Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry Topic 2: Thermochemistry
|
|
|
- Clarence Hart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Topic 2: Introduction, Topic 2: Thermochemistry Text: Chapter 7 and 19 (~ 3 weeks) 2.0 Introduction, terminology and scope 2.1 Enthalapy and Energy Change in a chemical process; 1st law of Thermodynamics 2.2 Enthalapy of Formation, Calorimetry, Heat capacity, Bond Energies, and Standard State 2.3 Entropy; 2nd and 3rd laws of thermodynamics 2.4 Free Energy; Spontaneity and Equilibrium. 2.5 Relationship between dh,ds, dg and K 2.6 Change of dg with Temperature adn Concentration; Effect of Temperature on K (van't Hoff) Winter 2009 Page Introduction, terminology and scope A System is the part of the universe under study. The Surroundings is anything outside of the System. An open system allows for exchange of both material and energy A closed system can exchange only energy An isolated system, does not permit the transfer of mass or Energy. Energy is the ability to do work Work occurs when a force acts through a distance. Kinetic Energy is the energy of a moving object. Thermal Energy is the kinetic energy associated with random molecular motion Winter 2009 Page 2 1
2 Kinetic Energy Work e k = w = Fd 1 2 mv 2 [e k ] = kg m s [w ] = kg m s 2 m 2 = J = J Winter 2009 Page 3 Understanding Calorie (cal): The quantity of heat required to change the temperature of one gram of water by one degree Celsius. Joule (J): International System of Units (SI) unit for heat 1 cal = J James Joule ( ) Winter 2009 Page 4 2
3 Heat Capacity The quantity of heat (q) required to change the temperature of a system by one degree. Molar heat capacity. System is one mole of substance. Specific heat capacity, c. System is one gram of substance Heat capacity Mass times c = C specific heat. Water: c = g j -1 C -1 q = m c ΔT q = C ΔT Winter 2009 Page 5 Winter 2009 Page 6 3
4 Conservation of Energy In interactions between a system and its surroundings the total energy remains constant energy is neither created nor destroyed. q system + q surroundings = 0 q system = -q surroundings Winter 2009 Page 7 Determination of Specific Heat Winter 2009 Page 8 4
5 EXAMPLE 7-2 Determining Specific Heat from Experimental Data. Using the data presented on the last slide to calculate the specific heat of lead. Water is the surroundings q lead = -q water q water = mcδt = (50.0 g)(4.184 J/g C)( ) C q water = J q lead = J = mcδt = (150.0 g)(c lead )( ) C c lead = 0.13 Jg -1 C -1 Winter 2009 Page 9 Heats of Reaction and Calorimetry Chemical energy. Contributes to the internal energy of a system. Heat of reaction, q rxn. The quantity of heat exchanged between a system and its surroundings when a chemical reaction occurs within the system, at constant temperature. Winter 2009 Page 10 5
6 Heats of Reaction and Calorimetry Exothermic reactions. Produces heat, q rxn < 0. Endothermic reactions. Consumes heat, q rxn > 0. Calorimeter A device for measuring quantities of heat. Add water Winter 2009 Page 11 Winter 2009 q rxn < 0 q rxn > 0 Page 12 6
7 q rxn = -q cal q cal = q bomb + q water + q wires + Define the heat capacity of the calorimeter: q cal = Σm i c i ΔT = CΔT heat all i C = heat capacity of the calorimeter Winter 2009 Page 13 Using Bomb Calorimetry Data to Determine a Heat of Reaction. The combustion of g sucrose, in a bomb calorimeter, causes the temperature to rise from to C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter assembly is 4.90 kj/ C. (a) What is the heat of combustion of sucrose, expressed in kj/ mol C 12 H 22 O 11? (b) Verify the claim of sugar producers that one teaspoon of sugar (about 4.8 g) contains only 19 calories. 1 food Calorie ( 1 Calorie with a capital C) is actually 1000 cal or Kcal Winter 2009 Page 14 7
8 Calculate q calorimeter : q cal = CΔT = (4.90 kj/ C)( ) C = (4.90)(3.41) kj = 16.7 kj Calculate q rxn : q rxn = -q cal = kj per g kj q rxn = -q cal = = kj/g g q rxn = kj/g g 1.00 mol = kj/mol (a) Calculate q rxn for one teaspoon: q rxn = (-16.5 kj/g)( 4.8 g 1 tsp 1.00 cal )( )= -19 kcal/tsp J (b) Winter 2009 Page 15 Coffee cup Calorimeter A simple calorimeter. Well insulated and therefore isolated. Measure temperature change. q rxn = -q cal Winter 2009 Page 16 8
9 Winter 2009 Page 17 Winter 2009 Page 18 9
10 Winter 2009 Page 19 Pressure- Volume Work of a reaction In addition to heat effects chemical reactions may also do work. Gas formed pushes against the atmosphere. Volume changes. Pressure-volume work. Winter 2009 Page 20 10
11 Pressure- Volume Work of a reaction Winter 2009 Page 21 Pressure- Volume Work of a reaction Assume an ideal gas and calculate the volume change: V i = nrt/p = (0.100 mol)( L atm mol -1 K -1 )(298K)/(2.40 atm) = 1.02 L V f = 2.04 L ΔV = 2.04 L-1.02 L = 1.02 L Calculating Pressure-Volume Work. Suppose the gas in the previous figure is mol He at 298 K and the each mass in the figure corresponds to an external pressure of 1.20 atm. How much work, in Joules, is associated with its expansion at constant pressure. w = -PΔV = -(1.20 atm)(1.02 L)( = J -101 J ) 1 L atm Winter 2009 Page 22 11
First Law of Thermodynamics
 Energy Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Types of energy 1) Potential energy - energy possessed by objects due to position or arrangement of particles. Forms of potential energy - electrical,
Energy Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Types of energy 1) Potential energy - energy possessed by objects due to position or arrangement of particles. Forms of potential energy - electrical,
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. Kozet YAPSAKLI The Nature of Energy Kinetic and Potential Energy Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy. E p = mgh
CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. Kozet YAPSAKLI The Nature of Energy Kinetic and Potential Energy Potential energy can be converted into kinetic energy. E p = mgh
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 5: Thermochemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 5: Thermochemistry Study of energy and its transformations is called thermodynamics Portion of thermodynamics that involves the relationships between chemical and
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 5: Thermochemistry Study of energy and its transformations is called thermodynamics Portion of thermodynamics that involves the relationships between chemical and
Energy Conversions. Energy. the ability to do work or produce heat. energy energy due to composition or position of an object
 Energy Energy the ability to do work or produce heat energy energy due to composition or position of an object energy the energy of motion Energy - SI unit for energy 1 J = 1 Kgm 2 / s 2 Energy Conversions
Energy Energy the ability to do work or produce heat energy energy due to composition or position of an object energy the energy of motion Energy - SI unit for energy 1 J = 1 Kgm 2 / s 2 Energy Conversions
Ch. 7: Thermochemistry
 Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Thermodynamics concerns itself with energy and its relationship to the large scale bulk properties of a system that are measurable: Volume, Temperature, Pressure, Heat
Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry Thermodynamics concerns itself with energy and its relationship to the large scale bulk properties of a system that are measurable: Volume, Temperature, Pressure, Heat
The Nature of Energy. Chapter Six: Kinetic vs. Potential Energy. Energy and Work. Temperature vs. Heat
 The Nature of Energy Chapter Six: THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationship between chemical reactions and energy changes
The Nature of Energy Chapter Six: THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationship between chemical reactions and energy changes
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Learning Outcomes: Interconvert energy units Distinguish between the system and the surroundings in thermodynamics Calculate internal energy from heat and work and state sign
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Learning Outcomes: Interconvert energy units Distinguish between the system and the surroundings in thermodynamics Calculate internal energy from heat and work and state sign
Topic 05 Energetics : Heat Change. IB Chemistry T05D01
 Topic 05 Energetics 5.1-5.2: Heat Change IB Chemistry T05D01 5.1 Exothermic and endothermic reactions - 1 hour 5.1.1 Define the terms exothermic reaction, endothermic reaction and standard enthalpy change
Topic 05 Energetics 5.1-5.2: Heat Change IB Chemistry T05D01 5.1 Exothermic and endothermic reactions - 1 hour 5.1.1 Define the terms exothermic reaction, endothermic reaction and standard enthalpy change
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
 Chapter 6: Thermochemistry 1. Light the Furnace: The Nature of Energy and Its Transformations a. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy i. This means that we will
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry 1. Light the Furnace: The Nature of Energy and Its Transformations a. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy i. This means that we will
AP CHEMISTRY. Unit 5 Thermochemistry. Jeff Venables Northwestern High School
 AP CHEMISTRY Unit 5 Thermochemistry Jeff Venables Northwestern High School Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy - the energy of motion: Ek = 1 mv 2 Potential energy - the energy an object
AP CHEMISTRY Unit 5 Thermochemistry Jeff Venables Northwestern High School Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy - the energy of motion: Ek = 1 mv 2 Potential energy - the energy an object
CHEM 1105 S10 March 11 & 14, 2014
 CHEM 1105 S10 March 11 & 14, 2014 Today s topics: Thermochemistry (Chapter 6) Basic definitions Calorimetry Enthalpy Thermochemical equations Calculating heats of reaction Hess s Law Energy and Heat Some
CHEM 1105 S10 March 11 & 14, 2014 Today s topics: Thermochemistry (Chapter 6) Basic definitions Calorimetry Enthalpy Thermochemical equations Calculating heats of reaction Hess s Law Energy and Heat Some
Thermochemistry. The study of the ENERGY CHANGES that accompany changes in matter. 3 Ways: Monday, February 3, 2014
 Thermochemistry The study of the ENERGY CHANGES that accompany changes in matter 3 Ways: 1 Thermodynamics FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS the total amount of energy in the universe is constant (conservation
Thermochemistry The study of the ENERGY CHANGES that accompany changes in matter 3 Ways: 1 Thermodynamics FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS the total amount of energy in the universe is constant (conservation
Chapter 11. Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change
 Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Chapter 11 Thermochemistry: Heat & Chemical Change The Flow of Energy Thermochemistry: Study of heat changes that occur during physical processes and chemical reactions Energy Energy is the capacity to
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry. 許富銀 ( Hsu Fu-Yin)
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry 許富銀 ( Hsu Fu-Yin) 1 Thermodynamics The study of energy and its transformations is known as thermodynamics The relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes that
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry 許富銀 ( Hsu Fu-Yin) 1 Thermodynamics The study of energy and its transformations is known as thermodynamics The relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes that
Thermochemistry Chapter 4
 Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions Focus is on heat and matter transfer between the system and the surroundings Energy The ability
Thermochemistry Chapter 4 Thermochemistry is the study of energy changes that occur during chemical reactions Focus is on heat and matter transfer between the system and the surroundings Energy The ability
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 許富銀
 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 許富銀 6.1 Chemical Hand Warmers Thermochemistry: the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy Hand warmers use the oxidation of iron as the exothermic reaction: Nature
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 許富銀 6.1 Chemical Hand Warmers Thermochemistry: the study of the relationships between chemistry and energy Hand warmers use the oxidation of iron as the exothermic reaction: Nature
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Preview Introduction to thermochemistry: Potential energy and kinetic energy. Chemical energy. Internal energy, work and heat. Exothermic vs. endothermic reactions.
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Dr. A. Al-Saadi 1 Preview Introduction to thermochemistry: Potential energy and kinetic energy. Chemical energy. Internal energy, work and heat. Exothermic vs. endothermic reactions.
I. Chemical Reactions that Involve Heat
 Unit 12 Energy I. Chemical Reactions that Involve Heat Thermochemistry: study of changes in heat in chemical reactions. Endothermic: absorbs heat; temp. goes down Exothermic: releases heat; temp. goes
Unit 12 Energy I. Chemical Reactions that Involve Heat Thermochemistry: study of changes in heat in chemical reactions. Endothermic: absorbs heat; temp. goes down Exothermic: releases heat; temp. goes
Law of conservation of energy: energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred One object to another One type of energy to another
 ch6blank Page 1 Chapter 6: Thermochemistry Thermochemistry: study of the relationships between chemistry and energy Energy: capacity to do work Work:result of a force acting over a certain distance, one
ch6blank Page 1 Chapter 6: Thermochemistry Thermochemistry: study of the relationships between chemistry and energy Energy: capacity to do work Work:result of a force acting over a certain distance, one
CHM 111 Dr. Kevin Moore
 CHM 111 Dr. Kevin Moore Kinetic Energy Energy of motion E k 1 2 mv 2 Potential Energy Energy of position (stored) Law of Conservation of Energy Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be converted
CHM 111 Dr. Kevin Moore Kinetic Energy Energy of motion E k 1 2 mv 2 Potential Energy Energy of position (stored) Law of Conservation of Energy Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be converted
Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy
 Unit 7: Energy Outline Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. The energy
Unit 7: Energy Outline Types of Energy Calorimetry q = mc T Thermochemical Equations Hess s Law Spontaneity, Entropy, Gibb s Free energy Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. The energy
Chapter 11. Thermochemistry. 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages
 Chapter 11 Thermochemistry 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages 293-94 The Flow of energy - heat Thermochemistry concerned with the heat changes that occur
Chapter 11 Thermochemistry 1. Let s begin by previewing the chapter (Page 292). 2. We will partner read Pages 293-94 The Flow of energy - heat Thermochemistry concerned with the heat changes that occur
Chapter 17 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Quantities in Chemical Reactions
 Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Chapter 15 Energy and Chemical Change
 Chapter 15 Energy and Chemical Change Chemical reactions usually absorb or release energy. Section 1: Energy Section 2: Heat Section 3: Thermochemical Equations Section 4: Calculating Enthalpy Change Section
Chapter 15 Energy and Chemical Change Chemical reactions usually absorb or release energy. Section 1: Energy Section 2: Heat Section 3: Thermochemical Equations Section 4: Calculating Enthalpy Change Section
Energy, Heat and Chemical Change
 Energy, Heat and Chemical Change Chemistry 35 Fall 2000 Thermochemistry A part of Thermodynamics dealing with energy changes associated with physical and chemical reactions Why do we care? -will a reaction
Energy, Heat and Chemical Change Chemistry 35 Fall 2000 Thermochemistry A part of Thermodynamics dealing with energy changes associated with physical and chemical reactions Why do we care? -will a reaction
Thermochemistry. Energy. 1st Law of Thermodynamics. Enthalpy / Calorimetry. Enthalpy of Formation
 Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy of motion:
Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy of motion:
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy
 I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
I. The Nature of Energy A. Energy is the ability to do work or produce heat. It exists in 2 forms: 1. Potential energy is energy due to the composition or position of an object. 2. Kinetic energy is energy
Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes involving heat.
 CHEM134- F18 Dr. Al- Qaisi Chapter 06: Thermodynamics Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes involving heat. Energy is anything that has the capacity
CHEM134- F18 Dr. Al- Qaisi Chapter 06: Thermodynamics Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical reactions and energy changes involving heat. Energy is anything that has the capacity
Thermochemistry. Energy. 1st Law of Thermodynamics. Enthalpy / Calorimetry. Enthalpy of Formation
 THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy
THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermochemistry Energy 1st Law of Thermodynamics Enthalpy / Calorimetry Hess' Law Enthalpy of Formation The Nature of Energy Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy Kinetic energy is the energy
Thermochemistry. Energy (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10. Energy. Energy
 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10 is defined as the ability to do work or produce
Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the science of the relationship between heat and other forms of energy. (and Thermochemistry) World of Chemistry Chapter 10 is defined as the ability to do work or produce
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Explain how energy, heat, and work are related. 2 Section 17.1 The Flow of Energy Heat and Work OBJECTIVES: Classify
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy Thermodynamics Study of the relationship between heat, work, and other forms of energy Thermochemistry A branch of thermodynamics Focuses on the study of heat given off
Chapter 6 Energy and Chemical Change. Brady and Senese 5th Edition
 Chapter 6 Energy and Chemical Change Brady and Senese 5th Edition Index 6.1 An object has energy if it is capable of doing work 6.2 Internal energy is the total energy of an object s molecules 6.3 Heat
Chapter 6 Energy and Chemical Change Brady and Senese 5th Edition Index 6.1 An object has energy if it is capable of doing work 6.2 Internal energy is the total energy of an object s molecules 6.3 Heat
Quantities in Chemical Reactions
 Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Quantities in Chemical Reactions 6-1 6.1 The Meaning of a Balanced Equation C 3 H 8(g) + 5 O 2(g) 3 CO 2(g) + 4 H 2 O (g) The balanced equation tells us: 1 molecule of propane reacts with 5 molecules of
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry. Molecular Kinetic Energy -Translational energy E k, translational = 1/2mv 2 -Rotational energy 5.
 Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 1. Thermodynamics 2. Energy 3. Specific Heat 4. Enthalpy 5. Enthalpies of Reactions 6. Hess s Law 7. State Functions 8. Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9. Determining Enthalpies
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 1. Thermodynamics 2. Energy 3. Specific Heat 4. Enthalpy 5. Enthalpies of Reactions 6. Hess s Law 7. State Functions 8. Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9. Determining Enthalpies
THERMOCHEMISTRY & DEFINITIONS
 THERMOCHEMISTRY & DEFINITIONS Thermochemistry is the study of the study of relationships between chemistry and energy. All chemical changes and many physical changes involve exchange of energy with the
THERMOCHEMISTRY & DEFINITIONS Thermochemistry is the study of the study of relationships between chemistry and energy. All chemical changes and many physical changes involve exchange of energy with the
First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot be created or destroyed.
 1 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERS energy = anything that has the capacity to do work work = force acting over a distance Energy (E) = Work = Force x Distance First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot
1 CHEMICAL THERMODYNAMICS ANSWERS energy = anything that has the capacity to do work work = force acting over a distance Energy (E) = Work = Force x Distance First Law of Thermodynamics: energy cannot
I. Energy A. Terms and Definitions B. Energy Transfer as Heat C. Energy Transfer as Work D. Internal Energy
 Chapter 7 1 Thermochemistry is HOT! I. Energy A. Terms and Definitions B. Energy Transfer as Heat C. Energy Transfer as Work D. Internal Energy II. Chemistry and Energy A. Enthalpy and Enthalpies of Reaction
Chapter 7 1 Thermochemistry is HOT! I. Energy A. Terms and Definitions B. Energy Transfer as Heat C. Energy Transfer as Work D. Internal Energy II. Chemistry and Energy A. Enthalpy and Enthalpies of Reaction
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry
 Chapter 6: Thermochemistry Section 6.1: Introduction to Thermochemistry Thermochemistry refers to the study of heat flow or heat energy in a chemical reaction. In a study of Thermochemistry the chemical
Chapter 6: Thermochemistry Section 6.1: Introduction to Thermochemistry Thermochemistry refers to the study of heat flow or heat energy in a chemical reaction. In a study of Thermochemistry the chemical
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 1. Thermodynamics 2. Energy 3. Specific Heat 4. Enthalpy 5. Enthalpies of Reactions 6. Hess s Law 7. State Functions 8. Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9. Determining Enthalpies
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 1. Thermodynamics 2. Energy 3. Specific Heat 4. Enthalpy 5. Enthalpies of Reactions 6. Hess s Law 7. State Functions 8. Standard Enthalpies of Formation 9. Determining Enthalpies
s Traditionally, we use the calorie as a unit of energy. The nutritional Calorie, Cal = 1000 cal. Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy
 AP Chemistry: Thermochemistry Lecture Outline 5.1 The Nature of Energy Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical
AP Chemistry: Thermochemistry Lecture Outline 5.1 The Nature of Energy Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry is the study of the relationships between chemical
Lecture Outline. 5.1 The Nature of Energy. Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy. 1 mv
 Chapter 5. Thermochemistry Common Student Misconceptions Students confuse power and energy. Students confuse heat with temperature. Students fail to note that the first law of thermodynamics is the law
Chapter 5. Thermochemistry Common Student Misconceptions Students confuse power and energy. Students confuse heat with temperature. Students fail to note that the first law of thermodynamics is the law
Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry Study of energy changes that accompany chemical rx s. I) Nature of Energy Energy / Capacity to do work Mechanical Work w = F x d Heat energy - energy used to cause the temperature
Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry Study of energy changes that accompany chemical rx s. I) Nature of Energy Energy / Capacity to do work Mechanical Work w = F x d Heat energy - energy used to cause the temperature
Ch 6. Energy and Chemical Change. Brady & Senese, 5th Ed.
 Ch 6. Energy and Chemical Change Brady & Senese, 5th Ed. Energy Is The Ability To Do Work Energy is the ability to do work (move mass over a distance) or transfer heat Types: kinetic and potential kinetic:
Ch 6. Energy and Chemical Change Brady & Senese, 5th Ed. Energy Is The Ability To Do Work Energy is the ability to do work (move mass over a distance) or transfer heat Types: kinetic and potential kinetic:
Heat. Heat Terminology 04/12/2017. System Definitions. System Definitions
 System Definitions Heat Physical Science 20 Ms. Hayduk Heat Terminology System: the part of the universe being studied (big Earth, or small one atom) Surroundings: the part of the universe outside the
System Definitions Heat Physical Science 20 Ms. Hayduk Heat Terminology System: the part of the universe being studied (big Earth, or small one atom) Surroundings: the part of the universe outside the
Introduction to Thermochemistry. Thermochemistry Unit. Definition. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology 07/04/2016. Chemistry 30
 Thermochemistry Unit Introduction to Thermochemistry Chemistry 30 Definition Thermochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the heat produced and used in chemical reactions. Most of thermochemistry
Thermochemistry Unit Introduction to Thermochemistry Chemistry 30 Definition Thermochemistry is the branch of chemistry concerned with the heat produced and used in chemical reactions. Most of thermochemistry
Thermochemistry-Part 1
 Brad Collins Thermochemistry-Part 1 Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics: The study of energy Thermochemistry: The study of energy in chemical reactions Energy: The capacity to do work Work = force
Brad Collins Thermochemistry-Part 1 Chapter 7 Thermochemistry Thermodynamics: The study of energy Thermochemistry: The study of energy in chemical reactions Energy: The capacity to do work Work = force
Energy and Chemical Change
 Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy Section 15.2 Heat Section 15.3 Thermochemical Equations Section 15.4 Calculating Enthalpy Change Section 15.5 Reaction Spontaneity Click a hyperlink or folder
Energy and Chemical Change Section 15.1 Energy Section 15.2 Heat Section 15.3 Thermochemical Equations Section 15.4 Calculating Enthalpy Change Section 15.5 Reaction Spontaneity Click a hyperlink or folder
Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chemical Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is a Greek term which means, heat power. Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. 2 Thermodynamics Thermochemistry how we observe,
Chemical Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is a Greek term which means, heat power. Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. 2 Thermodynamics Thermochemistry how we observe,
Chapter 6 Problems: 9, 19, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31-33, 37, 39, 43, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 57, 59, 65, 67, 73, 78-82, 85, 89, 93
 Chapter 6 Problems: 9, 19, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31-33, 37, 39, 43, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 57, 59, 65, 67, 73, 78-82, 85, 89, 93 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry The study of chemical reactions and the energy changes
Chapter 6 Problems: 9, 19, 24, 25, 26, 27, 31-33, 37, 39, 43, 45, 47, 48, 53, 55, 57, 59, 65, 67, 73, 78-82, 85, 89, 93 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry The study of chemical reactions and the energy changes
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry
 William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley http://academic.cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Edward J. Neth University of Connecticut Outline 1. Principles of heat flow 2. Measurement
William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley http://academic.cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 8 Thermochemistry Edward J. Neth University of Connecticut Outline 1. Principles of heat flow 2. Measurement
Don't forget to. Mastering Chemistry everyday! October 9 th, Next week in Lab: Next week in disc: 10/9/2014.
 Solutions of nitric acid, sodium bicarbonate, silver nitrate and iron (III) acetate are mixed. Write all NIE s. There are 4! H + (aq) + HCO 2 3 (aq) H 2 O(l) + CO 2 () (g) H + (aq) + C 2 H 3 O 2 (aq) HC
Solutions of nitric acid, sodium bicarbonate, silver nitrate and iron (III) acetate are mixed. Write all NIE s. There are 4! H + (aq) + HCO 2 3 (aq) H 2 O(l) + CO 2 () (g) H + (aq) + C 2 H 3 O 2 (aq) HC
Study Guide Chapter 5
 Directions: Answer the following 1. When writing a complete ionic equation, a. what types of substances should be shown as dissociated/ionized? soluble ionic compounds, acids, bases b. What types of substances
Directions: Answer the following 1. When writing a complete ionic equation, a. what types of substances should be shown as dissociated/ionized? soluble ionic compounds, acids, bases b. What types of substances
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 5. Thermochemistry. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 5 Thermochemistry John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry
Lecture Presentation Chapter 5 Thermochemistry John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Thermochemistry Thermodynamics is the study of energy and its transformations. Thermochemistry
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 5. Thermochemistry Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 5 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or transfer heat. Energy used to cause an object that has mass to move is called work. Energy used to cause the temperature of an
Lecture Presentation Chapter 5 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or transfer heat. Energy used to cause an object that has mass to move is called work. Energy used to cause the temperature of an
Gilbert Kirss Foster. Chapter 9. Thermochemistry. Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions
 Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 9 Thermochemistry Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Chapter Outline 9.1 Energy as a Reactant or Product 9.2 Transferring Heat and Doing Work 9.3 Enthalpy and Enthalpy Changes
Gilbert Kirss Foster Chapter 9 Thermochemistry Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Chapter Outline 9.1 Energy as a Reactant or Product 9.2 Transferring Heat and Doing Work 9.3 Enthalpy and Enthalpy Changes
Thermochemistry AP Chemistry Lecture Outline
 Thermochemistry AP Chemistry Lecture Outline Name: thermodynamics: the study of energy and its transformations -- thermochemistry: the subdiscipline involving chemical reactions and energy changes Energy
Thermochemistry AP Chemistry Lecture Outline Name: thermodynamics: the study of energy and its transformations -- thermochemistry: the subdiscipline involving chemical reactions and energy changes Energy
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is a part of Thermodynamics dealing with energy changes associated with physical and chemical reactions Why do we care? - Will a reaction proceed
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is a part of Thermodynamics dealing with energy changes associated with physical and chemical reactions Why do we care? - Will a reaction proceed
CHEM 103 CHEMISTRY I
 CHEM 103 CHEMISTRY I CHAPTER 5 THERMOCHEMISTRY Inst. Dr. Dilek IŞIK TAŞGIN Inter-Curricular Courses Department Çankaya University, Inc. Energy Energy is the ability to do work or transfer heat. Energy
CHEM 103 CHEMISTRY I CHAPTER 5 THERMOCHEMISTRY Inst. Dr. Dilek IŞIK TAŞGIN Inter-Curricular Courses Department Çankaya University, Inc. Energy Energy is the ability to do work or transfer heat. Energy
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 6. Thermochemistry. Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Chemical Hand Warmers Most hand warmers work by using the heat released from the slow oxidation of iron 4 Fe(s)
Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University Chemical Hand Warmers Most hand warmers work by using the heat released from the slow oxidation of iron 4 Fe(s)
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes
 Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Mr Chiasson Advanced Chemistry 12 / Chemistry 12 1 Unit B: Thermochemical Changes Students will be expected to: Compare the molar enthalpies of several combustion reactions involving organic compounds.
Thermochemistry 14.notebook. November 24, Thermochemistry. Energy the capacity to do work or produce heat. translational.
 Thermochemistry Energy the capacity to do work or produce heat POTENTIAL ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY (energy of motion) "stored" bond energy TEMPERATURE and HEAT vibrational rotational translational a measure
Thermochemistry Energy the capacity to do work or produce heat POTENTIAL ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY (energy of motion) "stored" bond energy TEMPERATURE and HEAT vibrational rotational translational a measure
47 people in recitation yesterday. Expect quizzes there and in class.
 Announcements 47 people in recitation yesterday. Expect quizzes there and in class. Chapter 6 Problems: 6.9, 6.11, 6.13(except c), 6.19, 6.23, 6.34, 6.38, 6.42, 6.51, 6.53, 6.54, 6.57, 6.64, 6.66, 6.69,
Announcements 47 people in recitation yesterday. Expect quizzes there and in class. Chapter 6 Problems: 6.9, 6.11, 6.13(except c), 6.19, 6.23, 6.34, 6.38, 6.42, 6.51, 6.53, 6.54, 6.57, 6.64, 6.66, 6.69,
Calculate the mass of L of oxygen gas at 25.0 C and 1.18 atm pressure.
 148 Calculate the mass of 22650 L of oxygen gas at 25.0 C and 1.18 atm pressure. 1 - Convert the volume of oxygen gas to moles using IDEAL GAS EQUATION 2 - Convert moles oxygen gas to mass using formula
148 Calculate the mass of 22650 L of oxygen gas at 25.0 C and 1.18 atm pressure. 1 - Convert the volume of oxygen gas to moles using IDEAL GAS EQUATION 2 - Convert moles oxygen gas to mass using formula
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry
 Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Ch. 17 Thermochemistry 17.1 The Flow of Energy Energy Transformations Thermochemistry: study of energy changes in chemical reactions and changes in state Chemical potential energy: energy stored in bonds
Measuring Energy Changes. Introducing Heat Capacity and Specific Heat
 Measuring Energy Changes Introducing Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Before Today s Discussion Begins Remember the differences between temperature, thermal energy, and heat Temperature is the average kinetic
Measuring Energy Changes Introducing Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Before Today s Discussion Begins Remember the differences between temperature, thermal energy, and heat Temperature is the average kinetic
Thermodynamics - Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions:
 Thermodynamics - Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions: energy - The capacity to do work. Types of Energy: radiant-energy from the sun. potential-energy due to an objects position. chemical-energy
Thermodynamics - Energy Relationships in Chemical Reactions: energy - The capacity to do work. Types of Energy: radiant-energy from the sun. potential-energy due to an objects position. chemical-energy
Thermodynamics. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Thermodynamics Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Thermodynamics is the scientific study of the interconversion of heat and other kinds of energy.
Thermodynamics Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Thermodynamics is the scientific study of the interconversion of heat and other kinds of energy.
Thermochemistry. Using Heats of Reaction - Hess s Law - Standard Enthalpies of Formation - Fuels Foods, Commercial Fuels, and Rocket Fuels
 Thermochemistry Understanding Heats of Reaction - Energy and Its Units - Heat of Reaction - Enthalpy and Enthalpy Change - Thermochemical Equations - Applying Stoichiometry to Heats of Reaction - Measuring
Thermochemistry Understanding Heats of Reaction - Energy and Its Units - Heat of Reaction - Enthalpy and Enthalpy Change - Thermochemical Equations - Applying Stoichiometry to Heats of Reaction - Measuring
AP* Chemistry THERMOCHEMISTRY
 AP* Chemistry THERMOCHEMISTRY Terms for you to learn that will make this unit understandable: Energy (E) the ability to do work or produce heat ; the sum of all potential and kinetic energy in a system
AP* Chemistry THERMOCHEMISTRY Terms for you to learn that will make this unit understandable: Energy (E) the ability to do work or produce heat ; the sum of all potential and kinetic energy in a system
Chapter 5 Principles of Chemical Reactivity: Energy and Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 5 Principles of Chemical Reactivity: Energy and Chemical Reactions Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Energy & Chemistry Questions that need to be addressed: How do we measure
Chapter 5 Principles of Chemical Reactivity: Energy and Chemical Reactions Jeffrey Mack California State University, Sacramento Energy & Chemistry Questions that need to be addressed: How do we measure
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions
 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions Outline thermodynamics internal energy definition, first law enthalpy definition, energy diagrams, calorimetry, theoretical calculation (heats of formation
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions Outline thermodynamics internal energy definition, first law enthalpy definition, energy diagrams, calorimetry, theoretical calculation (heats of formation
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy. Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy Chapter 8 1 Chemical Thermodynamics Chemical Thermodynamics is the study of the energetics of a chemical reaction. Thermodynamics deals with the absorption or
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy Chapter 8 1 Chemical Thermodynamics Chemical Thermodynamics is the study of the energetics of a chemical reaction. Thermodynamics deals with the absorption or
Chapter 6. Thermochemistry
 Chapter 6. Thermochemistry 1 1. Terms to Know: thermodynamics thermochemistry energy kinetic energy potential energy heat heat vs. temperature work work of expanding gases work of expanding gases under
Chapter 6. Thermochemistry 1 1. Terms to Know: thermodynamics thermochemistry energy kinetic energy potential energy heat heat vs. temperature work work of expanding gases work of expanding gases under
Energy Transformations
 Thermochemistry Energy Transformations Thermochemistry - concerned with heat changes that occur during chemical reactions Energy - capacity for doing work or supplying heat weightless, odorless, tasteless
Thermochemistry Energy Transformations Thermochemistry - concerned with heat changes that occur during chemical reactions Energy - capacity for doing work or supplying heat weightless, odorless, tasteless
Most hand warmers work by using the heat released from the slow oxidation of iron: The amount your hand temperature rises depends on several factors:
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Chemical Hand Warmers Most hand warmers work by using the heat released from the slow oxidation of iron: Exothermic reaction 4 Fe(s) + 3 O 2 (g) 2 Fe 2 O
Lecture Presentation Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Chemical Hand Warmers Most hand warmers work by using the heat released from the slow oxidation of iron: Exothermic reaction 4 Fe(s) + 3 O 2 (g) 2 Fe 2 O
Topic 5: Energetics. Heat & Calorimetry. Thursday, March 22, 2012
 Topic 5: Energetics Heat & Calorimetry 1 Heat is energy that is transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a body
Topic 5: Energetics Heat & Calorimetry 1 Heat is energy that is transferred from one object to another due to a difference in temperature Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a body
Major Concepts Calorimetry (from last time)
 Major Concepts Calorimetry (from last time) Heat capacity Molar heat capacity (per mole) Specific heat capacity (per mass) Standard state enthalpies: Hº Physical Changes Chemical Changes Hess's Law Balancing
Major Concepts Calorimetry (from last time) Heat capacity Molar heat capacity (per mole) Specific heat capacity (per mass) Standard state enthalpies: Hº Physical Changes Chemical Changes Hess's Law Balancing
Brown, LeMay Ch 5 AP Chemistry Monta Vista High School
 Brown, LeMay Ch 5 AP Chemistry Monta Vista High School 1 From Greek therme (heat); study of energy changes in chemical reactions Energy: capacity do work or transfer heat Joules (J), kilo joules (kj) or
Brown, LeMay Ch 5 AP Chemistry Monta Vista High School 1 From Greek therme (heat); study of energy changes in chemical reactions Energy: capacity do work or transfer heat Joules (J), kilo joules (kj) or
Energy and Chemical Change
 Energy and Chemical Change Section 16.1 Energy In your textbook, read about the nature of energy. In the space at the left, write true if the statement is true; if the statement is false, change the italicized
Energy and Chemical Change Section 16.1 Energy In your textbook, read about the nature of energy. In the space at the left, write true if the statement is true; if the statement is false, change the italicized
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry
 Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy -Very much a chemistry topic Every chemical change has an accompanying change of. Combustion of fossil fuels The discharging a battery Metabolism of foods If we are to
Chapter 5 Thermochemistry Energy -Very much a chemistry topic Every chemical change has an accompanying change of. Combustion of fossil fuels The discharging a battery Metabolism of foods If we are to
Calorimetry: Heat of Solution
 Calorimetry: Heat of Solution When a substance undergoes a change in temperature, the quantity of heat lost or gained can be calculated using the following relationship: (heat) = m s T (1) The specific
Calorimetry: Heat of Solution When a substance undergoes a change in temperature, the quantity of heat lost or gained can be calculated using the following relationship: (heat) = m s T (1) The specific
Ch. 14 Notes ENERGY AND CHEMICAL CHANGE NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics.
 Ch. 14 Notes ENERGY AND CHEMICAL CHANGE NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. I. Energy the capacity to do work or produce heat A. two basic types of
Ch. 14 Notes ENERGY AND CHEMICAL CHANGE NOTE: Vocabulary terms are in boldface and underlined. Supporting details are in italics. I. Energy the capacity to do work or produce heat A. two basic types of
Chapter 3. Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change. 5.1 Forms of Energy and Their Interconversion
 Chapter 3 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change 5.1 Forms of Energy and Their Interconversion 5.2 Enthalpy: Chemical Change at Constant Pressure 5.3 Calorimetry: Measuring the Heat of a Chemical
Chapter 3 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Change 5.1 Forms of Energy and Their Interconversion 5.2 Enthalpy: Chemical Change at Constant Pressure 5.3 Calorimetry: Measuring the Heat of a Chemical
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical reactions and phase changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall. Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes. Calorimetry
 Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes A burning match releases heat to its surroundings in all directions. How much heat does this exothermic reaction release? You will learn to measure heat flow in
Measuring and Expressing Enthalpy Changes A burning match releases heat to its surroundings in all directions. How much heat does this exothermic reaction release? You will learn to measure heat flow in
Thermochemistry. Questions to ponder. Because 4/20/14. an ice-cube? an ice-cube? Part 2: Calorimetry. But I KNOW. Q=mc T, but T=0
 Thermochemistry Part 2: Calorimetry p p If you leave your keys and your chemistry book sitting in the sun on a hot summer day, which one is hotter? Why is there a difference in temperature between the
Thermochemistry Part 2: Calorimetry p p If you leave your keys and your chemistry book sitting in the sun on a hot summer day, which one is hotter? Why is there a difference in temperature between the
Energy Ability to produce change or do work. First Law of Thermodynamics. Heat (q) Quantity of thermal energy
 THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics Study of energy and its interconversions Energy is TRANSFORMED in a chemical reaction (POTENTIAL to KINETIC) HEAT (energy transfer) is also usually produced or absorbed -SYSTEM:
THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics Study of energy and its interconversions Energy is TRANSFORMED in a chemical reaction (POTENTIAL to KINETIC) HEAT (energy transfer) is also usually produced or absorbed -SYSTEM:
CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry
 CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. Chemical Change: new substances created during chemical reaction
CHAPTER 17 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry The study of the heat changes that occur during chemical reactions and physical changes of state. Chemical Change: new substances created during chemical reaction
11B, 11E Temperature and heat are related but not identical.
 Thermochemistry Key Terms thermochemistry heat thermochemical equation calorimeter specific heat molar enthalpy of formation temperature enthalpy change enthalpy of combustion joule enthalpy of reaction
Thermochemistry Key Terms thermochemistry heat thermochemical equation calorimeter specific heat molar enthalpy of formation temperature enthalpy change enthalpy of combustion joule enthalpy of reaction
General Chemistry I. Dr. PHAN TẠI HUÂN Faculty of Food Science and Technology Nong Lam University. Module 4: Chemical Thermodynamics
 General Chemistry I Dr. PHAN TẠI HUÂN Faculty of Food Science and Technology Nong Lam University Module 4: Chemical Thermodynamics Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics. First Law of Thermodynamics (state quantities:
General Chemistry I Dr. PHAN TẠI HUÂN Faculty of Food Science and Technology Nong Lam University Module 4: Chemical Thermodynamics Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics. First Law of Thermodynamics (state quantities:
The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability to do work or produce Heat, q or Q, is ; flows due to temperature differences (always to )
 CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
CP Chapter 17 Thermochemistry 2014-2015 Thermochemistry Thermochemistry is the study of energy that occur during chemical and physical changes (changes of state) The Nature of Energy Energy is the ability
Chemistry 101 Chapter 10 Energy
 Chemistry 101 Chapter 10 Energy Energy: the ability to do work or produce heat. Kinetic energy (KE): is the energy of motion. Any object that is moving has kinetic energy. Several forms of kinetic energy
Chemistry 101 Chapter 10 Energy Energy: the ability to do work or produce heat. Kinetic energy (KE): is the energy of motion. Any object that is moving has kinetic energy. Several forms of kinetic energy
Enthalpy and Internal Energy
 Enthalpy and Internal Energy H or ΔH is used to symbolize enthalpy. The mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics is: ΔE = q + w, where ΔE is the change in internal energy, q is heat and
Enthalpy and Internal Energy H or ΔH is used to symbolize enthalpy. The mathematical expression of the First Law of Thermodynamics is: ΔE = q + w, where ΔE is the change in internal energy, q is heat and
Chapter 6. Thermochemistry. Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Thermochemistry. Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Matter vs Energy 2/16/2016
 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Chapter 6 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 6.1 Chemical Hand Warmers 6.2 The Nature of Energy: Key Definitions 6.3 The First Law of Thermodynamics: There is no Free Lunch 6.4 6.5 Measuring
Chapter 6 Thermochemistry Chapter 6 Chapter 6 Thermochemistry 6.1 Chemical Hand Warmers 6.2 The Nature of Energy: Key Definitions 6.3 The First Law of Thermodynamics: There is no Free Lunch 6.4 6.5 Measuring
Energy Ability to produce change or do work. First Law of Thermodynamics. Heat (q) Quantity of thermal energy
 THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics Study of energy and its interconversions Energy is TRANSFORMED in a chemical reaction (POTENTIAL to KINETIC) HEAT (energy transfer) is also usually produced or absorbed -SYSTEM:
THERMOCHEMISTRY Thermodynamics Study of energy and its interconversions Energy is TRANSFORMED in a chemical reaction (POTENTIAL to KINETIC) HEAT (energy transfer) is also usually produced or absorbed -SYSTEM:
This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is being transferred from the room/flask/etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) to the reaction itself (the SYSTEM).
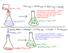 151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
151 This reaction is EXOTHERMIC. Energy is transferred from the reactants and products (the SYSTEM) to the water in the flask, the flask, etc. (the SURROUNDINGS) This reaction is ENDOTHERMIC. Energy is
THERMODYNAMICS 11/14/2018 THERMOCHEMISTRY OBJECT OF THE THERMODYNAMICS FUNDAMMENTAL ASPECT OF THERMODYNAMICS
 THERMODYNAMICS Thermochemistry In thermodynamics we study the energy changes that accompany physical and chemical processes. Usually these energy changes involve heat hence the thermo- part of the term.
THERMODYNAMICS Thermochemistry In thermodynamics we study the energy changes that accompany physical and chemical processes. Usually these energy changes involve heat hence the thermo- part of the term.
Energy. Different types of energy exist (heat, potential, kinetic, chemical, nuclear etc.)
 Change in Energy Energy Different types of energy exist (heat, potential, kinetic, chemical, nuclear etc.) Heat - the energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures. Unit of heat
Change in Energy Energy Different types of energy exist (heat, potential, kinetic, chemical, nuclear etc.) Heat - the energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures. Unit of heat
