Briefing The Ming Dynasty of China
|
|
|
- Philippa Johnson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Briefing The Ming Dynasty of China The Ming Dynasty of China was the superpower of its day. Here are a few key facts about the Ming: - The Dynasty lasted 276 years (from 1368 to 1644, longer than the United States so far). - It had more than 160 million people (the size of the United States after World War II). - It had a powerful navy and an army of more than a million soldiers. - Ming printers used metal movable type, 230 years before Gutenberg in Europe. - Ming scientists knew how to control gunpowder and use it for road construction. - Ming military engineers built the first effective cannons and rocket launchers. - Ming explorers used magnetic compasses and the first ocean navigation charts. One Ming-era explorer, Zheng He, made several long trips in the early 1400s. That was 60 years before Columbus sailed from Europe to America. Zheng He s fleets traveled as far as Arabia and Africa. Some people think he may even have sailed all the way to South America. His flagship was nearly 500 feet long. Columbus s largest ship, the Santa Maria, was less than 100. Early in the Ming dynasty, the government organized 165,000 workers to expand the Grand Canal. This artificial river was more than a thousand miles long, about 3 times as long as the Erie Canal. On this canal, boats could move millions of pounds of grain from the fertile Yangtze Valley in south China to northern cities like Beijing. When the climate changed, however, even that enormous system was not enough to prevent starvation. And when the people ran out of food, they rebelled against the government. The huge army was not able to stop the anti-government riots. To see why, read the Student Reading, The Fall of the Mighty Ming P Gersmehl Teachers may copy for use in their own classrooms. For other uses, contact pgersmehl@gmail.com
2 Reading The Fall of the Mighty Ming In 1644, some soldiers ended a battle by eating the dead soldiers. It s true it really happened, and we can learn something useful from it (not about eating people about what can happen when the climate changes!) The story is about the Ming Dynasty of China, the superpower in the year (The background briefing has more facts about this powerful country.) Here is the big question: If the Ming Dynasty was so powerful, why did it collapse? Let s start with a science fact: Cold air usually has high air pressure. In 1583, the climate changed. The whole world got cooler. High air pressure pushed storms south of their normal position in Asia. North China became very dry, starting in Meanwhile, the storms caused big floods in southern China in 1585 and By 1588, half of the provinces of China had famines. People started to riot. By 1594, there were reports of people eating animal skins and the bark of trees. But wait.... things will get a lot worse. In 1600, the largest volcano in South American history erupted. The explosion was huge, at least ten times as big as Mt. St. Helens, the largest eruption in U.S. history. Clouds of volcanic ash blocked the sun. Temperatures dropped all around the world. By 1610, the growing season in China was nearly a month shorter than normal. All over north China, people moved away from fields that could no longer grow any food. The Manchu nomads to the north began to attack the Great Wall was the coldest time in 600 years. You already know that cold air makes north China dry started the worst five years of drought in Chinese history. People stripped bark from trees. They even started digging up corpses for food. Rebellions started again in many areas, adding to the death toll. After one battle, the commander ordered the surviving soldiers to cook the dead ones and eat them. Then, just when it seemed that things could not get any worse, another huge volcano erupted in This eruption had even more effect on China, because it happened nearby, in the Philippine islands. Heavy snow fell in south China (where the weather is usually like Florida). Meanwhile, north China got even drier. Grasshoppers invaded from the dry northern grasslands and ate what little crop was left. Riots continued. To save the capital from the rebel forces, the Ming general opened the gates in the Great Wall and invited the Manchu army to come in and attack the rebels. The Manchu warriors easily defeated the rebels. Then they turned on the Ming army and destroyed what was left of it. Some history websites say the fall of the Ming Dynasty was due to police brutality, bureaucratic rules, and other government policies. These are part of the story, but the real cause is simpler. When climate changed, and especially after the volcanoes erupted, China was no longer able to grow enough food to feed all its people. Project: draw a causal diagram to show the relationships between temperature, drought, floods, volcanoes, rebellions, grasshoppers, and invading nomadic armies P Gersmehl Teachers may copy for use in their own classrooms. For other uses, contact pgersmehl@gmail.com
3 Six Statements about the Fall of the Mighty Ming When you read, you should try to figure out the kind of knowledge in each sentence: Fact. A fact is an observation or measurement about an object or place. It is something someone else could also see or measure. Here are some examples: The air temperature at 2 o clock was 53 degrees. The population of China at the time of the Ming Dynasty was about 160 million. Theory. A theory is a statement about links between facts. In most theories, one fact is identified as the cause of some kind of change. That change, called the effect, is also a fact that can be observed or measured. The air will soon get warmer, because the rising sun will add energy to the ground, which in turn will make the air warmer. The dry weather caused locusts to migrate southward from the grasslands. Opinion. An opinion is a statement about whether we think something is good, important, or useful (or not!). Different people can have different opinions. I like it best when the temperature is about 65 degrees not too hot, not too cold. The Ming Dynasty was the most important government in the world at the time. Here are six sentences from the story about the fall of the Ming Dynasty. - Circle F if you think the sentence is a statement of fact. Then write whether you think the statement is true or false, and explain why. - Circle T if you think the sentence is a theory about causes and effects. Then write whether you think the theory is plausible (believable, supported by the facts, probably true) or not plausible, and explain why. - Circle O if you think the sentence is a statement of the author s opinion. Then write whether you think the opinion is reasonable, and explain why. F T O 1. A sudden worldwide cooling began in F T O 2. When the climate changed, even a canal was not able to prevent famine. F T O 3. Low air pressure pushed the storm tracks south of the normal position. F T O 4. In 1590, half of the provinces of China had major famines. F T O 5. This [Philippine] volcano had an greater effect on the climate of China, because it was closer than the one that erupted in South America. F T O 6. Rebellion was less important than climate change in causing famine P Gersmehl Teachers may copy for use in their own classrooms. For other uses, contact pgersmehl@gmail.com
4 Nine Statements about the Fall of the Mighty Ming The reading about the end of the Ming dynasty in China is a mixture of historic fact, scientific theory, and personal opinion. For each of the nine sentences below - Circle F if you think the sentence is a statement of fact. Then write whether you think the statement is true or false, and explain why. - Circle T if you think the sentence is a theory about causes and effects. Then write whether you think the theory is plausible (believable, supported by the facts, probably true) or not plausible, and explain why. - Circle O if you think the sentence is a statement of the author s opinion. Then write whether you think the opinion is reasonable or not. Explain why. F T O 1. A worldwide cooling began in F T O 2. When climate changed, even a canal was not enough to prevent famine. F T O 3. Clouds of volcanic ash blocked the sun, causing temperatures to go down. F T O 4. By 1588, half of the provinces of China had famines. F T O 5. This [Philippine] volcano had a greater effect on the climate of China, because it was closer than the one that erupted in South America. F T O 6. Cold air had low air pressure which pushed the storm tracks south, causing drought in the southern provinces along the Yangtze River. F T O 7. War was less important than climate change in causing famines. F T O started the worst five years of drought in Chinese history. F T O 9. The Ming general opened the gates in the Great Wall, giving the rebel army a choice of moving into Mongol country or staying and fighting. Bonus point. Another book about climate change in Europe noted that more than 1000 women were burned alive after they were accused of being witches and causing crops to fail in the early 1600s. Which idea does this fact seem to support? A. Climate change is a local event, confined to a single continent at a time. B. Climate change is a global event, affecting the entire world at the same time P Gersmehl Teachers may copy for use in their own classrooms. For other uses, contact pgersmehl@gmail.com
5 Nine Statements about the Fall of the Mighty Ming The reading about the end of the Ming dynasty in China is a mixture of historic fact, scientific theory, and personal opinion. For each of the nine sentences below - Circle F if you think the sentence is a statement of fact. Then write whether you think the statement is true or false, and explain why. - Circle T if you think the sentence is a theory about causes and effects. Then write whether you think the theory is plausible (believable, supported by the facts, probably true) or not plausible, and explain why. - Circle O if you think the sentence is a statement of the author s opinion. Then write whether you think the opinion is reasonable or not. Explain why. F T O 1. A worldwide cooling began in This is a fact, and it is true. Many people observed evidence of this cooling. F T O 2. When climate changed, even a canal was not enough to prevent famine. This is an opinion; it sounds reasonable, but someone else could form a different opinion from the same facts and theories. F T O 3. Clouds of volcanic ash blocked the sun, causing temperatures to go down. This is a theory statement, and it is plausible. F T O 4. In 1590, half of the provinces of China had famines. This is a fact statement, but it is false. Half the provinces had famines by F T O 5. This [Philippine] volcano had a greater effect on the climate of China, because it was closer than the one that erupted in South America. This theory statement is plausible things that are nearby tend to have more effect. F T O 6. Cold air had low air pressure which pushed the storm tracks south, causing drought in the southern provinces along the Yangtze River. This theory statement is not plausible, because cold air makes high pressure. F T O 7. War was less important than climate change in causing famines. This is an opinion, though the author does try to provide evidence to support it. F T O started the worst five years of drought in Chinese history. This is a fact statement, but it is false. The 5 years of drought started in F T O 9. The Ming general opened the gates in the Great Wall, giving the rebel army a choice of moving into Mongol country or staying and fighting. This is a fact statement. It is a fairly complicated sentence, and it is wrong. Bonus point. Another book about climate change in Europe noted that more than 1000 women were burned alive after they were accused of being witches and causing crops to fail in the early 1600s. Which idea does this fact seem to support? A. Climate change is a local event, confined to a single continent at a time. X B. Climate change is a global event, affecting the entire world at the same time P Gersmehl Teachers may copy for use in their own classrooms. For other uses, contact pgersmehl@gmail.com
6 China s Population History Millions 300 Ming 200 Han T ang Song Mongol Manchu C A L E N D A R Y E A R The Qin (pronounced Chin) was the first time that China was a single country. A dynasty is a ruling family. The Qin gave us the word China, but the Dynasty did not last long. The Han Dynasty took over and ruled for more than 400 years. 1. Write the word Qin near the population line just to the left (older) than the Han. The population at the beginning of the Han Dynasty was less than 20 million. By the year 0, the population had reached a peak of about Circle: million. (That s more than California and New York put together.) 2. What happened to the population from the year 0 to the end of the Han Dynasty? 3. Put an X by the best generalization about the start of the four big dynasties: a. They all started at a time of high population and lost people for 100 years. b. They all started at a time of low population and had rapid growth for awhile. The T ang Dynasty started just after China lost more than half of its people. This was a big problem, but it was not the worst time in Chinese history. 4. What was the highest population near the end of the Han Dynasty? 5. What was the population shortly after the end of the Han Dynasty? In 1234 the Mongols invaded northern China; the Song continued to rule south China. By 1279 the Mongols finally conquered the southern part and ruled over all of China. 6. Did the population go down more when the Mongols attacked the north or when they finally captured the south? 7. What was the highest population during the Ming Dynasty? 8. What was the low population shortly after the end of the Ming Dynasty? 2012 P Gersmehl Teachers may copy for use in their classrooms. Contact pgersmehl@gmail.com regarding permission for any other use.
7 Climate as an Influence on History Truth or Myth? There are many possible links between weather conditions, floods, locust attacks, crop yields, rebellions, enemy invasions, population migrations, and government collapse. Moreover, effects are not the same everywhere. For example, cold weather makes floods in South China, but it may cause rivers to dry up in Arizona. Even though things are complicated, some cause-and-effect links are true all over the world. On the list below, circle the large T if you are pretty sure that the statement is generally true. Circle the small t if you think the statement is more often true than not. Circle the small m if you think it is more often a myth, and the large M if you think it is almost always a myth. Circle the? if you are not sure, or you think it can go different ways in different places. Be prepared to discuss your reasons for your choices. 1. Lower annual temperature makes more floods in south China. 2. Lower annual temperature makes dry soil in North China. 3. Dry soil and withered grass (drought) make more locusts. 4. Dry soil makes cooler average temperature. 5. Dry soil makes higher yields of most crops. 6. Dry weather makes governments collapse. 7. Food shortage makes soil dry. 8. Food shortage makes rebellion more likely. 9. Government collapse causes food shortages. 10. Food shortage causes government collapse. 11. Locust attacks cause food shortages. 12. Food shortage causes migration to other places. Now that you have evaluated a number of statements individually, try to put several statements together into a more complete causal model. Put the following six words into the sentences below in their most plausible order, with the primary cause first: Locust attack Government collapse Drought Cool climate Food shortage Rebellion usually causes in north China; this can cause. Together they can cause, which can cause. The end result might be P Gersmehl Teachers may copy for use in their own classrooms. For other uses, contact pgersmehl@gmail.com
8 Cold Weather in China - A Cause-and Effect Model The graph of China s population and the reading about the collapse of the Ming dynasty both point to the same conclusion - changing climate had effects on human history To make a visual display of possible causes and effects, follow these steps: 1. Use the diagram below, or make your own on a separate piece of paper (if you would prefer to have the boxes arranged in a different way). 2. Identify things on the diagram that you think might be causes of other things. 3. Draw arrows from each cause to every event that is an effect of that cause. 4. Remember: a cause can have several effects, and an effect can have several causes. 5. Make your arrows thicker if you think the causal connection is really strong. 6. Remember: an effect of one cause can in turn be the cause of another effect. 7. Write a letter (A, B, or C) next to three arrows that you would like to discuss. 8. Write a brief explanation of the links you marked with letters. The Fall of the Mighty Ming Rebellion War Migration Locusts Crop Failure Famine Drought in North Cold Climate Floods in South Low Time of Sun Cycle Volcanic Eruption Each of these boxes represents an event that occurred during the collapse of the powerful Ming Dynasty in China. The arrows indicate cause-and-effect connections between different parts of this complex climate-land-population system. A. B. C P Gersmehl Teachers may copy for use in their classrooms. Contact pgersmehl@gmail.com regarding permission for any other use.
4 Changes in Climate. TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why is more land exposed during glacial periods than at other times?
 Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Name. El Nino. by Cindy Grigg
 Name El Nino by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1. What do you already know about El Nino?
Name El Nino by Cindy Grigg Answer the following questions BEFORE you read this book. It is okay if you do not know as much as you thought. Do the best you can! 1. What do you already know about El Nino?
Year 4 Geography Revision Pack Summer 2018 Name
 Year 4 Geography Revision Pack Summer 2018 Name Welcome to your geography revision pack for the upcoming Summer exams. Everything that we have been working on in lessons since Christmas will be covered
Year 4 Geography Revision Pack Summer 2018 Name Welcome to your geography revision pack for the upcoming Summer exams. Everything that we have been working on in lessons since Christmas will be covered
Thunderstorms written by Alice Lee Folkins
 STAPLE HERE Cover Photo: A cloud-to-ground lightning strike during a nighttime thunderstorn. Taken by C. Clark. Released into the public domain by NOAA. Level D written by Alice Lee Folkins 2015 Elfrieda
STAPLE HERE Cover Photo: A cloud-to-ground lightning strike during a nighttime thunderstorn. Taken by C. Clark. Released into the public domain by NOAA. Level D written by Alice Lee Folkins 2015 Elfrieda
Drought lesson plan ITEMS. Teachers lesson plan. Student assignments. About droughts. Real life stories. Droughts: Be prepared.
 Drought lesson plan The drought lesson plan provides teachers and students with an opportunity to investigate the Australian climate, water table and the impacts of drought through individual or classroom
Drought lesson plan The drought lesson plan provides teachers and students with an opportunity to investigate the Australian climate, water table and the impacts of drought through individual or classroom
Why has climate changed in the past? There are 3 main theories: 1) The eruption theory 2) The sunspot theory 3) The orbital theory
 Climate and Change Why has climate changed in the past? There are 3 main theories: 1) The eruption theory 2) The sunspot theory 3) The orbital theory The eruption theory: When a volcano erupts it throws
Climate and Change Why has climate changed in the past? There are 3 main theories: 1) The eruption theory 2) The sunspot theory 3) The orbital theory The eruption theory: When a volcano erupts it throws
Winter. Here s what a weak La Nina usually brings to the nation with tempseraures:
 2017-2018 Winter Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2017-2018. El Nino /
2017-2018 Winter Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2017-2018. El Nino /
Not all eruptions are the same. Sometimes, there is a huge explosion. The hot magma shoots
 Natural Disasters A natural disaster is an event that happens in nature. It is an event that can cause a lot of damage. Volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis are all natural disasters. Volcanoes A volcano
Natural Disasters A natural disaster is an event that happens in nature. It is an event that can cause a lot of damage. Volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis are all natural disasters. Volcanoes A volcano
Visit us at...
 Thanks for your purchase. We hope you are pleased. We think you might like the website that we are working on. You will find websites that go along with your unit and word wall cards. We hope you enjoy.
Thanks for your purchase. We hope you are pleased. We think you might like the website that we are working on. You will find websites that go along with your unit and word wall cards. We hope you enjoy.
Question #1: What are some ways that you think the climate may have changed in the area where you live over the past million years?
 Reading 5.2 Environmental Change Think about the area where you live. You may see changes in the landscape in that area over a year. Some of those changes are weather related. Others are due to how the
Reading 5.2 Environmental Change Think about the area where you live. You may see changes in the landscape in that area over a year. Some of those changes are weather related. Others are due to how the
Activity 2.2: Recognizing Change (Observation vs. Inference)
 Activity 2.2: Recognizing Change (Observation vs. Inference) Teacher Notes: Evidence for Climate Change PowerPoint Slide 1 Slide 2 Introduction Image 1 (Namib Desert, Namibia) The sun is on the horizon
Activity 2.2: Recognizing Change (Observation vs. Inference) Teacher Notes: Evidence for Climate Change PowerPoint Slide 1 Slide 2 Introduction Image 1 (Namib Desert, Namibia) The sun is on the horizon
Hurricanes. Where's the Really Bad Weather 1. What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide
 Where's the Really Bad Weather 1 Hurricanes What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide Where: Start over oceans, fizzle out over land Investigation 1 What is Weather?
Where's the Really Bad Weather 1 Hurricanes What: Rotating wind/rain storm Winds from 75 to 200 mph As big as 600 miles wide Where: Start over oceans, fizzle out over land Investigation 1 What is Weather?
Name period date assigned date due date returned. Natural Disasters
 Name period date assigned date due date returned Match the following natural disaster to its description. Write the capital letter of the definition in the blank in front of the natural disaster. 1. tornado
Name period date assigned date due date returned Match the following natural disaster to its description. Write the capital letter of the definition in the blank in front of the natural disaster. 1. tornado
Which graph best shows the relationship between intensity of insolation and position on the Earth's surface? A) B) C) D)
 1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
1. The hottest climates on Earth are located near the Equator because this region A) is usually closest to the Sun B) reflects the greatest amount of insolation C) receives the most hours of daylight D)
Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China. How does China s geography affect the culture?
 Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China How does China s geography affect the culture? Con$nents of the World Label the continents. Where is China located? Where is China located? In your groups, begin filling
Sec$on 1: Geography and Early China How does China s geography affect the culture? Con$nents of the World Label the continents. Where is China located? Where is China located? In your groups, begin filling
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
For Creative Minds. Grassland Habitat
 For Creative Minds The For Creative Minds educational section may be photocopied or printed from our website by the owner of this book for educational, non-commercial uses. Cross-curricular teaching activities,
For Creative Minds The For Creative Minds educational section may be photocopied or printed from our website by the owner of this book for educational, non-commercial uses. Cross-curricular teaching activities,
Warm Up Vocabulary Check
 Warm Up Vocabulary Check Surface current Coriolis Effect global winds upwelling Gulf Stream deep current climate El Nino convection current continental deflection 1.The apparent curving of the path of
Warm Up Vocabulary Check Surface current Coriolis Effect global winds upwelling Gulf Stream deep current climate El Nino convection current continental deflection 1.The apparent curving of the path of
1 Earth s Oceans. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify What are the five main oceans?
 CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
How Geographers View the World: Human Geography. ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How does geography influence the way people live?
 How Geographers View the World: Human Geography ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How does geography influence the way people live? Geographers Think Spatially Gefffffdgfhfjgjp Guiding Question: What does it mean to
How Geographers View the World: Human Geography ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How does geography influence the way people live? Geographers Think Spatially Gefffffdgfhfjgjp Guiding Question: What does it mean to
Where, on Earth, are you?
 Where, on Earth, are you? We all live on a big planet called Earth, of course. But where on Earth? And if you want to go to a different spot on Earth other than the spot you are in, how do you know which
Where, on Earth, are you? We all live on a big planet called Earth, of course. But where on Earth? And if you want to go to a different spot on Earth other than the spot you are in, how do you know which
Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes!
 Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes! A. Overview 1. Ocean in Motion -- El Nino and hurricanes We will look at the ocean-atmosphere interactions that cause El Nino and hurricanes. Using vocabulary
Ocean in Motion 7: El Nino and Hurricanes! A. Overview 1. Ocean in Motion -- El Nino and hurricanes We will look at the ocean-atmosphere interactions that cause El Nino and hurricanes. Using vocabulary
After school one day, Chris s great-grandfather asked him what he
 8 The Dust Bowl R O L E P L A Y After school one day, Chris s great-grandfather asked him what he was studying in his science class. Chris began to tell him about the garden. When he described the problems
8 The Dust Bowl R O L E P L A Y After school one day, Chris s great-grandfather asked him what he was studying in his science class. Chris began to tell him about the garden. When he described the problems
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 CHAPTER 1 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How do
CHAPTER 1 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How do
GRADE 6 GEOGRAPHY TERM 1 LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE (degrees)
 1 GRADE 6 GEOGRAPHY TERM 1 LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE (degrees) Contents Lines of Latitude... 2 Lines of Longitude... 3 The hemispheres of The Earth... 4 Finding countries and cities on a map using latitude
1 GRADE 6 GEOGRAPHY TERM 1 LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE (degrees) Contents Lines of Latitude... 2 Lines of Longitude... 3 The hemispheres of The Earth... 4 Finding countries and cities on a map using latitude
Appendix A. Linear Relationships in the Real World Unit
 Appendix A The Earth is like a giant greenhouse. The sun s energy passes through the atmosphere and heats up the land. Some of the heat escapes back into space while some of it is reflected back towards
Appendix A The Earth is like a giant greenhouse. The sun s energy passes through the atmosphere and heats up the land. Some of the heat escapes back into space while some of it is reflected back towards
Contents. Section 1: Climate Factors. Section 2: Climate Types. Section 3: Climate Effects
 Contents Section 1: Climate Factors 1. Weather or Climate?.... 2 2. Elements of Climate.... 4 3. Factors Affecting Climate.... 10 4. Comparing Climates.... 15 5. Quiz 1.... 20 Section 2: Climate Types
Contents Section 1: Climate Factors 1. Weather or Climate?.... 2 2. Elements of Climate.... 4 3. Factors Affecting Climate.... 10 4. Comparing Climates.... 15 5. Quiz 1.... 20 Section 2: Climate Types
Pacific Decadal Oscillation ( PDO ):
 Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2015-2016. El Nino / La Nina: When looking
Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2015-2016. El Nino / La Nina: When looking
Who Loves the Sun? Iguanas!
 Name Teacher Date / 5 ER.DFA2.2.R.RI.02: Identify and explain the main topic of a multiparagraph text as well as the focus of specific paragraphs within the text. Directions. Read the passage and select
Name Teacher Date / 5 ER.DFA2.2.R.RI.02: Identify and explain the main topic of a multiparagraph text as well as the focus of specific paragraphs within the text. Directions. Read the passage and select
Tales of the Past. Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education
 Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
Tales of the Past Source: Sci-ber Text with the Utah State Office of Education http://www.uen.org/core/science/sciber/trb4/downloads/literacy4.pdf Do you like mystery and intrigue? Do you like to do detective
1 Earthquakes in the United States
 1 Earthquakes in the United States Pre-Reading Discussion/Reading Before you read the passage, work with one or two other students to answer these questions. Where do earthquakes occur? What kinds of things
1 Earthquakes in the United States Pre-Reading Discussion/Reading Before you read the passage, work with one or two other students to answer these questions. Where do earthquakes occur? What kinds of things
CLIMATE. SECTION 14.1 Defining Climate
 Date Period Name CLIMATE SECTION.1 Defining Climate In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual
Date Period Name CLIMATE SECTION.1 Defining Climate In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual
A Thermometer Graph That Shows the Temperature in Each Month At
 A Thermometer Graph That Shows the Temperature in Each Month At - - Describe the weather in this place: 12 P Gersmehl Teachers may copy for use in their classrooms. Contact pgersmehl@gmail.com regarding
A Thermometer Graph That Shows the Temperature in Each Month At - - Describe the weather in this place: 12 P Gersmehl Teachers may copy for use in their classrooms. Contact pgersmehl@gmail.com regarding
Where is the tropical zone? What are three biomes found in the tropical zone?
 Name CHAPTER 17 Class Date SECTION 2 The Tropics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Where is the tropical zone? What are three biomes found in the
Name CHAPTER 17 Class Date SECTION 2 The Tropics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Where is the tropical zone? What are three biomes found in the
SUMMER WORKSHEET.
 SUMMER WORKSHEET 1 Newton s Laws SUMMER WORKSHEET Page 1 Newton s Laws Check out Mosa Mack s mystery on Newton s Laws The Case of the Haunted Supermarket! LOOK Remember: Objects at rest tend to stay at
SUMMER WORKSHEET 1 Newton s Laws SUMMER WORKSHEET Page 1 Newton s Laws Check out Mosa Mack s mystery on Newton s Laws The Case of the Haunted Supermarket! LOOK Remember: Objects at rest tend to stay at
Introduction to the Night Sky
 Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use
Slide 1 / 106 Slide 2 / 106 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
The Variety of Maps By ReadWorks
 The Variety of Maps By ReadWorks Maps are known for helping us figure out how to get to a certain location: which road do I take to the ice-cream parlor? How do I get from my house to my best friend s?
The Variety of Maps By ReadWorks Maps are known for helping us figure out how to get to a certain location: which road do I take to the ice-cream parlor? How do I get from my house to my best friend s?
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Student Letter Exploring the Strategies Unit One: Play Unit Two: Fantasy Unit Three: Mystery...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Student Letter........................................... 2 Exploring the Strategies................................... 3 Unit One: Play........................................... 4 Unit
TABLE OF CONTENTS Student Letter........................................... 2 Exploring the Strategies................................... 3 Unit One: Play........................................... 4 Unit
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE
 TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 6 Plate Tectonics 1 6-1 What is continental drift? 2 6-2 Why is the seafloor spreading? 3 6-3 What evidence supports seafloor spreading?
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 6 Plate Tectonics 1 6-1 What is continental drift? 2 6-2 Why is the seafloor spreading? 3 6-3 What evidence supports seafloor spreading?
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 CHAPTER 15 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How
CHAPTER 15 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How
Meteorology Study Guide
 Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
Name: Date: Meteorology Study Guide 1. Label the following steps in the water cycle diagram. Be sure to include arrows to show the flow of water through the cycle. - Transpiration - Precipitation -Evaporation
L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment
 Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Virtual Design Center Deliverable 4-2: Three Levels of Assessment
 Virtual Design Center Deliverable 4-2: Three Levels of Assessment Project Name Operation Montserrat Test Questions 1. Which of these is an immediate result of the movement of tectonic plates: a) Ocean
Virtual Design Center Deliverable 4-2: Three Levels of Assessment Project Name Operation Montserrat Test Questions 1. Which of these is an immediate result of the movement of tectonic plates: a) Ocean
Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts)
 Name: Section: Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 1 Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts) As air rises, it cools due to the reduction in atmospheric pressure Air mainly consists of oxygen molecules and nitrogen
Name: Section: Clouds and Rain Unit (Topic 8A-2) page 1 Clouds and Rain Unit (3 pts) As air rises, it cools due to the reduction in atmospheric pressure Air mainly consists of oxygen molecules and nitrogen
Temperature. Grade Level: 1-3
 Temperature Grade Level: 1-3 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 4 Activity Page pages 5-7 Practice Page page 8 Homework Page page 9 Answer Key page 10 11 Classroom Procedure: Approximate
Temperature Grade Level: 1-3 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 4 Activity Page pages 5-7 Practice Page page 8 Homework Page page 9 Answer Key page 10 11 Classroom Procedure: Approximate
Climate.tgt, Version: 1 1
 Name: Key Concepts Choose the letter of the best answer. (5 points each) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Date: A city located in the middle of North America experiences extreme temperature changes during
Name: Key Concepts Choose the letter of the best answer. (5 points each) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Date: A city located in the middle of North America experiences extreme temperature changes during
Where is the tropical zone? What are three biomes found in the tropical zone?
 Name CHAPTER 3 Class Date Climate 2 The Tropics SECTION BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Where is the tropical zone? What are three biomes found
Name CHAPTER 3 Class Date Climate 2 The Tropics SECTION BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: Where is the tropical zone? What are three biomes found
Our Lady Immaculate Catholic Primary School History and Geography Curriculum Map Would the Bog Baby survive in Liverpool?
 Year 1 and 2 - *Year 1 and 2 work on a two year cycle due to mixed classes Autumn 1 National Curriculum link: Human and physical geography - identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the United Kingdom
Year 1 and 2 - *Year 1 and 2 work on a two year cycle due to mixed classes Autumn 1 National Curriculum link: Human and physical geography - identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the United Kingdom
Chapter 2 Earth s Interlocking Systems pg The Earth and Its Forces pg
 Chapter 2 Earth s Interlocking Systems pg. 24 55 2 1 The Earth and Its Forces pg. 27 33 Connecting to Your World and Internal Forces Shaping the Earth The Earth is unique in the solar system because it
Chapter 2 Earth s Interlocking Systems pg. 24 55 2 1 The Earth and Its Forces pg. 27 33 Connecting to Your World and Internal Forces Shaping the Earth The Earth is unique in the solar system because it
Winter 2010, Play That Tune One More Time. By Art Horn, Meteorologist
 Winter 2010, Play That Tune One More Time. By Art Horn, Meteorologist On October 21 st the Associated Press came out with a story entitled Sea Ice Melting as Arctic Temperatures Rise. The gulp in my throat
Winter 2010, Play That Tune One More Time. By Art Horn, Meteorologist On October 21 st the Associated Press came out with a story entitled Sea Ice Melting as Arctic Temperatures Rise. The gulp in my throat
There are many different habitats. While at Knowsley Safari, you might have talked about, the Savannah Grasslands, the Rainforests and the Deserts.
 What exactly is a Habitat? An animal s habitat is the place where the animal lives in the wild. It provides animals with two important things, shelter and food. It is a great place for animals to have
What exactly is a Habitat? An animal s habitat is the place where the animal lives in the wild. It provides animals with two important things, shelter and food. It is a great place for animals to have
The Desert Biome Review
 NAME DATE The Desert Biome Review 1) Which best describes the climate in the desert? a) a warm climate c) a hot climate b) a dry climate d) a windy climate 2) What kind of soil is found in the desert?
NAME DATE The Desert Biome Review 1) Which best describes the climate in the desert? a) a warm climate c) a hot climate b) a dry climate d) a windy climate 2) What kind of soil is found in the desert?
UNIT4. Ancient China. Geography and the Early Settlement of China. Three Chinese Philosophies The First Emperor of China
 UNIT4 Ancient China Lesson 19 Lesson 20 Lesson 21 Lesson 22 Lesson 23 Lesson 24 Geography and the Early Settlement of China The Shang Dynasty Three Chinese Philosophies The First Emperor of China The Han
UNIT4 Ancient China Lesson 19 Lesson 20 Lesson 21 Lesson 22 Lesson 23 Lesson 24 Geography and the Early Settlement of China The Shang Dynasty Three Chinese Philosophies The First Emperor of China The Han
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Climate. What is climate? STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY. Name Class Date
 Climate SECTION 14.1 What is climate? In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual wind speed 4.
Climate SECTION 14.1 What is climate? In your textbook, read about climate and different types of climate data. Put a check ( ) next to the types of data that describe climate. 1. annual wind speed 4.
Animals: Habitats & Adaptations
 Animals: Habitats & Adaptations 3.2.1 Illustrate the life cycles of seed plants and various animals and summarize how they grow and are adapted to conditions within their habitats. 3.2.2 Explain how physical
Animals: Habitats & Adaptations 3.2.1 Illustrate the life cycles of seed plants and various animals and summarize how they grow and are adapted to conditions within their habitats. 3.2.2 Explain how physical
Grade 5. Practice Test. Dust Bowl Disaster
 Name Date Grade 5 Dust Bowl Disaster Today you will read the following passage. Read this passage carefully to gather information to answer questions and write an essay. Excerpt from Dust Bowl Disaster
Name Date Grade 5 Dust Bowl Disaster Today you will read the following passage. Read this passage carefully to gather information to answer questions and write an essay. Excerpt from Dust Bowl Disaster
3 Weather and Climate
 CHAPTER 22 3 Weather and Climate SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are fronts? What are some types of severe weather? How is climate different
CHAPTER 22 3 Weather and Climate SECTION The Atmosphere KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: What are fronts? What are some types of severe weather? How is climate different
Maggie s Activity Pack
 Maggie s Activity Pack Name Date Nature Running Wild - Volcanoes! Everyone has heard of volcanoes. Often we think of them as making rivers of red lava. But volcanoes do more than that. In this article
Maggie s Activity Pack Name Date Nature Running Wild - Volcanoes! Everyone has heard of volcanoes. Often we think of them as making rivers of red lava. But volcanoes do more than that. In this article
News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons
 www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons The Breaking News English.com Resource Book 1,000 Ideas & Activities For Language Teachers http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html Map
www.breaking News English.com Ready-to-use ESL / EFL Lessons The Breaking News English.com Resource Book 1,000 Ideas & Activities For Language Teachers http://www.breakingnewsenglish.com/book.html Map
Elementary Social Studies Content Area Assessment Task. Winter 2010 EDUC 203
 1 Elementary Social Studies Content Area Assessment Task Winter 2010 EDUC 203 Students: Fourth grade class in Watsonville, CA. Approximately 90% Latino, primarily of Mexicandescent. About 80% participate
1 Elementary Social Studies Content Area Assessment Task Winter 2010 EDUC 203 Students: Fourth grade class in Watsonville, CA. Approximately 90% Latino, primarily of Mexicandescent. About 80% participate
Earth s Structure and Natural Processes Practice Test
 Name: Earth s Structure and Natural Processes Practice Test Section: Directions: For each of the questions or incomplete statements below, choose the best of the answer choices given and write your answer
Name: Earth s Structure and Natural Processes Practice Test Section: Directions: For each of the questions or incomplete statements below, choose the best of the answer choices given and write your answer
Chapter 1 The Nature Of Science. Scientists are much like detectives trying to solve a mystery. Problem: What caused the huge ocean waves?
 Chapter 1 The Nature Of Science Section 1 Science All Around Mysteries and Problems Scientists are much like detectives trying to solve a mystery. 1996- While looking through historical data, scientists
Chapter 1 The Nature Of Science Section 1 Science All Around Mysteries and Problems Scientists are much like detectives trying to solve a mystery. 1996- While looking through historical data, scientists
Maggie s Activity Pack
 Maggie s Activity Pack Name Date Nature Running Wild - Volcanoes! Everyone has heard of volcanoes. Often we think of them as producing rivers of red lava. But volcanoes do more than that. In this article
Maggie s Activity Pack Name Date Nature Running Wild - Volcanoes! Everyone has heard of volcanoes. Often we think of them as producing rivers of red lava. But volcanoes do more than that. In this article
3 Severe Weather. Critical Thinking
 CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
CHAPTER 2 3 Severe Weather SECTION Understanding Weather BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are some types of severe weather? How can you stay
DRAFT. Caption: An astronaut climbs down a lunar module on the surface of the Moon. <Insert figure 1.4 here; photograph of the surface of Mars>>
 01 Exploring Space TALKING IT OVER Throughout history, people have been fascinated by space. For a long time, people could only use their eyes to make observations of objects in the sky at night. In the
01 Exploring Space TALKING IT OVER Throughout history, people have been fascinated by space. For a long time, people could only use their eyes to make observations of objects in the sky at night. In the
READY. Book. CURRICULUM ASSOCIATES, Inc. A Quick-Study Program TEST
 A Quick-Study Program TEST Book 5 READY LONGER READING PASSAGES READY Reviews Key Concepts in Reading Comprehension Provides Practice Answering a Variety of Comprehension Questions Develops Test-Taking
A Quick-Study Program TEST Book 5 READY LONGER READING PASSAGES READY Reviews Key Concepts in Reading Comprehension Provides Practice Answering a Variety of Comprehension Questions Develops Test-Taking
The sun and water cycle
 reflect The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time
reflect The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time
Chapter 2 Planet Earth
 Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
Climate Change. Grades 5-8. Written by Darcy J. Gentleman Illustrated by S&S Learning Materials. ISBN Copyright 2008
 Climate Change Grades 5-8 Written by Darcy J. Gentleman Illustrated by S&S Learning Materials About the author: Darcy J. Gentleman has a Ph.D. in analytical chemistry from Arizona State University. His
Climate Change Grades 5-8 Written by Darcy J. Gentleman Illustrated by S&S Learning Materials About the author: Darcy J. Gentleman has a Ph.D. in analytical chemistry from Arizona State University. His
My Community vs. Nunavut Weather and Climate
 My Community vs. Nunavut Content Areas Social Studies, Science, Technology Objective Students will differentiate between weather and climate. For 1 month, they will collect and graph daily temperature
My Community vs. Nunavut Content Areas Social Studies, Science, Technology Objective Students will differentiate between weather and climate. For 1 month, they will collect and graph daily temperature
The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past
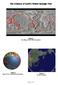 The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past Figure 1 The Ring of Fire (Flat Projection) Figure 2 Ring of Fire, (Spherical Projection) Figure 3 Ocean Trenches Page 1 of 10 Figure 4 Kamchatka Peninsula
The Evidence of Earth s Violent Geologic Past Figure 1 The Ring of Fire (Flat Projection) Figure 2 Ring of Fire, (Spherical Projection) Figure 3 Ocean Trenches Page 1 of 10 Figure 4 Kamchatka Peninsula
Pre and Post-Visit Activities. Water, Water Everywhere
 Pre and Post-Visit Activities Water, Water Everywhere Table of Contents: Important Information: 2 Vocabulary: 3 Pre-Visit Activities: 4 Post-Visit Activities: 5 Vocabulary Word Search: 6 Journey of Water
Pre and Post-Visit Activities Water, Water Everywhere Table of Contents: Important Information: 2 Vocabulary: 3 Pre-Visit Activities: 4 Post-Visit Activities: 5 Vocabulary Word Search: 6 Journey of Water
5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY ACTIVITIES/BOOKLET
 5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY ACTIVITIES/BOOKLET Choose two activites from each theme to complete LOCATION: 1) Using latitude and longitude lines on a world map, locate and note the following: the highest mountain
5 THEMES OF GEOGRAPHY ACTIVITIES/BOOKLET Choose two activites from each theme to complete LOCATION: 1) Using latitude and longitude lines on a world map, locate and note the following: the highest mountain
Weather: Air Patterns
 Weather: Air Patterns Weather: Air Patterns Weather results from global patterns in the atmosphere interacting with local conditions. You have probably experienced seasonal shifts, such as winter in New
Weather: Air Patterns Weather: Air Patterns Weather results from global patterns in the atmosphere interacting with local conditions. You have probably experienced seasonal shifts, such as winter in New
Chapter 12. Thermal Energy Transfer Drives Plate tectonics
 Chapter 12 Thermal Energy Transfer Drives Plate tectonics What is thermal energy Thermal energy with respect to plate tectonics is energy of molten rock that is constantly moving below your feet. Below
Chapter 12 Thermal Energy Transfer Drives Plate tectonics What is thermal energy Thermal energy with respect to plate tectonics is energy of molten rock that is constantly moving below your feet. Below
4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explore this Phenomena. The same sun shines on the entire Earth. Explain why these two areas have such different climates.
 Explore this Phenomena The same sun shines on the entire Earth. 4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explain why these two areas have such different climates. 89 6.3.3 Climate Develop and use a model to show how unequal
Explore this Phenomena The same sun shines on the entire Earth. 4.3 Climate (6.3.3) Explain why these two areas have such different climates. 89 6.3.3 Climate Develop and use a model to show how unequal
The Four World Zones Become Connected
 The Four World Zones Become Connected By Cynthia Stokes Brown, Big History Project, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.30.16 Word Count 812 TOP: Asia from space. Photo: Corbis. MIDDLE: Bering Land Bridge National
The Four World Zones Become Connected By Cynthia Stokes Brown, Big History Project, adapted by Newsela staff on 07.30.16 Word Count 812 TOP: Asia from space. Photo: Corbis. MIDDLE: Bering Land Bridge National
Sample. Contents SECTION 1: PLACE NAMES 6 SECTION 2: CONNECTING TO PLACES 21 SECTION 3: SPACES: NEAR AND FAR 53
 Contents Teachers' Notes 4 National Curriculum Links 5 SECTION 1: PLACE NAMES 6 Teachers' Notes 7-8 Activities Names Of Places 9 Place Names Are Important 1 10 Place Names Are Important 2 11 The Meanings
Contents Teachers' Notes 4 National Curriculum Links 5 SECTION 1: PLACE NAMES 6 Teachers' Notes 7-8 Activities Names Of Places 9 Place Names Are Important 1 10 Place Names Are Important 2 11 The Meanings
Ancient China. Teachers Curriculum Institute Geography and the Early Settlement of China 1. AW_ISN_U04_01 Ancient China Second Proof TCI18 108
 G e o g r a p h y C h a l l e n g e Ancient China N W E S 0 250 500 miles 0 250 500 kilometers Albers Conic Equal-Area Projection AW_ISN_U04_01 Ancient China Second Proof TCI18 108 Teachers Curriculum
G e o g r a p h y C h a l l e n g e Ancient China N W E S 0 250 500 miles 0 250 500 kilometers Albers Conic Equal-Area Projection AW_ISN_U04_01 Ancient China Second Proof TCI18 108 Teachers Curriculum
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 CHAPTER 15 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How
CHAPTER 15 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How
Living Near a Volcano
 living near a volcano Grade Level 3-5 Grade Level 3-5 (1) 15 minute prep lesson (3) 45 minute lessons Lesson overview: Is it possible to build a volcano-safe home? In this lesson, students will learn about
living near a volcano Grade Level 3-5 Grade Level 3-5 (1) 15 minute prep lesson (3) 45 minute lessons Lesson overview: Is it possible to build a volcano-safe home? In this lesson, students will learn about
A) usually less B) dark colored and rough D) light colored with a smooth surface A) transparency of the atmosphere D) rough, black surface
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which shows two identical houses, A and B, in a city in North Carolina. One house was built on the east side of a factory, and the other
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which shows two identical houses, A and B, in a city in North Carolina. One house was built on the east side of a factory, and the other
1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit?
 Pre/Post GCI Name (print) 1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit? 2. Referring to the same diagram as the previous question, which of the labeled rock units is the youngest?
Pre/Post GCI Name (print) 1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit? 2. Referring to the same diagram as the previous question, which of the labeled rock units is the youngest?
STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change TEK 8.11C: Explore how short- and long-term environmental changes affect organisms and traits in subsequent
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 48 TEK 8.11C: Effects of Environmental Change TEK 8.11C: Explore how short- and long-term environmental changes affect organisms and traits in subsequent
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7731101867* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/21 Paper 2 October/November 2014 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7731101867* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/21 Paper 2 October/November 2014 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
Student Packet session # 11 Name: Date:
 Student Packet session # 11 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Building Pangaea Big Idea 6: Earth Structures Benchmark: SC.7.E.6.4 Explain and give examples of how physical evidence supports scientific theories
Student Packet session # 11 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Building Pangaea Big Idea 6: Earth Structures Benchmark: SC.7.E.6.4 Explain and give examples of how physical evidence supports scientific theories
FLOODING. Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system.
 CATASTROPHIC EVENTS FLOODING Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system. Common Causes: Long-lasting rainfall over a broad area Locally intense
CATASTROPHIC EVENTS FLOODING Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system. Common Causes: Long-lasting rainfall over a broad area Locally intense
Introducing Planet Earth
 Introducing Planet Earth Reading A Z Level L Levelled Book Word Count: 511 LEVELLED BOOK L Introducing Planet Earth Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. Written by Celeste Fraser
Introducing Planet Earth Reading A Z Level L Levelled Book Word Count: 511 LEVELLED BOOK L Introducing Planet Earth Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. Written by Celeste Fraser
The Sun and Water Cycle
 The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time in the
The last time you took a shower, did you think about where the water came from? Sure, it came out of the showerhead, but what about before that? The water you used to wash could have spent time in the
5 Time Marches On. TAKE A LOOK 1. Identify What kinds of organisms formed the fossils in the picture?
 CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
CHAPTER 6 5 Time Marches On SECTION The Rock and Fossil Record BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do geologists measure time? How has life changed
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan
 Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) The Water Cycle UC Berkeley PhD students Grade Level 1 Standards Connection(s) Earth Sciences, physics sciences CA Science Content
Bay Area Scientists in Schools Presentation Plan Lesson Name Presenter(s) The Water Cycle UC Berkeley PhD students Grade Level 1 Standards Connection(s) Earth Sciences, physics sciences CA Science Content
Barlows Primary School Geography Curriculum Content Key Stage 1 and
 Geography Curriculum Content Key Stage 1 and 2 2017-2018 Curriculum Content Year 1 The content for Year 1 is detailed below: WHAT ARE SEASONS? WHAT SIT LIKE WHERE WE LIVE? WHERE DO DIFFERENT ANIMALS LIVE?
Geography Curriculum Content Key Stage 1 and 2 2017-2018 Curriculum Content Year 1 The content for Year 1 is detailed below: WHAT ARE SEASONS? WHAT SIT LIKE WHERE WE LIVE? WHERE DO DIFFERENT ANIMALS LIVE?
Module 2, Investigation 4: Log 1 Our coasts
 Module 2, Investigation 4: Log 1 Our coasts The coast is where the ocean meets land. Coastlines are always changing their shape. They are being worn away in some places and built up in others. Coasts can
Module 2, Investigation 4: Log 1 Our coasts The coast is where the ocean meets land. Coastlines are always changing their shape. They are being worn away in some places and built up in others. Coasts can
Describing Cause and Effect
 Introduction RI.3.3 Describe the relationship between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to... cause/effect.
Introduction RI.3.3 Describe the relationship between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to... cause/effect.
The Earth, the sun, the planets and the twinkling stars in the sky are all part of a galaxy, or family of stars. We call our galaxy the Milky Way
 Part One The Earth, the sun, the planets and the twinkling stars in the sky are all part of a galaxy, or family of stars. We call our galaxy the Milky Way because the lights from its billions of stars
Part One The Earth, the sun, the planets and the twinkling stars in the sky are all part of a galaxy, or family of stars. We call our galaxy the Milky Way because the lights from its billions of stars
Maps. All Kinds of Maps 104 words. How to Draw a Map 105 words. The Difference Between Maps and Globes 108 words. Learn About Maps 96 words
 ARTICLE-A-DAY Maps 8 Articles Check articles you have read: All Kinds of Maps 104 words How to Draw a Map 105 words The Difference Between Maps and Globes 108 words Learn About Maps 96 words Seven Large
ARTICLE-A-DAY Maps 8 Articles Check articles you have read: All Kinds of Maps 104 words How to Draw a Map 105 words The Difference Between Maps and Globes 108 words Learn About Maps 96 words Seven Large
WHAT IS WEATHER? many kinds of weather, such as hot, cold, sunny, rainy, snowy, and windy. Storms and winds can change the weather in a hurry.
 WHAT IS WEATHER? Weather tells us what the outside air is like. There are Why did the woman go outside with her purse open? She thought there was going to be some change in the weather! many kinds of weather,
WHAT IS WEATHER? Weather tells us what the outside air is like. There are Why did the woman go outside with her purse open? She thought there was going to be some change in the weather! many kinds of weather,
Introducing Inspector Tippington
 Introducing Inspector Tippington Inspector Tippington is a world-famous detective who is retired from Scotland Yard. He is also an expert in world history. He has spent his life traveling around the world
Introducing Inspector Tippington Inspector Tippington is a world-famous detective who is retired from Scotland Yard. He is also an expert in world history. He has spent his life traveling around the world
