Whole Genome based Phylogeny
|
|
|
- Brett Merritt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Whole Genome based Phylogeny Johanne Ahrenfeldt PhD student DTU Bioinformatics
2 Short about me Johanne Ahrenfeldt PhD student at DTU Bioinformatics Whole Genome based Phylogeny Graduate Engineer in Systems Biology and Bioinformatics from Technical University of Denmark Working in the CGE project since 2012 started as a student helper
3 Overview What is Phylogeny SNP methods CSI Phylogeny Nucleotide Differences NDtree Controlled Evolution study Good advice A cool new thing called Evergreen
4 What is phylogeny? Early phylogeny Classification Based on phenotypes Current phylogeny Based on genotypes DNA mutations as basis for evolution
5 Classification Carl Linnaeus Hierarchical system Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
6 Classification depicted as a tree
7 Classification depicted as a tree Species Genus Family Order Class
8 DNA mutations as basis for evolution
9 What are phylogenetic trees Phylogenetic trees are a visual representation of the genetic relationship between species Think of them as family trees Phylogeny can also be represented by distance matrices
10 What are phylogenetic trees Trees were traditionally made using aligned sequences of single genes or proteins Whole genome data can be used to create trees based on SNP calling K-mer overlap Alignment of genomes
11 What is a SNP A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) is a DNA sequence variation occurring commonly* within a population (e.g. 1%) in which a Single Nucleotide A, T, C or G in the genome (or other shared sequence) differs between members of a biological species or paired chromosomes.
12 How does it work Strain A ATTCAGTAGT Strain B ATGCAGTTGA Strain C ATGCAATTGT Strain D ATCCATTAGC
13 Construct distance matrix Strain A ATTCAGTAGT Strain B ATGCAGTTGA Strain C ATGCAATTGT Strain D ATCCATTAGC A B C D AA B C D
14 Make Tree Strain A Strain B Strain C Strain D ATTCAGTAGT ATGCAGTTGA ATGCAATTGT ATCCATTAGC A B C D A B C D A B C 1 D
15 How to read phylogenetic trees 16 The lineages leading to contemporary species have all b T. Ryan Gregory. Understanding Evolu<onary Trees. Evo Edu Outreach (2008) 1: DOI /s x 15
16 How to read phylogenetic trees T. Ryan Gregory. Understanding Evolu<onary Trees. Evo Edu Outreach (2008) 1: DOI /s x 16
17 What is phylogeny used for Classify taxonomy The classic use Outbreak detection Increasing with WGS data
18 What is phylogeny used for Cholera outbreak in Haiti 2010 Listeria outbreak 2014 Whole-genome Sequencing Used to Investigate a Nationwide Outbreak of Listeriosis Caused by Ready-to-eat Delicatessen Meat, Denmark, Kvistholm Jensen et al. Clin Infect Dis. (2016) 63 (1): doi: / cid/ciw192
19 Case story Vibrio Cholerae outbreak in Haiti followed the 2010 earthquake Rumors said that the outbreak may have come from Nepal, travelling along with UN soldiers from Nepal No proof had been given of this until the Hendriksen et al. paper in 2011 Popula<on Gene<cs of Vibrio cholerae from Nepal in 2010: Evidence on the Origin of the Hai<an Outbreak. Hendriksen et al. 23 August 2011 mbio vol. 2 no. 4 e doi: /mBio
20 Case story Data 24 recent V. cholerae strains from Nepal 10 previously sequenced V. cholerae isolates, including 3 from the Haitian outbreak Analysis Antimicrobial susceptibility testing PFGE (pulsed-field gel electrophoresis) to analyze for genetic relatedness Whole genome sequencing, SNP identification and phylogenetic analysis
21 Case story - Results Resistance profile Suscep5ble Decreased suscep5bility Nepalese strains Hendriksen et al Resistant Tetracycline Ciprofloxacin Trimethoprim, Sulfamethoxazole Nalidixic Hai<an outbreak strains Centers for Disease Control and Preven<on, 2010 Tetracycline Ciprofloxacin Trimethoprim, Sulfamethoxazole Nalidixic
22 Case story - Results Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFG)E Nepalese isolates divided in 4 groups Most common Haitian type in same group as four Nepalese strains
23 Case story - Results
24 10 minutes break!
25 snptree First online webserver for constructing phylogenetic trees based on whole genome sequencing snptree- - a web- server to iden<fy and construct SNP trees from whole genome sequence data. Leekitcharoenphon P, Kaas RS, Thomsen MC, Friis C, Rasmussen S, Aarestrup FM. BMC Genomics. 2012;13 Suppl 7:S6.
26 snptree flow
27 CSI Phylogeny SNP identification same as snptree Strict sorting of SNPs Depth Relative depth Distance between SNPs SNP quality Read mapping quality Rolf S. Kaas, Pimlapas Leekitcharoenphon, Frank M. Aarestrup, Ole Lund. Solving the Problem of Comparing Whole Bacterial Genomes across Different Sequencing Plaeorms. PLoS ONE 2014; 9(8): e
28 CSI Phylogeny Requires all SNPs to be significant Z-score higher than 1.96 for all SNPs Z = X Y X+Y X is the number of reads, with the most common nucleotide at that position, and Y the number of reads with any other nucleotide.
29 CSI Phylogeny Output Tree build by FastTree algorithm, in Newick format Branch lengths is substitutions per site at the variable sites Matrix of SNP pair counts in text (.txt) format Diagonal SNP matrix
30 CSI Phylogeny
31 NDtree Nucleotide calling A different approach where the main distinction is not between if a SNP should be called or not, but between whether or not there is solid evidence for the nucleotide at the given position. Real- Time Whole- Genome Sequencing for Rou<ne Typing, Surveillance, and Outbreak Detec<on of Verotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Joensen KG, Scheutz F, Lund O, Hasman H, Kaas RS, Nielsen EM, Aarestrup FM. J Clin Microbiol May;52(5):
32 NDtree Simple mapping approach Cuts all reads into K-mers Maps all K-mers to reference genome Makes an ungapped consensus sequences of equal lengths
33 Mapping K- mers Consensus sequence Reference genome Reference genome Genome 1 Genome 2 Genome 3 Genome 4 Genome 5 Genome 6 33
34 NDtree Nucleotide calling When all reads have been mapped the significance of the base call at each position was evaluated by calculating the number of reads X having the most common nucleotide at that position, and the number of reads Y supporting other nucleotides. A Z-score threshold is calculated Z = X Y X+Y > 1.96 (or 3.29) >90% of reads supporting the same base
35 NDtree Count nucleotide differences Method 1: Each pair of sequences was compared and the number of nucleotide differences in positions called in all sequences was counted. More accurate (Z=1.96 is used as threshold) Method 2: Each pair of sequences was compared and the number of nucleotide differences in positions called in both sequences was counted. More robust (Z=3.29 is used as threshold)
36 Method 1 all called Significant posi<ons in Genome 1 Significant posi<ons in Genome 2 Significant posi<ons in Genome 3 Posi<ons used for phylogeny Method 2 pairwise called Significant posi<ons in Genome 1 Significant posi<ons in Genome 2 Significant posi<ons in Genome 3 Posi<ons used between 1 and 2 Posi<ons used between 1 and 3 Posi<ons used between 2 and 3
37 NDtree Uses two different algorithms to make two different trees UPGMA Neighbor Joining Both algorithms are part of the PHYLIP Neighbor program package and make trees from distance matrices
38 UPGMA vs. Neighbor Joining UPGMA works when samples have been taken the same time Neighbor Joining is better when samples have been taken at different times
39 NDtree Output distance.txt: Distance matrix - tab separated dist.mat: Distance matrix - PHYLIP format tree.nj.newick: Neighbor Joining tree - Newick format Branch lengths is number of Nucleotide Differences tree.upgma.newick: UPGMA tree Newick format Branch lengths is number of Nucleotide Differences
40 Controlled Evolution study Single$ colonies$of$ CSH114$ Choose$colony$ Grow$for$8$h$$ Plate$out$ Grow$for$16$h$ Choose$colonies$ Grow$for$8$h$ Plate$out$ Grow$for$16$h$ Choose$colonies$ Grow$for$8$h$ 128x$ Day$1$ Day$2$ Day$3$ $$$$$ $$$$$$$$$$$$$$Day$8$$ For$each$8$hour$culture$a$sample$was$saved$for$DNA$sequencing$ J. Ahrenfeldt, C. Skaarup, H. Hasman, A. G. Pedersen, F. M. Aarestrup and O. Lund. Bacterial whole genome- based phylogeny: construc<on of a new benchmarking dataset and assessment of some exis<ng methods. BMC Genomics (2017) 18:19
41 Naming the descendants Day$1 Day$2 Day$3 Day$4 Day$5 S1111 S111 S1112 S11 S1121 S112 S1122 S1 S1211 S121 S1212 S12 S1221 S122 S1222 S S2111 S211 S2112 S21 S2121 S212 S2122 S2 S2211 S221 S2212 S22 S2221 S222 S2222
42 Mutations
43 Phylogenetic tree using NDtree (UPGMA) S1 S11 S112 S1121 S1122 S111 S1111 S1112 S1212 S121 S1211 S1221 S12 S1222 S122 S S2 S2211 S221 S2212 S22 S2221 S222 S2111 S211 S2112 S21 S212 S2121 S2122
44 Phylogenetic tree using NDtree (Neighbor Joining) S S11 S111 S1111 S1112 S112 S1121 S1122 S1212 S121 S1211 S1222 S1221 S122 S12 S1 S2111 S211 S2112 S212 S2121 S2122 S21 S2211 S2212 S221 S2221 S222 S22 S2
45 UPGMA vs. Neighbor Joining UPGMA works when samples have been taken the same time Neighbor Joining is better when samples have been taken at different times
46 CSI Phylogeny Default settings 1_1_1_1 1_1_1_2 1_1_1 1_1_2_1 1_1_2_2 1_1_2 1_1 1_2_1 1_2_2_1 1_2_2_2 1_2_2 1_2 1 c_1_1_1_2_1 e_1_1_2_1_1 f_1_1_2_1_2 f_2_1_1 g_1_1_2_2_1 h_1_1_2_2_2 m_1_2_2_1_1 n_1_2_2_1_2 o_1_2_2_2_1 d_1_1_1_2_2 b_1_1_1_1_2 1_2_1_1 i_1_2_1_1_1 1_2_1_2 k_1_2_1_2_1 l_1_2_1_2_2 a_1_1_1_1_1 j_1_2_1_1_2 b_1_2_2 0.2
47 CSI Phylogeny Pruning disabled S S1 S11 S112 S2 S121 S1211 S1212 S12 S122 S1221 S1222 S1112 S1111 S111 S1121 S1122 S21 S2111 S211 S2112 S2122 S2121 S212 S221 S2211 S2212 S2221 S222 S22 0.2
48 So What should I use when? CSI Phylogeny Has very good statistics and a good graphical overview. Advantageous to use when you expect the differences between the isolates to be larger than 5-10 mutations. Is faster NDtree Is able to find very small differences. Does not take recombination into consideration. Works best on raw reads. If given assembled genomes, it simulates reads.
49 Choosing a reference genome For comparison of very closely related isolates, a better level of detail is given by using a closely related reference genome.
50 What defines an outbreak We can t tell for certain It depends on the species But a rule of thump is: Within 10 SNPs it is definitely an outbreak Within 30 SNPs it might be an outbreak Above 60 SNPs it is most likely not an outbreak
51 A.C. Schürch et al. / Clinical Microbiology and Infection xxx (2018) 1e5 3 Table 1 Examples of relatedness criteria for wg/cgmlst and SNP typing schemes of representative clinically relevant bacteria Organism Relatedness threshold a References wg/cgmlst (allele) SNPs Acinetobacter baumannii 8 3 [25,26] Brucella spp. Epidemiologic validation in progress b Campylobacter coli, C. jejuni [27,28] Cronobacter spp. Epidemiologic validation in progress b Clostridium difficile Epidemiologic validation in progress b 4 [29], Enterococcus faecium [30] Enterococcus raffinosus Epidemiologic validation in progress b Escherichia coli [31,32], Francisella tularensis 1 2 [33,34] Klebsiella oxytoca Epidemiologic validation in progress b Klebsiella pneumonia [35,36] Legionella pneumophila 4 15 [37] Listeria monocytogenes 10 3 [38,39] Mycobacterium abscessus 30 [40] Mycobacterium tuberculosis [41] Neisseria gonorrhoeae Epidemiologic validation in progress b 14 [42], Neisseria meningitidis Epidemiologic validation in progress b Pseudomonas aeruginosa [31,43] Salmonella dublin Epidemiologic validation in progress b 13 [44], Salmonella enterica Epidemiologic validation in progress b 4 [45], Salmonella typhimurium Epidemiologic validation in progress b 2 [46], Staphylococcus aureus [47,48] Streptococcus suis 21 [49] Vibrio parahaemolyticus 10 [50] Yersinia spp. 0 [51] cg, core genome; MLST, multilocus sequence typing; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; wg, whole genome. a Data often represent single studies that can be used to begin formulation of species-specific interpretation criteria. Thus, these data should be coupled with newly published similar studies to ensure that resulting values are not atypical and can be generally applied. b Proposed wg/cgmlst schemes are available online ( but as yet have not been epidemiologically validated.
52 A cool new thing called Evergreen Every 24 hours For every sample Databases Download all new data from SRA/ENA Typing Find closest match in homology reduced database NCBI Infer/recalculate phylogenetic tree For each reference genome with new mapped samples. Infer tree from cluster representatives and add the redundant isolates to their respective nodes based on the clustering Map to closest match Find the phylogenetic distance to consensus sequences for the given reference. Cluster isolates with < 10 SNPs distance Hobohm 1 homology reduction on new, non-clustered isolates Homology reduced database Hobohm 1 clustering to 99% homology on all bacterial reference genomes from NCBI Database of previous homology reduced isolates (representative consensus sequence) and redundant isolates
53 Downloaded and identified by March 9 th 2018 Species Total Included in a tree Salmonella enterica Escherichia coli Listeria monocytogenes Campylobacter jejuni Shigella sonnei Shigella 8lexneri Shigella boydii Campylobacter coli Salmonella bongori 9 9 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 7 3 Escherichia albertii 6 5 Hafnia alvei 4 3 Klebsiella pneumoniae 4 3 Bacillus subtilis 3 3 Bacillus thuringiensis 3 0 Providencia stuartii 2 2 Enterobacter cloacae 2 1 Proteus mirabilis 2 2 Streptococcus agalactiae 1 1 Peptoclostridium dif=icile 1 1 Staphylococcus epidermidis 1 1 Leuconostoc citreum 1 0 Streptococcus pasteurianus 1 0 Shigella dysenteriae 1 1 Raoultella ornithinolytica 1 1 In total
54
55 Thank you for listening Questions?
Introduction to the SNP/ND concept - Phylogeny on WGS data
 Introduction to the SNP/ND concept - Phylogeny on WGS data Johanne Ahrenfeldt PhD student Overview What is Phylogeny and what can it be used for Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) methods CSI Phylogeny
Introduction to the SNP/ND concept - Phylogeny on WGS data Johanne Ahrenfeldt PhD student Overview What is Phylogeny and what can it be used for Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) methods CSI Phylogeny
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th November 2009
 Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
Tetracycline Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 20 th November 2009 Introduction The natural tetracyclines, including tetracycline, chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline and demethylchlortetracycline
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309. Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012
 MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
MICROBIAL BIOCHEMISTRY BIOT 309 Dr. Leslye Johnson Sept. 30, 2012 Phylogeny study of evoluhonary relatedness among groups of organisms (e.g. species, populahons), which is discovered through molecular
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures
 Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
Microbial Typing by Machine Learned DNA Melt Signatures Nadya Andini 1, Bo Wang 2, Pornpat Athamanolap 3, Justin Hardick 4, Billie J. Masek 5, Simone Thair 1, Annie Hu 1, Gideon Avornu 5, Stephen Peterson
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) - there s a new tool in town. Henrik Hasman DTU - Food
 Whole genome sequencing (WGS) - there s a new tool in town Henrik Hasman DTU - Food Welcome to the NGS world TODAY Welcome Introduction to Next Generation Sequencing DNA purification (Hands-on) Lunch (Sandwishes
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) - there s a new tool in town Henrik Hasman DTU - Food Welcome to the NGS world TODAY Welcome Introduction to Next Generation Sequencing DNA purification (Hands-on) Lunch (Sandwishes
Bacterial whole genome-based phylogeny: construction of a new benchmarking dataset and assessment of some existing methods
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 29, 2018 Bacterial whole genome-based phylogeny: construction of a new benchmarking dataset and assessment of some existing methods Ahrenfeldt, Johanne; Skaarup, Carina;
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 29, 2018 Bacterial whole genome-based phylogeny: construction of a new benchmarking dataset and assessment of some existing methods Ahrenfeldt, Johanne; Skaarup, Carina;
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) as a tool for monitoring purposes. Henrik Hasman DTU - Food
 Whole genome sequencing (WGS) as a tool for monitoring purposes Henrik Hasman DTU - Food The Challenge Is to: Continue to increase the power of surveillance and diagnostic using molecular tools Develop
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) as a tool for monitoring purposes Henrik Hasman DTU - Food The Challenge Is to: Continue to increase the power of surveillance and diagnostic using molecular tools Develop
Product Catalogue 2015 Clinical and Industrial Microbiology
 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aggregatibacter aphrophilus ATCC 7901 * 89091 Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC
Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aggregatibacter aphrophilus ATCC 7901 * 89091 Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC
Product Catalogue 2016 Clinical and Industrial Microbiology
 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 * 89174 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 35654
Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC BAA-747 * 89141 Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 19606 * 89174 Actinomyces odontolyticus ATCC 17929 * 89114 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 7966 * 89119 Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC 35654
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN
 INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
INTERPRETATION OF THE GRAM STAIN DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
Most common dose (mg) 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1. Maximum dose schedule (mg) 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1 1g x 1
 Ertapenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.3 1 st June 2009 Introduction Ertapenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Ertapenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
Ertapenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.3 1 st June 2009 Introduction Ertapenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Ertapenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table:
 Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
THEORY. Based on sequence Length According to the length of sequence being compared it is of following two types
 Exp 11- THEORY Sequence Alignment is a process of aligning two sequences to achieve maximum levels of identity between them. This help to derive functional, structural and evolutionary relationships between
Exp 11- THEORY Sequence Alignment is a process of aligning two sequences to achieve maximum levels of identity between them. This help to derive functional, structural and evolutionary relationships between
Gentamicin Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th February, 2009
 Gentamicin Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.2 16 th February, 2009 Introduction The aminoglycosides are a group of naturally occurring or semi-synthetic compounds with bactericidal
Gentamicin Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.2 16 th February, 2009 Introduction The aminoglycosides are a group of naturally occurring or semi-synthetic compounds with bactericidal
Taxonomy. Content. How to determine & classify a species. Phylogeny and evolution
 Taxonomy Content Why Taxonomy? How to determine & classify a species Domains versus Kingdoms Phylogeny and evolution Why Taxonomy? Classification Arrangement in groups or taxa (taxon = group) Nomenclature
Taxonomy Content Why Taxonomy? How to determine & classify a species Domains versus Kingdoms Phylogeny and evolution Why Taxonomy? Classification Arrangement in groups or taxa (taxon = group) Nomenclature
EZ-COMP EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Product Details
 EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Mixed microorganism populations Identified by codes rather than descriptions Refrigerated storage Traceable to reference culture Product warranty Product Details
EZ-COMP For Training and Proficiency Testing Mixed microorganism populations Identified by codes rather than descriptions Refrigerated storage Traceable to reference culture Product warranty Product Details
Comparative Genomics Background & Strategy. Faction 2
 Comparative Genomics Background & Strategy Faction 2 Overview Introduction to comparative genomics Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Heidelberg Comparative Genomics Faction 2 Objectives Genomic
Comparative Genomics Background & Strategy Faction 2 Overview Introduction to comparative genomics Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Heidelberg Comparative Genomics Faction 2 Objectives Genomic
Alternative tools for phylogeny. Identification of unique core sequences
 Alternative tools for phylogeny Identification of unique core sequences Workshop on Whole Genome Sequencing and Analysis, 19-21 Mar. 2018 Learning objective: After this lecture you should be able to account
Alternative tools for phylogeny Identification of unique core sequences Workshop on Whole Genome Sequencing and Analysis, 19-21 Mar. 2018 Learning objective: After this lecture you should be able to account
EUCAST Expert Rules Version 3.1. Intrinsic Resistance and Exceptional Phenotypes Tables
 EUCAST Expert s Version 3.1 Intrinsic Resistance and Exceptional Phenotypes Tables EUCAST Expert s version 2.0 was published on 29 October 2011(http://www.eucast.org/expert_rules). The expert rules have
EUCAST Expert s Version 3.1 Intrinsic Resistance and Exceptional Phenotypes Tables EUCAST Expert s version 2.0 was published on 29 October 2011(http://www.eucast.org/expert_rules). The expert rules have
Toronto General Hospital ANTIBIOGRAM Emergency Department January 1, December 31, 2016
 IV (meningitis) IV (non-meningitis) (meningitis) (non-meningitis) Blood Isolates % Susceptible 644 18 36 70 78 74 59 69 75 262 100 19 64 75 100 92 54 72 78 76 68 89 86 99 Escherichia coli 153 58 30 67
IV (meningitis) IV (non-meningitis) (meningitis) (non-meningitis) Blood Isolates % Susceptible 644 18 36 70 78 74 59 69 75 262 100 19 64 75 100 92 54 72 78 76 68 89 86 99 Escherichia coli 153 58 30 67
Microbial Taxonomy. Classification of living organisms into groups. A group or level of classification
 Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
Most common dose (mg) 1 g x 3 1 g x mg -1.0 g x 3 1 g x mg -1 g x mg -1 g x 3
 Meropenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.5 1 st June 2009 Introduction Meropenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Meropenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
Meropenem Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.5 1 st June 2009 Introduction Meropenem is a carbapenem, available only for parenteral use. Meropenem is relevant for therapy of septicaemia,
Nitroxoline Rationale for the NAK clinical breakpoints, version th October 2013
 Nitroxoline Rationale for the NAK clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 4 th October 2013 Foreword NAK The German Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Committee (NAK - Nationales Antibiotika-Sensitivitätstest
Nitroxoline Rationale for the NAK clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 4 th October 2013 Foreword NAK The German Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Committee (NAK - Nationales Antibiotika-Sensitivitätstest
Stepping stones towards a new electronic prokaryotic taxonomy. The ultimate goal in taxonomy. Pragmatic towards diagnostics
 Stepping stones towards a new electronic prokaryotic taxonomy - MLSA - Dirk Gevers Different needs for taxonomy Describe bio-diversity Understand evolution of life Epidemiology Diagnostics Biosafety...
Stepping stones towards a new electronic prokaryotic taxonomy - MLSA - Dirk Gevers Different needs for taxonomy Describe bio-diversity Understand evolution of life Epidemiology Diagnostics Biosafety...
Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes
 Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Department of Systems Biology Dave Ussery! DTU course 27105 - Comparative Genomics Oksana s 61 E. coli genomes paper! Monday, 23
Comparison of 61 E. coli genomes Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Department of Systems Biology Dave Ussery! DTU course 27105 - Comparative Genomics Oksana s 61 E. coli genomes paper! Monday, 23
Design of an Enterobacteriaceae Pan-genome Microarray Chip
 Design of an Enterobacteriaceae Pan-genome Microarray Chip Oksana Lukjancenko and David W. Ussery DTU CBS 2010 2 Background Pan-genome complete collection of variuos genes located within populations at
Design of an Enterobacteriaceae Pan-genome Microarray Chip Oksana Lukjancenko and David W. Ussery DTU CBS 2010 2 Background Pan-genome complete collection of variuos genes located within populations at
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm
 Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
3M Food Safety Technical Bulletin
 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count Plate Performance Summary 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count (AQHC) Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water. Each plate
3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count Plate Performance Summary 3M Petrifilm Aqua Heterotrophic Count (AQHC) Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water. Each plate
SENCA: A codon substitution model to better estimate evolutionary processes
 SENCA: A codon substitution model to better estimate evolutionary processes Fanny Pouyet Marc Bailly-Bechet, Dominique Mouchiroud and Laurent Guéguen LBBE - UCB Lyon - UMR 5558 June 2015, Porquerolles,
SENCA: A codon substitution model to better estimate evolutionary processes Fanny Pouyet Marc Bailly-Bechet, Dominique Mouchiroud and Laurent Guéguen LBBE - UCB Lyon - UMR 5558 June 2015, Porquerolles,
Figure S1. Pangenome plots of ten recombining bacterial species based on RAST annotated
 Figure S1 Figure S2 Supplementary Figure legends Figure S1. Pangenome plots of ten recombining bacterial species based on RAST annotated genomes. To generate these plots all strains within a species were
Figure S1 Figure S2 Supplementary Figure legends Figure S1. Pangenome plots of ten recombining bacterial species based on RAST annotated genomes. To generate these plots all strains within a species were
10ml. Set (4 poly and 17 monovalent, 2ml each)
 120314TR Bordetella pertussis Antigen 10ml Contents 1 Bordetella pertussis Antigen 1 Clostridium perfringens Type A 2 Escherichia coli 5 Legionella pneumophila 5 Listeria monocytogenes 6 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
120314TR Bordetella pertussis Antigen 10ml Contents 1 Bordetella pertussis Antigen 1 Clostridium perfringens Type A 2 Escherichia coli 5 Legionella pneumophila 5 Listeria monocytogenes 6 Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Domain Bacteria. BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College
 Domain Bacteria BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College John Ireland, Ph.D. 2006 Scientific Nomenclature Domain - Bacteria Phylum Important for gross characteristics Class Intermediate characteristics
Domain Bacteria BIO 220 Microbiology Jackson Community College John Ireland, Ph.D. 2006 Scientific Nomenclature Domain - Bacteria Phylum Important for gross characteristics Class Intermediate characteristics
MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas
 December 12 th 2017 MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas Jim Cole Center for Microbial Ecology Dept. of Plant, Soil & Microbial Sciences Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan U.S.A. Where I m From
December 12 th 2017 MiGA: The Microbial Genome Atlas Jim Cole Center for Microbial Ecology Dept. of Plant, Soil & Microbial Sciences Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan U.S.A. Where I m From
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary information S1 (box). Supplementary Methods description. Prokaryotic Genome Database Archaeal and bacterial genome sequences were downloaded from the NCBI FTP site (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/)
Supplementary information S1 (box). Supplementary Methods description. Prokaryotic Genome Database Archaeal and bacterial genome sequences were downloaded from the NCBI FTP site (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/all/)
Chapter 19. Microbial Taxonomy
 Chapter 19 Microbial Taxonomy 12-17-2008 Taxonomy science of biological classification consists of three separate but interrelated parts classification arrangement of organisms into groups (taxa; s.,taxon)
Chapter 19 Microbial Taxonomy 12-17-2008 Taxonomy science of biological classification consists of three separate but interrelated parts classification arrangement of organisms into groups (taxa; s.,taxon)
μ gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli gyra E. coli parc gyra parc gyra Escherichia coli E. coli E.
 gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli μ E. coli gyra parc gyra parc gyra parc μ μ gyra parc Key words Escherichia coli gyra parc Escherichia coli E. coli gyra
gyra parc Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa E. coli μ E. coli gyra parc gyra parc gyra parc μ μ gyra parc Key words Escherichia coli gyra parc Escherichia coli E. coli gyra
Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria
 Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material
Mechanisms of Infectious Disease Fall 2009 Genetics I Jonathan Dworkin, PhD Department of Microbiology jonathan.dworkin@columbia.edu Genetic Basis of Variation in Bacteria I. Organization of genetic material
Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-257430.04 Rev.: Mar 2013 Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG INTENDED USE Partially selective medium for the isolation and differentiation of Enterobacteriaceae
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE READY-TO-USE PLATED MEDIA PA-257430.04 Rev.: Mar 2013 Bile Chrysoidin Glycerol Agar with MUG INTENDED USE Partially selective medium for the isolation and differentiation of Enterobacteriaceae
_ + Discriminates aerobic organisms that produce catalase to degrade hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen
 Lab 11 Goals and Objectives: Catalase Test Exercise 39: Oxidation and Fermentation Tests (Catalase) Exercise 67: Staphylococci Identification (MSA & Coagulase) Exercise 68: Streptococci & Enterococci Identification
Lab 11 Goals and Objectives: Catalase Test Exercise 39: Oxidation and Fermentation Tests (Catalase) Exercise 67: Staphylococci Identification (MSA & Coagulase) Exercise 68: Streptococci & Enterococci Identification
3M Food Safety Technical Bulletin
 3M Petrifilm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae Count Plates Performance Summary 3M Petrifi lm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae (AQEB) Count Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water.
3M Petrifilm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae Count Plates Performance Summary 3M Petrifi lm Aqua Enterobacteriaceae (AQEB) Count Plates are sample ready media plates used in the microbial testing of bottled water.
The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome. The minimal prokaryotic genome
 Dr. Dirk Gevers 1,2 1 Laboratorium voor Microbiologie 2 Bioinformatics & Evolutionary Genomics The bacterial species in the genomic era CTACCATGAAAGACTTGTGAATCCAGGAAGAGAGACTGACTGGGCAACATGTTATTCAG GTACAAAAAGATTTGGACTGTAACTTAAAAATGATCAAATTATGTTTCCCATGCATCAGG
Dr. Dirk Gevers 1,2 1 Laboratorium voor Microbiologie 2 Bioinformatics & Evolutionary Genomics The bacterial species in the genomic era CTACCATGAAAGACTTGTGAATCCAGGAAGAGAGACTGACTGGGCAACATGTTATTCAG GTACAAAAAGATTTGGACTGTAACTTAAAAATGATCAAATTATGTTTCCCATGCATCAGG
Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity
 19 Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Taxonomy Introduction to Microbial Taxonomy
19 Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Taxonomy Introduction to Microbial Taxonomy
by author ESCMID Online Lecture Library Epidemiological cutoff values (ECOFFs) and Low Level resistance Gunnar Kahlmeter
 Epidemiological cutoff values (ECOFFs) and Low Level resistance ECCMID 2010 Gunnar Kahlmeter Sweden Gunnar.Kahlmeter@ltkronoberg.se The epidemiological cutoff value ECOFF When breakpoints fail to detect
Epidemiological cutoff values (ECOFFs) and Low Level resistance ECCMID 2010 Gunnar Kahlmeter Sweden Gunnar.Kahlmeter@ltkronoberg.se The epidemiological cutoff value ECOFF When breakpoints fail to detect
Microbial Bioinformatics
 1 Microbial Bioinformatics Introduction These exercises are for you to learn how to use bioinformatics tools to explore bacterial genomes, and complements the Microbiology of Safe Food 2 nd Edition (Wiley-
1 Microbial Bioinformatics Introduction These exercises are for you to learn how to use bioinformatics tools to explore bacterial genomes, and complements the Microbiology of Safe Food 2 nd Edition (Wiley-
Microbiological Testing Summary
 BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY EN 1276 - Chemical disinfectants and antiseptics - Quantitative suspension test for the evaluation of bactericidal activity of chemical disinfectants and antiseptics used in food,
BACTERICIDAL ACTIVITY EN 1276 - Chemical disinfectants and antiseptics - Quantitative suspension test for the evaluation of bactericidal activity of chemical disinfectants and antiseptics used in food,
PHE Food and Water Microbiology External Quality Assessment Schemes
 Schedule: 1 January to 31 December 2018 PHE Food and Water Microbiology External Quality Assessment Schemes 0006 We aim to meet all the s in this document you will be advised as soon as possible if any
Schedule: 1 January to 31 December 2018 PHE Food and Water Microbiology External Quality Assessment Schemes 0006 We aim to meet all the s in this document you will be advised as soon as possible if any
Phylogenetic Diversity of Coliform Isolates in USA. Phylogenetic Classification
 Phylogenetic Diversity of Coliform Isolates in USA Ya Zhang and Wen Tso Liu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Mark LeChevallier American Water Inc. Nov 2011 Phylogenetic Classification group organisms
Phylogenetic Diversity of Coliform Isolates in USA Ya Zhang and Wen Tso Liu University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Mark LeChevallier American Water Inc. Nov 2011 Phylogenetic Classification group organisms
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary information S3 (box) Methods Methods Genome weighting The currently available collection of archaeal and bacterial genomes has a highly biased distribution of isolates across taxa. For example,
Supplementary information S3 (box) Methods Methods Genome weighting The currently available collection of archaeal and bacterial genomes has a highly biased distribution of isolates across taxa. For example,
Phylogene)cs. IMBB 2016 BecA- ILRI Hub, Nairobi May 9 20, Joyce Nzioki
 Phylogene)cs IMBB 2016 BecA- ILRI Hub, Nairobi May 9 20, 2016 Joyce Nzioki Phylogenetics The study of evolutionary relatedness of organisms. Derived from two Greek words:» Phle/Phylon: Tribe/Race» Genetikos:
Phylogene)cs IMBB 2016 BecA- ILRI Hub, Nairobi May 9 20, 2016 Joyce Nzioki Phylogenetics The study of evolutionary relatedness of organisms. Derived from two Greek words:» Phle/Phylon: Tribe/Race» Genetikos:
A Phylogenetic Gibbs Recursive Sampler for Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites
 A for Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites Sean P. Conlan 1 Lee Ann McCue 2 1,3 Thomas M. Smith 3 William Thompson 4 Charles E. Lawrence 4 1 Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health
A for Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites Sean P. Conlan 1 Lee Ann McCue 2 1,3 Thomas M. Smith 3 William Thompson 4 Charles E. Lawrence 4 1 Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health
Microbiology Helmut Pospiech
 Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Dr. habil. Anna Salek. Mikrobiologist Biotechnologist Research Associate
 Dr. habil. Anna Salek Mikrobiologist Biotechnologist Research Associate BIOTECHNOLOGY of Food Science Cell Biology of Microorganisms Physiology of Microorganisms Biochemistry of Microorganisms Molecularbiology
Dr. habil. Anna Salek Mikrobiologist Biotechnologist Research Associate BIOTECHNOLOGY of Food Science Cell Biology of Microorganisms Physiology of Microorganisms Biochemistry of Microorganisms Molecularbiology
GenomeTrakr: Data Submission and Analysis
 GenomeTrakr: Data Submission and Analysis Ruth Timme and Hugh Rand Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition U.S. Food Drug Administration IFSH Whole Genome Sequencing for Food Safety Symposium SEPTEMBER
GenomeTrakr: Data Submission and Analysis Ruth Timme and Hugh Rand Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition U.S. Food Drug Administration IFSH Whole Genome Sequencing for Food Safety Symposium SEPTEMBER
Our product offering. The ATCC Licensed Derivative Program
 Our product offering Currently MECCONTI offers three different product lines of lyophilized micro-organisms: MicroSwabs: A MicroSwab consists of a lyophilized pellet of a single micro-organism strain inside
Our product offering Currently MECCONTI offers three different product lines of lyophilized micro-organisms: MicroSwabs: A MicroSwab consists of a lyophilized pellet of a single micro-organism strain inside
Multiple Sequence Alignment. Sequences
 Multiple Sequence Alignment Sequences > YOR020c mstllksaksivplmdrvlvqrikaqaktasglylpe knveklnqaevvavgpgftdangnkvvpqvkvgdqvl ipqfggstiklgnddevilfrdaeilakiakd > crassa mattvrsvksliplldrvlvqrvkaeaktasgiflpe
Multiple Sequence Alignment Sequences > YOR020c mstllksaksivplmdrvlvqrikaqaktasglylpe knveklnqaevvavgpgftdangnkvvpqvkvgdqvl ipqfggstiklgnddevilfrdaeilakiakd > crassa mattvrsvksliplldrvlvqrvkaeaktasgiflpe
InDel 3-5. InDel 8-9. InDel 3-5. InDel 8-9. InDel InDel 8-9
 Lecture 5 Alignment I. Introduction. For sequence data, the process of generating an alignment establishes positional homologies; that is, alignment provides the identification of homologous phylogenetic
Lecture 5 Alignment I. Introduction. For sequence data, the process of generating an alignment establishes positional homologies; that is, alignment provides the identification of homologous phylogenetic
A. Incorrect! In the binomial naming convention the Kingdom is not part of the name.
 Microbiology Problem Drill 08: Classification of Microorganisms No. 1 of 10 1. In the binomial system of naming which term is always written in lowercase? (A) Kingdom (B) Domain (C) Genus (D) Specific
Microbiology Problem Drill 08: Classification of Microorganisms No. 1 of 10 1. In the binomial system of naming which term is always written in lowercase? (A) Kingdom (B) Domain (C) Genus (D) Specific
The Evolution of DNA Uptake Sequences in Neisseria Genus from Chromobacteriumviolaceum. Cory Garnett. Introduction
 The Evolution of DNA Uptake Sequences in Neisseria Genus from Chromobacteriumviolaceum. Cory Garnett Introduction In bacteria, transformation is conducted by the uptake of DNA followed by homologous recombination.
The Evolution of DNA Uptake Sequences in Neisseria Genus from Chromobacteriumviolaceum. Cory Garnett Introduction In bacteria, transformation is conducted by the uptake of DNA followed by homologous recombination.
Dr. Amira A. AL-Hosary
 Phylogenetic analysis Amira A. AL-Hosary PhD of infectious diseases Department of Animal Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Assiut University-Egypt Phylogenetic Basics: Biological
Phylogenetic analysis Amira A. AL-Hosary PhD of infectious diseases Department of Animal Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Assiut University-Egypt Phylogenetic Basics: Biological
The impact of the neisserial DNA uptake sequence on genome evolution and stability
 The impact of the neisserial DNA uptake sequence on genome evolution and stability Ole Herman Ambur The Tønjum Group Transformation Neisserial transformation requires: DNA uptake sequence (DUS) Transformation
The impact of the neisserial DNA uptake sequence on genome evolution and stability Ole Herman Ambur The Tønjum Group Transformation Neisserial transformation requires: DNA uptake sequence (DUS) Transformation
Development of Compact Dry SL for Salmonella detection
 Development of Compact Dry SL for Salmonella detection S.Mizuochi 1),H.Teramura 1),S.Nirazuka 1),H.Kodaka 1),K.Inoue ) K.Tamura 3) 1)Research Dept., Nissui Pharmaceutical, ) Saitama Pref. Ranzango Hp.,
Development of Compact Dry SL for Salmonella detection S.Mizuochi 1),H.Teramura 1),S.Nirazuka 1),H.Kodaka 1),K.Inoue ) K.Tamura 3) 1)Research Dept., Nissui Pharmaceutical, ) Saitama Pref. Ranzango Hp.,
CHN62: REPORTING OF MICROBIOLOGY RESULTS
 CHN62: 1.1 Introduction This SOP provides guidance on reporting of all the microbiological results in the Microbiology laboratory for CHAIN study. 1.2 Purpose This SOP will aid in a standard reporting
CHN62: 1.1 Introduction This SOP provides guidance on reporting of all the microbiological results in the Microbiology laboratory for CHAIN study. 1.2 Purpose This SOP will aid in a standard reporting
Multivariate analysis of genetic data: an introduction
 Multivariate analysis of genetic data: an introduction Thibaut Jombart MRC Centre for Outbreak Analysis and Modelling Imperial College London XXIV Simposio Internacional De Estadística Bogotá, 25th July
Multivariate analysis of genetic data: an introduction Thibaut Jombart MRC Centre for Outbreak Analysis and Modelling Imperial College London XXIV Simposio Internacional De Estadística Bogotá, 25th July
By Eliza Bielak Bacterial Genomics and Epidemiology, DTU-Food Supervised by Henrik Hasman, PhD
 By Eliza Bielak Bacterial Genomics and Epidemiology, DTU-Food elibi@food.dtu.dk Supervised by Henrik Hasman, PhD 1. Introduction to plasmid biology 2. Plasmid encoded resistance to β- lactams (basic theories)
By Eliza Bielak Bacterial Genomics and Epidemiology, DTU-Food elibi@food.dtu.dk Supervised by Henrik Hasman, PhD 1. Introduction to plasmid biology 2. Plasmid encoded resistance to β- lactams (basic theories)
Essentiality in B. subtilis
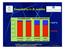 Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
Essentiality in B. subtilis 100% 75% Essential genes Non-essential genes Lagging 50% 25% Leading 0% non-highly expressed highly expressed non-highly expressed highly expressed 1 http://www.pasteur.fr/recherche/unites/reg/
The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Table 11.1 Classification of Selected Prokaryotes*
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Table 11.1 Classification of Selected Prokaryotes*
Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny
 Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny AP Curriculum Alignment Chapter 19 expands on the topics of phylogenies and cladograms, which are important to Big Idea 1. In order for students to understand
Chapter 19: Taxonomy, Systematics, and Phylogeny AP Curriculum Alignment Chapter 19 expands on the topics of phylogenies and cladograms, which are important to Big Idea 1. In order for students to understand
Phylogenetic analyses. Kirsi Kostamo
 Phylogenetic analyses Kirsi Kostamo The aim: To construct a visual representation (a tree) to describe the assumed evolution occurring between and among different groups (individuals, populations, species,
Phylogenetic analyses Kirsi Kostamo The aim: To construct a visual representation (a tree) to describe the assumed evolution occurring between and among different groups (individuals, populations, species,
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Microbiology Course Design 2015-2016 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 205 (SUN# BIO 2205) Title Microbiology Credits 4 Developed by Ed Butler/Revised by Willis
Stability. Received for publication 1 August to be fl-lactamase-producing strains.
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1978, p. 584-588 0066-4804/78/0013-0584$02.00/0 Copyright X) 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Cefaclor: In Vitro Spectrum
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Apr. 1978, p. 584-588 0066-4804/78/0013-0584$02.00/0 Copyright X) 1978 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Cefaclor: In Vitro Spectrum
Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Algorithms in Bioinformatics Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA khuri@cs.sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Distance Methods Character Methods
Algorithms in Bioinformatics Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA khuri@cs.sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Distance Methods Character Methods
Microbial Diversity and Assessment (II) Spring, 2007 Guangyi Wang, Ph.D. POST103B
 Microbial Diversity and Assessment (II) Spring, 007 Guangyi Wang, Ph.D. POST03B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/marinefungi/ocn403webpage.htm General introduction and overview Taxonomy [Greek
Microbial Diversity and Assessment (II) Spring, 007 Guangyi Wang, Ph.D. POST03B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/marinefungi/ocn403webpage.htm General introduction and overview Taxonomy [Greek
The emergence of a new phage type of Salmonella Typhimurium in humans and animals in New Zealand
 Introduction The emergence of a new phage type of Salmonella Typhimurium in humans and animals in New Zealand M Dufour AIMS NZIMLS South Pacific Congress Gold Coast, August 2011 New Zealand is a geographically
Introduction The emergence of a new phage type of Salmonella Typhimurium in humans and animals in New Zealand M Dufour AIMS NZIMLS South Pacific Congress Gold Coast, August 2011 New Zealand is a geographically
08/21/2017 BLAST. Multiple Sequence Alignments: Clustal Omega
 BLAST Multiple Sequence Alignments: Clustal Omega What does basic BLAST do (e.g. what is input sequence and how does BLAST look for matches?) Susan Parrish McDaniel College Multiple Sequence Alignments
BLAST Multiple Sequence Alignments: Clustal Omega What does basic BLAST do (e.g. what is input sequence and how does BLAST look for matches?) Susan Parrish McDaniel College Multiple Sequence Alignments
A (short) introduction to phylogenetics
 A (short) introduction to phylogenetics Thibaut Jombart, Marie-Pauline Beugin MRC Centre for Outbreak Analysis and Modelling Imperial College London Genetic data analysis with PR Statistics, Millport Field
A (short) introduction to phylogenetics Thibaut Jombart, Marie-Pauline Beugin MRC Centre for Outbreak Analysis and Modelling Imperial College London Genetic data analysis with PR Statistics, Millport Field
Amira A. AL-Hosary PhD of infectious diseases Department of Animal Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Assiut
 Amira A. AL-Hosary PhD of infectious diseases Department of Animal Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Assiut University-Egypt Phylogenetic analysis Phylogenetic Basics: Biological
Amira A. AL-Hosary PhD of infectious diseases Department of Animal Medicine (Infectious Diseases) Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Assiut University-Egypt Phylogenetic analysis Phylogenetic Basics: Biological
Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss
 Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss Methods Identification of orthologues, alignment and evolutionary distances A preliminary set of orthologues was
Supplementary Information for Hurst et al.: Causes of trends of amino acid gain and loss Methods Identification of orthologues, alignment and evolutionary distances A preliminary set of orthologues was
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Detailed overview of the primer-free full-length SSU rrna library preparation.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed overview of the primer-free full-length SSU rrna library preparation. Detailed overview of the primer-free full-length SSU rrna library preparation. Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed overview of the primer-free full-length SSU rrna library preparation. Detailed overview of the primer-free full-length SSU rrna library preparation. Supplementary Figure
Phylogenetic Gibbs Recursive Sampler. Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites
 A for Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites Sean P. Conlan 1 Lee Ann McCue 2 1,3 Thomas M. Smith 3 William Thompson 4 Charles E. Lawrence 4 1 Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health
A for Locating Transcription Factor Binding Sites Sean P. Conlan 1 Lee Ann McCue 2 1,3 Thomas M. Smith 3 William Thompson 4 Charles E. Lawrence 4 1 Wadsworth Center, New York State Department of Health
Bacterial clasification
 Bacterial clasification Describe bacterial classification: List taxon levels Define taxonomy and identification Describe principles of taxonomy Explain classification of bacteria Taxonomy the science of
Bacterial clasification Describe bacterial classification: List taxon levels Define taxonomy and identification Describe principles of taxonomy Explain classification of bacteria Taxonomy the science of
MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT FOR CONSTRUCTION OF PHYLOGENETIC TREE
 MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT FOR CONSTRUCTION OF PHYLOGENETIC TREE Manmeet Kaur 1, Navneet Kaur Bawa 2 1 M-tech research scholar (CSE Dept) ACET, Manawala,Asr 2 Associate Professor (CSE Dept) ACET, Manawala,Asr
MULTIPLE SEQUENCE ALIGNMENT FOR CONSTRUCTION OF PHYLOGENETIC TREE Manmeet Kaur 1, Navneet Kaur Bawa 2 1 M-tech research scholar (CSE Dept) ACET, Manawala,Asr 2 Associate Professor (CSE Dept) ACET, Manawala,Asr
HACCP: INTRODUCTION AND HAZARD ANALYSIS
 Food Hygiene HACCP: INTRODUCTION AND HAZARD ANALYSIS State: December 15, 2004 WPF 5/0 Important milestones in the development of food safety systems Time Activity Distant past Use of prohibition principle
Food Hygiene HACCP: INTRODUCTION AND HAZARD ANALYSIS State: December 15, 2004 WPF 5/0 Important milestones in the development of food safety systems Time Activity Distant past Use of prohibition principle
Figure Page 117 Microbiology: An Introduction, 10e (Tortora/ Funke/ Case)
 Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
Chapter 11 The Prokaryotes: Domains Bacteria and Archaea Objective Questions 1) Which of the following are found primarily in the intestines of humans? A) Gram-negative aerobic rods and cocci B) Aerobic,
11/5/2018. Update on Modern Bacterial Taxonomy for Bench Microbiologists. Why is Taxonomy Important? Bacterial Taxonomy for Clinical Microbiologists
 Update on Modern Bacterial Taxonomy for Bench Microbiologists J. Michael Janda Kern County Public Health Laboratory Bakersfield CA The Name Game Which Ones Different? Why is Taxonomy Important? Bacterial
Update on Modern Bacterial Taxonomy for Bench Microbiologists J. Michael Janda Kern County Public Health Laboratory Bakersfield CA The Name Game Which Ones Different? Why is Taxonomy Important? Bacterial
INTRODUCTION MATERIALS & METHODS
 Evaluation of Three Bacterial Transport Systems, The New Copan M40 Transystem, Remel Bactiswab And Medical Wire & Equipment Transwab, for Maintenance of Aerobic Fastidious and Non-Fastidious Organisms
Evaluation of Three Bacterial Transport Systems, The New Copan M40 Transystem, Remel Bactiswab And Medical Wire & Equipment Transwab, for Maintenance of Aerobic Fastidious and Non-Fastidious Organisms
Curriculum Links. AQA GCE Biology. AS level
 Curriculum Links AQA GCE Biology Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors Causes of variation 3.2.2
Curriculum Links AQA GCE Biology Unit 2 BIOL2 The variety of living organisms 3.2.1 Living organisms vary and this variation is influenced by genetic and environmental factors Causes of variation 3.2.2
Bacteria Outline. 1. Overview. 2. Structural & Functional Features. 3. Taxonomy. 4. Communities
 Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities Bacteria - Taxonomy PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES SUB-SPECIES & STRAINS Bacteria - Phyla Firmicutes
Bacteria Outline 1. Overview 2. Structural & Functional Features 3. Taxonomy 4. Communities Bacteria - Taxonomy PHYLUM CLASS ORDER FAMILY GENUS SPECIES SUB-SPECIES & STRAINS Bacteria - Phyla Firmicutes
CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing Technique for Salmonella Subtyping
 Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
Department of Biological Sciences Seminar Blog Seminar Date: 3/23/18 Speaker: Dr. Nikki Shariat, Gettysburg College Title: Probing Salmonella population diversity using CRISPRs CRISPR-SeroSeq: A Developing
8/23/2014. Phylogeny and the Tree of Life
 Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Phylogeny and the Tree of Life Chapter 26 Objectives Explain the following characteristics of the Linnaean system of classification: a. binomial nomenclature b. hierarchical classification List the major
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan
 Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Test Bank for Microbiology A Systems Approach 3rd edition by Cowan Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bankfor-microbiology-a-systems-approach-3rd-by-cowan/ Chapter 1: The Main Themes
Survey of plasmid profiles of Shigella species isolated in Malaysia during
 World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology (2005) 21: 271 278 Ó Springer 2005 DOI 10.1007/s11274-004-3631-0 Survey of plasmid profiles of Shigella species isolated in Malaysia during 1994 2000 C.H.
World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology (2005) 21: 271 278 Ó Springer 2005 DOI 10.1007/s11274-004-3631-0 Survey of plasmid profiles of Shigella species isolated in Malaysia during 1994 2000 C.H.
Whole Genome Alignment. Adam Phillippy University of Maryland, Fall 2012
 Whole Genome Alignment Adam Phillippy University of Maryland, Fall 2012 Motivation cancergenome.nih.gov Breast cancer karyotypes www.path.cam.ac.uk Goal of whole-genome alignment } For two genomes, A and
Whole Genome Alignment Adam Phillippy University of Maryland, Fall 2012 Motivation cancergenome.nih.gov Breast cancer karyotypes www.path.cam.ac.uk Goal of whole-genome alignment } For two genomes, A and
CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1
 CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 2/13 2/14 - B 2/15 2/16 - B 2/17 2/20 Intro to Viruses Viruses VS Cells 2/21 - B Virus Reproduction Q 1-2 2/22 2/23
CLASSIFICATION UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 3/1 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 2/13 2/14 - B 2/15 2/16 - B 2/17 2/20 Intro to Viruses Viruses VS Cells 2/21 - B Virus Reproduction Q 1-2 2/22 2/23
C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence. Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy
 C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development
C. elegans as an in vivo model to decipher microbial virulence Centre d Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy C. elegans : a model organism Mechanisms of apoptosis, RNA interference Neuronal function and development
MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTING DETAILS. S. No. Test Description Test Method 01 HPC APHA 9215 B. 02 Total Coliforms by Membrane Filtration APHA 9222 B
 MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTING DETAILS WATER SAMPLE ANALYSIS DETAILS: 1. DRINKING WATER OR POTABLE WATER OR UNBOTTLED WATER: 02 Total Coliforms by Membrane Filtration APHA 9222 B 03 Fecal Coliforms by Membrane
MICROBIOLOGICAL TESTING DETAILS WATER SAMPLE ANALYSIS DETAILS: 1. DRINKING WATER OR POTABLE WATER OR UNBOTTLED WATER: 02 Total Coliforms by Membrane Filtration APHA 9222 B 03 Fecal Coliforms by Membrane
Other tools for typing and phylogeny
 Other tools for typing and phylogeny Workshop on Whole Genome Sequencing and Analysis, 27-29 Mar. 2017 Learning objective: After this lecture you should be able to account for tools for typing Salmonella
Other tools for typing and phylogeny Workshop on Whole Genome Sequencing and Analysis, 27-29 Mar. 2017 Learning objective: After this lecture you should be able to account for tools for typing Salmonella
PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 11 Chapter 26 Activity #15 NAME DATE PERIOD PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS PHYLOGENY Evolutionary history of species or group of related species SYSTEMATICS Study
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 11 Chapter 26 Activity #15 NAME DATE PERIOD PHYLOGENY AND SYSTEMATICS PHYLOGENY Evolutionary history of species or group of related species SYSTEMATICS Study
Quantifying sequence similarity
 Quantifying sequence similarity Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, February 16 th 2016 After this lecture, you can define homology, similarity, and identity
Quantifying sequence similarity Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, February 16 th 2016 After this lecture, you can define homology, similarity, and identity
Phylogenetic inference
 Phylogenetic inference Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, March 7 th 016 After this lecture, you can discuss (dis-) advantages of different information types
Phylogenetic inference Bas E. Dutilh Systems Biology: Bioinformatic Data Analysis Utrecht University, March 7 th 016 After this lecture, you can discuss (dis-) advantages of different information types
A Phylogenetic Network Construction due to Constrained Recombination
 A Phylogenetic Network Construction due to Constrained Recombination Mohd. Abdul Hai Zahid Research Scholar Research Supervisors: Dr. R.C. Joshi Dr. Ankush Mittal Department of Electronics and Computer
A Phylogenetic Network Construction due to Constrained Recombination Mohd. Abdul Hai Zahid Research Scholar Research Supervisors: Dr. R.C. Joshi Dr. Ankush Mittal Department of Electronics and Computer
