Ross s Den. Welcome to Biology!!
|
|
|
- Toby Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ross s Den Welcome to Biology!!
2 BE READY Bring binder, books, pencils, pens Bring a good work ethic full effort every minute Work as a team, we are only as strong as the members in our class Don t touch anything without permission Treat everyone with respect
3 BLAME NO ONE EXPECT NOTHING DO SOMETHING
4 Stereo Types Was a NCAA Div. 1 Scholarship Athlete Was a High Fashion Model Wrote my first Science Research Paper and conducted my first dissection in 2 nd grade Won my High School Science Fair competition and went on to finals in the State Was in TV Commercial
5 Did Not Win the Science Fair
6 Name Game What is your name What do you like to do for fun
7 Class with the highest GPA wins a pizza party!
8 Binder 3X5 cards Metal Ring
9 Lab Safety
10 Metric Olympics
11 What are the measurements? Volume Length Mass
12 (Unit)
13 Metrics Meter = Length (Inches,feet, miles) Grams = weight (lbs, ounces) Liters = volume (Gallons, pints, quart) Celsius = Temperature
14 Chapter 1 Biology is the study of life People have always been curious about living things around them. What have you ever wondered about living things around you? You are now a young biologist!
15 Kilo Hecto Deca Meter. Deci Centi Milli Liter Gram
16 There are many life forms which have not been discovered yet. Are there organisms or livings things that you can t see? There is an order in the natural world even if you think things look strange. Section 1.1
17 Biologists study the interactions of life, or living things. There is a delicate balance to nature Living things depend on other living things and non-living things to survive. All living organisms fit into the dynamic pattern of life on our planet.
18 Nothing can live in isolation, the study of biology includes investigation of living interactions. Human existence is closely related to the existence of other living things. It is only through the understanding of the intricate web of nature that humans can understand and preserve life.
19
20 Biological research can lead to advances in medical treatment and disease prevention. Studies in biology can also teach you how you fit into the world and how to preserve it.
21 Characteristics of Living Things Is a flame alive????? Anything that that possesses all of the characteristics of life is considered to be an Organism.
22 The characteristics of life are: Have an orderly structure Produce offspring Grow and develop Adjust to changes in the environment
23 All living things show an orderly structure or Organization. All living things have cells one or more. Each cell contains genetic material DNA All living things have a cell or cells that function together in an orderly living system.
24 Living things make more living things: Reproduction. Organisms don t live forever Species is a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring in nature.
25 Life begins as a single cell Growth occurs, and the living organisms begins to develop. Development: the changes that take place over time to an organisms. Did you start as one cell? Where are you now? Are you done growing?
26 Environment: the water, air, weather, temperature, any other organisms in the areas and many other factors. Stimulus is an organisms reaction to external or internal environment. A reaction to a stimulus is a response.
27
28 Homeostasis occurs in all living things. It is important to survival. Sweating for humans is an example of homeostasis. STAND UP! Energy is the ability to cause change and organisms get it from food.
29 Living things adapt and evolve Adaptation is inherited structures, behaviors or internal process that enables an organism to respond to environmental factors and to reproduce. These are inherited from previous generations.
30 When organisms adapt it allows them to change and survive. Gradual changes in a species is evolution.
31 Observing and Hypothesizing To answer questions, scientists gather information using the scientific method. Investigations begin with identifying a problem. Observation one of the strongest traits of a scientist.
32 Read from page 12 through 18 The questions of brown tree snakes Fill out guides notes you have 15 minutes
33
34 Quantitative information use numbers or measurements Qualitative information expresses qualities and behaviors
35 Grades in Mrs. Ross s Class Quantitative Information A B C st Qtr 2nd Qtr 3rd Qtr 4th Qtr What conclusions can you make reading this graph?
36 Bar Graph activity
37 Line Graph A B C st Qtr 2nd Qtr 3rd Qtr 4th Qtr
38 Line Graph Activity
39 A pie chart with just the A s 1st Qtr 2nd Qtr 3rd Qtr 4th Qtr
40 Pie Graph Activity
41 Qualitative Information How do you show behavior? Observational data is just as important As a teacher, I need to collect observational data every day. How do you think scientists learned about the animal in the next clip?
42 Graph Lab
43
44 Scientific Discovery includes: Observations Formulating hypotheses Performing investigations Collecting and analyzing data Drawing conclusions Reporting results to scientific journals
45 What do you think happens when you run in place? What changes occur inside your body? Pg 17 Step #1 Observing what have you observed Step #2 Hypothesis what is a testable explanation Step #3 - Collect data, how can you do this? Step #4 Publish you theory Step #5 Form a theory is you hypothesis supported through data? Step #6 Do you need a new hypothesis? Step #7 Do you need to revise your theory?
46 Ethics refers to the moral principles and values held by humans. Can you think of any ethical issues in science at this time? Read from page 21-23
47 Mummy Lab
48 Test Book Review Do pages Cross Word Puzzle Test Review Game
Section Objectives: Recognize some possible benefits from studying biology. Summarize the characteristics of living things.
 Section Objectives: Recognize some possible benefits from studying biology. Summarize the characteristics of living things. The Science of Biology The concepts, principles, and theories that allow people
Section Objectives: Recognize some possible benefits from studying biology. Summarize the characteristics of living things. The Science of Biology The concepts, principles, and theories that allow people
Biologists Study the Interactions of Life
 What is Biology? Biologists Study the Interactions of Life Living things do not live in isolation. They interact with their environment and depend on other living/non-living things for survival. Biologists
What is Biology? Biologists Study the Interactions of Life Living things do not live in isolation. They interact with their environment and depend on other living/non-living things for survival. Biologists
9/19/2016 CHAPTER 1: THE STUDY OF LIFE SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION TO THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 1: THE STUDY OF LIFE SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY Ms. Diana THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology is the study of living things. In biology, you study the origins and history of life and once-living
CHAPTER 1: THE STUDY OF LIFE SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY Ms. Diana THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology is the study of living things. In biology, you study the origins and history of life and once-living
Section1.1 - What is Biology?
 Ch 1: What is Biology? Section1.1 - What is Biology? Inside This Section... What is Biology? What is an Organism? The 5 Characteristics of Living Things. What is Biology? Biology is The Study of - Life
Ch 1: What is Biology? Section1.1 - What is Biology? Inside This Section... What is Biology? What is an Organism? The 5 Characteristics of Living Things. What is Biology? Biology is The Study of - Life
All living things share the characteristics of life.
 Section 1: All living things share the characteristics of life. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What is biology? What are possible benefits of studying biology?
Section 1: All living things share the characteristics of life. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What is biology? What are possible benefits of studying biology?
Unit 1: Introduction WHAT IS BIOLOGY, NATURE OF SCIENCE, BIOCHEMISTRY
 Unit 1: Introduction WHAT IS BIOLOGY, NATURE OF SCIENCE, BIOCHEMISTRY BIO 9A BIO 9B Biology The science of life Includes Studies of: Evolution: Origins and history of life and once-living things Structures
Unit 1: Introduction WHAT IS BIOLOGY, NATURE OF SCIENCE, BIOCHEMISTRY BIO 9A BIO 9B Biology The science of life Includes Studies of: Evolution: Origins and history of life and once-living things Structures
Is this a living thing -? Why?
 Characteristics of Living Things Is this a living thing -? Why? Is this a living thing -? Why? Organism anything that possesses all of the characteristics of life Living things are organized Living things
Characteristics of Living Things Is this a living thing -? Why? Is this a living thing -? Why? Organism anything that possesses all of the characteristics of life Living things are organized Living things
Unit 1 Introduction Chapter 1 The Nature of Life watch?v=vyuokb3go7e
 Unit 1 Introduction Chapter 1 The Nature of Life https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=vyuokb3go7e Unit 1: Standards 1. Explain how events in the natural world are discovered. 2. Distinguish how the scientific
Unit 1 Introduction Chapter 1 The Nature of Life https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=vyuokb3go7e Unit 1: Standards 1. Explain how events in the natural world are discovered. 2. Distinguish how the scientific
Biology: The Study of Life
 Biology: The Study of Life Before You Read Use the What I Know column to list three things you know about biology. Then list three questions you have about biology in the What I Want to Find Out column.
Biology: The Study of Life Before You Read Use the What I Know column to list three things you know about biology. Then list three questions you have about biology in the What I Want to Find Out column.
Need to Know. How do you conduct science? What are the characteristics of life?
 Science and Biology Need to Know How do you conduct science? What is biology? What are the characteristics of life? Science Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural
Science and Biology Need to Know How do you conduct science? What is biology? What are the characteristics of life? Science Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology 1.1 What is science 1.2 Science in context 1.3 Studying life
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology 1.1 What is science 1.2 Science in context 1.3 Studying life Taking notes Why do we take notes? Restructuring information makes you think about it! Make it easier to later
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology 1.1 What is science 1.2 Science in context 1.3 Studying life Taking notes Why do we take notes? Restructuring information makes you think about it! Make it easier to later
Scientific Method - the universal approach to solving scientific problems. 1. Problem Statement - Define the problem - ask question
 Biology: 7 Character of Life: 1. Organization of Cells 2. Response to Stimuli 3. Homeostasis 4. Metabolism 5. Growth & Development 6. Reproduction 7. Change Through Time Levels of Organization Atoms molecules
Biology: 7 Character of Life: 1. Organization of Cells 2. Response to Stimuli 3. Homeostasis 4. Metabolism 5. Growth & Development 6. Reproduction 7. Change Through Time Levels of Organization Atoms molecules
Introduction to Science. Section 1: The Nature of Science Section 2: The Way Science Works Section 3: Organizing Data
 Introduction to Science Section 1: The Nature of Science Section 2: The Way Science Works Section 3: Organizing Data Section 1: The Nature of Science Key Terms Science Technology Scientific Law Scientific
Introduction to Science Section 1: The Nature of Science Section 2: The Way Science Works Section 3: Organizing Data Section 1: The Nature of Science Key Terms Science Technology Scientific Law Scientific
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 1: An Introduction to the Science of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 1: An Introduction to the Science of Life An Introduction to the Science of Life: Chapter Learning Outcomes 1.1) Describe the properties of life common to all living things. (Module
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 1: An Introduction to the Science of Life An Introduction to the Science of Life: Chapter Learning Outcomes 1.1) Describe the properties of life common to all living things. (Module
Unit 1 ~ Scientific Reasoning & Logic
 Unit 1 ~ Scientific Reasoning & Logic A) An Introduction to Biology What is the study of Biology? Every thing can be classified into one of 3 groups... o _ o _ o _ Why do people study it?... Or better
Unit 1 ~ Scientific Reasoning & Logic A) An Introduction to Biology What is the study of Biology? Every thing can be classified into one of 3 groups... o _ o _ o _ Why do people study it?... Or better
Chapter 1. Scientific Process and Themes of Biology
 Chapter 1 Scientific Process and Themes of Biology What is Science? u Scientific knowledge is acquired using a rigorous process u Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the
Chapter 1 Scientific Process and Themes of Biology What is Science? u Scientific knowledge is acquired using a rigorous process u Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the
Dr. Dennis Gervin Sections: 4252, 4253, 7734,
 BIOLOGY 111 Dr. Dennis Gervin Sections: 4252, 4253, 7734, 7736 http://www.mjc.edu/ http://gervind.faculty.mjc.edu/default.html A Guide to the Natural World How Does Science Impact Your Everyday World?
BIOLOGY 111 Dr. Dennis Gervin Sections: 4252, 4253, 7734, 7736 http://www.mjc.edu/ http://gervind.faculty.mjc.edu/default.html A Guide to the Natural World How Does Science Impact Your Everyday World?
CHAPTER 1 THE SCIENCE OF LIFE
 CHAPTER 1 THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology Bio - life Logy- the study of Biology is the study of life or living things Some branches of Biology include- Microbiology, Marine Biology, Botany, Zoology, Ecology
CHAPTER 1 THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology Bio - life Logy- the study of Biology is the study of life or living things Some branches of Biology include- Microbiology, Marine Biology, Botany, Zoology, Ecology
Life Science Notes Chapter 1 Exploring and Classifying Life
 Section 1.1 What is Science? Types of Science- Life Science Notes Chapter 1 Exploring and Classifying Life Life Science: Biology, Anatomy, Zoology Earth Science; Astronomy, Mineralogy, Meteorology Physical
Section 1.1 What is Science? Types of Science- Life Science Notes Chapter 1 Exploring and Classifying Life Life Science: Biology, Anatomy, Zoology Earth Science; Astronomy, Mineralogy, Meteorology Physical
MIDDLE SCHOOL BIOLOGY LABORATORY 1ST SEMESTER NAME: DATE: Activity: for each text we will highlight the most important information.
 NAME: DATE: TEACHER: Albert Hernandez. GRADE: 2 nd I. Read text carefully and answer the questions bellow. Activity: for each text we will highlight the most important information. The Goal of Science
NAME: DATE: TEACHER: Albert Hernandez. GRADE: 2 nd I. Read text carefully and answer the questions bellow. Activity: for each text we will highlight the most important information. The Goal of Science
1.1. KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. 4 Reinforcement Unit 1 Resource Book. Biology in the 21st Century CHAPTER 1
 1.1 THE STUDY OF LIFE KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. Biology is the scientific study of all forms of life. Living things are found almost everywhere on Earth, from very hot environments
1.1 THE STUDY OF LIFE KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. Biology is the scientific study of all forms of life. Living things are found almost everywhere on Earth, from very hot environments
INTRO TO BIOLOGY -GUIDED NOTES-
 INTRO TO BIOLOGY -GUIDED NOTES- DEFINING KEY SCIENCE TERMS - an organized way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Biology-. Observation- the process of. Data- the information gathered from
INTRO TO BIOLOGY -GUIDED NOTES- DEFINING KEY SCIENCE TERMS - an organized way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Biology-. Observation- the process of. Data- the information gathered from
Intro. My website is what you should turn to if you lose something or forget what your HW is, OR.if you are absent!!!
 Intro All of my powerpoints, notes, and most handouts can be found on my website at www.bohneoprfhs.weebly.com - please use this website regularly as it is always updated! My website is what you should
Intro All of my powerpoints, notes, and most handouts can be found on my website at www.bohneoprfhs.weebly.com - please use this website regularly as it is always updated! My website is what you should
1-3 Studying Life. Slide of 45. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Characteristics of Living Things What are some characteristics of living things? Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living
Characteristics of Living Things What are some characteristics of living things? Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living
SOL Study Book Fifth Grade Scientific Investigation, Reasoning, and Logic
 SOL Study Book Fifth Grade Scientific Investigation, Reasoning, and Logic Table of Contents Page 1: Measurement Page 2: Measuring Instruments Page 3: Data Collection, Recording, and Reporting Page 4-5:
SOL Study Book Fifth Grade Scientific Investigation, Reasoning, and Logic Table of Contents Page 1: Measurement Page 2: Measuring Instruments Page 3: Data Collection, Recording, and Reporting Page 4-5:
The Science of Biology Chapter 1. Sec. 1-1 What Is Science?
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Sec. 1-1 What Is Science? 1 What Science Is and Is Not Science a way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Goals of Science: Investigate and understand the
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Sec. 1-1 What Is Science? 1 What Science Is and Is Not Science a way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Goals of Science: Investigate and understand the
Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Block Honors Biology Mrs. Flannery Characteristics of Life READ AND UNDERLINE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living
Name Date Block Honors Biology Mrs. Flannery Characteristics of Life READ AND UNDERLINE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living
The Science of Biology
 The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary l Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms l Science-
The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary l Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms l Science-
Scientific Method. Chapter 1.3. Copyright Cmassengale
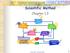 Scientific Method Chapter 1.3 1 Observation STEP 1 Employing your five senses to perceive objects or events 2 3 Asking a Question Based on observations; one or more questions are generated 4 Forming a
Scientific Method Chapter 1.3 1 Observation STEP 1 Employing your five senses to perceive objects or events 2 3 Asking a Question Based on observations; one or more questions are generated 4 Forming a
Scientific Inquiry. Deborah Turner
 Scientific Inquiry Deborah Turner CHAPTER 1 Scientific Inquiry The Scientific inquiry is a process of steps that scientist use in order to explain and idea. Steps normally are in order for the following
Scientific Inquiry Deborah Turner CHAPTER 1 Scientific Inquiry The Scientific inquiry is a process of steps that scientist use in order to explain and idea. Steps normally are in order for the following
Directed Reading A. Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS. a(n). LIVING THINGS SENSE AND RESPOND TO CHANGE
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS 1. The smallest unit that can perform all life processes is called a(n). 2. All living things are
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS 1. The smallest unit that can perform all life processes is called a(n). 2. All living things are
Grady Middle School Science 6th Grade Summer Packet Date. How do scientists measure things?
 Student name LESSON 1 Grady Middle School Science 6th Grade Summer Packet Date How do scientists measure things? How much do you weigh? What is your height? How many tiles will cover your kitchen floor?
Student name LESSON 1 Grady Middle School Science 6th Grade Summer Packet Date How do scientists measure things? How much do you weigh? What is your height? How many tiles will cover your kitchen floor?
Biology. Slide 1 of 21. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? 2 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is Not What Science Is and Is Not What is the goal of science? 3 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is
Biology 1 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? 2 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is Not What Science Is and Is Not What is the goal of science? 3 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is
1-3 Studying Life. Slide 1 of 45. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 45 2 of 45 Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living thing. Some nonliving things share one or more traits with living
1 of 45 2 of 45 Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living thing. Some nonliving things share one or more traits with living
The Science of Biology
 The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science- an
The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science- an
Warm Up: Vocabulary. Unit 1 Introduction to Biology. Defining Key Terms. Defining Key Terms. Defining Key Terms (continued) Think About It
 Unit 1 Introduction to Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science-
Unit 1 Introduction to Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science-
REVISION WORKSHEET (1) Diversity of life Syllabus coverage pgs
 United Arab Emirates Abu Dhabi Educational Council Int'l Jubilee Private School American Syllabus Student Name: Grade: 8 a,b Date: / / 2013 Subject: Science Revision REVISION WORKSHEET (1) Diversity of
United Arab Emirates Abu Dhabi Educational Council Int'l Jubilee Private School American Syllabus Student Name: Grade: 8 a,b Date: / / 2013 Subject: Science Revision REVISION WORKSHEET (1) Diversity of
The composition, structure, & functions of the Earth & it s place in the universe. The interactions between the living & nonliving parts of the Earth.
 Unit 1 Earth Science Environmental Science The composition, structure, & functions of the Earth & it s place in the universe. The interactions between the living & nonliving parts of the Earth. plate tectonics,
Unit 1 Earth Science Environmental Science The composition, structure, & functions of the Earth & it s place in the universe. The interactions between the living & nonliving parts of the Earth. plate tectonics,
Directed Reading A. Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS. a(n). LIVING THINGS SENSE AND RESPOND TO CHANGE
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS 1. The smallest unit that can perform all life processes is called a(n). 2. All living things are
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS 1. The smallest unit that can perform all life processes is called a(n). 2. All living things are
The Science of Biology
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Section 1 1 What Is Science? (pages 3 7) This section explains what the goal of science is and describes a scientific view of the world What Science Is and Is Not (page
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Section 1 1 What Is Science? (pages 3 7) This section explains what the goal of science is and describes a scientific view of the world What Science Is and Is Not (page
Standards of the past
 Metric Prefixes Measurement Must have a standard. A standard is an exact quantity people agree to use for comparison. A standard means two people using the same object should get close to the same results.
Metric Prefixes Measurement Must have a standard. A standard is an exact quantity people agree to use for comparison. A standard means two people using the same object should get close to the same results.
THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY SECTION 1-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank.
 SECTION 1-1 REVIEW THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. development 2. reproduction 3. organ 4. tissue MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. Biology
SECTION 1-1 REVIEW THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. development 2. reproduction 3. organ 4. tissue MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. Biology
Studying Life. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 1.3 Studying Life
 Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Measurement. Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure.
 chapter 32 Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You ll Learn how to estimate
chapter 32 Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You ll Learn how to estimate
Characteristics of Living Things
 Characteristics of Living Things All Living Things Are made up of units called cells A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive Types of Cellular Organisms Unicellular Uni
Characteristics of Living Things All Living Things Are made up of units called cells A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive Types of Cellular Organisms Unicellular Uni
Biology Assessment. Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 Biology Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules
Biology Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules
The Science of Biology. Chapter 1
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Warm Up Exercise Please complete the pretest that you picked up when you came in. Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary.
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Warm Up Exercise Please complete the pretest that you picked up when you came in. Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary.
Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Period Score Characteristics of Life READ AND HILITE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving
Name Date Period Score Characteristics of Life READ AND HILITE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving
STAAR Biology Assessment
 STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules as building blocks of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of
STAAR Biology Assessment Reporting Category 1: Cell Structure and Function The student will demonstrate an understanding of biomolecules as building blocks of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of
Defining Physical Science
 Defining Physical Science Physical Science is the study of matter & energy; a merging of two major branches of science: 1. Chemistry - study of the composition & changes of matter, 2. Physics - study of
Defining Physical Science Physical Science is the study of matter & energy; a merging of two major branches of science: 1. Chemistry - study of the composition & changes of matter, 2. Physics - study of
Prentice Hall Science Explorer: Life, Earth, and Physical Science 2005 Correlated to Oklahoma Priority Academic Student Skills for Science (Grade 8)
 Prentice Hall Science Explorer: Life, Earth, and 2005 Oklahoma Priority Academic Student Skills for Science (Grade 8) NOTE: Asterisks (*) have been used to identify standards and objectives that must be
Prentice Hall Science Explorer: Life, Earth, and 2005 Oklahoma Priority Academic Student Skills for Science (Grade 8) NOTE: Asterisks (*) have been used to identify standards and objectives that must be
Chapter 1 The Science of Life
 Chapter 1 The Science of Life (Sect. 1) Biology how living things work how living things interact w/the environment how living things change over time 7 Characteristics of Life 1.Organization & the presence
Chapter 1 The Science of Life (Sect. 1) Biology how living things work how living things interact w/the environment how living things change over time 7 Characteristics of Life 1.Organization & the presence
Change Over Time Concept Map
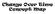 Change Over Time Concept Map Darwin reasoned that plants or animals that arrived on the Galapagos Islands faced conditions that were different from those on the mainland. Perhaps, Darwin hypothesized,
Change Over Time Concept Map Darwin reasoned that plants or animals that arrived on the Galapagos Islands faced conditions that were different from those on the mainland. Perhaps, Darwin hypothesized,
Metric System & Scientific Notation
 + Metric System & Scientific Notation + What Americans Are Used To The English Standard System Inches and gallons and pounds (oh my!) Many different units Inches, feet, yards, miles, Ounces, cups, pints,
+ Metric System & Scientific Notation + What Americans Are Used To The English Standard System Inches and gallons and pounds (oh my!) Many different units Inches, feet, yards, miles, Ounces, cups, pints,
BIOLOGY NOTES - CHAPTER 1
 BIOLOGY NOTES - CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1 and 2 Biology is the study of life Bio = life Logy = study of The scientific study of all forms of life, or all types of organisms Science means to know Science is a
BIOLOGY NOTES - CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1 and 2 Biology is the study of life Bio = life Logy = study of The scientific study of all forms of life, or all types of organisms Science means to know Science is a
rs Analyzing Data and "
 rs Analyzing Data and " I Communicating Results Kt!f Tenff/ communication: sharing information Analyzing Data When you organize information, you put it in a logical order. In scientific experiments, it
rs Analyzing Data and " I Communicating Results Kt!f Tenff/ communication: sharing information Analyzing Data When you organize information, you put it in a logical order. In scientific experiments, it
Other Organisms (Part 3)
 Name: Hour: Teacher: ROZEMA Biology Evolution Unit Addie Bacteria Other Organisms (Part 3) Let s Review What We Know So Far: Natural Selection is There are differences between the Junco birds that live
Name: Hour: Teacher: ROZEMA Biology Evolution Unit Addie Bacteria Other Organisms (Part 3) Let s Review What We Know So Far: Natural Selection is There are differences between the Junco birds that live
GRADE 7. Units of Study: Cell Structure and Function Energy and Life Cell Reproduction and Genetics Environmental Changes Through Time Classification
 GRADE 7 Course Overview: In seventh grade, students are actively engaged in the inquiry process as they collaborate with others to understand complex scientific concepts. Students identify a question,
GRADE 7 Course Overview: In seventh grade, students are actively engaged in the inquiry process as they collaborate with others to understand complex scientific concepts. Students identify a question,
Introduction to Science. Chapter 1. Section 1 The Nature of Science. Section 2 The Way Science Works. Section 3 Organizing Data
 Chapter 1 Introduction to Science Section 1 The Nature of Science Section 2 The Way Science Works Section 3 Organizing Data Skills Experiment Design SI Units and SI unit conversions Using graphs Scientific
Chapter 1 Introduction to Science Section 1 The Nature of Science Section 2 The Way Science Works Section 3 Organizing Data Skills Experiment Design SI Units and SI unit conversions Using graphs Scientific
15-1 The Puzzle of Life's Diversity Slide 1 of 20
 1 of 20 Evolution is the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. * Known as biological change over time A scientific theory is a well-supported testable explanation of
1 of 20 Evolution is the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. * Known as biological change over time A scientific theory is a well-supported testable explanation of
Name: Period: Date: Unit 1 Part 1 Introduction to Chemistry. What is the equation for density and its rearrangements for mass and volume?
 Unit 1 Part 1 Introduction to Chemistry Which element has a type of chemistry devoted to it? What is the equation for density and its rearrangements for mass and volume? Chemistry is often referred to
Unit 1 Part 1 Introduction to Chemistry Which element has a type of chemistry devoted to it? What is the equation for density and its rearrangements for mass and volume? Chemistry is often referred to
Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement
 Name Block Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You
Name Block Pre-Lab 0.2 Reading: Measurement section 1 Description and Measurement Before You Read Weight, height, and length are common measurements. List at least five things you can measure. What You
GRADE 6 SCIENCE REVISED 2014
 QUARTER 1 Developing and Using Models Develop and use a model to describe phenomena. (MS-LS1-2) Develop a model to describe unobservable mechanisms. (MS-LS1-7) Planning and Carrying Out Investigations
QUARTER 1 Developing and Using Models Develop and use a model to describe phenomena. (MS-LS1-2) Develop a model to describe unobservable mechanisms. (MS-LS1-7) Planning and Carrying Out Investigations
Biology. Evolution: History & Process
 Biology Evolution: History & Process Terms: A species is a group of organisms, or population, that can be interbreed & produce fertile offspring. Variations are the differences found within species. Ex:
Biology Evolution: History & Process Terms: A species is a group of organisms, or population, that can be interbreed & produce fertile offspring. Variations are the differences found within species. Ex:
Scientific Investigation, Reasoning and Logic
 Scientific Investigation, Reasoning and Logic Concept Sheet Scientific Investigation, Reasoning, and Logic LS.1 and PS.1: The student will plan and conduct investigations. 1. Investigations are classified
Scientific Investigation, Reasoning and Logic Concept Sheet Scientific Investigation, Reasoning, and Logic LS.1 and PS.1: The student will plan and conduct investigations. 1. Investigations are classified
INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE CHAPTER 1
 INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE CHAPTER 1 1 Science is the study of Everything!! A way of learning about the natural world. Scientist: a person who studies, or has expert WHAT IS SCIENCE? knowledge of a natural
INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE CHAPTER 1 1 Science is the study of Everything!! A way of learning about the natural world. Scientist: a person who studies, or has expert WHAT IS SCIENCE? knowledge of a natural
CELL AND MICROBIOLOGY Nadia Iskandarani
 7Course Title: Head of Department: Teacher(s) + e-mail: Cycle/Division: Biology IA: CELL AND MICROBIOLOGY Nadia Iskandarani Ms.Ibtessam: ibtissam.h@greenwood.sch.ae High School Grade Level: Grade 10 Credit
7Course Title: Head of Department: Teacher(s) + e-mail: Cycle/Division: Biology IA: CELL AND MICROBIOLOGY Nadia Iskandarani Ms.Ibtessam: ibtissam.h@greenwood.sch.ae High School Grade Level: Grade 10 Credit
SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY AND CONNECTIONS. Recognize questions and hypotheses that can be investigated according to the criteria and methods of science
 SUBAREA I. COMPETENCY 1.0 SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY AND CONNECTIONS UNDERSTAND THE PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY AND CONDUCTING SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATIONS SKILL 1.1 Recognize questions and hypotheses
SUBAREA I. COMPETENCY 1.0 SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY AND CONNECTIONS UNDERSTAND THE PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY AND CONDUCTING SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATIONS SKILL 1.1 Recognize questions and hypotheses
Observation: The process of gathering information, in a careful orderly way.
 Observation: The process of gathering information, in a careful orderly way. Prediction vs Hypothesis Predictions are meant to be proven once. A hypothesis can still end up as a hypothesis even if it has
Observation: The process of gathering information, in a careful orderly way. Prediction vs Hypothesis Predictions are meant to be proven once. A hypothesis can still end up as a hypothesis even if it has
Teacher: C. Hill Room: 113. Edmodo: Black or Blue Pens No. 2 Pencil Composition Notebook
 Teacher: C. Hill Room: 113 Email: chill2@houstonisd.org Telephone: 713-732-3623 (work) Edmodo: https://www.edmodo.com Materials Tape Graph Paper Colored Pencils Index Cards Black or Blue Pens No. 2 Pencil
Teacher: C. Hill Room: 113 Email: chill2@houstonisd.org Telephone: 713-732-3623 (work) Edmodo: https://www.edmodo.com Materials Tape Graph Paper Colored Pencils Index Cards Black or Blue Pens No. 2 Pencil
How To Complete and Experiment and Write a Lab Report: Using Questions to Write a Hypothesis With Clear Independent and Dependent Variables
 How To Complete and Experiment and Write a Lab Report: Using Questions to Write a Hypothesis With Clear Independent and Dependent Variables 1 I can How to Write a Hypothesis http://www.myteacherpages.com/webpages/jflynt/portfolio.cfm?subpage=1001394
How To Complete and Experiment and Write a Lab Report: Using Questions to Write a Hypothesis With Clear Independent and Dependent Variables 1 I can How to Write a Hypothesis http://www.myteacherpages.com/webpages/jflynt/portfolio.cfm?subpage=1001394
DO NOW. Each PAIR should take one white cloth and one cup of beans from the back desk. Make sure you have 20 white beans and 20 brown beans.
 DO NOW Each PAIR should take one white cloth and one cup of beans from the back desk. Make sure you have 20 white beans and 20 brown beans. Class Results Number of Brown Beans Picked Number of White Beans
DO NOW Each PAIR should take one white cloth and one cup of beans from the back desk. Make sure you have 20 white beans and 20 brown beans. Class Results Number of Brown Beans Picked Number of White Beans
Introduction Themes in the Study of Life
 BellRinger What is Biology? Introduction Themes in the Study of Life Chapter 1 1 What is science? What is the goal of science? Investigate and understand the natural world Explain events in the natural
BellRinger What is Biology? Introduction Themes in the Study of Life Chapter 1 1 What is science? What is the goal of science? Investigate and understand the natural world Explain events in the natural
Genetic Changes Lesson 2 CW
 Guiding Question What theory serves as the basis of what we believe about how evolutionary changes occur? 7 th GRADE SCIENCE Genetic Changes Lesson 2 CW # Name: Date: Homeroom: I can Activator At the beginning
Guiding Question What theory serves as the basis of what we believe about how evolutionary changes occur? 7 th GRADE SCIENCE Genetic Changes Lesson 2 CW # Name: Date: Homeroom: I can Activator At the beginning
Family Trees for all grades. Learning Objectives. Materials, Resources, and Preparation
 page 2 Page 2 2 Introduction Family Trees for all grades Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including this one, are available
page 2 Page 2 2 Introduction Family Trees for all grades Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including this one, are available
Defining Physical Science
 Defining Physical Science Defining Physical Science: Physical Science: The study of matter and energy A merging of two major braches of Science: 1. Chemistry: Study of the composition and changes of matter
Defining Physical Science Defining Physical Science: Physical Science: The study of matter and energy A merging of two major braches of Science: 1. Chemistry: Study of the composition and changes of matter
Note Taking in my class
 Note Taking in my class! If it is underlined you need to know it for the test.! I do not do notebook checks.! You are responsible for taking and keeping up with your notes.! Note material will be seen
Note Taking in my class! If it is underlined you need to know it for the test.! I do not do notebook checks.! You are responsible for taking and keeping up with your notes.! Note material will be seen
SYLLABUS INDEX CARD NAME MAJOR (IF YOU DON T HAVE ONE INTEREST) WHAT DO YOU WANT TO BE WHEN YOU GROW UP?
 WELCOME CHEMISTRY 131: PRINCIPLES OF CHEMISTRY Mrs. DeVos September 19, 2011 SYLLABUS INDEX CARD NAME MAJOR (IF YOU DON T HAVE ONE INTEREST) WHAT DO YOU WANT TO BE WHEN YOU GROW UP? WHY ARE YOU TAKING
WELCOME CHEMISTRY 131: PRINCIPLES OF CHEMISTRY Mrs. DeVos September 19, 2011 SYLLABUS INDEX CARD NAME MAJOR (IF YOU DON T HAVE ONE INTEREST) WHAT DO YOU WANT TO BE WHEN YOU GROW UP? WHY ARE YOU TAKING
Section 1: The Nature of Science
 Section 1: The Nature of Science Preview Key Ideas Bellringer How Science Takes Place The Branches of Science Scientific Laws and Theories Key Ideas How do scientists explore the world? How are the many
Section 1: The Nature of Science Preview Key Ideas Bellringer How Science Takes Place The Branches of Science Scientific Laws and Theories Key Ideas How do scientists explore the world? How are the many
HOUSE QUESTIONS (R) 1) How big is your house? 2) How many rooms? 3) Bathroom dimensions? 4) living room floor color?
 HOUSE QUESTIONS (R) 1) How big is your house? 2) How many rooms? 3) Bathroom dimensions? 4) living room floor color? 5) What is blue and smells like red paint? SCIENTIFIC METHOD What are the steps to the
HOUSE QUESTIONS (R) 1) How big is your house? 2) How many rooms? 3) Bathroom dimensions? 4) living room floor color? 5) What is blue and smells like red paint? SCIENTIFIC METHOD What are the steps to the
Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Period Score Characteristics of Life READ AND HILITE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving
Name Date Period Score Characteristics of Life READ AND HILITE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving
Measurements and Calculations. Chapter 2
 Measurements and Calculations Chapter 2 Scientific Method Section 2-1 The Scientific Method The scientific method is a logical approach to solving problems by observing and collecting data, formulating
Measurements and Calculations Chapter 2 Scientific Method Section 2-1 The Scientific Method The scientific method is a logical approach to solving problems by observing and collecting data, formulating
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1-1 THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1-1 THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. Name Period Date 1. A short segment of DNA that contains instructions for the development of a single
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 1-1 THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. Name Period Date 1. A short segment of DNA that contains instructions for the development of a single
PS. 1 - SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION
 PS. 1 - SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION Scientific Method: an organized set of investigative procedures which scientists follow to answer testable questions. Steps include: 1. Identify the problem or question.
PS. 1 - SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION Scientific Method: an organized set of investigative procedures which scientists follow to answer testable questions. Steps include: 1. Identify the problem or question.
6 th Grade Math. Full Curriculum Book. Sample file. A+ Interactive Math (by A+ TutorSoft, Inc.)
 6 th Grade Math Full Curriculum Book Release 7 A+ Interactive Math (by A+ TutorSoft, Inc.) Email: info@aplustutorsoft.com www.aplustutorsoft.com Page 3 of 518 Copyright 2014 A+ TutorSoft Inc., All Rights
6 th Grade Math Full Curriculum Book Release 7 A+ Interactive Math (by A+ TutorSoft, Inc.) Email: info@aplustutorsoft.com www.aplustutorsoft.com Page 3 of 518 Copyright 2014 A+ TutorSoft Inc., All Rights
Life Science Notes Chapter 1 Exploring and Classifying Life. Life Science:, Anatomy, Earth Science;, Mineralogy, Physical Science:,
 Section 1.1 What is Science? Types of Science- Life Science Notes Chapter 1 Exploring and Classifying Life Life Science:, Anatomy, Earth Science;, Mineralogy, Physical Science:, Critical thinking- looking
Section 1.1 What is Science? Types of Science- Life Science Notes Chapter 1 Exploring and Classifying Life Life Science:, Anatomy, Earth Science;, Mineralogy, Physical Science:, Critical thinking- looking
Math Study Guide Due: Monday, February 6, 2017 Semester 1 3 rd Grade Math Benchmark Study Guide
 Name: #: Math Study Guide Assigned to Student: Wednesday, January 25, 2017 Math Study Guide Due: Monday, February 6, 2017 Semester 1 3 rd Grade Math Benchmark Study Guide Your 35 question Math Benchmark
Name: #: Math Study Guide Assigned to Student: Wednesday, January 25, 2017 Math Study Guide Due: Monday, February 6, 2017 Semester 1 3 rd Grade Math Benchmark Study Guide Your 35 question Math Benchmark
7TH GRADE SCIENCE EXAM REVIEW. 1. The actual gene pair for a trait would be the.
 7TH GRADE SCIENCE EXAM REVIEW Genetics: 1. The actual gene pair for a trait would be the. 2. Strands of DNA that control information in the nucleus of a cell are called 3. Segments of DNA the code for
7TH GRADE SCIENCE EXAM REVIEW Genetics: 1. The actual gene pair for a trait would be the. 2. Strands of DNA that control information in the nucleus of a cell are called 3. Segments of DNA the code for
Name Date Period Handout A: Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Period Handout A: Characteristics of Life Directions: 1. Read and highlight the main ideas in each passage. 2. Circle Key vocabulary 3. Answer the questions below each passage. Most people feel
Name Date Period Handout A: Characteristics of Life Directions: 1. Read and highlight the main ideas in each passage. 2. Circle Key vocabulary 3. Answer the questions below each passage. Most people feel
Introduction to Biology
 Introduction to Biology Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Introduction to Biology Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Chapter Test A. It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Assessment Chapter Test A It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share?
Assessment Chapter Test A It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share?
Introduction to Biology
 1 Introduction to Biology 2 Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
1 Introduction to Biology 2 Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Charles Darwin became a naturalist, a scientist who studies nature, during a voyage on the British ship HMS Beagle.
 Theory of Evolution Darwin s Voyage What did Darwin observe? Charles Darwin became a naturalist, a scientist who studies nature, during a voyage on the British ship HMS Beagle. On his journey, Darwin observed
Theory of Evolution Darwin s Voyage What did Darwin observe? Charles Darwin became a naturalist, a scientist who studies nature, during a voyage on the British ship HMS Beagle. On his journey, Darwin observed
Evidence: Table 1: Group Forkbird Population Data 1-Tined Forkbirds 2-Tined Forkbirds 4-Tined Forkbirds Initial
 Activity #96 Battling Beaks Challenge Question: Initial Thoughts: Prediction: Evidence: Table 1: Group Forkbird Population Data 1-Tined Forkbirds 2-Tined Forkbirds 4-Tined Forkbirds Initial 1 2 3 4 5 6
Activity #96 Battling Beaks Challenge Question: Initial Thoughts: Prediction: Evidence: Table 1: Group Forkbird Population Data 1-Tined Forkbirds 2-Tined Forkbirds 4-Tined Forkbirds Initial 1 2 3 4 5 6
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life
 Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Figure 1.0_1 Chapter 1:
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Figure 1.0_1 Chapter 1:
Unit 1 Tools of Chemistry. Objective: To understand the fundamentals used throughout a study of chemistry
 Unit 1 Tools of Chemistry Objective: To understand the fundamentals used throughout a study of chemistry Learning Goals O I can describe the scientific method. O I can determine whether a hypothesis is
Unit 1 Tools of Chemistry Objective: To understand the fundamentals used throughout a study of chemistry Learning Goals O I can describe the scientific method. O I can determine whether a hypothesis is
METRIC CHART. The metric system has three units or bases.
 METRIC SYSTEM THE METRIC SYSTEM The metric system is much easier. All metric units are related by factors of 10. Nearly the entire world (95%), except the United States, now uses the metric system. Metric
METRIC SYSTEM THE METRIC SYSTEM The metric system is much easier. All metric units are related by factors of 10. Nearly the entire world (95%), except the United States, now uses the metric system. Metric
Scientific Units of Measurement & Conversion
 Scientific Units of Measurement & Conversion Principle or Rationale: Scientific measurements are made and reported using the metric system and conversion between different units is an integral part of
Scientific Units of Measurement & Conversion Principle or Rationale: Scientific measurements are made and reported using the metric system and conversion between different units is an integral part of
The Science of Life. Introduction to Biology
 The Science of Life Introduction to Biology What is Biology Bio = life logos = knowledge many branches - different things to study in biology Botany study of plants all types of plants - trees, flowers,
The Science of Life Introduction to Biology What is Biology Bio = life logos = knowledge many branches - different things to study in biology Botany study of plants all types of plants - trees, flowers,
1 Exploring Physical Science
 CHAPTER 3 1 Exploring Physical Science SECTION The World of Physical Science BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is science? How are matter and
CHAPTER 3 1 Exploring Physical Science SECTION The World of Physical Science BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is science? How are matter and
