Need to Know. How do you conduct science? What are the characteristics of life?
|
|
|
- Antonia Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Science and Biology
2 Need to Know How do you conduct science? What is biology? What are the characteristics of life?
3 Science Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural world Science is derived from the Latin word scientia, which means knowledge Science aims to find the best understanding of the natural world that current methods can reveal
4 Even though there is no one way to conduct scientific research there are several steps that most people utilize to solve problems in a scientific manner.
5 Scientific Methodology Step One = Observing and asking questions Scientific observation is noticing and describing events or processes in a careful, orderly way Observation is more than just looking
6 Scientific Methodology Step Two = Making inferences An inference is a logical interpretation based on what scientists already know
7 Scientific Methodology Step Three = Forming hypotheses A hypothesis is a scientific explanation for a set of observations that can be tested in ways that support or reject it
8 Scientific Methodology Step Four = Conducting controlled experiments A controlled experiment is an experiment in which only one variable is changed All other variables should be kept unchanged, or controlled The independent variable (IV) is the variable that is deliberately changed by the researcher The dependent variable (DV) is the variables that is observed and that changes in response to the IV
9 Scientific Methodology Step Four = Conducting controlled experiments A control group is exposed to the same conditions as the experimental group except for one independent variable
10 Scientific Methodology Step Five = Collecting and analyzing data Quantitative data are numbers obtained by counting or measuring Qualitative data are descriptive and involve characteristics that cannot be counted
11 Scientific Methodology Step Six = Drawing conclusions Scientists use experimental data as evidence to support, refute, or revise the hypothesis being tested, and to draw a valid conclusion
12 Observation and Asking Questions Researchers observed that marsh grass grows taller in some places than others This observation led to a question: Why do marsh grasses grow to different heights in different places?
13 Inferring and Forming a Hypothesis Researchers inferred that something limits grass growth in some places Based on their knowledge of salt marshes, they hypothesized that marsh grass growth is limited by available nitrogen
14 Designing Controlled Experiments The researchers selected similar plots of marsh grass (all plots had similar plant density, soil type, input of freshwater, and height above average tide level) The plots were divided into control and experimental groups and the researchers added nitrogen fertilizer (IV) to the experimental plots They then observed the growth of marsh grass (DV) in both experimental and control plots
15 Collecting and Analyzing Data The researchers recorded the height of each group of grasses each week
16 Drawing Conclusions Data analysis confirmed that marsh grasses in experimental plots with additional nitrogen fertilizer did, in fact, grow taller and larger than controls The hypothesis and its predictions were supported
17 Communicating Results Scientists share their findings to allow researchers to test and evaluate each other s work New findings will also spark new questions Peer review is utilized prior to publishing results to look for oversights, unfair influences, fraud, or mistakes in techniques or reasoning
18 Scientific Theory A scientific theory is a well-tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations and hypotheses and that enables scientists to make accurate predictions about new situations The word theory differs in science and daily life Science = A well-tested explanation Daily life = An idea or hunch
19 Limitations of Science Science does not include ethical or moral viewpoints Science reports facts; society applies the good or bad
20 Limitations of Science Science can be influenced by bias A bias is a particular preference or point of view that is personal, rather than scientific
21 Biology Biology is the science that employs scientific methodology to study living things
22 What makes something alive?
23 Biology Biology is the science that employs scientific methodology to study living things The Greek word bios = life and logy = study of
24 Characteristics of Living Things Living things are based on a universal genetic code The genetic code is written in a molecule called DNA All living things are fundamentally similar at the molecular level Living things contain carbon-based molecules, store genetic information in DNA, and make proteins
25
26 Characteristics of Living Things Living things grow and develop Growth is the increase in the amount of living material and the formation of new structures Development is all of the changes that take place during one s life During growth and development, generalized cells typically become more different and specialized for particular functions Specialized cells build tissues, such as brains, muscles, and digestive organs, that serve various functions
27 Characteristics of Living Things Living things respond to their environment A stimulus is a signal to which an organism responds
28 Characteristics of Living Things Living things reproduce Sexual reproduction is when cells from two parents unite to form the first cell of a new organism Asexual reproduction is when a single organism produces offspring identical to itself
29 Characteristics of Living Things Living things maintain a relatively stable internal environment (even when external conditions change dramatically) Homeostasis is the process whereby all living things Homeostasis is the process whereby all living things expend energy to keep conditions inside their cells within certain limits
30 Characteristics of Living Things Living things obtain and use material and energy The combination of chemical reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down materials is called metabolism Life requires matter that serves as nutrients to build body structures, and energy that fuels life s processes Some organisms (such as plants) obtain energy from sunlight and take up nutrients from air, water, and soil Other organisms (including most animals) eat plants or other animal to obtain both nutrients and energy
31 Characteristics of Living Things Living things are made up of one or more cells Cells are the smallest units considered fully alive Unicellular organisms are living things that consist of only a single cell Multicellular organisms are composed of many cells
32 Characteristics of Living Things Over generations, groups of organisms evolve Evolution is the gradual accumulation of adaptations over time Adaptations are any structure, behavior, or internal process that enables an organism to respond to stimuli and better survive in an environment
33 Bald Eagle Spoonbill Kiwi
Chapter 1. Scientific Process and Themes of Biology
 Chapter 1 Scientific Process and Themes of Biology What is Science? u Scientific knowledge is acquired using a rigorous process u Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the
Chapter 1 Scientific Process and Themes of Biology What is Science? u Scientific knowledge is acquired using a rigorous process u Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology 1.1 What is science 1.2 Science in context 1.3 Studying life
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology 1.1 What is science 1.2 Science in context 1.3 Studying life Taking notes Why do we take notes? Restructuring information makes you think about it! Make it easier to later
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology 1.1 What is science 1.2 Science in context 1.3 Studying life Taking notes Why do we take notes? Restructuring information makes you think about it! Make it easier to later
Unit 1 Introduction Chapter 1 The Nature of Life watch?v=vyuokb3go7e
 Unit 1 Introduction Chapter 1 The Nature of Life https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=vyuokb3go7e Unit 1: Standards 1. Explain how events in the natural world are discovered. 2. Distinguish how the scientific
Unit 1 Introduction Chapter 1 The Nature of Life https://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=vyuokb3go7e Unit 1: Standards 1. Explain how events in the natural world are discovered. 2. Distinguish how the scientific
Studying Life. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 1.3 Studying Life
 Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Lesson Overview 1.3 Characteristics of Living Things What characteristics do all living things share? Living things are made up of basic units called cells, are based on a universal genetic code, obtain
Scientific Method. Chapter 1.3. Copyright Cmassengale
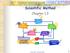 Scientific Method Chapter 1.3 1 Observation STEP 1 Employing your five senses to perceive objects or events 2 3 Asking a Question Based on observations; one or more questions are generated 4 Forming a
Scientific Method Chapter 1.3 1 Observation STEP 1 Employing your five senses to perceive objects or events 2 3 Asking a Question Based on observations; one or more questions are generated 4 Forming a
Unit 1 ~ Scientific Reasoning & Logic
 Unit 1 ~ Scientific Reasoning & Logic A) An Introduction to Biology What is the study of Biology? Every thing can be classified into one of 3 groups... o _ o _ o _ Why do people study it?... Or better
Unit 1 ~ Scientific Reasoning & Logic A) An Introduction to Biology What is the study of Biology? Every thing can be classified into one of 3 groups... o _ o _ o _ Why do people study it?... Or better
Study of Biology. copyright cmassengale
 Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
Study of Biology 1 What is Biology? Biology is the study of all living things Living things are called organisms Organisms include bacteria, protists, fungi, plants, & animals 2 All Living Things Share
1-3 Studying Life. Slide 1 of 45. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 45 2 of 45 Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living thing. Some nonliving things share one or more traits with living
1 of 45 2 of 45 Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living thing. Some nonliving things share one or more traits with living
All living things share the characteristics of life.
 Section 1: All living things share the characteristics of life. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What is biology? What are possible benefits of studying biology?
Section 1: All living things share the characteristics of life. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions What is biology? What are possible benefits of studying biology?
Unit 1: Introduction WHAT IS BIOLOGY, NATURE OF SCIENCE, BIOCHEMISTRY
 Unit 1: Introduction WHAT IS BIOLOGY, NATURE OF SCIENCE, BIOCHEMISTRY BIO 9A BIO 9B Biology The science of life Includes Studies of: Evolution: Origins and history of life and once-living things Structures
Unit 1: Introduction WHAT IS BIOLOGY, NATURE OF SCIENCE, BIOCHEMISTRY BIO 9A BIO 9B Biology The science of life Includes Studies of: Evolution: Origins and history of life and once-living things Structures
The Science of Biology Chapter 1. Sec. 1-1 What Is Science?
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Sec. 1-1 What Is Science? 1 What Science Is and Is Not Science a way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Goals of Science: Investigate and understand the
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Sec. 1-1 What Is Science? 1 What Science Is and Is Not Science a way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Goals of Science: Investigate and understand the
1-3 Studying Life. Slide of 45. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Characteristics of Living Things What are some characteristics of living things? Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living
Characteristics of Living Things What are some characteristics of living things? Characteristics of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things No single characteristic is enough to describe a living
Characteristics of Living Things
 Characteristics of Living Things All Living Things Are made up of units called cells A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive Types of Cellular Organisms Unicellular Uni
Characteristics of Living Things All Living Things Are made up of units called cells A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive Types of Cellular Organisms Unicellular Uni
Chapter 1 Biology 103
 Chapter 1 Biology 103 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal balance
Chapter 1 Biology 103 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal balance
The Science of Biology. Chapter 1
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Properties of Life Living organisms: are composed of cells are complex and ordered respond to their environment can grow and reproduce obtain and use energy maintain internal
Directed Reading A. Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS. a(n). LIVING THINGS SENSE AND RESPOND TO CHANGE
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS 1. The smallest unit that can perform all life processes is called a(n). 2. All living things are
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS 1. The smallest unit that can perform all life processes is called a(n). 2. All living things are
Introduction Themes in the Study of Life
 BellRinger What is Biology? Introduction Themes in the Study of Life Chapter 1 1 What is science? What is the goal of science? Investigate and understand the natural world Explain events in the natural
BellRinger What is Biology? Introduction Themes in the Study of Life Chapter 1 1 What is science? What is the goal of science? Investigate and understand the natural world Explain events in the natural
Directed Reading A. Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS. a(n). LIVING THINGS SENSE AND RESPOND TO CHANGE
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS 1. The smallest unit that can perform all life processes is called a(n). 2. All living things are
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: Characteristics of Living Things LIVING THINGS HAVE CELLS 1. The smallest unit that can perform all life processes is called a(n). 2. All living things are
CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE
 CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGICAL THEMES 1. Cell Structure & Function cell is the basic unit of life all organisms are composed of at least one cell Unicellular single celled ; bacteria,
CHAPTER 1 BIOLOGY THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGICAL THEMES 1. Cell Structure & Function cell is the basic unit of life all organisms are composed of at least one cell Unicellular single celled ; bacteria,
The Characteristics of Life. AP Biology Notes: #1
 The Characteristics of Life AP Biology Notes: #1 Life s Diversity & Unity Life has extensive diversity. Despite its diversity, all living things are composed of the same chemical elements that make-up
The Characteristics of Life AP Biology Notes: #1 Life s Diversity & Unity Life has extensive diversity. Despite its diversity, all living things are composed of the same chemical elements that make-up
Biology. Slide 1 of 21. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? 2 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is Not What Science Is and Is Not What is the goal of science? 3 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is
Biology 1 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? 2 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is Not What Science Is and Is Not What is the goal of science? 3 of 21 1-1 What Is Science? What Science Is and Is
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 1: An Introduction to the Science of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 1: An Introduction to the Science of Life An Introduction to the Science of Life: Chapter Learning Outcomes 1.1) Describe the properties of life common to all living things. (Module
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 1: An Introduction to the Science of Life An Introduction to the Science of Life: Chapter Learning Outcomes 1.1) Describe the properties of life common to all living things. (Module
Biologists Study the Interactions of Life
 What is Biology? Biologists Study the Interactions of Life Living things do not live in isolation. They interact with their environment and depend on other living/non-living things for survival. Biologists
What is Biology? Biologists Study the Interactions of Life Living things do not live in isolation. They interact with their environment and depend on other living/non-living things for survival. Biologists
Warm # 15. A scientist wanted to test if playing video games increased a person's reflexes (reaction time).
 Warm # 15 A scientist wanted to test if playing video games increased a person's reflexes (reaction time). What are the independent and dependent variables? 7:53 AM Warm # 16 Give 2 characteristics of
Warm # 15 A scientist wanted to test if playing video games increased a person's reflexes (reaction time). What are the independent and dependent variables? 7:53 AM Warm # 16 Give 2 characteristics of
GRADE 6 SCIENCE REVISED 2014
 QUARTER 1 Developing and Using Models Develop and use a model to describe phenomena. (MS-LS1-2) Develop a model to describe unobservable mechanisms. (MS-LS1-7) Planning and Carrying Out Investigations
QUARTER 1 Developing and Using Models Develop and use a model to describe phenomena. (MS-LS1-2) Develop a model to describe unobservable mechanisms. (MS-LS1-7) Planning and Carrying Out Investigations
WHAT IS SCIENCE? Chapter 1. Key concept: What is the goal of science?
 WHAT IS SCIENCE? Chapter 1 Key concept: What is the goal of science? SCIENCE: Is an Uses to events Collects and organizes Deals only with Looks for patterns and organized method evidence connections explain
WHAT IS SCIENCE? Chapter 1 Key concept: What is the goal of science? SCIENCE: Is an Uses to events Collects and organizes Deals only with Looks for patterns and organized method evidence connections explain
Warm Up: Vocabulary. Unit 1 Introduction to Biology. Defining Key Terms. Defining Key Terms. Defining Key Terms (continued) Think About It
 Unit 1 Introduction to Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science-
Unit 1 Introduction to Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science-
Introduction to Biology
 Introduction to Biology Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Introduction to Biology Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
Introduction to Biology
 1 Introduction to Biology 2 Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
1 Introduction to Biology 2 Biology The Study of Life Life arose more than 3.5 billion years ago First organisms (living things) were single celled Only life on Earth for millions of years Organisms changed
 All Living Things Share Common Characteristics 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, some cells do only
All Living Things Share Common Characteristics 1. Living Things are Composed of Cells: Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, some cells do only
9/19/2016 CHAPTER 1: THE STUDY OF LIFE SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION TO THE SCIENCE OF LIFE BIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 1: THE STUDY OF LIFE SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY Ms. Diana THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology is the study of living things. In biology, you study the origins and history of life and once-living
CHAPTER 1: THE STUDY OF LIFE SECTION 1: INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY Ms. Diana THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology is the study of living things. In biology, you study the origins and history of life and once-living
Science is the use of EVIDENCE to put together TESTABLE explanations and PREDICTIONS of the NATURAL world. Scientists also can gather KNOWLEDGE
 Science is the use of EVIDENCE to put together TESTABLE explanations and PREDICTIONS of the NATURAL world. Scientists also can gather KNOWLEDGE though this PROCESS. What is or is NOT science? Scientific
Science is the use of EVIDENCE to put together TESTABLE explanations and PREDICTIONS of the NATURAL world. Scientists also can gather KNOWLEDGE though this PROCESS. What is or is NOT science? Scientific
Section1.1 - What is Biology?
 Ch 1: What is Biology? Section1.1 - What is Biology? Inside This Section... What is Biology? What is an Organism? The 5 Characteristics of Living Things. What is Biology? Biology is The Study of - Life
Ch 1: What is Biology? Section1.1 - What is Biology? Inside This Section... What is Biology? What is an Organism? The 5 Characteristics of Living Things. What is Biology? Biology is The Study of - Life
Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Block Honors Biology Mrs. Flannery Characteristics of Life READ AND UNDERLINE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living
Name Date Block Honors Biology Mrs. Flannery Characteristics of Life READ AND UNDERLINE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living
Observation: The process of gathering information, in a careful orderly way.
 Observation: The process of gathering information, in a careful orderly way. Prediction vs Hypothesis Predictions are meant to be proven once. A hypothesis can still end up as a hypothesis even if it has
Observation: The process of gathering information, in a careful orderly way. Prediction vs Hypothesis Predictions are meant to be proven once. A hypothesis can still end up as a hypothesis even if it has
Chapter 1. How Do Biologists Study Life?
 Chapter 1 How Do Biologists Study Life? Biology is the study of life Biologists ask questions about all aspects of living organisms Bios logos means a discourse on life in Greek Biology has many sub-disciplines
Chapter 1 How Do Biologists Study Life? Biology is the study of life Biologists ask questions about all aspects of living organisms Bios logos means a discourse on life in Greek Biology has many sub-disciplines
The Science of Biology
 The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science- an
The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science- an
Growth & Development. Characteristics of Living Things. What is development? Movement. What is a cell?
 Characteristics of Living Things made of cells growth acquire and use energy reproduction movement adaptation respond to stimuli/homeostasis interdependence organization What is development? What are some
Characteristics of Living Things made of cells growth acquire and use energy reproduction movement adaptation respond to stimuli/homeostasis interdependence organization What is development? What are some
Chapter Test A. It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Assessment Chapter Test A It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share?
Assessment Chapter Test A It s Alive!! Or Is It? MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share?
Unit 1: Introduction to Biology
 Name: Unit 1: Introduction to Biology Students will be able to: 1.1 Plan and conduct an investigation: Define the question, develop a hypothesis, design an experiment and collect information, analyze and
Name: Unit 1: Introduction to Biology Students will be able to: 1.1 Plan and conduct an investigation: Define the question, develop a hypothesis, design an experiment and collect information, analyze and
The Science of Life. Introduction to Biology
 The Science of Life Introduction to Biology What is Biology Bio = life logos = knowledge many branches - different things to study in biology Botany study of plants all types of plants - trees, flowers,
The Science of Life Introduction to Biology What is Biology Bio = life logos = knowledge many branches - different things to study in biology Botany study of plants all types of plants - trees, flowers,
Section Objectives: Recognize some possible benefits from studying biology. Summarize the characteristics of living things.
 Section Objectives: Recognize some possible benefits from studying biology. Summarize the characteristics of living things. The Science of Biology The concepts, principles, and theories that allow people
Section Objectives: Recognize some possible benefits from studying biology. Summarize the characteristics of living things. The Science of Biology The concepts, principles, and theories that allow people
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science 7 th grade
 B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science 7 th grade ORGANIZING THEME/TOPIC UNIT 1: CELLS Structure and Function of Cells MS-LS1-1. Conduct an investigation to provide evidence that
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M Science 7 th grade ORGANIZING THEME/TOPIC UNIT 1: CELLS Structure and Function of Cells MS-LS1-1. Conduct an investigation to provide evidence that
Alive or Not??? You be the Judge!
 Alive or Not??? You be the Judge! Information summarized from Holt Science & Technology: Life Science, copyright 2005 How do we know something is alive? What are the characteristics of life? We Begin with
Alive or Not??? You be the Judge! Information summarized from Holt Science & Technology: Life Science, copyright 2005 How do we know something is alive? What are the characteristics of life? We Begin with
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life
 Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Figure 1.0_1 Chapter 1:
Chapter 1 Biology: Exploring Life PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Seventh Edition Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Figure 1.0_1 Chapter 1:
The Science of Biology
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Section 1 1 What Is Science? (pages 3 7) This section explains what the goal of science is and describes a scientific view of the world What Science Is and Is Not (page
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Section 1 1 What Is Science? (pages 3 7) This section explains what the goal of science is and describes a scientific view of the world What Science Is and Is Not (page
Name Date Period Handout A: Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Period Handout A: Characteristics of Life Directions: 1. Read and highlight the main ideas in each passage. 2. Circle Key vocabulary 3. Answer the questions below each passage. Most people feel
Name Date Period Handout A: Characteristics of Life Directions: 1. Read and highlight the main ideas in each passage. 2. Circle Key vocabulary 3. Answer the questions below each passage. Most people feel
Life Science Notes Chapter 1 Exploring and Classifying Life
 Section 1.1 What is Science? Types of Science- Life Science Notes Chapter 1 Exploring and Classifying Life Life Science: Biology, Anatomy, Zoology Earth Science; Astronomy, Mineralogy, Meteorology Physical
Section 1.1 What is Science? Types of Science- Life Science Notes Chapter 1 Exploring and Classifying Life Life Science: Biology, Anatomy, Zoology Earth Science; Astronomy, Mineralogy, Meteorology Physical
Biology: The Study of Life
 Biology: The Study of Life Before You Read Use the What I Know column to list three things you know about biology. Then list three questions you have about biology in the What I Want to Find Out column.
Biology: The Study of Life Before You Read Use the What I Know column to list three things you know about biology. Then list three questions you have about biology in the What I Want to Find Out column.
Characteristics of Life
 Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
Characteristics of Life All living things share some basic characteristics: 1. Organization 2. Movement 3. Made up of cells 4. Reproduce 5. Grow and / or develop 6. Obtain and use energy 7. Respond to
Ross s Den. Welcome to Biology!!
 Ross s Den Welcome to Biology!! BE READY Bring binder, books, pencils, pens Bring a good work ethic full effort every minute Work as a team, we are only as strong as the members in our class Don t touch
Ross s Den Welcome to Biology!! BE READY Bring binder, books, pencils, pens Bring a good work ethic full effort every minute Work as a team, we are only as strong as the members in our class Don t touch
The Science of Biology
 The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary l Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms l Science-
The Science of Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary l Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms l Science-
7 th Grade Science Curriculum
 (1 st 9 Weeks- 1 st 4.5 9 Weeks) Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. NM & 1 Scientific Thinking and Practice Understand the
(1 st 9 Weeks- 1 st 4.5 9 Weeks) Date Hobbs Science By being embedded throughout the, these Processing Skills will be addressed throughout the year. NM & 1 Scientific Thinking and Practice Understand the
Warm-up: DO NOT TOUCH THE LAB BENCHES!!!
 Warm-up: DO NOT TOUCH THE LAB BENCHES!!! Turn in Are Viruses Alive Response on the front counter Pick up a Warm-up: Graphing & Intro to Science worksheet on the front counter Get started on the warm-up
Warm-up: DO NOT TOUCH THE LAB BENCHES!!! Turn in Are Viruses Alive Response on the front counter Pick up a Warm-up: Graphing & Intro to Science worksheet on the front counter Get started on the warm-up
7 th Grade GLEs (Draft Alignment 4/22/08) EARL 1 Systems
 7 th Grade GLEs (Draft Alignment 4/22/08) EARL 1 Systems Diversity of Life (DL) Characteristics of Living Matter 1.1.6 Understand how to classify organisms by their external and internal structures. W
7 th Grade GLEs (Draft Alignment 4/22/08) EARL 1 Systems Diversity of Life (DL) Characteristics of Living Matter 1.1.6 Understand how to classify organisms by their external and internal structures. W
MIDDLE SCHOOL BIOLOGY LABORATORY 1ST SEMESTER NAME: DATE: Activity: for each text we will highlight the most important information.
 NAME: DATE: TEACHER: Albert Hernandez. GRADE: 2 nd I. Read text carefully and answer the questions bellow. Activity: for each text we will highlight the most important information. The Goal of Science
NAME: DATE: TEACHER: Albert Hernandez. GRADE: 2 nd I. Read text carefully and answer the questions bellow. Activity: for each text we will highlight the most important information. The Goal of Science
Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Period Score Characteristics of Life READ AND HILITE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving
Name Date Period Score Characteristics of Life READ AND HILITE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 2 FLASHCARDS
 LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 2 FLASHCARDS Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share? A. ability to taste and smell B. ability to grow and develop C. ability to use energy D. ability
LIFE SCIENCE CHAPTER 2 FLASHCARDS Which of the following is NOT a characteristic that all organisms share? A. ability to taste and smell B. ability to grow and develop C. ability to use energy D. ability
Chapter 1. An Introduction To Life On Earth
 Chapter 1 An Introduction To Life On Earth John Klock, MA, MS 16 th year teaching life sciences 5 colleges (LBCC, OSU, Univ. of Maryland,..) Two children 15 years abroad, climbing (Mt.Mckinley) traveling
Chapter 1 An Introduction To Life On Earth John Klock, MA, MS 16 th year teaching life sciences 5 colleges (LBCC, OSU, Univ. of Maryland,..) Two children 15 years abroad, climbing (Mt.Mckinley) traveling
The Science of Biology. Chapter 1
 The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Warm Up Exercise Please complete the pretest that you picked up when you came in. Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary.
The Science of Biology Chapter 1 Warm Up Exercise Please complete the pretest that you picked up when you came in. Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary.
6.12A: You will understand that all organisms are composed of one or more cells.
 TEKS: 6.12A, B 6.12A: You will understand that all organisms are composed of one or more cells. Purpose: You will get to see and identify the smallest unit of life! As well as learn about who discovered
TEKS: 6.12A, B 6.12A: You will understand that all organisms are composed of one or more cells. Purpose: You will get to see and identify the smallest unit of life! As well as learn about who discovered
What Is Biology? Biologists Study? The study of living things. Characteristics Classifications Interactions between organisms Health & Disease
 What Is Biology? The study of living things. Biologists Study? Characteristics Classifications Interactions between organisms Health & Disease Goal of Science To investigate To understand To explain To
What Is Biology? The study of living things. Biologists Study? Characteristics Classifications Interactions between organisms Health & Disease Goal of Science To investigate To understand To explain To
Unit One: The Science of Biology
 Unit One: The Science of Biology 1 The process by which an organism reaches death In an organism, a condition in which there is reproduction, growth, development, metabolism, use of energy, excretion,
Unit One: The Science of Biology 1 The process by which an organism reaches death In an organism, a condition in which there is reproduction, growth, development, metabolism, use of energy, excretion,
LIVING THINGS CONTAIN ONE OR MORE CELLS
 LIVING THINGS CONTAIN ONE OR MORE CELLS Scientists know that all living things are organized. The smallest unit of organization of a living thing is the cell. A cell is a collection of living matter enclosed
LIVING THINGS CONTAIN ONE OR MORE CELLS Scientists know that all living things are organized. The smallest unit of organization of a living thing is the cell. A cell is a collection of living matter enclosed
1.1. KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. 4 Reinforcement Unit 1 Resource Book. Biology in the 21st Century CHAPTER 1
 1.1 THE STUDY OF LIFE KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. Biology is the scientific study of all forms of life. Living things are found almost everywhere on Earth, from very hot environments
1.1 THE STUDY OF LIFE KEY CONCEPT Biologists study life in all its forms. Biology is the scientific study of all forms of life. Living things are found almost everywhere on Earth, from very hot environments
Biology: Life on Earth
 Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 1 An Introduction to Life on Earth Section 1.3 Outline 1.3 What Are the Characteristics of Living Things? Living Things Are Both Complex, Organized,
Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 1 An Introduction to Life on Earth Section 1.3 Outline 1.3 What Are the Characteristics of Living Things? Living Things Are Both Complex, Organized,
BIOLOGY NOTES - CHAPTER 1
 BIOLOGY NOTES - CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1 and 2 Biology is the study of life Bio = life Logy = study of The scientific study of all forms of life, or all types of organisms Science means to know Science is a
BIOLOGY NOTES - CHAPTER 1 SECTION 1 and 2 Biology is the study of life Bio = life Logy = study of The scientific study of all forms of life, or all types of organisms Science means to know Science is a
How do we define what it means to be alive?
 How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional definition: must
How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional definition: must
Interest Grabber. Understanding Fossil Butte
 Interest Grabber Section 1-1 Understanding Fossil Butte In the southwest corner of Wyoming, there is a flat-topped mountain called Fossil Butte. A fossil of a fish was found near the top of Fossil Butte
Interest Grabber Section 1-1 Understanding Fossil Butte In the southwest corner of Wyoming, there is a flat-topped mountain called Fossil Butte. A fossil of a fish was found near the top of Fossil Butte
BIO 111: Biological Diversity and Evolution
 BIO 111: Biological Diversity and Evolution Varsha 2017 Ullasa Kodandaramaiah & Hema Somanathan School of Biology Ullasa Kodandaramaiah Assistant Professor, School of Biology, IISER- Thiruvananthapuram
BIO 111: Biological Diversity and Evolution Varsha 2017 Ullasa Kodandaramaiah & Hema Somanathan School of Biology Ullasa Kodandaramaiah Assistant Professor, School of Biology, IISER- Thiruvananthapuram
Use evidence of characteristics of life to differentiate between living and nonliving things.
 Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards All living things have a common set characteristic needs and functions that separate them from nonliving things such as:
INTRO TO BIOLOGY -GUIDED NOTES-
 INTRO TO BIOLOGY -GUIDED NOTES- DEFINING KEY SCIENCE TERMS - an organized way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Biology-. Observation- the process of. Data- the information gathered from
INTRO TO BIOLOGY -GUIDED NOTES- DEFINING KEY SCIENCE TERMS - an organized way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Biology-. Observation- the process of. Data- the information gathered from
Basic Biological Principles
 Basic Biological Principles Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Moth Life Cycle larva egg pupa Adult 1. Which characteristic of life is best shown by this diagram? A. DNA is the genetic code in
Basic Biological Principles Use the diagram below to answer question 1. Moth Life Cycle larva egg pupa Adult 1. Which characteristic of life is best shown by this diagram? A. DNA is the genetic code in
Grade Seven Science Focus on Life Sciences. Main Ideas in the Study of Cells
 Grade Seven Science Focus on Life Sciences Main Ideas in the Study of Cells Research is an effective way to develop a deeper understanding of challenging content. The following fill-in-the-blanks activity
Grade Seven Science Focus on Life Sciences Main Ideas in the Study of Cells Research is an effective way to develop a deeper understanding of challenging content. The following fill-in-the-blanks activity
Biology the study of life. Lecture 15
 Biology the study of life Lecture 15 Life (a life form: an organism ) can be defined as an organized genetic unit capable of metabolism, reproduction, & evolution (Purves et al., 2003) There is order to
Biology the study of life Lecture 15 Life (a life form: an organism ) can be defined as an organized genetic unit capable of metabolism, reproduction, & evolution (Purves et al., 2003) There is order to
Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis
 Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis Homeostasis - maintenance of internal stable conditions in a constantly changing environment that are necessary for life's functions Maintaining
Cell Theory Levels of Organization Cell Parts - Homeostasis Homeostasis - maintenance of internal stable conditions in a constantly changing environment that are necessary for life's functions Maintaining
Characteristics of Living Things
 Characteristics of Living Things What is biology? The study of living things All living things share certain characteristics The Characteristics of Living Things Living things are called organisms. All
Characteristics of Living Things What is biology? The study of living things All living things share certain characteristics The Characteristics of Living Things Living things are called organisms. All
Organizing Diversity Taxonomy is the discipline of biology that identifies, names, and classifies organisms according to certain rules.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Outline 1.1 Introduction to AP Biology 1.2 Big Idea 1: Evolution 1.3 Big Idea 2: Energy and Molecular Building Blocks 1.4 Big Idea 3: Information Storage, Transmission, and Response
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Outline 1.1 Introduction to AP Biology 1.2 Big Idea 1: Evolution 1.3 Big Idea 2: Energy and Molecular Building Blocks 1.4 Big Idea 3: Information Storage, Transmission, and Response
BIOLOGY. What exactly is biology anyway?
 BIOLOGY What exactly is biology anyway? Biology has to do with.. Living things, of course!! Don t forget things that are not alive (nonliving)! What about things too small to see (microscopic)? And how
BIOLOGY What exactly is biology anyway? Biology has to do with.. Living things, of course!! Don t forget things that are not alive (nonliving)! What about things too small to see (microscopic)? And how
THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY SECTION 1-1 REVIEW. VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank.
 SECTION 1-1 REVIEW THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. development 2. reproduction 3. organ 4. tissue MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. Biology
SECTION 1-1 REVIEW THE WORLD OF BIOLOGY VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. 1. development 2. reproduction 3. organ 4. tissue MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. Biology
Fundamentals of Biology Valencia College BSC1010C
 1 Fundamentals of Biology Valencia College BSC1010C 1 Studying Life Chapter objectives: What Is Biology? Is All Life on Earth Related? How Do Biologists Investigate Life? How Does Biology Influence Public
1 Fundamentals of Biology Valencia College BSC1010C 1 Studying Life Chapter objectives: What Is Biology? Is All Life on Earth Related? How Do Biologists Investigate Life? How Does Biology Influence Public
02/02/ Living things are organized. Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures. Learning Outcome B1
 Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
How do we define what it means to be alive?
 How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life-7 Characteristics of Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional
How do we define what it means to be alive? Defining Life-7 Characteristics of Life There is no universal definition of life. To define life in unequivocal terms is still a challenge for scientists. Conventional
Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Block Characteristics of Life Directions: Read the passages and answer the questions to the best of your ability. ALL the answers are in the reading. A good strategy when reading a passage is
Name Date Block Characteristics of Life Directions: Read the passages and answer the questions to the best of your ability. ALL the answers are in the reading. A good strategy when reading a passage is
STEMscopedia: CELL STRUCTURES AND HOMEOSTASIS B1A
 Reflect B1A Have you wondered why you shiver in the cold? Or maybe why your stomach gets upset after eating something bad? These and many other reactions are ways your body is responding to a change in
Reflect B1A Have you wondered why you shiver in the cold? Or maybe why your stomach gets upset after eating something bad? These and many other reactions are ways your body is responding to a change in
MODULE 1 Biology: The Study of Life
 Biology: The Study of Life ON YOUR OWN QUESTIONS 1.1 Classify the following organisms as herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores: a. tigers b. cows c. humans d. sheep 1.2 Classify the following organisms
Biology: The Study of Life ON YOUR OWN QUESTIONS 1.1 Classify the following organisms as herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores: a. tigers b. cows c. humans d. sheep 1.2 Classify the following organisms
Classification Notes
 Name Living Environment Classification Notes Characteristics of Living Things All living things have a cellular organization, contain similar chemicals, use energy, grow and develop, respond to their surroundings,
Name Living Environment Classification Notes Characteristics of Living Things All living things have a cellular organization, contain similar chemicals, use energy, grow and develop, respond to their surroundings,
I. How do you design an experiment?
 Unit 1: The Nature of Biology Module 1: How to Define Life Day, Mudd, Werstlein NC Essential Standard: Science as Inquiry 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish life functions Is Ebola a living
Unit 1: The Nature of Biology Module 1: How to Define Life Day, Mudd, Werstlein NC Essential Standard: Science as Inquiry 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish life functions Is Ebola a living
Learning Objective. Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology. Class Exercise: What does it mean to be living? Properties of Life
 1 2 Introduction to Biology Learning Objective Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology Describe the properties and levels of organization of living things 1.1: Themes and Concepts of Biology 1.2: The Process
1 2 Introduction to Biology Learning Objective Chapter 1: Introduction to Biology Describe the properties and levels of organization of living things 1.1: Themes and Concepts of Biology 1.2: The Process
Characteristics of Life
 Name Date Period Score Characteristics of Life READ AND HILITE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving
Name Date Period Score Characteristics of Life READ AND HILITE THE MAIN IDEAS IN EACH PASSAGE THEN ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Most people feel confident that they could identify a living thing from a nonliving
Science 8 Unit 4: Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems
 Science 8 Unit 4: Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems How do you know when something is alive? How do we know when something is alive? All living things: Are made up of cells The smallest unit of life, often
Science 8 Unit 4: Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems How do you know when something is alive? How do we know when something is alive? All living things: Are made up of cells The smallest unit of life, often
Chapter 1. An Introduction To Life On Earth
 Chapter 1 An Introduction To Life On Earth John Klock, MA, MS 16 th year teaching life sciences 5 colleges (LBCC, OSU, Univ. of Maryland,..) Two children 15 +years abroad, climbing (Mt.Mckinley) traveling
Chapter 1 An Introduction To Life On Earth John Klock, MA, MS 16 th year teaching life sciences 5 colleges (LBCC, OSU, Univ. of Maryland,..) Two children 15 +years abroad, climbing (Mt.Mckinley) traveling
Dr. Dennis Gervin Sections: 4252, 4253, 7734,
 BIOLOGY 111 Dr. Dennis Gervin Sections: 4252, 4253, 7734, 7736 http://www.mjc.edu/ http://gervind.faculty.mjc.edu/default.html A Guide to the Natural World How Does Science Impact Your Everyday World?
BIOLOGY 111 Dr. Dennis Gervin Sections: 4252, 4253, 7734, 7736 http://www.mjc.edu/ http://gervind.faculty.mjc.edu/default.html A Guide to the Natural World How Does Science Impact Your Everyday World?
Mission to Mars Day 4. Defining Life
 Mission to Mars Day 4 Defining Life Remember this quote? Mark Watney: If the oxygenator breaks down, I'll suffocate. If the water reclaimer breaks down, I'll die of thirst. If the hab breaches, I'll just
Mission to Mars Day 4 Defining Life Remember this quote? Mark Watney: If the oxygenator breaks down, I'll suffocate. If the water reclaimer breaks down, I'll die of thirst. If the hab breaches, I'll just
An Introduction to the Science of Botany. Chapter 1
 An Introduction to the Science of Botany Chapter 1 TTU MS 43131 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Briefly describe the field of botany, and give short definitions of at least five subdisciplines of plant biology Summarize
An Introduction to the Science of Botany Chapter 1 TTU MS 43131 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Briefly describe the field of botany, and give short definitions of at least five subdisciplines of plant biology Summarize
Do NOT write on this test. Thank you!
 Organization and Development of Living Organisms (SC.6.L.14.1,2,3,4 and 5) 1. The diagram below represents a plant cell. Letter X represents a structure in the cell. Which structure is represented by X?
Organization and Development of Living Organisms (SC.6.L.14.1,2,3,4 and 5) 1. The diagram below represents a plant cell. Letter X represents a structure in the cell. Which structure is represented by X?
HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about the properties of life is false?
HA Biology: Practice Quiz 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements about the properties of life is false?
CHAPTER 1 THE SCIENCE OF LIFE
 CHAPTER 1 THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology Bio - life Logy- the study of Biology is the study of life or living things Some branches of Biology include- Microbiology, Marine Biology, Botany, Zoology, Ecology
CHAPTER 1 THE SCIENCE OF LIFE Biology Bio - life Logy- the study of Biology is the study of life or living things Some branches of Biology include- Microbiology, Marine Biology, Botany, Zoology, Ecology
A A A A B B1
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR EACH BIG IDEA WITH ASSOCIATED SCIENCE PRACTICES AND ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Learning Objectives will be the target for AP Biology exam questions Learning Objectives Sci Prac Es Knowl
LEARNING OBJECTIVES FOR EACH BIG IDEA WITH ASSOCIATED SCIENCE PRACTICES AND ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Learning Objectives will be the target for AP Biology exam questions Learning Objectives Sci Prac Es Knowl
Chapter 1 - An Introduction to Life on Earth
 Chapter 1 - An Introduction to Life on Earth Characteristics of Living Things What are the characteristics of living things? Living things: ORGANISMS 1. Living Things are Organized subatomic particles
Chapter 1 - An Introduction to Life on Earth Characteristics of Living Things What are the characteristics of living things? Living things: ORGANISMS 1. Living Things are Organized subatomic particles
