Palazzo Franchetti - Venice (Italy), January 2018
|
|
|
- Hortense McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 XXII INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF PURE AND APPLIED BIOPHYSICS Intracellular ion channels and transporters in plant and animal cells DIRECTORS OF THE SCHOOLS: Armando CARPANETO - CNR Genoa and University of Genoa Giorgio GIACOMETTI - IVSLA and University of Padua SCIENTIFIC COMMITTEE: Armando CARPANETO - CNR Genoa and University of Genoa Anna BOCCACCIO - CNR Genoa Joachim SCHOLZ-STARKE - CNR Genoa Giorgio GIACOMETTI - IVSLA and University of Padua Palazzo Franchetti - Venice, January 2018 ORGANISING COMMITTEE: Elisabetta VALLARINO - CNR Genoa Michela LA FERLA - CNR Genoa Laura PADOAN - IVSLA Venice Francesco IMPALLARI - CNR Palermo - Website, online help
2 JANUARY, MONDAY 15 9:30-9:45 Giorgio M. GIACOMETTI, IVSLA and University of Padua Armando CARPANETO, CNR Genoa and University of Genoa Cristiano VIAPPIANI, President of SIBPA, University of Parma Welcome Addresses OPENING LECTURE - Chair: Armando CARPANETO 9:45-10:30 Franco GAMBALE Italian Biophysics and the International School of Pure and Applied Biophysics in Venice 10:30-11:00 SESSION 1: COMPARTMENTS AND ORGANELLES IN PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS - Chair: Franco GAMBALE Ildiko SZABÒ Mitochondria and chloroplasts Gerhard THIEL The sorting secret of mitochondrial K + channels SESSION 2: EXPERIMENTAL METHODS AND TECHNIQUES (Part 1) - Chair: Michael PUSCH Anna BOCCACCIO The patch-clamp technique 17:30-18:20 Alberto DIASPRO Optical Microscopy at the Nanoscale: an overview Enrico MARTINOIA The plant vacuole: proton pumps and transporters Alessandro VITALE Quality control and proteostasis of membrane proteins in the plant secretory pathway LUNCH TIME IN PALAZZO FRANCHETTI
3 JANUARY, TUESDAY 16 Matteo CECCARELLI In-silico electrophysiology: basic principles, limits and benefits (part 1) 10:20-11:00 Vito DE PINTO Progress in Molecular Biology Alberto DIASPRO Optical Microscopy at the Nanoscale: converging technologies, applications and perspectives LUNCH TIME Matteo CECCARELLI In-silico electrophysiology: basic principles, limits and benefits (part 2) Alex COSTA In vivo analysis of Ca 2+ dynamics in Arabidopsis: tools and applications (part 1) SESSION 3: INTRACELLULAR ION CHANNEL AND TRANSPORTER FAMILIES (Part 1) - Chair: Enrico MARTINOIA and Anna MORONI Enrico MARTINOIA Vacuolar ion channels 17:30-18:20 Petra DIETRICH Regulation and function of plant two pore channels
4 JANUARY, WEDNESDAY 17 Anna BOCCACCIO TMEM16 channels and scramblases 10:20-11:00 Vito DE PINTO VDAC channels Dejian REN Endo-lysosomal ion channels LUNCH TIME Sebastien THOMINE Metal storage and export from the plant vacuole Nobuyuki UOZUMI Examination of prokaryotic channel/transporter reveals eukaryotic membrane transport system Paolo TROST The family of cytochrome b561 SPECIAL LECTURE - Chair: Armando CARPANETO 17:30-18:30 Michael PUSCH When physics and biology meet: functional measurements of ion channels and transporters
5 JANUARY, THURSDAY 18 SESSION 2: EXPERIMENTAL METHODS AND TECHNIQUES (Part 2) - Chair: Michael PUSCH Alex COSTA In vivo analysis of Ca 2+ dynamics in Arabidopsis: tools and applications (part 2) 10:20-11:00 Christian M. GRIMM New tools to gate endolysosomal cation channels Anna MORONI Engineering ion channels for optogenetics LUNCH TIME SESSION 3: INTRACELLULAR ION CHANNEL AND TRANSPORTER FAMILIES (Part 2) - Chair: Anna MORONI Mauro DALLA SERRA Activity of pore forming proteins and antimicrobial peptides Bruno GASNIER Lysosomal amino acid transporters SESSION 4: INTRACELLULAR CHANNELS AND TRANSPORTERS IN HUMAN DISEASE (Part 1) - Chair: Bruno GASNIER Diego MEDINA Role of TRPML1 in lysosomal signaling and autophagy SKYPE LECTURE - Chair: Armando CARPANETO 17:30-18:20 Antony GALIONE The discovery of the NAADP receptor
6 JANUARY, FRIDAY 19 SESSION 4: INTRACELLULAR CHANNELS AND TRANSPORTERS IN HUMAN DISEASE (Part 2) - Chair: Bruno GASNIER Antonio FILIPPINI Angiogenesis and intracellular channels 10:20-10:50 10:50-11:40 Michael PUSCH CLC channels and transporters from biophysics to human genetic diseases 11:40-12:30 Ildiko SZABÒ Exploiting mitochondrial ion channels as oncological targets LUNCH TIME IN PALAZZO FRANCHETTI In the recent years we have witnessed an incredible progress in the understanding of the biophysical structure and function and the physiological role of membrane ion channels and transporters. These proteins are involved in major physiological functions in all phylae. However, a large class of ion channels and transporters is still not so much explored: those expressed in endo-membranes of intracellular organelles like endosomes, lysosomes, and other. The reason is that endomembranes are poorly accessible to standard electrophysiological techniques. Nevertheless, the importance of these intracellular channels and transporters is becoming increasingly evident, for example through their involvement in human genetic diseases or in fundamental physiological functions in plant cells. Anna BOCCACCIO, CNR - Genoa - Italy Matteo CECCARELLI, University of Cagliari - Italy Alex COSTA, University of Milan Italy Mauro DALLA SERRA, CNR - Trento - Italy Vito DE PINTO, University of Catania - Italy Alberto DIASPRO, IIT - Genoa - Italy Petra DIETRICH, University of Erlangen - Germany Antonio FILIPPINI, University of Rome - Italy Antony GALIONE, University of Oxford UK Franco GAMBALE, CNR - Genoa - Italy Bruno GASNIER, Paris Descartes University - CNRS - France Christian M. GRIMM, University of München - Germany Enrico MARTINOIA, University of Zürich - Switzerland Diego MEDINA, Tigem - Pozzuoli (NA) - Italy Anna MORONI, University of Milan - Italy Michael PUSCH, CNR - Genoa - Italy Dejian REN, University of Pennsylvania - Philadelphia - USA Ildiko SZABÒ, University of Padua Italy Gerhard THIEL, University of Darmstadt - Germany Sebastien THOMINE, CNRS - Paris - France Paolo TROST, University of Bologna - Italy Nobuyuki UOZUMI, Tohoku University - Japan Alessandro VITALE, CNR - Milan - Italy
3.1 Cell Theory. KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life.
 3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. Many scientists contributed to
3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the Basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. Many scientists contributed to
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab
 Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
The Discovery of Cells
 The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
The Discovery of Cells Microscope observations! General Cell & Organelle Discovery 1600s Observations made by scientists using more powerful microscopes in the 1800s led to the formation of the cell theory.
3.2 Cell Organelles. KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities.
 KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
Cell Biology. Code: ECTS Credits: 6. Degree Type Year Semester
 2018/2019 Cell Biology Code: 100892 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2500252 Biochemistry FB 1 1 Contact Name: Elena Ibáñez de Sans Email: Elena.Ibanez@uab.cat Prerequisites Use of languages Principal
2018/2019 Cell Biology Code: 100892 ECTS Credits: 6 Degree Type Year Semester 2500252 Biochemistry FB 1 1 Contact Name: Elena Ibáñez de Sans Email: Elena.Ibanez@uab.cat Prerequisites Use of languages Principal
and their organelles
 and their organelles Discovery Video: Cells REVIEW!!!! The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest
and their organelles Discovery Video: Cells REVIEW!!!! The Cell Theory 1. Every living organism is made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. It is the smallest
Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
 Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were
Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were
Cell (Learning Objectives)
 Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
Cell (Learning Objectives) 1. Understand & describe the basic components necessary for a functional cell. 2. Review the order of appearance of cells on earth and explain the endosymbiotic theory. 3. Compare
Biology Summer Assignments
 Biology Summer Assignments Welcome Mustangs! The following summer assignments are to assist you in obtaining background information for topics we will be learning during 1 st quarter, in Biology. Please
Biology Summer Assignments Welcome Mustangs! The following summer assignments are to assist you in obtaining background information for topics we will be learning during 1 st quarter, in Biology. Please
The Cell. The basic unit of all living things
 The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
The Cell The basic unit of all living things 1 Robert Hooke was the first to name the cell (1665) 2 The Cell Theory The cell is the unit of Structure of all living things. The cell is the unit of Function
Programme. Cellular dynamics: membrane-cytoskeleton interface
 Programme Cellular dynamics: membrane-cytoskeleton interface Southbridge, MA, USA, 21-24 May 2017 Programme Sunday 21 May 2017 12:30 Lunch 14:00 Sharon Ahmad Journal of Cell Science, UK Welcome 14:15 Jennifer
Programme Cellular dynamics: membrane-cytoskeleton interface Southbridge, MA, USA, 21-24 May 2017 Programme Sunday 21 May 2017 12:30 Lunch 14:00 Sharon Ahmad Journal of Cell Science, UK Welcome 14:15 Jennifer
Components of a functional cell. Boundary-membrane Cytoplasm: Cytosol (soluble components) & particulates DNA-information Ribosomes-protein synthesis
 Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Cell (Outline) - Components of a functional cell - Major Events in the History of Earth: abiotic and biotic phases; anaerobic and aerobic atmosphere - Prokaryotic cells impact on the biosphere - Origin
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell The cell is the basic unit of life Although cells differ substantially from one another, they all share certain characteristics that reflect a common ancestry and remind us
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell The cell is the basic unit of life Although cells differ substantially from one another, they all share certain characteristics that reflect a common ancestry and remind us
Division Ave. High School AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures u specialized functions cilia
Tour of the Cell 1 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Why organelles? Specialized structures u specialized functions cilia
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.2 Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 1. Which two domains consist of prokaryotic cells? 2. A major difference between
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.2 Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions 1. Which two domains consist of prokaryotic cells? 2. A major difference between
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 1 of 49 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic
1 of 49 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic
Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell Section 1 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 4 Active Reading Guide A Tour of the Cell Section 1 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when
Chapter 7.2. Cell Structure
 Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Name: Period: Week of: January 28- February 1 Root Words In-Class Homework
 Day 1/28: Monday Biology Week #22 Week of: January 28- February 1 Root Words In-Class Homework Word: Definition: As in: - Picture: -Organize Binder -Draw a City and List Parts -Begin notes on Parts of
Day 1/28: Monday Biology Week #22 Week of: January 28- February 1 Root Words In-Class Homework Word: Definition: As in: - Picture: -Organize Binder -Draw a City and List Parts -Begin notes on Parts of
A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart
 CELLS, CELLS, CELLS A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart Cells Defined as the basic unit of living things. Cell Theory All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic units of structure
CELLS, CELLS, CELLS A Look At Cells Graphics: Microsoft Clipart Cells Defined as the basic unit of living things. Cell Theory All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic units of structure
Biology: Life on Earth
 Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
Teresa Audesirk Gerald Audesirk Bruce E. Byers Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 4 Cell Structure and Function Copyright 2008 Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. Chapter 4 Outline 4.1 What
Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life
 Name Period Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life 1. What are the three critical components of the cell theory? 2. What are the two important conceptual implications of the cell theory? 3. Which
Name Period Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life 1. What are the three critical components of the cell theory? 2. What are the two important conceptual implications of the cell theory? 3. Which
AS Biology Summer Work 2015
 AS Biology Summer Work 2015 You will be following the OCR Biology A course and in preparation for this you are required to do the following for September 2015: Activity to complete Date done Purchased
AS Biology Summer Work 2015 You will be following the OCR Biology A course and in preparation for this you are required to do the following for September 2015: Activity to complete Date done Purchased
Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil Privacy Folder DFAD
 Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil Privacy Folder DFAD Do First: Answer in your DFAD Answer the following questions in your DFAD. Match the correct vocabulary terms to the correct definitions. Haveouts Guided
Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil Privacy Folder DFAD Do First: Answer in your DFAD Answer the following questions in your DFAD. Match the correct vocabulary terms to the correct definitions. Haveouts Guided
Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called
 The Cell Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of
The Cell Cell Is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life and are often called the "building blocks of life". The study of
Biology. 7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure 10/29/2013. Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Biology Biology 1of 49 2of 49 Eukaryotic Cell Structures Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists
Biology Biology 1of 49 2of 49 Eukaryotic Cell Structures Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists
Cell Organelles. Wednesday, October 22, 14
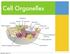 Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting
 Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Cells have many distinct compartments (What are they? What do they do?) Specific mechanisms are
Chapter 12: Intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Principles of intracellular sorting Cells have many distinct compartments (What are they? What do they do?) Specific mechanisms are
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote Eukaryotes animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria 1-10 microns eukaryotic
Importance of Protein sorting. A clue from plastid development
 Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Cell functions depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Examples: A. Energy production
Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Cell functions depend on sorting proteins to their right destination. Examples: A. Energy production
Cell Structure and Function. Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Chapter 4: Cell Structure Section 1: The History of Cell Biology Section 2: Introduction to Cells Section 3: Cell Organelles and Features Section 4: Unique Features
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Chapter 4: Cell Structure Section 1: The History of Cell Biology Section 2: Introduction to Cells Section 3: Cell Organelles and Features Section 4: Unique Features
Class XI Chapter 8 Cell The Unit of Life Biology
 Question 1: Which of the following is not correct? (a) Robert Brown discovered the cell. (b) Schleiden and Schwann formulated the cell theory. (c) Virchow explained that cells are formed from pre-existing
Question 1: Which of the following is not correct? (a) Robert Brown discovered the cell. (b) Schleiden and Schwann formulated the cell theory. (c) Virchow explained that cells are formed from pre-existing
7.L.1.2 Plant and Animal Cells. Plant and Animal Cells
 7.L.1.2 Plant and Animal Cells Plant and Animal Cells Clarifying Objective: 7.L.1.2 Compare the structures and functions of plant and animal cells; include major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus,
7.L.1.2 Plant and Animal Cells Plant and Animal Cells Clarifying Objective: 7.L.1.2 Compare the structures and functions of plant and animal cells; include major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus,
Read It! Read It! The jellylike fluid inside the cell is called the. Plant cells and animal cells. have many of the same.
 Read It! Read It! 1. The smallest part of a living thing that carries out actions to keep the thing alive is a. 2. The jellylike fluid inside the cell is called the. Read It! Plant cells and animal cells
Read It! Read It! 1. The smallest part of a living thing that carries out actions to keep the thing alive is a. 2. The jellylike fluid inside the cell is called the. Read It! Plant cells and animal cells
 Question 1: Which of the following is not correct? (a) Robert Brown discovered the cell. (b) Schleiden and Schwann formulated the cell theory. (c) Virchow explained that cells are formed from pre-existing
Question 1: Which of the following is not correct? (a) Robert Brown discovered the cell. (b) Schleiden and Schwann formulated the cell theory. (c) Virchow explained that cells are formed from pre-existing
Turns sunlight, water & carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) into sugar & oxygen through photosynthesis
 CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
CELL PART/ ORGANELLE FUNCTION (what it does) PICTURE Plant, Animal, or Both Cell Membrane controls what goes in & out of the cell protects the cell Nucleus directs all the cell s activities contains cell
REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Name AP Biology REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
Name AP Biology REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
 Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Unit 3: Cells. Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells.
 Unit 3: Cells Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. The Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells (unicellular or multicellular).
Unit 3: Cells Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. The Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells (unicellular or multicellular).
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology?
 Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
Chapter 3: Cells. Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College
 Chapter 3: Cells Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Be able to describe: what a cell is & two main classes of cells. structure & functions of cell membranes. how
Chapter 3: Cells Lectures by Mark Manteuffel, St. Louis Community College Learning Objectives Be able to describe: what a cell is & two main classes of cells. structure & functions of cell membranes. how
02/02/ Living things are organized. Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures. Learning Outcome B1
 Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Cell Organelles Tutorial
 1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions
 Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Overview of Cell Structures and Functions Vocabulary
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Overview of Cell Structures and Functions Vocabulary
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure
 UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
UNIT 3 CP BIOLOGY: Cell Structure Page CP: CHAPTER 3, Sections 1-3; HN: CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-2 Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of cells and their
University of Bremen and Jacobs University Bremen, June 15 26, A: Simulation of biological systems and their functionalization
 Program of the International WE Heraeus Summer School ``Quantum and Classical Simulation of Biological Systems and their Interaction with Technical Materials University of Bremen and Jacobs University
Program of the International WE Heraeus Summer School ``Quantum and Classical Simulation of Biological Systems and their Interaction with Technical Materials University of Bremen and Jacobs University
The Cell. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 2 The Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
C h a p t e r 2 The Cell PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
Eukaryotic Cell Structure. 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines Comparing the cell to a factory In order for a cell to maintain its internal environment (homeostasis), many things must go on. This is similar to a factory.
Eukaryotic Cell Structure 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines Comparing the cell to a factory In order for a cell to maintain its internal environment (homeostasis), many things must go on. This is similar to a factory.
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Biology. Introduction to Cells. Sunday, November 8, 15
 Biology Introduction to Cells Cell Theory Biology is the study of life. Ideas about cells are built on the cell theory which states: 1. All living things are made of cells and their products. 2. The cell
Biology Introduction to Cells Cell Theory Biology is the study of life. Ideas about cells are built on the cell theory which states: 1. All living things are made of cells and their products. 2. The cell
Function and Illustration. Nucleus. Nucleolus. Cell membrane. Cell wall. Capsule. Mitochondrion
 Intro to Organelles Name: Block: Organelles are small structures inside cells. They are often covered in membranes. Each organelle has a job to do in the cell. Their name means little organ. Just like
Intro to Organelles Name: Block: Organelles are small structures inside cells. They are often covered in membranes. Each organelle has a job to do in the cell. Their name means little organ. Just like
Tuesday 9/6/2018 Mike Mueckler
 Tuesday 9/6/2018 Mike Mueckler mmueckler@wustl.edu Intracellular Targeting of Nascent Polypeptides Mitochondria are the Sites of Oxidative ATP Production Sugars Triglycerides Figure 14-10 Molecular Biology
Tuesday 9/6/2018 Mike Mueckler mmueckler@wustl.edu Intracellular Targeting of Nascent Polypeptides Mitochondria are the Sites of Oxidative ATP Production Sugars Triglycerides Figure 14-10 Molecular Biology
How do cell structures enable a cell to carry out basic life processes? Eukaryotic cells can be divided into two parts:
 Essential Question How do cell structures enable a cell to carry out basic life processes? Cell Organization Eukaryotic cells can be divided into two parts: 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm-the portion of the cell
Essential Question How do cell structures enable a cell to carry out basic life processes? Cell Organization Eukaryotic cells can be divided into two parts: 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm-the portion of the cell
The cell. The cell theory. So what is a cell? 9/20/2010. Chapter 3
 The cell Chapter 3 The cell theory all living organisms are made up of one or more cells, and all cells arise from other, pre-existing cells So what is a cell? The most basic unit of any organism The smallest
The cell Chapter 3 The cell theory all living organisms are made up of one or more cells, and all cells arise from other, pre-existing cells So what is a cell? The most basic unit of any organism The smallest
protein synthesis cell theory Centrioles specialization. unicellular ribosomes. mitochondria cell interdependence prokaryotes
 All cells must generate proteins. Cells make protein through a process called protein synthesis All living things are made of cells, Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms,
All cells must generate proteins. Cells make protein through a process called protein synthesis All living things are made of cells, Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all organisms,
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology.
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the diagram below which represents a typical green plant cell and on your knowledge of biology. 5. Which letter corresponds to that of the endoplasmic reticulum?
122-Biology Guide-5thPass 12/06/14. Topic 1 An overview of the topic
 Topic 1 http://bioichiban.blogspot.com Cellular Functions 1.1 The eukaryotic cell* An overview of the topic Key idea 1: Cell Organelles Key idea 2: Plasma Membrane Key idea 3: Transport Across Membrane
Topic 1 http://bioichiban.blogspot.com Cellular Functions 1.1 The eukaryotic cell* An overview of the topic Key idea 1: Cell Organelles Key idea 2: Plasma Membrane Key idea 3: Transport Across Membrane
Cell Biology Review. The key components of cells that concern us are as follows: 1. Nucleus
 Cell Biology Review Development involves the collective behavior and activities of cells, working together in a coordinated manner to construct an organism. As such, the regulation of development is intimately
Cell Biology Review Development involves the collective behavior and activities of cells, working together in a coordinated manner to construct an organism. As such, the regulation of development is intimately
Life is Cellular Section 7.1
 Life is Cellular Section 7.1 Objectives Understand Cell theory Distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes Understand different types of microscopy, and how they work in more detail What is a Cell?
Life is Cellular Section 7.1 Objectives Understand Cell theory Distinguish between prokaryotes and eukaryotes Understand different types of microscopy, and how they work in more detail What is a Cell?
prokaryotic eukaryotic
 Cell Basics Two Basic Cell Types All cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells a.k.a. Bacteria Prokaryotes, which includes all bacteria. They are the simplest cellular organisms. They
Cell Basics Two Basic Cell Types All cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells a.k.a. Bacteria Prokaryotes, which includes all bacteria. They are the simplest cellular organisms. They
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when Robert Hooke first looked at dead cells from an oak tree.
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when Robert Hooke first looked at dead cells from an oak tree.
Parts of the Cell book pgs
 Parts of the Cell book pgs. 12-18 Animal Cell Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell: Organelles & Functions 1. Cell Membrane (Nickname: skin ) Function: A protective layer that covers
Parts of the Cell book pgs. 12-18 Animal Cell Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Go to Section: Eukaryotic Cell: Organelles & Functions 1. Cell Membrane (Nickname: skin ) Function: A protective layer that covers
Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce and to maintain dynamic homeostasis.
 Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. Enduring understanding 2.B: Growth, reproduction and dynamic
Big Idea 2: Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. Enduring understanding 2.B: Growth, reproduction and dynamic
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell. Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components.
 NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
NAME: PERIOD: DATE: A View of the Cell Use Chapter 8 of your book to complete the chart of eukaryotic cell components. Cell Part Cell Wall Centriole Chloroplast Cilia Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Endoplasmic
10/1/2014. Chapter Explain why the cell is considered to be the basic unit of life.
 Chapter 4 PSAT $ by October by October 11 Test 3- Tuesday October 14 over Chapter 4 and 5 DFA- Monday October 20 over everything covered so far (Chapters 1-5) Review on Thursday and Friday before 1. Explain
Chapter 4 PSAT $ by October by October 11 Test 3- Tuesday October 14 over Chapter 4 and 5 DFA- Monday October 20 over everything covered so far (Chapters 1-5) Review on Thursday and Friday before 1. Explain
Biology I. Chapter 7
 Biology I Chapter 7 Interest Grabber NOTEBOOK #1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1.
Biology I Chapter 7 Interest Grabber NOTEBOOK #1 Are All Cells Alike? All living things are made up of cells. Some organisms are composed of only one cell. Other organisms are made up of many cells. 1.
Biology. Introduction to Cells. Tuesday, February 9, 16
 Biology Introduction to Cells Biology Biology is the study of life. In Biology, we are going to start small (the cell) and end with explaining a larger system (organisms) How small? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
Biology Introduction to Cells Biology Biology is the study of life. In Biology, we are going to start small (the cell) and end with explaining a larger system (organisms) How small? http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology?
 Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology
 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. One early piece of evidence supporting the cell theory was the observation
STUDY GUIDE SECTION 4-1 The History of Cell Biology Name Period Date Multiple Choice-Write the correct letter in the blank. 1. One early piece of evidence supporting the cell theory was the observation
Cells Function And Organelles Answer Key
 We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cells function and organelles
We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing it on your computer, you have convenient answers with cells function and organelles
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location ALL CELLS DNA Common in Animals Uncommon in Plants Lysosome
 CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
CELL PART Expanded Definition Cell Structure Illustration Function Summary Location is the material that contains the Carry genetic ALL CELLS information that determines material inherited characteristics.
Summer School in Cosmology. Programme
 printed on:29th Jul 2010 Summer School in Cosmology Cosponsor(s): The Italian Institute for Nuclear Physics (INFN) Organizer(s): P. Creminelli (ICTP), U. Seljak (UC & LBNL Berkeley & Zürich U.), M. Viel
printed on:29th Jul 2010 Summer School in Cosmology Cosponsor(s): The Italian Institute for Nuclear Physics (INFN) Organizer(s): P. Creminelli (ICTP), U. Seljak (UC & LBNL Berkeley & Zürich U.), M. Viel
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6. Microscopes pp Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes
 Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells
 Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Why? Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells What are the functions of different organelles in a cell? The cell is the basic unit and building block of all living things. Organisms rely on their cells to perform
Biology Cell Organelle Webquest. Name Period Date
 Biology Cell Organelle Webquest Name Period Date This webquest has TWO parts to it. You need to go to www.rodensclassroom.com and click on the "BIOLOGY" link. Once there click on the Unit 3-Cell Organelles
Biology Cell Organelle Webquest Name Period Date This webquest has TWO parts to it. You need to go to www.rodensclassroom.com and click on the "BIOLOGY" link. Once there click on the Unit 3-Cell Organelles
Week: 8 10 Dates: 10/5 10/23 Unit: Cells Structure & Function Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday
 BishopAgEd.weebly.com Name: Period: Week: 8 10 Dates: 10/5 10/23 Unit: Cells Structure & Function Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 5 O *Life is Cellular *Section Review 4-2 *Cell Organelles Coloring
BishopAgEd.weebly.com Name: Period: Week: 8 10 Dates: 10/5 10/23 Unit: Cells Structure & Function Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 5 O *Life is Cellular *Section Review 4-2 *Cell Organelles Coloring
Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com
 Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com Mr. Zamarripa If found return to room 206 Week of 09/12/2016 65A Warm-Up Tuesday A student walks 2 km in 30 minutes. What is the student s average speed in
Science Interactive Notebook ZcienceClass.com Mr. Zamarripa If found return to room 206 Week of 09/12/2016 65A Warm-Up Tuesday A student walks 2 km in 30 minutes. What is the student s average speed in
Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals Fungi Bacteria. Loose DNA DNA Nucleus Membrane-Bound Organelles Humans
 UNIT 3: The Cell DAYSHEET 45: Introduction to Cellular Organelles Name: Biology I Date: Bellringer: Place the words below into the correct space on the Venn Diagram: Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals
UNIT 3: The Cell DAYSHEET 45: Introduction to Cellular Organelles Name: Biology I Date: Bellringer: Place the words below into the correct space on the Venn Diagram: Cell Alive Homeostasis Plants Animals
2015 AP Biology Unit 2 Quiz 1- Introduction to the Cell and Biochemistry Week of 28Sept- 08Oct
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ 2015 AP Biology Unit 2 Quiz 1- Introduction to the Cell and Biochemistry Week of 28Sept- 08Oct Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Name: Class: _ Date: _ 2015 AP Biology Unit 2 Quiz 1- Introduction to the Cell and Biochemistry Week of 28Sept- 08Oct Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the
Trading Card Activity--Cells
 Animal Cell Eukaryotic Cell Characteristics of Animal Cells Complex and can be specialized for different jobs inside an animal. Has a nucleus with DNA inside Contains organelles. Many small vacuoles. Does
Animal Cell Eukaryotic Cell Characteristics of Animal Cells Complex and can be specialized for different jobs inside an animal. Has a nucleus with DNA inside Contains organelles. Many small vacuoles. Does
Cellular Biology. Cells: theory, types, form & function, evolution
 Cellular Biology Cells: theory, types, form & function, evolution The Cell Theory Problems with the Cell Theory? The cell theory has three components: 1. all living organisms are made up of one or more
Cellular Biology Cells: theory, types, form & function, evolution The Cell Theory Problems with the Cell Theory? The cell theory has three components: 1. all living organisms are made up of one or more
Van Leeuwenhoek. 1 st crude microscope made by the Dutchman
 The Cell History of Cells In 1665, English scientist Robert Hooke used the first compound light microscope to see plant tissues He viewed several thin slices of cork He called the small chambers within
The Cell History of Cells In 1665, English scientist Robert Hooke used the first compound light microscope to see plant tissues He viewed several thin slices of cork He called the small chambers within
CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
 7-1 Life Is Cellular CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall The Discovery of the Cell 1665: Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to look at a thin slice of cork. Cork looked
7-1 Life Is Cellular CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall The Discovery of the Cell 1665: Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to look at a thin slice of cork. Cork looked
How might the cells of a plant be like the cells of an animal? How might they be different? Write your ideas in the space below.
 Cells Textbook pages 22 39 Before You Read How might the cells of a plant be like the cells of an animal? How might they be different? Write your ideas in the space below. Section 1.2 Summary Mark the
Cells Textbook pages 22 39 Before You Read How might the cells of a plant be like the cells of an animal? How might they be different? Write your ideas in the space below. Section 1.2 Summary Mark the
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
Basic Structure of a Cell Prokaryotic Cells No nucleus Archaea & Eubacteria One circular chromosome Extremely small Eukaryotic Cells Has a nucleus!!! Membrane-bound organelles Plants, Animals, Fungi, &
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Chapter Questions 1) What limits the resolving power of a light microscope? A) the type of lens used to magnify the object under study B) the shortest
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Chapter Questions 1) What limits the resolving power of a light microscope? A) the type of lens used to magnify the object under study B) the shortest
Biology Homework Chapter 5: The Cell Pages Answer the questions with complete thoughts!
 Name Biology Homework Chapter 5: The Cell Pages 115-133 Answer the questions with complete thoughts! Per. * Sections 5.1 through 5.3: Cells Are the Units of Life: Read pages 115 to 122 PART A: Define the
Name Biology Homework Chapter 5: The Cell Pages 115-133 Answer the questions with complete thoughts! Per. * Sections 5.1 through 5.3: Cells Are the Units of Life: Read pages 115 to 122 PART A: Define the
Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (55 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (55
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Unit 2: Cells Guided Reading Questions (55
Molecular Evolution in the Genomic Era
 University of Roma Tre Department of Biology Molecular Evolution in the Genomic Era September 29 th - October 1 st A Meeting sponsored by: University of Roma Tre Genome Biology and Evolution International
University of Roma Tre Department of Biology Molecular Evolution in the Genomic Era September 29 th - October 1 st A Meeting sponsored by: University of Roma Tre Genome Biology and Evolution International
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
REPORT ON THE RESEARCH UNIT: Laboratory of Molecular and Cellular Biology of Eukaryotes (LBMCE)
 Research evaluation REPORT ON THE RESEARCH UNIT: Laboratory of Molecular and Cellular Biology of Eukaryotes (LBMCE) UNDER THE SUPERVISION OF THE FOLLOWING INSTITUTIONS AND RESEARCH BODIES: Université Pierre
Research evaluation REPORT ON THE RESEARCH UNIT: Laboratory of Molecular and Cellular Biology of Eukaryotes (LBMCE) UNDER THE SUPERVISION OF THE FOLLOWING INSTITUTIONS AND RESEARCH BODIES: Université Pierre
Just Print Science. Pack
 Just Print Science Pack Plant and Animal Cells Jennifer Findley Note to Teacher This resource includes several resources for teaching and reviewing plant and animal cells. The resource includes a one-page
Just Print Science Pack Plant and Animal Cells Jennifer Findley Note to Teacher This resource includes several resources for teaching and reviewing plant and animal cells. The resource includes a one-page
To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry [2].
![To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry [2]. To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry [2].](/thumbs/84/91204507.jpg) GUIDED READING - Ch. 6 - THE CELL NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted. Importantly,
GUIDED READING - Ch. 6 - THE CELL NAME: Please print out these pages and HANDWRITE the answers directly on the printouts. Typed work or answers on separate sheets of paper will not be accepted. Importantly,
CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS
 CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS PRBS 131 BIOSCI131 CELL BIOLOGY 3 units 3 hours lec Course Number Course Title Descriptive Title Credit Unit(s) Hour(s)/Week
CENTRO ESCOLAR UNIVERSITY Biological Sciences Department Manila*Malolos*Makati SYLLABUS PRBS 131 BIOSCI131 CELL BIOLOGY 3 units 3 hours lec Course Number Course Title Descriptive Title Credit Unit(s) Hour(s)/Week
Cell Theory Essential Questions
 Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
Cells Vocab words 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Nucleus 4. Eukaryote 5. Prokaryote 6. Organelle 7. Cytoplasm 8. Nuclear envelope 9. Chromatin 10. Chromosome 11. Nucleolus 12. Ribosome 13. Endoplasmic reticulum
What is a cell? A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Who discovered cells?
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CELL What is a cell? A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Who discovered cells? Robert Hooke (by looking at a piece of cork under a microscope What is
INTRODUCTION TO THE CELL What is a cell? A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Who discovered cells? Robert Hooke (by looking at a piece of cork under a microscope What is
Biology Teach Yourself Series Topic 2: Cells
 Biology Teach Yourself Series Topic 2: Cells A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au TSSM 2013 Page 1 of 14 Contents Cells... 3 Prokaryotic
Biology Teach Yourself Series Topic 2: Cells A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au TSSM 2013 Page 1 of 14 Contents Cells... 3 Prokaryotic
Cellular Transportation & Respiration
 Cellular Transportation & Respiration Passive Transport A cell membrane is semiperamble, which means that it allows only certain substances to enter or leave a cell. Passive transport is the movement of
Cellular Transportation & Respiration Passive Transport A cell membrane is semiperamble, which means that it allows only certain substances to enter or leave a cell. Passive transport is the movement of
