A concept of sustainable development for regional land use planning: Lithuanian experience
|
|
|
- Toby Melton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ukio Technologinis ir Ekonominis Vystymas ISSN: (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: A concept of sustainable development for regional land use planning: Lithuanian experience Paulius Kavaliauskas To cite this article: Paulius Kavaliauskas (2008) A concept of sustainable development for regional land use planning: Lithuanian experience, Ukio Technologinis ir Ekonominis Vystymas, 14:1, To link to this article: Published online: 21 Oct Submit your article to this journal Article views: 833 View related articles Citing articles: 17 View citing articles Full Terms & Conditions of access and use can be found at Download by: [ ] Date: 29 November 2017, At: 03:30
2 TECHNOLOGICAL AND ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT OF ECONOMY Baltic Journal on Sustainability (1): A CONCEPT OF SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT FOR REGIONAL LAND USE PLANNING: LITHUANIAN EXPERIENCE Paulius Kavaliauskas Dept of Geography and Land Management, Faculty of Nature Sciences, Vilnius University, M. K. Èiurlionio g. 21, LT Vilnius, Lithuania paulius.kavaliauskas@gf.vu.lt Received 6 Nov 2007; accepted 5 March 2008 Abstract. A concept of sustainable development is a critical key for regional planning. The article deals with the methodology of sustainable land use system adopted in the documents of regional space planning in Lithuania. The structure of the concept includes determination of problem areas, formation of integrated spatial framework with localised functional priorities and regional regimes and organisation of spatial regional policy. The main spatial axes urban and nature frames, as well as recreation or conservation belts are the integrated components of sustainable spatial structure of a region. Regional policy making could be organised by constructive, conservative and temperate scenarios, what is the prerogative of regional officials. Keywords: sustainable land use, town and country planning, regional policy, Lithuania. Reference to this paper should be made as follows: Kavaliauskas P. (2008) A concept of sustainable development for regional land use planning: Lithuanian experience, Technological and Economical Development of Technology, 14(1): Introduction Regional land use (or physical) planning is a constituent part of spatial organisation of human activities and environment management implemented by land use management and spatial planning methods. It is designed as a means of coordination of social, economic and ecological interests and creation of harmonious cultural landscape (Kavaliauskas 1992). The spatial physical (or territorial) planning as described in the Law of Territorial Planning of the RL (Lietuvos, 2004) is an instituted procedure of territorial development designed to facilitate the elaboration of the general spatial concept and land use priorities, determination of environment and monument protection conditions, formation of a system of residential, productive and infrastructural areas, regulation of employment of the population, and reservation of ISSN print / ISSN online 51
3 52 P. Kavaliauskas. A concept of sustainable development for regional land use planning... the territories for expansion of activity of private and legal entities. Comprehensive land use planning is regarded as its main constituent. It means an integral planning for determining a policy of spatial development of a territory, priorities of territory use, protection and basic principles of management. Unfortunately, traditional priority of sectorial (branch) approach, even in national and regional planning, is one of the main demerits in realising this idea. Sometimes integral approach is only a declared principle, but not a systemic one. Even one of the most developed planning system in Great Britain (Baker 1998; Hall 2002; Neill 2003; Bishop and Phillips 2004; Cullingworth and Nadin 2006) could be recognised unsatisfactory in real spatial integrity, especially in land use strategy. The second significant warp in space planning could be the predomination of its strategic or demographical, social and economical directions and insufficient development land use or physical planning, especially on regional and national levels (Alexander 1992; Österreichisches ; Ministry of State 1994; Allmendinger 2001; Faludi 2002; Zonneveld 2005; Larice and Mcdonald 2006). The German planning system makes an exception: the autonomous land use planning is named officially as landscape planning, but on the highest levels it is also convertible to administrative strategic programming (Kiemstedt 1993). All these prerequisites provide a necessity to surmount the strategic sector and to strengthen the integral land use (territorial) approach, especially on national and regional levels of state planning. A document of land use planning is a result of comprehensive analysis and synthesis. It determines a spatial development concept of the planned territory and principles of use and protection of a territory taking into account the levels and tasks of territorial planning. A document on complex planning of a state or county territory, which defines a spatial development concept for the planned territory and principles of use and protection of a territory taking into account the levels and tasks of territorial planning, is called a master or general plan. The basic tasks of the comprehensive physical planning are as follows: 1) to form a concept of management, use and protection of a territory; 2) to optimise the urban structure and infrastructural system of a territory; 3) to provide measures and restrictions ensuring a rational use of natural resources, ecological equilibrium of a landscape, formation of natural frame, and preservation of natural and cultural heritage; 4) to envisage means for improving the urban spatial composition of territories under buildings and living and environment quality and formation of a system of green areas for public use; 5) to define main formation principles of regional policy and implementation; 6) to reserve territories for developing the objects necessary for communication corridors, engineering and service infrastructure and other public needs. Adaptation of the concept of sustainable (sparing and balanced) development for the level of regional planning is one of the basic methodological tasks of physical planning. Today, the conditions for solving this task in Lithuania are favourable. Approval of the new National Comprehensive Plan of the Republic of Lithuania (Ministry 2002), Lithuanian Strategy
4 Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 2008, 14(1): for Sustainable Development (Ministry 2003), the new Law of Territorial Planning (Lietuvos 2004) and principles of their implementation have activated territorial planning works (on a regional level in particular). The present article introduces the generalised methodological experience of regional planning carried out in , which could be useful to planners in other countries. Most similar attempts in the sphere of strengthening the land use approach and its autonomy were made in the Finland s space planning system (Bell and Komulainen 2001; Miettinen 2002; Finland s 2005). 2. The essence of the concept of regional master plan According to the Law of Territorial Planning of the Republic of Lithuania the planning process includes the following phases: preliminary work, preparation of a document on territorial planning, assessment of solutions and the final stage. The concept is worked out in the second (preparation of a document) phase, which includes the following stages: 1) examination of the actual state of a territory based on investigation of its natural, social, cultural, and economic status, assessment of its perspective and quality potential and analysis of development trends and problematic situations and areas; 2) elaboration of the concept: determining the general spatial development concept of a territory, its functional priorities and specific features of territorial management regulation; 3) concretisation of solutions on the issues of formation of urban and natural frame, preservation of landscape, biological diversity and cultural heritage, use and management of bioproduction farms and recreational, industrial, trade and other territories, as well as territorial development and reservation of territories for social, cultural, communication and other infrastructures. The rules of developing the master regional territorial plan (Apskrities 2004) obliges that detailed task complexes and solutions shall be specified based on assessing of plans and strategies worked out for a territory, system of strategic territorial development tasks formulated in the National Territorial (Spatial) Development Plan adopted by Seimas (Parliament) of the Republic of Lithuania as well as the actual status and development trends of a territory. The specified tasks and solutions must: 1) define the general spatial concept of land use development adopted in the document of national comprehensive spatial planning and localise in detail the territories; 2) define the functional priorities of land use and revise and itemise the complexes of functional priorities provided for in the document of national comprehensive spatial planning specifying them according to the implementation feasibility; 3) define principles of territorial management, regulation, use and protection itemising them on municipality level; 4) itemise the ways and mechanisms of spatial regional policy organisation in the territory of a planned county. The practical experience of developing the comprehensive plans enabled forming the below structure of the concept elaboration stage: 1. The background and tasks of territorial development The place of the region in the national and external system of relations.
5 54 P. Kavaliauskas. A concept of sustainable development for regional land use planning Problematic situations and areas of territorial management. 2. General spatial concept Localisation of urban economic activity axes Localisation of the principal axes of ecological stabilisation Types of territorial development. 3. Differentiation of land use development Functional priorities of land use Specific features of regulation of land use and protection. 4. Organisation of spatial regional policy Formation of the principles of regional policy General priorities of organisation. Below are introduced the most methodologically uncertain issues of physical regional planning whose solutions must be based on the ideology of sustainable land use development. 3. Setting the problem areas The problem areas were introduced into the land use planning practice with the Complex Scheme of Nature Protection of Lithuania (Kavaliauskas and Rilys 1995). Today it is a mandatory element of the documents of territorial planning completing the first stage of their preparation (examination of the actual state of a territory). The projecting experience of the company UAB Urbanistika showed an expedience of returning to this issue in the stage of elaboration of the concept, making it a point of departure in formulating solutions. This offers a possibility of reviewing the previously distinguished problematic situations (understood as entrenchment of unfavourable signs of social, economic or ecological development or contraposition of legal status and different interests in a territory) and problematic areas (understood as wide zones combining assemblages of problematic situations or conflict territories), itemising them and reconciling in the context of conceptual planning. A few groups of problematic situations are advisable in regional planning. They are related to: 1) populated localities, 2) environmental quality preservation, 3) territorial nature protection, 4) demographic and social environment, 5) economic environment, 6) communication system, and 7) land use. Each group should have at least 3 assessment indices. The gravity of the problematic situation is indicated by relative numbers from 1 to 3. The categories of relatively low (<15), medium (1,5 2,0) and high (>2,0) gravity problematic situations are distinguished. There are 3 trends in distinguishing problematic areas: 1) determining relative (compared with the average value over the country) problems of formal territorial units (municipalities, counties) according to a set of social-economic indices and distinguishing the so-called depressive regions, 2) determining relative problems of formal territorial units (municipalities and the smallest territorial administrative units communes) according to a set of demographic social, economic, environmental, and urban infrastructural indices, 3) distinguishing special unformalised land management problematic areas and localities. The recognised land management problematic areas and localities in the mainland part of Lithuania are:
6 Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 2008, 14(1): a) the main lakes and valleys where conflicting situations are implicated by recreational interests, economic activity and realisation of actual or requisite status of preserved territories; b) the preserved large forest tracts where conflict situations are implicated by an interest to preserve natural and cultural heritage and realisation of regulations for preserved territories; c) hilly agrarian low forestation areas where conflict situations are implicated by interests of bioproduction economy, soil protection from erosion and realisation of nature frame; d) urban localities marked in the comprehensive plan as possible new centres of municipalities. Practical experience of regional planning in Lithuania and other countries shows a great variety of possible solutions, diversity of natural cultural and social economic environments of different regions and inconsistency of territorial development. Failure in finding problem solutions makes the sustainable development of a territory an impossible task. 4. Sustainable development and the general spatial concept Principles of regional spatial concept must be based on the ideology of sustainable development adopted in the European Union (Baker 2005). Such a development is understood as a compromise between environmental, economic and social objectives. It stands for a better quality of life for everyone, now and for generations to come within the limits of permissible environmental impacts (Pike et al. 2006). Unfortunately, the idea of sustainable development (Hales 2000; Owens and Cowell 2002; Williams et al. 2004; Wheeler and Beatley 2004; Baker 2005; Пузаченко 2006), in spite of its pervasive popularity in all EU countries, often remains a summary of trivial well-wishing objectives with some desirable quantitative indices (CEC 2003) of natural, economic and social environment quality. Spatial physical planning of regions based on sustainable development must ensure a rational use of territories, ie an effective social economic development must go together with maximal preservation of natural resources and landscape. The basic components of spatial composition of a territory in this context are: 1) urban framework as a territorial system of centres and axes of active economic and cultural development with most strongly transformed natural environment and highly developed complexes of technical engineering infrastructure; 2) nature frame as an integrated network of natural ecological compensation territories ensuring ecological equilibrium of landscape, natural links between preserved territories and other environmentally important areas or habitats, and wild life migration (Kavaliauskas 1995). The main goal of the regional landscape management is to ensure a healthy environment, protect landscape stability and biological diversity and optimise the natural resources use. The protected natural areas and other areas important from the ecological point of view create the nature frame as an ecological compensation network. Lithuanian concept of nature frame (Kavaliauskas 1995; 2007) has some significant differences from pan-european concept of
7 56 P. Kavaliauskas. A concept of sustainable development for regional land use planning... ecological networks or American greenways (Jongman and Pungetti 2004) and presents a more integral spatial structure without confining strictly the interests of biological protection. The nature frame really enables us to regulate the urban and industrial development. The main statements of the development of the nature frame are: a nature frame is localised in physical planning documents as a spatial system of landscape ecological stabilisation; nature frame in the regional master plan consists of: geo-ecological watersheds, internal stabilisation areas of geosystems and migration corridors; landscape management in the nature frame embraces: 1) territories where the existing natural landscape is maintained and protected (mostly areas covered by forests), 2) territories in which areas of natural landscape need to be expanded (areas covered by forests and agricultural lands or by forests with a damaged natural potential) and 3) territories in which natural elements of landscape need to be returned or restored (areas covered by intensive agricultural lands or other lands changed by human activities); main factors influencing the localisation of nature frame are as follows: compensation importance of the nature frame areas on national or regional levels, status of natural compensation potential, existence of protected areas, richness of biodiversity, intensity of recreation. Functional structures of the territories of bioproductive economy, recreational use and conservation serve as background (continuous) formations developing the regional comprehensive spatial concept (Fig. 1). All these components are included into the plan after a preliminary assessment of a region position in the system of internal and extern links. The national context of a region is predetermined firstly by its location in the national functional backbone, ie zone of activity of social, economic and urban functions surrounding the main axes of urban integration. It is also expedient to assess the region location in the system of macroregions (NUTS-2) and ethnocultural territories of the country (Lietuvos 2004). The level of urban economic integration of a region is reflected by its proximity to the directions of international and national transport main roads, axes of internal integration of the region, and presence in it of perspective regional and local centres. Determining these centres is one of the main tasks of regional planning and spatial interactions between region centre and municipality centres are accented in case of determining the basic self-regional urban framework. The level of regional integration of other character is reflected by recreational potential and main elements of ecological integration: geoecological divides and migration corridors of nature frame of international, national and regional importance. Still differentiation and localisation of the types of territorial development are the principal tasks when forming the concept of sustainable regional development. The following nomenclature of the types of development of regional land use is recommended: 1. Urban development; regional centre and its immediate surroundings; perspective development areas in the first place. 2. Sparing urban development; municipality centres and their immediate surroundings. 3. Intensification of the existing bioproductive use; plain areas without major ecological restrictions. 4. Sparing bioproductive use; eroded morainic and sandy hills and areas surrounding valleys requiring ecological restrictions.
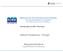
8 Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 2008, 14(1): Bioproductive conservational use and conversion; areas of the present biosphere polygons and other protected areas. 6. Development of conservational protection; territories of special conservation priority (usually nature or biosphere reserves). 7. Conservational recreational development and conversion; territories of the existing and perspective national and regional parks. 8. Recreational development and conversion; poorly used lakes and river valleys in agrarian landscapes. 9. Intensification of the present recreational use; existing resorts and recreational resort localities and their immediate surroundings. 10. Extraction development and conversion; present and perspective quarries and peat bogs. Fig. 1. Principal scheme of sustainable spatial structure of the region
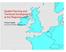
9 58 P. Kavaliauskas. A concept of sustainable development for regional land use planning... The first 3 types and the last 2 represent the zones of dominant intensive development strategy, whereas types 4 to 7 form the zone of dominant sparing (extensive) development and conversion. It is a territorial guarantee of integrated regional sustainable development and requires a special concern and strict environmental regulations. In the concept of master plan, the functional differentiation trends of regional territorial development are specified determining functional priorities and regional regulations. The Lithuanian experience showed that from the point of view of sustainable development it is expedient to distinguish the following general complexes of functional priorities of a region: 1. Institutionalised conservation and sparing forestry and farming economy. 2. Institutionalised conservation and various kinds of recreation and sparing forestry. 3. Legally established conservation, sparing forestry and various kinds of recreation. 4. Sparing forestry and farming, extensive recreation and legally established conservation. 5. Various kinds of forestry and farming, extensive recreation and fishery. 6. Intensive recreation, sparing forestry and farming and legally established conservation. 7. Dispersed urbanisation, various kinds of recreation and sparing forestry. 8. Agglomerated urbanisation and intensive recreation. 5. Problem of sustainable regional policy The ideology of sustainable development emphasises the governance of regional planning process, where the strategic and physical planning subsystems are coordinated and balanced. The solutions worked out in the documents of territorial planning must be recognised as one of the main factors for determining national regional policy. Rational concept of integrated regional policy implicates sustainable and balanced measures in social, economical and ecological policy, human space activity, and landscape and environmental maintenance. It is a result of planning efforts in the sphere of spatial integration of social, economic and ecological development, realised by strategic and especially by physical planning system. The special scheme given in Fig. 2 presents the proposed organisational model of sustainable regional policy. The projected landscape management models must be developed in all land use plans and as the basic result of the physical planning becomes a significant component in the integrated programme of regional policy. Herewith, the regional policy itself obtains the sense of spatially determinate regulation of social-economical-ecological land management trying for complex avail of the local peculiarities, conserving identity of regions and softening regional disproportions of development and life quality. As the main principles for developing and implementing the sustainable governance of land management, the functional complexity, regional conditionality, historical continuity, spatial polarisation, geo-systemic equilibrium, social expediency and economical reality (Kavaliauskas 1992) could be determined. Priorities of territorial development depend on many independent and qualitatively different factors and criteria 1 what determines multi-variant or alternative solutions. Priorities of 1 The impossibility theorem obtains regarding solution of multi-criteria tasks. It demonstrates that one optimal solution is impossible when there are 5 or more options to choose from. A few sub-optimal solutions are possible whose relative correctness assessment is a task of choice of values rather than objective reasoning or analysis.
10 Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 2008, 14(1): Fig. 2. The proposed model of the regional planning system
11 60 P. Kavaliauskas. A concept of sustainable development for regional land use planning... regional policy can be motivated by problems of a region or its parts, relative importance of territorial development sectors or perspective relevance of development of some basic elements of spatial structure or territorial differentiation. Therefore it is reasonable to distinguish sectorial and territorial priorities and their joint complexes in a region as possible scenarios or a regional policy. A relative preference may be classed to scenarios (even its temporal rotation is possible) during their consideration and coordination. The final choice is a prerogative of regional government. The following scenarios or regional policy formation are competitive from the point of view of sustainable development: A. Constructive scenario. Emphasis is placed on conversional and inovational trends of regional development which could activate the territorial development of a region and change the tradition of territorial use. Recreation and tourism, social infrastructure and land use development, and protection and rational use of natural and cultural values of landscape are recognised as priority sectors. Special emphasis is placed on structural development of the most problematic municipalities, formation of priority recreational territories, optimisation of use and protection of existing conserved territories, and formation of new local centres of urban framework. B. Conservative scenario. It includes maintenance of common tradition of territorially undifferentiated development when solutions are based on concrete local motivation. New sectoral priorities are not formed. Efforts are put to maintain all trends of territorial development paying an equal attention to all muinicipalities and giving priority to already existing trends of social-economic and urban development. Greater emphasis is placed on developing the bioproductive economy, the economic and technical infrastructure, accelerated development of the areas of intensive bioproductive use, and further consistent development of regional centre and social-economic potential. C. Moderate scenario. Efforts are directed at harmonisation of the trends of conversional and traditional development. Recreation and tourism, improvement of bioproductive economy and economic and technical infrastructure, and protection and rational use of natural and cultural values of regional landscape are recognised as priority sectors. Much attention is paid to formation of arterial corridors, protection of natural and cultural landscape, development of preserved territories (national parks in the first place), and development of sustainable bioproductive and recreational use in the main axes of nature frame. 6. Conclusions Based on the experience of physical planning of regional territories in Lithuania, the following principal conclusions about implementation of the concept of sustainable development in regional planning are drawn: 1. The concept of master plans of regions must include the following constituent parts: background and aims of development of the region; general spatial concept of the region; differentiation of regional land use development; development of spatial regional policy.
12 Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 2008, 14(1): The relevance of the problems of regional territorial development may be assessed taking into consideration the relative level of social economic ecological urban development (compared with the national or regional average values) of administrative territorial units and distinguishing special unformalised problematic areas and localities of land management. 3. The principle of sustainable development applied in physical planning of regions must ensure governance of rational use of territories and harmony between effective social economic development and maximal protection of natural resources and landscape. Urban and nature frames and continuous functional structures of bioproductive economy, recreational use and conservation of territories are in this context the main components of spatial structure of a territory. 4. Setting the spatial equilibrium between territories of urban (axes of activity) and nature (axes of ecological compensation) frames, defining the territorial strategies of intensifying, sustaining, conserving and conversion as well as zones with various complexes of functional priorities, especially with preference of conservation, recreation and sustainable agriculture or forestry are the main tasks of the concept of sustainable development for physical regional planning. 5. The strategic and land use planning sub-systems must be coordinated and balanced and solutions worked out in the documents of territorial planning must be recognised as one of the main factors for determining the state s regional policy. 6. Constructive, conservative and moderate scenarios of regional policy are competitive from the point of view of a sustainable development. The choice of any of them is a prerogative of regional government. References Alexander, E. R Approaches to planning: introduction current planning theories, concepts and issues. Gordon and Beach, Philadelphia. Allmendinger, P Planning theory. Palgrave Macmillan, Balsingstoke. Apskrities teritorijos bendrojo (generalinio) plano rengimo taisykles. 2004, Þinios Baker, M Planning for the English regions, Planning Practice and Research 13(2): Baker, S Sustainable Development. Routledge, Cardiff. Bell, S.; Komulainen, M. (eds) Cross-plan: integrated participatory planning as a tool for rural development. University of Oulu press, Aberdeen. Bishop, K.; Phillips, A Countryside planning: new approaches to management and conservation. Earthscan, London. CEC (Eurostat) Measuring program towards a more sustainable Europe. OOEPC, Luxembourg. Cullingworth, B.; Nadin, V Town and country planning in UK, Routledge. London. Faludi, A. (ed.) European spatial planning. Lincoln institute of land policy, Cambridge. Finland s Ministry of the environment Regional land use planning in Finland. Soprano communications, Helsinki. Hales, R Land use development planning and the notion of sustainable development: exploring constraint and facilitation within the English planning system, Journal of Environment Planning and Management 43(1):
13 62 P. Kavaliauskas. A concept of sustainable development for regional land use planning... Hall, P Urban and regional planning. Routledge, London. Jongman, R. H. B.; Pungetti, G Ecological networks and greenways. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. Kavaliauskas, P Methodological fundamentals of land management. Academia, Vilnius. Kavaliauskas, P The nature frame: Lithuanian experience, Landscape 95(3): Kavaliauskas, P A sustainable landscape planning system and landscape ecology, Ekologija 53(Suppl): 4 9. Kavaliauskas, P.; Rilys, N Lietuvos TSR kompleksinë gamtos apsaugos schema laikotarpiu iki 2000 metø. Þinija, Vilnius. Kiemstedt, H Landschaftsplanung: Inhalte und Verfahrensweisen, Service E. Böhm, Bonn. Larice, M.; Mcdonald, E. (eds.) The urban design reader. Routledge, New York. Lietuvos Respublikos teritorijø planavimo ástatymas. 2004, Þinios Ministry of Environment of the Republic of Lithuania Comprehensive Plan of the Territory of the Republic of Lithuania. Vilnius. Ministry of State for Environment of the Republic of Lithuania The Lithuanian Strategy for Sustainable Development. Vilnius. Ministry of State for Environment and Regional Development Regional strategy for Saxony, Dresden. Miettinen, A Finland s national land use guidelines. LUD, Helsinki. Neill, W Urban planning and culture identity. Routledge, London. Österreichisches Institut für Raumplannung Österreichisches Raumordnungskonzept, Wiener Verlag, Wien. Owens, S.; Cowell, R Land and limit interpreting sustainability in the planning process. Routledge, London. Pike, A.; Tomaney, J.; Rodrigues, A Local and Regional Development. Routledge, London. Wheeler, S. M.; Beatley, T. (eds) The sustainable urban development reader. Routledge, New York. Williams, K.; Burton, E.; Jenks, M Achieving sustainable urban forms. E&FN Spon, London. Zonneveld, W Expansive spatial planning: the new European transnational spatial visions, European Planning Studies 13(1): Пузаченко, Ю. Г Наука и концепция устойчивого развития, Ландшафтное планирование: общие основания, методология, технология. Москва: Изд-во МГУ, REGIONINIO TERITORIJØ PLANAVIMO TVARAUS VYSTYMO KONCEPCIJA: LIETUVOS PATIRTIS P. Kavaliauskas S a n t r a u k a Rengiant ðiuolaikinius regioninius teritorijø planus tvaraus vystymo koncepcija pamaþu ágauna esminës metodologinës nuostatos vaidmená. Pagrindinæ problemà sudaro visuotinai pripaþintø, taèiau gana prieðtaringø tvaraus (tausojanèio ir subalansuoto) vystymo tikslø realizavimas erdviniuose regionø planuose. Ypaè tvaraus vystymo idëjai taikyti trukdo nacionaliniu ir regioniniu lygmenimis iðlikæs tradicinio ðakinio (sektorinio), o ne integruoto sisteminio màstymo vyravimas bei daugelio ðaliø teritorijø
14 Technological and Economic Development of Economy, 2008, 14(1): planavimui didelæ reikðmæ daranti strateginio (vadybinio) planavimo metodologija. Lietuvoje, remiantis naujausiu teritorijø planavimo reglamentavimu, stengiamasi áveikti minëtus trûkumus ir sukurti savità regionø planavimo sistemà, turinèià panaðumø á egzistuojanèià Suomijoje. Pagrindinës planavimo nuostatos iðreiðkiamos regionø vystymo koncepcijoje, kurios metodologija apima probleminiø arealø iðaiðkinimà, bendrosios funkcinës erdvinës struktûros nustatymà, funkciniø prioritetø, regioniniø teritorijos tvarkymo reglamentø parengimà bei erdvinës regioninës politikos organizavimà. Kuriamos erdvinës struktûros tvarumà teritorijø harmoningos plëtros kontekste uþtikrina tinkamas svarbiausiø erdviniø aðiø urbanistinio ir gamtinio karkaso santykiø nustatymas, taip pat regionø bioprodukcinio, rekreacinio bei konservacinio vystymo strategijø subalansuotas lokalizavimas. Regioninë teritorijø planavimo politika formuojama pagal tris strateginius scenarijus: konstruktyvøjá, konservatyvøjá ir nuosaikøjá, kuriø elementø pasirinkimas yra regionø valdþios prioritetas. Reikðminiai þodþiai: tvari þemënauda, ðalies ir miestø planavimas, regioninë politika, Lietuva. Prof Paulius KAVALIAUSKAS. Head of Dept of Geography and Land Management at the Vilnius University (Lithuania). He was a scientific leader and executer of more than 60 projects on land use and strategic planning, a winner of National Environmental (1995) and Research (2004) awards. His major areas of interests: methodology of land use management, sustainable development and protected areas. Other interests include regional policy, landscape ecology and architecture, recreational and political geography.
Country Fiche Lithuania
 Country Fiche Lithuania Updated June 2018 1. General information The Lithuanian maritime space is delimited by the Decree of the Government of the Republic of Lithuania of 6 December, 2004, No. 1597 and
Country Fiche Lithuania Updated June 2018 1. General information The Lithuanian maritime space is delimited by the Decree of the Government of the Republic of Lithuania of 6 December, 2004, No. 1597 and
The Governance of Land Use
 The planning system Levels of government and their responsibilities The Governance of Land Use COUNTRY FACT SHEET NORWAY Norway is a unitary state with three levels of government; the national level, 19
The planning system Levels of government and their responsibilities The Governance of Land Use COUNTRY FACT SHEET NORWAY Norway is a unitary state with three levels of government; the national level, 19
Navigable maritime and river waterways in the seaside - Danube Delta area and the connected rural development
 SUMMARY OF Ph-D Thesis, with title RESEARCH STUDIES ON MANAGEMENT IMPROVEMENT OF MARITIME AND RIVER TRANSPORT ACTIVITY IN THE COASTAL AND DANUBE DELTA AREA FROM AN ENVIROMENTAL, ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL PERSPECTIVE
SUMMARY OF Ph-D Thesis, with title RESEARCH STUDIES ON MANAGEMENT IMPROVEMENT OF MARITIME AND RIVER TRANSPORT ACTIVITY IN THE COASTAL AND DANUBE DELTA AREA FROM AN ENVIROMENTAL, ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL PERSPECTIVE
PROTOCOL ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE ALPINE CONVENTION OF 1991 RELATING TO SPATIAL PLANNING AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
 PROTOCOL ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE ALPINE CONVENTION OF 1991 RELATING TO SPATIAL PLANNING AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT SPATIAL PLANNING AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT" PROTOCOL Preamble The Republic of
PROTOCOL ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE ALPINE CONVENTION OF 1991 RELATING TO SPATIAL PLANNING AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT SPATIAL PLANNING AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT" PROTOCOL Preamble The Republic of
The National Spatial Strategy
 Purpose of this Consultation Paper This paper seeks the views of a wide range of bodies, interests and members of the public on the issues which the National Spatial Strategy should address. These views
Purpose of this Consultation Paper This paper seeks the views of a wide range of bodies, interests and members of the public on the issues which the National Spatial Strategy should address. These views
Legal problems of environmental management. Spatial planning and space management. M. Gajewski 2014 / 2015
 Legal problems of environmental management Spatial planning and space management M. Gajewski 2014 / 2015 Course contents (in brief) Constitutional basis of the environment protection system. General principles
Legal problems of environmental management Spatial planning and space management M. Gajewski 2014 / 2015 Course contents (in brief) Constitutional basis of the environment protection system. General principles
Natura 2000 and spatial planning. Executive summary
 Natura 2000 and spatial planning Executive summary DISCLAIMER The information and views set out in this study are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official opinion of the Commission.
Natura 2000 and spatial planning Executive summary DISCLAIMER The information and views set out in this study are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official opinion of the Commission.
Spatial planning policies and conceptions on the European level influences on national spatial planning systems
 Karina M. Pallagst Spatial planning policies and conceptions on the European level influences on national spatial planning systems Despite of its informal character, spatial planning on the European level
Karina M. Pallagst Spatial planning policies and conceptions on the European level influences on national spatial planning systems Despite of its informal character, spatial planning on the European level
Spatial Planning in the Republic of Armenia
 Spatial Planning in the Republic of Armenia According to the Law of the Republic of Armenia on Urban Development, the main issues of the Republic s spatial development and actions for their solution are
Spatial Planning in the Republic of Armenia According to the Law of the Republic of Armenia on Urban Development, the main issues of the Republic s spatial development and actions for their solution are
Local Development Pilot Project: Island of Cres. Ranka Saračević Würth, Ministry of Culture, Republic of Croatia
 Local Development Pilot Project: Island of Cres Ranka Saračević Würth, Ministry of Culture, Republic of Croatia BACKGROUND, RATIFICATION OF THE FARO CONVENTION BY REPUBLIC OF CROATIA The Framework Convention
Local Development Pilot Project: Island of Cres Ranka Saračević Würth, Ministry of Culture, Republic of Croatia BACKGROUND, RATIFICATION OF THE FARO CONVENTION BY REPUBLIC OF CROATIA The Framework Convention
16540/14 EE/cm 1 DG E 1A
 Council of the European Union Brussels, 5 December 2014 (OR. en) 16540/14 ENV 965 CULT 139 NOTE From: To: Subject: General Secretariat of the Council Delegations Charter of Rome on Natural and Cultural
Council of the European Union Brussels, 5 December 2014 (OR. en) 16540/14 ENV 965 CULT 139 NOTE From: To: Subject: General Secretariat of the Council Delegations Charter of Rome on Natural and Cultural
CLLD Cooperation OFFER
 Title of the proposed project (English) CLLD Cooperation OFFER PARKS PROTECTION III - Management, Protection and Economic Development in Protected Areas Type of project (select as many as you want) Cooperation
Title of the proposed project (English) CLLD Cooperation OFFER PARKS PROTECTION III - Management, Protection and Economic Development in Protected Areas Type of project (select as many as you want) Cooperation
Country Fiche Latvia Updated October 2016
 Country Fiche Latvia Updated October 2016 1. General information Marine area under Latvian jurisdiction includes inland sea waters, Territorial sea (12 nautical miles from the baseline) and exclusive economic
Country Fiche Latvia Updated October 2016 1. General information Marine area under Latvian jurisdiction includes inland sea waters, Territorial sea (12 nautical miles from the baseline) and exclusive economic
TOWARDS STRATEGIC SPATIAL PLANNING IN JAMAICA: THE NATIONAL SPATIAL PLAN
 TOWARDS STRATEGIC SPATIAL PLANNING IN JAMAICA: THE NATIONAL SPATIAL PLAN JIEP 5th Biennial Conference on the Environment: Balancing National Development and Environmental Protection June 6, 2011 Jamaica
TOWARDS STRATEGIC SPATIAL PLANNING IN JAMAICA: THE NATIONAL SPATIAL PLAN JIEP 5th Biennial Conference on the Environment: Balancing National Development and Environmental Protection June 6, 2011 Jamaica
HELSINKI COMMISSION Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission
 HELSINKI COMMISSION Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission HELCOM RECOMMENDATION 24/10 Adopted 25 June 2003, having regard to Article 20, Paragraph 1 b) of the 1992 Helsinki Convention IMPLEMENTATION
HELSINKI COMMISSION Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission HELCOM RECOMMENDATION 24/10 Adopted 25 June 2003, having regard to Article 20, Paragraph 1 b) of the 1992 Helsinki Convention IMPLEMENTATION
Figure 10. Travel time accessibility for heavy trucks
 Figure 10. Travel time accessibility for heavy trucks Heavy truck travel time from Rotterdam to each European cities respecting the prescribed speed in France on the different networks - Road, motorway
Figure 10. Travel time accessibility for heavy trucks Heavy truck travel time from Rotterdam to each European cities respecting the prescribed speed in France on the different networks - Road, motorway
The Governance of Land Use
 The Governance of Land Use Country fact sheet Czech Republic The planning system Levels of government and their responsibilities The Czech Republic is a unitary state with 3 levels of government: the national
The Governance of Land Use Country fact sheet Czech Republic The planning system Levels of government and their responsibilities The Czech Republic is a unitary state with 3 levels of government: the national
Land Use in the context of sustainable, smart and inclusive growth
 Land Use in the context of sustainable, smart and inclusive growth François Salgé Ministry of sustainable development France facilitator EUROGI vice president AFIGéO board member 1 Introduction e-content+
Land Use in the context of sustainable, smart and inclusive growth François Salgé Ministry of sustainable development France facilitator EUROGI vice president AFIGéO board member 1 Introduction e-content+
MiniStRy of national DevelopMent, MiniStRy for national economy. Regional Status Report of Hungary
 MiniStRy of national DevelopMent, MiniStRy for national economy Regional Status Report of Hungary 2010 Ministry of National Development, Ministry for National Economy Regional Status Report of Hungary
MiniStRy of national DevelopMent, MiniStRy for national economy Regional Status Report of Hungary 2010 Ministry of National Development, Ministry for National Economy Regional Status Report of Hungary
The ESPON Programme. Goals Main Results Future
 The ESPON Programme Goals Main Results Future Structure 1. Goals Objectives and expectations Participation, organisation and networking Themes addressed in the applied research undertaken in ESPON projects
The ESPON Programme Goals Main Results Future Structure 1. Goals Objectives and expectations Participation, organisation and networking Themes addressed in the applied research undertaken in ESPON projects
State initiative following up the 2006 national planning report
 18 ness districts and public institutions, should be integrated with the opportunities for public transport services. State initiative following up the 2006 national planning report The Ministry of the
18 ness districts and public institutions, should be integrated with the opportunities for public transport services. State initiative following up the 2006 national planning report The Ministry of the
Declaration Population and culture
 Declaration Population and culture The ministers of the parties to the Alpine Convention regard the socio-economic and socio-cultural aspects mentioned in Article 2, Paragraph 2, Item a., as being central
Declaration Population and culture The ministers of the parties to the Alpine Convention regard the socio-economic and socio-cultural aspects mentioned in Article 2, Paragraph 2, Item a., as being central
Carpathians Unite mechanism of consultation and cooperation for implementation of the Carpathian Convention
 Carpathians Unite mechanism of consultation and cooperation for implementation of the Carpathian Convention Zbigniew Niewiadomski, UNEP/GRID-Warsaw Centre First Joint Meeting of the Carpathian Convention
Carpathians Unite mechanism of consultation and cooperation for implementation of the Carpathian Convention Zbigniew Niewiadomski, UNEP/GRID-Warsaw Centre First Joint Meeting of the Carpathian Convention
The European territory: Strategic developmentd
 The European territory: Strategic developmentd Peter Mehlbye Workshop Strategic Development Catalonia 11 June 2002 THE LECTURE Structure I. Territorial trends II. Strategy for European spatial development
The European territory: Strategic developmentd Peter Mehlbye Workshop Strategic Development Catalonia 11 June 2002 THE LECTURE Structure I. Territorial trends II. Strategy for European spatial development
Mapping and Assessment of Ecosystems and their Services
 Mapping and Assessment of Ecosystems and their Services ALTER-Net Conference 2013: Science underpinning the EU 2020 Biodiversity Strategy. April 2013 Gent Joachim MAES 1 This presentation is based on the
Mapping and Assessment of Ecosystems and their Services ALTER-Net Conference 2013: Science underpinning the EU 2020 Biodiversity Strategy. April 2013 Gent Joachim MAES 1 This presentation is based on the
SPATIAL PLANNING AND REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT OF GREECE
 SPATIAL PLANNING AND REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT OF GREECE by Evangelos Baltas General Secretary, Ministry for the Environment, Physical Planning & Public Works This article analytically presents the historical
SPATIAL PLANNING AND REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT OF GREECE by Evangelos Baltas General Secretary, Ministry for the Environment, Physical Planning & Public Works This article analytically presents the historical
MODELS AND TOOLS FOR GOVERNANCE OF
 Working Papers Collection No. 1/2015 MODELS AND TOOLS FOR GOVERNANCE OF THE ADRIATIC AND IONIAN SEAS www.unimc.it/maremap NATIONAL POLITICS AND EU POLITICS: THE MARITIME SPATIAL PLANNING AND INTEGRATED
Working Papers Collection No. 1/2015 MODELS AND TOOLS FOR GOVERNANCE OF THE ADRIATIC AND IONIAN SEAS www.unimc.it/maremap NATIONAL POLITICS AND EU POLITICS: THE MARITIME SPATIAL PLANNING AND INTEGRATED
Country Fiche Sweden Updated May 2018
 Country Fiche Sweden Updated May 2018 1. General information 2 the territorial sea (12-nm zone) 70,000 km2 the Exclusive Economic Zone 60,000 km2 the EEZ is limited to the central line between adjacent
Country Fiche Sweden Updated May 2018 1. General information 2 the territorial sea (12-nm zone) 70,000 km2 the Exclusive Economic Zone 60,000 km2 the EEZ is limited to the central line between adjacent
Making maps: Traditions and perceptions in Europe. European spatial planning and cartographic representations
 ESPON Create Europe! Making maps: Traditions and perceptions in Europe Dr. Stefanie Dühr University of the West of England, Bristol, UK European spatial planning and cartographic representations Scenarios.
ESPON Create Europe! Making maps: Traditions and perceptions in Europe Dr. Stefanie Dühr University of the West of England, Bristol, UK European spatial planning and cartographic representations Scenarios.
WELCOME & INTRODUCTION
 MPA Management Capacity Building Training Module 1: WELCOME & INTRODUCTION Participants Distinguished Guests Welcome Site Overviews of MPAs represented Overview of Training Program What are Today s Objectives?
MPA Management Capacity Building Training Module 1: WELCOME & INTRODUCTION Participants Distinguished Guests Welcome Site Overviews of MPAs represented Overview of Training Program What are Today s Objectives?
National planning report for Denmark
 National planning report for Denmark from the Minister for Environment and Energy Local identity and new challenges Summary 2000 1 CONTENTS 4 PREFACE: REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT AND SPATIAL PLANNING 6 1. BALANCED
National planning report for Denmark from the Minister for Environment and Energy Local identity and new challenges Summary 2000 1 CONTENTS 4 PREFACE: REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT AND SPATIAL PLANNING 6 1. BALANCED
Regional Plan 4: Integrating Ecosystem Services Mapping into Regional Land Use Planning
 Rural-Urban Outlooks: Unlocking Synergies (ROBUST) ROBUST receives funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 727988.* October 2018 Natural
Rural-Urban Outlooks: Unlocking Synergies (ROBUST) ROBUST receives funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 727988.* October 2018 Natural
The Contested Cultural Landscape of a Lebanese Border Town: MARJA AYOUN
 The Contested Cultural Landscape of a Lebanese Border Town: MARJA AYOUN IBD 2013 FNAS MAY 2013 Dr. Christine Mady, City & Regional Planning NDU -FAAD In this Presentation A PLANNING PERSPECTIVE INTRODUCING
The Contested Cultural Landscape of a Lebanese Border Town: MARJA AYOUN IBD 2013 FNAS MAY 2013 Dr. Christine Mady, City & Regional Planning NDU -FAAD In this Presentation A PLANNING PERSPECTIVE INTRODUCING
The Governance of Land Use
 The planning system Levels of government and their responsibilities The Governance of Land Use Country fact sheet Germany Germany is a federal country with four levels of government. Below the national
The planning system Levels of government and their responsibilities The Governance of Land Use Country fact sheet Germany Germany is a federal country with four levels of government. Below the national
Experience and perspectives of using EU funds and other funding for the implementation of district renovation projects
 Experience and perspectives of using EU funds and other funding for the implementation of district renovation projects Ministry of the Interior of Lithuania Regional policy department Administration, coordination,
Experience and perspectives of using EU funds and other funding for the implementation of district renovation projects Ministry of the Interior of Lithuania Regional policy department Administration, coordination,
THE SEVILLE STRATEGY ON BIOSPHERE RESERVES
 THE SEVILLE STRATEGY ON BIOSPHERE RESERVES 1 VISION FOR BIOSPHERE RESERVES IN THE 21 ST CENTURY The international Seville Conference on Biosphere Reserves, organised by UNESCO, adopted a two-pronged approach,
THE SEVILLE STRATEGY ON BIOSPHERE RESERVES 1 VISION FOR BIOSPHERE RESERVES IN THE 21 ST CENTURY The international Seville Conference on Biosphere Reserves, organised by UNESCO, adopted a two-pronged approach,
CHAPTER 4 HIGH LEVEL SPATIAL DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK (SDF) Page 95
 CHAPTER 4 HIGH LEVEL SPATIAL DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK (SDF) Page 95 CHAPTER 4 HIGH LEVEL SPATIAL DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK 4.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter provides a high level overview of George Municipality s
CHAPTER 4 HIGH LEVEL SPATIAL DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK (SDF) Page 95 CHAPTER 4 HIGH LEVEL SPATIAL DEVELOPMENT FRAMEWORK 4.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter provides a high level overview of George Municipality s
Land Use Planning and Agriculture: Austrian Experiences and Challenges I
 Land Use Planning and Agriculture: Austrian Experiences and Challenges I SULANET Summer School 2016 Walter Seher BOKU Vienna 1 Land Use Planning and Agriculture 2 Land Use Planning and Agriculture Agriculture
Land Use Planning and Agriculture: Austrian Experiences and Challenges I SULANET Summer School 2016 Walter Seher BOKU Vienna 1 Land Use Planning and Agriculture 2 Land Use Planning and Agriculture Agriculture
National Spatial Development Perspective (NSDP) Policy Coordination and Advisory Service
 National Spatial Development Perspective (NSDP) Policy Coordination and Advisory Service 1 BACKGROUND The advances made in the First Decade by far supersede the weaknesses. Yet, if all indicators were
National Spatial Development Perspective (NSDP) Policy Coordination and Advisory Service 1 BACKGROUND The advances made in the First Decade by far supersede the weaknesses. Yet, if all indicators were
Margarita Stancheva Hristo Stanchev & Robert Young 2. MEDCOAST JUBILEE WORKSHOP May 2015, Iberotel Sarigerme Park, Dalaman, Turkey
 Margarita Stancheva Hristo Stanchev & Robert Young 2 INTRODUCTION: Bulgarian Black Sea coast INTRODUCTION: Increasing pressure on Bulgarian coastal zone In 2011, of the 7 364 570 people that lived in Bulgaria,
Margarita Stancheva Hristo Stanchev & Robert Young 2 INTRODUCTION: Bulgarian Black Sea coast INTRODUCTION: Increasing pressure on Bulgarian coastal zone In 2011, of the 7 364 570 people that lived in Bulgaria,
Jordan's Strategic Research Agenda in cultural heritage
 Jordan's Strategic Research Agenda in cultural heritage Analysis of main results Alessandra Gandini Amman, Jordan 3 rd November 2013 Main objectives The work performed had the main objective of giving
Jordan's Strategic Research Agenda in cultural heritage Analysis of main results Alessandra Gandini Amman, Jordan 3 rd November 2013 Main objectives The work performed had the main objective of giving
Bishkek City Development Agency. Urban Planning Bishkek
 Bishkek City Development Agency Urban Planning Bishkek Bishkek City Development Agency Official name City budget Population Area GRP Import value Export value External trade turnover Foreign direct investments
Bishkek City Development Agency Urban Planning Bishkek Bishkek City Development Agency Official name City budget Population Area GRP Import value Export value External trade turnover Foreign direct investments
New Prospects for Peripheral Rural Regions Helmut Hiess Glasgow, 19th of May 2010
 New Prospects for Peripheral Rural Regions Helmut Hiess Glasgow, 19th of May 2010 ÖROK: Organisation & Tasks Austrian Conference on Spatial Planning (ÖROK, since 1971): Joint organisation by Federal level,
New Prospects for Peripheral Rural Regions Helmut Hiess Glasgow, 19th of May 2010 ÖROK: Organisation & Tasks Austrian Conference on Spatial Planning (ÖROK, since 1971): Joint organisation by Federal level,
COMPREHENSIVE LAND-USE MANAGEMENT UNDERSTANDING THE INTERRELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SPATIAL PLANNING, LAND MANAGEMENT AND LAND ADMINISTRATION
 COMPREHENSIVE LAND-USE MANAGEMENT UNDERSTANDING THE INTERRELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SPATIAL PLANNING, LAND MANAGEMENT AND LAND ADMINISTRATION Daniel Galland & Stig Enemark Department of Development and Planning
COMPREHENSIVE LAND-USE MANAGEMENT UNDERSTANDING THE INTERRELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SPATIAL PLANNING, LAND MANAGEMENT AND LAND ADMINISTRATION Daniel Galland & Stig Enemark Department of Development and Planning
2. Defining fisheries areas
 What does fisheries area mean in the context of the EFF? Axis 4 of the European Fisheries Fund (EFF) is different from the other three Axes in that it targets fisheries areas (it is titled Sustainable
What does fisheries area mean in the context of the EFF? Axis 4 of the European Fisheries Fund (EFF) is different from the other three Axes in that it targets fisheries areas (it is titled Sustainable
European Landscape Convention in the Slovak Republic
 13th COUNCIL OF EUROPE MEETING OF THE WORKSHOPS FOR THE EUROPEAN LANDSCAPE CONVENTION European Landscape Convention in the Slovak Republic Mrs. Ida Vanáková, state advisor, Department of Spatial Planning
13th COUNCIL OF EUROPE MEETING OF THE WORKSHOPS FOR THE EUROPEAN LANDSCAPE CONVENTION European Landscape Convention in the Slovak Republic Mrs. Ida Vanáková, state advisor, Department of Spatial Planning
Law on Spatial Planning
 UNITED NATIONS United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo UNMIK NATIONS UNIES Mission d Administration Intérimaire des Nations Unies au Kosovo PROVISIONAL INSTITUTIONS OF SELF GOVERNMENT Law
UNITED NATIONS United Nations Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo UNMIK NATIONS UNIES Mission d Administration Intérimaire des Nations Unies au Kosovo PROVISIONAL INSTITUTIONS OF SELF GOVERNMENT Law
Tackling urban sprawl: towards a compact model of cities? David Ludlow University of the West of England (UWE) 19 June 2014
 Tackling urban sprawl: towards a compact model of cities? David Ludlow University of the West of England (UWE) 19 June 2014 Impacts on Natural & Protected Areas why sprawl matters? Sprawl creates environmental,
Tackling urban sprawl: towards a compact model of cities? David Ludlow University of the West of England (UWE) 19 June 2014 Impacts on Natural & Protected Areas why sprawl matters? Sprawl creates environmental,
Riga. Riga City Planning Region. Legal framework
 Riga http://www.rpr.gov.lv/ Riga City Planning Region Riga Planning Region as a territory is situated in the central part of Latvia, and its centre is Riga - the capital of Latvia. Riga is internationally
Riga http://www.rpr.gov.lv/ Riga City Planning Region Riga Planning Region as a territory is situated in the central part of Latvia, and its centre is Riga - the capital of Latvia. Riga is internationally
Summary. Recommendations on the Fifth Policy Document on Spatial Planning September 2001
 Summary Recommendations on the Fifth Policy Document on Spatial Planning September 2001 2 Introduction In December 2000 the Dutch Cabinet issued Part 1 of the Fifth National Policy Document on Spatial
Summary Recommendations on the Fifth Policy Document on Spatial Planning September 2001 2 Introduction In December 2000 the Dutch Cabinet issued Part 1 of the Fifth National Policy Document on Spatial
Cross-border Maritime Spatial Plan for the Black sea - Romania and Bulgaria project
 Cross-border Maritime Spatial Plan for the Black sea - Romania and Bulgaria project in Romania and Bulgaria Plan Presentation A first step in the management of the marine areas of Romania and Bulgaria
Cross-border Maritime Spatial Plan for the Black sea - Romania and Bulgaria project in Romania and Bulgaria Plan Presentation A first step in the management of the marine areas of Romania and Bulgaria
The importance of visioning in urban strategic planning By Peter Robinson. MILE Master Class Urban Strategic Planning March 2016
 The importance of visioning in urban strategic planning By Peter Robinson MILE Master Class Urban Strategic Planning March 2016 Typical strategic planning process Where are we now? Where are we going?
The importance of visioning in urban strategic planning By Peter Robinson MILE Master Class Urban Strategic Planning March 2016 Typical strategic planning process Where are we now? Where are we going?
Urban-rural relations in Europe
 Urban-rural relations in Europe Typology of urban and rural characteristics developed by the ESPON 1.1.2 project Kaisa Schmidt-Thomé 14.12.2006 Sevilla JRC/IPTS Rural typologies -workshop ESPON 2006 Programme
Urban-rural relations in Europe Typology of urban and rural characteristics developed by the ESPON 1.1.2 project Kaisa Schmidt-Thomé 14.12.2006 Sevilla JRC/IPTS Rural typologies -workshop ESPON 2006 Programme
The Governance of Land Use
 The planning system The Governance of Land Use United Kingdom Levels of government and their responsibilities The United Kingdom is a unitary state with three devolved governments in Northern Ireland,
The planning system The Governance of Land Use United Kingdom Levels of government and their responsibilities The United Kingdom is a unitary state with three devolved governments in Northern Ireland,
CAMP SLOVENIA. Mezek Slavko RRC Koper. Project coordinator November 2005
 CAMP SLOVENIA Mezek Slavko RRC Koper Project coordinator November 2005 http://camp.rrc-kp.si/ Content About MAP CAMP programme CAMP Slovenia Project background CAMP Slovenia Project area CAMP Slovenia
CAMP SLOVENIA Mezek Slavko RRC Koper Project coordinator November 2005 http://camp.rrc-kp.si/ Content About MAP CAMP programme CAMP Slovenia Project background CAMP Slovenia Project area CAMP Slovenia
National Land Use Policy and National Integrated Planning Framework for Land Resource Development
 Title National Land Use Policy and National Integrated Planning Framework for Land Resource Development Duration: 32 Weeks Objective: Adoption of appropriate land use planning approaches to: Maintain the
Title National Land Use Policy and National Integrated Planning Framework for Land Resource Development Duration: 32 Weeks Objective: Adoption of appropriate land use planning approaches to: Maintain the
Date: June 19, 2013 Meeting Date: July 5, Consideration of the City of Vancouver s Regional Context Statement
 Section E 1.5 To: From: Regional Planning and Agriculture Committee Lee-Ann Garnett, Senior Regional Planner Planning, Policy and Environment Department Date: June 19, 2013 Meeting Date: July 5, 2013 Subject:
Section E 1.5 To: From: Regional Planning and Agriculture Committee Lee-Ann Garnett, Senior Regional Planner Planning, Policy and Environment Department Date: June 19, 2013 Meeting Date: July 5, 2013 Subject:
May kindly Tim Page prepare the Bulgaria page header with the same design as the others? Bulgaria Urban Region of Sofia
 May kindly Tim Page prepare the Bulgaria page header with the same design as the others? Bulgaria Urban Region of Sofia National Planning Context Urban Region of Sofia Geography Statistics Trends Historical
May kindly Tim Page prepare the Bulgaria page header with the same design as the others? Bulgaria Urban Region of Sofia National Planning Context Urban Region of Sofia Geography Statistics Trends Historical
CEMAT results - over the years
 CEMAT results - over the years Technical Conference on Functional Areas capitalization of local potential within the territorial development policies in Europe European Conference of Ministers responsible
CEMAT results - over the years Technical Conference on Functional Areas capitalization of local potential within the territorial development policies in Europe European Conference of Ministers responsible
National Perspectives - Portugal. Margarida Almodovar
 National Perspectives - Portugal Margarida Almodovar margarida.almodovar@mam.gov.pt from base line to the external limit of the continental shelf behind 200 miles and according to UNCLOS definitions Economic
National Perspectives - Portugal Margarida Almodovar margarida.almodovar@mam.gov.pt from base line to the external limit of the continental shelf behind 200 miles and according to UNCLOS definitions Economic
Spatial Planning and Territorial Development at the Regional Level
 Spatial Planning and Territorial Development at the Regional Level Vincent Nadin University of the West of England, UK Spatial Planning and Territorial Development at the Regional Level Vincent Nadin University
Spatial Planning and Territorial Development at the Regional Level Vincent Nadin University of the West of England, UK Spatial Planning and Territorial Development at the Regional Level Vincent Nadin University
COURSES OUTSIDE THE JOURNALISM SCHOOL
 COURSES OUTSIDE THE JOURNALISM SCHOOL Students are not limited to the science courses on this list and may select classes from additional specialties. In accordance with University policy, 400-level courses
COURSES OUTSIDE THE JOURNALISM SCHOOL Students are not limited to the science courses on this list and may select classes from additional specialties. In accordance with University policy, 400-level courses
The HELCOM Baltic Sea Action Plan and Marine Spatial Planning
 The HELCOM Baltic Sea Action Plan and Marine Spatial Planning Anne Christine Brusendorff Executive Secretary HELCOM The Baltic Sea Our common responsibility. Workshop on Integrated Sea Use management Stockholm
The HELCOM Baltic Sea Action Plan and Marine Spatial Planning Anne Christine Brusendorff Executive Secretary HELCOM The Baltic Sea Our common responsibility. Workshop on Integrated Sea Use management Stockholm
SPLAN-Natura Towards an integrated spatial planning approach for Natura th January, 2017 Brussels. Commissioned by DG Environment
 SPLAN-Natura 2000 Towards an integrated spatial planning approach for Natura 2000 Commissioned by DG Environment 17 th January, 2017 Brussels V. Simeonova (Ph.D.) Drivers towards integrating Biodiversity
SPLAN-Natura 2000 Towards an integrated spatial planning approach for Natura 2000 Commissioned by DG Environment 17 th January, 2017 Brussels V. Simeonova (Ph.D.) Drivers towards integrating Biodiversity
Maritime Spatial Planning in the Baltic Sea Region
 Maritime Spatial Planning in the Baltic Sea Region Talis Linkaits Head of VASAB Secretariat 20 May 2015 Helsinki A cooperation of ministers of the 11 Baltic Sea Region countries responsible for spatial
Maritime Spatial Planning in the Baltic Sea Region Talis Linkaits Head of VASAB Secretariat 20 May 2015 Helsinki A cooperation of ministers of the 11 Baltic Sea Region countries responsible for spatial
Key Indicators for Territorial Cohesion & Spatial Planning Stakeholder Workshop - Project Update. 13 th December 2012 San Sebastián, Basque Country
 Key Indicators for Territorial Cohesion & Spatial Planning Stakeholder Workshop - Project Update 13 th December 2012 San Sebastián, Basque Country Key Aims Explore the use of territorial data in developing
Key Indicators for Territorial Cohesion & Spatial Planning Stakeholder Workshop - Project Update 13 th December 2012 San Sebastián, Basque Country Key Aims Explore the use of territorial data in developing
TERRITORIAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT: AN APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL INTEGRATION OF EU POLICIES
 TERRITORIAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT: AN APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL INTEGRATION OF EU POLICIES Naja Marot & Mojca Golobič Biotehnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia RSA Workshop
TERRITORIAL IMPACT ASSESSMENT: AN APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL INTEGRATION OF EU POLICIES Naja Marot & Mojca Golobič Biotehnical Faculty, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia RSA Workshop
The Problems of Large Protected Areas in the Process of Planning: A Case Study in the Municipality Ig, Slovenia
 The Problems of Large Protected Areas in the Process of Planning: A Case Study in the Municipality Ig, Slovenia Nadja PENKO SEIDL, Alenka COF, Lidija BRESKVAR ŽAUCER and Ivan MARUŠIČ 1 Introduction The
The Problems of Large Protected Areas in the Process of Planning: A Case Study in the Municipality Ig, Slovenia Nadja PENKO SEIDL, Alenka COF, Lidija BRESKVAR ŽAUCER and Ivan MARUŠIČ 1 Introduction The
PURR: POTENTIAL OF RURAL REGIONS UK ESPON WORKSHOP Newcastle 23 rd November Neil Adams
 PURR: POTENTIAL OF RURAL REGIONS UK ESPON WORKSHOP Newcastle 23 rd November 2012 Neil Adams PURR: Potential of Rural Regions Introduction Context for the project A spectrum of knowledge Rural Potentials
PURR: POTENTIAL OF RURAL REGIONS UK ESPON WORKSHOP Newcastle 23 rd November 2012 Neil Adams PURR: Potential of Rural Regions Introduction Context for the project A spectrum of knowledge Rural Potentials
Management Planning & Implementation of Communication Measures for Terrestrial Natura 2000 Sites in the Maltese Islands Epsilon-Adi Consortium
 Management Planning & Implementation of Communication Measures for Terrestrial Natura 2000 Sites in the Maltese Islands Epsilon-Adi Consortium Briefing Meetings, February 2013 CT3101/2011, MEPA, Malta
Management Planning & Implementation of Communication Measures for Terrestrial Natura 2000 Sites in the Maltese Islands Epsilon-Adi Consortium Briefing Meetings, February 2013 CT3101/2011, MEPA, Malta
I. INTRODUCTION. 1 Regulation EU No 1303/2013 on the Common Provisions on the ESI Funds.
 Boletín de la Asociación de Geógrafos Españoles N.º 73-2017, págs. 543-549 I.S.S.N.: 0212-9426 HERITAGE AS A DRIVING FORCE FOR THE SOCIOECONOMIC REVITALIZATION OF LOCAL COMMUNITIES WITHIN THE FRAMEWORK
Boletín de la Asociación de Geógrafos Españoles N.º 73-2017, págs. 543-549 I.S.S.N.: 0212-9426 HERITAGE AS A DRIVING FORCE FOR THE SOCIOECONOMIC REVITALIZATION OF LOCAL COMMUNITIES WITHIN THE FRAMEWORK
Community Engagement in Cultural Routes SiTI Higher Institute on Territorial Systems for Innovation Sara Levi Sacerdotti
 Transnational Workshop Wroclaw, 7th-8th December 2016 Community Engagement in Cultural Routes SiTI Higher Institute on Territorial Systems for Innovation Sara Levi Sacerdotti levi@siti.polito.it TAKING
Transnational Workshop Wroclaw, 7th-8th December 2016 Community Engagement in Cultural Routes SiTI Higher Institute on Territorial Systems for Innovation Sara Levi Sacerdotti levi@siti.polito.it TAKING
European spatial policy and regionalised approaches
 Findings of the ESPON 2006 Programme COMMIN Final Conference 26-27 April 2007 European spatial policy and regionalised approaches by Dr. Kai BöhmeB ! Territory matters Structure of presentation! Territorial
Findings of the ESPON 2006 Programme COMMIN Final Conference 26-27 April 2007 European spatial policy and regionalised approaches by Dr. Kai BöhmeB ! Territory matters Structure of presentation! Territorial
Maritime Spatial Planning: Transboundary Cooperation in the Celtic Seas Looking Ahead
 Maritime Spatial Planning: Transboundary Cooperation in the Celtic Seas Looking Ahead Looking ahead MSP in the context of the European Maritime and Fisheries Fund (EMFF) and beyond SIMCelt Final Conference
Maritime Spatial Planning: Transboundary Cooperation in the Celtic Seas Looking Ahead Looking ahead MSP in the context of the European Maritime and Fisheries Fund (EMFF) and beyond SIMCelt Final Conference
Measurement of the Urban-Housing Deficit:
 Measurement of the Urban-Housing Deficit: Strategies, tools and sources of information The International Network for Urban and Regional Statistics Standing Committee of the International Association for
Measurement of the Urban-Housing Deficit: Strategies, tools and sources of information The International Network for Urban and Regional Statistics Standing Committee of the International Association for
Towards a Polycentric Europe
 Towards a Polycentric Europe European Spatial Perceptions The Blue Banana Brunet, 1989 A Bunch of Grapes Kunzmann & Wegener, 1991 Economic Imbalances Core area of the EU: Pentagon of the metropolises of
Towards a Polycentric Europe European Spatial Perceptions The Blue Banana Brunet, 1989 A Bunch of Grapes Kunzmann & Wegener, 1991 Economic Imbalances Core area of the EU: Pentagon of the metropolises of
GIS, Maps and Spatial Analyses in Urban Planning
 GIS, Maps and Spatial Analyses in Urban Planning LOOM.02.331 ANTO AASA PhD, researcher Power of visualization: What s this? Economic spaces in Europe (chorems based approach) Europe economy 1646 General:
GIS, Maps and Spatial Analyses in Urban Planning LOOM.02.331 ANTO AASA PhD, researcher Power of visualization: What s this? Economic spaces in Europe (chorems based approach) Europe economy 1646 General:
Dutch spatial planning: from implicit to explicit sustainable urban development
 Dutch spatial planning: from implicit to explicit sustainable urban development Jan Goedman (VROM*) Wim Heiko Houtsma (VROM) Wil Zonneveld (Delft University) *Dutch Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning
Dutch spatial planning: from implicit to explicit sustainable urban development Jan Goedman (VROM*) Wim Heiko Houtsma (VROM) Wil Zonneveld (Delft University) *Dutch Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning
This document has been verified by the responsible MSP authority (or representative) of Lithuania on
 Contact MSP in general Ms. Algimantė Treinienė Head of Spatial Planning Urban Development and Architecture Division Construction and Territorial Planning Department Ministry of Environment A. Jakšto 4
Contact MSP in general Ms. Algimantė Treinienė Head of Spatial Planning Urban Development and Architecture Division Construction and Territorial Planning Department Ministry of Environment A. Jakšto 4
Economic development in rural regions in the EU: empirical findings and theories
 Economic development in rural regions in the EU: empirical findings and theories Presentation at the IAMO Forum 2013 Rural areas in transition, June 19-21, 2013 Dr. Ida Terluin, Agricultural Economics
Economic development in rural regions in the EU: empirical findings and theories Presentation at the IAMO Forum 2013 Rural areas in transition, June 19-21, 2013 Dr. Ida Terluin, Agricultural Economics
THE ROLE OF SPATIAL PLANNING IN INTEGRATED COASTAL ZONE MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS FROM THE INTERREG III B BALTCOAST PROJECT
 THE ROLE OF SPATIAL PLANNING IN INTEGRATED COASTAL ZONE MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS FROM THE INTERREG III B BALTCOAST PROJECT DISCUSSION PAPER FOR THE TRANSNATIONAL WORKING GROUP DECEMBER 2004 CONTENT 1.
THE ROLE OF SPATIAL PLANNING IN INTEGRATED COASTAL ZONE MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS FROM THE INTERREG III B BALTCOAST PROJECT DISCUSSION PAPER FOR THE TRANSNATIONAL WORKING GROUP DECEMBER 2004 CONTENT 1.
SIF_7.1_v2. Indicator. Measurement. What should the measurement tell us?
 Indicator 7 Area of natural and semi-natural habitat Measurement 7.1 Area of natural and semi-natural habitat What should the measurement tell us? Natural habitats are considered the land and water areas
Indicator 7 Area of natural and semi-natural habitat Measurement 7.1 Area of natural and semi-natural habitat What should the measurement tell us? Natural habitats are considered the land and water areas
Strengthening the cooperation in the region: Carpathian, Tisa,, Danube and Black Sea areas
 Strengthening the cooperation in the region: Carpathian, Tisa,, Danube and Black Sea areas 14th October 2009 SEE Annual Conference Advancing development through transnational cooperation in South East
Strengthening the cooperation in the region: Carpathian, Tisa,, Danube and Black Sea areas 14th October 2009 SEE Annual Conference Advancing development through transnational cooperation in South East
The Euroregion, which puts into practice the determination for active cooperation, has led to concrete actions such as:
 Contribution of the Euroregion Pyrenees-Mediterranean to the conclusions of the 5th report on economic, social and territorial cohesion: the future of the cohesion policy A. Introduction The Euroregion
Contribution of the Euroregion Pyrenees-Mediterranean to the conclusions of the 5th report on economic, social and territorial cohesion: the future of the cohesion policy A. Introduction The Euroregion
Poland, European Territory, ESPON Programme Warsaw, 2 July 2007 STRATEGY OF THE ESPON 2013 PROGRAMME
 Poland, European Territory, ESPON Programme 2007-2013 Warsaw, 2 July 2007 STRATEGY OF THE ESPON 2013 PROGRAMME Territory matters Regional diversity as asset Territorial potentials increasing in importance
Poland, European Territory, ESPON Programme 2007-2013 Warsaw, 2 July 2007 STRATEGY OF THE ESPON 2013 PROGRAMME Territory matters Regional diversity as asset Territorial potentials increasing in importance
Alps Results from the ESPON Project. Common spatial perspectives for the Alpine area. Towards a common vision
 Results from the ESPON Project Alps 2050 Common spatial perspectives for the Alpine area. Towards a common vision Tobias Chilla, University of Erlangen Cooperation Alps 2020+ 1 & 2 October 2018 Salzburg
Results from the ESPON Project Alps 2050 Common spatial perspectives for the Alpine area. Towards a common vision Tobias Chilla, University of Erlangen Cooperation Alps 2020+ 1 & 2 October 2018 Salzburg
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION. Brussels, 2 May /14 CULT 68
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 2 May 2014 9129/14 CULT 68 NOTE from: General Secretariat of the Council to: Permanent Representatives Committee (Part 1) / Council No. prev. doc.: 8892/14 CULT
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Brussels, 2 May 2014 9129/14 CULT 68 NOTE from: General Secretariat of the Council to: Permanent Representatives Committee (Part 1) / Council No. prev. doc.: 8892/14 CULT
What is Spatial Planning?
 Spatial Planning in the context of the Responsible Governance of Tenure What is Spatial Planning? Text-only version This course is funded by the European Union through the EU-FAO Improved Global Governance
Spatial Planning in the context of the Responsible Governance of Tenure What is Spatial Planning? Text-only version This course is funded by the European Union through the EU-FAO Improved Global Governance
Possibilities for applying ES assessment results in spatial planning in Latvia
 Possibilities for applying ES assessment results in spatial planning in Latvia Inga Hoņavko LIFE EcosystemServices project manager LIFE Viva Grass seminar, Sigulda, 17.05.2018 Projekts LIFE EcosystemServices,
Possibilities for applying ES assessment results in spatial planning in Latvia Inga Hoņavko LIFE EcosystemServices project manager LIFE Viva Grass seminar, Sigulda, 17.05.2018 Projekts LIFE EcosystemServices,
Third Cohesion report February 2004
 February 2004 A new partnership for cohesion Convergence, Competitiveness and Co-operation METREX meeting S. Sebastian, Luisa Sanches DG REGIO The 3rd CR structure 1. Analysis of situation and trends in
February 2004 A new partnership for cohesion Convergence, Competitiveness and Co-operation METREX meeting S. Sebastian, Luisa Sanches DG REGIO The 3rd CR structure 1. Analysis of situation and trends in
The view of Europaforum Northern Sweden concerning the future of EU cohesion policy
 Northern Sweden 2008-01-31 The view of Europaforum Northern Sweden concerning the future of EU cohesion policy Europaforum Northern Sweden Europaforum Northern Sweden is a partnership and network for councillors
Northern Sweden 2008-01-31 The view of Europaforum Northern Sweden concerning the future of EU cohesion policy Europaforum Northern Sweden Europaforum Northern Sweden is a partnership and network for councillors
INTERNATIONAL CULTURAL TOURISM CHARTER Managing Tourism at Places of Heritage Significance (1999)
 INTERNATIONAL CULTURAL TOURISM CHARTER Managing Tourism at Places of Heritage Significance (1999) Adopted by ICOMOS at the 12th General Assembly in Mexico, October 1999. INTRODUCTION The Charter Ethos
INTERNATIONAL CULTURAL TOURISM CHARTER Managing Tourism at Places of Heritage Significance (1999) Adopted by ICOMOS at the 12th General Assembly in Mexico, October 1999. INTRODUCTION The Charter Ethos
Marine/Maritime Spatial Planning Andrej Abramić
 Marine/Maritime Spatial Planning Andrej Abramić EcoAqua SUMMER SCHOOL: Ecosystem approach to aquaculture 26-29th of October 2015 Research and Technology to enhance excellence in Aquaculture development
Marine/Maritime Spatial Planning Andrej Abramić EcoAqua SUMMER SCHOOL: Ecosystem approach to aquaculture 26-29th of October 2015 Research and Technology to enhance excellence in Aquaculture development
European Regional and Urban Statistics
 European Regional and Urban Statistics Dr. Berthold Feldmann berthold.feldmann@ec.europa.eu Eurostat Structure of the talk Regional statistics in the EU The tasks of Eurostat Regional statistics Urban
European Regional and Urban Statistics Dr. Berthold Feldmann berthold.feldmann@ec.europa.eu Eurostat Structure of the talk Regional statistics in the EU The tasks of Eurostat Regional statistics Urban
Assessment of Sustainable Land Use within the Town Planning Process Experiences with a Multi Criteria Approach (MCA)
 Assessment of Sustainable Land Use within the Town Planning Process Experiences with a Multi Criteria Approach (MCA) Dipl.-Geogr. Sophie Schetke Dipl.-Ing. Benedikt Frielinghaus, University of Bonn, Germany
Assessment of Sustainable Land Use within the Town Planning Process Experiences with a Multi Criteria Approach (MCA) Dipl.-Geogr. Sophie Schetke Dipl.-Ing. Benedikt Frielinghaus, University of Bonn, Germany
GIS FOR MAZOWSZE REGION - GENERAL OUTLINE
 GIS FOR MAZOWSZE REGION - GENERAL OUTLINE S. Bialousz 1), K Mączewski 2), E. Janczar 2), K. Osinska-Skotak 1) 1) Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland 2) Office of the Surveyor of the Mazowieckie
GIS FOR MAZOWSZE REGION - GENERAL OUTLINE S. Bialousz 1), K Mączewski 2), E. Janczar 2), K. Osinska-Skotak 1) 1) Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw, Poland 2) Office of the Surveyor of the Mazowieckie
Maria Andrzejewska UNEP/GRID Warsaw Centre
 Maria Andrzejewska UNEP/GRID Warsaw Centre Agenda 1. Environment matters! 2. Spatial data to benefit environment 3. Environment management with cadastral data 4. Cadaster in spatial planning 5. Conclusions
Maria Andrzejewska UNEP/GRID Warsaw Centre Agenda 1. Environment matters! 2. Spatial data to benefit environment 3. Environment management with cadastral data 4. Cadaster in spatial planning 5. Conclusions
Topic 4: Changing cities
 Topic 4: Changing cities Overview of urban patterns and processes 4.1 Urbanisation is a global process a. Contrasting trends in urbanisation over the last 50 years in different parts of the world (developed,
Topic 4: Changing cities Overview of urban patterns and processes 4.1 Urbanisation is a global process a. Contrasting trends in urbanisation over the last 50 years in different parts of the world (developed,
Multifunctional theory in agricultural land use planning case study
 Multifunctional theory in agricultural land use planning case study Introduction István Ferencsik (PhD) VÁTI Research Department, iferencsik@vati.hu By the end of 20 th century demands and expectations
Multifunctional theory in agricultural land use planning case study Introduction István Ferencsik (PhD) VÁTI Research Department, iferencsik@vati.hu By the end of 20 th century demands and expectations
Territorial evidence for a European Urban Agenda TOWN in Europe
 Territorial evidence for a European Urban Agenda TOWN in Europe Loris Servillo Brussels, 25 November 2014 Outline 1. SMSTs in the EU territory 2. General vs specific trends? 3. Evidences for more appropriated
Territorial evidence for a European Urban Agenda TOWN in Europe Loris Servillo Brussels, 25 November 2014 Outline 1. SMSTs in the EU territory 2. General vs specific trends? 3. Evidences for more appropriated
