushrooms and dust
Eukaryotic Cells Figure 1: A mitochondrion How do cells accomplish all their functions in such a tiny, crowded package? Eukaryotic cells those that make up cattails and apple trees, mushrooms and dust
Part 2. The Basics of Biology:
 Part 2 The Basics of Biology: An Engineer s Perspective Chapter 2 An Overview of Biological Basics 21 2.1 Cells 2.2 Cell Construction 2.3 Cell Nutrient 2.1 Are all cells the same? Cells Basic unit of living
Part 2 The Basics of Biology: An Engineer s Perspective Chapter 2 An Overview of Biological Basics 21 2.1 Cells 2.2 Cell Construction 2.3 Cell Nutrient 2.1 Are all cells the same? Cells Basic unit of living
Bacteria. The Three Types of Important Heterotrophic Bacteria
 Bacteria Kingdom Monera Prokaryote (their genetic material is not bound with a membrane) Classified according to shape - Spherical (cocci) - Spiral - Rod Shaped -TWO TYPES: Heterotrophic (organism that
Bacteria Kingdom Monera Prokaryote (their genetic material is not bound with a membrane) Classified according to shape - Spherical (cocci) - Spiral - Rod Shaped -TWO TYPES: Heterotrophic (organism that
Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages )
 Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
Origin of Life. What is Life? The evolutionary tree of life can be documented with evidence. The Origin of Life on Earth is another
 sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 500 Paleozoic 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago 1000 PROTEROZOIC Cenozoic Mesozoic 4000
sparked by just the right combination of physical events & chemical processes Origin of Life 500 Paleozoic 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 ARCHEAN Millions of years ago 1000 PROTEROZOIC Cenozoic Mesozoic 4000
Cells & Bacteria Notes
 Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
Cells & Bacteria Notes 4 Major Macromolecules Macromolecules are large molecules. The four groups of macromolecules are essential to the structure and function of a cell. Group Building Block Large Molecule
End of Course Biology Reporting Category 1 Cell Structure and Function
 End of Course Biology Reporting Category 1 Cell Structure and Function 1. An iodine solution is placed on the cut side of a potato. Within seconds, a blue-black color appears. What is most likely occurring?
End of Course Biology Reporting Category 1 Cell Structure and Function 1. An iodine solution is placed on the cut side of a potato. Within seconds, a blue-black color appears. What is most likely occurring?
BACTERIA. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
BACTERIA CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Prokaryotes Prokaryotic cells possess simpler structures than eukaryotic cells, since they do not have a nucleus or a lot of cytoplasmic organelles.
Chapter 28 - Bacteria and Archaea
 Chapter 28 - Bacteria and Archaea Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Defend the statement that bacteria and archaea are the most important, diverse, and abundant organisms on the planet.
Chapter 28 - Bacteria and Archaea Learning Objectives: Students should be able to... Defend the statement that bacteria and archaea are the most important, diverse, and abundant organisms on the planet.
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: 90 / 90 Name: Answer Key Date:
 Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: 90 / 90 Name: Answer Key Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your
Ladue Microbe Mission Test SCORE: 90 / 90 Name: Answer Key Date: You may not return to previous stations. However, you can move to another station early if you want to do so. I won t judge you for your
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria
 Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
Chapter 19 Notes Kingdoms Archaebacteria andeubacteria All bacteria are Prokaryotic. This means that they are organisms that are one-celled and do not contain a nucleus or other membrane bound organelles.
chapter one: the history of microbiology
 chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 6/19/2018 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
chapter one: the history of microbiology Revised 6/19/2018 microbes microscopic (small) organisms, viruses, prions prefix sci. notation frac. equivalent dec. equivalent kilo- (k) 1 10 3 1000/1 = 1000 1000
Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Biology
 Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1) Microorganisms that prepares their food from water and carbon dioxide
Grade 08 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November, 2017 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1) Microorganisms that prepares their food from water and carbon dioxide
Ch. 19 Viruses & Bacteria: What Is a Virus?
 Ch. 19 Viruses & Bacteria: What Is a Virus? Define virus. What are viruses? Define and translate bacteriophage. Review virus composition. What two classes of compounds are found in all viruses? Define
Ch. 19 Viruses & Bacteria: What Is a Virus? Define virus. What are viruses? Define and translate bacteriophage. Review virus composition. What two classes of compounds are found in all viruses? Define
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists
 Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Biology Test 2 The Cell. For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form.
 Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
Name Block Date Biology Test 2 The Cell For questions 1 15, choose ONLY ONE correct answer and fill in that choice on your Scantron form. 1. Which pair of structures best shows that plant cells have functions
CHAPTER 7.1 OUTLINE SHEET
 CHAPTER 7.1 OUTLINE SHEET A. Development of Cell Theory 1. Identifying Cells a. Anton van Leeuwenhoek b. Robert Hooke 2. Development of Cell Theory a. Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow 1. Schleiden 2. Schwann
CHAPTER 7.1 OUTLINE SHEET A. Development of Cell Theory 1. Identifying Cells a. Anton van Leeuwenhoek b. Robert Hooke 2. Development of Cell Theory a. Schleiden, Schwann, and Virchow 1. Schleiden 2. Schwann
Biology. Slide 1 of 40. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 40 (p471-477) 2 of 40 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other
Biology 1 of 40 (p471-477) 2 of 40 Microorganisms = Microbes Microbiology is the study of living creatures too small to see with the unaided eye including : bacteria protozoa fungi algae viruses other
WHAT DO CELLS DO? CHALLENGE QUESTION. What are the functions of the structures inside of cells?
 WHAT DO CELLS DO? CHALLENGE QUESTION What are the functions of the structures inside of cells? WHAT DO CELLS DO? Understanding normal cell structures and their functions help scientists understand how
WHAT DO CELLS DO? CHALLENGE QUESTION What are the functions of the structures inside of cells? WHAT DO CELLS DO? Understanding normal cell structures and their functions help scientists understand how
Introduction to Microbiology
 Introduction to Microbiology Norazli Ghadin Norazli.ghadin@city.edu.my norazlicucst.weebly.com (online note) DNEH 1292: Environmental Microbiology 1 Lecture 1 Environmental Microbiology Assesment: Formative:
Introduction to Microbiology Norazli Ghadin Norazli.ghadin@city.edu.my norazlicucst.weebly.com (online note) DNEH 1292: Environmental Microbiology 1 Lecture 1 Environmental Microbiology Assesment: Formative:
I. Early Theory! A. Spontaneous Generation - The hypothesis that life arises regularly from non-living things
 ORIGIN OF LIFE! I. Early Theory! A. Spontaneous Generation - The hypothesis that life arises regularly from non-living things II. Experiments That Helped to Disprove Spontaneous Generation! A. Italian
ORIGIN OF LIFE! I. Early Theory! A. Spontaneous Generation - The hypothesis that life arises regularly from non-living things II. Experiments That Helped to Disprove Spontaneous Generation! A. Italian
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment
 Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
Education Transformation Office (ETO) 8 th Grade Unit #4 Assessment 1. Which of these shows the correct hierarchical sequence? A. organs cells tissues organ systems B. cells tissues organs organ systems
- A virus is a short piece of DNA or RNA, sometimes with some associated enzymes.
 Viruses, bacteria, protists & fungi (just the basics!) I. Viruses: - parasites postponed until we discuss them in class. - A virus is a short piece of DNA or RNA, sometimes with some associated enzymes.
Viruses, bacteria, protists & fungi (just the basics!) I. Viruses: - parasites postponed until we discuss them in class. - A virus is a short piece of DNA or RNA, sometimes with some associated enzymes.
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria
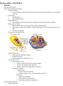 Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
Bacteria outline-- CHAPTER 19 Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and 1.5 billion
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA 10/15/2012
 BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr
 Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr Learning Target: B.1.a Analyze the similarities and differences
Lincoln County Schools Patriot Day Instructional Expectations Patriot Day 1 School: Course/Subject: Biology Teacher: Cox Brock Gilbert Carr Learning Target: B.1.a Analyze the similarities and differences
CELL PRACTICE TEST
 Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Name: Date: 1. As a human red blood cell matures, it loses its nucleus. As a result of this loss, a mature red blood cell lacks the ability to (1) take in material from the blood (2) release hormones to
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
 Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are of immense importance because of their rapid growth, reproduction, and mutation rates, as well as, their ability to exist under adverse conditions. The oldest
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Bacteria are of immense importance because of their rapid growth, reproduction, and mutation rates, as well as, their ability to exist under adverse conditions. The oldest
TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING
 BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
BACTERIA! TRACING BACK TO THE BEGINNING PROKARYOTES KINGDOM EUBACTERIA KINGDOM ARCHAEBACTERIA CHARACTERISTICS: 1. NO NUCLEUS 2. NO MEMBRANE BOUND ORGANELLES 4. MOST ARE SMALLER THAN EUKARYOTES 5. ARE SINGLE-CELLED
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes Bacteria
 20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
20 Viruses and Prokaryotes 20.2 - Bacteria Classifying Prokaryotes Prokaryote unicellular organisms that lacks a nucleus Most abundant and widespread organisms on Earth Divided into two groups Bacteria
Chapter 01 The Evolution of Microorganisms and Microbiology
 Chapter 01 The Evolution of Microorganisms and Microbiology True / False Questions 1. Extant microorganisms are organisms from the fossil record that are no longer present on Earth today. FALSE ASM Objective:
Chapter 01 The Evolution of Microorganisms and Microbiology True / False Questions 1. Extant microorganisms are organisms from the fossil record that are no longer present on Earth today. FALSE ASM Objective:
Some history. Now, we know that Robert Hooke was not looking at living cells, but the remains of dead cell walls.
 The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
The Life of a Cell Some history In 1665, Robert Hooke examined the bark of an oak tree under an early microscope. He thought he was looking at something similar to the small rooms of dormitories and prisons;
Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes
 The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
Basic Biological Principles
 Basic Biological Principles Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Moth Life Cycle larva egg pupa Adult 1. Which characteristic of life is best shown by this diagram? A. DNA is the genetic code in
Basic Biological Principles Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Moth Life Cycle larva egg pupa Adult 1. Which characteristic of life is best shown by this diagram? A. DNA is the genetic code in
Dr. Raj Ramakrishnan, Ph.D.
 CONCEPT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMINATION I - Biology 2420, Talaro & Chess 9 th NOTE: The topic sheets prepared by Dr. David Schwartz are being used by me with his kind permission. I have modified them in this
CONCEPT QUESTIONS FOR EXAMINATION I - Biology 2420, Talaro & Chess 9 th NOTE: The topic sheets prepared by Dr. David Schwartz are being used by me with his kind permission. I have modified them in this
How to use this book. How the book is organised. Answering questions. Learning and using the terminology. Developing skills
 How to use this book Welcome to the beginning of your Human and Social Biology course! We hope that you really enjoy your course, and that this book will help you to understand your work, and to do well
How to use this book Welcome to the beginning of your Human and Social Biology course! We hope that you really enjoy your course, and that this book will help you to understand your work, and to do well
THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE 5/14/18
 THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE Introduction: The identification of bacteria is important in order for us to differentiate one microorganism
THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE Introduction: The identification of bacteria is important in order for us to differentiate one microorganism
