Intro to Geomorphology Key Concepts
|
|
|
- Dwain Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intro to Geomorphology Key Concepts
2 Geomorphology Literally means the study of earth landforms - Geo = Earth - Morph=Form - Logos= Study of Involves understanding of - Mineralogy - Structure - Tectonics - Stratigraphy - Chemistry - Physics - Meteorology & Climatology
3 Why Bother? Critical toward understanding - Climate change > systems respond differently to changes in rainfall, temperature changes, and changes in storm strength - Past tectonic activity > distinctive stratigraphic and landform features form in response to tectonics - Engineering problems > Construction of bridges, highways, houses, etc depend on past, current and future understanding of potentially destructive events - Hazard assessment > map out locations that have good have high risk of potential changes - Stratigraphy > all of the sedimentary stratigraphic record is the end product of geomorphic activity/ processes
4 Agents of Change... Rivers & Oceans Gravity Glaciers Wind
5 And human beings... Significant agents of Geomorphic change - causes changes themselves > remove or oversteepening slopes causes mass wasting > improperly operated dams and levee management cause catastrophic failures - Accelerate processes already occurring > Build buildings along cliffs that are poised to fail > construct jettis along coastlines that are experiencing erosion problems
6 Significant Why we are agents significant of change agents of change - Accelerate processes already occurring > Build buildings along cliffs that are poised to fail > construct jettis along coastlines that are experiencing erosion problems > construct dams, often where they shouldn't be
7 Paradigms (1 of 2) Two end members - 1. Evolutionary Geomorphology > championed by William Morris Davis > part of trend toward seeing everything in light of Darwinian Evolutionary Theory > landscapes evolve throughout time, > stage of evolution can be determined by examining the characteristics of the landscape > implies that TIME is the critical factor in determining what the landscape looks like
8 Davis' Landscape evolution model (most notably identified for streams and mountains as in this example from an intro geology textbook)
9 Paradigms (2 of 2) Process Geomorphology > Originally proposed by G.K. Gilbert > Drew upon his Engineering background > landforms are a balance between resisting framework and the forces acting to alter the landscape > Implies that time is one component of many that affect the appearance of the Earth > Inferred that the landscape was in equilibrium Between driving forces and resisting forces
10 Landscape in equilibrium- slope example from Gilbert Time = 0 Time = 1 Time = 2
11 Dynamic Equilibrium Davisian Geomorphology & TIME as dominant factor dominated the scientific literature until the 1960's John Hack proposed landscape development occurred similarly to the way Gilbert had espoused - Hack recognized, however, that there was considerable variability in most geomorphic systems > most were in dynamic equilibrium i.e., There is a balance between opposing forces that has considerable variation. Once overcome, balance must be re-established under the new conditions
12 Equilibrium & Time Steady - no changes over short time Graded Time - small changes over longer time - due to fluctuations in boundary conditions Cyclic time - the same changes occur over time - as conditions dictate - Average conditions change with time
13 Driving Forces in geomorphology Climate - Originally recognized as an agent of change by Walther Penck - Ultimately driven by the Sun and incoming solar radiation (insolation) interacting with Earth s major systems - Variable at a number of temporal and spatial scales - includes temperature, moisture, and pressure/wind systems Gravity - acts in conjunction with other driving forces - determines how much work will operate on all systems Internal Heat - drives plate motion and tectonic activity - Ultimately controls potential energy for work
14 Work = Force (F) x distance (s) Fs = Potential Energy (PE) F=mass (m) x acceleration (a) on earth F=mg Weight (W) = m x gravity (g) In simplified terms work is related to the amount of potential energy and the mass of the stuff being transported
15 Resisting Framework Rocks! - Strength of the rocks/sediments affects the potential processes that might act upon the materials - e.g., some lithologies behave as a brittle solid, some behave as a plastic solid - controls processes at a variety of temporal and spatial scales Structure (Tectonics) - causes zones of weakness - causes redistribution of lithologies - causes climatic variability
16 Basin and Range- Structure and geomorphology
17 Ridge and Valley - structure and geomorphology
18
19 San Andreas Fault on the Carrizo Plain in California Structure, climate and geomorphology
20 Thresholds of Change Implied within dynamic equilibrium - some variability is absorbed by the systems without discernable changes - some variability forces the system to change creating permanent changes two kinds of thresholds - Extrinsic= external thresholds > e.g., climate changes - Intrinsic=internal to the system > e.g., gullying of streams? Difficult to identify when and what controls the intrinsic thresholds.
21 Complex response can occur at a variety of scales - common in larger systems different areas in the systems respond differently depending on a variety of factors some may respond in exactly the opposite way to the same event Stream gradient profiles adjusting to climatically driven change
22 Process Linkage Operates on domino principle one part of a system changes, which triggers changes in another part Complicates what is known as complex response Example the Post Creek Cut-off of the Cache River in Southern Illinois
23 Internal Influences Endogenic changes - keep the world from progressing to a featureless ball - In theory this could occur - idea proposed by William Morris Davis called peneplanation - doesn't happen on earth (in most areas) because internal forces cause uplift > increases potential energy > usually initiates change
24 Categories of Endogenic influence Epeirogeny - regional uplift with minimal deformation of strata > Geomorphic responses are less than with other categories - influenced by GEOID > equipotential surface of the Oceans > has considerable distortions that appear as topography > hypothetical equipotential surface called the SPHEROID > all the minor perturbations in the surface due to interaction of all the gravitational forces are removed - Isostasy > adjustment of crust due to mass of rocks, sediments, & water > elevation of continents and other crust is a function of density of crustal materials and the forces acting inside the earth
25 Geoid / Spheroid
26 Why worry about this? Motion dictates geomorphic reaction - Upward vertical motion > increases potential energy- can be used by exogenic processes to act on the surface- see slide 13 of this set - Downward vertical motion > decreases potential energy Isostatic equilibrium continents are in some balance with the internal materials
27 Exogenic Forces- Climate change Primary influence on surface processes Has its own subcategory called climatic geomorphology relates climate to why certain landforms form under a given set of climate conditions Glacial and periglacial landforms Aeolian and arid region landforms Mass wasting landforms River response and form Coastal processes
28 Major climatic zones influencing Earth s surface processes What are the dominant agents and processes likely to influence surface processes in each zone?
29 Climatic implications? Langbein and Schumm, 1958
30 Moisture distribution- where are worlds largest rivers? Maximum precipitation
31 Climate-related geomorphology August 2004 Flood Event in Death Valley, CA aggradation scour line aggradation degradation Remnant debris flow deposit(s), indicating significant aggradation and then in later stages degradation during the event. Note the high water scour line above the deposit.
32 Eustasy- Changes in the volume of water in ocean basins relative to the size of the basins Strong influence on climate AND geomorphic processes in coastal and fluvial settings
3. creep- The slow gradual motion of soil/sediment downslope by a combination of gravity and heaving of particles by frost or shrink swell action.
 Exam 1 GEOL 407- Geomorphology Name I. Define and describe any 10 of the following terms- Be CONCISE, yet THOROUGH 1. epeirogeny- Regional uplift (and increase in potential energy) with minimal deformation
Exam 1 GEOL 407- Geomorphology Name I. Define and describe any 10 of the following terms- Be CONCISE, yet THOROUGH 1. epeirogeny- Regional uplift (and increase in potential energy) with minimal deformation
Active Tectonics. Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape. Edward A. Keller University of California, Santa Barbara
 Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Prentice Hall Earth Science Series SUB Gottingen 214 80416X, im ^, 2002 A 7883 lllllllilwii Active Tectonics Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape Second Edition V Edward A. Keller University of California,
Geomorphology: Mechanics and Evolution of Landscapes (GES )
 Geomorphology: Mechanics and Evolution of Landscapes (GES 206.2.5401) Instructor: Itai Haviv, haviv@bgu.ac.il, room 331, building 58, office hours: Tuesday 11:15-13:15 Teaching assistant: May-Tal Sadeh,
Geomorphology: Mechanics and Evolution of Landscapes (GES 206.2.5401) Instructor: Itai Haviv, haviv@bgu.ac.il, room 331, building 58, office hours: Tuesday 11:15-13:15 Teaching assistant: May-Tal Sadeh,
Landscape evolution. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities and life
 Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Forces That Shape Earth. How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle?
 Forces That Shape Earth How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle? Plate Motion Mountain ranges are produced by plate tectonics. The theory of plate
Forces That Shape Earth How do continents move? What forces can change rocks? How does plate motion affect the rock cycle? Plate Motion Mountain ranges are produced by plate tectonics. The theory of plate
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10)
 Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Landscape Development
 CHAPTER 22 Landscape Development Chapter Summary Landscapes are described in terms of their topography: elevation, the altitude of the surface of the Earth above sea level; relief, the difference between
CHAPTER 22 Landscape Development Chapter Summary Landscapes are described in terms of their topography: elevation, the altitude of the surface of the Earth above sea level; relief, the difference between
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
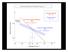 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Earth Science 14 th Edition, 2015 Tarbuck Lutgens - Tasa
 A Correlation of Tarbuck Lutgens - Tasa To the Oklahoma Academic Standards for Earth & Space Science A Correlation of, EARTH & SPACE SCIENCE HS-ESS1 Earth s Place in the Universe HS-ESS1-1 Students who
A Correlation of Tarbuck Lutgens - Tasa To the Oklahoma Academic Standards for Earth & Space Science A Correlation of, EARTH & SPACE SCIENCE HS-ESS1 Earth s Place in the Universe HS-ESS1-1 Students who
Table 6.1 Progress in the identification of equilibrium states in geomorphology
 6 The concept of equilibrium emerged in geomorphology once ideas of catastrophism had been succeeded by the understanding that gradual land-forming processes were responsible for the shape of the Earth
6 The concept of equilibrium emerged in geomorphology once ideas of catastrophism had been succeeded by the understanding that gradual land-forming processes were responsible for the shape of the Earth
GEOL 23100: Principles of Geomorphology
 GEOL 23100: Principles of Geomorphology 1 Geomorphology The word geomorphology" comes from the Greek roots "geo, morph, and logos, meaning earth, form, and study, respectively. Therefore, geomorphology
GEOL 23100: Principles of Geomorphology 1 Geomorphology The word geomorphology" comes from the Greek roots "geo, morph, and logos, meaning earth, form, and study, respectively. Therefore, geomorphology
A Living Planet. Chapter PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. What you will learn in this chapter. Summary of the chapter
 QUIT Main Ideas What you will learn in this chapter Summary Summary of the chapter Test your geographic knowledge by playing the. Main Ideas Section 1: The Earth Inside and Out The earth is the only habitable
QUIT Main Ideas What you will learn in this chapter Summary Summary of the chapter Test your geographic knowledge by playing the. Main Ideas Section 1: The Earth Inside and Out The earth is the only habitable
Name: Which rock layers appear to be most resistant to weathering? A) A, C, and E B) B and D
 Name: 1) The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream deposition and runoff B) precipitation and wind erosion C) stream erosion and mass movement D) weathering and biological activity 2)
Name: 1) The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream deposition and runoff B) precipitation and wind erosion C) stream erosion and mass movement D) weathering and biological activity 2)
Fundamentals of THE PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT. David Briggs, Peter Smithson, Kenneth Addison and Ken Atkinson
 Fundamentals of THE PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT Second Edition David Briggs, Peter Smithson, Kenneth Addison and Ken Atkinson LONDON AND NEW YORK Contents L,ISI Of colour piates List of black and white plates
Fundamentals of THE PHYSICAL ENVIRONMENT Second Edition David Briggs, Peter Smithson, Kenneth Addison and Ken Atkinson LONDON AND NEW YORK Contents L,ISI Of colour piates List of black and white plates
Table 6.1 Progress in the identification of equilibrium states in geomorphology
 6 The concept of equilibrium emerged in geomorphology once ideas of catastrophism had been succeeded by the understanding that gradual land-forming processes were responsible for the shape of the Earth
6 The concept of equilibrium emerged in geomorphology once ideas of catastrophism had been succeeded by the understanding that gradual land-forming processes were responsible for the shape of the Earth
Shape Earth. Plate Boundaries. Building. Building
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Chapter Wrap-Up Forces That Shape Earth Landforms at Plate Boundaries Mountain Building Continent Building How is Earth s surface shaped by plate
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Chapter Wrap-Up Forces That Shape Earth Landforms at Plate Boundaries Mountain Building Continent Building How is Earth s surface shaped by plate
Day 3 Weathering and Erosion.notebook. October 02, Section 7.2. Erosion and Deposition. Objectives
 Objectives Describe the relationship of gravity to all agents of erosion. Contrast the features left from different types of erosion. Analyze the impact of living and nonliving things on the processes
Objectives Describe the relationship of gravity to all agents of erosion. Contrast the features left from different types of erosion. Analyze the impact of living and nonliving things on the processes
Fresh Water: Streams, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands
 Fresh Water:, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands Oct 27 Glaciers and Ice Ages Chp 13 Nov 3 Deserts and Wind and EXAM #3 Slope hydrologic cycle P = precip I = precip intercepted by veg ET = evapotranspiration
Fresh Water:, Lakes Groundwater & Wetlands Oct 27 Glaciers and Ice Ages Chp 13 Nov 3 Deserts and Wind and EXAM #3 Slope hydrologic cycle P = precip I = precip intercepted by veg ET = evapotranspiration
Earth Science. Explain how Earth's biogeochemical cycles create a balance of materials. Examine the importance of biogeochemical cycles.
 Unit 1: DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF EARTH Introduction to Understand that earth science is based upon the four sciences of astronomy, geology, meteorology, and oceanography. Identify topics studied within the
Unit 1: DYNAMIC STRUCTURE OF EARTH Introduction to Understand that earth science is based upon the four sciences of astronomy, geology, meteorology, and oceanography. Identify topics studied within the
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow Citation for published version: Attal, M 2009, 'GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow' Nature Geoscience, vol. 2, no. 11,
Edinburgh Research Explorer GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow Citation for published version: Attal, M 2009, 'GEOMORPHOLOGY Rivers split as mountains grow' Nature Geoscience, vol. 2, no. 11,
PART II. Physical Landscape Chapters 2 5
 PART II Physical Landscape Chapters 2 5 Prof. Anthony Grande 2016 Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0616. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright. R E M I N D E
PART II Physical Landscape Chapters 2 5 Prof. Anthony Grande 2016 Lecture design, content and presentation AFG 0616. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright. R E M I N D E
Course Description. Course Objectives and Standards
 Earth and Space Science Curriculum Course Description Earth and Space Science 1 State # 3044 Grades offered: 10-12 Credits: A two credit course Prerequisite: none Counts as a Science Course for the General,
Earth and Space Science Curriculum Course Description Earth and Space Science 1 State # 3044 Grades offered: 10-12 Credits: A two credit course Prerequisite: none Counts as a Science Course for the General,
Fluvial Systems Lab Environmental Geology Lab Dr. Johnson
 Fluvial Systems Lab Environmental Geology Lab Dr. Johnson *Introductory sections of this lab were adapted from Pidwirny, M. (2006). "Streamflow and Fluvial Processes". Fundamentals of Physical Geography,
Fluvial Systems Lab Environmental Geology Lab Dr. Johnson *Introductory sections of this lab were adapted from Pidwirny, M. (2006). "Streamflow and Fluvial Processes". Fundamentals of Physical Geography,
1. Erosion by Running Water Most powerful cause of erosion
 I. Destructive Forces Notes: Destructive force: a process in which land is destroyed or changed such as weathering and erosion. All landforms are a result of a combination of constructive and destructive
I. Destructive Forces Notes: Destructive force: a process in which land is destroyed or changed such as weathering and erosion. All landforms are a result of a combination of constructive and destructive
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PROLOGUE The Local Environment... 1 Observation, Inference, Classification Properties of the Environment...
 CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PROLOGUE The Local Environment... 1 Observation, Inference, Classification Properties of the Environment... 3 Measurement, Percent Deviation From Accepted Value Density... 6 Density
CONTENTS CHAPTER 1: PROLOGUE The Local Environment... 1 Observation, Inference, Classification Properties of the Environment... 3 Measurement, Percent Deviation From Accepted Value Density... 6 Density
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
GLG101: What-To-Know List
 Exam 3, Page 1 GLG101: What-To-Know List (Derived from Before You Leave This Page Lists) This list is intended to guide your reading and to help you prepare for the online multiple-choice quizzes. Each
Exam 3, Page 1 GLG101: What-To-Know List (Derived from Before You Leave This Page Lists) This list is intended to guide your reading and to help you prepare for the online multiple-choice quizzes. Each
Important information from Chapter 1
 Important information from Chapter 1 Distinguish between: Natural hazard // Disaster // Catastrophe What role does human population play in these categories? Know how to read a Hazard Map, such as Figure
Important information from Chapter 1 Distinguish between: Natural hazard // Disaster // Catastrophe What role does human population play in these categories? Know how to read a Hazard Map, such as Figure
Slide #2. What is the drainage pattern that you can see on this hillslope? What hillslope hydrologic phenomenon is well exemplified on this hillslope?
 Geology 22 Process Geomorphology Final Exam Fall, 1999 Name This exam is closed book and closed notes. Take some time to read the questions carefully before you begin writing. Answer the questions concisely
Geology 22 Process Geomorphology Final Exam Fall, 1999 Name This exam is closed book and closed notes. Take some time to read the questions carefully before you begin writing. Answer the questions concisely
Isostasy and Tectonics Lab Understanding the Nature of Mobile Floating Lithospheric Plates
 Isostasy and Tectonics Lab Understanding the Nature of Mobile Floating Lithospheric Plates Crust Mantle Dynamics Introductory Geology Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Isostasy and Tectonics Laboratory Topics
Isostasy and Tectonics Lab Understanding the Nature of Mobile Floating Lithospheric Plates Crust Mantle Dynamics Introductory Geology Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Isostasy and Tectonics Laboratory Topics
Arizona Educator Proficiency Assessments (AEPA )
 Arizona Educator Proficiency Assessments (AEPA ) TEST OBJECTIVES January 2011 Subarea Range of Objectives Approximate Test Proportions I. Characteristics of Science 1 5 22% II. Origin and Evolution of
Arizona Educator Proficiency Assessments (AEPA ) TEST OBJECTIVES January 2011 Subarea Range of Objectives Approximate Test Proportions I. Characteristics of Science 1 5 22% II. Origin and Evolution of
OKLAHOMA SUBJECT AREA TESTS (OSAT )
 CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONS FOR OKLAHOMA EDUCATORS (CEOE ) OKLAHOMA SUBJECT AREA TESTS (OSAT ) June 1998 Subarea Range of Competencies I. Foundations of Scientific Inquiry 01 07 II. Space Systems 08 12
CERTIFICATION EXAMINATIONS FOR OKLAHOMA EDUCATORS (CEOE ) OKLAHOMA SUBJECT AREA TESTS (OSAT ) June 1998 Subarea Range of Competencies I. Foundations of Scientific Inquiry 01 07 II. Space Systems 08 12
Debris flow: categories, characteristics, hazard assessment, mitigation measures. Hariklia D. SKILODIMOU, George D. BATHRELLOS
 Debris flow: categories, characteristics, hazard assessment, mitigation measures Hariklia D. SKILODIMOU, George D. BATHRELLOS Natural hazards: physical phenomena, active in geological time capable of producing
Debris flow: categories, characteristics, hazard assessment, mitigation measures Hariklia D. SKILODIMOU, George D. BATHRELLOS Natural hazards: physical phenomena, active in geological time capable of producing
Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property.
 Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
Assessment Schedule Year 9 2015/6 Term Knowledge Using and applying Grade Criteria Autumn 1 Assessment window October 2015 3.1.1.2 Tectonic Natural hazards pose major risks to people and property. Definition
Ch 10 Deposition Practice Questions
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
GRAVITY AND ISOSTASY
 GRAVITY AND ISOSTASY Gravity The Geoid is the oblate spheroid -- the sea level surface over the entire Earth's surface Physically, the Geoid is an equipotential surface for gravity (i.e. the surface for
GRAVITY AND ISOSTASY Gravity The Geoid is the oblate spheroid -- the sea level surface over the entire Earth's surface Physically, the Geoid is an equipotential surface for gravity (i.e. the surface for
Setting the Stage 8/28/09 1. Review. Landscape history of WY. Climate, geology and vegetation patterns in Wyoming
 Setting the Stage Climate, geology and vegetation patterns in Wyoming 8/28/09 1 Review Vegetation ecology has its roots in phytogeography: Observation and description of PATTERNS of plant species distributions
Setting the Stage Climate, geology and vegetation patterns in Wyoming 8/28/09 1 Review Vegetation ecology has its roots in phytogeography: Observation and description of PATTERNS of plant species distributions
Class Notes: Surface Processes
 Name: Date: Period: Surface Processes The Physical Setting: Earth Science Class Notes: Surface Processes I. Weathering and Soils Weathering -! Sediments -! Weathering occurs when rocks are exposed to:
Name: Date: Period: Surface Processes The Physical Setting: Earth Science Class Notes: Surface Processes I. Weathering and Soils Weathering -! Sediments -! Weathering occurs when rocks are exposed to:
Physical Geography A Living Planet
 Physical Geography A Living Planet The geography and structure of the earth are continually being changed by internal forces, like plate tectonics, and external forces, like the weather. Iguaçu Falls at
Physical Geography A Living Planet The geography and structure of the earth are continually being changed by internal forces, like plate tectonics, and external forces, like the weather. Iguaçu Falls at
8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review
 8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review #1 Scientists believe that the land masses of Earth were once joined together as one supercontinent called. A: Australia B: Wegner C: Pangaea D:
8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review #1 Scientists believe that the land masses of Earth were once joined together as one supercontinent called. A: Australia B: Wegner C: Pangaea D:
Chapter 15 Structures
 Chapter 15 Structures Plummer/McGeary/Carlson (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. TECTONIC FORCES AT WORK Stress & Strain Stress Strain Compressive stress Shortening strain Tensional stress stretching
Chapter 15 Structures Plummer/McGeary/Carlson (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. TECTONIC FORCES AT WORK Stress & Strain Stress Strain Compressive stress Shortening strain Tensional stress stretching
12. The diagram below shows the collision of an oceanic plate and a continental plate.
 Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Prentice Hall: Science Explorer, 16 Book Series 2005 Correlated to: Alabama Science Standards for Earth and Space Science Core (Grade 6)
 Alabama Science Standards for Earth and Space Science Core (Grade 6) 1. Identify global patterns of atmospheric movement, including El Niño, the Gulf Stream, the jet stream, the Coriolis effect, and global
Alabama Science Standards for Earth and Space Science Core (Grade 6) 1. Identify global patterns of atmospheric movement, including El Niño, the Gulf Stream, the jet stream, the Coriolis effect, and global
Earth Systems Standards
 Earth Systems Earth Systems Standards The Cobb Teaching and Learning Standards (CT & LS) for Science are designed to provide foundational knowledge and skills for all students to develop proficiency in
Earth Systems Earth Systems Standards The Cobb Teaching and Learning Standards (CT & LS) for Science are designed to provide foundational knowledge and skills for all students to develop proficiency in
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA
 UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
Correlation: California State Curriculum Standards of Science for Grade 6 Focus on Earth Science
 Correlation: California State Curriculum Standards of Science for Grade 6 Focus on Earth Science To Science Workshop Series Earth Science: Geology The Universe Oceans and Atmosphere Plate Tectonics and
Correlation: California State Curriculum Standards of Science for Grade 6 Focus on Earth Science To Science Workshop Series Earth Science: Geology The Universe Oceans and Atmosphere Plate Tectonics and
COURSE OUTLINE GEOLOGY 101, Sec 002 Fall 2008, Diecchio Text: Lutgens, Tarbuck and Tasa, Essentials of Geology, 10 th edition
 COURSE OUTLINE GEOLOGY 101, Sec 002 Fall 2008, Diecchio Text: Lutgens, Tarbuck and Tasa, Essentials of Geology, 10 th edition Overview Of Earth ch 1 Earth's place in solar system, galaxy, universe Atmosphere,
COURSE OUTLINE GEOLOGY 101, Sec 002 Fall 2008, Diecchio Text: Lutgens, Tarbuck and Tasa, Essentials of Geology, 10 th edition Overview Of Earth ch 1 Earth's place in solar system, galaxy, universe Atmosphere,
Environmental Science EES B02H3 PRINCIPLES OF GEOMORPHOLOGY
 THE UNIVERSITY of TORONTO at SCARBOROUGH January, 2009 Department of Physical & Environmental Sciences Environmental Science EES B02H3 PRINCIPLES OF GEOMORPHOLOGY The earth s surface form and its dynamic
THE UNIVERSITY of TORONTO at SCARBOROUGH January, 2009 Department of Physical & Environmental Sciences Environmental Science EES B02H3 PRINCIPLES OF GEOMORPHOLOGY The earth s surface form and its dynamic
FLUVIAL LANDFORMS. Floodplains
 FLUVIAL LANDFORMS Floodplains fairly flat & continuous surface occupying much of a valley bottom normally underlain by unconsolidated sediments subject to periodic flooding (usually once every year or
FLUVIAL LANDFORMS Floodplains fairly flat & continuous surface occupying much of a valley bottom normally underlain by unconsolidated sediments subject to periodic flooding (usually once every year or
Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands
 Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
Page - 1 Laboratory Exercise #4 Geologic Surface Processes in Dry Lands Section A Overview of Lands with Dry Climates The definition of a dry climate is tied to an understanding of the hydrologic cycle
New Paltz Central School District Earth Science
 UNIT 1: MEASUREMENT AND DENSITY Measure volume, length, weight, and rate of Practicum during exam How do you accurately measure length, weight, change. Full lab write-up of density determination of and
UNIT 1: MEASUREMENT AND DENSITY Measure volume, length, weight, and rate of Practicum during exam How do you accurately measure length, weight, change. Full lab write-up of density determination of and
Grade 8 Learning Objectives MS-PS2-4.
 MS-PS2-4. Construct and present arguments using evidence to support the claim that gravitational interactions are attractive and depend on the masses of interacting objects. [Clarification Statement: Examples
MS-PS2-4. Construct and present arguments using evidence to support the claim that gravitational interactions are attractive and depend on the masses of interacting objects. [Clarification Statement: Examples
FOSS LANDFORMS 8/1/2012. Content Professional Development Tools Contributor: Ben Fackler Adams. Assessing with Learning Progressions in Science
 8/1/2012 Assessing with Learning Progressions in Science FOSS LANDFORMS Photo by Joanne Johnson Content Professional Development Tools Contributor: Ben Fackler Adams Learning Progression Landforms Prerequisite
8/1/2012 Assessing with Learning Progressions in Science FOSS LANDFORMS Photo by Joanne Johnson Content Professional Development Tools Contributor: Ben Fackler Adams Learning Progression Landforms Prerequisite
TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID: GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom
 TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID:1542715 GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows
TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID:1542715 GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School
 COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR GEOLOGY GEO4311 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman or sophomore
COWLEY COLLEGE & Area Vocational Technical School COURSE PROCEDURE FOR GEOLOGY GEO4311 5 Credit Hours Student Level: This course is open to students on the college level in either the freshman or sophomore
Planetary Surface Processes
 Planetary Surface Processes Nathan Bridges Applied Physics Laboratory (and former JPLer and ongoing coworker with many at JPL and Caltech) rippled sand in Gale Crater MSL landing ellipse HiRISE image ESP_023957_1755
Planetary Surface Processes Nathan Bridges Applied Physics Laboratory (and former JPLer and ongoing coworker with many at JPL and Caltech) rippled sand in Gale Crater MSL landing ellipse HiRISE image ESP_023957_1755
Earth Space EOC Review Test #1
 Earth Space EOC Review Test #1 NAME: Use test for questions 1 and 2 Jack studied the effects of light pollution on turtles and their offspring. He observed that areas with a high amounts of light pollution
Earth Space EOC Review Test #1 NAME: Use test for questions 1 and 2 Jack studied the effects of light pollution on turtles and their offspring. He observed that areas with a high amounts of light pollution
core mantle crust the center of the Earth the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock
 core the center of the Earth mantle the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock crust the surface layer of the Earth that includes the continents and oceans 1 continental drift the theory
core the center of the Earth mantle the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock crust the surface layer of the Earth that includes the continents and oceans 1 continental drift the theory
The Effects of Hydraulic Structures on Streams Prone to Bank Erosion in an Intense Flood Event: A Case Study from Eastern Hokkaido
 Symposium Proceedings of the INTERPRAENENT 2018 in the Pacific Rim The Effects of Hydraulic Structures on Streams Prone to Bank Erosion in an Intense Flood Event: A Case Study from Eastern Hokkaido Daisuke
Symposium Proceedings of the INTERPRAENENT 2018 in the Pacific Rim The Effects of Hydraulic Structures on Streams Prone to Bank Erosion in an Intense Flood Event: A Case Study from Eastern Hokkaido Daisuke
Erosion and Deposition along Rivers and Seashores - Part 1: Modeling in the Classroom
 Erosion and Deposition along Rivers and Seashores - Part 1: Modeling in the Classroom Lesson Focus: Erosion and Deposition Learning Objectives: Students will learn to recognize landforms found on Earth.
Erosion and Deposition along Rivers and Seashores - Part 1: Modeling in the Classroom Lesson Focus: Erosion and Deposition Learning Objectives: Students will learn to recognize landforms found on Earth.
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction
 East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Geology of National Parks Course(s): Geology of the National Parks Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period (average minutes):
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Geology of National Parks Course(s): Geology of the National Parks Grades: 10-12 Department: Science Length of Period (average minutes):
Environmental Science Institute The University of Texas - Austin
 Environmental Science Institute The University of Texas - Austin Geologic Wonders of Central Texas Dr. Leon Long This file contains suggestions for how to incorporate the material from this CDROM into
Environmental Science Institute The University of Texas - Austin Geologic Wonders of Central Texas Dr. Leon Long This file contains suggestions for how to incorporate the material from this CDROM into
Elemental Geosystems, 5e (Christopherson) Chapter 10 Weathering, Karst Landscapes, and Mass Movement
 Elemental Geosystems, 5e (hristopherson) hapter 10 Weathering, Karst Landscapes, and Mass Movement 1) The science that specifically studies the origin, evolution, form, and spatial distribution of landforms
Elemental Geosystems, 5e (hristopherson) hapter 10 Weathering, Karst Landscapes, and Mass Movement 1) The science that specifically studies the origin, evolution, form, and spatial distribution of landforms
SAN DIEGO COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CITY, MESA, AND MIRAMAR COLLEGES ASSOCIATE DEGREE COURSE OUTLINE
 GEOL 100 CIC Approval: 12/12/2002 BOT APPROVAL: STATE APPROVAL: EFFECTIVE TERM: Spring 2003 SECTION I SAN DIEGO COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CITY, MESA, AND MIRAMAR COLLEGES ASSOCIATE DEGREE COURSE OUTLINE
GEOL 100 CIC Approval: 12/12/2002 BOT APPROVAL: STATE APPROVAL: EFFECTIVE TERM: Spring 2003 SECTION I SAN DIEGO COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CITY, MESA, AND MIRAMAR COLLEGES ASSOCIATE DEGREE COURSE OUTLINE
Plate Boundaries & Resulting Landforms
 Plate Boundaries & Resulting Landforms Divergent Plate Boundaries (plates being pulled apart) Type: oceanic plates Description: rising magma gently lifts the crust creating a ridge. The flow of convection
Plate Boundaries & Resulting Landforms Divergent Plate Boundaries (plates being pulled apart) Type: oceanic plates Description: rising magma gently lifts the crust creating a ridge. The flow of convection
CT Science Standard 4.3 Erosion Water has a major role in shaping the earth s surface. Trail Guides
 Trail Guides We have created a set of Trail Guides for use by you and your students as you explore our galleries on your field trip. The first section consists of the trail guides with teacher notes (pages
Trail Guides We have created a set of Trail Guides for use by you and your students as you explore our galleries on your field trip. The first section consists of the trail guides with teacher notes (pages
EXPLORING. liarxh # AN INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL GEOLOGY JON P. DAVIDSON UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES WALTER E. REED
 EXPLORING liarxh # AN INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL GEOLOGY JON P. DAVIDSON UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES WALTER E. REED UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES PAUL M. DAVIS UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA,
EXPLORING liarxh # AN INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL GEOLOGY JON P. DAVIDSON UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES WALTER E. REED UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, LOS ANGELES PAUL M. DAVIS UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA,
CPO Science Middle School Earth Science Learning System Correlated to Ohio Science Academic Content Standards for Earth Science, grades 6-8
 CPO Science Middle School Earth Science Learning System Correlated to Ohio Science Academic Content Standards for Earth Science, grades 6-8 Earth and Space Science Benchmark A - Describe how the positions
CPO Science Middle School Earth Science Learning System Correlated to Ohio Science Academic Content Standards for Earth Science, grades 6-8 Earth and Space Science Benchmark A - Describe how the positions
Date: / Page # Version A Page 1
 Name: Plate Tectonics Quiz 1. Which best describes a major characteristic of both volcanoes and earthquakes? (1) They are centered at the poles. (2) They are located in the same geographic areas. (3) They
Name: Plate Tectonics Quiz 1. Which best describes a major characteristic of both volcanoes and earthquakes? (1) They are centered at the poles. (2) They are located in the same geographic areas. (3) They
The Dynamic Earth Section 1. Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1
 Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1 The Earth as a System The Earth is an integrated system that consists of rock, air, water, and living things that all interact with each other.
Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1 The Earth as a System The Earth is an integrated system that consists of rock, air, water, and living things that all interact with each other.
Geologic Influences GEOLOGIC CYCLE. Definitions. PART II: People and their 3/27/2018. GEOG 101 Part II People and their
 R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by March 27, 2018. A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay. ESSAY TOPICS (choose any two): Contributions of a noted geographer,
R E M I N D E R S Two required essays are due by March 27, 2018. A third may be used for extra credit in place of a Think Geographically essay. ESSAY TOPICS (choose any two): Contributions of a noted geographer,
Missouri Educator Gateway Assessments
 Missouri Educator Gateway Assessments FIELD 019: EARTH SCIENCE June 2014 Content Domain Range of Competencies Approximate Percentage of Test Score I. Science and Engineering Practices 0001 0003 18% II.
Missouri Educator Gateway Assessments FIELD 019: EARTH SCIENCE June 2014 Content Domain Range of Competencies Approximate Percentage of Test Score I. Science and Engineering Practices 0001 0003 18% II.
Required Materials Plummer, C., Physical geology. Columbus, OH: McGraw Hill Higher Education
 Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 Textbook Update Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Physical Geology Course
Butler Community College Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math Division Robert Carlson Revised Fall 2017 Implemented Spring 2018 Textbook Update Spring 2018 COURSE OUTLINE Physical Geology Course
The performance expectation above was developed using the following elements from the NRC document A Framework for K-12 Science Education:
 MS-ESS2-1 Earth's Systems Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth's materials and the flow of energy that drives this process. [Clarification
MS-ESS2-1 Earth's Systems Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth's materials and the flow of energy that drives this process. [Clarification
Crustal Boundaries. As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries they interact in various ways. Convergent Transform Divergent
 Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
New Paltz Central School District
 Forces Shaping the Earth s Surface What are the structures of the Earth? What internal and external forces have shaped and continue to change the surface of the Earth? What are the impacts of these changes?
Forces Shaping the Earth s Surface What are the structures of the Earth? What internal and external forces have shaped and continue to change the surface of the Earth? What are the impacts of these changes?
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas FLUVIAL PROCESSES Fluvial Processes The Impact of Fluvial Processes on the Landscape Streams and Stream Systems Stream Channels Structural Relationships The Shaping and
PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas FLUVIAL PROCESSES Fluvial Processes The Impact of Fluvial Processes on the Landscape Streams and Stream Systems Stream Channels Structural Relationships The Shaping and
CAPE Unit 1 Module 2 & 3. Topic Specific Objectives Content Explain the main concepts, flows and processes associated with coastal environments
 # Week(s) Wks 1-3 CAPE Unit 1 Module 2 & 3 Topic Specific Objectives Content Explain the main concepts, flows and processes associated with coastal environments Wave formation, structure, types Textbook
# Week(s) Wks 1-3 CAPE Unit 1 Module 2 & 3 Topic Specific Objectives Content Explain the main concepts, flows and processes associated with coastal environments Wave formation, structure, types Textbook
What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley
 1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
GLY Coastal Geomorphology Notes
 GLY 4734 - Coastal Geomorphology Notes Dr. Peter N. Adams Spring 2011 2 Coastal Classification In this lecture, we discuss some successful classification schemes of the coastal landscape, and pay particular
GLY 4734 - Coastal Geomorphology Notes Dr. Peter N. Adams Spring 2011 2 Coastal Classification In this lecture, we discuss some successful classification schemes of the coastal landscape, and pay particular
Hydrologic System. What is a Natural System? Hydrologic System
 31 The Changing Face of the Earth Before After Flooding of Mississippi & Illinois Rivers 1993 According to plate tectonic theory, which of these should have the most violent earthquakes, on average? 1.
31 The Changing Face of the Earth Before After Flooding of Mississippi & Illinois Rivers 1993 According to plate tectonic theory, which of these should have the most violent earthquakes, on average? 1.
CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS FOCUS ON EARTH SCIENCE, Grade 6. Correlated to AGS EARTH SCIENCE
 CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS FOCUS ON EARTH SCIENCE, Grade 6 Correlated to AGS EARTH SCIENCE PLATE TECTONICS AND EARTH S STRUCTURE 1. Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface
CALIFORNIA CONTENT STANDARDS FOCUS ON EARTH SCIENCE, Grade 6 Correlated to AGS EARTH SCIENCE PLATE TECTONICS AND EARTH S STRUCTURE 1. Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface
Tuesday, September 05, 2017 Planet Earth
 Tuesday, September 05, 2017 Planet Earth Objective: Describe the solar system and Earth s location in it. Identify Earth s shape. Discuss Earth s structure. List Earth s landforms Do Now: What is a compass
Tuesday, September 05, 2017 Planet Earth Objective: Describe the solar system and Earth s location in it. Identify Earth s shape. Discuss Earth s structure. List Earth s landforms Do Now: What is a compass
Environmental Geology
 GEO106 Environmental Geology SF movie Have your clicker ready 1906: San Francisco on fire 1906: San Francisco: a destroyed city 1 1994: Northridge earthquake December 26 th, 2003 Bam earthquake, Iran magnitude
GEO106 Environmental Geology SF movie Have your clicker ready 1906: San Francisco on fire 1906: San Francisco: a destroyed city 1 1994: Northridge earthquake December 26 th, 2003 Bam earthquake, Iran magnitude
Name. 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different soil horizons, A, B, C, and D, are shown.
 Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
Name 1. In the cross section of the hill shown below, which rock units are probably most resistant to weathering? 4. The diagram below shows a soil profile formed in an area of granite bedrock. Four different
8 th Grade Earth Science Scope and Sequence
 8 th Grade Earth Science Scope and Sequence 2016-2017 Unit One: Earth s Place in the Universe ESS1-HS-2. Construct an explanation of the Big Bang theory based on astronomical evidence of light spectra,
8 th Grade Earth Science Scope and Sequence 2016-2017 Unit One: Earth s Place in the Universe ESS1-HS-2. Construct an explanation of the Big Bang theory based on astronomical evidence of light spectra,
Processes that Shape the Earth
 Grade 8 Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1 Processes that Shape the Earth Overview Number of instructional days: 20 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Explain the role of differential heating and convection
Grade 8 Science, Quarter 4, Unit 4.1 Processes that Shape the Earth Overview Number of instructional days: 20 (1 day = 45 minutes) Content to be learned Explain the role of differential heating and convection
ENVIRONMENTAL GEOSCIENCE UNIFORM SYLLABUS
 ENVIRONMENTAL GEOSCIENCE UNIFORM SYLLABUS The Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of the Province of British Columbia Note: 1. This Syllabus May Be Subject To Change 2. These Courses
ENVIRONMENTAL GEOSCIENCE UNIFORM SYLLABUS The Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of the Province of British Columbia Note: 1. This Syllabus May Be Subject To Change 2. These Courses
Earth s Geological Cycle
 Earth s Geological Cycle What Are the Earth s Major Geological Processes? Main Processes: 1. Plate Tectonics 2. Rock Cycle 3. Soil Formation LITHOSPHERE The Earth s Structure Earth s Interior Core (Nickel
Earth s Geological Cycle What Are the Earth s Major Geological Processes? Main Processes: 1. Plate Tectonics 2. Rock Cycle 3. Soil Formation LITHOSPHERE The Earth s Structure Earth s Interior Core (Nickel
How do glaciers form?
 Glaciers What is a Glacier? A large mass of moving ice that exists year round is called a glacier. Glaciers are formed when snowfall exceeds snow melt year after year Snow and ice remain on the ground
Glaciers What is a Glacier? A large mass of moving ice that exists year round is called a glacier. Glaciers are formed when snowfall exceeds snow melt year after year Snow and ice remain on the ground
THE EARTH S RELIEF SOCIAL SCIENCES 1º ESO
 THE EARTH S RELIEF SOCIAL SCIENCES 1º ESO 1. THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH The Earth is divided into layers: The crust is the surface layer. It is a thin, solid layer made of rock. The Earth s crust has a
THE EARTH S RELIEF SOCIAL SCIENCES 1º ESO 1. THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH The Earth is divided into layers: The crust is the surface layer. It is a thin, solid layer made of rock. The Earth s crust has a
Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2
 Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Create a mind map with the driving question, Why are Oceans Important? Remember: Why are oceans so important? Why are oceans so important? Primary water source
Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Create a mind map with the driving question, Why are Oceans Important? Remember: Why are oceans so important? Why are oceans so important? Primary water source
TEACHER CERTIFICATION STUDY GUIDE FOUNDATIONS OF SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY
 Table of Contents SUBAREA I. COMPETENCY 1.0 FOUNDATIONS OF SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY UNDERSTAND THE GENERAL RELATIONSHIPS AND COMMON THEMES THAT CONNECT MATHEMATICS, SCIENCE, AND TECHNOLOGY...1 SKILL 1.1 SKILL
Table of Contents SUBAREA I. COMPETENCY 1.0 FOUNDATIONS OF SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY UNDERSTAND THE GENERAL RELATIONSHIPS AND COMMON THEMES THAT CONNECT MATHEMATICS, SCIENCE, AND TECHNOLOGY...1 SKILL 1.1 SKILL
EROSION AND DEPOSITION
 CHAPTER 8 EROSION AND DEPOSITION SECTION 8 1 Changing Earth s Surface (pages 252-255) This section explains how sediment is carried away and deposited elsewhere to wear down and build up Earth s surface.
CHAPTER 8 EROSION AND DEPOSITION SECTION 8 1 Changing Earth s Surface (pages 252-255) This section explains how sediment is carried away and deposited elsewhere to wear down and build up Earth s surface.
The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8
 The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8 Kindergarten The Earth is composed of land, air and water. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. characteristics
The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8 Kindergarten The Earth is composed of land, air and water. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. characteristics
1. Any process that causes rock to crack or break into pieces is called physical weathering. Initial product = final product
 Weathering 1. Any process that causes rock to crack or break into pieces is called physical weathering. Initial product = final product End Result of physical weathering is increased surface area. 2. Physical
Weathering 1. Any process that causes rock to crack or break into pieces is called physical weathering. Initial product = final product End Result of physical weathering is increased surface area. 2. Physical
water erosion lithosphere Describe the process of erosion and deposition. chemical weathering Dissolving limestone is an example of.
 At one time, there was one large island off the coast of Mississippi and now it is two separate islands. What caused the island to be split into two? water erosion The crust and the top part of the upper
At one time, there was one large island off the coast of Mississippi and now it is two separate islands. What caused the island to be split into two? water erosion The crust and the top part of the upper
Engineering Geology ECIV 3302
 Engineering Geology ECIV 3302 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2019-2018 Chapter (5) Weathering & Soil Chapter 5: Weathering, Soil, and Mass Wasting External processes include : (1) Weathering (2) Mass wasting
Engineering Geology ECIV 3302 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2019-2018 Chapter (5) Weathering & Soil Chapter 5: Weathering, Soil, and Mass Wasting External processes include : (1) Weathering (2) Mass wasting
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
